Submitted:
01 September 2025
Posted:
03 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Biomarkers Help Monitor Responses to Medications
3. Emerging Theories of the Pathophysiology of T2DM
- Subtype 1 – Severe autoimmune diabetes mellitus
- Subtype 2 – Severe insulin-deficient diabetes mellitus
- Subtype 3 – Severe insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus
- Subtype 4 – Mild obesity-related diabetes
- Subtype 5 – Mild age-related diabetes
4. Prescription Antihyperglycemic Drugs
4.1. Current Landscape of Oral Antihyperglycemic Drugs in T2DM Management
4.2. Mechanisms of Action, Benefits, and Risks of Oral Antihyperglycemics
4.2.1. Metformin
4.2.2. Sulfonylureas
4.2.3. Meglitinide
4.2.4. Thiazolidinedione
4.2.5. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
4.2.6. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Agonist
4.2.7. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors
5. Emerging Biomarkers in T2DM
6. Vascular Complications Associated with T2DM
6.1. Microvascular Complications
6.1.1. Retinopathy
Potential Biomarker Options of Retinopathy
- Proangiogenic agents
- Proinflammatory agents
- Metabolite- and lipid-derived biomarkers
- Thickness changes in outer plexiform layer may correlates with renal-related diseases such as diabetes
6.1.2. Nephropathy
Potential Biomarker Options of Nephropathy
- Dysregulated miRNA in diabetic kidney disease
- Growth Factors
- Biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Hepatic and cardiac biomarkers
6.1.3. Neuropathy
Potential Biomarker Options in Neuropathies
- Neuroinflammatory mediators
- Hyperglycemia-induced molecules affecting metabolic and hemodynamic pathways
6.2. Macrovascular Complications
6.2.1. Coronary Artery Disease
Potential Biomarkers in Coronary Arterial Disease
- Hormones as biomarkers
- Oxidative stress
- Metabolic messengers
- Indicators of cell damage
6.2.2. Cerebrovascular Disease
Potential Biomarkers of Cerebrovascular Disease
- Biochemical indicators
- Neovasculogenesis
6.2.3. Peripheral Artery Disease
Potential Biomarker Options for Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Blood-based factors
- Inflammatory mediators
- Cell-derived molecules
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACCORD | Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes |
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| DCCT | Diabetes Control and Complications Trial |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| HbA1c | Plasma glycosylated hemoglobin A1C |
| HHS | Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| UKPDS | United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Diabetes Facts and Figures | The International Diabetes Federation (IDF). 2025, https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/ .
- MARKANDU, K.; DEKHNE, A.; ISLAM, H.; ISLAM, R.; MADDINENI, K.; POTLURI, G.; PARISAPOGU, A.; TEJA CHINTHAPALLI, M.; DINESHBHAI DESAI, H. 1420-P: Global Burden and Trend of Type 2 DM in 38 OECD Countries from 1990–2019—A Benchmarking Systematic Analysis. Diabetes 2024, 73, (Supplement_1).
- Koya, D.; Araki, S.; Haneda, M. Therapeutic management of diabetic kidney disease. J Diabetes Investig 2011, 2, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Petrie, J.R.; Guzik, T.J.; Touyz, R.M. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical Insights and Vascular Mechanisms. Can J Cardiol 2018, 34, 575–584. [Google Scholar]
- Rajbhandari, J.; Fernandez, C.J.; Agarwal, M.; Yeap, B.X.Y.; Pappachan, J.M. Diabetic heart disease: A clinical update. World J Diabetes 2021, 12, 383–406. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, R.I.; Morgan, S.E.; Bahnson, E.M. Diabetic vasculopathy: macro and microvascular injury. Curr Pathobiol Rep 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Beccia, D.; Brin, C.; Alfano, M.; Di Salvo, J.; Epifani, R.; Piacevole, A.; Tagliaferri, G.; Rocco, M.; Iadicicco, I.; Docimo, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Sardu, C.; Salvatore, T.; Marfella, R.; Sasso, F.C. Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabete | World Health Organization (WHO). 2024, https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes .
- Umemura, T.; Kawamura, T. Effect of diabetes on stroke symptoms and mortality: Lessons from a recent large population-based cohort study. J Diabetes Investig 2014, 5, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, S. Vascular complications of diabetes: A narrative review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023, 102, e35285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Worker, C.J.; Feng Earley, Y. The hypothalamus as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis: emerging roles of the brain renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2023, 325, C141–c154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Geiss, L.S.; Gregg, E.W.; Albright, A. Trends in Diabetic Ketoacidosis Hospitalizations and In-Hospital Mortality - United States, 2000-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018, 67, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabchi, A.E.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Miles, J.M.; Fisher, J.N. Hyperglycemic Crises in Adult Patients With Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.R.; Care, t. J. B. D. S. f. I.; group, t. J. h. h. g. Management of hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state in adults with diabetes. Diabetic Medicine 2015, 32, 714–724. [Google Scholar]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Davis, G.M.; ElSayed, N.A.; Fadini, G.P.; Galindo, R.J.; Hirsch, I.B.; Klonoff, D.C.; McCoy, R.G.; Misra, S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Bannuru, R.R.; Dhatariya, K.K. Hyperglycaemic crises in adults with diabetes: a consensus report. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 1455–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.T.; Lin, S.M.; Hsu, J.Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Loh, C.H.; Huang, H.K.; Liu, P.P. Association between Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State and Venous Thromboembolism in Diabetes Patients: A Nationwide Analysis in Taiwan. J Pers Med 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabshomali, A.; Bazzazzadehgan, S.; Mahdi, F.; Shariat-Madar, Z. Potential Benefits of Antioxidant Phytochemicals in Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2023, 28, 7209. [Google Scholar]
- Karslioglu French, E.; Donihi, A.C.; Korytkowski, M.T. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ 2019, 365, l1114. [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi, A.E.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Murphy, M.B.; Kreisberg, R.A. Hyperglycemic Crises in Adult Patients With Diabetes: A consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2739–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, S.Z.; Bejaimal, S.A.; Sontrop, J.M.; Iansavichus, A.V.; Haynes, R.B.; Weir, M.A.; Garg, A.X. Retrieving clinical evidence: a comparison of PubMed and Google Scholar for quick clinical searches. J Med Internet Res 2013, 15, e164. [Google Scholar]
- Morshed, T.; Hayden, S. Google Versus PubMed: Comparison of Google and PubMed’s Search Tools for Answering Clinical Questions in the Emergency Department. Ann Emerg Med 2020, 75, 408–415. [Google Scholar]
- Laakso, M. Biomarkers for type 2 diabetes. Molecular Metabolism 2019, 27, S139–S146. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tankova, T.; Tsapas, A.; Buse, J.B. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2753–2786. [Google Scholar]
- Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia, World Health Organization (WHO)/IDF consultation, https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/definition-and-diagnosis-of-diabetes-mellitus-and-intermediate-hyperglycaemia; 9241594934; 2006.
- Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 1989, 12, 365–368. [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Moffet, H.H.; John, P.M.; Karter, A.J. Glycemic Control, Complications, and Death in Older Diabetic Patients: The Diabetes and Aging Study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Bilal, A. Understanding Diabetes Overtreatment in Older Adults: Are We at an Intersection? Diabetes Care 2024, 48, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlqvist, E.; Storm, P.; Käräjämäki, A.; Martinell, M.; Dorkhan, M.; Carlsson, A.; Vikman, P.; Prasad, R.B.; Aly, D.M.; Almgren, P.; Wessman, Y.; Shaat, N.; Spégel, P.; Mulder, H.; Lindholm, E.; Melander, O.; Hansson, O.; Malmqvist, U.; Lernmark, Å.; Lahti, K.; Forsén, T.; Tuomi, T.; Rosengren, A.H.; Groop, L. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018, 6, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.-Z.; Gerszten, R.E. Metabolomics and Proteomics in Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation Research 2020, 126, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Deckert, T. Effect of two years of strict metabolic control on progression of incipient nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet 1986, 2, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Reichard, P.; Berglund, B.; Britz, A.; Cars, I.; Nilsson, B.Y.; Rosenqvist, U. Intensified conventional insulin treatment retards the microvascular complications of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM): the Stockholm Diabetes Intervention Study (SDIS) after 5 years. J Intern Med 1991, 230, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Brinchmann-Hansen, O.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Sandvik, L.; Hanssen, K.F. Blood glucose concentrations and progression of diabetic retinopathy: the seven year results of the Oslo study. Bmj 1992, 304, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar]
- Committee, A.D.A.P.P. 13. Older Adults: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48, (Supplement_1), S266-S282.
- Mukonda, E.; van der Westhuizen, D.J.; Dave, J.A.; Cleary, S.; Hannan, L.; Rusch, J.A.; Lesosky, M. Understanding the relationship between the frequency of HbA1c monitoring, HbA1c changes over time, and the achievement of targets: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2025, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.P.L.; DeMarco, J.P. A 7.0-7.7% value for glycated haemoglobin is better than a .
