Submitted:
14 November 2025
Posted:
17 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
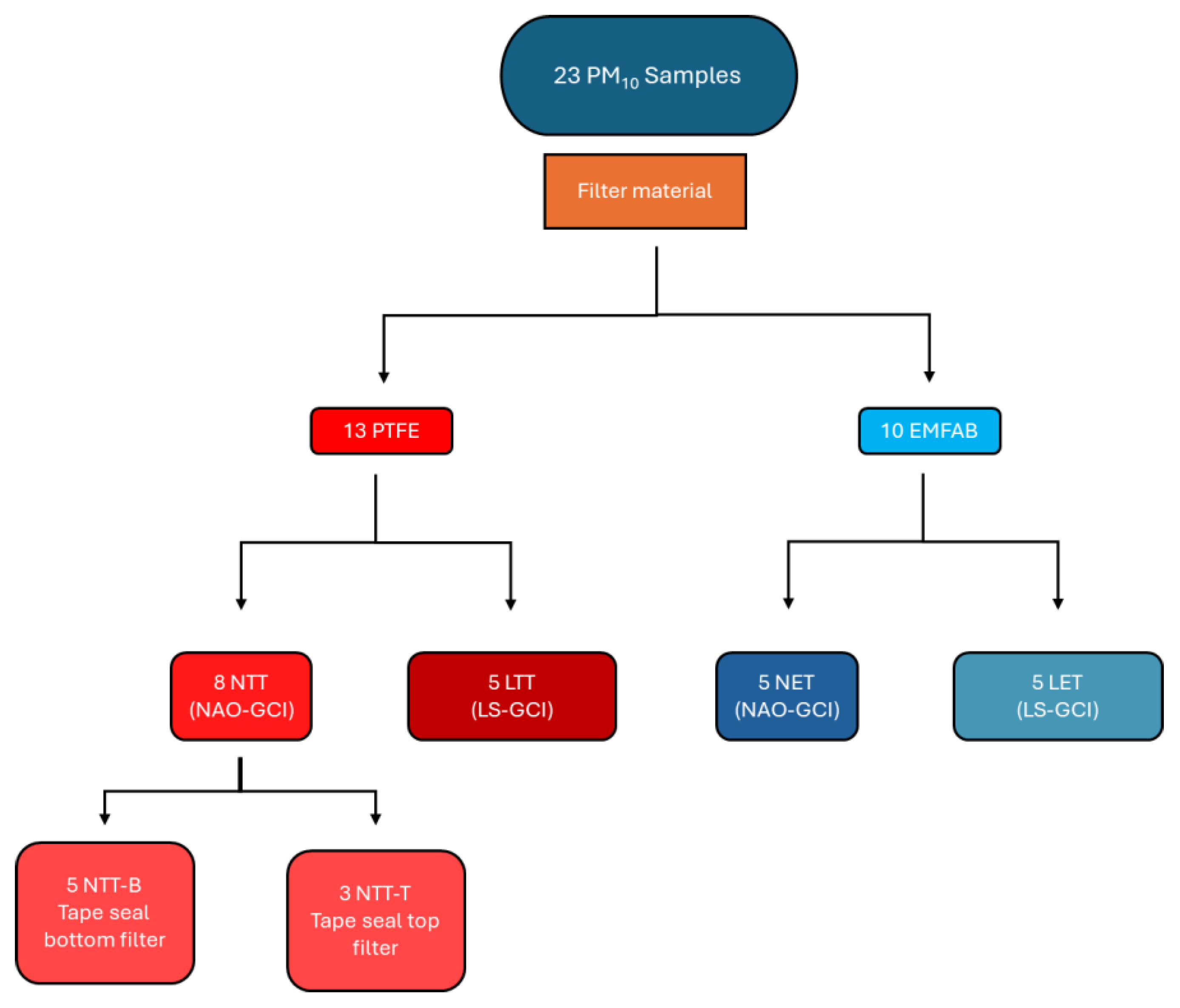
1.1. Sample Pretreatment Results
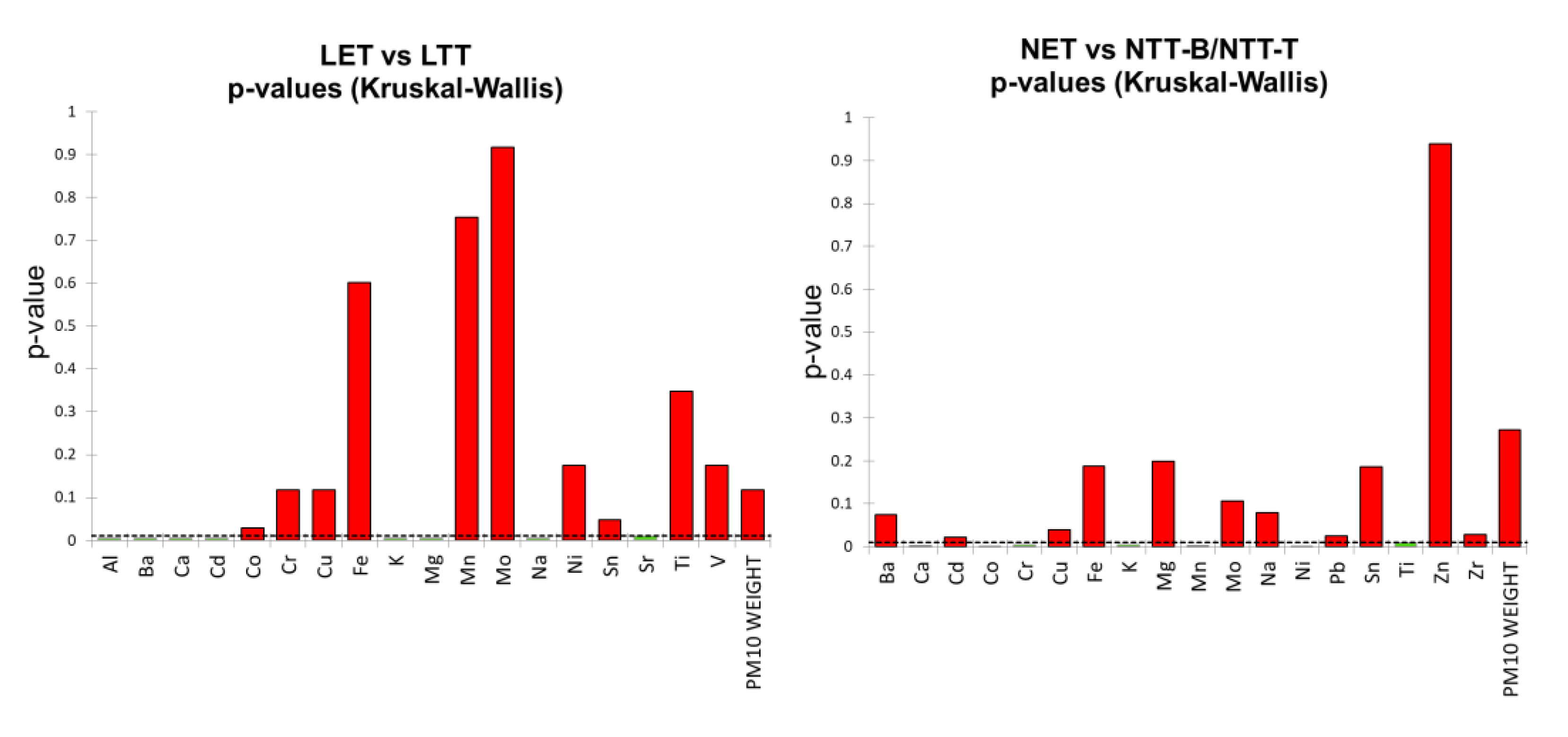
1.1. Tribometer/Dynamometer PM10 Sample Comparison
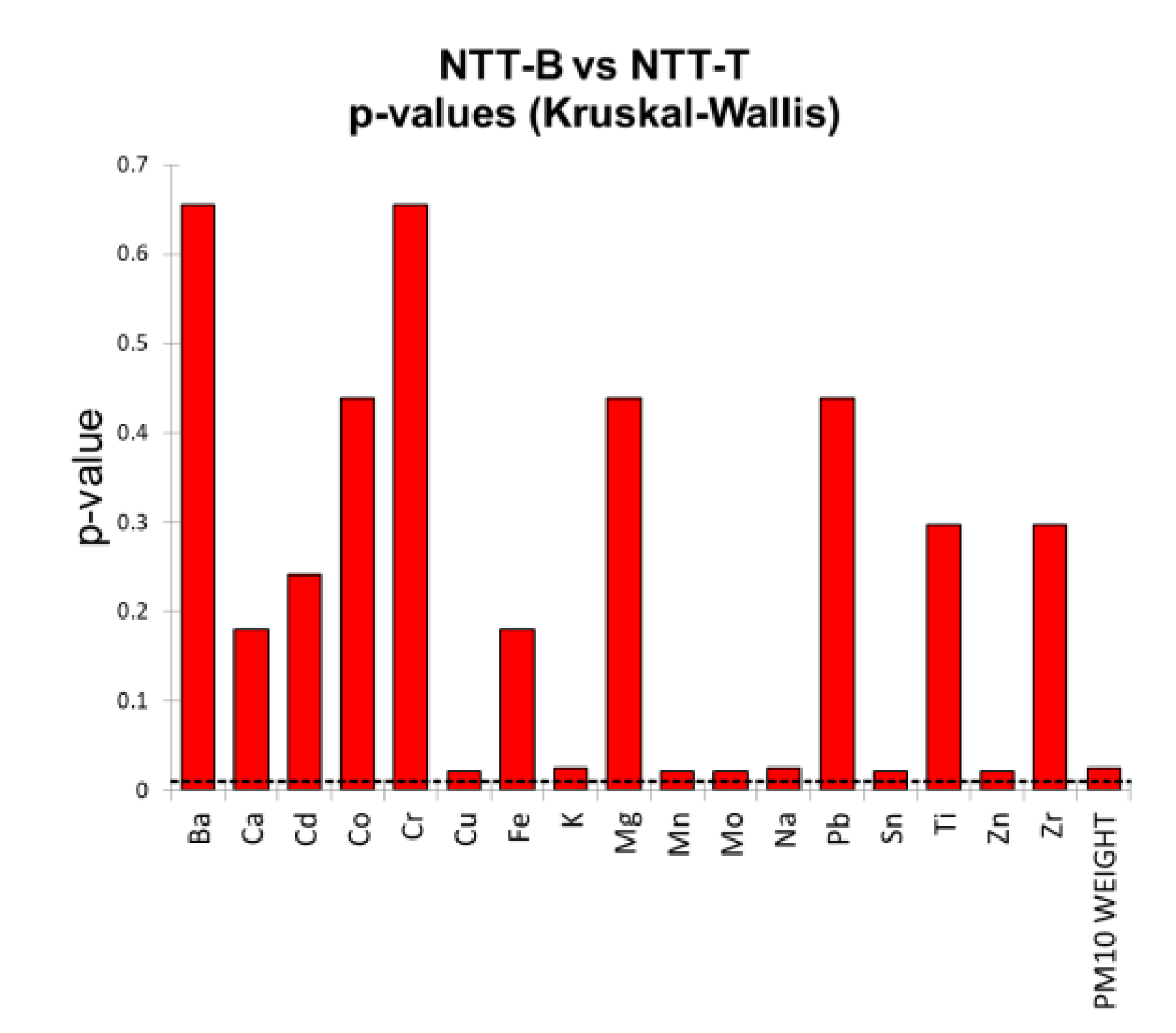
1.1. Filter Blanks Comparison
1.1. PM10 Samples Results
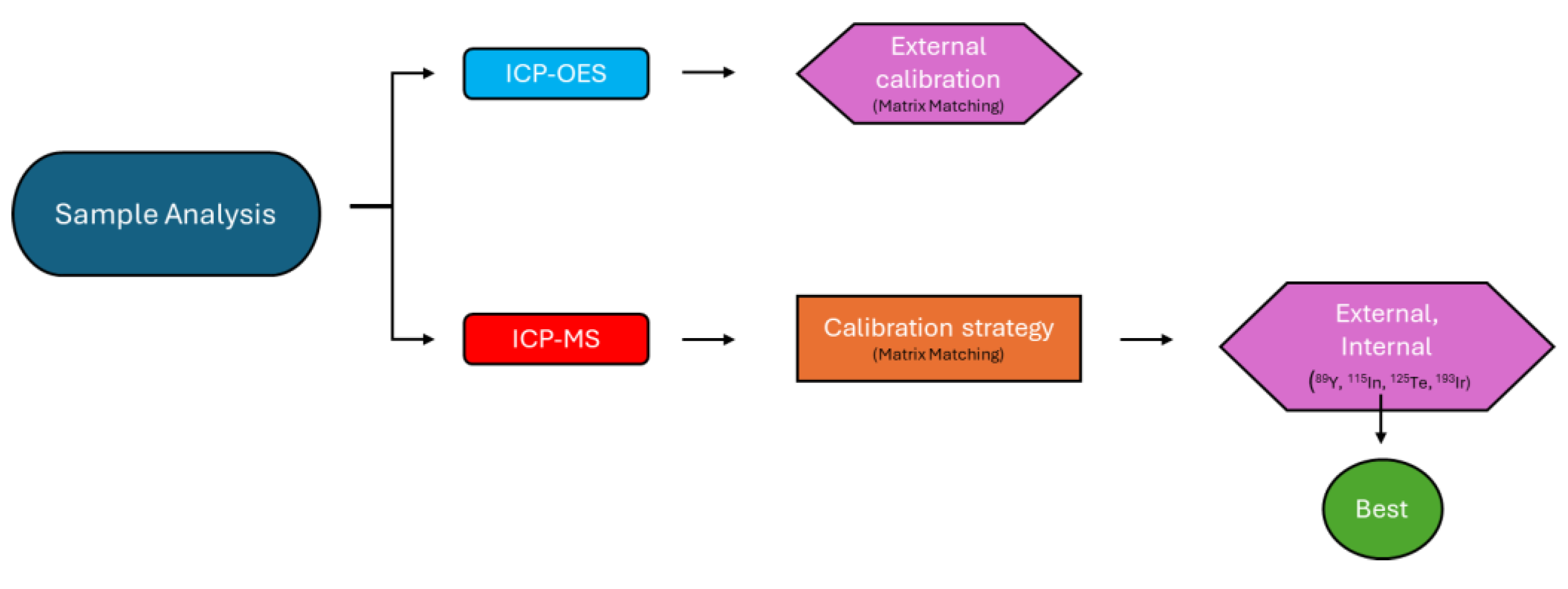
3. Materials and Methods
1.1. PM10 Tribometer Samples
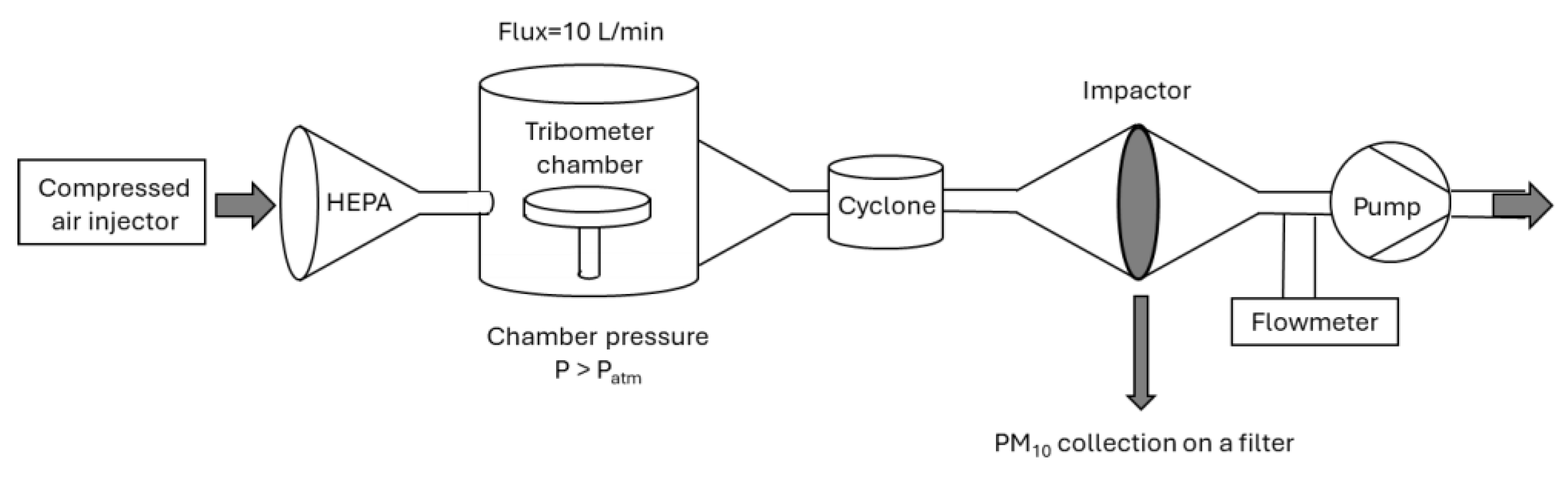
1.1. Tribometer Set-Up
1.1. Sampling Filter Blanks
1.1. Reagents
1.1. Sample Pretreatment
1.1. Chemical Analysis
1.1. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amato, F. (Ed.) Non-Exhaust Emissions: An Urban Air Quality Problem for Public Health: Impact and Mitigation Measures; Academic Press: London, UK; San Diego, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Non-Exhaust Particulate Emissions from Road Transport: An Ignored Environmental Policy Challenge; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Piscitello, A.; Bianco, C.; Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Non-exhaust traffic emissions: Sources, characterization, and mitigation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, P.G.; Xu, N.; Dalka, T.M.; Maricq, M.M. Airborne brake wear debris: Size distributions, composition, and a comparison of dynamometer and vehicle tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4060–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietl, J.K.; Lawrence, R.; Thorpe, A.J.; Harrison, R.M. Identification of brake wear particles and derivation of a quantitative tracer for brake dust at a major road. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, N.; Glisovic, J.; Abdullah, O.I.; Belhocine, A.; Grujic, I. Particle formation due to brake wear, influence on human health and measures for their reduction: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9606–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paithankar, J.G.; Saini, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Sharma, A.; Chowdhuri, D.K. Heavy metal associated health hazards: An interplay of oxidative stress and signal transduction. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukutschová, J.; Filip, P. Chapter 6—Review of brake wear emissions: A review of brake emission measurement studies: Identification of gaps and future needs. In Non-Exhaust Emissions; Amato, F., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK; San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Philippe, F.; et al. ; et al. Representativeness of airborne brake wear emission for the automotive industry: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part D: J. Automob. Eng. 2021, 235, 2651–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagino, H. Feasibility of Measuring Brake-Wear Particle Emissions from a Regenerative-Friction Brake Coordination System via Dynamometer Testing. Atmosphere.. 2024; 15(1):75.
- Brembo S.p.A.; et al. Comparative study of size distribution and chemical composition of emissions from low-steel and NAO friction materials. In EuroBrake 2022—Technical Content; FISITA, May 2022.
- Kadachi, A.N.; Al-Eshaikh, M.A. Limits of detection in XRF spectroscopy. X-Ray Spectrom. 2012, 41, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbury, D.E.; Ritchie, N.W.M. Is scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (SEM/EDS) quantitative? Scanning 2013, 35, 141–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachchhav, B.D.; Hendre, K.N. Wear performance of asbestos-free brake pad materials. Jordan J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2022, 16, 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- Löber, M.; et al. Investigations of airborne tire and brake wear particles using a novel vehicle design. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 53521–53531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.-H.; Lee, G.; Han, B.; Lee, S.-H. Development of dust collectors to reduce brake wear PM emissions. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, Z.; Rosenkranz, A.; Song, Y.; Xue, T.; Fang, F. Surface- and tip-enhanced Raman scattering in tribology and lubricant detection—A prospective. Lubricants 2019, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, S.; Bellatreccia, F.; Casanova Municchia, A.; Della Ventura, G.; Sodo, A. Raman spectra of natural manganese oxides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S. Tracer-gas-integrated measurements of brake-wear particulate matter emissions from heavy-duty vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15968–15978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchett, L.C.; Abou-Ghanem, M.; Stix, K.A.R.; McGrath, D.T.; Styler, S.A. Ozone uptake by commercial brake pads and brake pad components: Assessing the potential indirect air quality impacts of non-exhaust emissions. Environ. Sci.: Atmos. 2022, 2, 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Neukirchen, C.; et al. Comprehensive elemental and physical characterization of vehicle brake wear emissions from two different brake pads following the global technical regulation methodology. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conca, E.; et al. Methods for elemental analysis of size-resolved PM samples collected on aluminium foils: Results of an intercomparison exercise. Molecules 2022, 27, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiec, E.; Jarosz-Krzemińska, E.; Wieszała, R. Heavy metals from non-exhaust vehicle emissions in urban and motorway road dusts. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussan, D.D. An environmentally compatible and less costly (greener) microwave digestion method of bone samples using dilute nitric acid for analysis by ICP-MS. Research Square 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakkani, M.F. Guideline of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): Fundamentals, practices, determination of the limits, quality control, and method validation parameters. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldabe, J.; Santamaría, C.; Elustondo, D.; Lasheras, E.; Santamaría, J.M. Application of microwave digestion and ICP-MS to simultaneous analysis of major and trace elements in aerosol samples collected on quartz filters. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Assimomytis, N.; Varvaresou, A. Sample preparation of cosmetic products for the determination of heavy metals. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moursy, A.R.; Ahmed, N.; Sahoo, R. Determination of total content of some microelements in soil using two digestion methods. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 2510–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNI EN 14902:2005. Qualità dell’aria ambiente—Metodo normalizzato per la misurazione di Pb, Cd, As e Ni nella frazione PM10 del particolato in sospensione. Available online: https://webstore.uni.com/uni-en-14902-2005 (accessed on 7 November 2025).
