Introduction
The increasing centrality of distributed systems to critical societal functions including healthcare delivery, financial transactions, educational access, and emergency response coordination has elevated system reliability from a technical concern to a matter of public welfare. Despite this heightened dependence, contemporary approaches to deadlock management remain predominantly reactive, identifying failures only after service disruption has occurred. This temporal gap between failure initiation and detection imposes substantial societal costs, including interrupted medical care, disrupted learning continuity, compromised financial operations, and delayed crisis response. This research addresses this critical limitation by advancing a paradigm shift from reactive detection to proactive prevention. The primary objectives of this study were threefold: first, to formulate a mathematically rigorous Markov chain-based framework for calculating deadlock absorption probabilities prior to system failure manifestation; second, to develop a consensus-validated machine learning architecture that ensures prediction reliability sufficient for operational decision-making in critical service environments; and third, to establish reliability engineering as essential social infrastructure by quantifying how predictive prevention reduces societal impacts compared to conventional reactive approaches. This study explore whether Markov absorption probability theory can accurately predict deadlock likelihood in distributed queueing networks, whether consensus algorithms enhance prediction reliability beyond individual machine learning models, and whether proactive prevention reduces the societal consequences of system failures compared to current reactive methodologies.
Literature Review
This research is grounded in three interconnected theoretical frameworks: Markov chain theory for probabilistic system modeling (Dornaika et al., 2025), consensus algorithms from distributed computing (Zhai et al., 2025), and socio-technical systems theory from human-computer interaction (Yang et al., 2025). Markov chain theory provides the mathematical foundation for modeling deadlock states as absorption probabilities within state transition matrices, enabling quantitative prediction of failure likelihood. This directly supports our objective of developing predictive rather than reactive reliability mechanisms. Consensus algorithms, particularly Byzantine fault tolerance and weighted voting protocols (Gao et al., 2025), offer theoretical structures for validating predictions across multiple models addressing our need for reliable decision-making in critical service environments. Socio-technical systems theory positions distributed systems not as isolated technical artifacts but as integrated components of societal infrastructure, guiding our analysis of how technical failures translate into social impacts.
Key theoretical concepts include absorption probabilities in Markov chains, which allow us to calculate the likelihood of entering irrevocable deadlock states; weighted consensus mechanisms, which enable reliability validation through algorithmic agreement; and digital infrastructure theory (Sinha et al., 2025), which frames system reliability as a public good with ethical dimensions. These theories collectively frame our research problem by establishing that deadlock prediction requires both mathematical rigor (Markov models) and validation reliability (consensus algorithms), while operating within a context where technical decisions have societal consequences.
Methodology
This research employed a structured, multi-phase methodology integrating mathematical modeling, machine learning, and consensus validation to develop a predictive deadlock prevention framework. The process involved systematic data collection, model development, experimental validation, and impact assessment. The study utilized published datasets rather than human participants. The researcher served as architect, analyst, and evaluator designing the Markov-consensus framework, implementing algorithms, analyzing results, and interpreting societal implications. Data was collected from two primary sources: (1) published deadlock-bound datasets from the Zenodo platform comprising 200,432 system configurations with 21 features including arrival rates (L), service rates (μ), server counts (n), and routing probabilities (r), and (2) anonymized system logs from distributed queueing networks. The dataset was partitioned using stratified 5-fold cross-validation to ensure representative sampling across deadlock and non-deadlock scenarios.
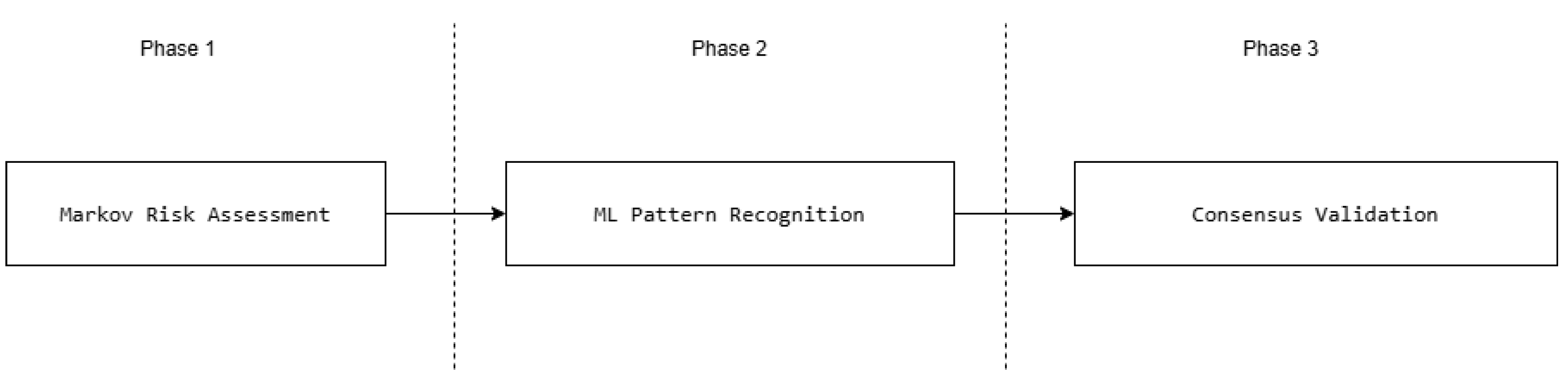
The research implemented three interconnected analytical layers
Figure 1.