- Gerstein, H.C.; Miller, M.E.; Byington, R.P.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Bigger, J.T.; Buse, J.B.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Grimm, R.H., Jr.; Probstfield, J.L.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Friedewald, W.T. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008, 358, 2545–2559. [Google Scholar]
- Buse, J.B.; Bigger, J.T.; Byington, R.P.; Cooper, L.S.; Cushman, W.C.; Friedewald, W.T.; Genuth, S.; Gerstein, H.C.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Grimm, R.H., Jr.; Margolis, K.L.; Probstfield, J.L.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Sullivan, M.D. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial: design and methods. Am J Cardiol 2007, (12a), 21i–33i. [Google Scholar]
- Stimson, R.H.; Dover, A.R.; Forbes, S.; Strachan, M.W.J.; McKnight, J.A.; Gibb, F.W. HbA1c Is Disproportionately Higher in Women and Older People With Type 1 Diabetes Compared With Flash Glucose Monitoring Metrics of Glycemic Control. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2022, 16, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceves, B.; Ezekiel-Herrera, D.; Marino, M.; Datta, R.; Lucas, J.; Giebultowicz, S.; Heintzman, J. Disparities in HbA1c testing between aging US Latino and non-Latino white primary care patients. Prev Med Rep 2022, 26, 101739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Sheffer, K.E.; Bennett, J.E.; Gregg, E.W.; Danaei, G.; Singleton, R.K.; Shaw, J.E.; Mishra, A.; Lhoste, V.P.F.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Kengne, A.P.; Phelps, N.H.; Heap, R.A.; Rayner, A.W.; Stevens, G.A.; Paciorek, C.J.; Riley, L.M.; Cowan, M.J.; Savin, S.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Lu, Y.; Pavkov, M.E.; Imperatore, G.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Ahmad, N.A.; Anjana, R.M.; Davletov, K.; Farzadfar, F.; González-Villalpando, C.; Khang, Y.-H.; Kim, H.C.; Laatikainen, T.; Laxmaiah, A.; Mbanya, J.C.N.; Narayan, K.M.V.; Ramachandran, A.; Wade, A.N.; Zdrojewski, T.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Rahim, H.F.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Adambekov, S.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Agdeppa, I.A.; Aghazadeh-Attari, J.; Agyemang, C.; Ahmadi, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Ahmadi, N.; Ahmed, S.H.; Ajlouni, K.; Al-Hinai, H.; Al-Lahou, B.; Al-Lawati, J.A.; Asfoor, D.A.; Al Qaoud, N.M.; Alarouj, M.; AlBuhairan, F.; AlDhukair, S.; Aldwairji, M.A.; Ali, M.M.; Alinezhad, F.; Alkandari, A.; Alomirah, H.F.; Aly, E.; Amarapurkar, D.N.; Andersen, L.B.; Anderssen, S.A.; Andrade, D.S.; Ansari-Moghaddam, A.; Aounallah-Skhiri, H.; Aris, T.; Arlappa, N.; Aryal, K.K.; Assah, F.K.; Assembekov, B.; Auvinen, J.; Avdičová, M.; Azad, K.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Azizi, F.; Bacopoulou, F.; Balakrishna, N.; Bamoshmoosh, M.; Banach, M.; Bandosz, P.; Banegas, J.R.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Barceló, A.; Baretić, M.; Barrera, L.; Basit, A.; Batieha, A.M.; Batista, A.P.; Baur, L.A.; Belavendra, A.; Ben Romdhane, H.; Benet, M.; Berkinbayev, S.; Bernabe-Ortiz, A.; Berrios Carrasola, X.; Bettiol, H.; Beybey, A.F.; Bhargava, S.K.; Bika Lele, E.C.; Bikbov, M.M.; Bista, B.; Bjerregaard, P.; Bjertness, E.; Bjertness, M.B.; Björkelund, C.; Bloch, K.V.; Blokstra, A.; Bo, S.; Bobak, M.; Boggia, J.G.; Bonaccio, M.; Bonilla-Vargas, A.; Borghs, H.; Bovet, P.; Brajkovich, I.; Brenner, H.; Brewster, L.M.; Brian, G.R.; Briceño, Y.; Brito, M.; Bugge, A.; Buntinx, F.; Cabrera de León, A.; Caixeta, R.B.; Can, G.; Cândido, A.P.C.; Capanzana, M.V.; Čapková, N.; Capuano, E.; Capuano, R.; Capuano, V.; Cardoso, V.C.; Carlsson, A.C.; Casanueva, F.F.; Censi, L.; Cervantes-Loaiza, M.; Chamnan, P.; Chamukuttan, S.; Chan, Q.; Charchar, F.J.; Chaturvedi, N.; Chen, H.; Cheraghian, B.; Chirlaque, M.-D.; Chudek, J.; Cifkova, R.; Cirillo, M.; Claessens, F.; Cohen, E.; Concin, H.; Cooper, C.; Costanzo, S.; Cowell, C.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Cruz, J.J.; Cureau, F.V.; Cuschieri, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; d’Orsi, E.; Dallongeville, J.; Damasceno, A.; Dastgiri, S.; De Curtis, A.; de Gaetano, G.; De Henauw, S.; Deepa, M.; DeGennaro, V.; Demarest, S.; Dennison, E.; Deschamps, V.; Dhimal, M.; Dika, Z.; Djalalinia, S.; Donfrancesco, C.; Dong, G.; Dorobantu, M.; Dörr, M.; Dragano, N.; Drygas, W.; Du, Y.; Duante, C.A.; Duboz, P.; Dushpanova, A.; Dziankowska-Zaborszczyk, E.; Ebrahimi, N.; Eddie, R.; Eftekhar, E.; Efthymiou, V.; Egbagbe, E.E.; Eghtesad, S.; El-Khateeb, M.; El Ati, J.; Eldemire-Shearer, D.; Elosua, R.; Enang, O.; Erasmus, R.T.; Erbel, R.; Erem, C.; Ergor, G.; Eriksen, L.; Eriksson, J.G.; Esmaeili, A.; Evans, R.G.; Fakhradiyev, I.; Fall, C.H.; Faramarzi, E.; Farjam, M.; Farzi, Y.; Fattahi, M.R.; Fawwad, A.; Felix-Redondo, F.J.; Ferguson, T.S.; Fernández-Bergés, D.; Ferrari, M.; Ferreccio, C.; Ferreira, H.S.; Ferrer, E.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Flood, D.; Forsner, M.; Fosse, S.; Fottrell, E.F.; Fouad, H.M.; Francis, D.K.; Frontera, G.; Furusawa, T.; Gaciong, Z.; Garnett, S.P.; Gasull, M.; Gazzinelli, A.; Gehring, U.; Ghaderi, E.; Ghamari, S.-H.; Ghanbari, A.; Ghasemi, E.; Gheorghe-Fronea, O.-F.; Ghimire, A.; Gialluisi, A.; Giampaoli, S.; Gianfagna, F.; Gill, T.K.; Gironella, G.; Giwercman, A.; Goltzman, D.; Gomula, A.; Gonçalves, H.; Gonçalves, M.; Gonzalez-Chica, D.A.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; González-Rivas, J.P.; González-Villalpando, M.-E.; Gonzalez, A.R.; Gottrand, F.; Grafnetter, D.; Grodzicki, T.; Grøntved, A.; Guerrero, R.; Gujral, U.P.; Gupta, R.; Gutierrez, L.; Gwee, X.; Haghshenas, R.; Hakimi, H.; Hambleton, I.R.; Hamzeh, B.; Hanekom, W.A.; Hange, D.; Hantunen, S.; Hao, J.; Hari Kumar, R.; Harooni, J.; Hashemi-Shahri, S.M.; Hata, J.; Heidemann, C.; Henrique, R. d. S.; Herrala, S.; Herzig, K.-H.; Heshmat, R.; Ho, S.Y.; Holdsworth, M.; Homayounfar, R.; Hopman, W.M.; Horimoto, A.R.V.R.; Hormiga, C.; Horta, B.L.; Houti, L.; Howitt, C.; Htay, T.T.; Htet, A.S.; Htike, M.M.T.; Huerta, J.M.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Collaboration, N.C.D.R.F. Global variation in diabetes diagnosis and prevalence based on fasting glucose and hemoglobin A1c. Nature Medicine 2023, 29, 2885–2901. [Google Scholar]
- de Miranda, V.A.; Cruz Filho, R.A.; de Oliveira, T.S.; Moscavitch, S.D.; Kang, H.C.; Miranda Chagas, S.V.; Costa, D.M.; Vianna Araújo, D.; Garcia Rosa, M.L. Racial differences in HbA1c: a cross-sectional analysis of a Brazilian public primary care population. Prim Care Diabetes 2013, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorst, C.; Kwok, C.S.; Aslam, S.; Buchan, I.; Kontopantelis, E.; Myint, P.K.; Heatlie, G.; Loke, Y.; Rutter, M.K.; Mamas, M.A. Long-term Glycemic Variability and Risk of Adverse Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2354–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, H.; Home, P.; Leiter, L.A. Should A1C targets be individualized for all people with diabetes? Arguments for and against. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 Suppl 2, (Suppl 2), S191-6.
- Anderson, J.J.; Welsh, P.; Ho, F.K.; Ferguson, L.D.; Welsh, C.E.; Pellicori, P.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Forbes, J.; Iliodromiti, S.; Boyle, J.; Lindsay, R.; Celis-Morales, C.; Gray, S.R.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Gill, J.M.R.; Pell, J.P.; Sattar, N. Ethnic differences in prevalence of actionable HbA1c levels in UK Biobank: implications for screening. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 2021, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Oshima, M.; Jun, M.; Ohkuma, T.; Toyama, T.; Wada, T.; Cooper, M.E.; Hadjadj, S.; Hamet, P.; Harrap, S.; Mancia, G.; Marre, M.; Williams, B.; Chalmers, J.; Woodward, M.; Perkovic, V.; on behalf of the, A.C.G. The relationship between eGFR slope and subsequent risk of vascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes: the ADVANCE-ON study. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marx, N.; Federici, M.; Schütt, K.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Ajjan, R.A.; Antunes, M.J.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Crawford, C.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Eliasson, B.; Espinola-Klein, C.; Fauchier, L.; Halle, M.; Herrington, W.G.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Lambrinou, E.; Lesiak, M.; Lettino, M.; McGuire, D.K.; Mullens, W.; Rocca, B.; Sattar, N.; Group, E.S.D. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes: Developed by the task force on the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal 2023, 44, 4043–4140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Cardiovascular Diabetology 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alijla, F.; Buttia, C.; Reichlin, T.; Razvi, S.; Minder, B.; Wilhelm, M.; Muka, T.; Franco, O.H.; Bano, A. Association of diabetes with atrial fibrillation types: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinstatler, L.; Qi, Y.P.; Williamson, R.S.; Garn, J.V.; Oakley, G.P., Jr. Association of Biochemical B12 Deficiency With Metformin Therapy and Vitamin B12 Supplements: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2006. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Wile, D.J.; Toth, C. Association of Metformin, Elevated Homocysteine, and Methylmalonic Acid Levels and Clinically Worsened Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2009, 33, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A.W. 10-Year Follow-up of Intensive Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Shurrab, N.T.; Arafa, E.-S. A. Metformin: A review of its therapeutic efficacy and adverse effects. Obesity Medicine 2020, 17, 100186. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Feng, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Hua, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, C. Metformin attenuates atherosclerosis and plaque vulnerability by upregulating KLF2-mediated autophagy in apoE−/- mice. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2021, 557, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, B.; Cameron, C.; Singh, S.R.; Yu, C.; Dolovich, L.; Houlden, R. Choice of therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin and a sulphonylurea: a systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison meta-analysis. Open Med 2012, 6, e62–e74. [Google Scholar]
- Riddle, M. Combining sulfonylureas and other oral agents. Am J Med 2000, 108 Suppl 6a, 15s-22s.
