Submitted:
31 December 2025
Posted:
02 January 2026
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Motivation
- RQ-1: How do domain experts perceive the role of AI in advancing the achievement of UN SDGs?
- RQ-2: How do domain experts perceive the role of AI in hindering the achievement of the UN SDGs?
3. Methodology
4. Overview and Analysis
SDG –1: No Poverty
SDG –2: Zero Hunger
SDG –3: Good Health and Well-Being
- Enhancing Female-Centric Research: Historically, medical research has been Male-centric, owing to lack of resources, scarce resource allocation towards female centric research, various biases and lack of opportunities; all leading to gaps in understanding women’s health conditions. AI-driven analytics can help in redesigning research experiments and aid in the analysis of large data outcomes, thus making gender-inclusive clinical trials possible and helping identify treatment responses specific to female physiology.
- Reducing Bias in Healthcare AI Models: Many healthcare AI models have been trained on datasets lacking diversity in gender, race, and socioeconomic background. This may be attributed to lack of data around those races, due to various socio-economic reasons. The lack of data, coupled with data set standardization using incomplete datasets creates further imbalance in the analysis of symptoms and outcomes amongst marginalized communities and races. All of these play a major role in disease manifestation and taboo around timely treatment. This has led to misdiagnoses and inadequate treatment recommendations for women and marginalized communities. Ensuring AI models are trained on larger and more diverse datasets can lead to improved diagnosis and higher accuracy for more personalized treatment plans aligned with patient recovery and treatment outcome.
- Improving Access to Healthcare: AI-powered telemedicine, chatbots, and predictive analytics can provide accessible health consultation and possible solutions for medical concern to individuals in remote and underserved areas, ensuring that gender and economic status do not hinder access to essential primary medical care. Primary consultations made accessible can help patient identification and start of treatment at the manageable stage before a condition spiral onto the chronic stage.
SDG –4: Quality Education
- More targeted training and education for researchers and academics in AI technologies.
- Research into communicating AI output and policy making.
- Research and education on bias in AI.
- Investment in AI in the education sector for training, research, and infrastructure.
SDG-5: Gender Equality
AI in Workplace Gender Inclusion
Building Unbiased AI for a Fairer Future
- Curating Diverse and Inclusive Data: AI models should be trained on datasets that accurately represent all genders, races, and socio-economic backgrounds to avoid reinforcing historical biases.
- Ethical AI Design and Auditing: Regular audits of AI systems should be conducted to detect and correct any biased patterns.
- Human Oversight and Ethical AI Governance: AI should complement human judgment rather than replace it, ensuring fairness and accountability in decision-making processes.
Conclusion: AI as a Catalyst for Gender Equality
SDG-6: Clean Water and Sanitation
SDG – 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- AI-driven tools must be validated across populations and health systems to ensure all users benefit.
- Community engagement, transparent algorithms, and ethics guidelines help prevent biases and build trust (Dankwa-Mullan, 2024).
- Initiatives like WHO’s Global AI for Health prioritize robust governance and equitable roll-out of AI in every country.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
SDG 13: Climate Action
SDG 14: Life Below Water
SDG 15: Life on Land
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Accountability - Developing transparent and explainable AI models that ensure accountability at every stage.
- Regulation - Making and Implementing stringent policies against AI-generated gender-based violence and misinformation.
- Ethics - Encouraging ethical AI practices in organizations and governments through regulatory oversight and sensitization programs.
- Universal approach - Each one of us as an individual should take responsibility for our actions and help train the AI models available to us with the data content we consume using unbiased opinions devoid of harshness, wherever possible.