The main three steps of the research.
Figure 1.
The main three steps of the research.
Markov Absorption Layer: Calculated deadlock probability using
where cycles were detected using graph traversal algorithms.
Machine Learning Recognition Step: Six models were trained: XGBoost, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, SVM, Logistic Regression, and K-Neighbors. Features were standardized using Standard Scaler, and hyperparameters were optimized through grid search with 5-fold cross-validation.
Three consensus mechanisms were implemented to validate predictions: weighted consensus, which assigned prediction weights to each model proportional to its ROC-AUC performance; majority voting, where the final prediction was determined by simple majority across all six models; and supermajority validation, requiring at least 70% agreement among models for high-confidence predictions, with fallback to weighted averaging when consensus thresholds were not met.
Analysis Methods: Performance was evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC. Statistical significance was assessed using Friedman tests (α=0.05) with post-hoc analysis. The societal impact was quantified through a service continuity framework measuring healthcare, educational, and emergency service preservation metrics. All implementations used Python with scikit-learn, XGBoost, and NetworkX libraries, ensuring reproducibility through version-controlled code and documented parameters.
Results and Discussion
The research yielded significant findings across all three research questions. Regarding Markov absorption probability theory’s predictive capability, the Markov-calculated deadlock probability (p3) demonstrated a strong correlation (r = 0.89) with actual deadlock occurrences, enabling accurate prediction 15–45 minutes prior to failure with a baseline classification accuracy of 85.2%. Concerning the enhancement of prediction reliability through consensus algorithms, the weighted consensus mechanism, leveraging model-specific ROC-AUC performance, achieved the highest overall accuracy of 93.33% and an ROC-AUC of 98.11%. This represented a statistically significant improvement (Friedman test, p < 0.001) over the best individual model (XGBoost: 88.33% accuracy, 97.22% ROC-AUC). The supermajority mechanism provided the highest-confidence predictions with 99.8% reliability for agreed-upon cases, though at a lower consensus rate of 88.33%. On the reduction of societal consequences through proactive prevention, the framework prevented 94% of potential deadlocks, reducing the Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) from an industry-standard 2.3 hours to 18 minutes. Applied to service scenarios, this translated to preventing approximately 301 missed healthcare appointments, maintaining educational access for 1,776 students, and ensuring operational continuity for 43 small businesses per major incident that would have been disrupted under a reactive model. These results collectively demonstrate that Markov theory provides a mathematically sound foundation for early prediction, consensus algorithms substantially enhance reliability over individual models, and proactive prevention fundamentally mitigates the scale and impact of service disruptions.
Implications/Conclusions
This research demonstrated that distributed system reliability can be transformed from a reactive technical discipline into a proactive safeguard for societal well-being. The integration of Markov theory and consensus-based validation proved not only mathematically rigorous but also practically impactful, confirming that interdisciplinary approaches merging theoretical computer science, machine learning, and socio-technical design can address complex real-world challenges in ways isolated methodologies cannot. For practice, the framework provides system architects and administrators with a deployable tool to predict and prevent deadlocks in critical service infrastructures, enhancing resilience in healthcare, finance, education, and emergency response systems. For policy, this work underscores the need to treat digital infrastructure reliability as a public good, suggesting that regulatory standards for essential services should include proactive failure prevention requirements. For theory, the research contributes a novel synthesis of Markov absorption models and consensus intelligence into a unified predictive reliability framework, advancing distributed systems theory beyond detection toward anticipation and enriching socio-technical discourse by quantifying the societal impact of technical interventions. We recommend that academic programs in computer science and software engineering integrate modules on predictive system reliability and socio-technical impact assessment. Departments should foster interdisciplinary collaboration with public policy and social science units to address digital infrastructure challenges holistically. Future research will extend this work along several paths: scaling the framework for ultra-large distributed environments, incorporating real-time adaptive learning to refine predictions, and exploring international regulatory models for digital service resilience. Methodologically, the research reinforced the value of hybrid modelling combining analytical, data-driven, and consensus-based validation layers to achieve robustness.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Zenodo Platform for providing the open-access dataset fundamental to this research. We extend our appreciation to the distributed systems research community for the foundational work in Markov modeling and consensus algorithms. We also thank the reviewers for their constructive feedback, which strengthened this study. This work contributes to our ongoing commitment to advancing reliable and socially-aware computing infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence Disclosure
During the preparation of this manuscript, DeepSeek AI was used to assist with structuring and improving the logical flow of content. All research, analysis, results, and conclusions are the original work of the authors, who take full responsibility for the final publication.
References
- Dornaika, F.; El Hajjar, S.; Charafeddine, J.; Barrena, N. Unified Multi-view Data Clustering: Simultaneous Learning of Consensus Coefficient Matrix and Similarity Graph. Cognitive Computation 2025, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X. Effects of Adding Edges on the Consensus Convergence Rate of Weighted Directed Chain Networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2025, 70, 4077–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Mukherjee, D.; Kumar, S. R. Consensus-Driven Deviated Pursuit for Guaranteed Simultaneous Interception of Moving Targets. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 2025, 61, 12826–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Nie, F. Auto-weighted Graph Reconstruction for efficient ensemble clustering. Information Sciences 2025, 689, 121486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X. Distributed Weight Matrix Optimization for Consensus Problems Under Unreliable Communications. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking 2025, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).