Submitted:
26 December 2025
Posted:
30 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Phycocyanin and Its Enzyme-Digested Products
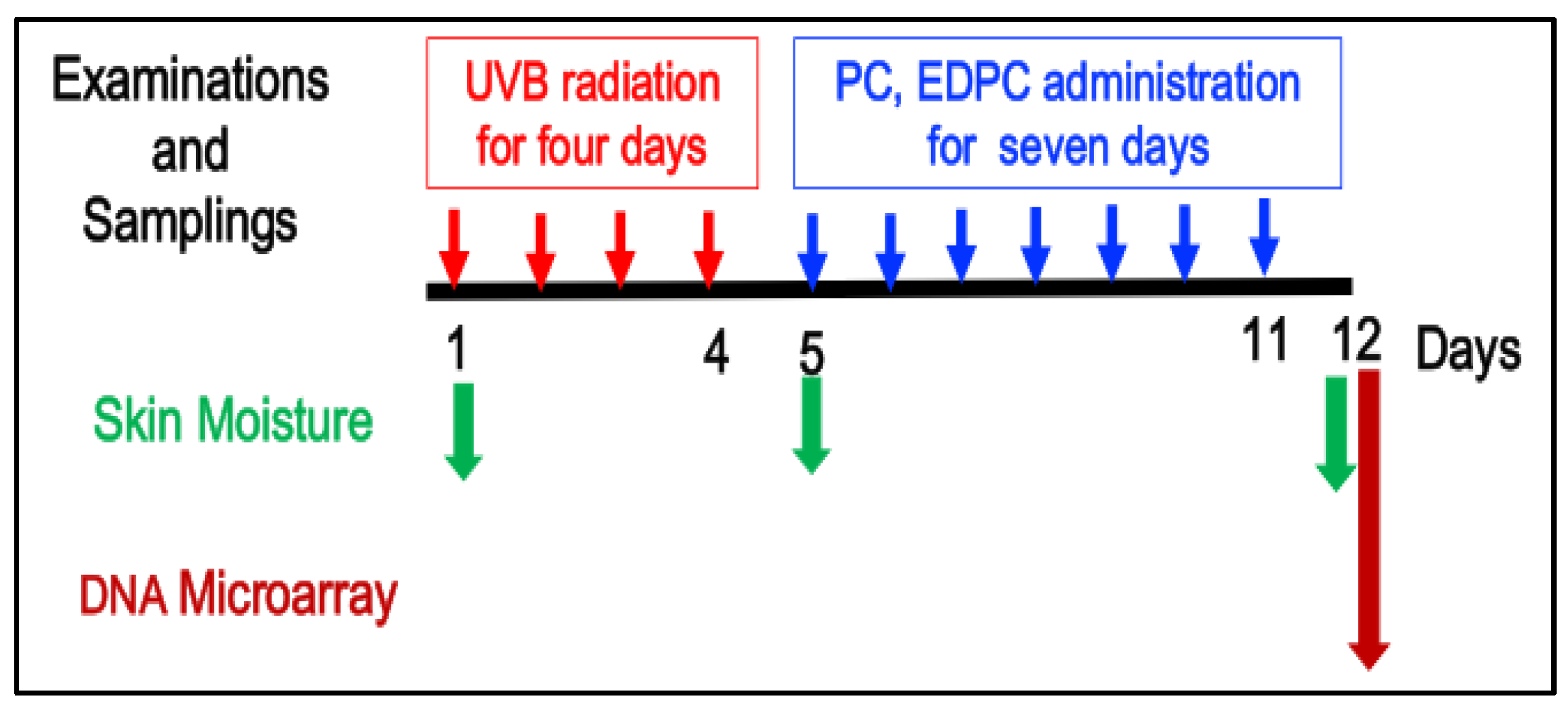
2.4. UVB Exposure
2.5. PC and EDPC Administration
2.6. Skin Moisture Measurement
2.7. Collagen Assay
2.8. RNA Extraction and Isolation
2.9. DNA Microarray Analyses
2.10. Bioinformatics Analysis of Microarray Data
3. Results
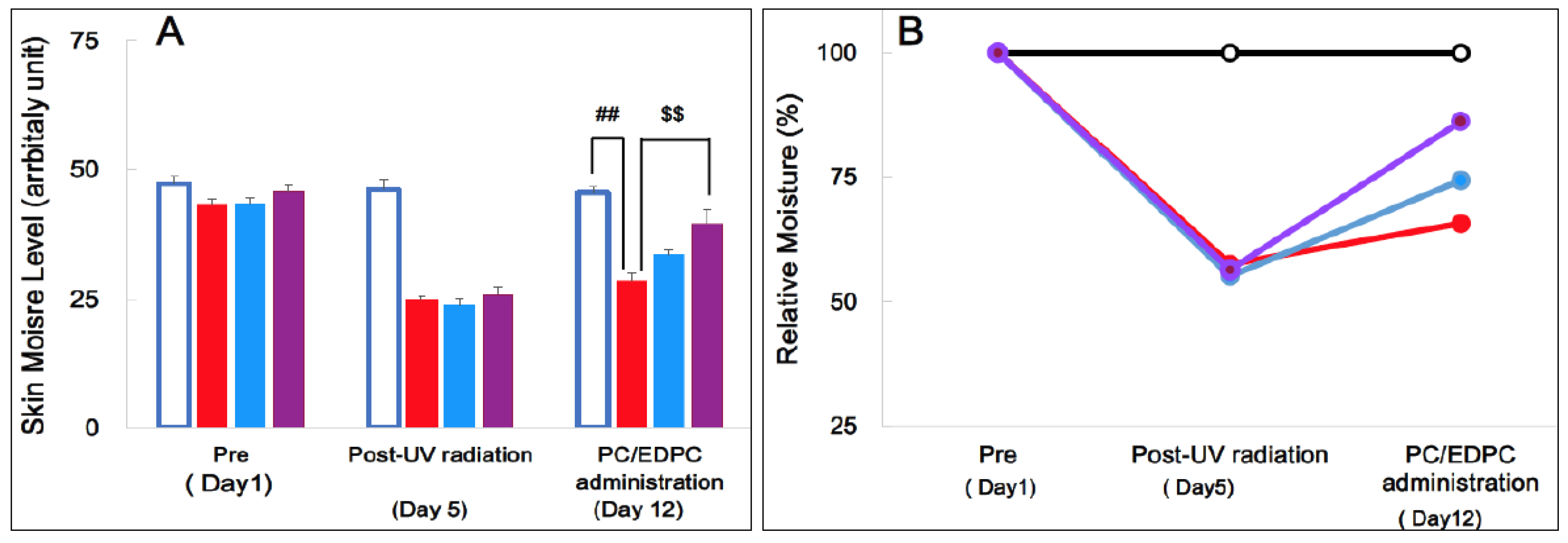
3.1.. Skin Moisture Level
3.2. Skin Collagen Amount