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
References
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. Robots and jobs: Evidence from US labor markets. Journal of Political Economy 2020, 128(6), 2188–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- African Business. Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Good Health: The New Frontier in Social Innovation to accelerate progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3); African Business, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Shakoor, N. Advancing agriculture through IoT, Big Data, and AI: a review of smart technologies enabling sustainability. Smart Agricultural Technology 2025, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Smadi, T.; Handam, A.; Gaeid, K. S.; Al-Smadi, A.; Al-Husban, Y.; & smadi Khalid, A. Artificial intelligent control of energy management PV system. Results in Control and Optimization 2024, 14, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasnawi, B. N.; Almutoki, S. M. M.; Hussain, F. F. K.; Harrison, A.; Bazooyar, B.; Zanker, M.; Bureš, V. A new methodology for reducing carbon emissions using multi-renewable energy systems and artificial intelligence. Sustainable Cities and Society 2024, 114, 105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkrush, A. A.; Salem, M. S.; Abdelrehim, O.; Hegazi, A. A. Data centers cooling: A critical review of techniques, challenges, and energy saving solutions. International Journal of Refrigeration 2024, 160, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Metternicht, G.; Wiedmann, T. Initial progress in implementing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A review of evidence from countries. Sustainability science 2018, 13(5), 1453–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkem, Y.; Biswas, S. K.; Varanasi, A. Smart farming using artificial intelligence: A review. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 120, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awogbemi, O.; Von Kallon, D. V.; Kumar, K. S. Contributions of artificial intelligence and digitization in achieving clean and affordable energy. Intelligent Systems with Applications 2024, 22, 200389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, G.S.; Kumar, V.S.; Raj, S.A. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Methods and Applications for Post-Crisis Supply Chain Resiliency and Recovery; Supply Chain Analytics, 2025; p. 100121. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C. M.; Nasrabadi, N. M. Pattern recognition and machine learning; New York; springer, 2006; Vol. 4, No. 4, p. 738. [Google Scholar]
- Cachero, C.; Grao-Gil, O.; Pérez-delHoyo, R.; Ordóñez-García, M. C.; Andújar-Montoya, M. D.; Lillo-Ródenas, M. Á.; Torres, R. Perception of the Sustainable Development Goals among university students: A multidisciplinary perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 429, 139682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, T. A new generation of AI: A review and perspective on machine learning technologies applied to smart energy and electric power systems. International Journal of Energy Research 2019, 43(6), 1928–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowls, J.; Tsamados, A.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. The AI gambit: leveraging artificial intelligence to combat climate change—opportunities, challenges, and recommendations. Ai & Society 2023, 38(1), 283–307. [Google Scholar]
- Dankwa-Mullan, I. Health equity and ethical considerations in using artificial intelligence in public health and medicine. Preventing Chronic Disease 2024, 21, E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M. W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies; 2019; volume 1 (long and short papers), pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, Y. K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A.; Galanos, V.; Ilavarasan, P. V.; Janssen, M.; Jones, P.; Kar, A. K.; Kizgin, H.; Kronemann, B.; Lal, B.; Lucini, B.; Williams, M. D. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, A.; Bexten, T.; Sieker, T.; Lehna, M.; Schütt, J.; Scholz, C.; Wirsum, M. AI agents envisioning the future: Forecast-based operation of renewable energy storage systems using hydrogen with Deep Reinforcement Learning. Energy Conversion and Management 2022, 258, 115401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, S.; Vu, S. T.; Likhith, E.; Qiu, T. Inclusive AI literacy for kids around the world. In Proceedings of FabLearn; 2019; pp. 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, D.; Soifer, E. AI technologies, privacy, and security. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence 2022, 5, 826737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M. AI Uses How Much Water? Navigating Regulation Of AI Data Centers’ Water Footprint Post-Watershed Loper Bright Decision. Navigating Regulation Of AI Data Centers’ Water Footprint Post-Watershed Loper Bright Decision (December 13, 2024), 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gichoya, J. W.; Thomas, K.; Celi, L. A.; Safdar, N.; Banerjee, I.; Banja, J. D.; Purkayastha, S. AI pitfalls and what not to do: mitigating bias in AI. The British Journal of Radiology 2023, 96(1150), 20230023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Rashid, M.; Tariq, M. A. U. R.; Nadeem, A. The role of artificial intelligence (AI) and Chatgpt in water resources, including its potential benefits and associated challenges. Discover Water 2024, 4(1), 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, D.; Bouhoula, A.; Al-Zubari, W. K. Unlocking the Potential of Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Water Management Focusing Operational Applications. Water (20734441) 2024, 16(22). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JetLearn. How AI Can Help Identify and Support Learning Disabilities; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, D. R.; Nalvade, J.; Randive, P. S.; Hirve, S. Artificial intelligence in sustainable agriculture: Enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Industrial Engineering Journal 2024, 53(9). [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, S.; Datta, P.; Pal, P.; Ghosh, K.; Das, A.; Das, B. K. Unveiling the hidden connections: Using explainable artificial intelligence to assess water quality criteria in nine giant rivers. Journal of Cleaner Production 2025, 492, 144861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwobah, E. K.; Turissini, M.; Barasa, J.; Kimaiyo, M.; Okeyo, L.; Araka, J.; Njiriri, F.; Matundura, R.; Jaguga, F. Mental healthcare services in Kenyan counties: a descriptive survey of four counties in Western Kenya. BMC Health Services Research 2023, 23(1), 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardy, R.; Ruin, Q.; Veissier, I. Discriminating pathological, reproductive or stress conditions in cows using machine learning on sensor-based activity data. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2023, 204, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Herdem, M. S.; Nathwani, J.; Wen, J. Z. Methods and applications for Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Internet of Things, and Blockchain in smart energy management. Energy and AI 2023, 11, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, Y.; Xu, W. Cross-lingual named entity recognition using parallel corpus: A new approach using xlm-roberta alignment. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.11112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Yassin, B.; Nan, Z.; Luo, J. AI for earth: rainforest conservation by acoustic surveillance. ArXiv Preprint 2019, 1908.07517. [Google Scholar]
- Mathaba, M.; Banza, J. A comprehensive review on artificial intelligence in water treatment for optimization. Clean water now and the future. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A 2023, 58(14), 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhie, S.H. Novel approaches and practices to sustainable agriculture. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research 2022, 10, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, N.; Burns, S. D.; Riang’a, R. M.; Mwangi, E. M.; Sayed, S.; Gichu, M.; Langa, K. M.; Miguel, E.; Ngugi, A. K.; Ehrlich, J. R. Development of the Longitudinal Study of Health and Ageing in Kenya (LOSHAK). Innovation in Aging 2024, 8(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallottino, F.; Violino, S.; Figorilli, S.; Pane, C.; Aguzzi, J.; Colle, G.; Nemmi, E. N.; Montaghi, A.; Chatzievangelou, D.; Antonucci, F.; others. Applications and perspectives of Generative Artificial Intelligence in agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2025, 230, 109919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panch, T.; Mattie, H.; Celi, L. A. The “inconvenient truth” about AI in healthcare. NPJ digital medicine 2019, 2(1), 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, G.; Papantonatou, M.Z.; Uyar, H.; Kriezi, O.; Mavrommatis, A.; Psiroukis, V.; Kasimati, A.; Tsiplakou, E.; Fountas, S. Economic and Environmental Benefits of Digital Agricultural Technological Solutions in Livestock Farming: A Review. Smart Agricultural Technology 2025, 100783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Parkash, V.; Sharma, N. K. Technological aspects, utilization and impact on power system for distributed generation: A comprehensive survey. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2024, 192, 114257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayhan, A. The role of AI in sustainable development: Opportunities and challenges; DOI, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Roselli, D.; Matthews, J.; Talagala, N. Managing bias in AI. In Companion proceedings of the 2019 world wide web conference; May 2019; pp. 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Sarpong, H. A.; Getty, D.; Rolston, A.; Linnane, S.; Dowd Smith, R. Water demand and usage trends among group water schemes: Implication for water conservation in Ireland. Water International 2024, 49(7), 908–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, N. Should robots replace teachers? AI and the future of education; John Wiley & Sons, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaprakash, K. N.; Swami, N.; Mysorekar, S.; Arora, R.; Gangadharan, A.; Vohra, K.; Jadeyegowda, M.; Kiesecker, J. M. Potential for artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications in biodiversity conservation, managing forests, and related services in India. Sustainability 2022, 14(12), 7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojamo, S.; Rudebeck, T.; others. Corporate Engagement in Water Policy and Governance: A Literature Review on Water Stewardship and Water Security. Water Alternatives 2024, 17(2), 292–324. [Google Scholar]
- Topol, E. Deep medicine: how artificial intelligence can make healthcare human again; Hachette UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tarafdar, M.; Beath, C. M.; Ross, J. W. Using AI to enhance business operations. MIT Sloan Management Review 2019, 60(4). [Google Scholar]
- Truby, J. Governing artificial intelligence to benefit the UN sustainable development goals. Sustainable Development 2020, 28(4), 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Story Artificial intelligence in education: UNESCO advances key competencies for teachers and learners. 20 January 2025. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/artificial-intelligence-education-unesco-advances-key-competencies-teachers-and-learners.
- UNSECO. SDG 4 - Education 2030. 2030. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/sdg4education2030/en, 0.13140/RG.2.2.20993.02407.
- United Nations. Goal 1: End poverty in all its forms everywhere. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal1.
