Submitted:
16 October 2025
Posted:
17 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
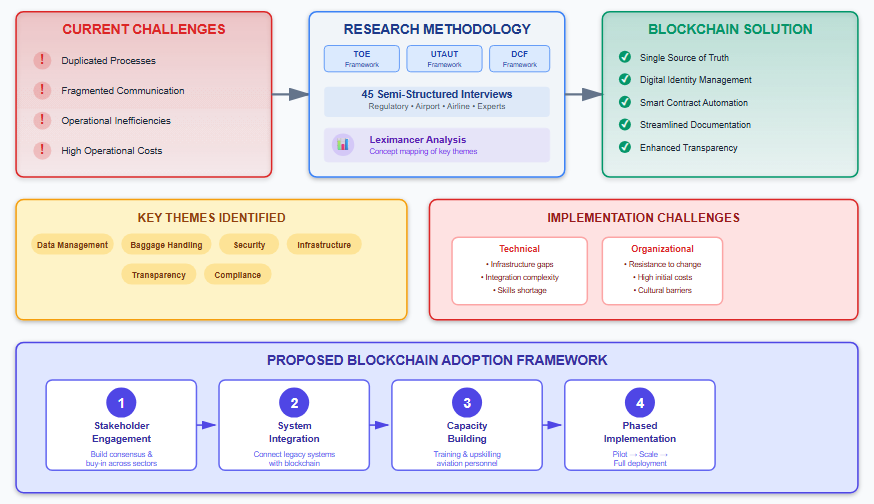
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Aim
1.2. Research Objectives
- − To undertake a robust and comprehensive assessment of the current operational redundancies in Nigerian airport management systems and narrowing down on specific areas where the blockchain technology can drive advancement.
- − To gauge the potential impact of blockchain technology on, process integration and streamlining, Data management efficiency, operational cost reduction and service delivery enhancement.
- − We also developed a framework for the implementing blockchain technology in Nigerian airports to address redundancy.
- − The research will also identify potential bottlenecks in the implementation and develop suggest mitigation strategies that is specific to the Nigerian aviation context.
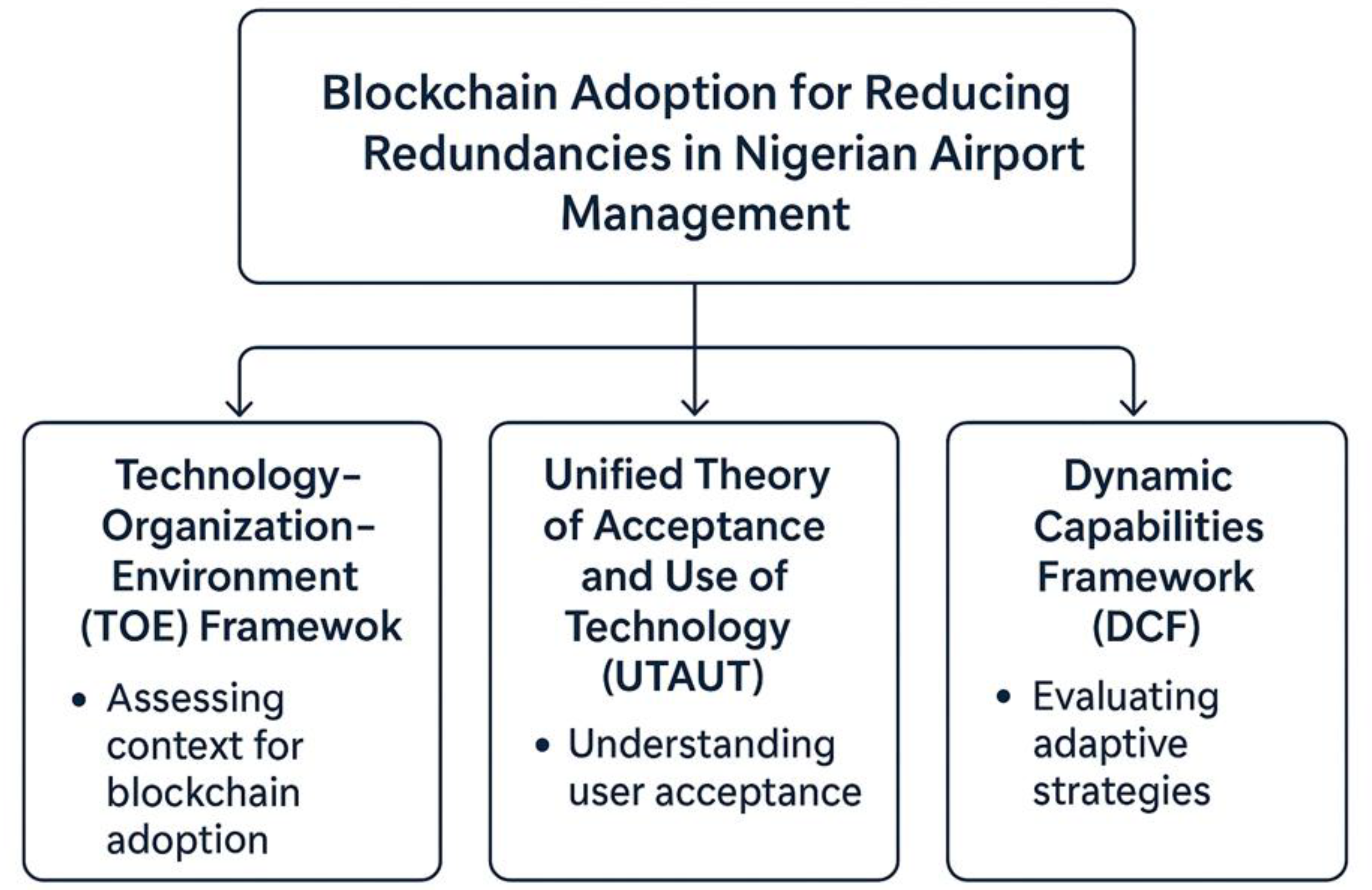
1.3. Theoretical Framework
2. Literature Review
2.1. Blockchain Technology in Airport Management: A Literature Review with Focus on Nigerian Aviation Sector
- I.
- Smart Contracts; Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code [22]. Aircraft manufacturers, airlines, travel agencies, airports, ground handlers, and other industry suppliers are just a few of the numerous organizations that make up the commercial aviation value chain. These businesses rely on one another for goods and services in order to serve the clients. By utilizing Smart Contracts, Blockchain technology can effectively expedite the procure-to-pay procedure.
- II.
- Tokenization; In addition to making accounting and reconciliation easier, tokenizing assets stops digital assets from being used twice [24] . For example, a passenger’s compensation voucher shouldn’t be used more than once. Until the traveler uses them, compensation vouchers—and especially frequent flyer loyalty points remain listed as a liability on the balance sheet.
