Submitted:
21 August 2025
Posted:
22 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
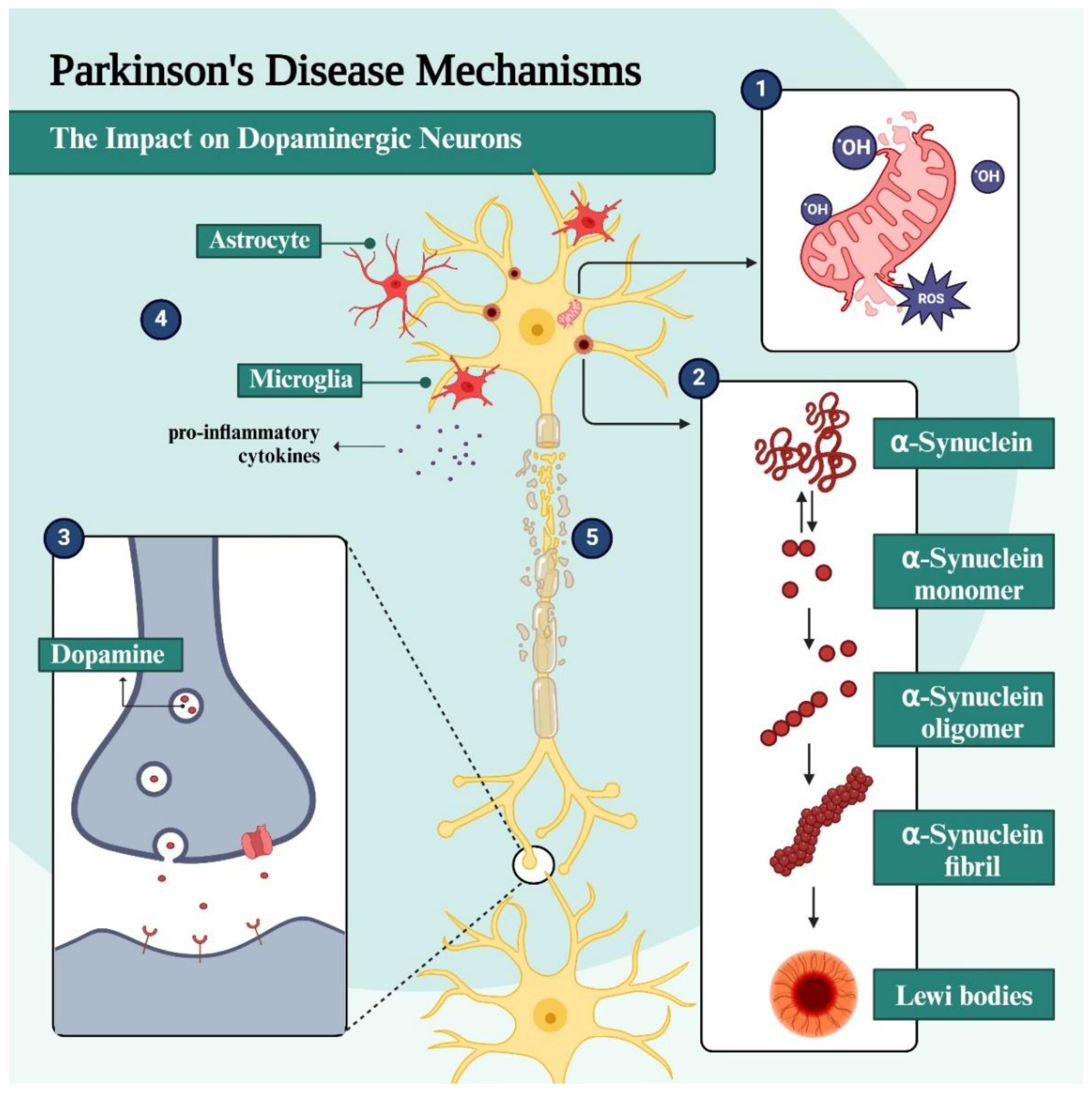
1.1. General Pathophysiological Aspects of Parkinson’s Disease
1.2. The Role of α-Synuclein and Lewy Bodies in PD Pathogenesis
1.3. Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in PD
1.4. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PD Pathogenesis
1.5. Glutamate Production and Excitotoxicity in PD
1.6. Monoamine Oxidases: Functional Aspects and Its Relevance in the PD Pathogenesis
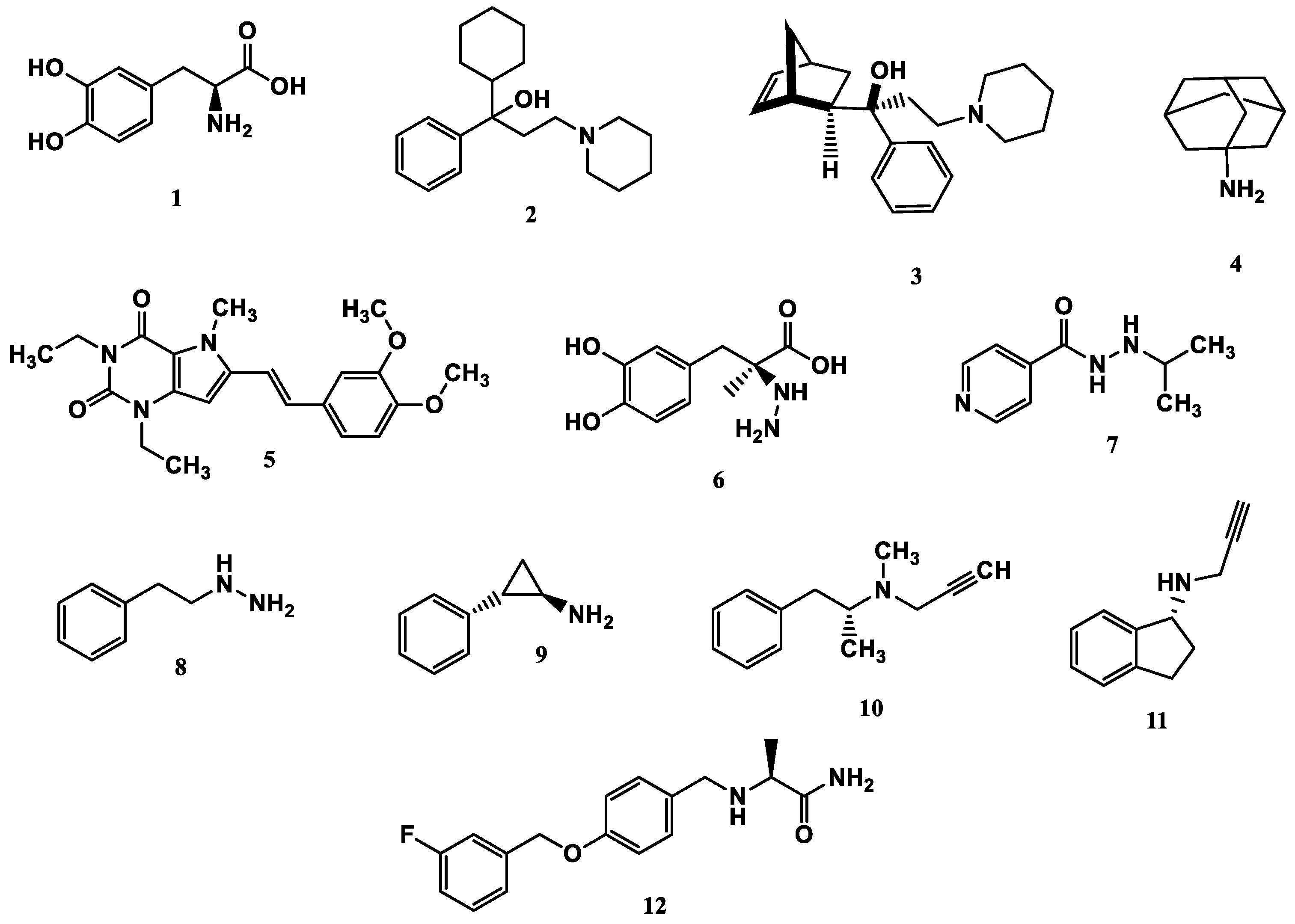
1.7. Current Available Drugs for PD Therapy
2. Recent Advances in the Search for MAO Inhibitors as Drug Candidates for PD
2.1. Selective MAO Inhibitors
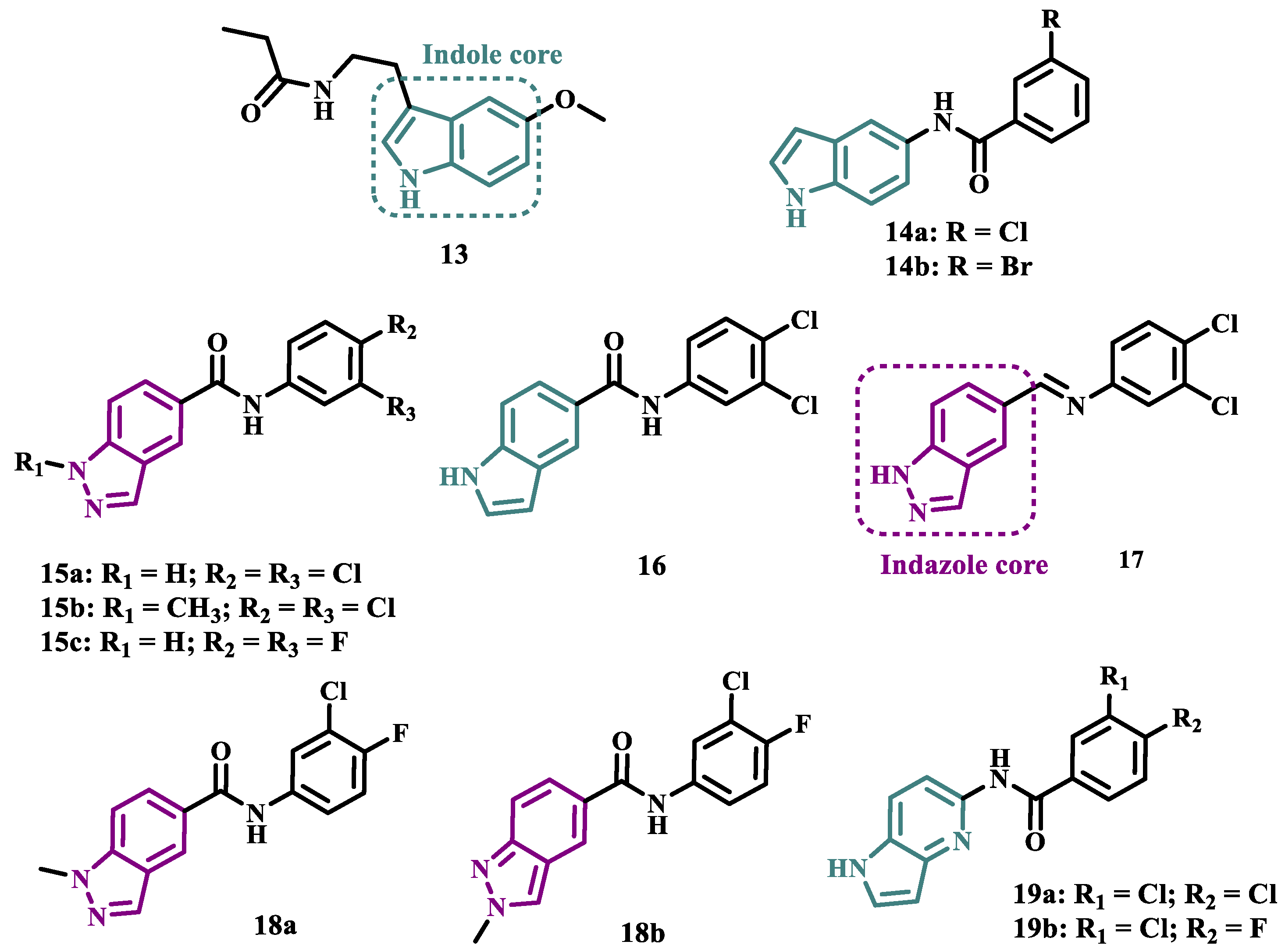
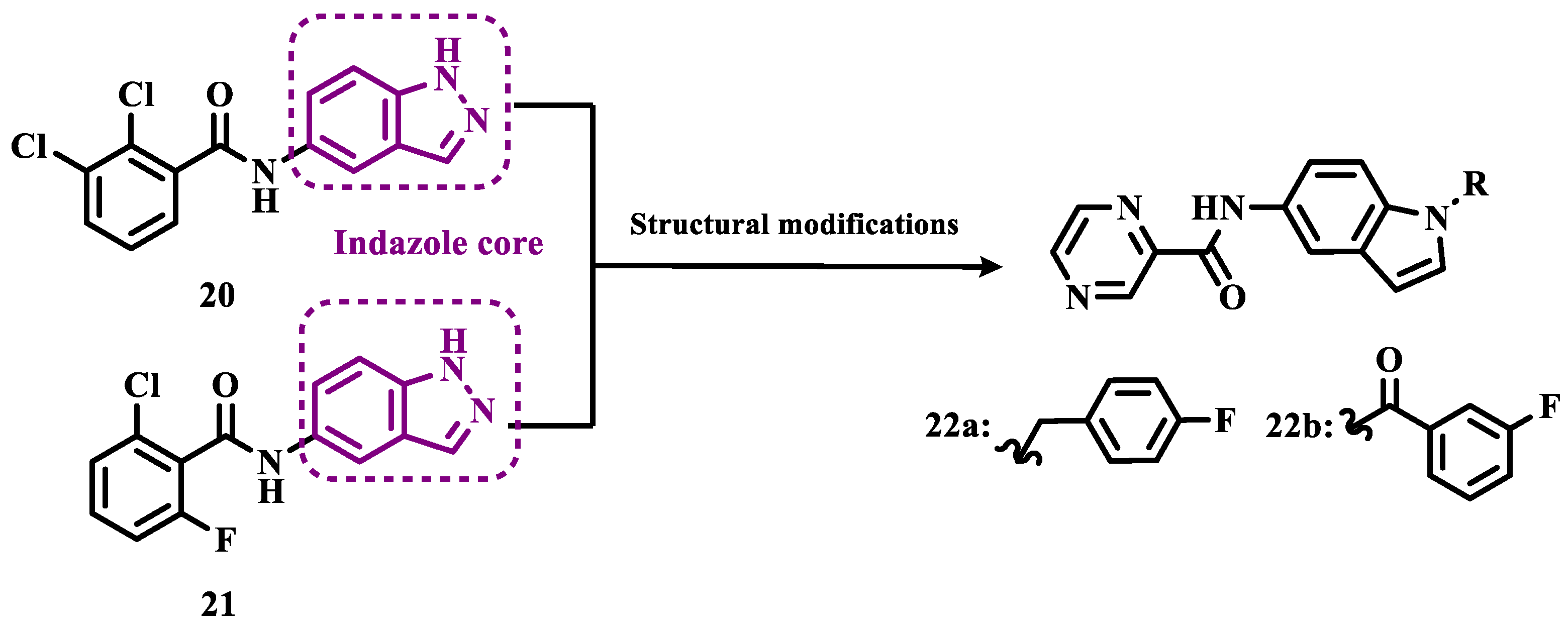
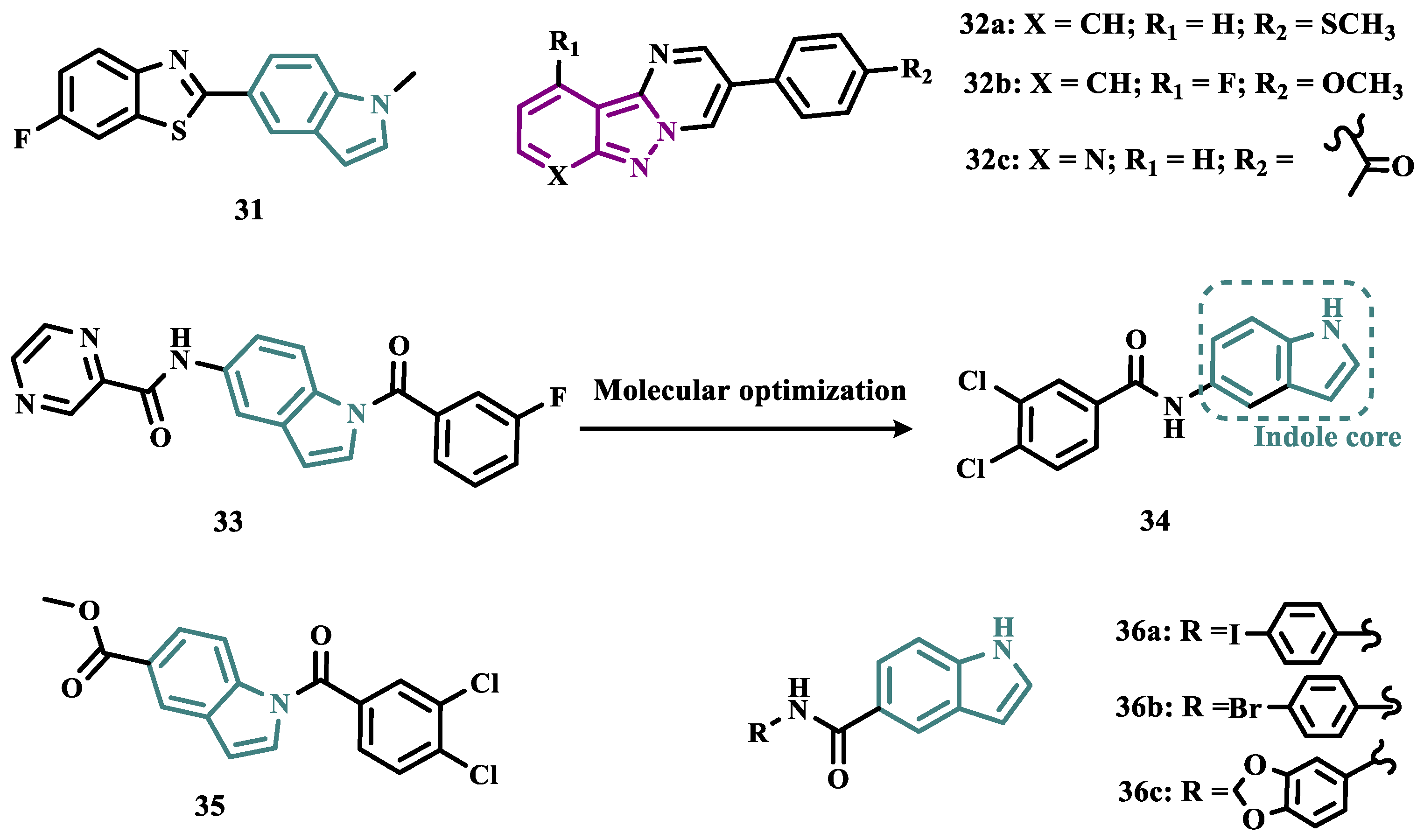
2.1.1. Indazole and Indole/Melatonin-like Inhibitors
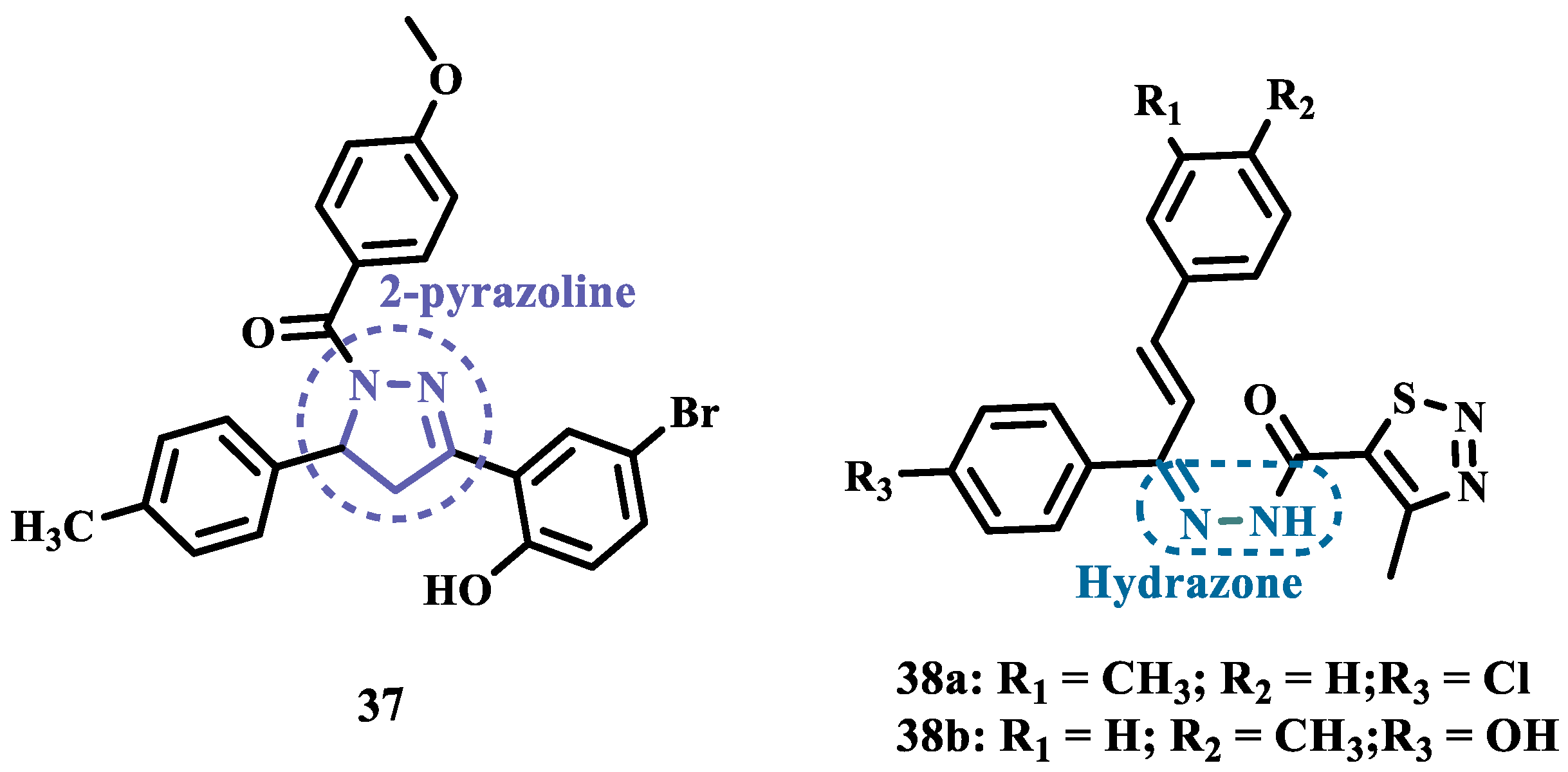
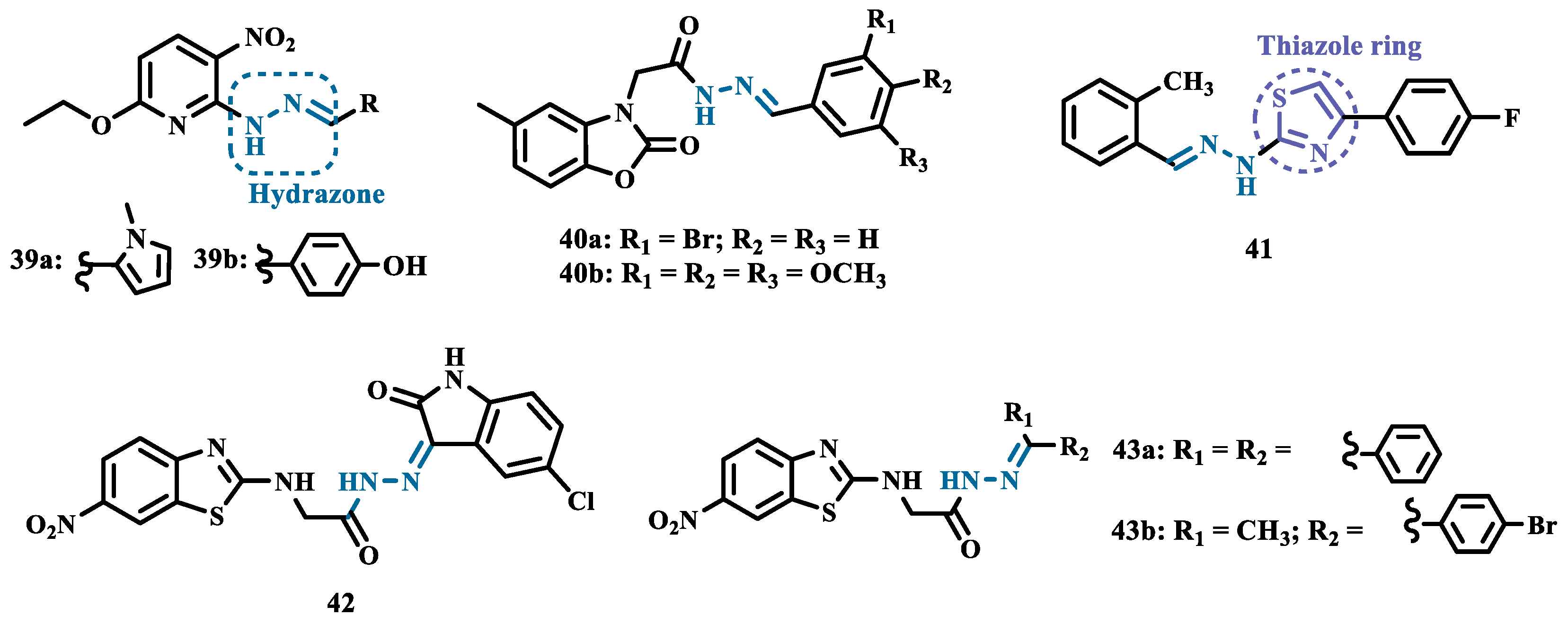
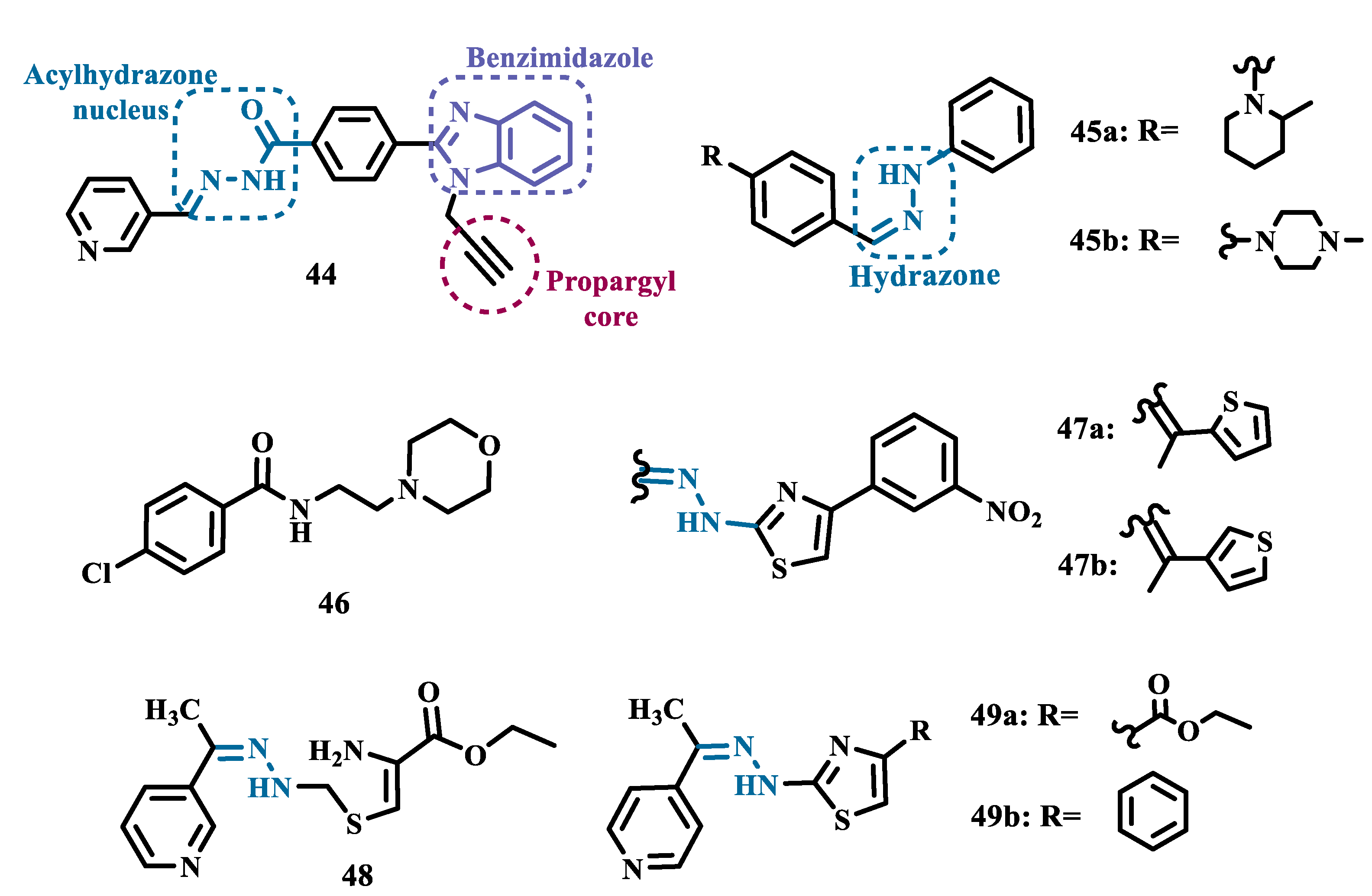
2.1.2. Hydrazide and Hydrazone-Based Analogues
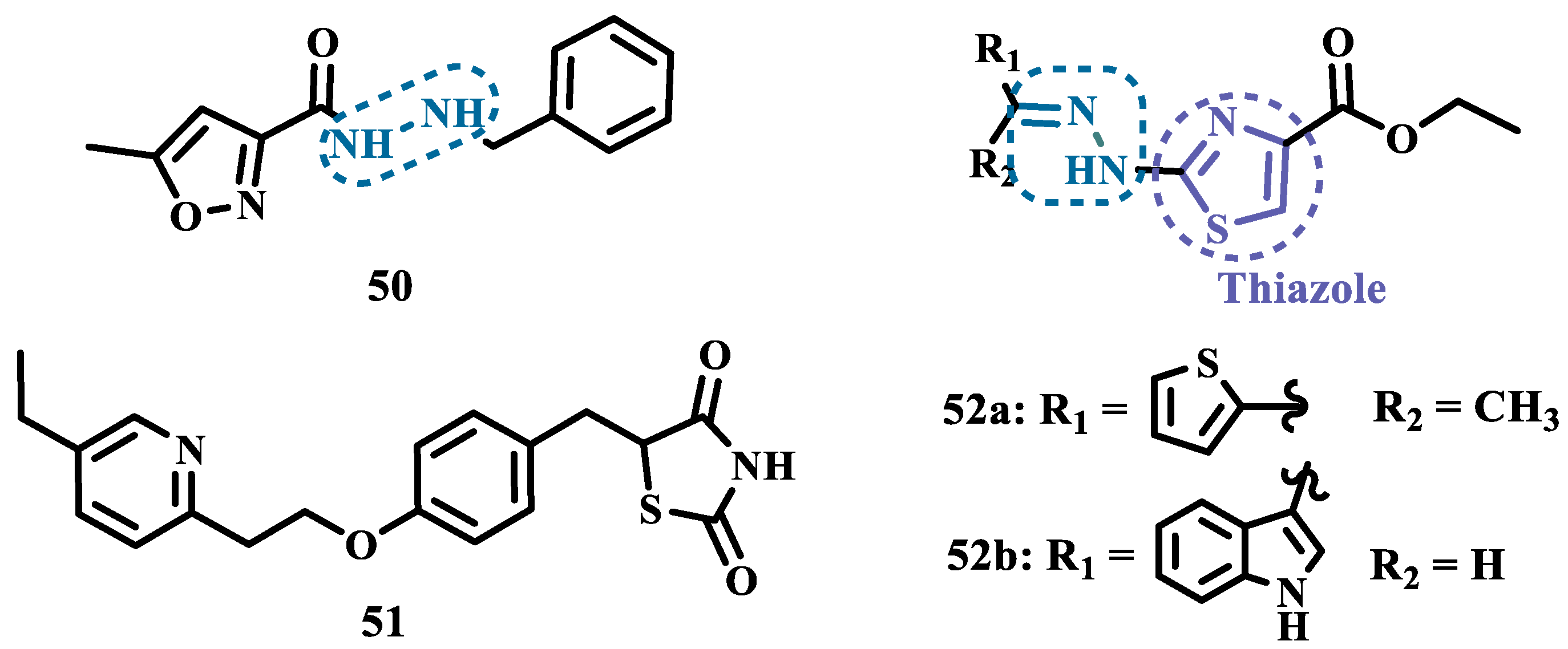
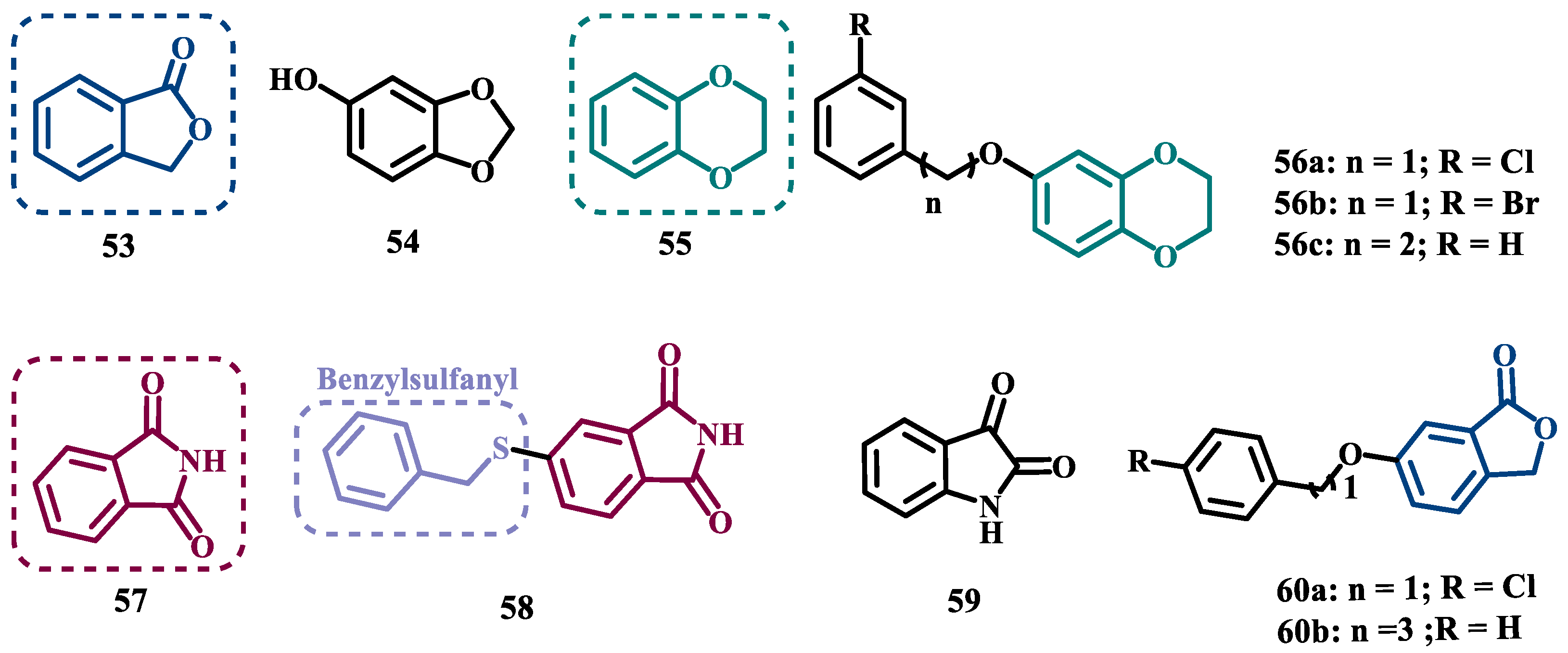
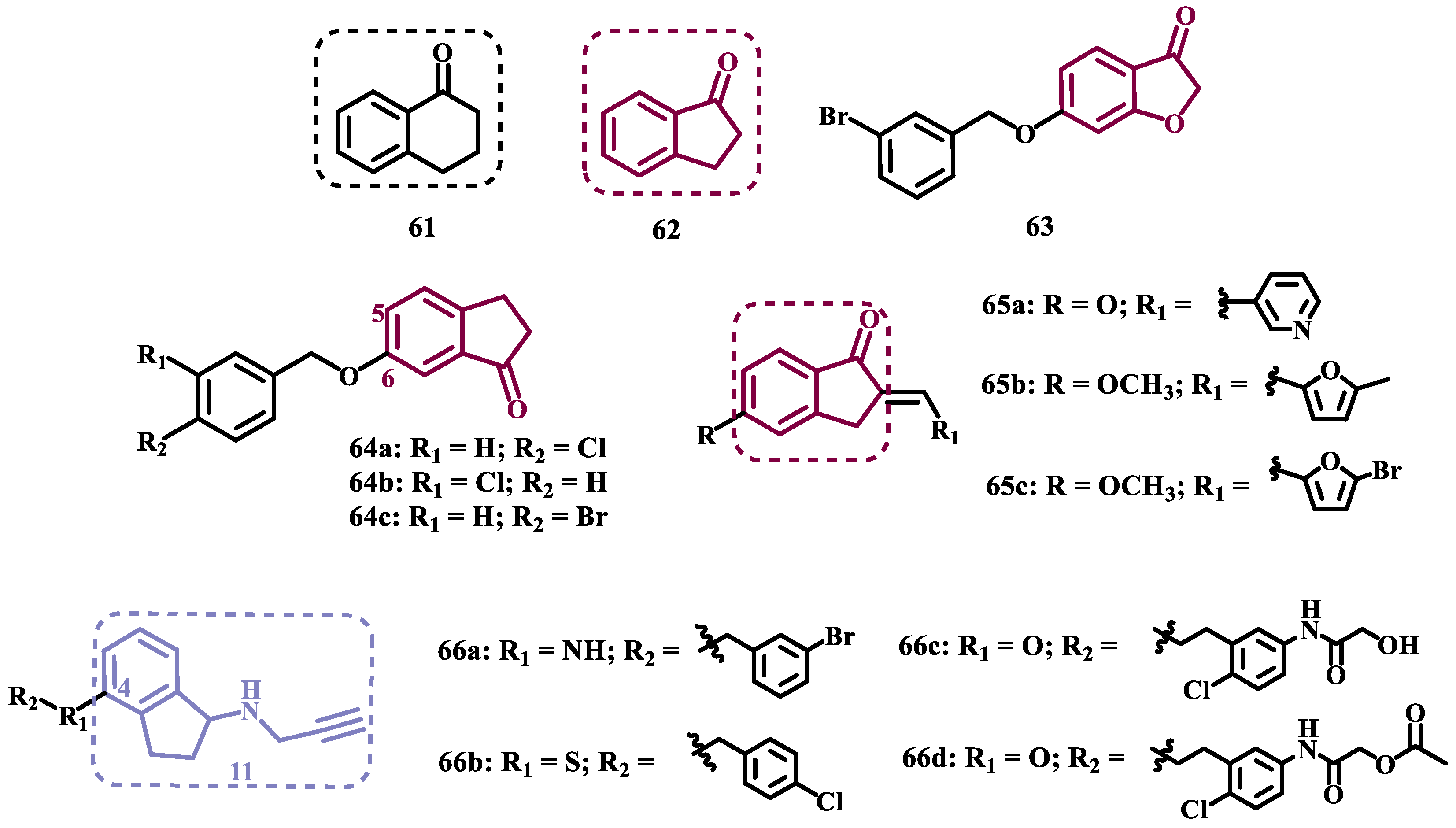
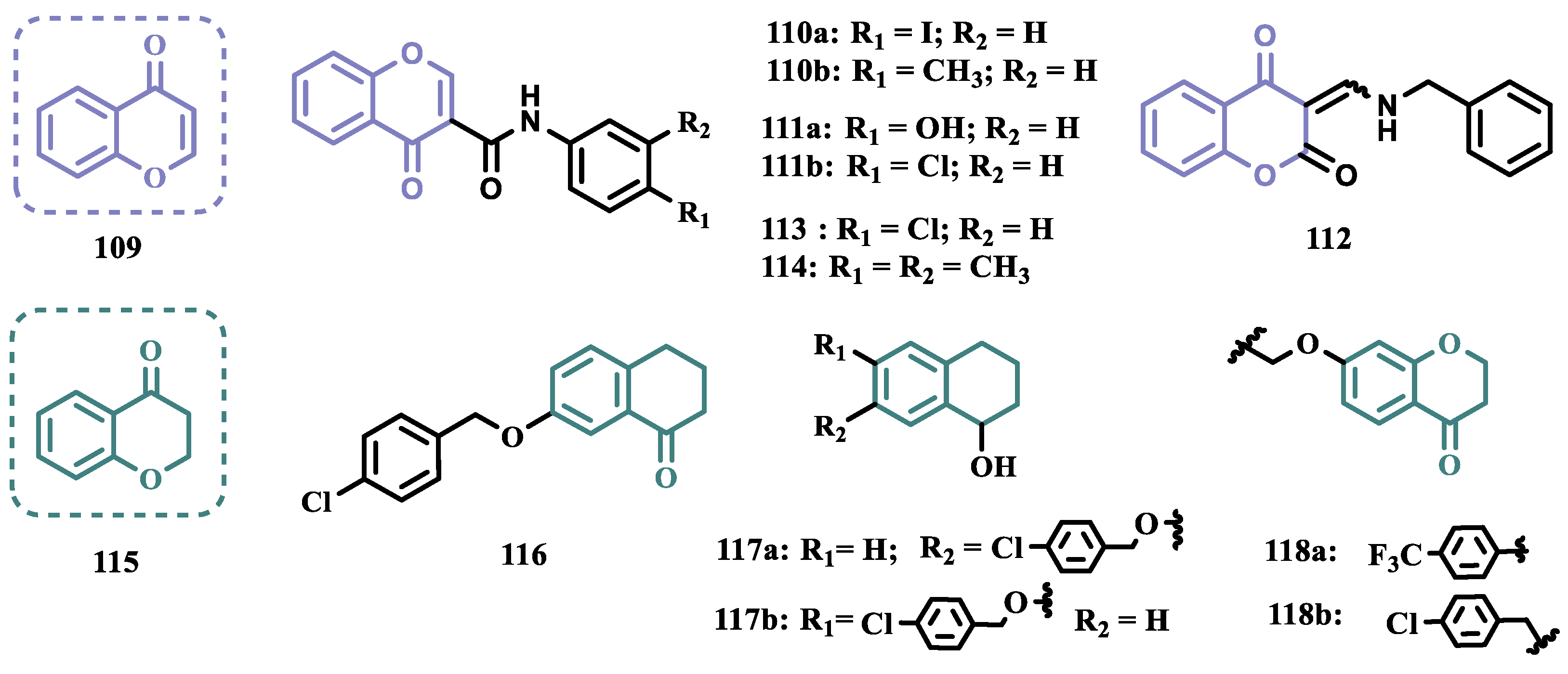
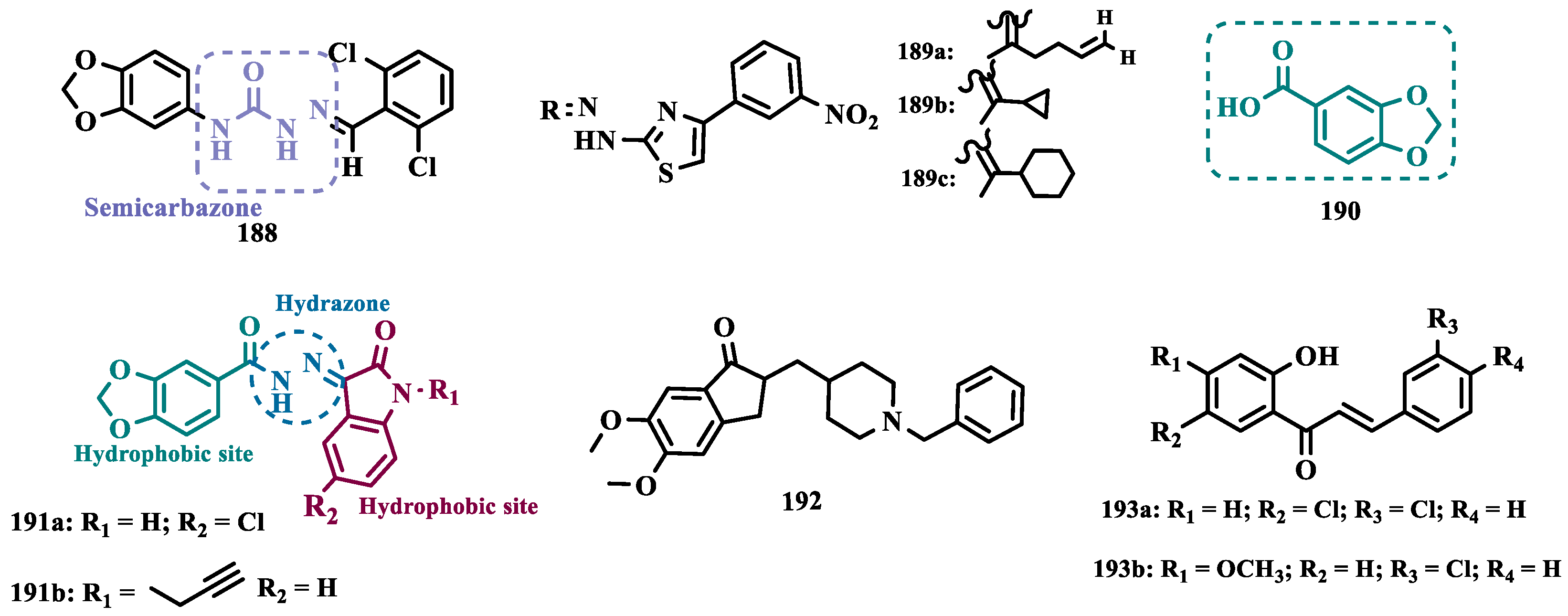
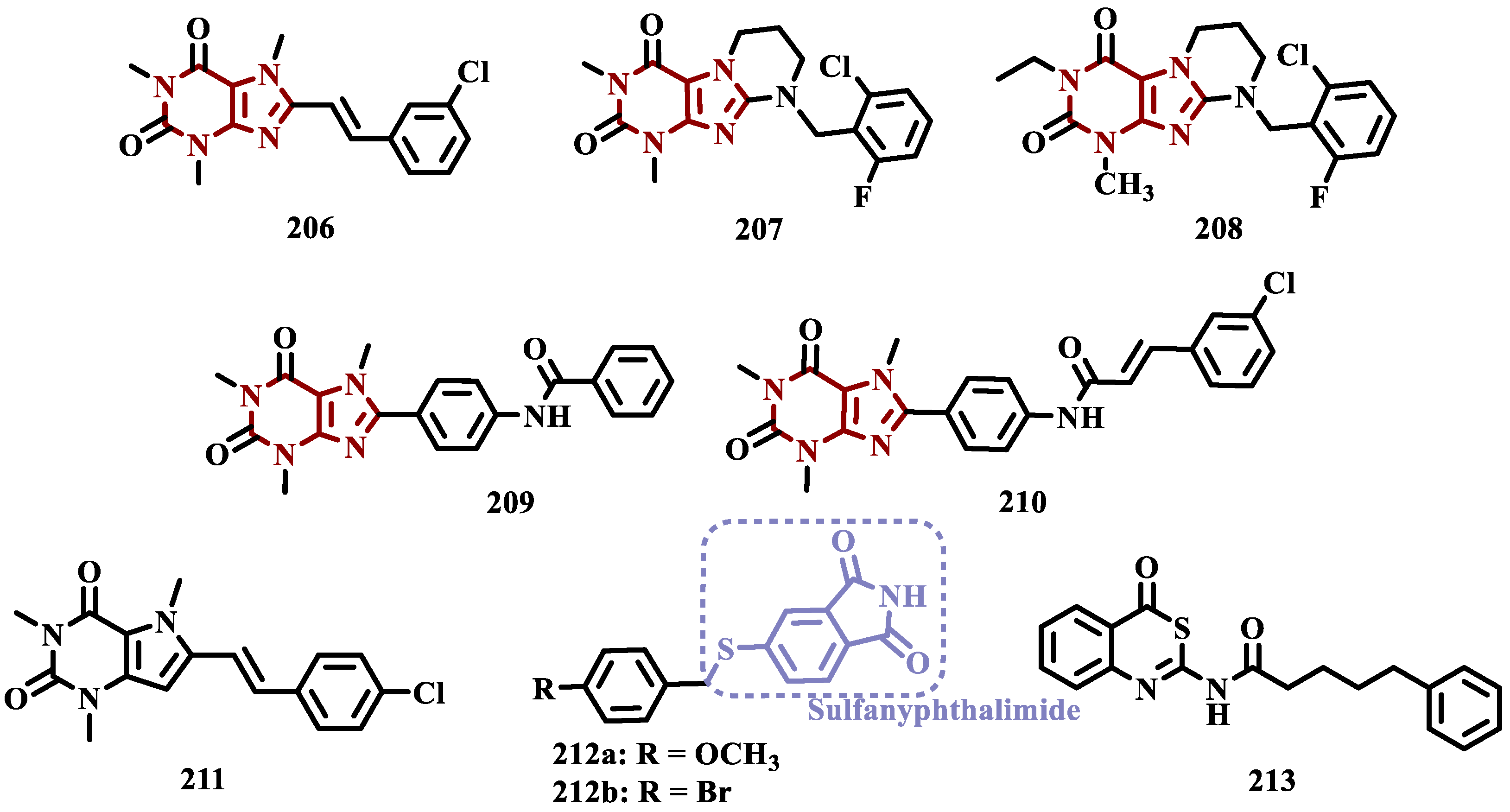
2.1.3. Phthalide, Phthalimide and Indanone Derivatives
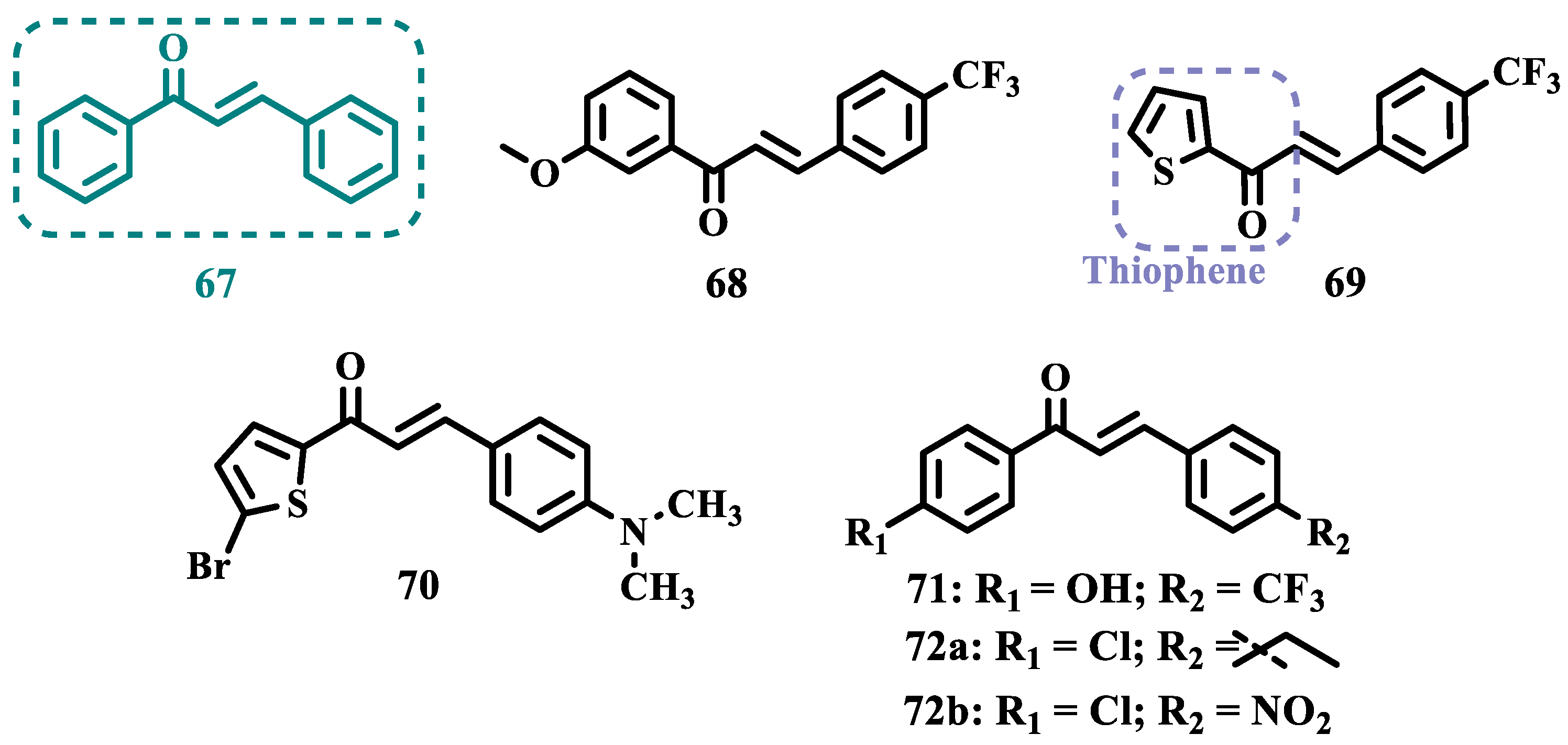
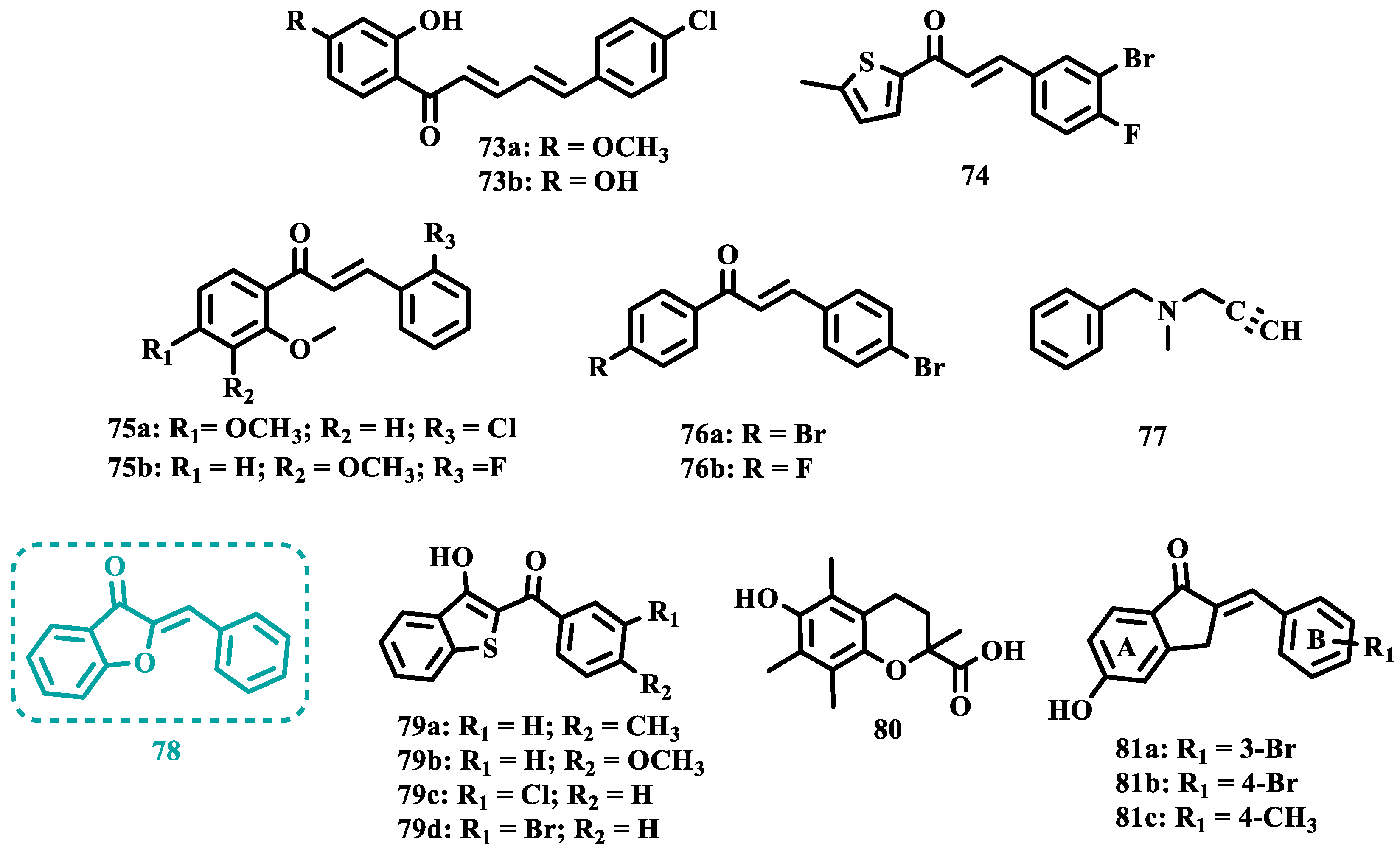
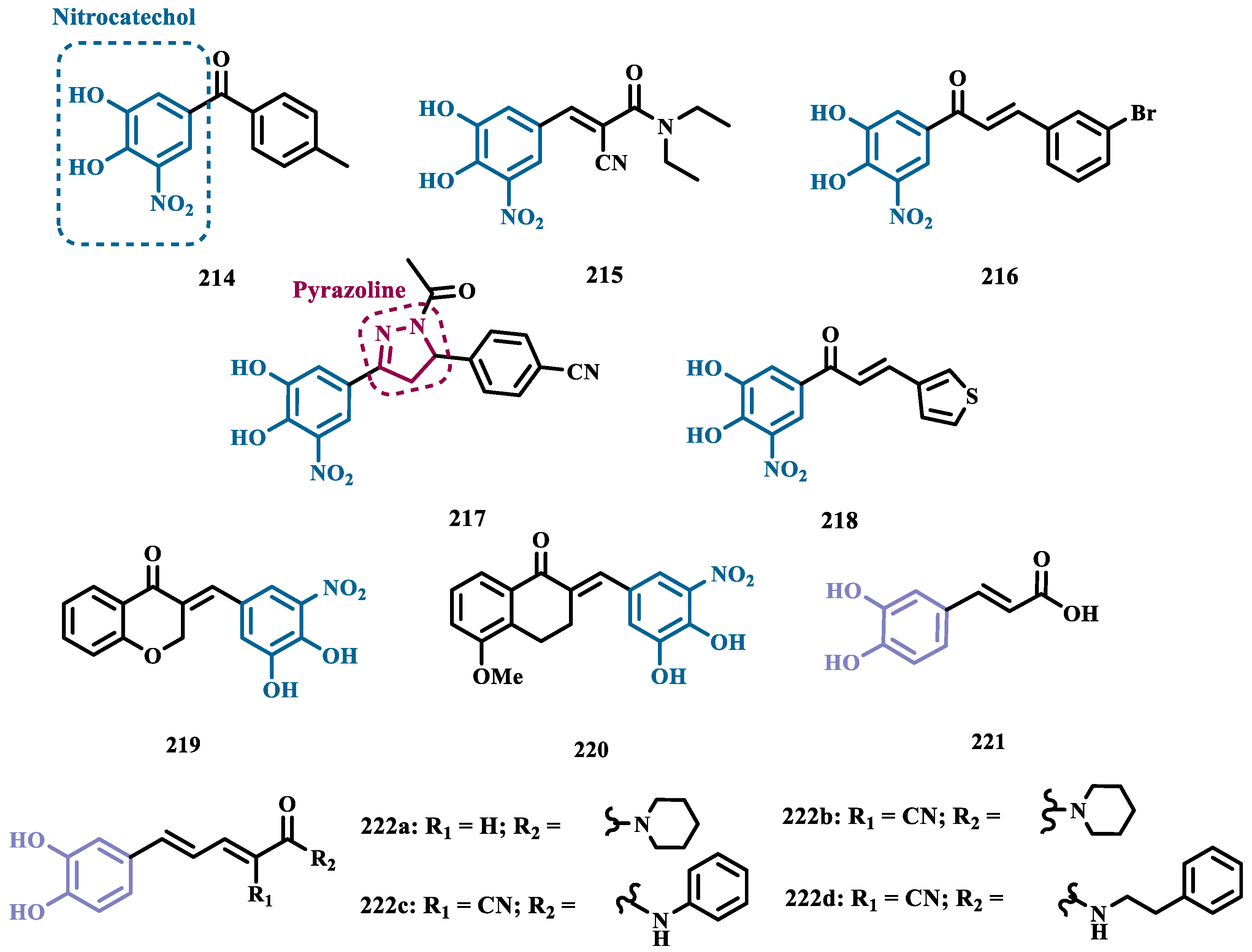
2.1.4. Chalcones
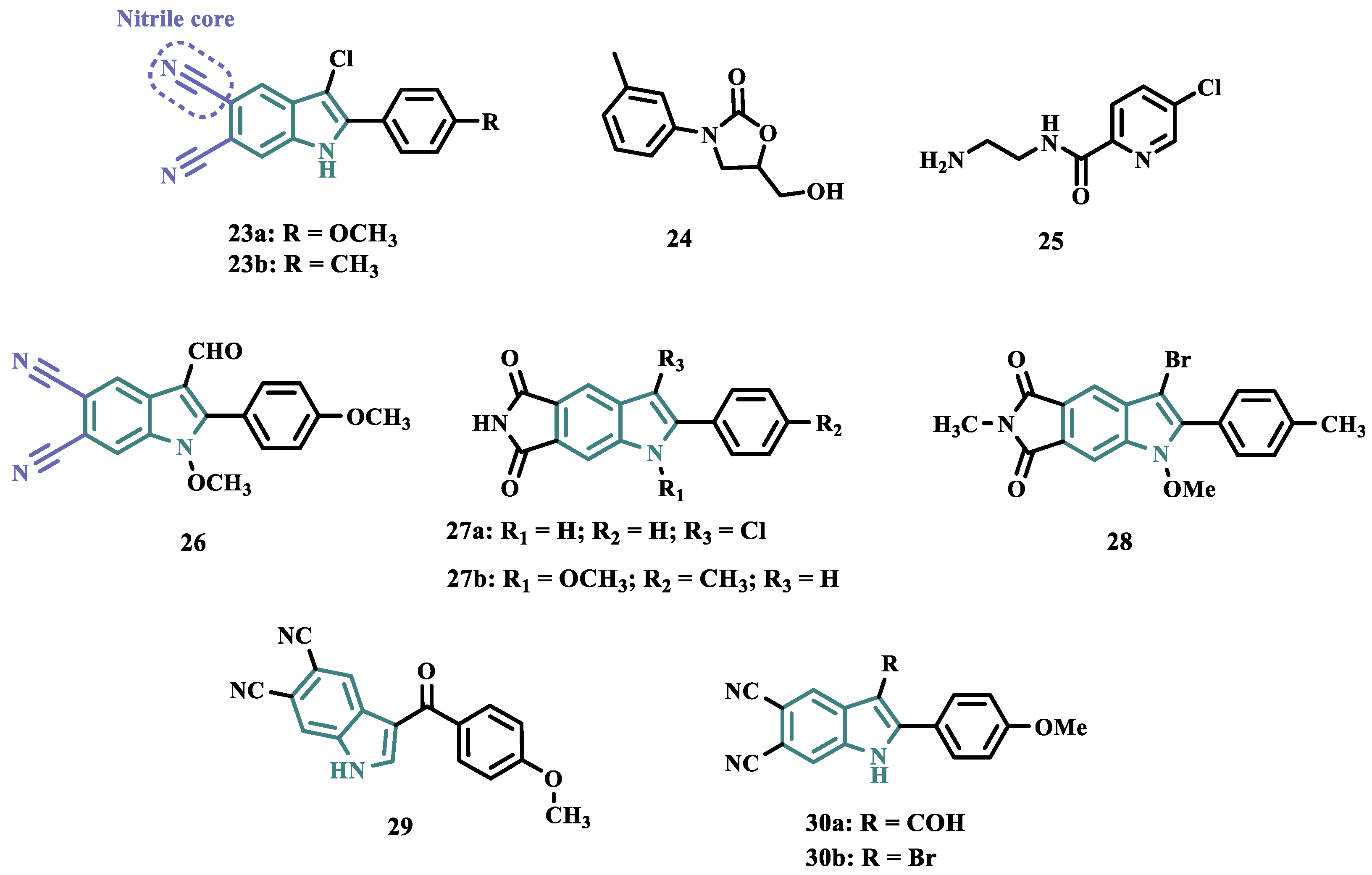
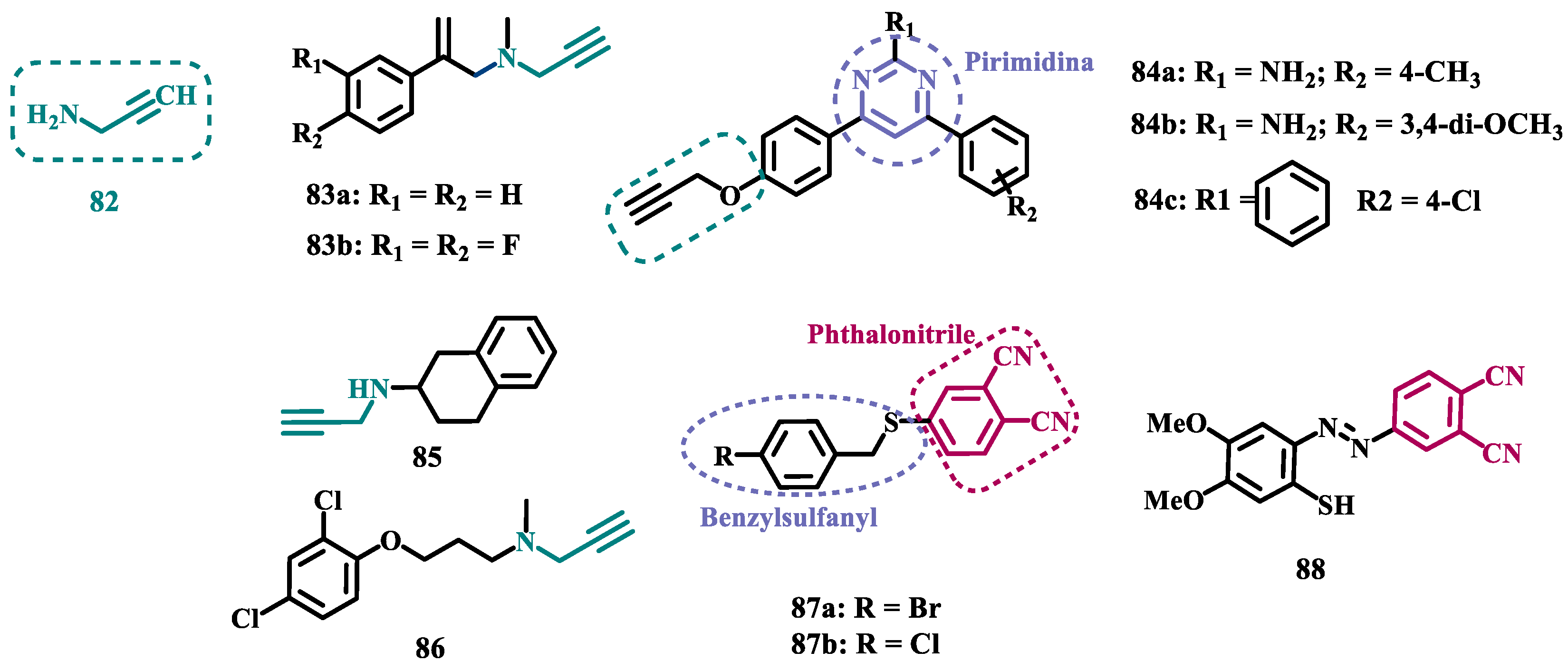
2.1.5. Propargylamine and Phtalonitrile Derivatives
2.1.6. Alkaloids
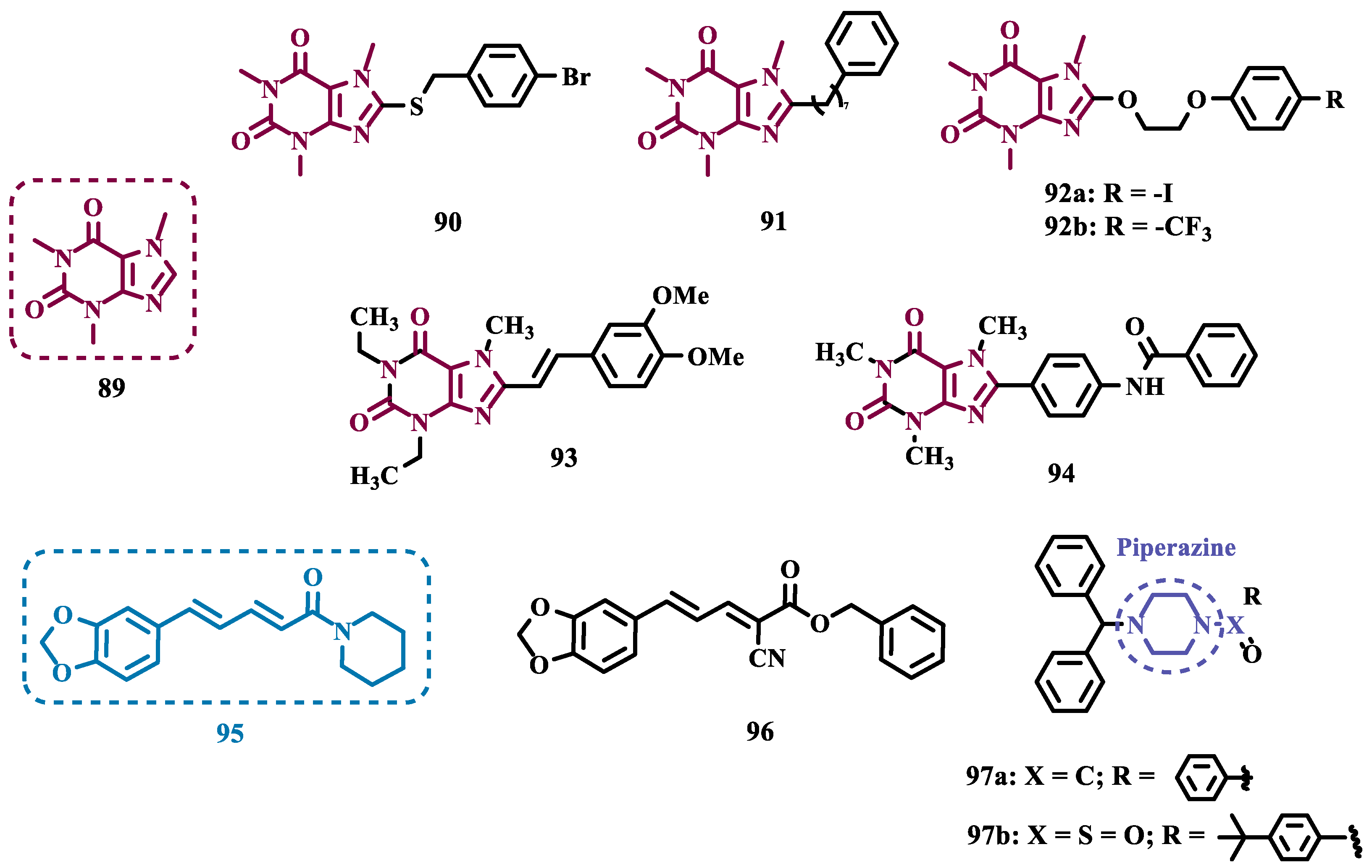
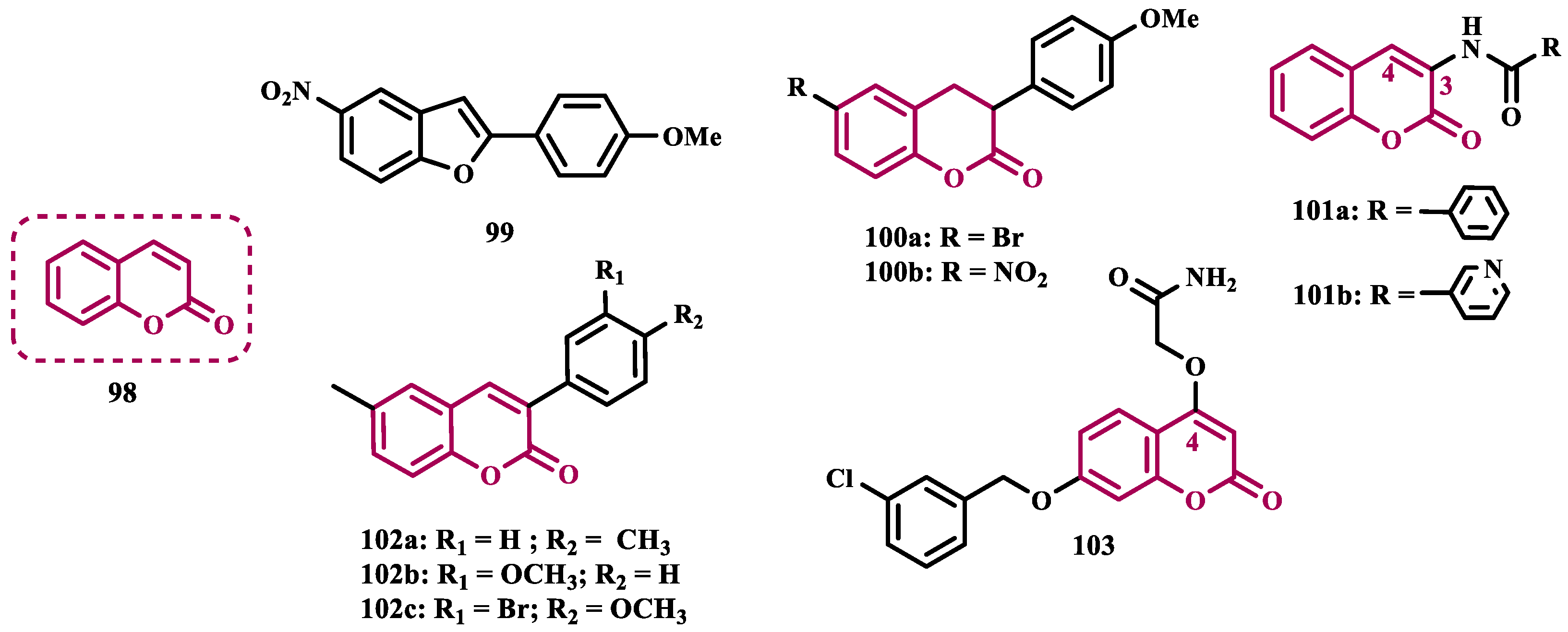
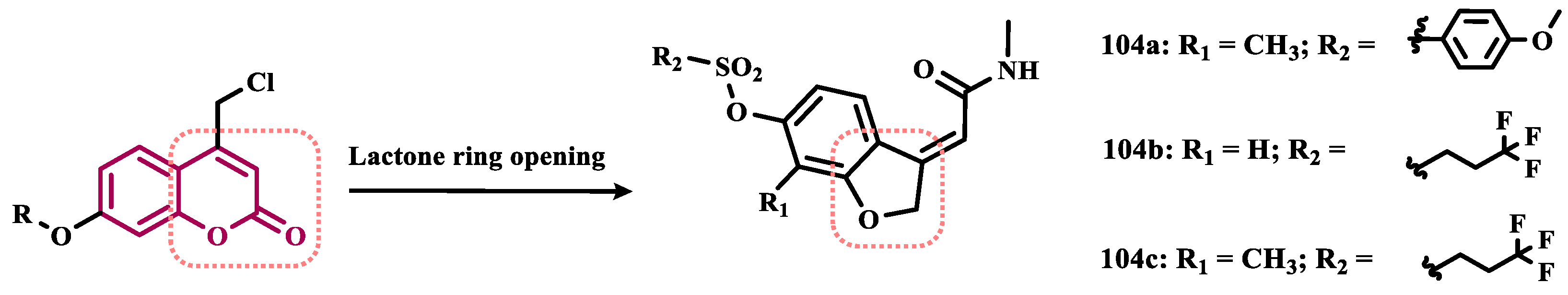
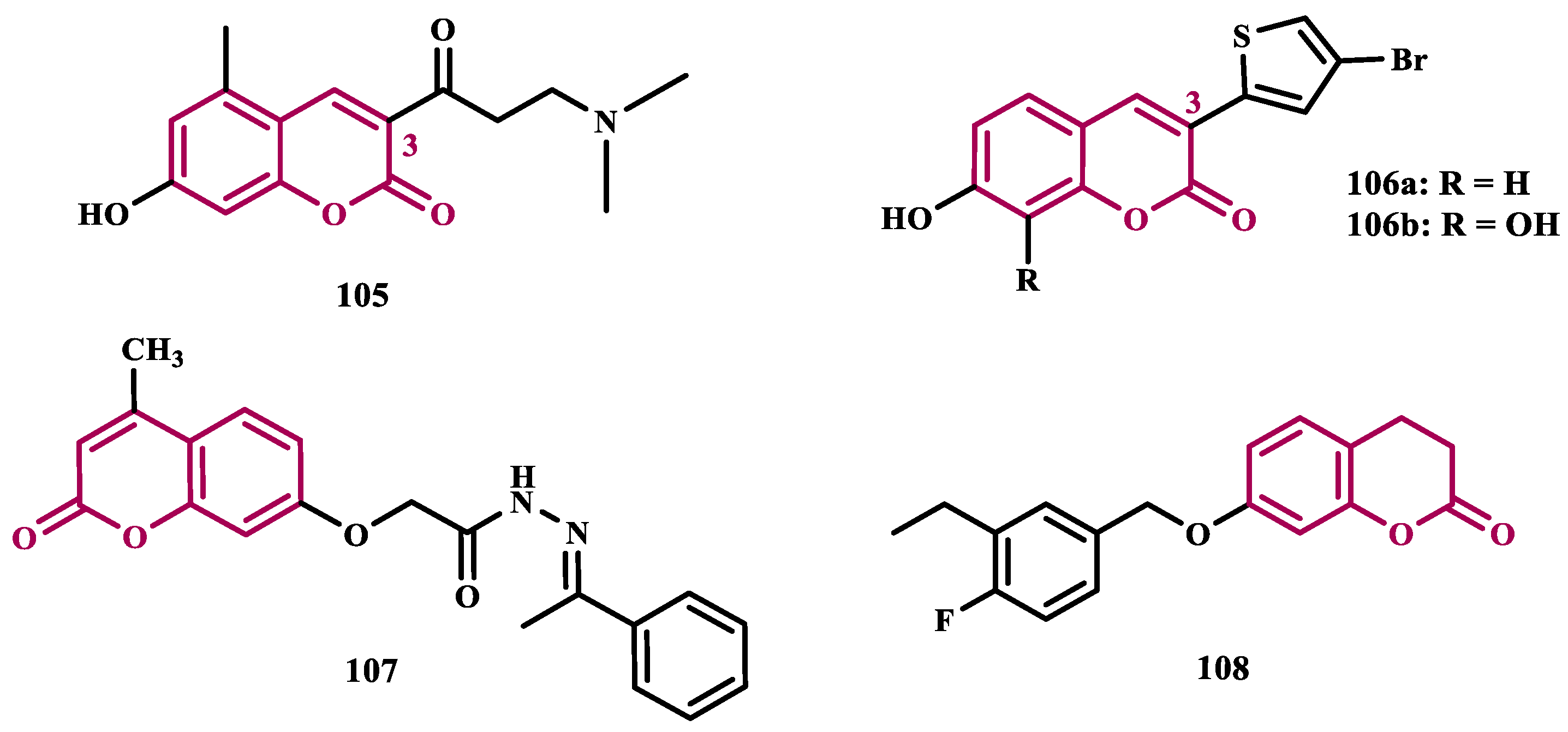
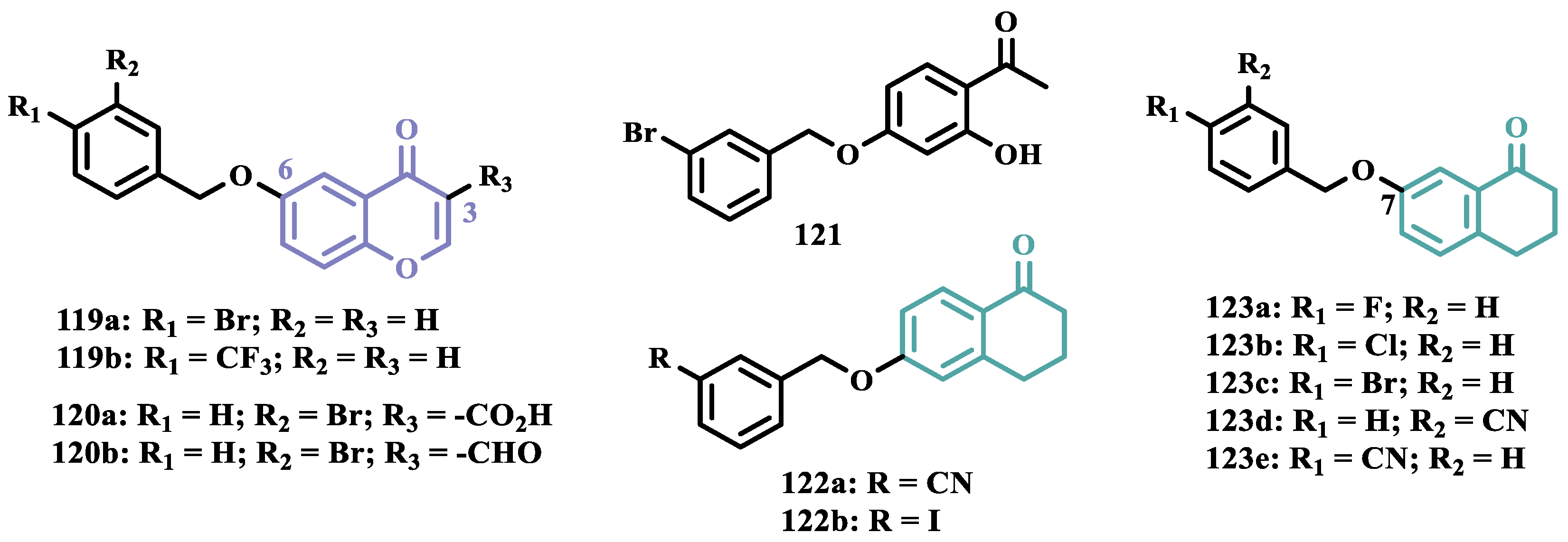
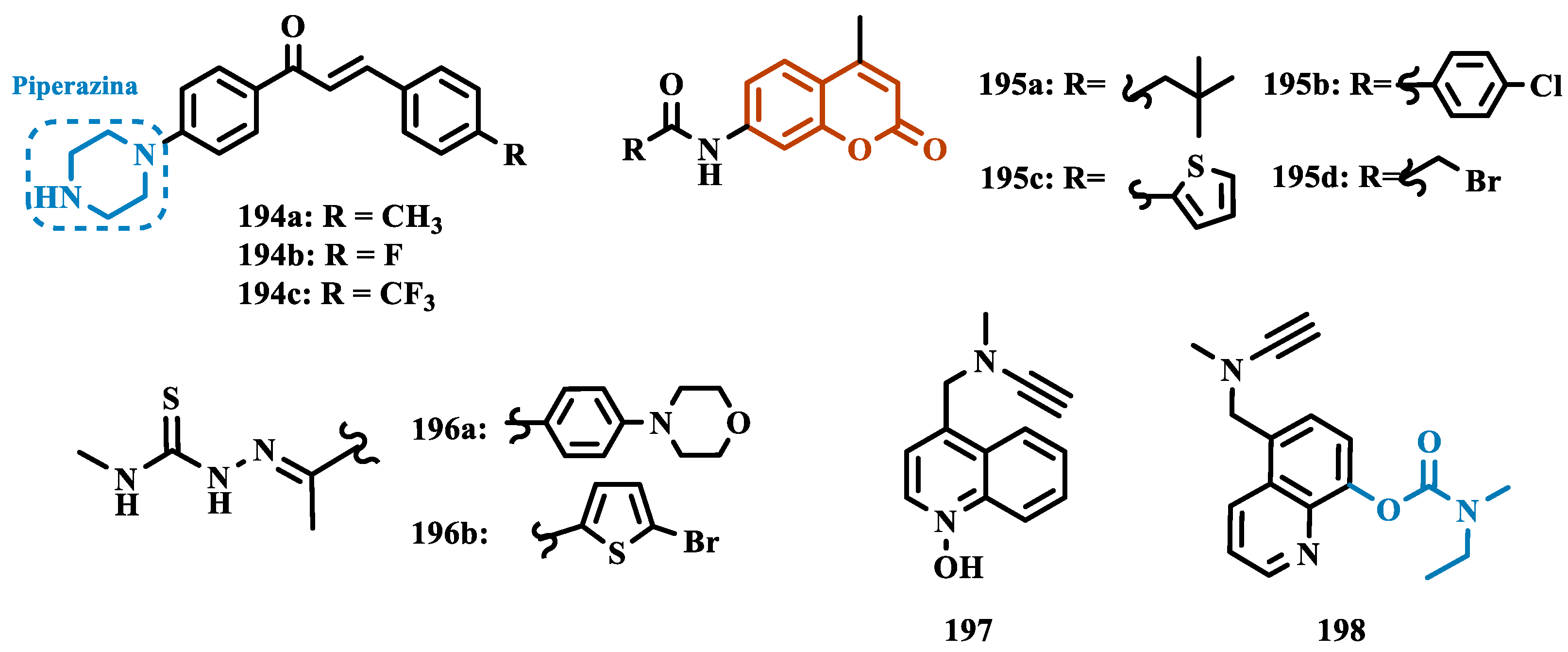
2.1.7. Benzopyrone Derivatives
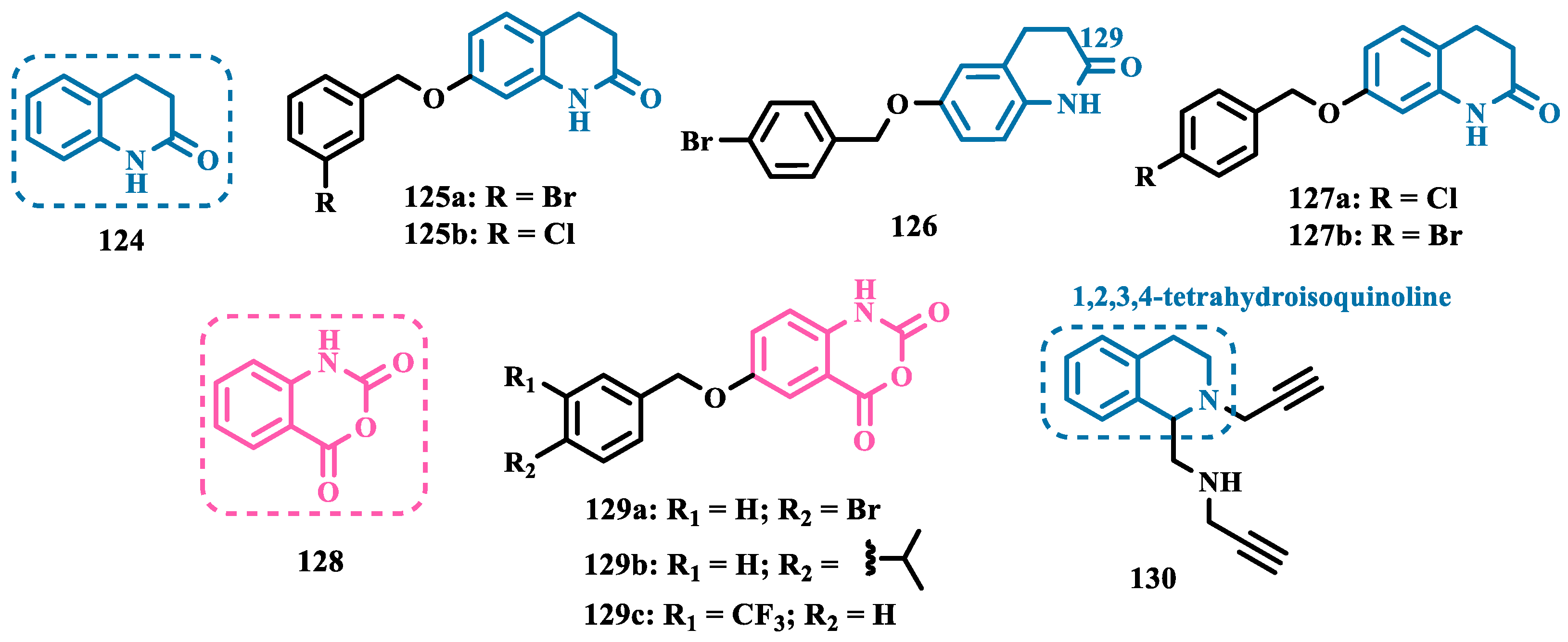
2.1.8. Benzyloxy-Based Analogues
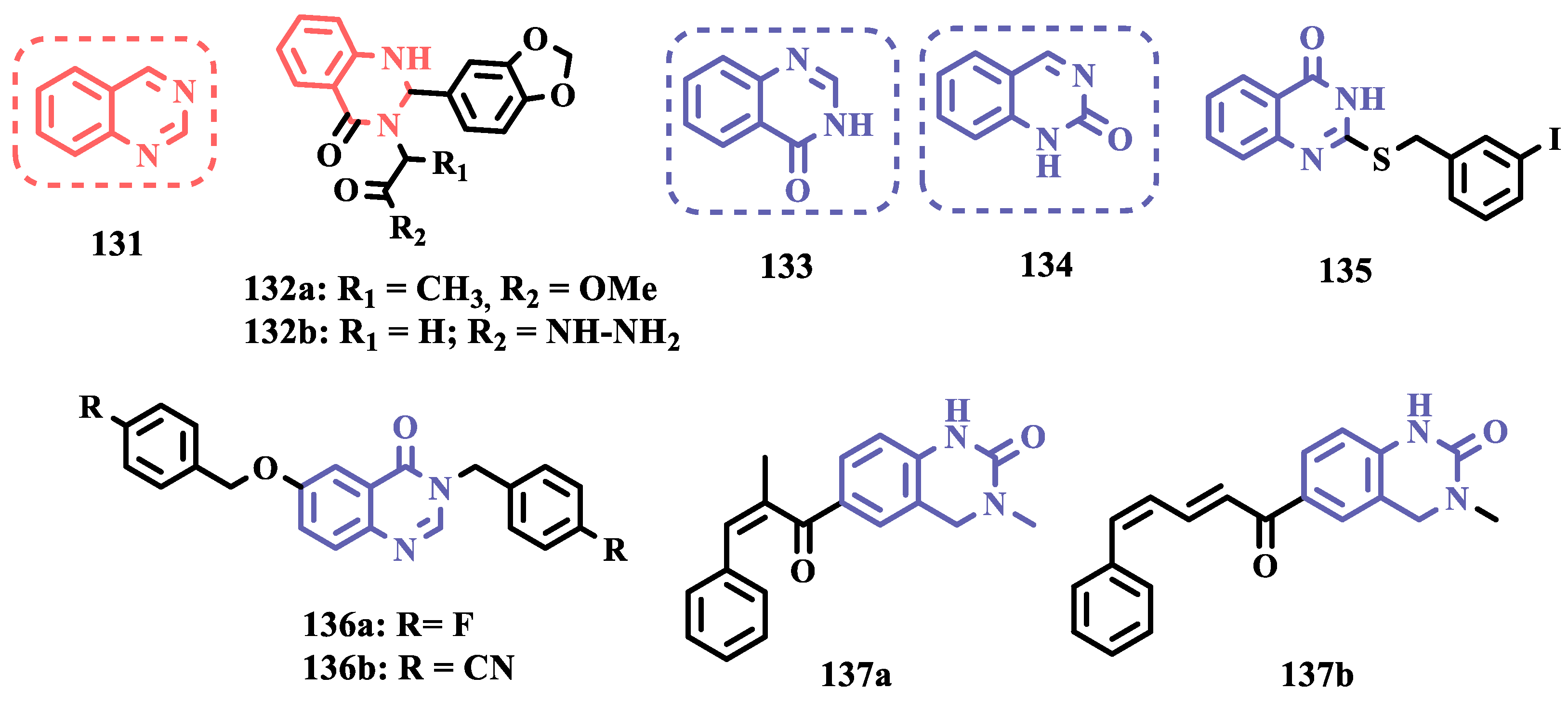
2.1.9. Azole-Based Derivatives
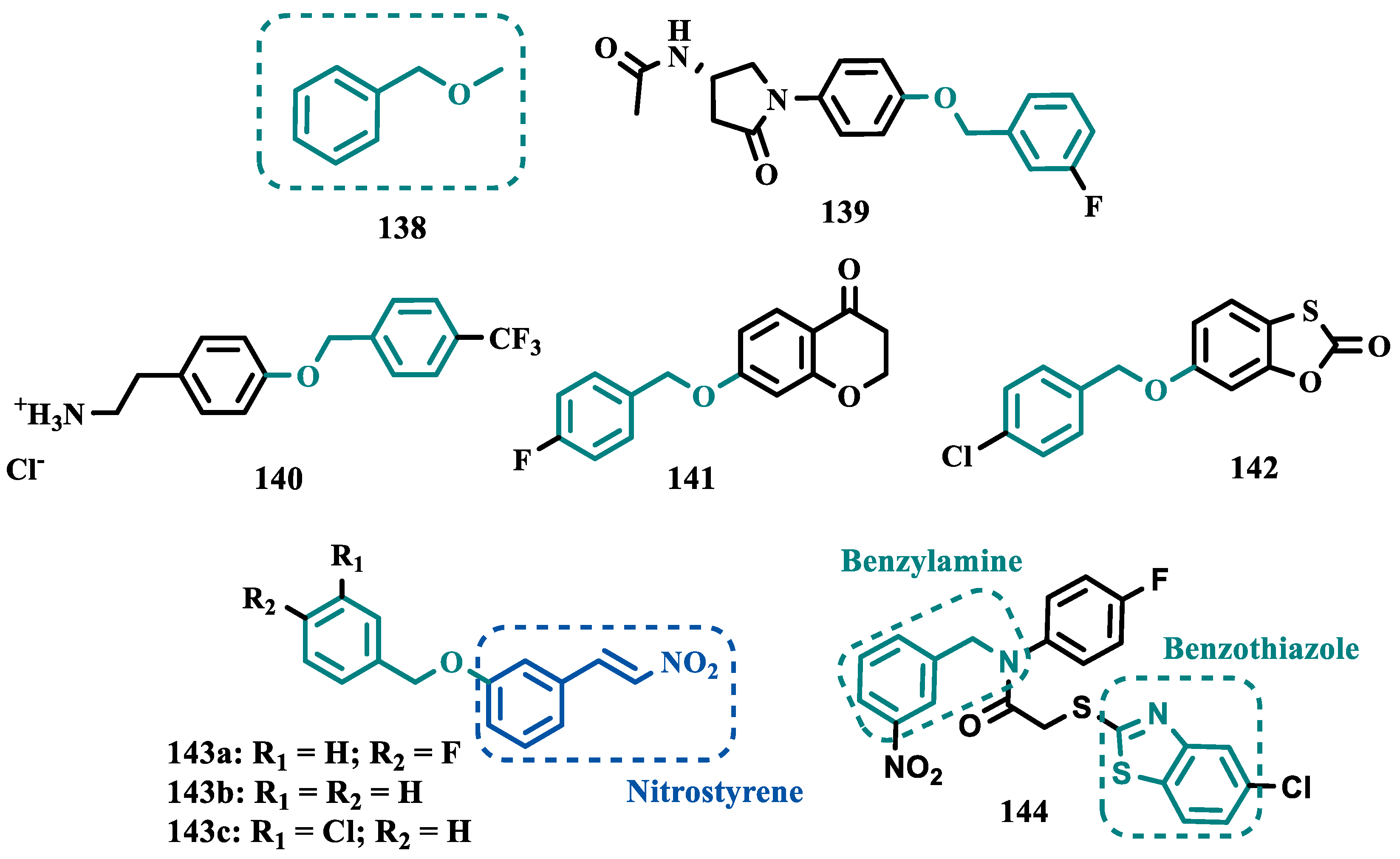
2.1.10. Diverse Molecular Hybrids
2.2. Dual and Multi-Target MAO Inhibitors
2.2.1. Dual Histamine Receptor Modulators and MAO Inhibitors
2.2.2. Dual Cholinesterase and MAO Inhibitors
2.2.3. Dual Adenosine Receptors Antagonists and MAO Inhibitors
2.2.4. Dual MAO and Catechol O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors
2.2.5. Caspase and MAO-Inhibitors
3. Discussion
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| ATP synthase | Adenosine triphosphate synthase |
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| CI | Complex I |
| CIII | Complex III |
| LB | Lewy’s bodies |
| COMT | Catechol O-methyltransferase |
| DpA | Dopamine |
| ND | Neurodegenerative disease |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DOPAC | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid |
| DOPAL | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde |
| FAD | Flavine-adenine dinucleotide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| OS | Oxidative stress |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| LAS | Lysosomal autophagic system |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| MAO | Monoamine oxidase |
| MnSOD | Manganese superoxide dismutase |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| NM | Neuromelanin |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PTP | Permeability transition pore |
| SN | Substantia nigra |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| SAR | Structure-activity relationship |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric |
| AChEs | Acetylcholinesterases |
| α-SYN | α-synuclein |
References
- Connolly, B.S.; Lang, A.E. Pharmacological Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association 2014, 311, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Vélez, G.E.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Parkinson’s Disease Genetics and Pathophysiology. The Annual Review of Neuroscience 2021, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.; Savva, G.M.; Bedarf, J.R.; Charles, I.G.; Hildebrand, F.; Narbad, A. Meta-Analysis of the Parkinson’s Disease Gut Microbiome Suggests Alterations Linked to Intestinal Inflammation. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, J.; Svenningsson, P. Potential Effects of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist Montelukast in Treatment of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nuaimi, S.K.; MacKenzie, E.M.; Baker, G.B. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and Neuroprotection: A Review. Am J Ther 2012, 19, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Georgieva, M.G.; Atanasov, A.G.; Tzvetkov, N.T. Monoamine Oxidases (MAOs) as Privileged Molecular Targets in Neuroscience: Research Literature Analysis. Front Mol Neurosci 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barodia, S.K.; Creed, R.B.; Goldberg, M.S. Parkin and PINK1 Functions in Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull 2017, 133, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology of Parkinson Disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2018, 46, S30–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, B.L.B.; de Souza, L.R.; Sousa, K.P.A.; Ferreira, J. V.; Padilha, E.C.; da Silva, C.H.T.P.; Taft, C.A.; Hage-Melim, L.I.S. Parkinson’s Disease: A Review from Pathophysiology to Treatment. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 2019, 20, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, J. Dopamine in Parkinson’s Disease: Precise Supplementation with Motor Planning. Neurosci Bull 2018, 34, 873–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson Disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindeya Gebreyesus, H.; Gebrehiwot Gebremichael, T. The Potential Role of Astrocytes in Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Med Sci (Basel) 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berstad, K.; Berstad, J.E.R. Parkinson’s Disease; the Hibernating Spore Hypothesis. Med Hypotheses 2017, 104, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, G. Impact of Dopamine Oxidation on Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019, 10, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Raymick, J.; Imam, S. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies against Parkinson’s Disease: Recent Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Meng, L.; He, M.; Zhang, Z. Tau in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 2021, 71, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludtmann, M.H.R.; Angelova, P.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; Choi, M.L.; Rodrigues, M.; Baev, A.Y.; Berezhnov, A. V.; Yao, Z.; Little, D.; Banushi, B.; et al. α-Synuclein Oligomers Interact with ATP Synthase and Open the Permeability Transition Pore in Parkinson’s Disease. Nat Commun 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbulla, L.F.; Song, P.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Zampese, E.; Wong, Y.C.; Jeon, S.; Santos, D.P.; Blanz, J.; Obermaier, C.D.; Strojny, C.; et al. Dopamine Oxidation Mediates Mitochondrial and Lysosomal Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Science (1979) 2017, 357, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, P.C.; Kurzawa, M.; Blain, P.G.; Morris, C.M. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Cui, L.