- Douros, A.; Dell’Aniello, S.; Yu, O.H.Y.; Filion, K.B.; Azoulay, L.; Suissa, S. Sulfonylureas as second line drugs in type 2 diabetes and the risk of cardiovascular and hypoglycaemic events: population based cohort study. BMJ 2018, 362, k2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Tawaramoto, K.; Kawasaki, F.; Hashiramoto, M.; Matsuki, M.; Kaku, K. Effects of sulfonylurea drugs on adiponectin production from 3T3-L1 adipocytes: implication of different mechanism from pioglitazone. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2008, 81, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasslacher, C.; Group, f. t. M. R. R. S. Safety and Efficacy of Repaglinide in Type 2 Diabetic Patients With and Without Impaired Renal Function. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.J.; Abrahamson, M.J.; Barzilay, J.I.; Blonde, L.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Bush, M.A.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Einhorn, D.; Fonseca, V.A.; Garber, J.R.; Garvey, W.T.; Grunberger, G.; Handelsman, Y.; Hirsch, I.B.; Jellinger, P.S.; McGill, J.B.; Mechanick, J.I.; Rosenblit, P.D.; Umpierrez, G.E. CONSENSUS STATEMENT BY THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS AND AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY ON THE COMPREHENSIVE TYPE 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ALGORITHM - 2018 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Endocr Pract 2018, 24, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.X.; Zhang, J.G.; Tao, S.; Yan, H.L. Effect of Repaglinide on Blood Glucose, Endothelial Function, Lipid Metabolism, and Inflammatory Reaction in a Rat Model of Atherosclerosis. Dose Response 2020, 18, 1559325820918762. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, B.L.; Erbel, R.; Janssen, O.E.; Mann, K. [Cardiovascular effects of oral hypoglycemie drugs]. Herz 2004, 29, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bloomgarden, Z.T. Thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, U. Pioglitazone: mechanism of action. Int J Clin Pract Suppl 2001, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon, N. Overview of the gliptin class (dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors) in clinical practice. Postgrad Med 2009, 121, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Drakul, M.; Čolić, M. Immunomodulatory activity of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in immune-related diseases. European Journal of Immunology 2023, 53, 2250302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanami, D.; Takashi, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Motonaga, R.; Tanabe, M. Renoprotective Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sen, U. More than just an enzyme: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) and its association with diabetic kidney remodelling. Pharmacol Res 2019, 147, 104391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Jia, Y.; Sun, S.; Meng, L. Adverse event profiles of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: data mining of the public version of the FDA adverse event reporting system. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2020, 21, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, R.; Bridgeman, M.B. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors In the Management of Diabetes. P t 2010, 35, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patoulias, D.I.; Boulmpou, A.; Teperikidis, E.; Katsimardou, A.; Siskos, F.; Doumas, M.; Papadopoulos, C.E.; Vassilikos, V. Cardiovascular efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: A meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. World J Cardiol 2021, 13, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Chai, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhan, S. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on lipid profiles among type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Ther 2015, 37, 225–241.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F.; Mannucci, E.; Ahrén, B. Glycaemic efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors as add-on therapy to metformin in subjects with type 2 diabetes-a review and meta analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012, 14, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes: Pleiotropic Cardiometabolic Effects and Add-on Value of a Combined Therapy. Drugs 2024, 84, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.A.; Wong, C.K.; Kaur, K.D.; Seeley, R.J.; Drucker, D.J. Differential importance of endothelial and hematopoietic cell GLP-1Rs for cardiometabolic versus hepatic actions of semaglutide. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, J.F.K.; Franco, D. Oral GLP-1 analogue: perspectives and impact on atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021, 20, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddio, A.E.; Vasudevan, R.S.; Gouzoulis, M.J.; Ansah-Twum, J.K.; Grauer, J.N.; Rubin, L.E. As Few as Three Months of Preoperative Semaglutide Exposure Prior to Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Associated With Reduced Postoperative Adverse Events in Patients With Type II Diabetes. J Arthroplasty 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lixi, F.; Calabresi, V.; Cukurova, F.; Giannaccare, G. Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy in an Otherwise Healthy Young Adult Patient Treated with Liraglutide and Semaglutide for Weight Loss: A Cautionary Tale. Int Med Case Rep J 2025, 18, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Inzucchi, S.E. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Heftdal, L.D.; Ko, H.J.; Overvad, M.; Shimomura, I.; Thamattoor, U.K.; Kim, K.K.; Investigators, O. Oral Semaglutide in an East Asian Population With Overweight or Obesity, With or Without Type 2 Diabetes: The OASIS 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suki, M.; Amer, J.; Milgrom, Y.; Massarwa, M.; Hazou, W.; Tiram, Y.; Perzon, O.; Sharif, Y.; Sackran, J.; Alon, R.; Lourie, N.E.E.; Raz, I.; Imam, A.; Khalaileh, A.; Safadi, R. Semaglutide in MASLD Patients: Improved Survival and Liver Outcomes. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2025, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristizabal-Colorado, D.; Vernaza Trujillo, D.A.; Sierra Castillo, S.; Rivera Martinez, W.A.; Badiel, M.; Abreu Lomba, A. Semaglutide Versus Empagliflozin in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes: A Cohort Study With 18 Months of Follow-Up (SEMPA18). Cureus 2025, 17, e83416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Fan, J. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin for the acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Med 2025, 57, 2514078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Burrack, N.; Heymann, A.; Grossman, A.; Neuman, T.; Abuhasira, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, Erythrocytosis, and Thrombosis in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Netw Open 2025, 8, e2517086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmedt, N.; Alhamdow, A.; Tskhvarashvili, G.; Saarelainen, L.; Qiao, X.; Lobier, M.; Hoti, F. Post-authorisation safety study to assess the risk of urinary tract cancer in people with type 2 diabetes initiating empagliflozin: A multi-country European study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2025, 27, 4401–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.X.; Wu, H.T.; Yang, J.; Yang, M. [Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin in the treatment of glycogen storage disease-associated inflammatory bowel disease]. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2025, 27, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hauwanga, W.N.; Abdalhamed, T.Y.; Ezike, L.A.; Chukwulebe, I.S.; Ko Oo, A.; Wilfred, A.; Khan, A.; Chukwuwike, J.; Florial, E.; Lawan, H.; Felix, A.; McBenedict, B. The Pathophysiology and Vascular Complications of Diabetes in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e76498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, P.F.; Li, Q.; Khamaisi, M.; Qiang, G.F. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Macrovascular Complications. Int J Endocrinol 2017, 2017, 4301461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Tan, K.H.X.; Tan, C.S.; Lim, W.Y.; Tai, E.S.; Venkataraman, K. Longitudinal trends in HbA(1c) patterns and association with outcomes: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2018, 34, e3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, L.; Zhao, D. The relationship between HbA1c control pattern and atherosclerosis progression of diabetes: a prospective study of Chinese population. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome 2024, 16, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzazzadehgan, S.; Shariat-Madar, Z.; Mahdi, F. Distinct Roles of Common Genetic Variants and Their Contributions to Diabetes: MODY and Uncontrolled T2DM. Biomolecules 2025, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colayco, D.C.; Niu, F.; McCombs, J.S.; Cheetham, T.C. A1C and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A nested case-control study. Diabetes Care 2010, 34, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.; Mohamed Abuelass, F.K.; Hamd Abdelwahab, S.B.; Mukhtar, M.; Ahmed, Y.; Elfahal, M.; Mohmed Elhussein, N.S. Determinants of Poor Glycemic Control Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e82464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesti, L.; Natali, A. Metformin effects on the heart and the cardiovascular system: A review of experimental and clinical data. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2017, 27, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.J.; Leaver, J.K.; Irving, G.J. Impact of metformin on cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomised trials among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpeter, S.R.; Greyber, E.; Pasternak, G.A.; Salpeter, E.E. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 2003, 163, 2594–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, B.; Wu, A.; Shin, J.I.; Sang, Y.; Alexander, G.C.; Secora, A.; Inker, L.A.; Coresh, J.; Chang, A.R.; Grams, M.E. Association of Metformin Use With Risk of Lactic Acidosis Across the Range of Kidney Function: A Community-Based Cohort Study. JAMA Intern Med 2018, 178, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, K.S.; Wang, D.; Jones, A.K.; Nash, M.J.; O’Rourke, R.; Takahashi, D.L.; Kievit, P.; Hennebold, J.D.; Aagaard, K.M.; Friedman, J.E.; Jones, K.L.; Rozance, P.J.; Brown, L.D.; Wesolowski, S.R. Metformin Disrupts Signaling and Metabolism in Fetal Hepatocytes. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarry-Adkins, J.L.; Aiken, C.E.; Ozanne, S.E. Neonatal, infant, and childhood growth following metformin versus insulin treatment for gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS Medicine 2019, 16, e1002848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, J.H.; Økland, I. Metformin use in pregnancy: What about long-term effects in offspring? Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2024, 103, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicine Agency Science Medicines Health. Use of metformin to treat diabetes now expanded to patients with moderately reduced kidney function. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/referrals/metformin-metformin-containing-medicines#topics. Accessed October, 2016.