- Kayaba, S.; Kajino, M. Potential impacts of energy and vehicle transformation through 2050 on oxidative-stress-inducing PM2.5 metals concentration in Japan. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2023GH000789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowiecki, N.; Lienemann, P.; Hill, M.; Figi, R.; Richard, A.; Furger, M.; Rickers, K.; Falkenberg, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cliff, S.S.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U.; Buchmann, B.; Gehrig, R. Y.; Cliff, S.S.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U.; Buchmann, B.; Gehrig, R. Real-world emission factors for antimony and other brake wear related trace elements: Size-segregated values for light- and heavy-duty vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8072–8078. [Google Scholar]
- Diana, A.; et al. PM10 element distribution and environmental-sanitary risk analysis in two Italian industrial cities. Atmosphere 2022, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Bhowmik, D.; Sikder, N. Direct determination of zirconium and silicon in zircon by flame atomic absorption spectrometry using two rapid decomposition methods. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, R.; Stark, C.; Vella, A.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Aquilina, N.J. Validation of an optimised microwave-assisted acid digestion method for trace and ultra-trace elements in indoor PM2.5 by ICP-MS analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lough, G.C.; Schauer, J.J.; Park, J.-S.; Shafer, M.M.; DeMinter, J.T.; Weinstein, J.P. Emissions of metals associated with motor vehicle roadways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamser, C.A. Hydrolysis of fluoboric acid in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.B.; Grant-Weaver, I.; Shotyk, W. An optimized HNO3 and HBF4 digestion method for multielemental soil and sediment analysis using inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 100, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucharová, J.; Suchara, I. ; Suchara, I. Determination of 36 elements in plant reference materials with different Si contents by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: Comparison of microwave digestions assisted by three types of digestion mixtures. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 576, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krachler, M.; Mohl, C.; Emons, H.; Shotyk, W. Influence of digestion procedures on the determination of rare earth elements in peat and plant samples by USN-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, T.; von der Au, M.; Reese, A.; Klein, O.; Hildebrandt, L.; Pröfrock, D. Substituting HF by HBF4—An optimized digestion method for multi-elemental sediment analysis via ICP-MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 3778–3787. [Google Scholar]
- PMP—Particle Measurement Programme Informal Working Group Task Force 2—Brake Dust Sampling and Measurement. Minimum Specifications for Measuring and Characterizing Brake Emissions, July, 20 July.
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Wang, X.; Abbasi, B.; Reed, W.R.; Parks, D. Review of filters for air sampling and chemical analysis in mining workplaces. Minerals 2022, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; et al. Elemental and isotopic compositions in blank filters collecting atmospheric particulates. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U. S. EPA. Guidelines for PM-10 Sampling and Analysis Applicable to State Implementation Plans; Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1987; EPA-450/4-87-013. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, W. AOAC Guidelines for Single-Laboratory Validation of Chemical Methods for Dietary Supplements and Botanicals; AOAC INTERNATIONAL: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; et al. Iron dissolution kinetics of mineral dust at low pH during simulated atmospheric processing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereshchak, M.; Manakova, I.; Shokanov, A.; Sakhiyev, S. Mössbauer studies of narrow fractions of fly ash formed after combustion of Ekibastuz coal. Materials 2021, 14, 7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzałkowska, E. Morphology, chemical and mineralogical composition of magnetic fraction of coal fly ash. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2021, 240, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Rimstidt, J.D. Solubility and dissolution rate of silica in acid fluoride solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 7045–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, F.E.; Huffman, G.P.; Robertson, J.D. Speciation of elements in NIST particulate matter SRMs 1648 and 1650. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 74, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, A.; et al. Particulate matter emissions from brake pads: A comparative study of low-steel and non-asbestos organic materials. SSRN 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einax, J.W.; Zwanziger, H.W.; Geiß, S. Chemometrics in Environmental Analysis; Wiley, 1997. Available online: https://books.google.it/books?id=UNBfKNh0E1gC (accessed on 7 November 2025).
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C.; Miller, R.D. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 7th ed.; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
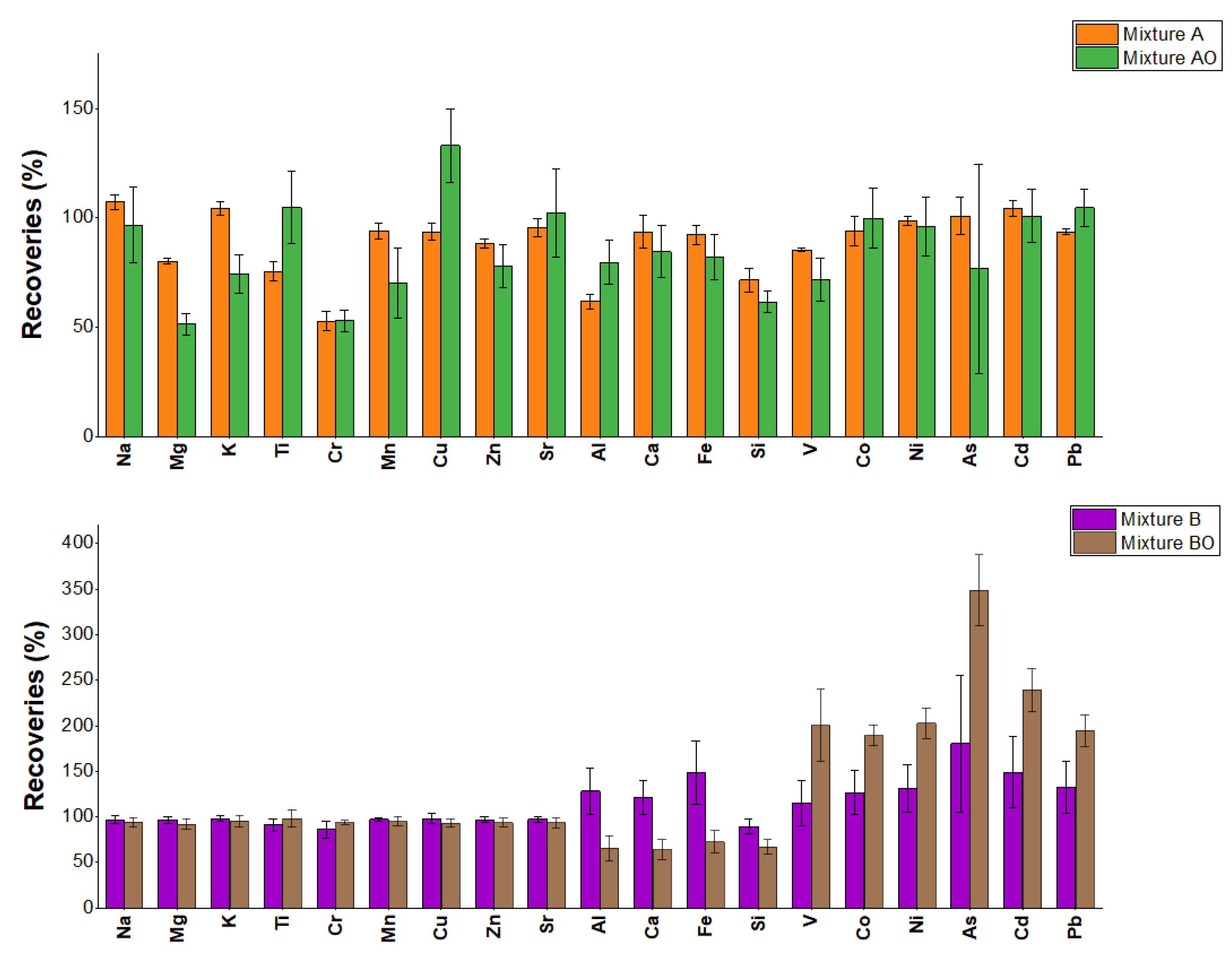
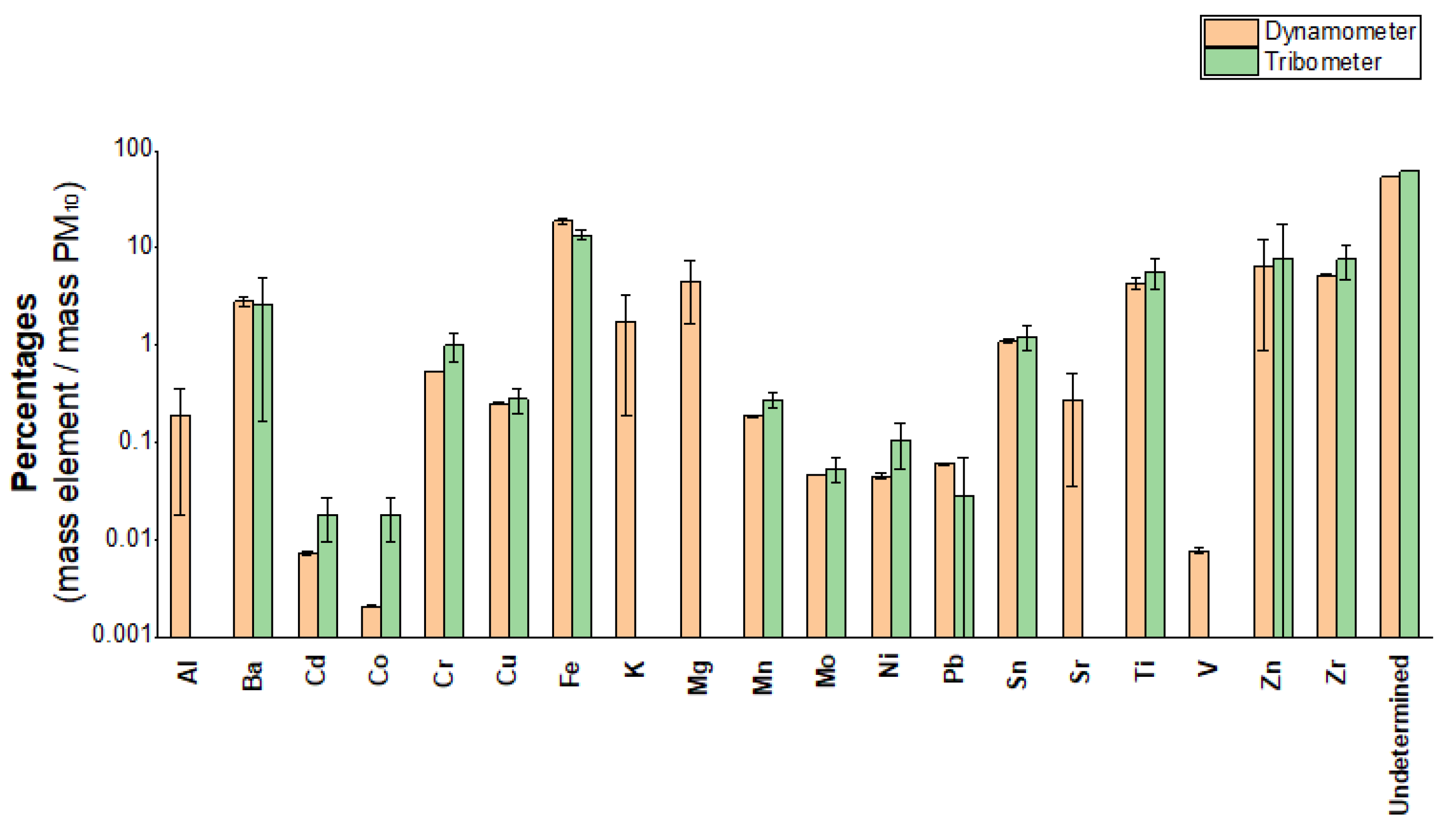

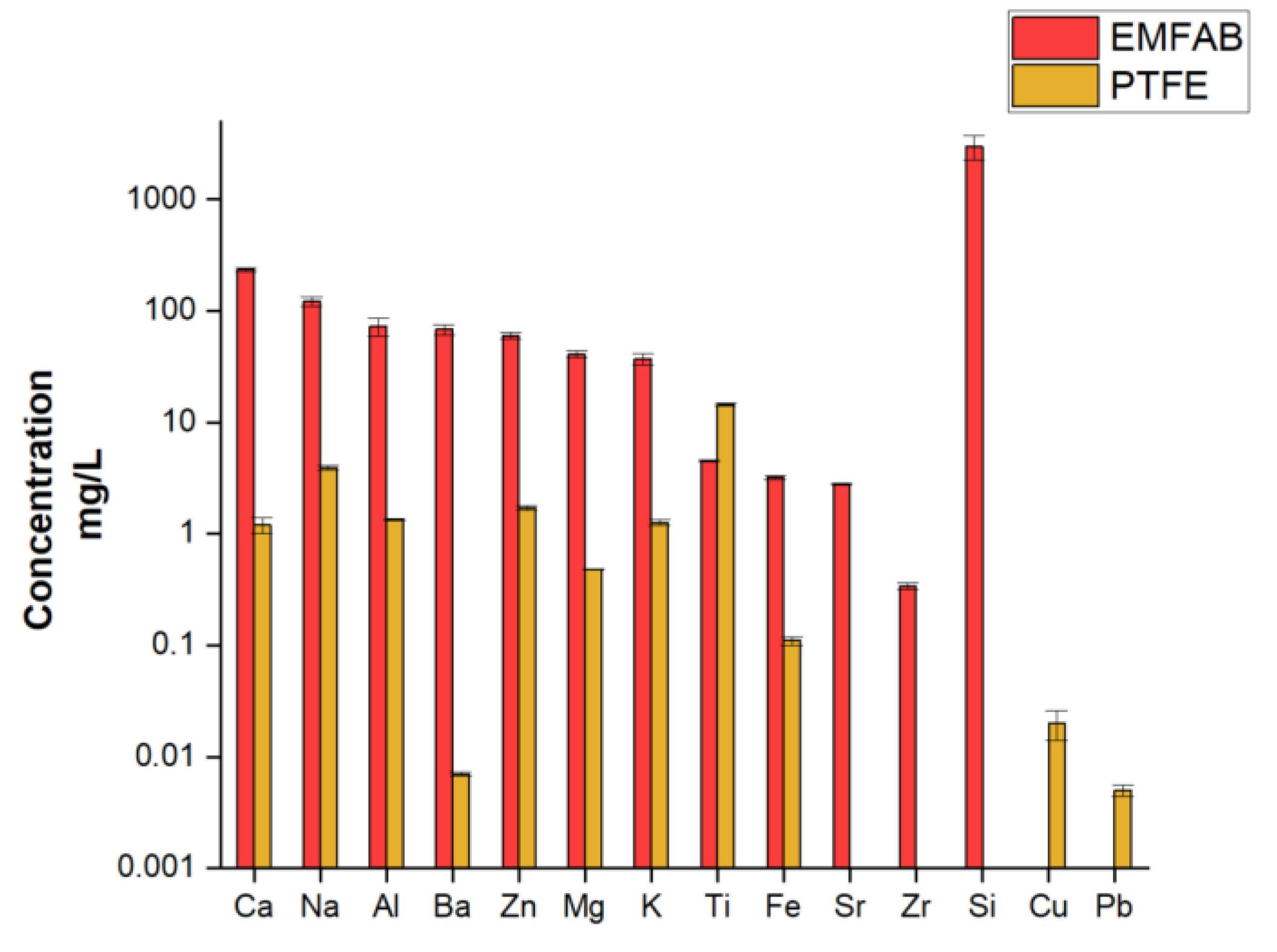
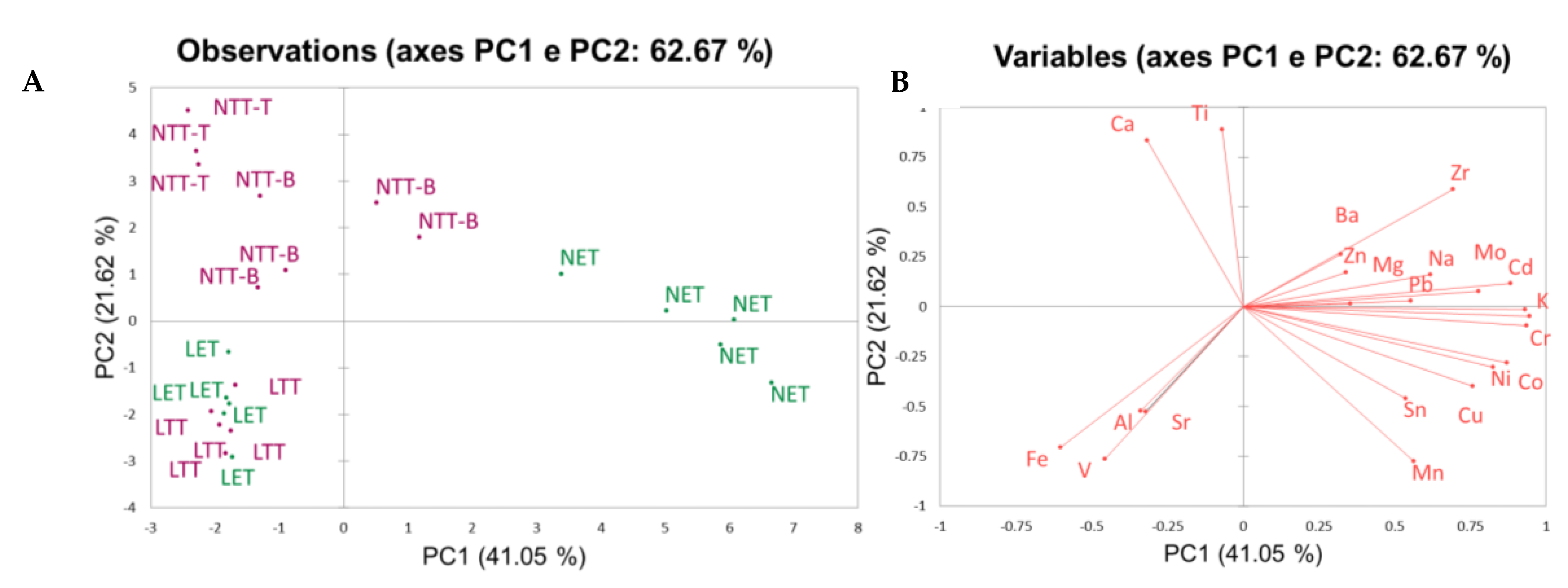
| Analyte | A mean recoveries (%) |
A HORRATr |
B mean recoveries (%) |
B HORRATr |
C mean recoveries (%) |
C HORRATr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 107 | 1.0 | 97 | 1.4 | 44 | 8.0 |
| Mg | 80 | 0.8 | 97 | 1.9 | 77 | 1.0 |
| K | 104 | 1.4 | 98 | 1.8 | 47 | 10.6 |