- III.
- Provenance; Blockchain can make it easier to track the location and status of valuable assets that frequently change custody, like passenger bags, cargo, spare parts, and even airplanes. This is especially useful if there is a lack of trust between the parties or between the people and organizations involved in the process[25]. Blockchain technology provides an easy-to-use method for tamper-proof and immutable event recording. The ability of blockchain technology to create an immutable record of baggage transfer could ones and for all address the reoccurring challenge of lost luggage in Nigerian airports. Adopting of blockchain-based baggage tracking systems has revealed potentials to cut down on mishandling of passengers’ luggage by up to 47% in pilot studies carried out at major international airports
- IV.
- Certification; Airlines and the larger value chain place a high priority on safety and security, and blockchain technology can help the sector maintain these standards by streamlining the certification process for people, equipment, and other entities [26]. The certification would facilitate the authentication procedure for, Employees of the company, such as pilots, crew, airport employees, security personnel and secondly for Partners along the value chain, such as fuel into-plane service providers, ground handlers, providers of upkeep, repairs, and overhauls. Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO)The blockchain technology offers major potentials for enhancing aircraft maintenance records[20], by creating permanent, tamper-proof maintenance histories, guaranteeing compliance with regulatory requirements, ensuring or facilitating parts tracking and authentication and Reducing documentation errors and fraud.
- V.