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.L. Gut Microbial Metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease: Implications of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol Neurobiol 2021, 58, 3745–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.U.; Kim, S.; Sim, J.; Yang, S.; An, H.; Nam, M.H.; Jang, D.P.; Lee, C.J. Redefining Differential Roles of MAO-A in Dopamine Degradation and MAO-B in Tonic GABA Synthesis. Exp Mol Med 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Wadood, A.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Anichkina, O.; Ghufran, M. In-Silico Evaluations of the Isolated Phytosterols from Polygonum Hydropiper L against BACE1 and MAO Drug Targets. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2021, 0, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoi, M.; Riederer, P.; Maruyama, W. Modulation of Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Expression in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Genetic and Environmental Factors Involved in Type A MAO Expression. J Neural Transm 2016, 123, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.C.; Upadhyay, S.; Paliwal, S.; Saraf, S.K. Privileged Scaffolds as MAO Inhibitors: Retrospect and Prospects. Eur J Med Chem 2018, 145, 445–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Binda, C. Monoamine Oxidases. Subcell Biochem 2018, 87, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vysakh Visweswaran; Roshni PR Role of Enzymes in Causing Neurological Disorders. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021, 12, 466–476. [CrossRef]
- R. Ramsay, R. Monoamine Oxidases: The Biochemistry of the Proteins As Targets in Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery. Curr Top Med Chem 2013, 12, 2189–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, P.C.; Buckley, D.A. The Structure and Function of the Dopamine Transporter and Its Role in CNS Diseases, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc., 2015; Volume 98. [Google Scholar]
- Biosa, A.; Arduini, I.; Soriano, M.E.; Giorgio, V.; Bernardi, P.; Bisaglia, M.; Bubacco, L. Dopamine Oxidation Products as Mitochondrial Endotoxins, a Potential Molecular Mechanism for Preferential Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 2018, 9, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follmer, C. Monoamine Oxidase and α-Synuclein as Targets in Parkinson’s Disease Therapy. Expert Rev Neurother 2014, 14, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.G.; Mariappan, S.V.S.; Buettner, G.R.; Doorn, J.A. Oxidation of 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, a Toxic Dopaminergic Metabolite, to a Semiquinone Radical and an Ortho-Quinone. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2011, 286, 26978–26986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiopathogenesis and Treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Yadav, K.S. Parkinson’s Disease: Current Drug Therapy and Unraveling the Prospects of Nanoparticles. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, L.; Marconi, R.; Colosimo, C. Treatment Strategies in Early Parkinson’s Disease. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press Inc., 2017; Vol. 132, pp. 345–360.
- Cera, N.; Bifolchetti, S.; Martinotti, G.; Gambi, F.; Sepede, G.; Onofrj, M.; Di Giannantonio, M.; Thomas, A. Amantadine and Cognitive Flexibility: Decision Making in Parkinson’s Patients with Severe Pathological Gambling and Other Impulse Control Disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2014, 10, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovac, J.A. Side Effects of a Dopamine Agonist Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: A Mini-Review of Clinical Pharmacology. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Finberg, J.P.M. Inhibitors of MAO-B and COMT: Their Effects on Brain Dopamine Levels and Uses in Parkinson’s Disease. J Neural Transm 2019, 126, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S. ichi; Kadowaki-Horita, T.; Kanda, T. Effects of the Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonist on Cognitive Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press Inc., 2014; Vol. 119, pp. 169–189.
- Hong, R.; Li, X. Discovery of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors by Medicinal Chemistry Approaches. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H. Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease A Review of Symptomatic and Potential Disease-Modifying Effects.
- Elkamhawy, A.; Paik, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Lee, K.; Park, K.D.; Roh, E.J. Discovery of Novel and Potent Safinamide-Based Derivatives as Highly Selective HMAO-B Inhibitors for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease (PD): Design, Synthesis, in Vitro, in Vivo and in Silico Biological Studies. Bioorg Chem 2021, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Woo, J.; Gouda, N.A.; Kim, J.; Nada, H.; Roh, E.J.; Park, K.D.; Cho, J.; Lee, K. Melatonin Analogues Potently Inhibit Mao-b and Protect Pc12 Cells against Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Kim, H.J.; Elsherbeny, M.H.; Paik, S.; Park, J.H.; Gotina, L.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Gouda, N.A.; Cho, J.; Lee, K.; et al. Discovery of 3,4-Dichloro-N-(1H-Indol-5-Yl)Benzamide: A Highly Potent, Selective, and Competitive HMAO-B Inhibitor with High BBB Permeability Profile and Neuroprotective Action. Bioorg Chem 2021, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbeny, M.H.; Kim, J.; Gouda, N.A.; Gotina, L.; Cho, J.; Pae, A.N.; Lee, K.; Park, K.D.; Elkamhawy, A.; Roh, E.J. Highly Potent, Selective, and Competitive Indole-Based MAO-B Inhibitors Protect PC12 Cells against 6-Hydroxydopamine-and Rotenone-Induced Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, Z. V.; Kabanova, M. V.; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Suponitsky, K.Y. An Evaluation of Synthetic Indole Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2016, 26, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Cheng, W.; Duan, Y.-T.; Yang, H.; Yao, Y. Indazole as a Privileged Scaffold: The Derivatives and Their Therapeutic Applications. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2020, 21, 839–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkov, N.T.; Hinz, S.; Küppers, P.; Gastreich, M.; Müller, C.E. Indazole-and Indole-5-Carboxamides: Selective and Reversible Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors with Subnanomolar Potency. J Med Chem 2014, 57, 6679–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkov, N.T.; Stammler, H.G.; Neumann, B.; Hristova, S.; Antonov, L.; Gastreich, M. Crystal Structures, Binding Interactions, and ADME Evaluation of Brain Penetrant N-Substituted Indazole-5-Carboxamides as Subnanomolar, Selective Monoamine Oxidase B and Dual MAO-A/B Inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 2017, 127, 470–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzvetkov, N.T.; Stammler, H.G.; Hristova, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Antonov, L. (Pyrrolo-Pyridin-5-Yl)Benzamides: BBB Permeable Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors with Neuroprotective Effect on Cortical Neurons. Eur J Med Chem 2019, 162, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkov, N.T.; Hinz, S.; Küppers, P.; Gastreich, M.; Müller, C.E. Indazole-and Indole-5-Carboxamides: Selective and Reversible Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors with Subnanomolar Potency. J Med Chem 2014, 57, 6679–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Paik, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Londhe, A.M.; Lee, K.; Pae, A.N.; Park, K.D.; Roh, E.J. Discovery of N-(1-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-1H-Indol-5-Yl)Pyrazine-2-Carboxamide: A Novel, Selective, and Competitive Indole-Based Lead Inhibitor for Human Monoamine Oxidase B. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2020, 35, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirkova, Z. V.; Kabanova, M. V.; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Firgang, S.I.; Suponitsky, K.Y. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Indole-5,6-Dicarbonitrile Derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, Z. V.; Kabanova, M. V.; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Suponitsky, K.Y. An Evaluation of Synthetic Indole Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2016, 26, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirkova, Z. V; Kabanova, M. V; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Engelbrecht, I.; Petzer, J.P.; Abramov, I.G.; Suponitsky, K.Y.; Veselovsky, A. V. An Investigation of the Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of Pyrrolo [3,4-f] Indole-5, 7-Dione and Indole-5, 6-Dicarbonitrile Derivatives. Drug Dev Res 2018, 79, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, Z. V.; Kabanova, M. V.; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Firgang, S.I.; Suponitsky, K.Y. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Indole-5,6-Dicarbonitrile Derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, Z. V; Kabanova, M. V; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Engelbrecht, I.; Petzer, J.P.; Abramov, I.G.; Suponitsky, K.Y.; Veselovsky, A. V. An Investigation of the Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of Pyrrolo [3,4-f] Indole-5, 7-Dione and Indole-5, 6-Dicarbonitrile Derivatives. Drug Dev Res 2018, 79, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, Z. V; Kabanova, M. V; Filimonov, S.I.; Abramov, I.G.; Petzer, A.; Hitge, R.; Petzer, J.P.; Suponitsky, K.Y. Optimization of Pyrrolo[3,4-f]Indole-5,7-Dione and Indole- 5,6-Dicarbonitrile Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Drug Dev Res 2019, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.; Park, M.; Park, H.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, S.; Sawant, V.S.; Choi, J.W.; Park, J.; Park, K.D.; Min, S.; et al. Indole-Substituted Benzothiazoles and Benzoxazoles as Selective and Reversible MAO- B Inhibitors for Treatment of Parkinson ’ s Disease. ACS Chem. Neuroscience 2017, 8, 1430–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jismy, B.; El Qami, A.; Pišlar, A.; Frlan, R.; Kos, J.; Gobec, S.; Knez, D.; Abarbri, M. Pyrimido[1,2-b]Indazole Derivatives: Selective Inhibitors of Human Monoamine Oxidase B with Neuroprotective Activity. Eur J Med Chem 2021, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Paik, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.; Londhe, A.M.; Lee, K.; Pae, A.N.; Park, K.D.; Roh, E.J. Discovery of N-(1-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-1H-Indol-5-Yl ) Pyrazine-2-Carboxamide: A Novel, Selective, and Competitive Indole-Based Lead Inhibitor for Human Monoamine Oxidase B. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2020, 35, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Kim, H.J.; Elsherbeny, M.H.; Paik, S.; Park, J.; Gotina, L.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Gouda, N.; Cho, J.; Lee, K.; et al. Discovery of 3, 4-Dichloro- N - (1H-Indol-5-Yl)Benzamide: A Highly Potent Selective and Competitive h MAO-B Inhibitor with High BBB Permeability Profile and Neuroprotective Action. Bioorg Chem 2021, 116, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, N.Ö.; Osmaniye, D.; Levent, S.; Sağlik, B.N.; ˙Inci, B.; Lgın, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis of New Hydrazone Derivatives for MAO Enzymes Inhibitory Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evranos-Aksöz, B.; Yabanoglu-Çiftçi, S.; Uçar, G.; Yelekçi, K.; Ertan, R. Synthesis of Some Novel Hydrazone and 2-Pyrazoline Derivatives : Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities and Docking Studies. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2014, 24, 3278–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan-zitouni, G.; Hussein, W.; Saglık, B.N.; Tabbi, A.; Korkut, B. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel N -Pyridyl-Hydrazone Derivatives as Potential Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgin-Gökşen, U.; Gökhan-Kelekçi, N.; Yabanoglu-Çiftci, S.; Yelekçi, K.; Uçar, G. Synthesis, Molecular Modeling, and in Vitro Screening of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities of Some Novel Hydrazone Derivatives. J Neural Transm 2013, 120, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimenti, F.; Maccioni, E.; Secci, D.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Granese, A.; Befani, O.; Turini, P.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F.; et al. Selective Inhibitory Activity against MAO and Molecular Modeling Studies of 2-Thiazolylhydrazone Derivatives. J Med Chem 2007, 50, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distinto, S.; Yáñez, M.; Alcaro, S.; Cardia, M.C.; Gaspari, M.; Sanna, M.L.; Meleddu, R.; Ortuso, F.; Kirchmair, J.; Markt, P.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Assessment of Novel 2-Thiazolylhydrazones and Computational Analysis of Their Recognition by Monoamine Oxidase B. Eur J Med Chem 2012, 48, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Ayyannan, S.R. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of 2-Amino-6-Nitrobenzothiazole-Derived Hydrazones as MAO Inhibitors: Role of the Methylene Spacer Group. ChemMedChem 2016, 1551–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, Ö.D.; Osmaniye, D.; Özkay, Ü.D.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Ilgın, S.; Baysal, M.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. MAO Enzymes Inhibitory Activity of New Benzimidazole Derivatives Including Hydrazone and Propargyl Side Chains. Eur J Med Chem 2017, 131, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, N.Ö.; Osmaniye, D.; Levent, S.; Sağlik, B.N.; ˙Inci, B.; Lgın, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis of New Hydrazone Derivatives for MAO Enzymes Inhibitory Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, D.; Carradori, S.; Petzer, A.; Guglielmi, P.; D’Ascenzio, M.; Chimenti, P.; Bagetta, D.; Alcaro, S.; Zengin, G.; Petzer, J.P.; et al. 4-(3-Nitrophenyl)Thiazol-2-Ylhydrazone Derivatives as Antioxidants and Selective HMAO-B Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Activity and Computational Analysis. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2019, 34, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, P.; Petzer, A.; Carradori, S.; Ascenzio, M.D.; Silvestri, R.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F.; Petzer, J.P.; Secci, D. Exploring 4-Substituted-2-Thiazolylhydrazones from 2-, 3-, and 4-Acetylpyridine as Selective and Reversible HMAO-B Inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 2013, 66, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; D’Ascenzio, M.; Monte, C. De; Secci, D.; Yáñez, M. Synthesis and Selective Human Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibition of Heterocyclic Hybrids Based on Hydrazine and Thiazole Scaffolds. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 2013, 346, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strydom, B.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Phthalide Analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013, 23, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, I.