- Mohan, V.; Saboo, B.; Khader, J.; Modi, K.D.; Jindal, S.; Wangnoo, S.K.; Amarnath, S. Position of Sulfonylureas in the Current ERA: Review of National and International Guidelines. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes 2022, 15, 11795514221074663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahardoust, M.; Mehrabi, Y.; Hadaegh, F.; Khalili, D.; Delpisheh, A. Impact of duration of treatments with metformin and sulfonylureas, individually or in combination, on diabetic retinopathy among newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients: a pooled cohort’s analysis. Int J Retina Vitreous 2025, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuth, S. Should Sulfonylureas Remain an Acceptable First-Line Add-on to Metformin Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes? No, It’s Time to Move On! Diabetes Care 2014, 38, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovitz, H.E.; Feinglos, M.N. Mechanism of action of the second-generation sulfonylurea glipizide. The American Journal of Medicine 1983, 75, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, P. New IDF clinical practice recommendations for managing type 2 diabetes in primary care. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2017, 132, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaczynski, W.M.; Hankins, M.; Ong, S.H.; Richter, H.; Clemens, A.; Toussi, M. Microvascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Vildagliptin vs. Sulfonylurea: A Retrospective Study Using German Electronic Medical Records. Diabetes therapy : research, treatment and education of diabetes and related disorders 2016, 7, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoulay, L.; Suissa, S. Sulfonylureas and the Risks of Cardiovascular Events and Death: A Methodological Meta-Regression Analysis of the Observational Studies. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.T.L.; Hui, J.M.H.; Lee, Y.H.A.; Satti, D.I.; Shum, Y.K.L.; Kiu, P.T.H.; Wai, A.K.C.; Liu, T.; Wong, W.T.; Chan, J.S.K.; Cheung, B.M.Y.; Wong, I.C.K.; Cheng, S.H.; Tse, G. Sulfonylurea Is Associated With Higher Risks of Ventricular Arrhythmia or Sudden Cardiac Death Compared With Metformin: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of the American Heart Association 2022, 11, e026289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, K.T.; Mafauzy, M.; Bin, L.X. Systematic Review of Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sulfonylureas, GLP-1 RA, and DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Diabetology 2024, 15, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerich, J.E. Clinical significance, pathogenesis, and management of postprandial hyperglycemia. Arch Intern Med 2003, 163, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, O.; Lund, S.; Andersen, P.H.; Jønler, M.; Pørksen, N. Optimizing Insulin Secretagogue Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A randomized double-blind study with repaglinide. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.; Fernandez, C.J. Efficacy and Cardiovascular Safety of Meglitinides. Curr Drug Saf 2021, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Pharmacologic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 1999, 131, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.; Donnelly, P.; McIntyre, L.; Royle, P.L.; Shepherd, J.P.; Thomas, S. Meglitinide analogues for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007, 2007, Cd004654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, L.; Dailey, G., 3rd; Huang, W.C.; Strange, P.; Goldstein, B.J. Repaglinide in type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, fixed-dose efficacy and safety study. J Clin Pharmacol 2000, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Schramm, T.K.; Gislason, G.H.; Vaag, A.; Rasmussen, J.N.; Folke, F.; Hansen, M.L.; Fosbøl, E.L.; Køber, L.; Norgaard, M.L.; Madsen, M.; Hansen, P.R.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Mortality and cardiovascular risk associated with different insulin secretagogues compared with metformin in type 2 diabetes, with or without a previous myocardial infarction: a nationwide study. Eur Heart J 2011, 32, 1900–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, G.; Fedele, V.; Rizzo, M.R.; Fioravanti, M.; Leotta, C.; Solerte, S.B.; Purrello, F.; Paolisso, G. Safety of Type 2 Diabetes Treatment With Repaglinide Compared With Glibenclamide in Elderly People : A randomized, open-label, two-period, cross-over trial. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1918–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamori, R.; Kaku, K.; Hanafusa, T.; Ioriya, K.; Kageyama, S.; Hotta, N. Clinical study of repaglinide efficacy and safety in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with blood glucose levels inadequately controlled by sitagliptin. J Diabetes Investig 2016, 7, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-K.; Yeh, J.-I. Comparison of mortality and cardiovascular event risk associated with various insulin secretagogues: A nationwide real-world analysis. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2019, 152, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Abdelmoneim, A.S.; Light, P.; Qiu, W.; Simpson, S.H. Comparative cardiovascular safety of insulin secretagogues following hospitalization for ischemic heart disease among type 2 diabetes patients: a cohort study. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications 2015, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soccio, R.E.; Chen, E.R.; Lazar, M.A. Thiazolidinediones and the promise of insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab 2014, 20, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.E.; Han, X.; Brensinger, C.M.; Bilker, W.B.; Cardillo, S.; Flory, J.H.; Hennessy, S. Comparative risk of serious hypoglycemia with oral antidiabetic monotherapy: A retrospective cohort study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2018, 27, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Benny, T.; Hale, G.; Seamon, M. What is the role of pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes in value-based care settings? Drugs & Therapy Perspectives 2024, 40, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Dormandy, J.A.; Charbonnel, B.; Eckland, D.J.; Erdmann, E.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Moules, I.K.; Skene, A.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lefèbvre, P.J.; Murray, G.D.; Standl, E.; Wilcox, R.G.; Wilhelmsen, L.; Betteridge, J.; Birkeland, K.; Golay, A.; Heine, R.J.; Korányi, L.; Laakso, M.; Mokán, M.; Norkus, A.; Pirags, V.; Podar, T.; Scheen, A.; Scherbaum, W.; Schernthaner, G.; Schmitz, O.; Skrha, J.; Smith, U.; Taton, J. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernan, W.N.; Viscoli, C.M.; Furie, K.L.; Young, L.H.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Gorman, M.; Guarino, P.D.; Lovejoy, A.M.; Peduzzi, P.N.; Conwit, R.; Brass, L.M.; Schwartz, G.G.; Adams, H.P., Jr.; Berger, L.; Carolei, A.; Clark, W.; Coull, B.; Ford, G.A.; Kleindorfer, D.; O’Leary, J.R.; Parsons, M.W.; Ringleb, P.; Sen, S.; Spence, J.D.; Tanne, D.; Wang, D.; Winder, T.R. Pioglitazone after Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. N Engl J Med 2016, 374, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza-Arnedo, R.; Rico-Fontalvo, J.-E.; Pájaro-Galvis, N.; Leal-Martínez, V.; Abuabara-Franco, E.; Raad-Sarabia, M.; Montejo-Hernández, J.; Cardona-Blanco, M.; Cabrales-Juan, J.; Uparella-Gulfo, I.; Montiel, L.S. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review. Kidney Medicine 2021, 3, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Drucker, D.J. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of action of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Endocr Rev 2014, 35, 992–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, V.A. New developments in diabetes management: medications of the 21st century. Clin Ther 2014, 36, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Incretin hormones: Their role in health and disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018, 20 Suppl 1, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, C.F. Peptide degradation and the role of DPP-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Peptides 2018, 100, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayanati, M.; Ismail Mahboubi Rabbani, M.; Sirous Kabiri, S.; Mir, B.; Rezaee, E.; Tabatabai, S.A. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: A Systematic Review of Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. Iran J Pharm Res 2024, 23, e151581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. DPP-4 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes: A critical review of head-to-head trials. Diabetes & Metabolism 2012, 38, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J.B.; Bethel, M.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; Buse, J.B.; Engel, S.S.; Garg, J.; Josse, R.; Kaufman, K.D.; Koglin, J.; Korn, S.; Lachin, J.M.; McGuire, D.K.; Pencina, M.J.; Standl, E.; Stein, P.P.; Suryawanshi, S.; Van de Werf, F.; Peterson, E.D.; Holman, R.R. Effect of Sitagliptin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015, 373, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirica, B.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Braunwald, E.; Steg, P.G.; Davidson, J.; Hirshberg, B.; Ohman, P.; Frederich, R.; Wiviott, S.D.; Hoffman, E.B.; Cavender, M.A.; Udell, J.A.; Desai, N.R.; Mosenzon, O.; McGuire, D.K.; Ray, K.K.; Leiter, L.A.; Raz, I. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2013, 369, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, E.; Mosenzon, O.; Avogaro, A. Analyses of Results From Cardiovascular Safety Trials With DPP-4 Inhibitors: Cardiovascular Outcomes, Predefined Safety Outcomes, and Pooled Analysis and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, (Supplement_2), S196-S204.
- BERRA, C.C.; MANFRINI, R.; GHELARDI, R.; BOLLATI, P.M.; BUCCIARELLI, L.; MIRANI, M.; MURATORI, M.; FOLLI, F.; GROUP, A.S. 367-P: Cardiovascular Risk Categories in Patients with Diabetes According to 2019 ESC/EASD Guidelines in Clinical Practice: Use of a Dedicated App (AWARE). Diabetes 2021, 70, (Supplement_1).
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, C.; Xue, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 721135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, M.; Yuan, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L. The effects of non-insulin anti-diabetic medications on the diabetic microvascular complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. BMC Endocr Disord 2025, 25, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefits of Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: A State-of-the-Art Review. JACC Basic Transl Sci 2020, 5, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, P.; Tunnicliffe, D.J.; Toyama, T.; Palmer, S.C.; Saglimbene, V.M.; Ruospo, M.; Gargano, L.; Stallone, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Strippoli, G.F. Sodium-glucose co-transporter protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for people with chronic kidney disease and diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2024, 5, Cd015588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Hsu, T.-W.; Liu, J.-H.; Pan, H.-C.; Lai, C.-F.; Yang, S.-Y.; Wu, V.-C. Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes Among Patients With CKD Receiving GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2025, 85, 555–569.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merovci, A.; Mari, A.; Solis-Herrera, C.; Xiong, J.; Daniele, G.; Chavez-Velazquez, A.; Tripathy, D.; Urban McCarthy, S.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; DeFronzo, R.A. Dapagliflozin lowers plasma glucose concentration and improves β-cell function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015, 100, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Mechanisms of enhanced renal and hepatic erythropoietin synthesis by sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Eur Heart J 2023, 44, 5027–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.A.; Terenzi, D.C.; Trac, J.Z.; Quan, A.; Mason, T.; Al-Omran, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dhingra, N.; Rotstein, O.D.; Leiter, L.A.; Zinman, B.; Sabongui, S.; Yan, A.T.; Teoh, H.; Mazer, C.D.; Connelly, K.A.; Verma, S. SGLT2 Inhibition with Empagliflozin Increases Circulating Provascular Progenitor Cells in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cell Metabolism 2019, 30, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.N.; Bright, R.; Truong, V.-K.; Li, J.; Juneja, R.; Vasilev, K. Key biomarkers in type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2025, 27, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2006, 8, S3. [Google Scholar]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nature Reviews Immunology 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Goyal, A.; Patel, B.C. C-Reactive Protein: Clinical Relevance and Interpretation. In StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing.
- Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2025.
- Rees, R.F.; Gewurz, H.; Siegel, J.N.; Coon, J.; Potempa, L.A. Expression of a C-reactive protein neoantigen (neo-CRP) in inflamed rabbit liver and muscle. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1988, 48, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khreiss, T.; József, L.; Potempa, L.A.; Filep, J.G. Opposing Effects of C-Reactive Protein Isoforms on Shear-Induced Neutrophil-Platelet Adhesion and Neutrophil Aggregation in Whole Blood. Circulation 2004, 110, 2713–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, S.U.; Habersberger, J.; Murphy, A.; Chen, Y.-C.; Woollard, K.J.; Bassler, N.; Qian, H.; von zur Muhlen, C.; Hagemeyer, C.E.; Ahrens, I.; Chin-Dusting, J.; Bobik, A.; Peter, K. Dissociation of Pentameric to Monomeric C-Reactive Protein on Activated Platelets Localizes Inflammation to Atherosclerotic Plaques. Circulation Research 2009, 105, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.-R.; Ma, L.; Bai, C.-J.; Shi, J.-M.; Li, H.-Y.; Potempa, L.A.; Filep, J.G.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y. Monomeric C-reactive protein activates endothelial cells via interaction with lipid raft microdomains. The FASEB Journal 2009, 23, 1806–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, N.; Shah, R.L.; Sharp, S.J.; Luan, J. a.; Stewart, I.D.; Wheeler, E.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Baras, A.; Wareham, N.J.; Langenberg, C.; Lotta, L.A. Meta-analysis investigating the role of interleukin-6 mediated inflammation in type 2 diabetes. eBioMedicine 2020, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Adler, A.I.; Sandhu, M.S.; Sharp, S.J.; Forouhi, N.G.; Erqou, S.; Luben, R.; Bingham, S.; Khaw, K.T.; Wareham, N.J. Association of C-reactive protein with type 2 diabetes: prospective analysis and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anness, A.R.; Baldo, A.; Webb, D.R.; Khalil, A.; Robinson, T.G.; Mousa, H.A. Effect of metformin on biomarkers of placental- mediated disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Placenta 2021, 107, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A.C.Y. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shabrawey, M.; Zhang, W.; McDonald, D. Diabetic retinopathy: mechanism, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 854593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapanga, R.F.; Essop, M.F. Damaging effects of hyperglycemia on cardiovascular function: spotlight on glucose metabolic pathways. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 2016, 310, H153–H173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Han, J.; Xia, P.; Shen, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P. Advances in the study of RNA-binding proteins in diabetic complications. Molecular Metabolism 2022, 62, 101515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, E.J.; Sun, J.K.; Stitt, A.W. Diabetic retinopathy: current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropp, M.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Mazurakova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Sargheini, N.; Vo, T.K.S.; de Clerck, E.; Polivka, J., Jr.; Potuznik, P.; Polivka, J.; Stetkarova, I.; Kubatka, P.; Thumann, G. Diabetic retinopathy as the leading cause of blindness and early predictor of cascading complications-risks and mitigation. Epma j 2023, 14, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng-Miller, K.W.; Baumal, C.R. Chapter 5 - Genetics of Diabetic Retinopathy. In Current Management of Diabetic Retinopathy, Baumal, C.R.; Duker, J.S., Eds. Elsevier: 2018; pp 37-40.