- Digital Identity; It is increasingly common in the commercial aviation sector and beyond to conduct business online. Companies want to advertise their goods and services, gain access to a wide audience, and manage the risks involved in doing so while being aware of who they are doing business with. Blockchain technology is ideally suited to serve as the foundation for digital identity management systems because to its intrinsically strong security features (such as integrity and immutability)[27]. Research suggests that blockchain-based digital identity systems have the possibility to revolutionize passengers processing in Nigerian airports. In research by [3] they suggested that adopting blockchain-based ID verification could significantly reduce check-in times by about 65% while improving the overall security protocols.
2.2. Redundancies in Airport Management
Understanding Redundancies as a Concept
2.3. Current Redundancies in Airport Management
Operational Redundancies
Administrative Redundancies
Data Redundancies
2.4. Impact of Redundancies on Airport Operations
- Financial Impact; One usual measure of redundancy is the expense of maintaining redundant elements. While redundant systems may be more dependable, they are less efficient because of the costs of maintenance[42]. Higher operational costs as a result of higher staffing requirements. On the flip side, there will be additional expenses on IT infrastructure, increase in data storage costs and lastly higher maintenance and support costs.
- Operational Impact; Longer processing times for every given task, secondly, increased possibility of errors because of many interferences, reduced efficiency and effectiveness. Customer satisfaction challenges and resource allocation inadequacies [36]. Proponents claim that duplicating organizational structures, people, programs, or facilities are unnecessary and wasteful.
2.5. Blockchain Solutions for Reducing Redundancies
Single Source of Truth
Smart Contract Automation
Digital Identity Management