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A. The Synthesis and Evaluation of Sesamol and Benzodioxane Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Walt, M.M.; Terre’Blanche, G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Novel Sulfanylphthalimide Analogues as Highly Potent Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012, 22, 6632–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, I.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A. The Synthesis and Evaluation of Sesamol and Benzodioxane Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Walt, M.M.; Terre’Blanche, G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Novel Sulfanylphthalimide Analogues as Highly Potent Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012, 22, 6632–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, B.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Phthalide Analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013, 23, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A. S., V.D.; J.P., P.; A., P.; L.J., L. 3-Coumaranone Derivatives As Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Drug Des Devel Ther 2015, 9, 5479–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Indanones as High-Potency Reversible Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, M.S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Legoabe, L.J. 2-Heteroarylidene-1-Indanone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Chem 2016, 69, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lv, X.; Cheng, K.; Tian, Y.; Huang, X.; Kong, H.; Duan, Y.; Han, J.; Liao, C.; Xie, Z. Discovery of Novel 2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-Amine Derivatives as Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2019, 29, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Lakshmanan, B.; Jayaprakash, V. Synthesis, Biochemistry, and Computational Studies of Brominated Thienyl Chalcones : A New Class of Reversible. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1109–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, M.; Salas, C.O.; Uriarte, E.; Viña, D.; Jara-Gutiérrez, C.; Matos, M.J.; Cuellar, M. Design, Synthesis and Docking Calculations of Prenylated Chalcones as Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors with Antioxidant Activity. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 7659–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitge, R.; Smit, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Evaluation of Nitrocatechol Chalcone and Pyrazoline Derivatives as Inhibitors of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase and Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2020, 30, 127188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamecki, F.; Knez, D.; Carvalho, D.; Marcucci, C.; Rademacher, M.; Higgs, J.; Zakelj, S.; Marcos, A.; Pinto, F. de T.; Abin-Carriquiry, J.A.; et al. Multitarget 2′-Hydroxychalcones as Potential Drugs for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders and Their Comorbidities. Neuropharmacology journal 2021, 201, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.E.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Vilapurathu, J.K.; Prakasan, A.; Suresh, J.K.; Thomas, A. Development of Fluorinated Methoxylated Chalcones as Selective Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors : Synthesis, Biochemistry and Molecular Docking Studies. Bioorg Chem 2015, 62, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Uçar, G.; Yabanog¢lu-Çiftçi, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Mathew, G.E.; Vilapurathu, J.K.; Nadeena, A.M.; Nabeela, P.; Lakshmi, V.; et al. Development of Fluorinated Thienylchalcones as Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors : Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Dock- Ing Studies. Lett Org Chem 2015, 12, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Lakshmanan, B.; Jayaprakash, V. Synthesis, Biochemistry, and Computational Studies of Brominated Thienyl Chalcones : A New Class of Reversible. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1109–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.E.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Mathew, S.; Haridas, A.; Jayaprakash, V. Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitory Activity: Fluoro- vs. Trifluoromethyl-4-Hydroxylated Chalcones Derivatives. Chem Biodivers 2016, 13, 969–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Uçar, G.; Mathew, G.E.; Mathew, S.; Purapurath, P.K.; Moolayil, F.; Mohan, S.; Gupta, S.V. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity : Methyl- versus Chlorochalcone Derivatives. 2016; 11, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, N.; Fioravanti, R.; Proietti Monaco, L.; Biava, M.; Yáñez, M.; Ortuso, F.; Alcaro, S. 1,5-Diphenylpenta-2,4-Dien-1-Ones as Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 2013, 59, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minders, C.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Lourens, A.C.U. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities of Heterocyclic Chalcones. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 5270–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehuman, N.A.; Oh, J.M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Beshr, E.A.M.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; Jat, R.K.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Development of Halogenated-Chalcones Bearing with Dimethoxy Phenyl Head as Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, M.A.; Oh, J.M.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Kumar, S.; Musa, A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Nayl, A.A.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Ahmad, I.; Patel, H.; et al. Development of Bromo- and Fluoro-Based α, β-Unsaturated Ketones as Highly Potent MAO-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Struct 2022, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, P.; Secci, D.; Petzer, A.; Bagetta, D.; Rotondi, G.; Ferrante, C.; Recinella, L.; Leone, S.; Alcaro, S.; Zengin, G.; et al. Benzo[b] Tiophen-3-Ol Derivatives as Effective Inhibitors of Human Monoamine Oxidase : Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2019, 34, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, M.S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Legoabe, L.J. 2-Benzylidene-1-Indanone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2016, 26, 4599–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łażewska, D.; Olejarz-maciej, A.; Reiner, D.; Kaleta, M.; Latacz, G.; Zygmunt, M.; Doroz-Płonka, A.; Karcz, T.; Frank, A.; Stark, H.; et al. Dual Target Ligands with 4-Tert-Butylphenoxy Scaffold as Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists and Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
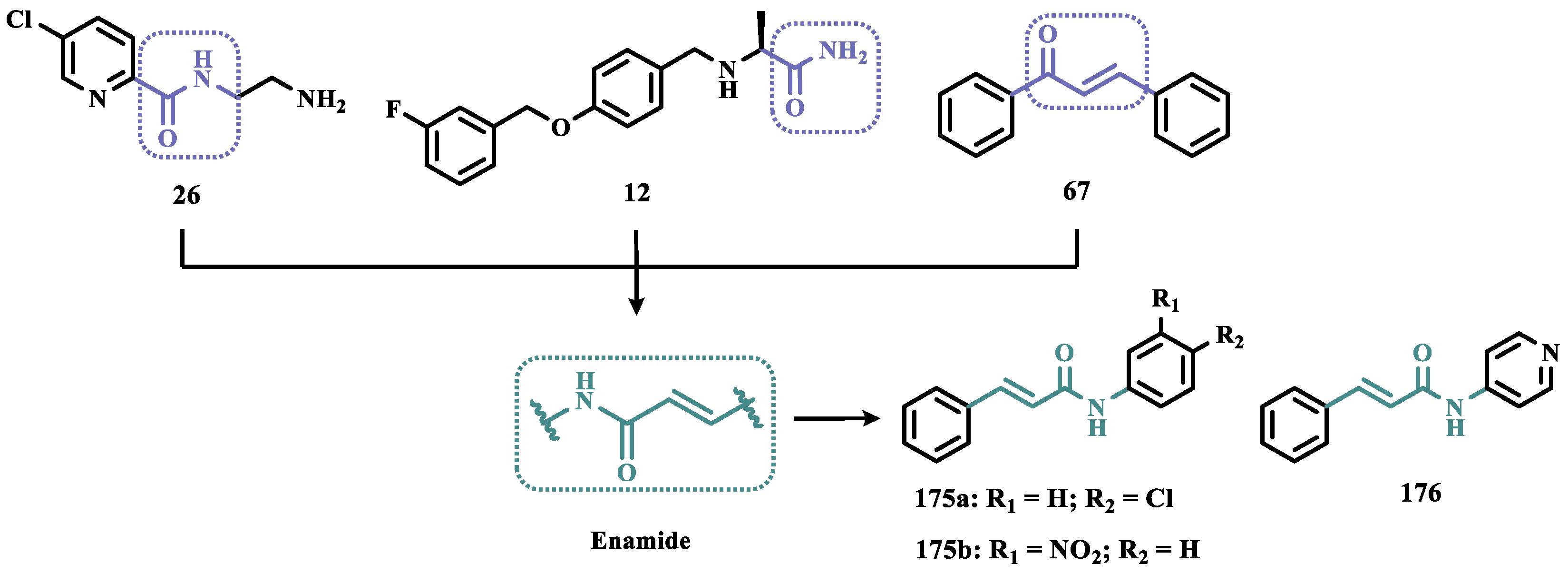
- Huleatt, P.B.; Khoo, M.L.; Chua, Y.Y.; Tan, T.W.; Liew, R.S.; Balogh, B.; Deme, R.; Gölöncsér, F.; Magyar, K.; Sheela, D.P.; et al. Novel Arylalkenylpropargylamines as Neuroprotective, Potent, and Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J Med Chem 2015, 58, 1400–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huleatt, P.B.; Khoo, M.L.; Chua, Y.Y.; Tan, T.W.; Liew, R.S.; Balogh, B.; Deme, R.; Gölöncsér, F.; Magyar, K.; Sheela, D.P.; et al. Novel Arylalkenylpropargylamines as Neuroprotective, Potent, and Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J Med Chem 2015, 58, 1400–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kumar, M.; Dwivedi, A.R.; Kumar, V. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies of Propargyl-Containing 2,4,6-Trisubstituted Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potential Anti-Parkinson Agents. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
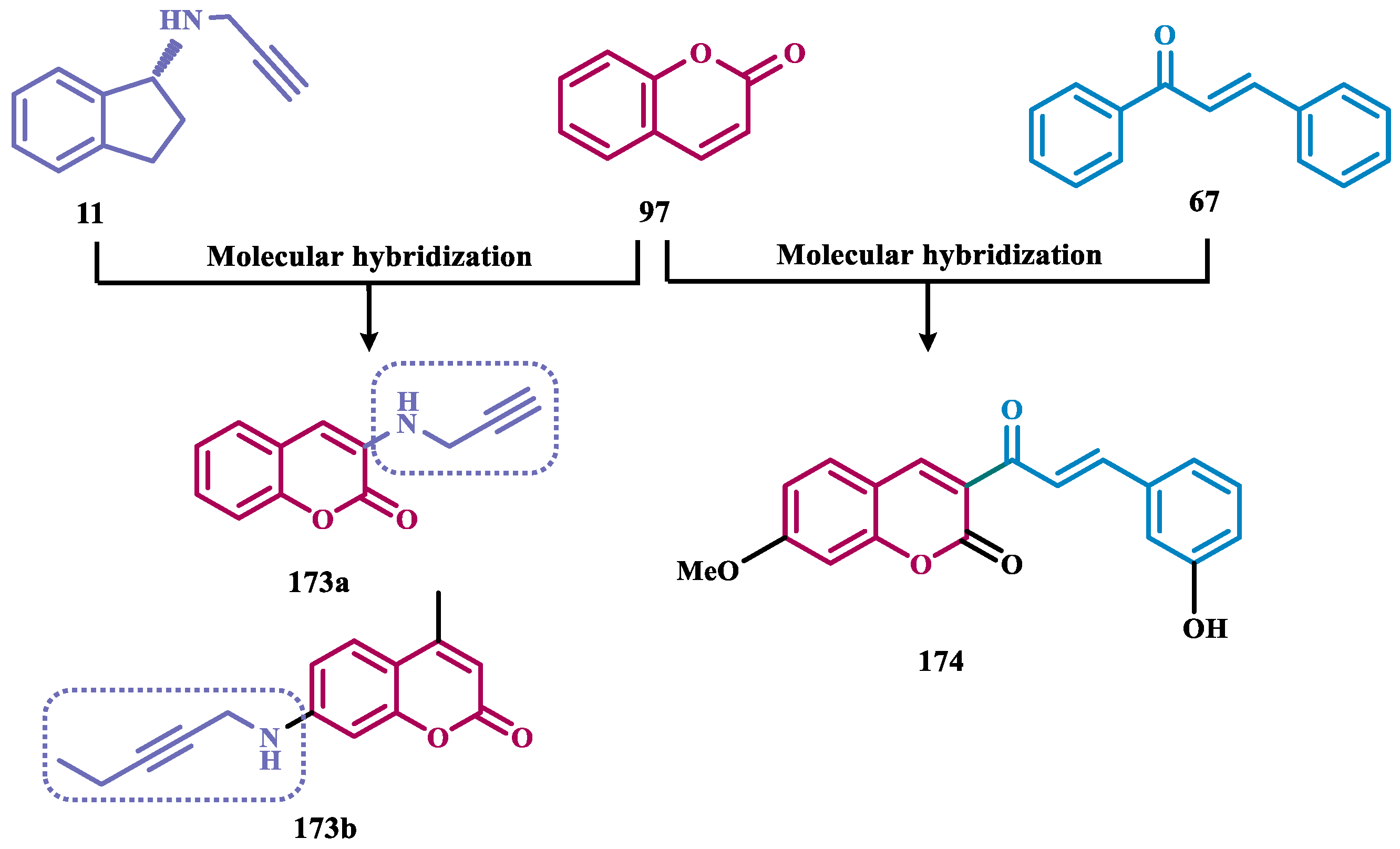
