Submitted:
05 December 2025
Posted:
08 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
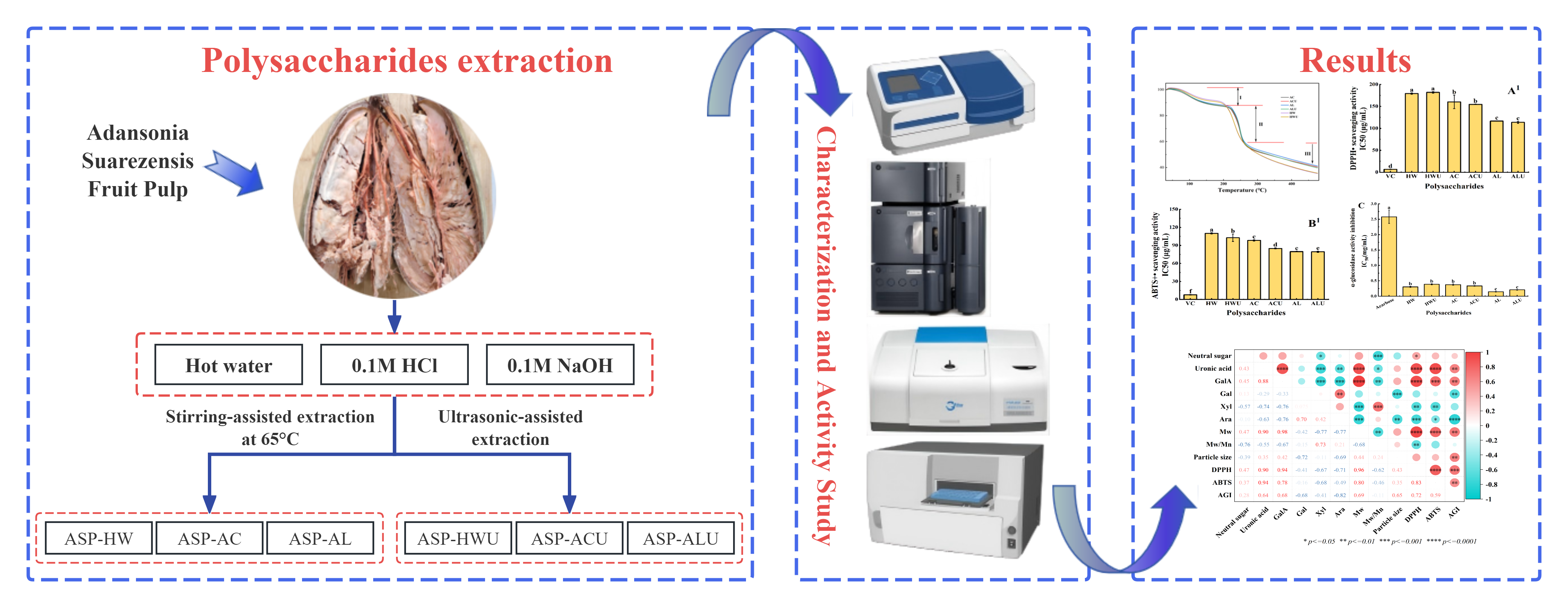
This study extracted polysaccharides from Adansonia Suarezensis fruit pulp using various methods: hot water (ASP-HW), acid (ASP-AC), alkaline (ASP-AL), ultrasound-assisted hot water (ASP-HWU), ultrasound-assisted acid (ASP-ACU), and ultrasound-assisted alkaline (ASP-ALU). A comparison was conducted on the yield, chemical composition, structural properties, and biological activities. The findings indicated that the extraction solvent significantly influenced various essential properties of the ASPs, such as yield, monosaccharide composition, molecular weight, particle size, and thermal stability. The polysaccharides consisted of galacturonic acid, galactose, xylose, and arabinose.ASP-AL and ASP-ALU exhibited smaller molecular weight and particle size, with molecular weights of 19,813 Da and 19,600 Da, and particle sizes of 146.67 ± 22.46 nm and 140.97 ± 20.38 nm, respectively. The ASPs displayed characteristic polysaccharide structures, with ASP-AC, ASP-ACU, ASP-AL, and ASP-ALU possessing a triple-helix conformation. Bioactivity assays demonstrated that ASP-AL and ASP-ALU had enhanced DPPH radical scavenging activity (IC50 116.67 ± 0.58 μg/mL and 113.67 ± 2.31 μg/mL, respectively), ABTS radical scavenging activity (IC50 79.67 ± 0.58 μg/mL and 79.33 ± 1.15 μg/mL, respectively), and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (IC50 0.146 ± 0.01 mg/mL and 0.206 ± 0.01 mg/mL, respectively).These findings indicate that ASPs possess significant bioactivity, supporting their potential use in pharmaceuticals and functional foods.