- Gupta, S.; Thool, A.R. A Narrative Review of Retinopathy in Diabetic Patients. Cureus 2024, 16, e52308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Takeda, N.; Hara, H.; Ishii, S.; Numata, G.; Tokiwa, H.; Katoh, M.; Maemura, S.; Suzuki, T.; Takiguchi, H.; Yanase, T.; Kubota, Y.; Nomura, S.; Hatano, M.; Ueda, K.; Harada, M.; Toko, H.; Takimoto, E.; Akazawa, H.; Morita, H.; Nishimura, S.; Komuro, I. PGC-1α–mediated angiogenesis prevents pulmonary hypertension in mice. JCI Insight 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, K.F.; Beeson, G.C.; Beeson, C.C.; Baicu, C.F.; Zile, M.R.; McDermott, P.J. Estrogen-Related Receptor α (ERRα) is required for adaptive increases in PGC-1 isoform expression during electrically stimulated contraction of adult cardiomyocytes in sustained hypoxic conditions. International Journal of Cardiology 2015, 187, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Shoag, J.; Arany, Z. Regulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Genes by PGC-1α. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2010, 30, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willy, P.J.; Murray, I.R.; Qian, J.; Busch, B.B.; Stevens, W.C.; Martin, R.; Mohan, R.; Zhou, S.; Ordentlich, P.; Wei, P.; Sapp, D.W.; Horlick, R.A.; Heyman, R.A.; Schulman, I.G. Regulation of PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) signaling by an estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) ligand. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 8912–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Nawaz, M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Siddiquei, M.M.; Allegaert, E.; Gikandi, P.W.; De Hertogh, G.; Opdenakker, G. A key role of the PGC-1alpha/ERR-alpha pathway in regulation of angiogenic factors in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2025, 16, 1615103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Neumaier, M. Erythropoietin levels in aqueous humour in eyes with exudative age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2007, 35, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, A.A.R.; Jayashree, K.; Senthilkumar, G.P.; Thomas, S.E.; Babu, K.R. An Assessment of Serum Irisin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 as Potential Indicators of Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Niger Postgrad Med J 2025, 32, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, H.; Yu, X. Postprandial C-Peptide to Glucose Ratio as a Promising Systemic Marker of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes. Transl Vis Sci Technol 2025, 14, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.M.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, R.R.; Zeng, Y.S.; Zeng, Z.; He, Z.T.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.J.; Yu, J.G.; You, C.Y. Combination of red blood cell distribution width and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting severity of diabetic retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol 2025, 18, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Zheng, Y.; He, M. Unveiling biomarkers via plasma metabolome profiling for diabetic macrovascular and microvascular complications. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2025, 24, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, S.A.; Benedikter, B.J.; Mokhtar, S.B.A.; van der Heide, F.C.T.; Kumaramanickavel, G.; van Greevenbroek, M.M.J.; Webers, C.A.B.; Berendschot, T. Plasma Sphingomyelins as Biomarkers for Diabetic Retinal Neurodegeneration: The Maastricht Study. Ophthalmol Sci 2025, 5, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; She, X.; Huang, G.; Chu, X.; Zhao, S.; Lv, Z.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y. Metabolomic insights into vitreous humor with therapy outcome in type 2 diabetic retinopathy. BMC Ophthalmol 2025, 25, 460. [Google Scholar]
- Zooravar, D.; Shojaei, S.; Mousavi, A.; Soltani, P.; Amiri, B.S.; Radkhah, H. Novel Lipid Biomarkers and Microvascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes 2025, 18, 11795514251365301. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Yang, Q.; Hong, Y.; Tan, R.; Ibrahim, F.N.I.; Lim, C.; Choo, J.; Sabanayagam, C.; Coffman, T.M.; Wong, T.Y.; Tan, G.S.W. Retinal Neuronal Changes and Kidney Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conserva, F.; Gesualdo, L.; Papale, M. A Systems Biology Overview on Human Diabetic Nephropathy: From Genetic Susceptibility to Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications. Journal of Diabetes Research 2016, 2016, 7934504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, B.P. Diabetic Nephropathy and End-Stage Renal Disease. In Complete Nurse’s Guide to Diabetes Care, Childs, B.P.; Cypress, M.; Spollett, G.R., Eds. American Diabetes Association: p 0.
- Agarwal, R. Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Compendia 2021, 2021, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, V.; Kim, S.J. Diabetic Nephropathy - a Review of Risk Factors, Progression, Mechanism, and Dietary Management. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2021, 29, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetter, T.H.; Rennke, H.G.; Brenner, B.M. The case for intrarenal hypertension in the initiation and progression of diabetic and other glomerulopathies. Am J Med 1982, 72, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Ding, L.; Andoh, V.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. The Mechanism of Hyperglycemia-Induced Renal Cell Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy Disease: An Update. Life (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, R.; Yao, Y.; Guan, H.; Tian, J. Discovering diabetes complications-related microRNAs: meta-analyses and pathway modeling approach. BMC Med Genomics 2025, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawab, M.S.; Mohamed, M.G.; Doudar, N.A.; Rateb, E.E.; Reyad, H.R.; Elazeem, N.A.A. Circulating hsa-miR-221 as a possible diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of diabetic nephropathy. Mol Biol Rep 2023, 50, 9793–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgayed, G.; Hosni, A.; Abdel-Moneim, A.; Malik, A.; Zaky, M.Y.; Hasona, N.A. Integrated analysis of long non-coding RNA megacluster, microRNA-132 and microRNA-133a and their implications for cardiovascular risk and kidney failure progression in diabetic patients. Exp Ther Med 2025, 29, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Liu, Y.; Sattar, N.; Yavin, Y.; Pollock, C.A.; Butler, J.; Jardine, M.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Masson, S.; Breyer, M.; Hansen, M.K. Vascular endothelial growth factors and risk of cardio-renal events: Results from the CREDENCE trial. Am Heart J 2024, 271, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kralisch, S.; Fasshauer, M. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein: a novel adipokine involved in the pathogenesis of metabolic and vascular disease? Diabetologia 2013, 56, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Leung, P.S. Fibroblast growth factor 21: a regulator of metabolic disease and health span. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2017, 313, E292–e302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Quan, X.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chao, Z.; Jia, C.; Qin, H.; Zhang, H. Pigment epithelium-derived factor and its role in microvascular-related diseases. Biochimie 2022, 200, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.Y.Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Tang, C.S.; Xu, A.; Au, K.-W.; Fong, C.H.Y.; Ng, K.K.K.; Kwok, K.H.M.; Chow, W.-S.; Woo, Y.-C.; Yuen, M.M.A.; Hai, J.; Tan, K.C.B.; Lam, T.-H.; Tse, H.-F.; Sham, P.-C.; Lam, K.S.L. Genetic Regulation of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF): An Exome-Chip Association Analysis in Chinese Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2018, 68, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sbriscia, M.; Caccese, S.; Marchegiani, F.; Recchioni, R.; Matacchione, G.; Giordani, C.; Francini, E.; Salvioli, S.; Conte, M.; Landolfo, M.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Turchi, F.; Sabbatinelli, J.; Olivieri, F.; Giuliani, A. A scoring model integrating CXCL9, GDF15, FGF21, and NfL, predicts long-term mortality in type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2025, 24, 270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Heck, J.I.P.; Ajie, M.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Tack, C.J.; Stienstra, R. Circulating inflammatory proteins are elevated in type 1 and type 2 diabetes and associated to complications. Diabetes Obes Metab 2025, 27, 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- AlMajed, H.T.; Abu-Farha, M.; Alshawaf, E.; Devarajan, S.; Alsairafi, Z.; Elhelaly, A.; Cherian, P.; Al-Khairi, I.; Ali, H.; Jose, R.M.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Al-Mulla, F.; Al Attar, A.; Abubaker, J. Increased Levels of Circulating IGFBP4 and ANGPTL8 with a Prospective Role in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, C.G.; Ma, L.J. Role of GDF-15 in diabetic nephropathy: mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapeutic potential. Int Urol Nephrol 2025, 57, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Huang, K.; Liang, Y.; Yu, W.; Long, L.; Wang, K.; Yi, B. Associations between serum JAML, nesfatin-1, and 25(OH)D and the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 27438. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; van Goor, H.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Bilo, H.J.G.; Dullaart, R.P.F.; van Dijk, P.R. Serum peroxiredoxin-4, a biomarker of oxidative stress, is associated with the development of nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes (Zodiac-65). Free Radic Biol Med 2024, 212, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareghani, O.; Ghareghani, S.; Takhshid, M.A. Diagnostic values of ischemia modified albumin in diabetes-related complications: a narrative review. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2023, 22, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, B.; Politi, C.; Pizzini, P.; Parlongo, R.M.; Testa, A.; Mobrici, M.; Tripepi, G.L.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine, a biomarker of oxidative DNA injury, in diabetic kidney disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2025, 35, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roointan, A.; Shafieizadegan, S.; Ghaeidamini, M.; Gheisari, Y.; Hudkins, K.L.; Gholaminejad, A. The potential of cardiac biomarkers, NT-ProBNP and troponin T, in predicting the progression of nephropathy in diabetic patients: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023, 204, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagihashi, S.; Mizukami, H.; Sugimoto, K. Mechanism of diabetic neuropathy: Where are we now and where to go? J Diabetes Investig 2011, 2, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, J.K.; Inglis, J.T.; Madden, K.M.; Boyd, L.A. Brain and Body: A Review of Central Nervous System Contributions to Movement Impairments in Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 69, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erus, G.; Battapady, H.; Zhang, T.; Lovato, J.; Miller, M.E.; Williamson, J.D.; Launer, L.J.; Bryan, R.N.; Davatzikos, C. Spatial patterns of structural brain changes in type 2 diabetic patients and their longitudinal progression with intensive control of blood glucose. Diabetes care 2015, 38, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Kawamura, N.; Dyck, P.J.; Dyck, P.J.B.; Kihara, M.; Low, P.A. Spectrum of diabetic neuropathies. Diabetol Int 2020, 11, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.Y.; Lee, M.K. Autonomic dysfunction, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. J Diabetes Investig 2021, 12, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhiyenko, V.A.; Serhiyenko, A.A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. World J Diabetes 2018, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, M.; Gylfadottir, S.S.; Krøigård, T.; Kristensen, A.G.; Christensen, D.H.; Karlsson, P.; Möller, S.; Andersen, H.; Tankisi, H.; Nielsen, J.S.; Jensen, T.S.; Thomsen, R.W.; Finnerup, N.B.; Sindrup, S.H. Small and large fiber sensory polyneuropathy in type 2 diabetes: Influence of diagnostic criteria on neuropathy subtypes. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System 2021, 26, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Xue, L.; Zhao, T.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Ding, H. Plantar Tissue Characteristics in People With Diabetes With and Without Peripheral Neuropathy: A Novel Explanatory Model for DPN Risk Assessment. J Diabetes 2025, 17, e70094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascaso, P.; Palanca, A.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Sanz, M.J.; Ascaso, J.F.; Piqueras, L.; Real, J.T. Peripheral blood levels of CXCL10 are a useful marker for diabetic polyneuropathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract 2021, 75, e14302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A.; Bose, C.; Pramanik, S.; Dash, D.; Mukherjee, B.; Malik, R.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Circulating netrin-1 levels are reduced and related to corneal nerve fiber loss in patients with diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Investig 2024, 15, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.K.W. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: from intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends in Neurosciences 2015, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.; Rocca, D.; Henley, J.M. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1): structure, distribution and roles in brain function and dysfunction. Biochem J 2016, 473, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hviid, C.V.B.; Rasmussen, N.H.; Roikjer, J. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: a potential biomarker for small fiber neuropathy? Acta Diabetol 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.; Petroianu, G.; Adem, A. Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, P.; Luo, E. Advanced glycation end products and reactive oxygen species: uncovering the potential role of ferroptosis in diabetic complications. Molecular Medicine 2024, 30, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Jakhotia, S.; Sivaprasad, M.; Shalini, T.; Reddy, P.Y.; Viswanath, K.; Jakhotia, K.; Sahay, R.; Sahay, M.; Reddy, G.B. Circulating levels of Hsp27 in microvascular complications of diabetes: Prospects as a biomarker of diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications 2018, 32, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Matuschik, L.; Riabov, V.; Schmuttermaier, C.; Sevastyanova, T.; Weiss, C.; Klüter, H.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Hyperglycemia Induces Inflammatory Response of Human Macrophages to CD163-Mediated Scavenging of Hemoglobin-Haptoglobin Complexes. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Jeune, S.; Sadoudi, S.; Charue, D.; Abid, S.; Guigner, J.M.; Helley, D.; Bihan, H.; Baudry, C.; Lelong, H.; Mirault, T.; Vicaut, E.; Dhote, R.; Mourad, J.J.; Boulanger, C.M.; Blanc-Brude, O.P. Low grade intravascular hemolysis associates with peripheral nerve injury in type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0275337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Tang, Y.-d. Coronary Artery Disease: From Mechanism to Clinical Practice. In Coronary Artery Disease: Therapeutics and Drug Discovery, Wang, M., Ed. Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp 1-36.