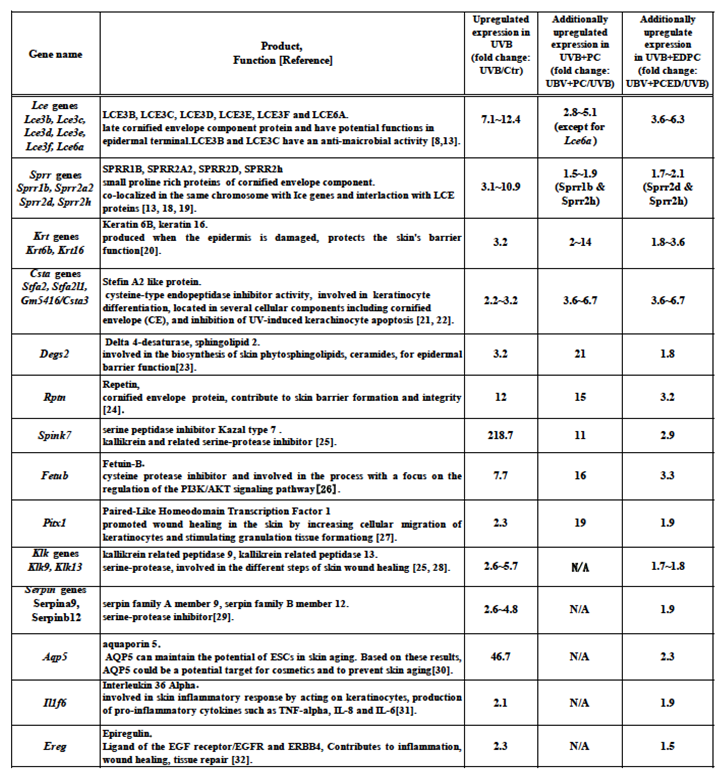
3.3. DNA Microarray Analyses and Bioinformatics
3.3.1. Additionally Upregulated PC/EDPC-Related Genes
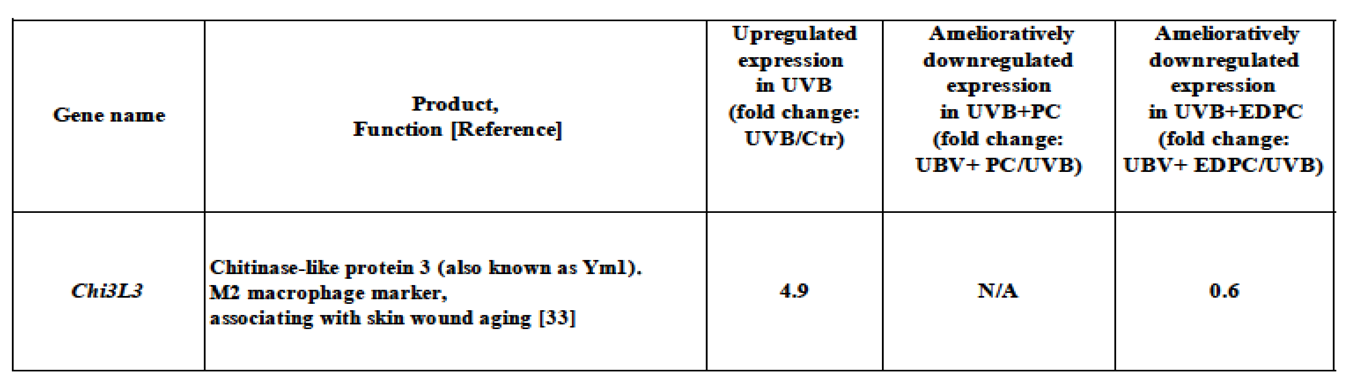
3.3.2. Amelioratively Downregulated EDPC-Related Genes.
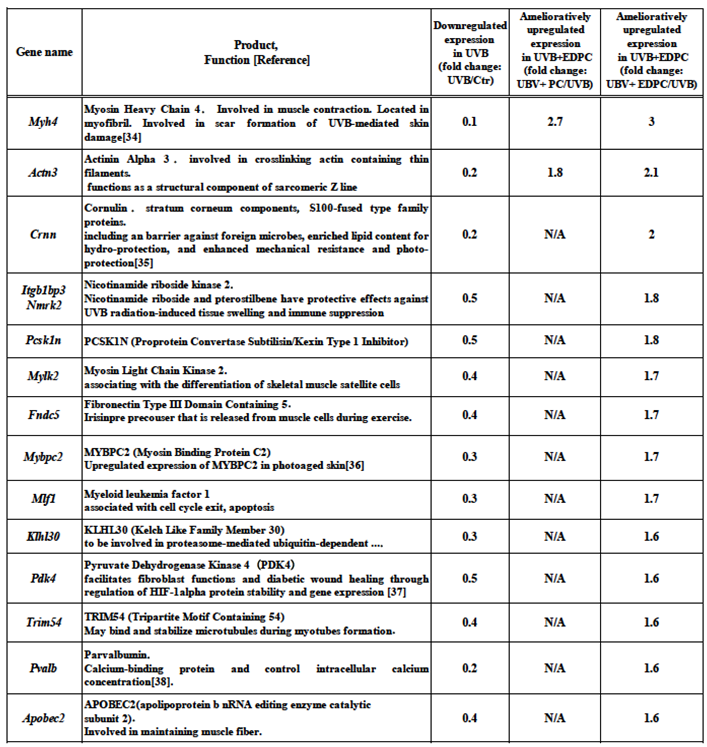
3.3.3. Amelioratively Upregulated PC/EDPC-Related Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. UVB Rays
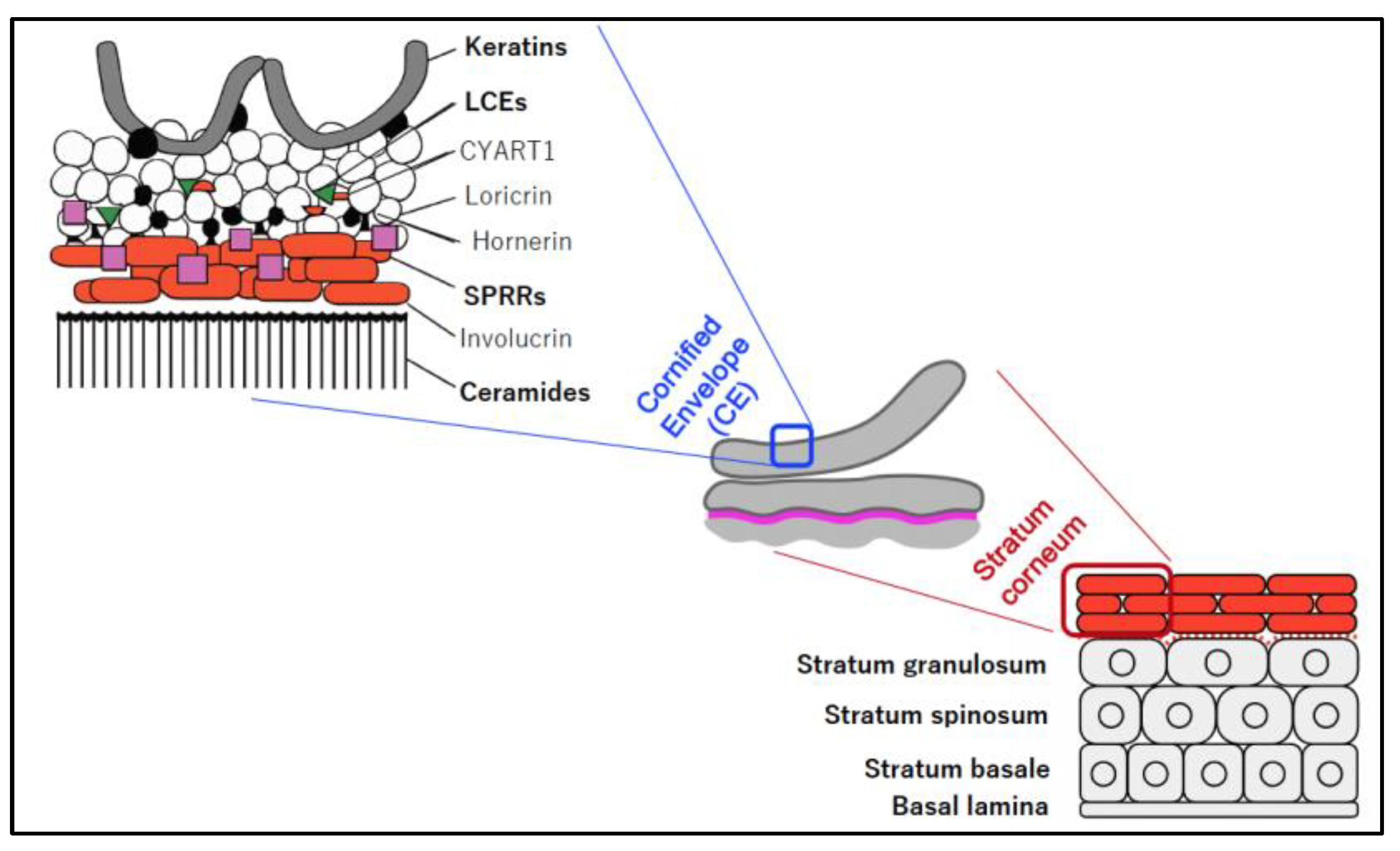
4.2. Epidermis: Its Structure and Function
4.3. Phycocyanin (PC), Enzyme-Digested Product (EDPC), and Skin Moisture
4.4. Skin Collagen
4.5. Change in Expression of Functional Genes, DNA Microarray Analyses, and Informatics
4.5.1. Additionally Upregulated PC/EDPC-Related Genes
4.5.2. Amelioratively Downregulated EDPC-Related Gene
4.5.3. Amelioratively Upregulated PC/EDPC-Related Gene
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A.T. Slominski, et al., How UV light touches the brain and endocrine system through skin, and why, Endocrinology 159 (5) (2018) 1992–2007. [CrossRef]
- R.M. Slominski, J.Y. Chen, C. Raman, A.T. Slominski, Photo-neuro-immuno- endocrinology: how the ultraviolet radiation regulates the body, brain, and immune system, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121 (14) (2024) e2308374121. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhang, E. Duan, Fighting against skin aging: the way from bench to bedside, Cell Transplant. 27 (5) (2018) 729–738.