Document Management
2.6. Implementation Challenges in Nigerian Context
- a.
- Technical Challenges
- b.
- Organizational Challenges
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Research Population and Sampling
3.3. Data Collection Method
Semi-structured Interviews
3.4. Interview Protocol
3.5. Data Analysis
 |
4. Findings
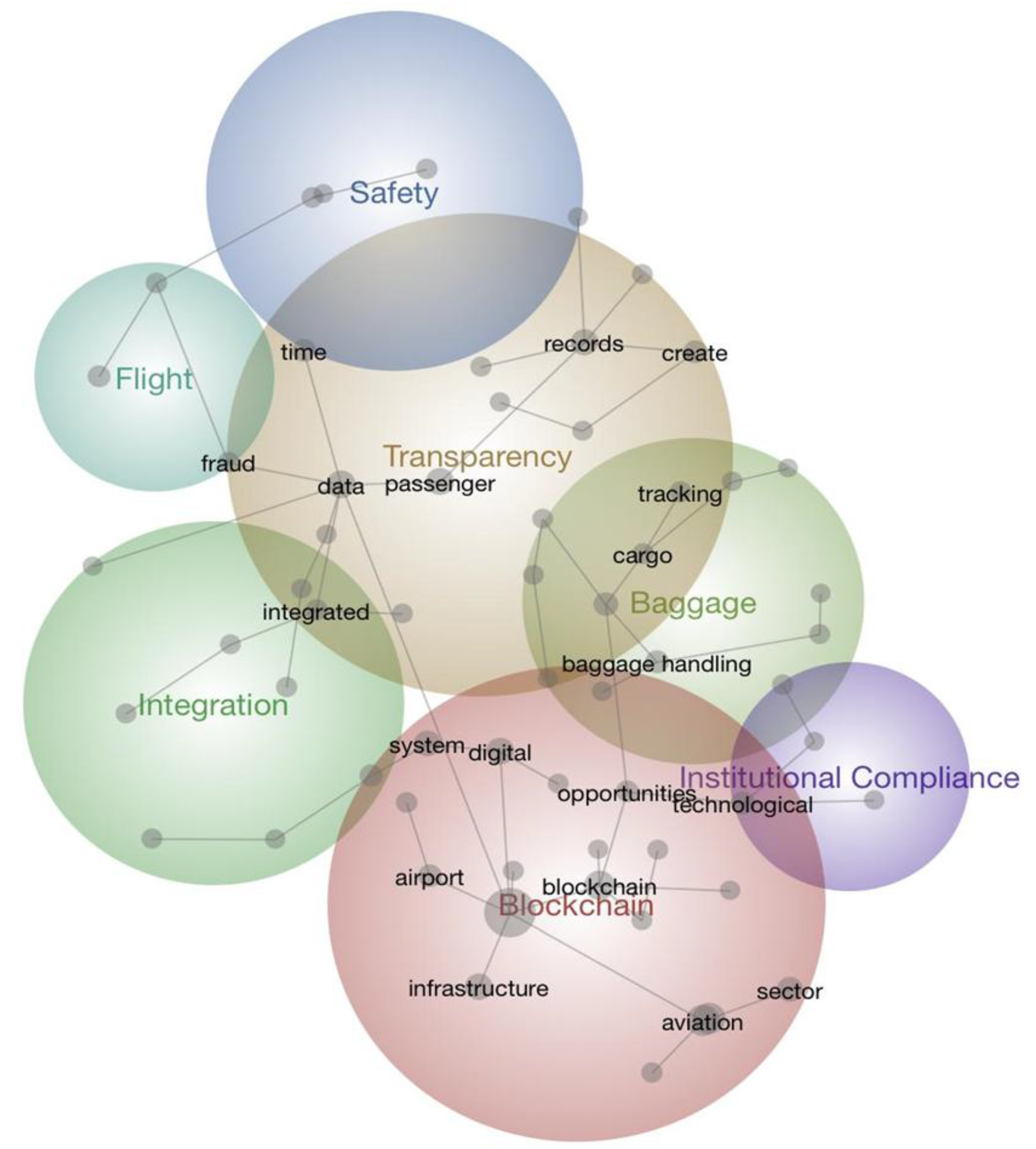
4.1. Blockchain Theme (Large Beige Circle)
4.2. Baggage and Operations Theme (Green Cluster)
4.3. Flight (Light Blue/Turquoise)
4.4. Safety Themes (Purple/Blue Circles)
4.5. Integration
4.6. Institutional Compliance
4.7. Central Role of Transparency
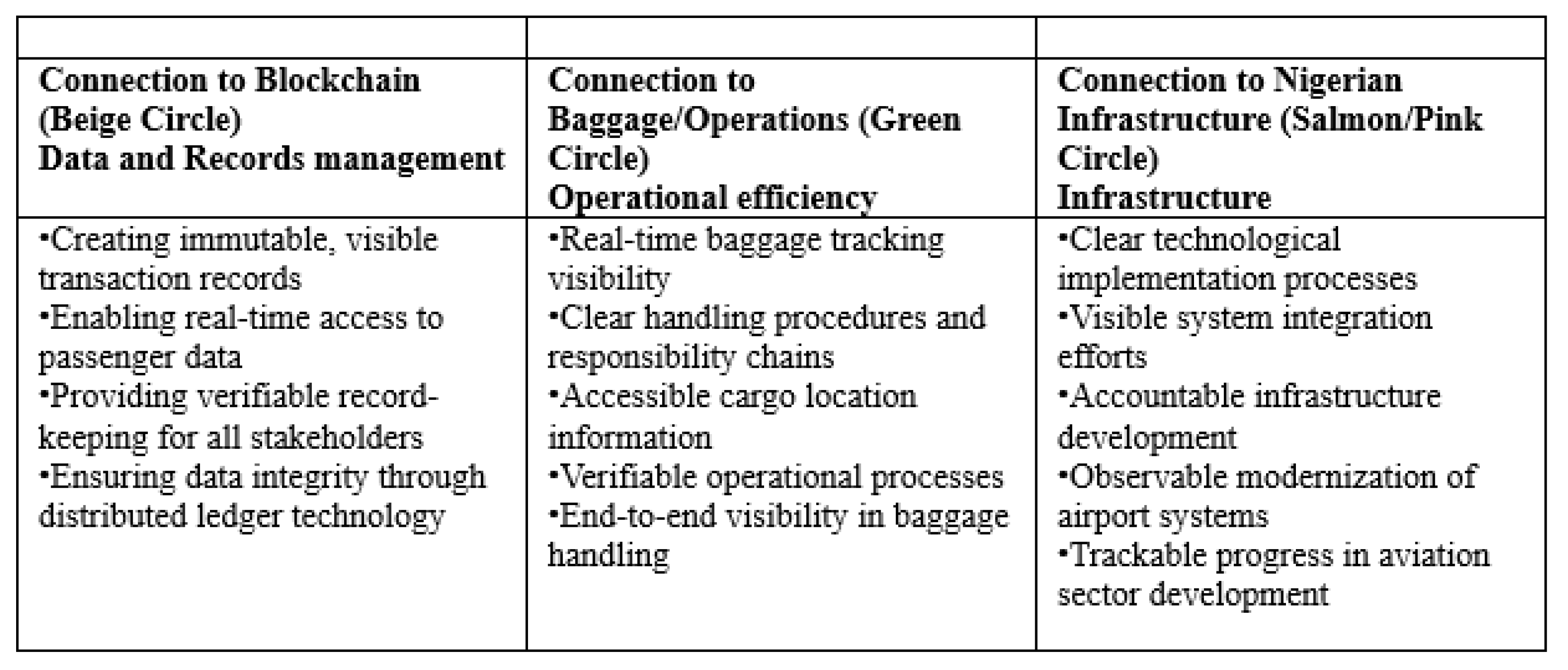 |
The Strategic Importance
4.2. Reducing Operational Redundancies in Nigerian Airport Management Through Blockchain Technology
Primary Thematic Analysis
Operational Redundancy Insights
Blockchain Implementation Implications
Research Implications
7. Framework for Adoption of Blockchain Technology
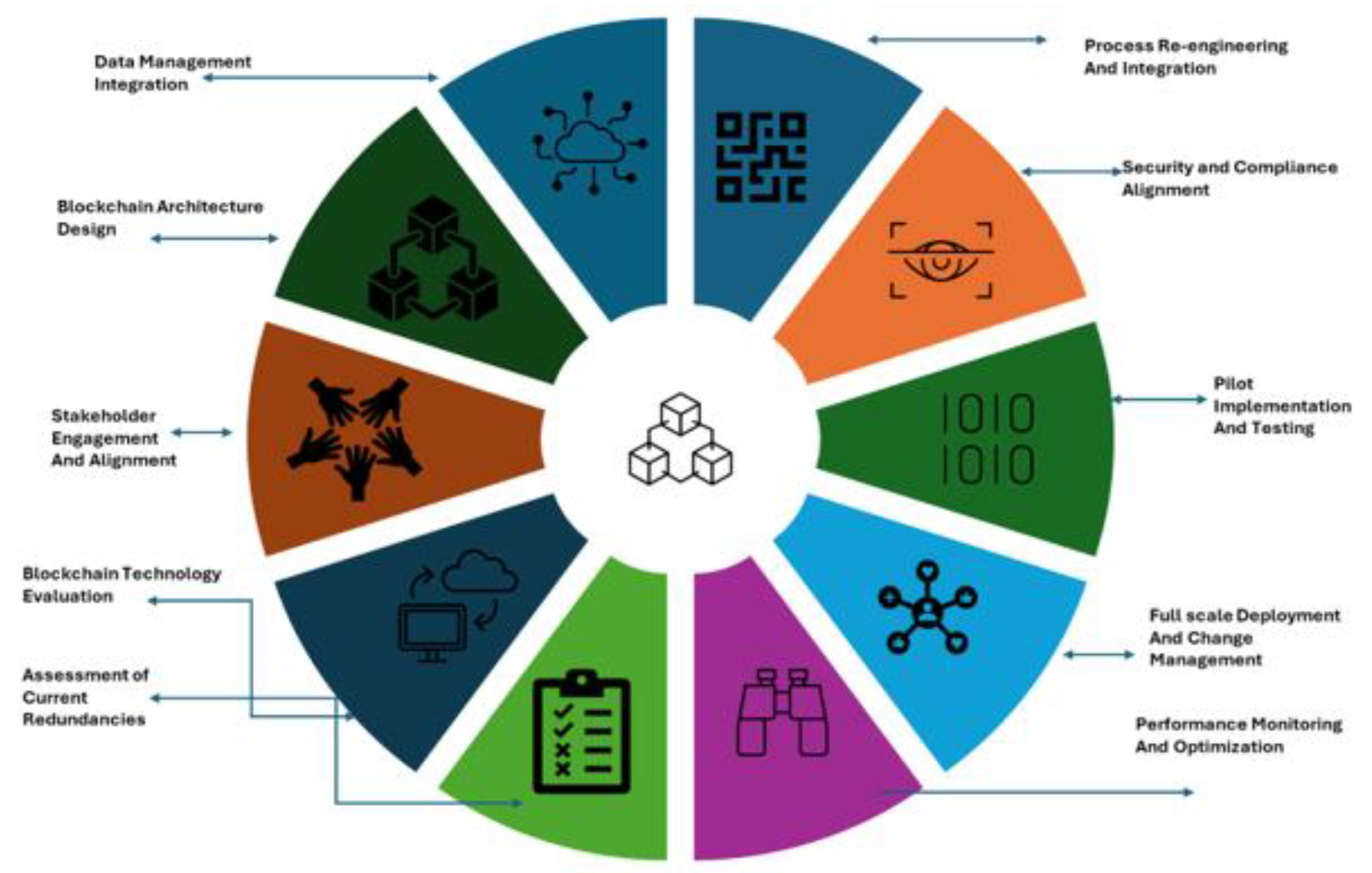
8. Discussion
- a).