- United Nations. Goal 2: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal2.
- United Nations. Goal 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3.
- United Nations. Goal 4: Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal4.
- United Nations. Goal 5: Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal5.
- United Nations. Goal 6: Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal6.
- United Nations. Goal 7: Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal7.
- United Nations. Goal 8: Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal8.
- United Nations. Goal 9: Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal9.
- United Nations. Goal 10: Reduce inequality within and among countries. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal10.
- United Nations. Goal 11: Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal11.
- United Nations. Goal 12: Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal12.
- United Nations. Goal 13: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal13.
- United Nations. Goal 14: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal14.
- United Nations. Goal 15: Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal15.
- United Nations. Goal 16: Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal16.
- United Nations. Goal 17: Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development. United Nations Sustainable Development. 2025. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal17.
- UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Global Sustainable Development Report, 2015 edition; United Nations, 2015; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/gsdr.
- United Nations. Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda.
- Upreti, N. C.; Singh, V.; Nagpal, N. R. Towards a Healthier Future: The Transformative Role of AI in Promoting Good Health & Well-being (SDG-3). AISD 2023, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Felländer, A.; Langhans, S. D.; Tegmark, M.; Fuso Nerini, F. The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nature Communications 2020, 11(1), 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnu, B.R.; Sivapirakasam, S.P.; Satpathy, K.K.; Shaju, K.A. Cr6+ reduction in welding fumes by nano composite coatings on stainless steel manual metal arc welding electrodes. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2018, 114, 334–346. [Google Scholar]
- Visvizi, A. Artificial intelligence (AI) and sustainable development goals (SDGs): exploring the impact of AI on politics and society. Sustainability 2022, 14(3), 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Eschenbach, W. J. Transparency and the black box problem: Why we do not trust AI. Philosophy & technology 2021, 34(4), 1607–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Sustainable Development Goal 4; Wikipedia, 7 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank Group. Tracking SDG 7 – The Energy Progress Report 2022. June 1; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Health; 15 September 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. J.; Raghavendra, R.; Gupta, U.; Acun, B.; Ardalani, N.; Maeng, K.; Hazelwood, K. Sustainable ai: Environmental implications, challenges and opportunities. Proceedings of machine learning and systems 2022, 4, 795–813. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, Y. Machine learning and artificial intelligence-distributed renewable energy sources: technologies, perspectives, and challenges. Advances in Digitalization and Machine Learning for Integrated Building-Transportation Energy Systems 2024, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Chu, X.; Chai, C. S.; Jong, M. S. Y.; Istenic, A.; Spector, M.; Li, Y. A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education from 2010 to 2020. Complexity 2021, 2021(1), 8812542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zowghi, D.; Bano, M. AI for all: Diversity and Inclusion in AI. AI and Ethics 2024, 4(4), 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