- McCarty, M.F.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. A Fundamental Role for Oxidants and Intracellular Calcium Signals in Alzheimer’s Pathogenesis-And How a Comprehensive Antioxidant Strategy May Aid Prevention of This Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2140. [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Koseki, Y.; Hirano,M.; Nakamura, S. Nutrigenomic Studies on the Ameliorative Effect of Enzyme-Digested Phycocyanin in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice.Nutrients 2021, 13, 4431. [CrossRef]
- Jang YA, Kim BA. Protective Effect of Spirulina-Derived C-Phycocyanin against Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in HaCaT Cells, Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Mar 16;57(3):273. [CrossRef]
- Favas R, Morone J, Martins R, Vasconcelos V, Lopes G. Cyanobacteria Secondary Metabolites as Biotechnological Ingredients in Natural Anti-Aging Cosmetics: Potential to Overcome Hyperpigmentation, Loss of Skin Density and UV Radiation-Deleterious Effects, Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 1;20(3):183. [CrossRef]
- Ramos SDP, Bürck M, Costa SFFD, Assis M, Braga ARC., Spirulina as a Key Ingredient in the Evolution of Eco-Friendly Cosmetics, BioTech (Basel). 2025 May 30;14(2):41. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y, Bai R, Huang Y, Li W, Chen J, Cheng Z, Wu X, Diao Y.The anti-photoaging effect of C-phycocyanin on ultraviolet B-irradiated BALB/c-nu mouse skin, Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023 Aug 22:11:1229387. [CrossRef]
- lmai Y, Hirahashil T, Fukuda M. Phycocyanin Reduces Transepidermal water Loss and lmproves Skin Barrier Function in Healthy subjects-A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Paralle-group Comparison Trial-, Jpn Pharmacol Ther 2019; 47:1833-40, UMINID:000035205.
- Knuschke P, Sun Exposure and Vitamin D,Curr Probl Dermatol, 2021:55:296-315. [CrossRef]
- Niehues H, Rikken G, Kersten FFJ, Eeftens JM, van Vlijmen-Willems IMJJ, Rodijk-Olthuis D, et al. CYSRT1: an antimicrobial epidermal protein that can interact with late cornified envelope proteins. J Invest Dermatol, 2023;143:1498e1508.e7.
- Nathalie Jonca1,2 and Michel Simon, The Cornified Envelope: A Versatile Contributor to the Epidermal Barrier, Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2023) 143, 1335e1337; [CrossRef]
- Tanaka M, Koyama Y, Nomura Y.,Effects of collagen peptide ingestion on UV-B-induced skin damage.,Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009 Apr 23;73(4):930-2. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Mitsunaga, F.; Wasaki, K.; Kotani, A.; Tajima, K.; Tanji, M.; Nakamura, S. Mechanism Underlying the Immune Responses of Sublingual Vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 with RBD Antigen and Adjuvant, Poly(I:C) or AddaS03, in Non-human Primates. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 7, 150–164.
- Yamamoto, T.; HIrano, M.; Mitsunaga, F.;Wasaki, K.; Kotani, A.; Tajima, K.; Nakamura, S. Molecular Events in Immune Responses to Sublingua Influenza Vaccine with Hemagglutinin Antigen and Poly(I:C) Adjuvant in Nonhuman Primates, Cynomolgus Macaques. Vaccines 2024, 12, 643.
- Shen C, Gao J, Yin X, Sheng Y, Sun L, Cui Y, Zhang X, Association of the late cornified envelope-3 genes with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review, J Genet Genomics. 2015 Feb 20;42(2):49-56. [CrossRef]
- Gibbs S, Fijneman R, Wiegant J, van Kessel AG, van De Putte P, Backendorf C.,Molecular characterization and evolution of the SPRR family of keratinocyte differentiation markers encoding small proline-rich proteins, Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):630-7. [CrossRef]
- Tian S, Chen S, Feng Y, Li Y., The Interactions of Small Proline-Rich Proteins with Late Cornified Envelope Proteins are Involved in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis,Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Sep 24:14:1355-1365. [CrossRef]
- Romashin DD, Tolstova TV, Varshaver AM, Kozhin PM, Rusanov AL, Luzgina NG., Keratins 6, 16, and 17 in Health and Disease: A Summary of Recent Findings., Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 6;46(8):8627-8641. [CrossRef]
- Kim SY, Bae CD., Calpain inhibitors reduce the cornified cell envelope formation by inhibiting proteolytic processing of transglutaminase 1, Exp Mol Med. 1998 Dec 31;30(4):257-62. [CrossRef]