- Informational Redundancies (Data-Records-Integration Nexus)
- b).
- Procedural Redundancies (Flight-Safety-Passenger-Baggage Intersections)
- c).
- Structural Redundancies (Integration-System-Infrastructure Linkages)
Critical Implementation Dimensions
Synthesized Findings
- I.
- Administrative redundancy through unified record management (Data-Integration cluster)
- II.
- Process redundancy via automated verification protocols (Passenger-Safety-Baggage intersection)
- III.
- Verification redundancy via a transparent, distributed consensus mechanisms (Transparency-Safety nexus)
Implementation Imperatives
9. Conclusions
10. Theoretical Implications
References
- Cheung, T.; Li, B.; Lei, Z. Chapter 11: A Paradigm Shift in the Aviation Industry with Digital Twin, Blockchain, and AI Technologies. In Handbook on Artificial Intelligence and Transport; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2023; pp. 323–346 ISBN 9781803929545.
- Mazhar, S.; Wu, P.P.-Y.; Rosemann, M. Designing Complex Socio-Technical Process Systems – the Airport Example. Business Process Management Journal 2019, 25, 1101–1125. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.W.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Hasan, H.R.; Yaqoob, I.; Omar, M. The Role of Blockchain Technology in Aviation Industry. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine 2021, 36, 4–15. [CrossRef]
- Patunola-Ajayi, B.J. PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH THE MANAGEMENT OF AIRPORT FACILITIES: THE CASE STUDY OF MURITALA MUHAMMED AIRPORT, LAGOS, NIGERIA; 2019; Vol. 1;.
- Sahoo, R.; Bhowmick, B.; Tiwari, M.K. Smart Integration of Blockchain in Air Cargo Handling for Profit Maximization. In; 2021; pp. 107–114.
- Jiang, Y.; Tran, T.H.; Williams, L. Journal of Airline Operations and Aviation Management The Netherlands Press Article Journal of Airline Operations and Aviation Management Volume 2 Issue 2 Journal of Airline Operations and Aviation Management. 2023, 2. [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.U.; Nandal, V.; Uppal, H. Blockchain Applications in Aviation Securing Transactions, Streamlining Operations, and Improving Passenger Experience. In; 2025; pp. 131–154.
- Bierrings, M.J.; Sivakumar, G.; Wunderlich, N. Blockchain in the Aviation Industry: A Decentralized Solution to the Transparency Issue in Baggage Handling. In Business Digital Transformation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2024; pp. 45–72.
- Ashiru, A.; Ariff, O.K. Rural Air Mobility in Developing Countries: Opportunities, Challenges, and Requirements in the Use of Blockchain to Enhance Growth. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION FORUM AND ASCEND 2024; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, Virginia, July 29 2024.