- Meiring, L.; Petzer, J.P.; Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A. The Evaluation of N -Propargylamine-2-Aminotetralin as an Inhibitor of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2022, 67, 128746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Walt, M.M.; Terre’Blanche, G.; Lourens, A.C.U.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Sulfanylphthalonitrile Analogues as Selective and Potent Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012, 22, 7367–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.E.A.; Ozalp, L.; Danıs, O.; Odabas, Z. Synthesis and Human Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity of Novel C2-, C3- and C4-Substituted Phthalonitriles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2022, 74, 128917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, B.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P. The Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by 8-(2-Phenoxyethoxy)Caffeine Analogues. Arzneimittelforschung - Drug Research 2012, 62, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzer, A.; Grobler, P.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Selected Phenylalkylcaffeine Analogues. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2014, 66, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booysen, H.P.; Moraal, C.; Terre’Blanche, G.; Petzer, A.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P. Thio- and Aminocaffeine Analogues as Inhibitors of Human Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem 2011, 19, 7507–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Xiao, T.; Qi, X.; Li, L.N.; Qin, K.; Nian, S.; Hu, G.X.; Yu, Y.; Liang, G.; Ye, F. Design and Synthesis of 8-Substituted Benzamido-Phenylxanthine Derivatives as MAO-B Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012, 22, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarria, D.; Cagide, F.; Pinto, M.; Gomes, L.R.; Low, J.N.; Borges, F. Development of Piperic Acid-Based Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Structural Characterization and Biological Evaluation. J Mol Struct 2019, 1182, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarria, D.; Fernandes, C.; Silva, V.; Silva, C.; Gil-Martins, E.; Soares, P.; Silva, T.; Silva, R.; Remião, F.; Oliveira, P.J.; et al. Design of Novel Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors Based on Piperine Scaffold: Structure-Activity-Toxicity, Drug-Likeness and Efflux Transport Studies. Eur J Med Chem 2020, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Oh, J.M.; Baty, R.S.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H. Piperazine-Substituted Chalcones: A New Class of MAO-B, AChE, and BACE-1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 38855–38866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Sheetal, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Mantha, A.K.; Kumar, V. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies of Phenyl-/Benzhydrylpiperazine Derivatives as Potential MAO Inhibitors. Bioorg Chem 2018, 77, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Enríquez, F.; Viña, D.; Uriarte, E.; Laguna, R.; Matos, M.J. 7-Amidocoumarins as Multitarget Agents against Neurodegenerative Diseases: Substitution Pattern Modulation. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Rodríguez-Enríquez, F.; Borges, F.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Estrada, M.; Rodríguez-Franco, M.I.; Laguna, R.; Viña, D. 3-Amidocoumarins as Potential Multifunctional Agents against Neurodegenerative Diseases. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Ferino, G.; Cadoni, E.; Matos, M.J.; Quezada, E.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Vilar, S.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Yáñez, M.; et al. Benzopyran-2-Ones as Attractive Scaffold for MAO Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies. 15th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry (ECSOC-13) 1-30 November, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, R.F.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S.S.; Lan, J.S.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T. Design and Synthesis of Novel 3,4-Dihydrocoumarins as Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors with the Neuroprotection against Parkinson’s Disease. Bioorg Chem 2021, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Terán, C.; Pérez-Castillo, Y.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L.; Viña, D. Synthesis and Study of a Series of 3-Arylcoumarins as Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2011, 54, 7127–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Nicolotti, O.; Grossi, G.; Di Braccio, M.; Soto-Otero, R.; Mendez-Alvarez, E.; Stefanachi, A.; Gadaleta, D.; Carotti, A. Fine Molecular Tuning at Position 4 of 2H-Chromen-2-One Derivatives in the Search of Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 2013, 70, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L.; Barletta, M.; Soto-Otero, R.; Nicolotti, O.; Mendez-Alvarez, E.; Catto, M.; Introcaso, A.; Stefanachi, A.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.; et al. Discovery, Biological Evaluation, and Structure-Activity and -Selectivity Relationships of 6′-Substituted (E)-2-(Benzofuran-3(2H)-Ylidene)-N- Methylacetamides, a Novel Class of Potent and Selective Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2013, 56, 2651–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Wang, Y.; Bao, X.Q.; Yang, B.B.; Gao, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, L. Discovery of Coumarin Mannich Base Derivatives as Multifunctional Agents against Monoamine Oxidase B and Neuroinflammation for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Eur J Med Chem 2019, 173, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Viña, D.; Janeiro, P.; Borges, F.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. New Halogenated 3-Phenylcoumarins as Potent and Selective MAO-B Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2010, 20, 5157–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, D.; Matos, M.J.; Ferino, G.; Cadoni, E.; Laguna, R.; Borges, F.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L. 8-Substituted 3-Arylcoumarins as Potent and Selective MAO-B Inhibitors: Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation, and Docking Studies. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Enríquez, F.; Viña, D.; Uriarte, E.; Fontenla, J.A.; Matos, M.J. Discovery and Optimization of 3-Thiophenylcoumarins as Novel Agents against Parkinson’s Disease: Synthesis, in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Bioorg Chem 2020, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N, S.E.; P, V.C.; Balan, S.; Lakshmi G, A.A.; Vatakeel, B. DESIGN, SYNTHESIS AND EVALUATION OF SUBSTITUTED COUMARIN DERIVATIVES AS NEW SCAFFOLD ON PARKINSON’S DISEASE. 2020. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research SJIF Impact Factor 8 9, 1702–1717.
