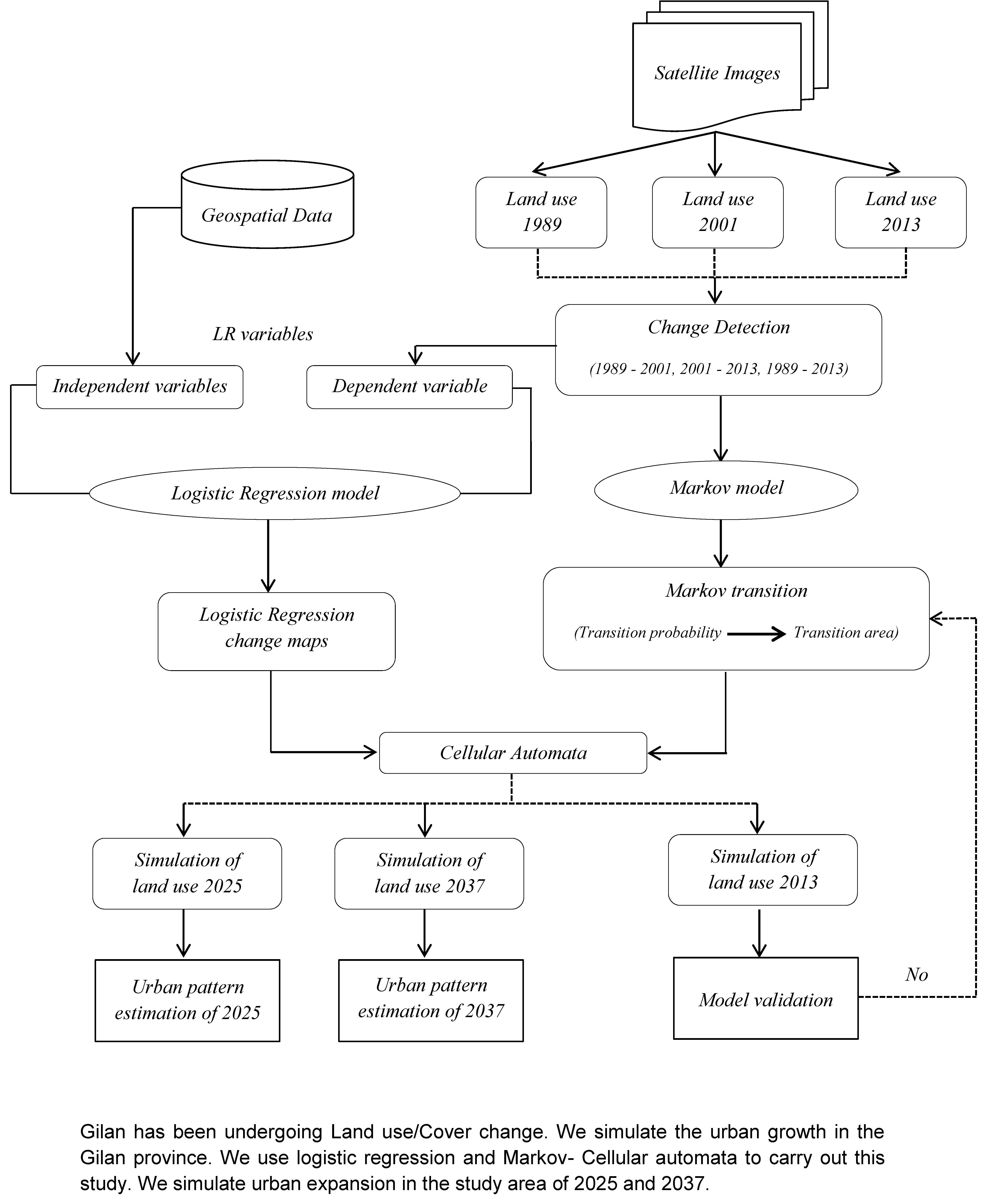
Although, promotion of urbanization culture in recent decades has made inevitable development of cities in the world, however, the development can be guided in a direction that leave, to the extent possible, minimum socioeconomic and environmental impacts. For this, it is required to first forecast auto-spreading orientation of cities and suburbs in rural areas over time and then avoid shapeless growth of cities. This paper is an attempt to develop a dynamic hybrid model based on logistic regression (LR), Markov chain (MC), and cellular automata (CA) for prediction of future urban sprawl in fast-growing cities. The model was developed using 12 widely-used urban development criteria, whose significant coefficient was determined by logistic regression, and validated by relative operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The validated model was run in Guilan, a tourist province in northern Iran with a very high rate of urban development. For this, changes in the area of urban land use were detected over the period of 1989 to 2013 and then, future sprawl of the province was forecasted by the years 2025 and 2037. The analysis results revealed that the area of urban land use was increased by more than 1.7 % from 36012.5 ha in 1989 to 59754.8 ha in 2013, and the area of Caspian Hyrcanian forestland was reduced by 31628 ha. The results also predicted an alarming increase in the rate of urban development in the province by the years 2025 and 2037, during which urban land use is predicted to develop 0.9 % and 1.38 %, respectively. The development pattern is expected to be uneven and scattered, without following any particular direction. The development will occur close to the existing or newly-formed urban basements as well as around major roads and commercial areas. This development, if not controlled, will lead to the loss of 13863 ha of Hyrcanian forests and if the trend continues, 21013 ha of Hyrcanian forests and 20208 ha of Barren/open lands are expected to be destroyed by the year 2037. In general, the proposed model is an efficient tool for the support of urban planning decisions and facilitates the process of sustainable development of cities by providing decision-makers with an overview on future development of cities where the growth rate is very fast.