- Dziopa, K.; Chaturvedi, N.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Schmidt, A.F. Identifying and ranking non-traditional risk factors for cardiovascular disease prediction in people with type 2 diabetes. Commun Med (Lond) 2025, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Villegas, E. Dyslipidemia, Hypertension and Diabetes Metaflammation. A Unique Mechanism for 3 Risk Factors. Curr Hypertens Rev 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, R.M.; Nesto, R.W. Acute myocardial infarction in the diabetic patient: Pathophysiology, clinical course and prognosis. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 1992, 20, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Fragakis, N. Diabetes-Driven Atherosclerosis: Updated Mechanistic Insights and Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Int J Mol Sci 2025, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.E.; Claggett, B.; Skali, H.; Solomon, S.D.; Cunningham, J.W.; Matsushita, K.; Konety, S.H.; Kitzman, D.W.; Mosley, T.H.; Clark, D.; Chang, P.P.; Shah, A.M. Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: The ARIC Study. Journal of the American Heart Association 2022, 11, e021660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E.; Morrow, D.A. Unstable Angina. Circulation 2013, 127, 2452–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, R.A. Chapter 15 - Chronic Stable Angina. In Cardiology Secrets (Fifth Edition), Levine, G.N., Ed. Elsevier: 2018; pp 135-142.
- Kannel, W.B.; McGee, D.L. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. Jama 1979, 241, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Ning, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhao, H.; Feng, J.; Lin, L.; Ruan, C.; Chen, S.; Tian, J.; Jin, C. Modifiable Factors and 10-Year and Lifetime Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults With New-Onset Diabetes: The Kailuan Cohort Study. Journal of the American Heart Association 2025, 14, e041223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasaszwili, M.; Billert, M.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W.; Skrzypski, M. Adropin as A Fat-Burning Hormone with Multiple Functions-Review of a Decade of Research. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushala, B.A.S.; Scott, I. Adropin: a hepatokine modulator of vascular function and cardiac fuel metabolism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2021, 320, H238–h244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezina, T.A.; Berezin, O.O.; Novikov, E.V.; Berezin, A.E. The Association of Adropin with Asymptomatic Coronary Calcification in Patients in Early Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2025, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, C.G.; Guo, Y.L.; Wu, N.Q.; Dong, Q.; Xu, R.X.; Wu, Y.J.; Qian, J.; Li, J.J. Prognostic Value of Plasma Endothelin-1 in Predicting Worse Outcomes in Patients with Prediabetes and Diabetes and Stable Coronary Artery Diseases. Diabetes Metab J 2024, 48, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boieriu, A.M.; Luca, C.D.; Neculoiu, C.D.; Bisoc, A.; Tint, D. Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Severe Coronary Artery Disease: Does Diabetes Play a Contributing Role? Medicina (Kaunas) 2025, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Park, S.-H.; Koo, B.-K. Ischemia With Nonobstructive Coronary Artery Disease. JACC: Asia 2023, 3, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, M.; Ciccarelli, M.; Varzideh, F.; Kansakar, U.; Guerra, G.; Cerasuolo, F.A.; Buonaiuto, A.; Fiordelisi, A.; Venga, E.; Esposito, M.; Rainone, A.; Ricciardi, R.; Del Giudice, C.; Minicucci, F.; Tesorio, T.; Visco, V.; Iaccarino, G.; Gambardella, J.; Santulli, G.; Mone, P. Endothelial microRNAs in INOCA patients with diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2024, 23, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; NaveenKumar, S.K.; Navaz, S.; Liang, W.; Sugur, K.; Kmetova, K.; Ayers, C.R.; Kluge, L.; Chong, E.; Shah, A.M.; Rohatgi, A.; Berry, J.D.; Knight, J.S.; de Lemos, J.A. Epidemiological and Translational Study of Calprotectin and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Cardiol 2025, 10, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnazzo, V.; Redi, S.; Basile, V.; Natali, P.; Gulli, F.; Equitani, F.; Marino, M.; Basile, U. Calprotectin: two sides of the same coin. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2024, 63, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, B.; Chen, Q.; Bjorkbacka, H.; Bjornson, E.; Brinck, J.; Chorell, E.; Djekic, D.; Edsfeldt, A.; Engstrom, G.; Eriksson, J.W.; Gottsater, A.; Gummesson, A.; Hagstrom, E.; Hedin, U.; Jernberg, T.; Johnston, N.; Nilsson, L.; Nystrom, F.; Otten, J.; Rosengren, A.; Soderberg, S.; Haglow, J.T.; Ostgren, C.J. Lipoproteins and lipoprotein lipid composition are associated with stages of dysglycemia and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol 2025, 419, 132698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, W.; Bourron, O.; Materne, C.; Galier, S.; Phan, F.; Tan-Chen, S.; Guillas, I.; Hartemann, A.; Salem, J.E.; Redheuil, A.; Foufelle, F.; Le Stunff, H.; Hajduch, E.; Guerin, M. Inverse relationship between circulating sphingosine-1-phosphate and precursor species and coronary artery calcification score in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2025, 24, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yan, X.; Tang, Z.; Feng, B. Association between circulating oxidized OxLDL/LDL-C ratio and the severity of coronary atherosclerosis, along with other emerging biomarkers of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 191, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultgårdh-Nilsson, A.; Borén, J.; Chakravarti, S. The small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans in tissue repair and atherosclerosis. J Intern Med 2015, 278, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirankaya, A.; Tugrul, S.; Ozcan, S.; Ince, O.; Donmez, E.; Atici, A.; Hancioglu, E.; Okuyan, E.; Sahin, I. Correlation between the serum lumican level and the severity of coronary artery disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2023, 27, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hershenson, R.; Nardi-Agmon, I.; Leshem-Lev, D.; Kornowski, R.; Eisen, A. The effect of empagliflozin on circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with diabetes and stable coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2024, 23, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, H.; Chiti, H.; Reshadmanesh, T.; Gohari, S.; Jalilvand, A.; Arsang-Jang, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Ghanbari, S.; Dadashi, M.; Asgari, A.; Mahjani, M.; Karbalaee-Hasani, A.; Ahangar, H. Empagliflozin improves high-sensitive cardiac troponin-I and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease: a post-hoc analysis of EMPA-CARD Trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2023, 22, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Ma, R.C.W. Metabolomics in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications: Insights from Epidemiological Studies. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriach, M.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Romero, F.J.; Barcia, J.M. Diabetes and the brain: oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014, 2014, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Sas, K.M.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Feldman, E.L.; Gardner, T.W.; Pennathur, S.; Fort, P.E. New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications: role of lipids and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, C.A.; Lingaraju, A.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Zhou, G.; Cui, C.; Jacobs-El, H.; Babenko, I.; Hoofnagle, A.; Czyz, D.; Shuman, H.; Vaisar, T.; Becker, L. Obesity and Insulin Resistance Promote Atherosclerosis through an IFNγ-Regulated Macrophage Protein Network. Cell Reports 2018, 23, 3021–3030. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, P.F.; Zhang, H.S.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.Y.; Mao, J.N.; Hang, C.H.; Li, W. Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 1092431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.-Q.; Yang, S.; Dong, M.-H.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Chu, Y.-H.; Xu, L.-L.; Pang, X.-W.; Zhu, L.-F.; Xu, T.; Yong, T.-y.; Wang, W.; Tian, D.-S.; Qin, C. The foam cell-derived exosomes exacerbate ischemic white matter injury via transmitting metabolic defects to microglia. Cell Metabolism 2025, 37, 1636–1654.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, L.; Akbar, N.; Braithwaite, A.T.; Krausgruber, T.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Bailey, J.; Corbin, A.L.; Khoyratty, T.E.; Chai, J.T.; Alkhalil, M.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Ziberna, K.; Arya, R.; Cahill, T.J.; Bock, C.; Laurencikiene, J.; Crabtree, M.J.; Lemieux, M.E.; Riksen, N.P.; Netea, M.G.; Wheelock, C.E.; Channon, K.M.; Rydén, M.; Udalova, I.A.; Carnicer, R.; Choudhury, R.P. Hyperglycemia Induces Trained Immunity in Macrophages and Their Precursors and Promotes Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2021, 144, 961–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavridis, A.; Viktorisson, A.; Eliasson, B.; von Euler, M.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Risk of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Individuals With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Sweden. Neurology 2025, 104, e213480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Z.; Senyigit, A.; Durmus, S.; Duvarci, C.; Gelisgen, R.; Uzun, H.; Tabak, O. The relationship between oxLDL, sLOX-1, PCSK9 and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Sharma, L.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Chitotriosidase: a marker and modulator of lung disease. European Respiratory Review 2020, 29, 190143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artieda, M.; Cenarro, A.; Gañán, A.; Jericó, I.; Gonzalvo, C.; Casado, J.M.; Vitoria, I.; Puzo, J.; Pocoví, M.; Civeira, F. Serum Chitotriosidase Activity Is Increased in Subjects With Atherosclerosis Disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2003, 23, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, A.; Quelhas-Santos, J.; Ferreira, I.; Sampaio, S.; Relvas, M.; Marques, N.; Dias, C.C.; Pestana, M. Circulating Renalase as Predictor of Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Pre-Dialysis CKD Patients: A 5-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Life (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Z. Molecular basis of Klotho: from gene to function in aging. Endocr Rev 2015, 36, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.C.; Chou, K.M.; Lee, C.C.; Yang, N.I.; Sun, C.Y. Circulating Klotho levels can predict long-term macrovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 2018, 276, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Liao, Y.F.; Zeng, T.S.; Li, Y.M.; Yu, F.; Li, H.Q. [Number and function of circulating endothelial progenitor cell in diabetics with different vascular complications]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 89, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, D.; Gao, P.; Su, J.; Yang, H.; Gao, X.; Ni, W.; Lei, Y.; Gu, Y. Progression in Moyamoya Disease: Clinical Features, Neuroimaging Evaluation, and Treatment. Curr Neuropharmacol 2022, 20, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.Y.; Fan, Y.N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Liu, B.; Duan, L. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells in moyamoya disease. Brain Behav 2018, 8, e01035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paneni, F.; Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Cosentino, F. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: part I. Eur Heart J 2013, 34, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvoipati, T.; Kielhorn, C.E.; Armstrong, E.J. Peripheral artery disease in patients with diabetes: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and outcomes. World J Diabetes 2015, 6, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Jableh, W.; Younis, A.; Hjazeen, A.; Mashaqbeh, E.; Al-Sharif, E. Asymptomatic Peripheral Arterial Disease Among Jordanian Patients With Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Cureus 2024, 16, e73722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolderen, K.G.; Ujueta, F.; Buckley Behan, D.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Jackson, E.A.; Peters, M.; Whipple, M.; Phillips, K.; Chung, J.; Mena-Hurtado, C.; Disease, o. b. o. t. A. H. A. C. o. P. V.; Cardiovascular, C. o.; Nursing, S.; Care, C. o. Q. o.; Research, O. Understanding the Pain Experience and Treatment Considerations Along the Spectrum of Peripheral Artery Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes 2025, 18, e000135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeeta, S.; Siripuram, C.; Konka, S.; Vaithilingam, K.; Periasamy, P.; Velu, R.K.; Kandimalla, R. Biomarkers of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Endothelial Dysfunction in Early Detection of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Cureus 2025, 17, e82174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jude, E.B. Intermittent claudication in the patient with diabetes. The British Journal of Diabetes & Vascular Disease 2004, 4, 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau, M.; Rosas-Arellano, M.P.; Gurr, K.R.; Bailey, S.I.; Taylor, D.C.; Grewal, R.; Lawlor, D.K.; Bailey, C.S. The reliability of differentiating neurogenic claudication from vascular claudication based on symptomatic presentation. Can J Surg 2013, 56, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Zeb, S.; Ashraf; Rumman; Ali, A.; Aleem, F.; Omair, F. The Relationship Between Plasma Fibrinogen Levels and the Severity of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Diabetic Patients. Cureus 2025, 17, e81118.