- Doleckova I, Vidovic T, Jandova L, Gretzmeier C, Navarini AA, MacArthur MR, Goksel O, Nyström A, Ewald CY., Calpain Inhibition Protects against UVB-Induced Degradation of Dermal-Epidermal Junction-Associated Proteins, J Invest Dermatol., 2024 Sep;144(9):2103-2107.e2. [CrossRef]
- Ota A, Morita H, Naganuma T, Miyamoto M, Jojima K, Nojiri K, Matsuda J, Kihara A., Bifunctional DEGS2 has higher hydroxylase activity toward substrates with very-long-chain fatty acids in the production of phytosphingosine ceramides, J. Biol Chem., 2023 Apr;299(4):104603. [CrossRef]
- Krieg P, Schuppler M, Koesters R, Mincheva A, Lichter P, Marks F., Repetin (Rptn), a new member of the "fused gene" subgroup within the S100 gene family encoding a murine epidermal differentiation protein, GEnomics., 1997 Aug 1;43(3):339-48. [CrossRef]
- Liddle J, Beneton V, Benson M, Bingham R, Bouillot A, Boullay AB, et al., A Potent and Selective Kallikrein-5 Inhibitor Delivers High Pharmacological Activity in Skin from Patients with Netherton Syndrome, J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Sep;141(9):2272-2279. [CrossRef]
- Zhang W, Yao J, Chen C, Wang J, Zhou A., Fetuin-B Overexpression Promotes Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy Through Activating Microglia and the NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Curr Eye Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):168-179. [CrossRef]
- Overmiller AM, Uchiyama A, Hope ED, Nayak S, O'Neill CG, Hasneen K, Chen YW, Reprogramming of epidermal keratinocytes by PITX1 transforms the cutaneous cellular landscape and promotes wound healing., JCI Insight. 2024 Dec 20;9(24):e182844. [CrossRef]
- Nauroy P, Nyström A, Kallikreins: Essential epidermal messengers for regulation of the skin microenvironment during homeostasis, repair and disease, Matrix Biol Plus, 2019 Nov 21:6-7:100019. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Li J, Zhou L, Hou H, Zhang K., Regulation of epidermal barrier function and pathogenesis of psoriasis by serine protease inhibitors, Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 16:15:1498067. [CrossRef]
- Zhou J, Dong Y, Liu J, Ren J, Wu J, Zhu N., AQP5 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of epidermal stem cells in skin aging, Braz J Med Biol Res 2020 Sep 18;53(11):e10009. [CrossRef]
- Calabrese L, Fiocco Z, Satoh TK, Peris K, French LE., Herapeutic potential of targeting interleukin-1 family cytokines in chronic inflammatory skin diseases, Br J Dermatol. 2022 Jun;186(6):925-941. [CrossRef]
- Odell ID, Steach H, Gauld SB, Reinke-Breen L, Karman J, Carr TL, Epiregulin is a dendritic cell-derived EGFR ligand that maintains skin and lung fibrosis, Sci Immunol. 2022 Dec 16;7(78):eabq6691. [CrossRef]
- Murase T, Shinba Y, Mitsuma M, Abe Y, Yamashita H, Ikematsu K., Wound age estimation based on chronological changes in chitinase 3-like protein 1 expression. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2022 Nov;59:102128. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Inoue Y, Fardous J, Doi R, Ijima T, Fujibuchi T, et al, Prevention and Repair of Ultraviolet B-Induced Skin Damage in Hairless Mice via Transdermal Delivery of Growth Factors Immobilized in a Gel-in-Oil Nanoemulsion.,ACS Omega. 2023 Mar 3;8(10):9239-9249. [CrossRef]
- Makino T, Mizawa M, Takemoto K, Shimizu T., Ultraviolet B irradiation increases the expression of cornulin and retepin in human skin xenotransplants. Exp Dermatol. 2024 May;33(5):e15109. [CrossRef]
- Zhao J, Zhang X, Zhang D, Tang Q, Bi Y, Yuan L, Yang B, Li X, Li Z, Deng D, Cao W., Critical genes in human photoaged skin identified using weighted gene co-expression network analysis., Genomics. 2023 Sep;115(5):110682. [CrossRef]
- Ma Z, Mo R, Yang P, Ding Y, Zhang H, Dong Z, Chen Y, Tan Q., PDK4 facilitates fibroblast functions and diabetic wound healing through regulation of HIF-1α protein stability and gene expression., FASEB J. 2023 Oct;37(10):e23215. [CrossRef]
- Yáñez M, Gil-Longo J, Campos-Toimil M., Calcium binding proteins., Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;740:461-82. [CrossRef]
- Schäfer M, Werner S., The cornified envelope: a first line of defense against reactive oxygen species., J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Jul;131(7):1409-11. [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