- Mpitimpiti, A.N.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Jordaan, J.H.L.; Lourens, A.C.U. Synthesis and Evaluation of Chromone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Mol Divers 2019, 23, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, J.; Cagide, F.; Chavarria, D.; Silva, T.; Fernandes, C.; Gaspar, A.; Uriarte, E.; Remião, F.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F.; et al. Discovery of New Chemical Entities for Old Targets: Insights on the Lead Optimization of Chromone-Based Monoamine Oxidase B (MAO-B) Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2016, 59, 5879–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.; Reis, J.; Fonseca, A.; Milhazes, N.; Viña, D.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F. Chromone 3-Phenylcarboxamides as Potent and Selective MAO-B Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2011, 21, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.; Silva, T.; Yáñez, M.; Vina, D.; Orallo, F.; Ortuso, F.; Uriarte, E.; Alcaro, S.; Borges, F. Chromone, a Privileged Scaffold for the Development of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2011, 54, 5165–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagide, F.; Silva, T.; Reis, J.; Gaspar, A.; Borges, F.; Gomes, L.R.; Low, J.N. Discovery of Two New Classes of Potent Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors by Tricky Chemistry. Chemical Communications 2015, 51, 2832–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloete, S.J.; N’Da, C.I.; Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. The Evaluation of 1-Tetralone and 4-Chromanone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Mol Divers 2021, 25, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Selected C6-Substituted Chromone Derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 2012, 49, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaro, S.; Gaspar, A.; Ortuso, F.; Milhazes, N.; Orallo, F.; Uriarte, E.; Yáñez, M.; Borges, F. Chromone-2- and -3-Carboxylic Acids Inhibit Differently Monoamine Oxidases A and B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2010, 20, 2709–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Selected Chromone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012, 22, 5480–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. α-Tetralone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2014, 24, 2758–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. The Synthesis and Evaluation of C7-Substituted α-Tetralone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Chem Biol Drug Des 2015, 86, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiring, L.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by 3,4-Dihydro-2(1H)-Quinolinone Derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013, 23, 5498–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiring, L.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A. C6- and C7-Substituted 3,4-Dihydro-2(1H)-Quinolinones as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Drug Res 2017, 67, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitge, R.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Isatoic Anhydrides as Novel Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem 2022, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Lu, Z.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolines Derivatives as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors for Treatment of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Asian Journal of Chemistry 2015, 27, 3651–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, S.N.; Haiba, N.S.; Asal, A.M.; Bekhit, A.A.; Amer, A.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; El-Faham, A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Quinazoline Amino Acid Derivatives as Mono Amine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2015, 23, 3574–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qhobosheane, M.A.; Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. The Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of C6-Mono- and N3/C6-Disubstituted Derivatives of 4(3H)-Quinazolinone. Bioorg Chem 2019, 85, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qhobosheane, M.A.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Legoabe, L.J. Synthesis and Evaluation of 2-Substituted 4(3H)-Quinazolinone Thioether Derivatives as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2018, 26, 5531–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, L.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Legoabe, L.J. The Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of C6- and N1-Substituted 3-Methyl-3,4-Dihydroquinazolin-2(1H)-One Derivatives. Mol Divers 2020, 24, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
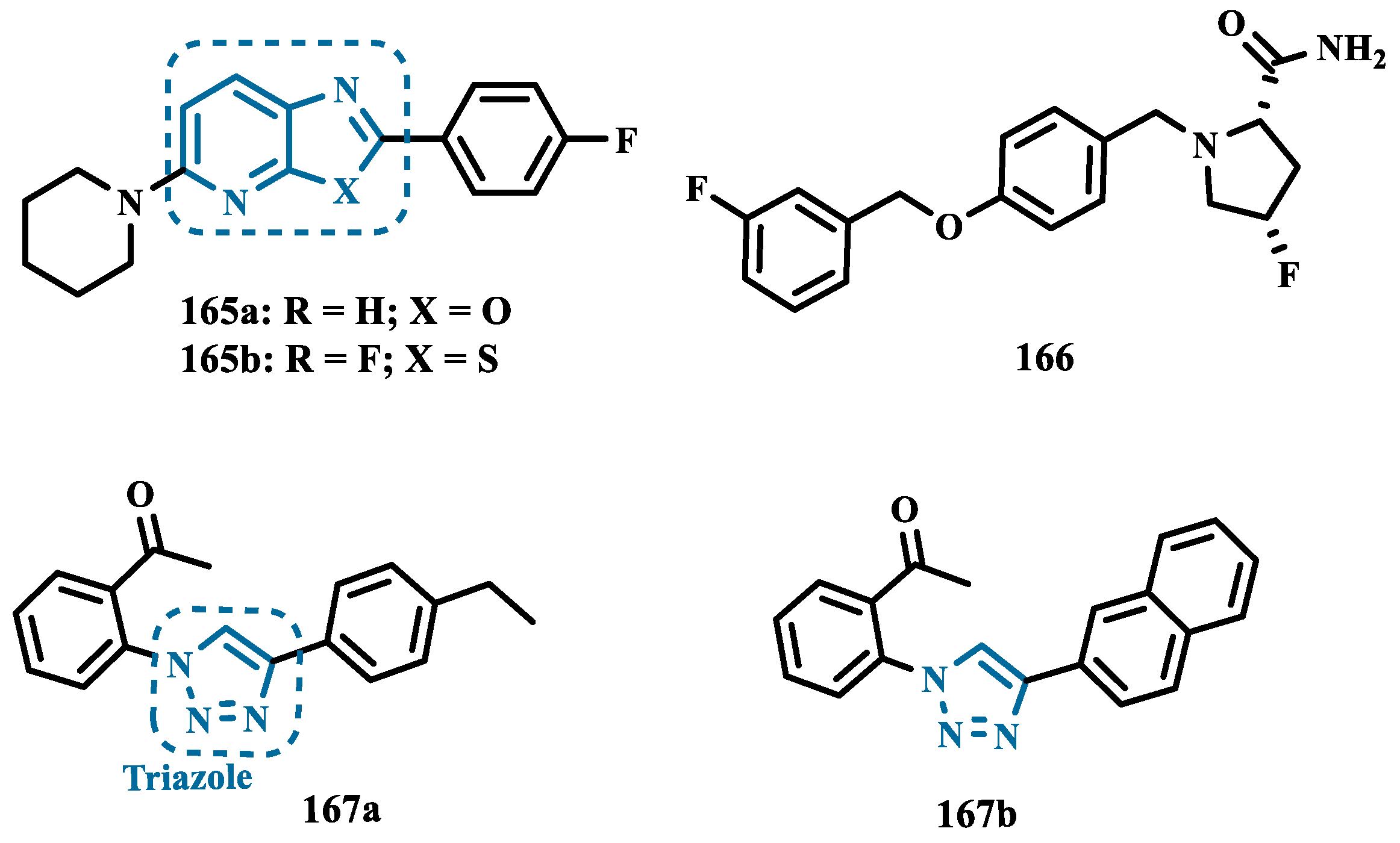
- Yeon, S.K.; Choi, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.J.; Jang, B.K.; Kim, S.; Bahn, Y.S.; Han, G.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Biaryl Derivatives for Structural Characterization of Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors toward Parkinson’s Disease Therapy. Bioorg Med Chem 2018, 26, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
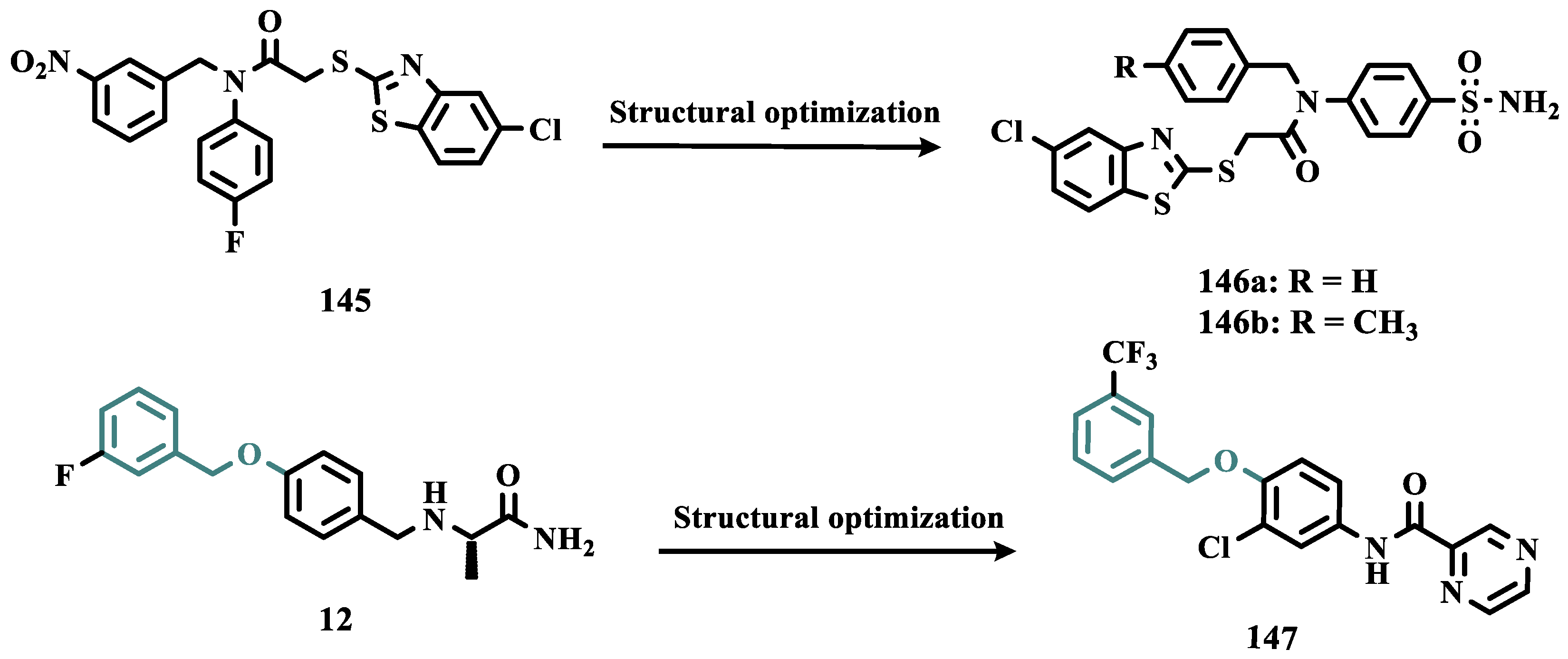
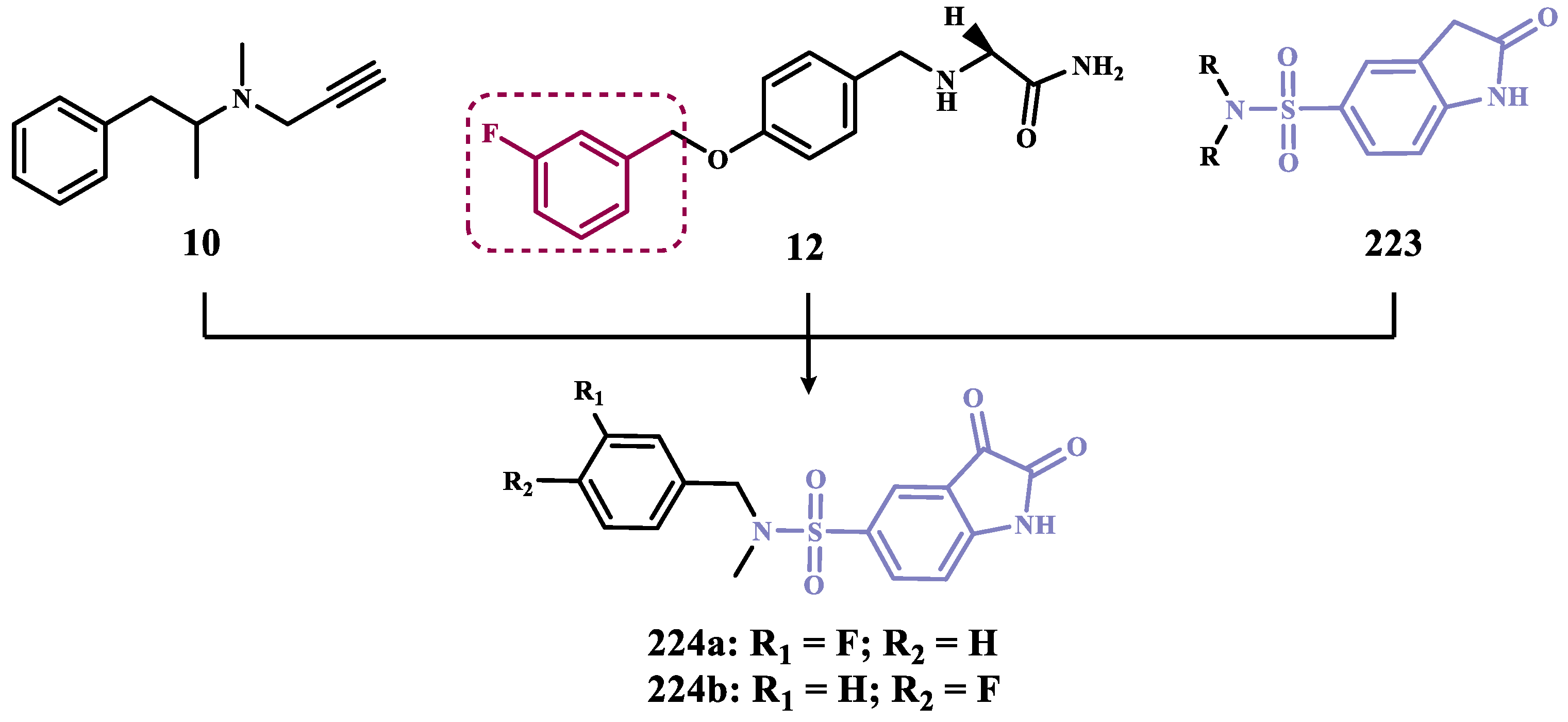
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Cai, P.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.D.G.; Kong, L.; Wang, X. Neuroprotective Effects of Benzyloxy Substituted Small Molecule Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors in Parkinson’s Disease. Bioorg Med Chem 2016, 24, 5929–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostert, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Benzoxathiolone Analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2016, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Walt, M.M.; Terre’Blanche, G.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A. Benzyloxynitrostyrene Analogues – A Novel Class of Selective and Highly Potent Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase B. Eur J Med Chem 2017, 125, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, B.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis of Some Novel 2-Substituted Benzothiazole Derivatives Containing Benzylamine Moiety as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Agents. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2016, 31, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağlık, B.N.; Osmaniye, D.; Acar Çevik, U.; Levent, S.; Kaya Çavuşoğlu, B.; Atlı Eklioğlu, Ö.; Özkay, Y.; Koparal, A.S.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis, in Vitro Enzyme Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of New Benzylamine-Sulfonamide Derivatives as Selective MAO-B Inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2020, 35, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Paik, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Lee, K.; Park, K.D.; Roh, E.J. Discovery of Novel and Potent Safinamide-Based Derivatives as Highly Selective HMAO-B Inhibitors for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease (PD): Design, Synthesis, in Vitro, in Vivo and in Silico Biological Studies. Bioorg Chem 2021, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
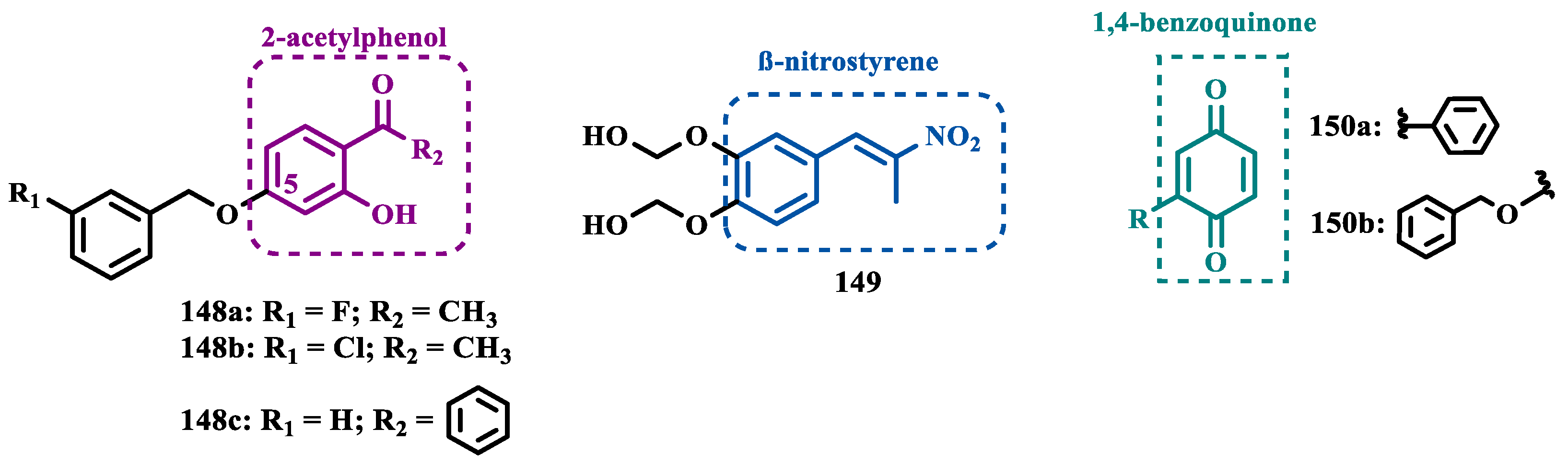
- Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. 2-Acetylphenol Analogs As Potent Reversible Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Drug Des Devel Ther 2015, 9, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Oliveira, C.; Milhazes, N.; Vina, D.; Borges, F. Exploring Nitrostyrene as a Scaffold for a New Class a of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Lett Drug Des Discov 2012, 9, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. The Evaluation of 1,4-Benzoquinones as Inhibitors of Human Monoamine Oxidase. Eur J Med Chem 2017, 135, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
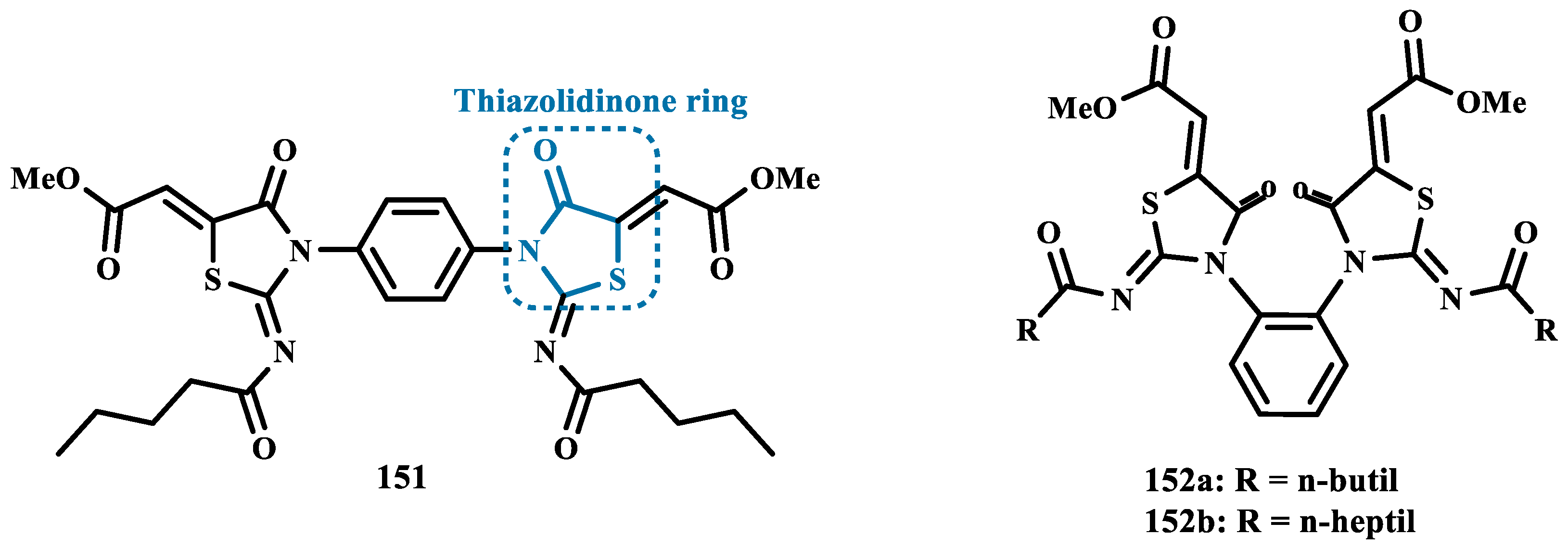
- Abbas, N.; Zaib, S.; Bakht, S.M.; Ibrar, A.; Khan, I.; Batool, S.; Saeed, A.; Iqbal, J. Symmetrical Aryl Linked Bis-Iminothiazolidinones as New Chemical Entities for the Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidases: Synthesis, in Vitro Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modelling Analysis. Bioorg Chem 2017, 70, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