- Ojonemi Paul, S.; Ofuebe, C.; Ojonemi PAUL salisupaul, S. AVIATION ROADMAP AND DEVELOPMENT OF AIRPORTS IN NIGERIA. Journal of Good Governance and Sustainable Development in Africa (JGGSDA) 2019, 5. [CrossRef]
- 1990; 11. Louis Tornatzky; M Fleischer The Processes of Technological Innovation; Lexington, MA, 1990;
- Oliveira, T.; Martins, M.F. Information Technology Adoption Models at Firm Level: Review of Literature; 2010;
- Venkatesh; Morris; Davis; Davis User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Quarterly 2003, 27, 425. [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.D.; Rana, N.P.; Dwivedi, Y.K. The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT): A Literature Review. Journal of Enterprise Information Management 2015, 28, 443–488. [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management. Strategic Management Journal 1997, 18, 509–533. [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Explicating Dynamic Capabilities: The Nature and Microfoundations of (Sustainable) Enterprise Performance. Strategic Management Journal 2007, 28, 1319–1350. [CrossRef]
- Helfat, C.E.; Peteraf, M.A. Managerial Cognitive Capabilities and the Microfoundations of Dynamic Capabilities. Strategic Management Journal 2015, 36, 831–850. [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Chadhar, M.; Vatanasakdakul, S.; Chetty, M. Factors Affecting the Organizational Adoption of Blockchain Technology: Extending the Technology–Organization–Environment (TOE) Framework in the Australian Context. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9404. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, L.-Y. Exploring the Role of Dynamic Capabilities in Firm Performance under the Resource-Based View Framework. J Bus Res 2014, 67, 407–413. [CrossRef]
- Crosby Nachiappan Pradan Pattanayak Sanjeev Verma, M.; Kalyanaraman, V. BlockChain Technology: Beyond Bitcoin; 2016;
- Bhutta, M.N.M.; Khwaja, A.A.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, H.F.; Khan, M.K.; Hanif, M.A.; Song, H.; Alshamari, M.; Cao, Y. A Survey on Blockchain Technology: Evolution, Architecture and Security. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 61048–61073. [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, M. Blockchain Technology: Principles and Applications. In Research Handbook on Digital Transformations; Edward Elgar Publishing, 2016.
- Blockchain-in-Aviation-White-Paper.
- Risius, M.; Spohrer, K. A Blockchain Research Framework: What We (Don’t) Know, Where We Go from Here, and How We Will Get There. Business and Information Systems Engineering 2017, 59, 385–409. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhou, L. Navigating the Blockchain-Driven Transformation in Industry 4.0: Opportunities and Challenges for Economic and Management Innovations. Journal of the Knowledge Economy 2024, 16, 3507–3549. [CrossRef]
- Cuccuru, P. Beyond Bitcoin: An Early Overview on Smart Contracts. International Journal of Law and Information Technology 2017, 25, 179–195. [CrossRef]
- Nikhil Ghadge Analyzing the Role of Blockchain in Identity and Access Management Systems. International Journal of Science and Research Archive 2024, 12, 2249–2256. [CrossRef]
- Falazi, G.; Hahn, M.; Breitenbücher, U.; Leymann, F. Modeling and Execution of Blockchain-Aware Business Processes. In Proceedings of the Software-Intensive Cyber-Physical Systems; Springer, June 1 2019; Vol. 34, pp. 105–116.
- Politou, E.; Casino, F.; Alepis, E.; Patsakis, C. Blockchain Mutability: Challenges and Proposed Solutions. IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput 2021, 9, 1972–1986. [CrossRef]
- Landau, M. Redundancy, Rationality, and the Problem of Duplication and Overlap. Public Adm Rev 1969, 29, 346. [CrossRef]
- Streeter, C.L. Redundancy in Organizational Systems. Social Service Review 1992, 66, 97–111. [CrossRef]
- Thornhill, A.; Saunders, M.N.K. The Meanings, Consequences and Implications of the Management of Downsizing and Redundancy: A Review. Personnel Review 1998, 27, 271–295. [CrossRef]
- Chewning, L. V.; Lai, C.-H.; Doerfel, M.L. Organizational Resilience and Using Information and Communication Technologies to Rebuild Communication Structures. Manag Commun Q 2013, 27, 237–263. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D. V.; Mendleson, B.E. Redundancy. Journal of Business Communication 1984, 21, 43–61. [CrossRef]
- Jonathan B. Bendor Parallel Systems: Redundancy in Government; University of California, 1985;
- Adeniran, A.O., & G.K.T. Concessioning a Strategy for Enhancing Nigeria’s Airport Operational Efficiency - Lessons from Developed Countries. International journal of research in industrial engineering 2017, 6, 228–245.
- Patience E. Orukpe; Christian T. Onianwa; Abdullahi Abuh; Adebisi K. Aderanti Reliability Assessment of Power Distribution System in the Nigerian Aviation Industry. The Journal of Engineering, Science and Computing 2020, 2.