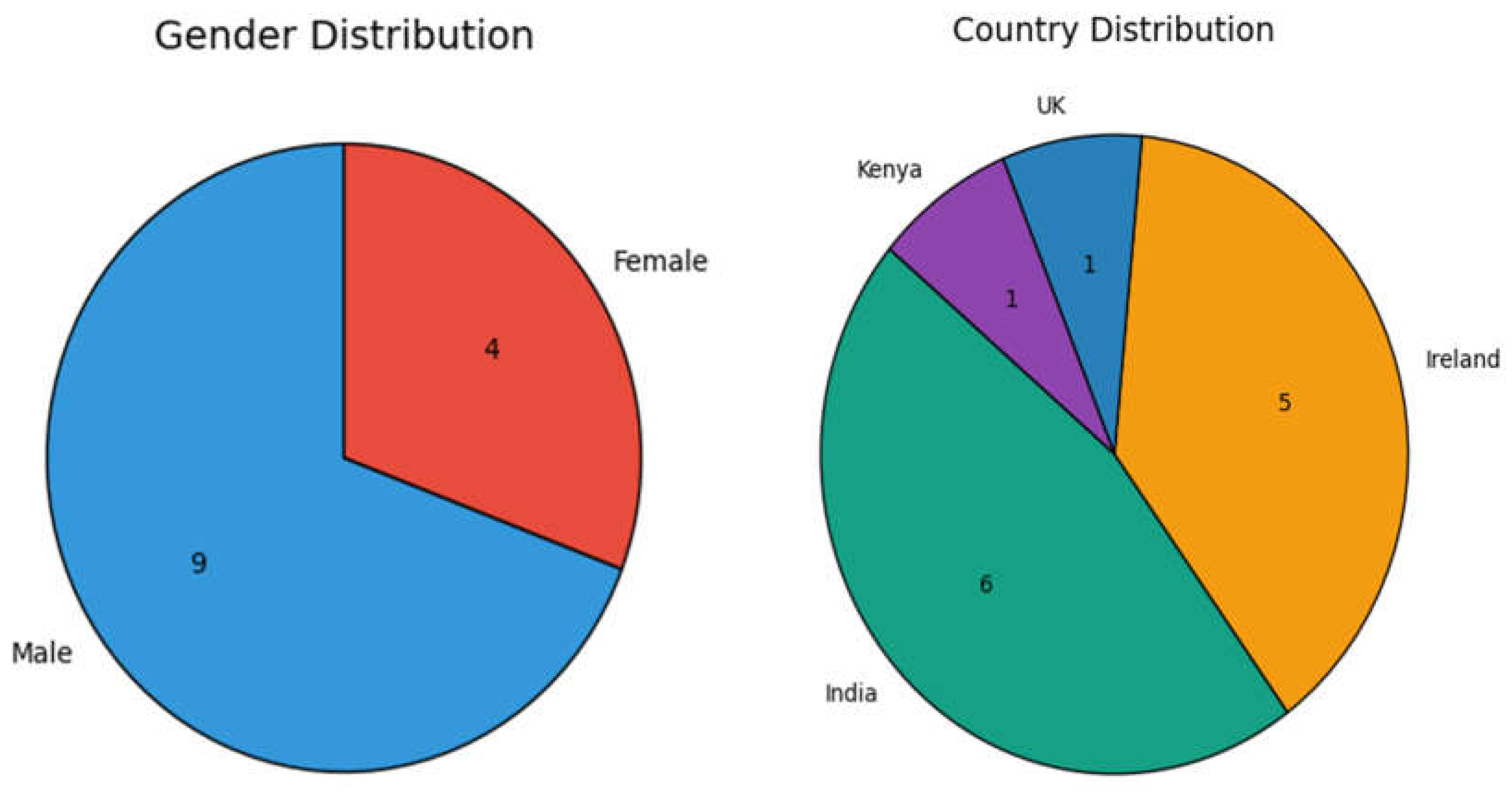
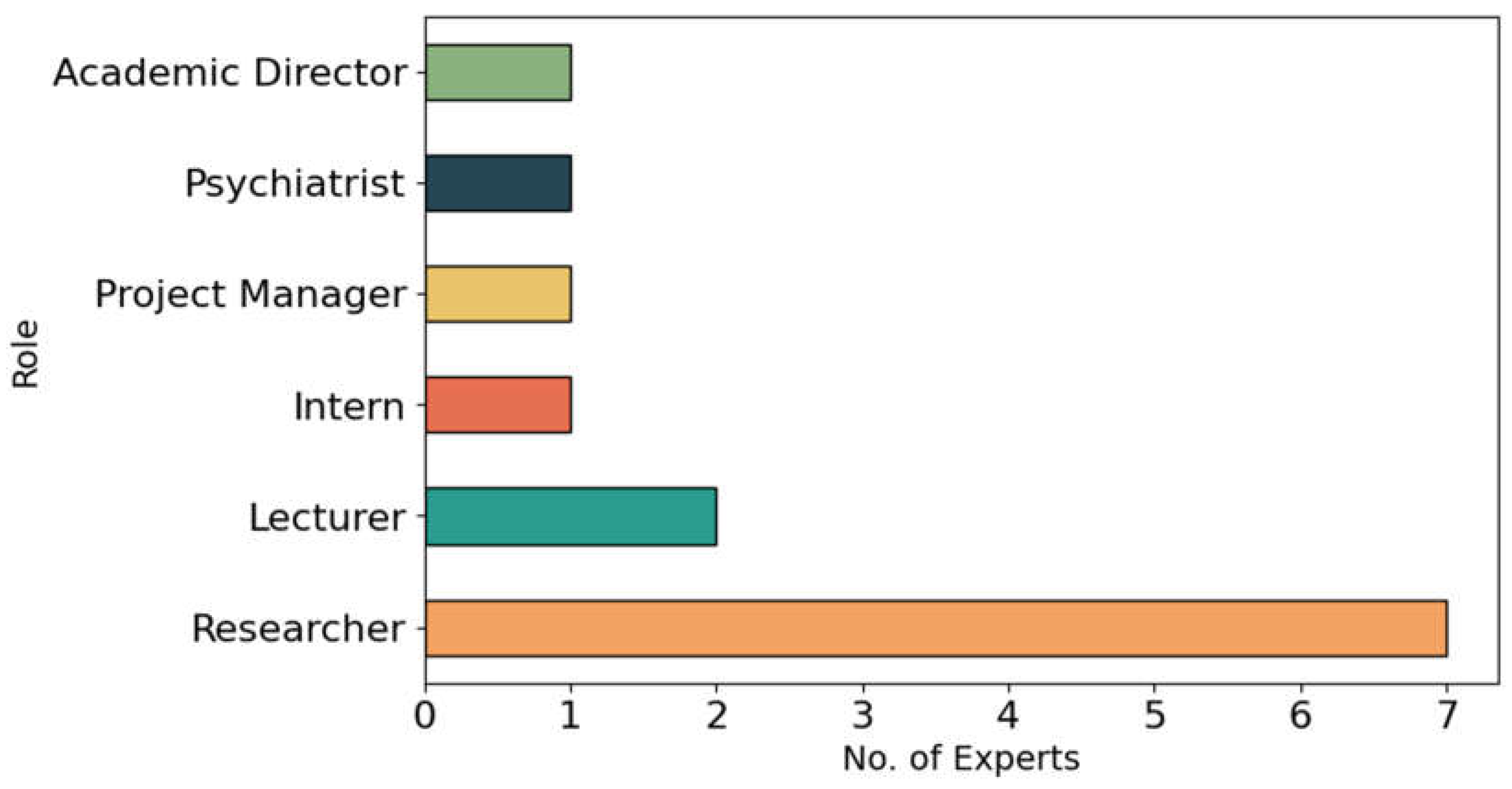
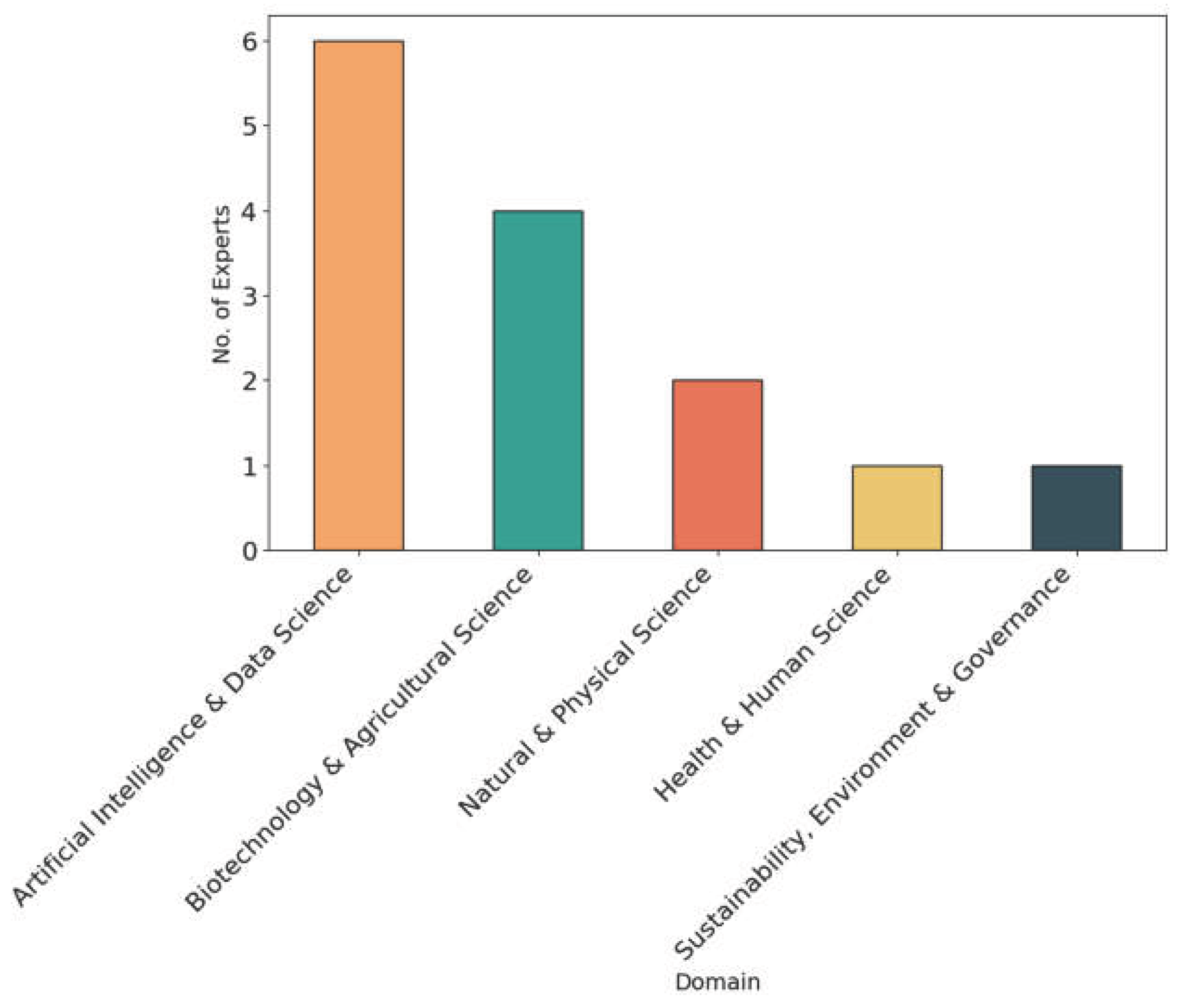
| SDG | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No Poverty (United Nations, 2025, Goal 1) | End poverty in all its forms everywhere. |
| 2 | Zero Hunger (United Nations, 2025, Goal 2) | End hunger, achieve food security and improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. |
| 3 | Good Health and Well-being (United Nations, 2025, Goal 3) | Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all ages. |
| 4 | Quality Education (United Nations, 2025, Goal 4) | Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. |
| 5 | Gender Equality (United Nations, 2025, Goal 5) | Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. |
| 6 | Clean Water and Sanitation (United Nations, 2025, Goal 6) | Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. |
| 7 | Affordable and Clean Energy (United Nations, 2025, Goal 7) | Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. |
| 8 | Decent Work and Economic Growth (United Nations, 2025, Goal 8) | Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all. |
| 9 | Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure (United Nations, 2025, Goal 9) | Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialisation, and foster innovation. |
| 10 | Reduced Inequalities (United Nations, 2025, Goal 10) | Reduce inequality within and among countries. |
| 11 | Sustainable Cities and Communities (United Nations, 2025, Goal 11) | Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. |
| 12 | Responsible Consumption and Production (United Nations, 2025, Goal 12) | Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. |