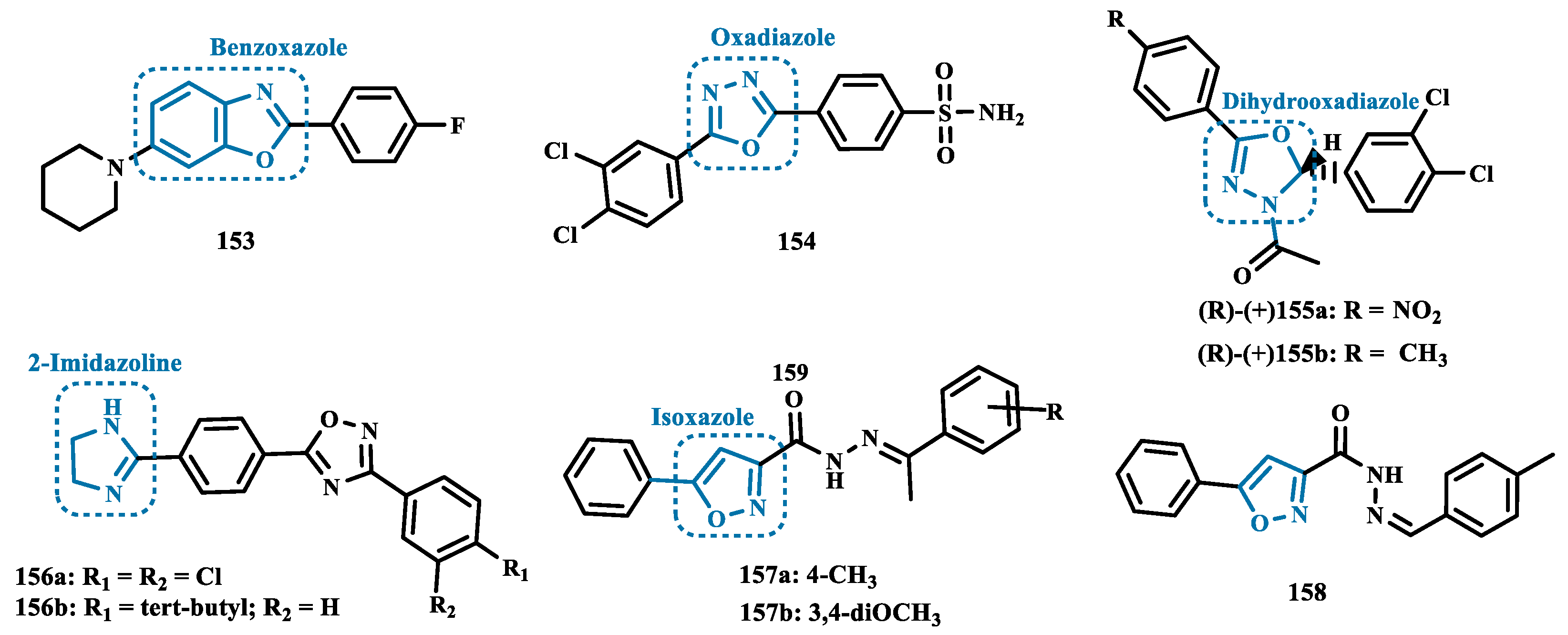
- Nam, M.H.; Park, M.; Park, H.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, S.; Sawant, V.S.; Choi, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Park, K.D.; Min, S.J.; et al. Indole-Substituted Benzothiazoles and Benzoxazoles as Selective and Reversible MAO-B Inhibitors for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 2017, 8, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, V.S.; Park, H.; Baek, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.W.; Park, K.D.; Choi, K. Il; Seong, J.; Lee, S.; Choo, H. Benzoxazoles as Selective Monoamine Oxidase B (MAO-B) Inhibitors. Bull Korean Chem Soc 2019, 40, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetnev, A.; Shlenev, R.; Efimova, J.; Ivanovskii, S.; Tarasov, A.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. 1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-Ylbenzenesulfonamides as Privileged Structures for the Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distinto, S.; Meleddu, R.; Yanez, M.; Cirilli, R.; Bianco, G.; Sanna, M.L.; Arridu, A.; Cossu, P.; Cottiglia, F.; Faggi, C.; et al. Drug Design, Synthesis, in Vitro and in Silico Evaluation of Selective Monoaminoxidase B Inhibitors Based on 3-Acetyl-2-Dichlorophenyl-5-Aryl-2,3-Dihydro-1,3,4-Oxadiazole Chemical Scaffold. Eur J Med Chem 2016, 108, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetnev, A.; Osipyan, A.; Baykov, S.; Sapegin, A.; Chirkova, Z.; Korsakov, M.; Petzer, A.; Engelbrecht, I.; Petzer, J.P. Novel Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on the Privileged 2-Imidazoline Molecular Framework. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2019, 29, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Mishra, P. Novel Isoxazole Derivatives as Potential Antiparkinson Agents: Synthesis, Evaluation of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity and Docking Studies. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2019, 28, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Mishra, P. Synthesis, Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity and Computational Study of Novel Isoxazole Derivatives as Potential Antiparkinson Agents. Comput Biol Chem 2019, 79, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panova, V.A.; Filimonov, S.I.; Chirkova, Z. V.; Kabanova, M. V.; Shetnev, A.A.; Korsakov, M.K.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Suponitsky, K.Y. Investigation of Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Quinoxalin-4-Ones as Novel Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Bioorg Chem 2021, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
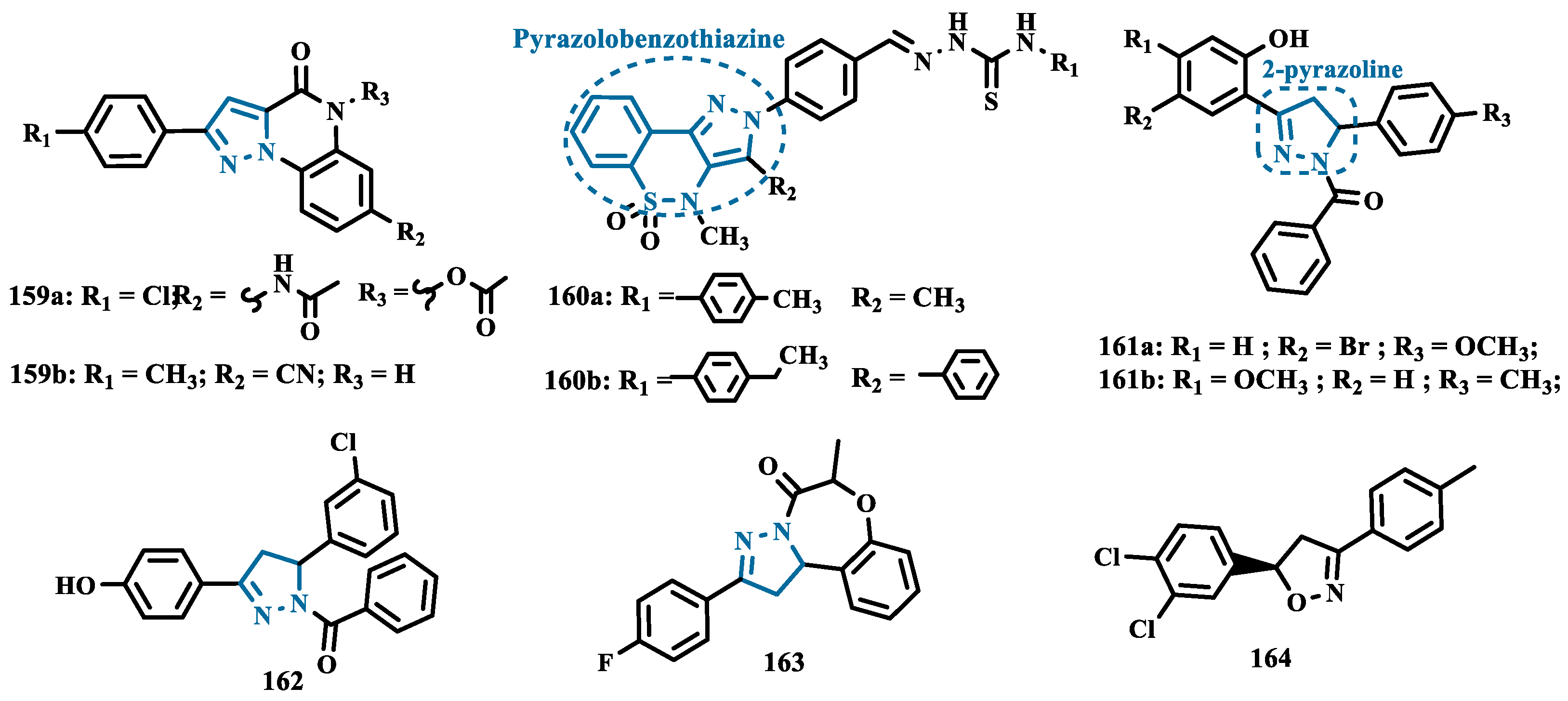
- Abid, S.M.A.; Aslam, S.; Zaib, S.; Bakht, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Athar, M.M.; Gardiner, J.M.; Iqbal, J. Pyrazolobenzothiazine-Based Carbothioamides as New Structural Leads for the Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidases: Design, Synthesis, in Vitro Bioevaluation and Molecular Docking Studies. Medchemcomm 2017, 8, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evranos-Aksoz, B.; Ucar, G.; Yelekci, K. Design, Synthesis and HMAO Inhibitory Screening of Novel 2-Pyrazoline Analogues. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 2017, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.N.; Zhang, L.H.; Ge, R.; Feng, X.E.; Li, Q.S. Triphenylpyrazoline Ketone Chlorophenols as Potential Candidate Compounds against Parkinson’s Disease: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2022, 31, 1517–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Xiao, J.; Ni, Y.; Xu, H.F.; Zheng, M.; Tong, X.; Zhang, T.T.; Liao, C.; Tang, W.J. Novel Tricyclic Pyrazolo[1,5-d][1,4]Benzoxazepin-5(6H)-One: Design, Synthesis, Model and Use as HMAO-B Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2016, 24, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardia, M.C.; Sanna, M.L.; Meleddu, R.; Distinto, S.; Yañez, M.; Viña, D.; Lamela, M.; Maccioni, E. A Novel Series of 3,4-Disubstituted Dihydropyrazoles: Synthesis and Evaluation for MAO Enzyme Inhibition. J Heterocycl Chem 2013, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Silvestri, R. New Frontiers in Selective Human MAO-B Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2015, 58, 6717–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccioni, E.; Alcaro, S.; Orallo, F.; Cardia, M.C.; Distinto, S.; Costa, G.; Yanez, M.; Sanna, M.L.; Vigo, S.; Meleddu, R. Synthesis of New 3-Aryl-4,5-Dihydropyrazole-1-Carbothioamide Derivatives. An Investigation on Their Ability to Inhibit Monoamine Oxidase. Eur J Med Chem 2010, 45, 4490–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secci, D.; Carradori, S.; Bolasco, A.; Bizzarri, B.; D’Ascenzio, M.; Maccioni, E. Discovery and Optimization of Pyrazoline Derivatives As Promising Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem 2012, 12, 2240–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerioni, G.; Maccioni, E.; Cardia, M.C.; Vigo, S.; Mocci, F. Characterization of 2,5-Diaryl-1,3,4-Oxadiazolines by Multinuclear Magnetic Resonance and Density Functional Theory Calculations. Investigation on a Case of Very Remote Hammett Correlation. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry 2009, 47, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimenti, F.; Secci, D.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Granese, A.; Carradori, S.; Befani, O.; Turini, P.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F. Synthesis, Molecular Modeling Studies, and Selective Inhibitory Activity against Monoamine Oxidase of N,N′-Bis[2-Oxo-2H-Benzopyran]-3-Carboxamides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2006, 16, 4135–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCioni, E.; Alcaro, S.; Cirilli, R.; Vigo, S.; Cardia, M.C.; Sanna, M.L.; Meleddu, R.; Yanez, M.; Costa, G.; Casu, L.; et al. 3-Acetyl-2,5-Diaryl-2,3-Dihydro-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles: A New Scaffold for the Selective Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase B. J Med Chem 2011, 54, 6394–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleddu, R.; Distinto, S.; Cirilli, R.; Alcaro, S.; Yanez, M.; Sanna, M.L.; Corona, A.; Melis, C.; Bianco, G.; Matyus, P.; et al. Through Scaffold Modification to 3,5-Diaryl-4,5-Dihydroisoxazoles: New Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase B. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2017, 32, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Jo, S.; Yeom, M.; Moon, B.; Choo, I.H.; Lee, J.; Lim, E.J.; Park, K.D.; et al. Oxazolopyridines and Thiazolopyridines as Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Bioorg Med Chem 2013, 21, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yi, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, T.; Deng, K.; Jin, C.; Hao, G. Enhancing Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitory Activity via Chiral Fluorination: Structure-Activity Relationship, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Study. Eur J Med Chem 2022, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.P.; Dias, Í.F.C.; Fronza, M.G.; Besckow, E.M.; Fetter, J.; Nascimento, J.E.R.; Jacob, R.G.; Savegnago, L.; Bortolatto, C.F.; Brüning, C.A.; et al. Synthesis of 2′-(1,2,3-Triazoyl)-Acetophenones: Molecular Docking and Inhibition of: In Vitro Monoamine Oxidase Activity. New Journal of Chemistry 2021, 45, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.; Tuor, U.I.; Thompson, R.; Institoris, A.; Kulynych, A.; Zhang, X.; Kinniburgh, D.W.; Bari, F.; Busija, D.W.; Barber, P.A. Protection against Recurrent Stroke with Resveratrol: Endothelial Protection. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.; Gao, N.; Zhang, T. Resveratrol Attenuates Oxidative Damage through Activating Mitophagy in an in Vitro Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Toxicol Lett 2018, 282, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drygalski, K.; Fereniec, E.; Koryciński, K.; Chomentowski, A.; Kiełczewska, A.; Odrzygóźdź, C.; Modzelewska, B. Resveratrol and Alzheimer’s Disease. From Molecular Pathophysiology to Clinical Trials. Exp Gerontol 2018, 113, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