- Waribugo Sylva; Chiedu Florence Amah Challenges of Airlines Operations in Sub-Saharan Africa: An Empirical Investigation of the Nigerian Civil Aviation Sector. International Journal of Business and Management Invention 2021, 10.
- Okafor, C.C.; Ezeoyili, M.N. Assessment of Infrastructure Maintenance Practices of Three Airports in Southern Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Technology 2020, 39, 744–751. [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, O.; Fasola, O.O. TMLAI TRANSACTIONS ON MACHINE LEARNING AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE A Proposed Control System for Checkmating an Aeronautics Agency Riddled with Fraud. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Momoh, M.O.; Shobowale, K.O.; Abubakar, Z.M.; Yahaya, B.; Ibrahim, Y. Blockchain Adoption in Aviation: Opportunities and Challenges. IJEEC - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTING 2022, 6. [CrossRef]
- Zolghadri, A. A Redundancy-Based Strategy for Safety Management in a Modern Civil Aircraft. Control Eng Pract 2000, 8, 545–554. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; L’heureux, F. A Regulatory Framework for Cryptocurrency. European Business Law Review 2020, 31, 423–446. [CrossRef]
- Woodside, J.M.; Augustine, F.K.; Giberson, W. Blockchain Technology Adoption Status and Strategies. Journal of International Technology and Information Management 2017, 26, 65–93. [CrossRef]
- Korolyuk, T.; Spivak, S.; Seniv, B.; Stetsko, M.; Horodetskyy, M.; Ivanova, A. Advantages of Blockchain for Efficient Electronic Documents Flow in the Enterprise Accounting System. In Proceedings of the 2024 14th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT); IEEE, September 19 2024; pp. 434–438.
- Pinto Lopes, D.; Rita, P.; Treiblmaier, H. The Impact of Blockchain on the Aviation Industry: Findings from a Qualitative Study. Research in Transportation Business & Management 2021, 41, 100669. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lai, P.-L.; Yang, C.-C.; Yuen, K.F. Determinants of Blockchain Adoption in the Aviation Industry: Empirical Evidence from Korea. J Air Transp Manag 2021, 97, 102139. [CrossRef]
- Aktas, E.; Demir, S.; Paksoy, T. The Use of Blockchain in Aviation Safety Reporting Systems: A Framework Proposal. The International Journal of Aerospace Psychology 2022, 32, 283–306. [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, G.A.; Tawfik, H.F.; Elseyoufi, T.S. Challenges Facing Airline’s Social Innovation. Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Management 2017. [CrossRef]
- Tenny, S.; Brannan, J.M.; Brannan, G.D. Qualitative Study; 2022;
- 2015; 51. Neetij Rai; Bikash Thapa A STUDY ON PURPOSIVE SAMPLING METHOD IN RESEARCH; 2015;
- Maxwell, J.A. Designing a Qualitative Study;
- Adams, W.C. Conducting Semi-Structured Interviews. In Handbook of Practical Program Evaluation; Wiley, 2015; pp. 492–505.
- Olorunsola, V.O.; Saydam, M.B.; Lasisi, T.T.; Eluwole, K.K. Customer Experience Management in Capsule Hotels: A Content Analysis of Guest Online Review. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights 2023, 6, 2462–2483. [CrossRef]
- Arasli, H.; Saydam, M.B.; Kilic, H. Cruise Travelers’ Service Perceptions: A Critical Content Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6702. [CrossRef]
- Azman, M.; Sharma, K. Smart Boarding System with E-Passports for Secure and Independent Interoperability. SN Comput Sci 2022, 3, 52. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.K.; Verma, D.C.; Jangirala, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Aman, M.N. Blockchain for Aviation Industry: Applications and Used Cases. In; 2022; pp. 475–486.
- Sánchez, E.; Calderón, R.; Herrera, F. Artificial Intelligence Adoption in SMEs: Survey Based on TOE–DOI Framework, Primary Methodology and Challenges. Applied Sciences 2025, 15, 6465. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.A.; Gstrein, O.J.; Zwitter, A.J. Exploring the Governance and Implementation of Sustainable Development Initiatives through Blockchain Technology. Futures 2020, 122, 102611. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