- Yachmaneni, A., Jr.; Jajoo, S.; Mahakalkar, C.; Kshirsagar, S.; Dhole, S. A Comprehensive Review of the Vascular Consequences of Diabetes in the Lower Extremities: Current Approaches to Management and Evaluation of Clinical Outcomes. Cureus 2023, 15, e47525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsararatee, H.H.; Langley, J.C.S.; Thorburn, M.; Burton-Gow, H.; Whitby, S.; Powell, S. Assessment of the diabetic foot in inpatients. Br J Nurs 2025, 34, S12–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; Kimura, E.; Harada, R.K.; Nair, N.; Narasimhan, B.; Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, F.; Beck, K.R.; Olin, J.W.; Fung, E.T.; Cooke, J.P. Beta2-microglobulin as a biomarker in peripheral arterial disease: proteomic profiling and clinical studies. Circulation 2007, 116, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kafaji, G.; Al-Mahroos, G.; Abdulla Al-Muhtaresh, H.; Sabry, M.A.; Abdul Razzak, R.; Salem, A.H. Circulating endothelium-enriched microRNA-126 as a potential biomarker for coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 268–278. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-Valdés, G.; Gómez-Hevia, F.; Lillo-Moya, J.; González-Fernández, T.; Abelli, J.; Cereceda-Cornejo, A.; Bragato, M.C.; Saso, L.; Rodrigo, R. Endostatin and Cancer Therapy: A Novel Potential Alternative to Anti-VEGF Monoclonal Antibodies. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Golledge, J.; Clancy, P.; Hankey, G.J.; Yeap, B.B.; Norman, P.E. Serum endostatin concentrations are higher in men with symptoms of intermittent claudication. Dis Markers 2014, 2014, 298239. [Google Scholar]
- Naka, K.K.; Papathanassiou, K.; Bechlioulis, A.; Pappas, K.; Tigas, S.; Makriyiannis, D.; Antoniou, S.; Kazakos, N.; Margeli, A.; Papassotiriou, I.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Michalis, L.K. Association of vascular indices with novel circulating biomarkers as prognostic factors for cardiovascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Biochem 2018, 53, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I. Adiponectin as a routine clinical biomarker. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014, 28, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samman Tahhan, A.; Hayek, S.S.; Sandesara, P.; Hajjari, J.; Hammadah, M.; O’Neal, W.T.; Kelli, H.M.; Alkhoder, A.; Ghasemzadeh, N.; Ko, Y.A.; Aida, H.; Gafeer, M.M.; Abdelhadi, N.; Mohammed, K.H.; Patel, K.; Arya, S.; Reiser, J.; Vaccarino, V.; Sperling, L.; Quyyumi, A. Circulating soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor levels and peripheral arterial disease outcomes. Atherosclerosis 2017, 264, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Younes, H.; Abuhalimeh, B.; Zamzam, A.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 2025, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb 2019, 26, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragones, G.; Ferre, R.; Lazaro, I.; Cabre, A.; Plana, N.; Merino, J.; Heras, M.; Girona, J.; Masana, L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 is associated with endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Younes, H.; Abuhalimeh, B.; Zamzam, A.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Matrix Metalloproteinases 7 and 10 Are Prognostic Biomarkers for Systemic Cardiovascular Risk in Individuals with Peripheral Artery Disease. Biomolecules 2025, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
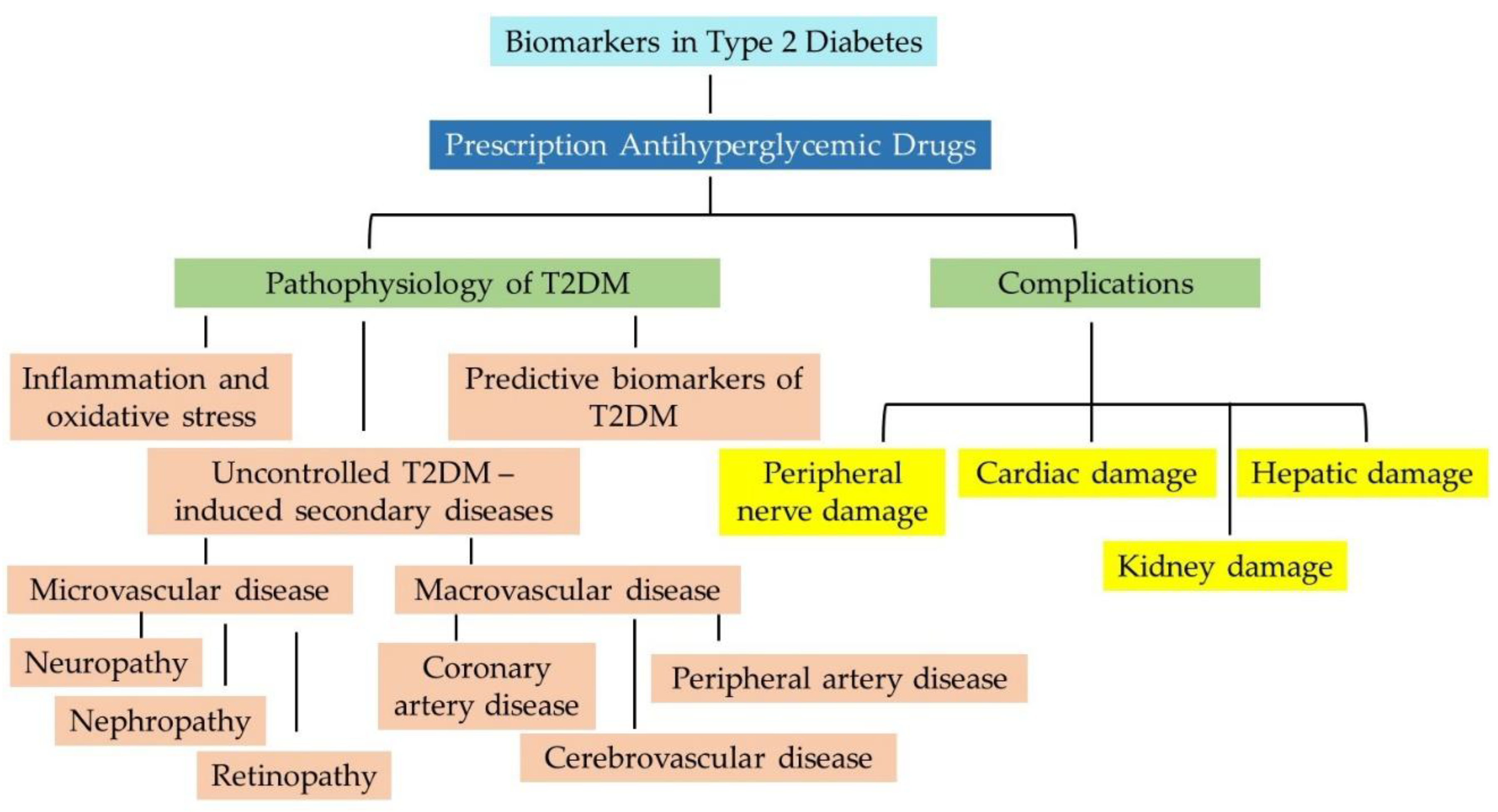
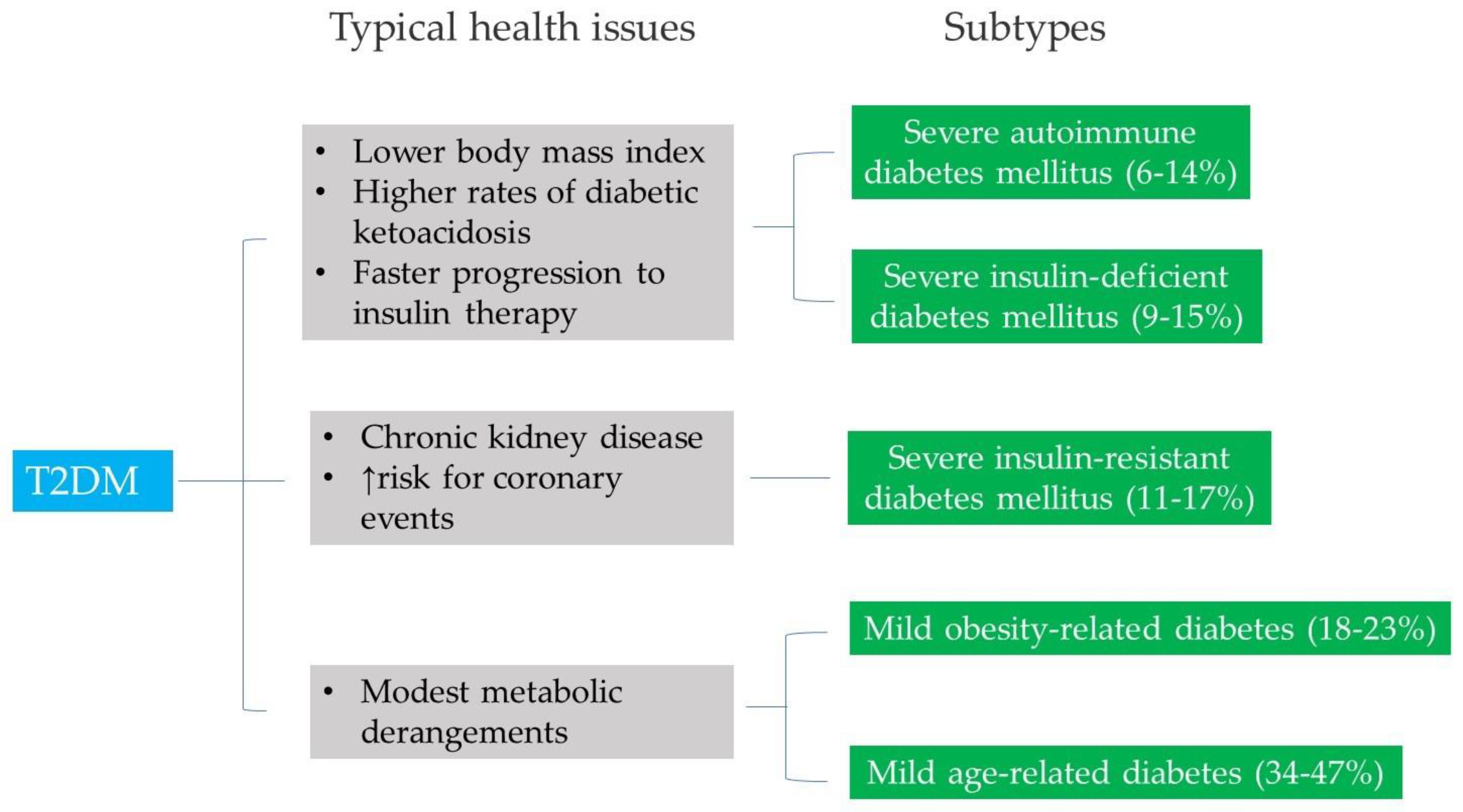
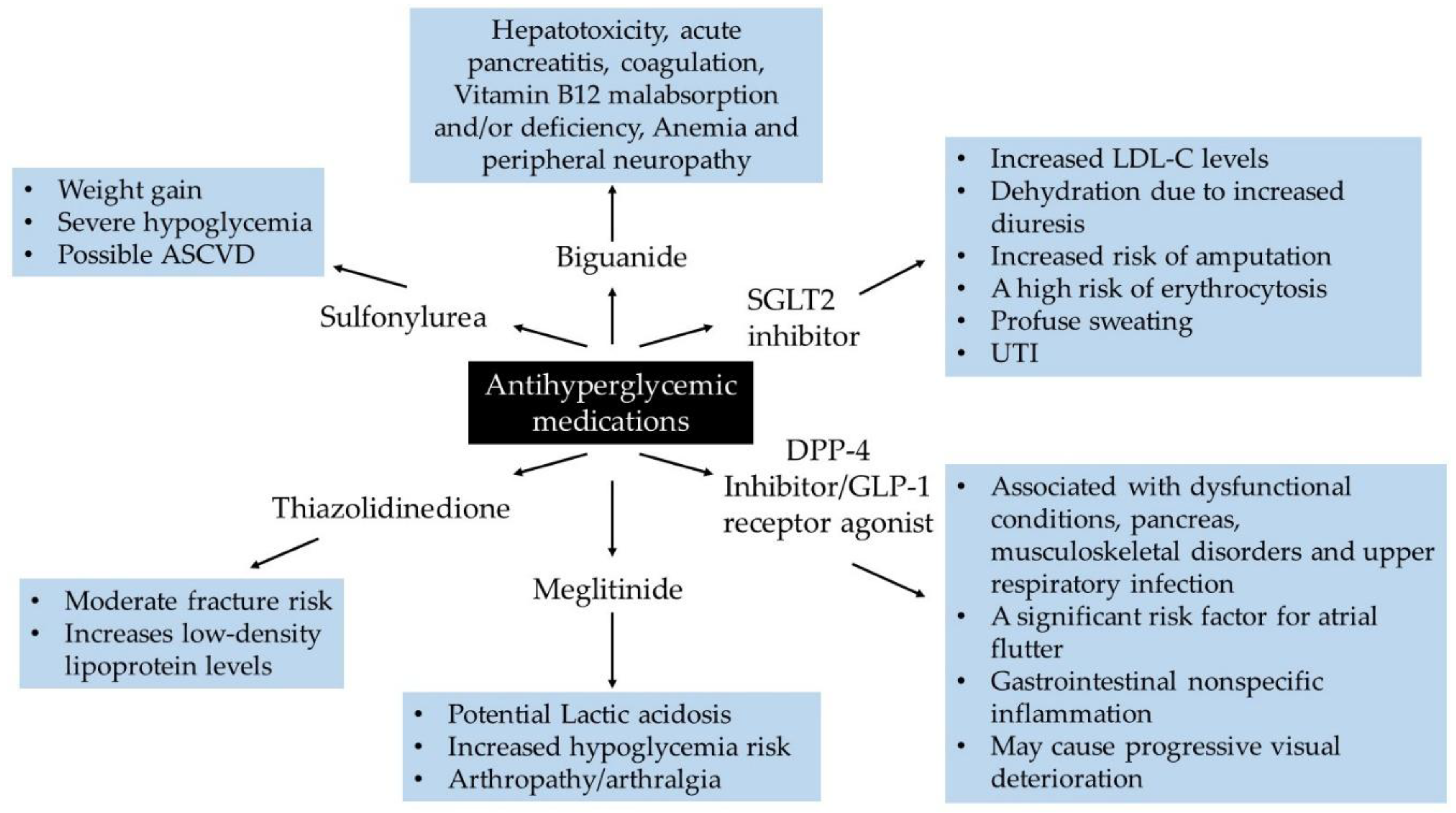
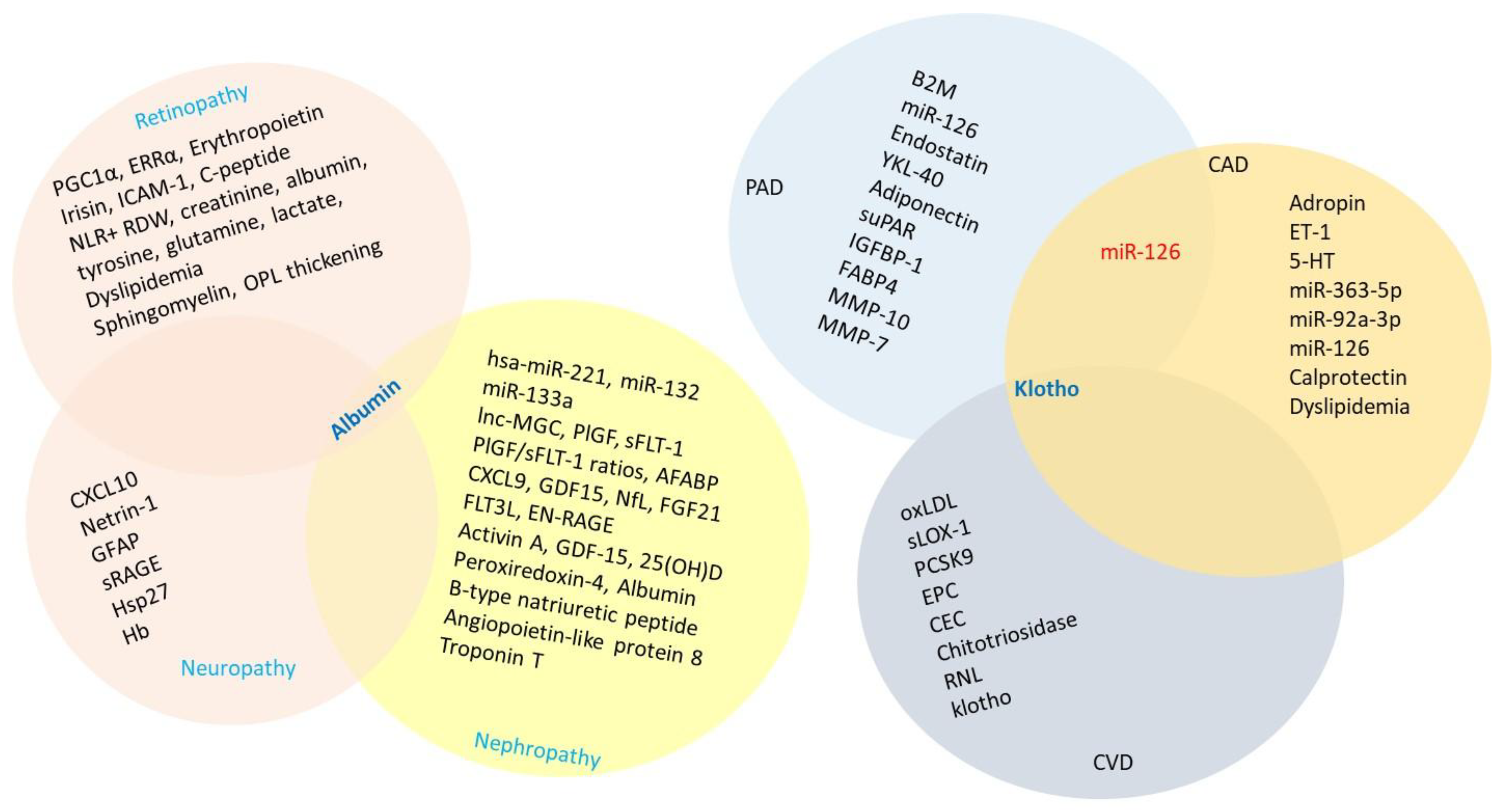
| Drug Class | Generic name | Clinical outcomes | Clinical condition of concern | Anti-atherogenic mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biguanide | Metformin, metformin extended release | Affects metabolic pathway (s):
|
|
|
[47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55] |
| Sulfonylurea | Glipizide |
|
|
|
[56,57,58,59] |
| Meglitinide | Repaglinide |
|
|
|
[60,61,62,63] |
| Thiazolidinedione | Pioglitazone |
|
|
|
[64,65] |
| DPP-4 inhibitor | Sitagliptin |
|
|
|
[66,67,68,69,70,71,72] |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist | Semaglutide |
|
|
|
[73,74,75,76,77,78,79] |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | Empagliflozin, Canagliflozin |
|
|
|
[80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