| Ti | 76 | 1.9 | 91 | 2.5 | 19 | 3.6 |
| Cr | 53 | 2.1 | 86 | 2.8 | 33 | 4.3 |
| Mn | 94 | 1.2 | 97 | 0.6 | 92 | 0.5 |
| Cu | 94 | 1.4 | 98 | 1.8 | 93 | 1.2 |
| Zn | 88 | 0.8 | 97 | 1.1 | 91 | 1.8 |
| Sr | 96 | 1.1 | 97 | 0.8 | 72 | 0.5 |
| Al | 62 | 1.8 | 128 | 6.6 | 39 | 8.5 |
| Ca | 94 | 4.0 | 121 | 7.5 | 94 | 0.9 |
| Fe | 92 | 1.6 | 148 | 7.8 | 81 | 1.1 |
| Si | 72 | 3.8 | 89 | 4.6 | 1 | 64.0 |
| V | 85 | 0.2 | 115 | 3.6 | 76 | 1.5 |
| Co | 94 | 0.9 | 127 | 2.4 | 79 | 0.5 |
| Ni | 98 | 0.5 | 131 | 5.0 | 89 | 0.6 |
| As | 101 | 1.4 | 180 | 7.0 | 102 | 0.4 |
| Cd | 104 | 0.6 | 149 | 4.4 | 97 | 0.5 |
| Pb | 94 | 0.5 | 133 | 7.1 | 91 | 0.9 |
| Analyte | Mean recoveries (%) | HORRATr |
|---|---|---|
| Mn | 90 | 1.2 |
| Fe | 91 | 0.9 |
| Na | 101 | 1.5 |
| Zn | 88 | 1.1 |
| Ba | 94 | 0.9 |
| Cr | 78 | 1.2 |
| Cu | 103 | 0.5 |
| V | 109 | 0.6 |
| Ni | 104 | 1.5 |
| As | 97 | 1.9 |
| Pb | 103 | 1.0 |
| Group | Intra-sample RSD% | Inter-sample RSD% |
|---|---|---|
| NET | 10 | 50 |
| NTT-B | 18 | 41 |
| NTT-T | 15 | 24 |
| LET | 8 | 22 |
| LTT | 7 | 20 |
| Sample ID | Type of friction material | Type of filter | PM10 weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| NTT-B 26 | NAO | PTFE | 0.46 |
| NTT-B 43 | NAO | PTFE | 0.57 |
| NTT-B 54 | NAO | PTFE | 0.80 |
| NTT-B 55 | NAO | PTFE | 0.28 |
| NTT-B 56 | NAO | PTFE | 0.44 |
| NTT-T 80 | NAO | PTFE | 0.16 |
| NTT-T 81 | NAO | PTFE | 0.15 |
| NTT-T 82 | NAO | PTFE | 0.14 |
| NET 14 | NAO | EMFAB | 0.56 |
| NET 16 | NAO | EMFAB | 0.56 |
| NET 41 | NAO | EMFAB | 0.47 |
| NET 47 | NAO | EMFAB | 0.23 |
| NET 42 | NAO | EMFAB | 0.44 |
| LTT 28 | LS | PTFE | 7.09 |
| LTT 37 | LS | PTFE | 12.52 |
| LTT 38 | LS | PTFE | 7.47 |
| LTT 40 | LS | PTFE | 13.93 |
| LTT 49 | LS | PTFE | 8.05 |
| LET 17 | LS | EMFAB | 17.34 |
| LET 33 | LS | EMFAB | 8.96 |
| LET 34 | LS | EMFAB | 10.64 |
| LET 35 | LS | EMFAB | 13.26 |
| LET 36 | LS | EMFAB | 16.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