| 13 | Climate Action (United Nations, 2025, Goal 13) | Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. |
| 14 | Life Below Water (United Nations, 2025, Goal 14) | Focuses on reducing pollution, protecting marine ecosystems, and managing fisheries responsibly. |
| 15 | Life on Land (United Nations, 2025, Goal 15) | Protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems. |
| 16 | Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions (United Nations, 2025, Goal 16) | Promote peaceful and inclusive societies, provide access to justice for all, and build effective, accountable institutions. |
| 17 | Partnerships for the Goals (United Nations, 2025, Goal 17) | Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalise the global partnership for sustainable development. |
| Essay | Author | Gender | Role | Country | Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | M | Researcher | India | Artificial Intelligence & Data Science, Biotechnology & Agricultural Science |
| 2 | 2 | M | Intern | India | Artificial Intelligence & Data Science |
| 3 | 3 | F | Project Manager | India | Biotechnology & Agricultural Science |
| 4 & 5 | 4 | M | Researcher | India | Biotechnology & Agricultural Science |
| 4 & 5 | 5 | M | Researcher | India | Biotechnology & Agricultural Science |
| 6 | 6 | M | Researcher | Ireland | Artificial Intelligence & Data Science |
| 7 | 7 | M | Researcher | UK | Artificial Intelligence & Data Science |
| 7 | 8 | F | Psychiatrist | Kenya | Health & Human Science |
| 8 | 9 | M | Academic Director | Ireland | Artificial Intelligence & Data Science |
| 9 | 10 | F | Lecturer | India | Natural & Physical Science |
| 10 | 11 | F | Lecturer | Ireland | Natural & Physical Science |
| 11 | 12 | M | Researcher | Ireland | Sustainability, Environment & Governance |
| 12 | 13 | M | Researcher | Ireland | Artificial Intelligence & Data Science |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