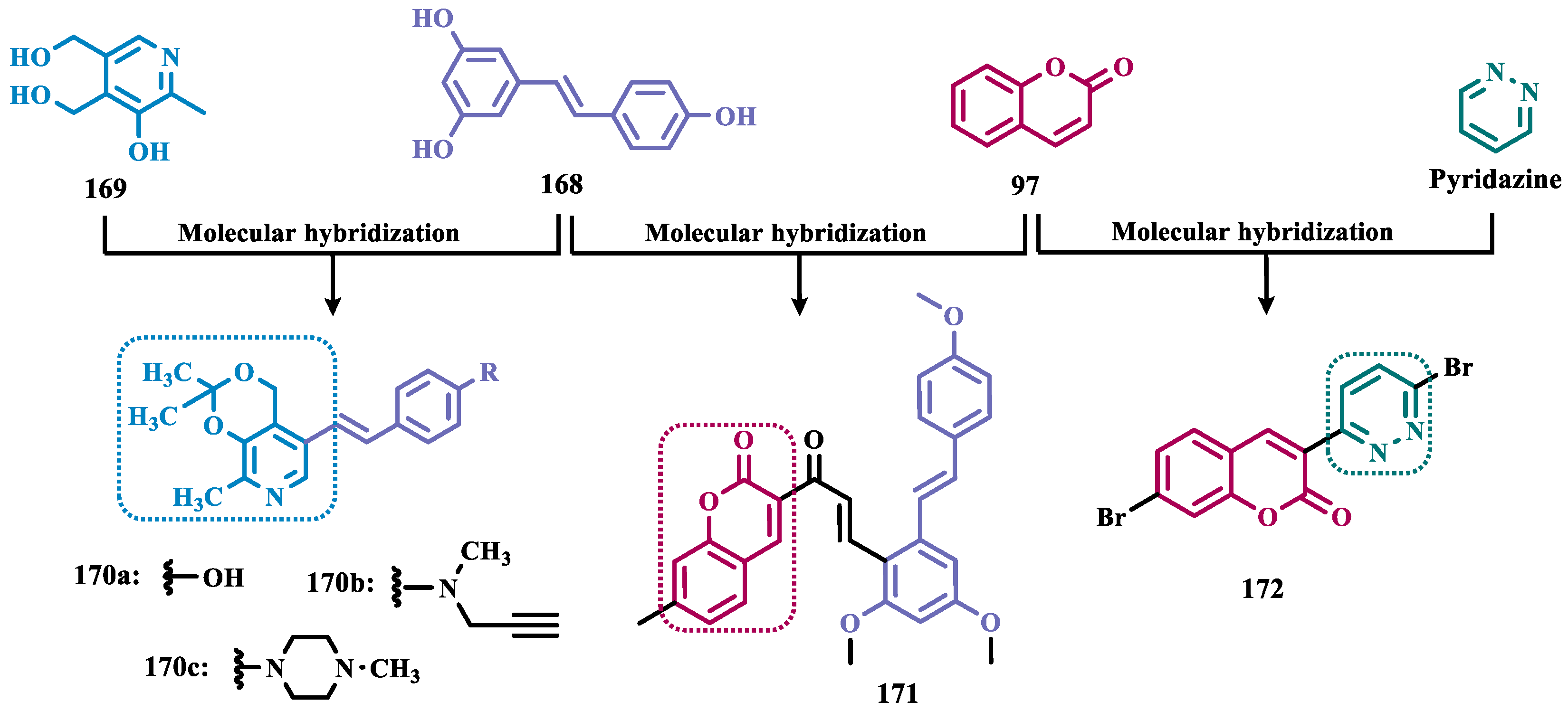
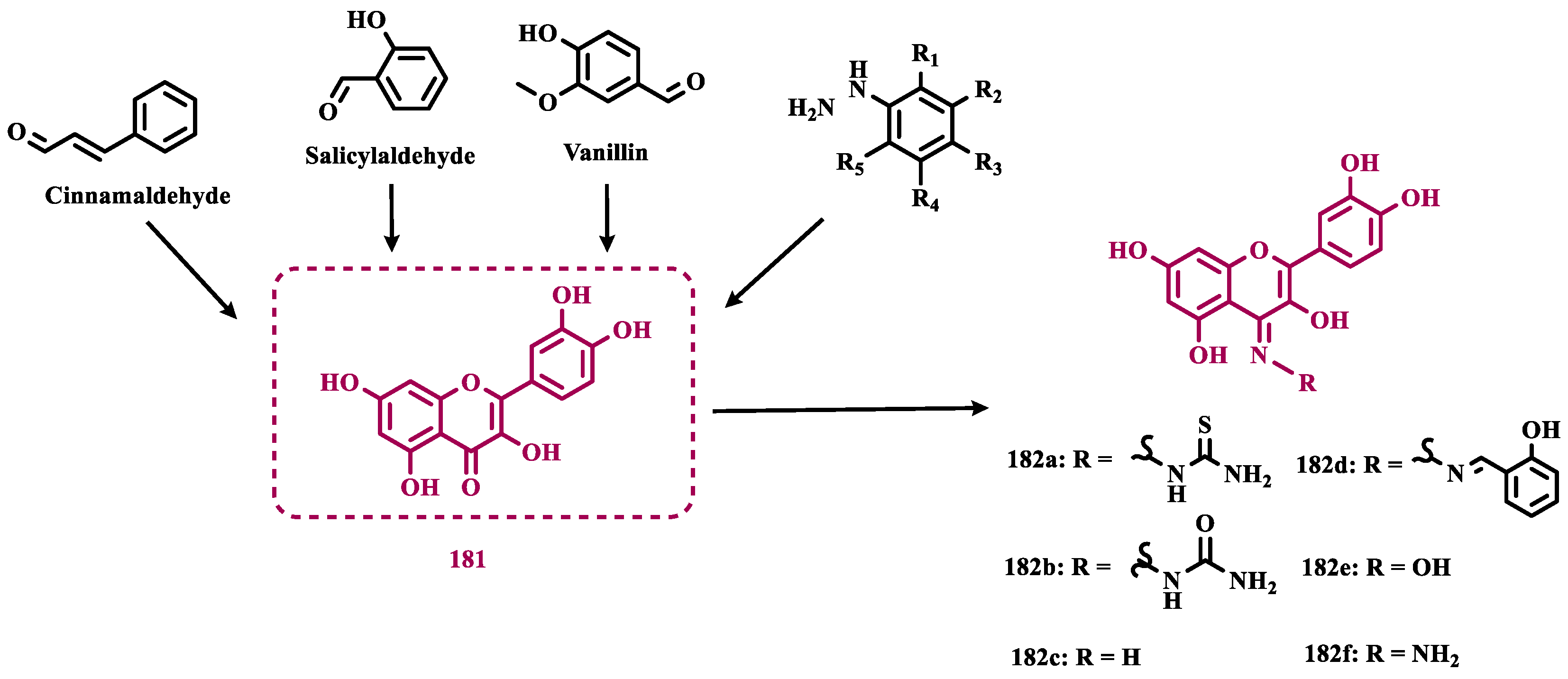
- Li, W.; Yang, X.; Song, Q.; Cao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, L. Pyridoxine-Resveratrol Hybrids as Novel Inhibitors of MAO-B with Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Activities for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Bioorg Chem 2020, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Enríquez, F.; Costas-Lago, M.C.; Besada, P.; Alonso-Pena, M.; Torres-Terán, I.; Viña, D.; Fontenla, J.Á.; Sturlese, M.; Moro, S.; Quezada, E.; et al. Novel Coumarin-Pyridazine Hybrids as Selective MAO-B Inhibitors for the Parkinson’s Disease Therapy. Bioorg Chem 2020, 104, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.F.; Cheng, H.J.; Ren, J.; Li, H.L.; Guo, L.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Liao, C. Novel 2H-Chromen-2-One Derivatives of Resveratrol: Design, Synthesis, Modeling and Use as Human Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 2015, 103, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Herrera Ibatá, D.M.; Uriarte, E.; Viña, D. Coumarin-Rasagiline Hybrids as Potent and Selective HMAO-B Inhibitors, Antioxidants, and Neuroprotective Agents. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Alvarado, G.; Yañez, O.; Morales, N.; González-González, A.; Areche, C.; Núñez, M.T.; Fierro, A.; García-Beltrán, O. Coumarin-Chalcone Hybrids as Inhibitors of MAO-B: Biological Activity and in Silico Studies. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavully, F.S.; Oh, J.M.; Dev, S.; Kaipakasseri, S.; Palakkathondi, A.; Vengamthodi, A.; Abdul Azeez, R.F.; Tondo, A.R.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H.; et al. Design of Enamides as New Selective Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2020, 72, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
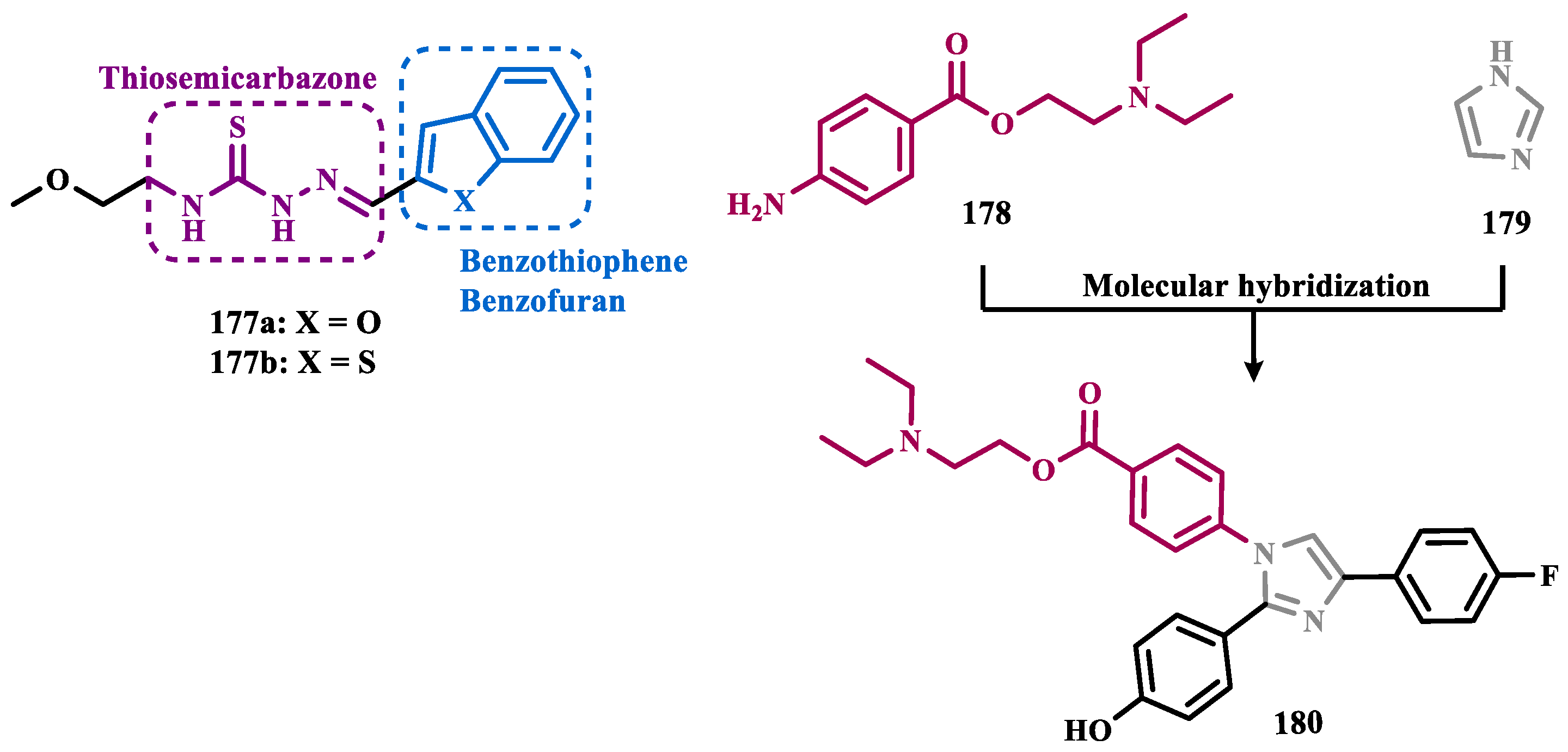
- Osmaniye, D.; Kurban, B.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Novel Thiosemicarbazone Derivatives: In Vitro and in Silico Evaluation as Potential Mao-b Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, X. Discovery of Novel Procaine-Imidazole Derivative as Inhibitor of Monoamine Oxidase-B for Potential Benefit in Parkinson’s Disease. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 10928–10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, P.; Malik, N.; Khatkar, A. In Silico Design, Synthesis of Hybrid Combinations: Quercetin Based MAO Inhibitors with Antioxidant Potential. Curr Top Med Chem 2019, 19, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsenko, K.; Hagenow, S.; Affini, A.; Reiner, D.; Stark, H. Rasagiline Derivatives Combined with Histamine H3 Receptor Properties. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
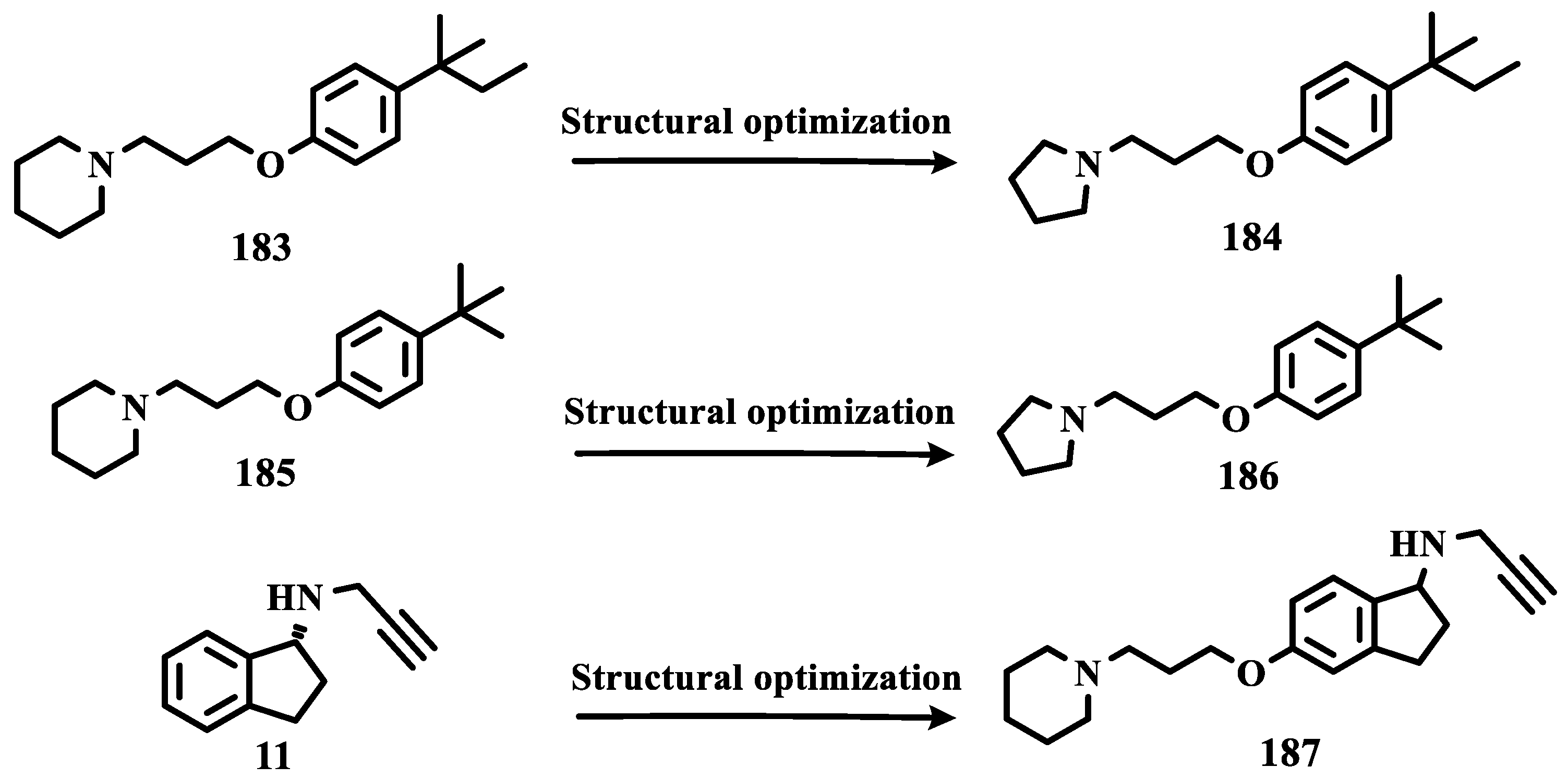
- Łażewska, D.; Olejarz-Maciej, A.; Kaleta, M.; Bajda, M.; Siwek, A.; Karcz, T.; Doroz-Płonka, A.; Cichoń, U.; Kuder, K.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. 4-Tert-Pentylphenoxyalkyl Derivatives – Histamine H3 Receptor Ligands and Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2018, 28, 3596–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łażewska, D.; Ligneau, X.; Schwartz, J.-C.; Schunack, W.; Stark, H.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Ether Derivatives of 3-Piperidinopropan-1-Ol as Non-Imidazole Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 2006, 14, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, N.; Khan, N.; Ojha, S.K.; Lazewska, D.; Kiec-Kononowicz, K.; Sadek, B. The Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist DL77 Ameliorates MK801-Induced Memory Deficits in Rats. Front Neurosci 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, B.; Saad, A.; Subramanian, D.; Shafiullah, M.; Łażewska, D.; Kieć-Kononowiczc, K. Anticonvulsant and Procognitive Properties of the Non-Imidazole Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist DL77 in Male Adult Rats. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łażewska, D.; Olejarz-Maciej, A.; Reiner, D.; Kaleta, M.; Latacz, G.; Zygmunt, M.; Doroz-Płonka, A.; Karcz, T.; Frank, A.; Stark, H.; et al. Dual Target Ligands with 4-Tert-Butylphenoxy Scaffold as Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists and Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Rai, G.K.; Ayyannan, S.R. Exploration of a Library of 3,4-(Methylenedioxy)Aniline-Derived Semicarbazones as Dual Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Acetylcholinesterase: Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation. ChemMedChem 2016, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Ortuso, F.; Petzer, A.; Bagetta, D.; De Monte, C.; Secci, D.; De Vita, D.; Guglielmi, P.; Zengin, G.; Aktumsek, A.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biochemical Evaluation of Novel Multi-Target Inhibitors as Potential Anti-Parkinson Agents. Eur J Med Chem 2018, 143, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, M.S.; Pavankumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Raja, A.S. Experimental and Computational Evaluation of Piperonylic Acid Derived Hydrazones Bearing Isatin Moieties as Dual Inhibitors of Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamecki, F.; Knez, D.; Carvalho, D.; Marcucci, C.; Rademacher, M.; Higgs, J.; Žakelj, S.; Marcos, A.; de Tezanos Pinto, F.; Abin-Carriquiry, J.A.; et al. Multitarget 2′-Hydroxychalcones as Potential Drugs for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders and Their Comorbidities. Neuropharmacology 2021, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.E.; Oh, J.M.; Mohan, K.; Tengli, A.; Mathew, B.; Kim, H. Development of Methylthiosemicarbazones as New Reversible Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2021, 39, 4786–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupershmidt, L.; Weinreb, O.; Amit, T.; Mandel, S.; Bar-Am, O.; Youdim, M.B.H. Novel Molecular Targets of the Neuroprotective/Neurorescue Multimodal Iron Chelating Drug M30 in the Mouse Brain. Neuroscience 2011, 189, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramovich-Tirosh, Y.; Amit, T.; Bar-Am, O.; Zheng, H.; Fridkin, M.; Youdim, M.B.H. Therapeutic Targets and Potential of the Novel Brain- Permeable Multifunctional Iron Chelator–Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drug, M-30, for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease 1. J Neurochem 2007, 100, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H. M30, a Brain Permeable Multi Target Neurorestorative Drug in Post Nigrostriatal Dopamine Neuron Lesion of Parkinsonism Animal Models. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2012, 18, S151–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, S.; Zheng, H.; Fridkin, M.; Youdim, M.B.H. Restoration of Nigrostriatal Dopamine Neurons in Post-MPTP Treatment by the Novel Multifunctional Brain-Permeable Iron Chelator-Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drug, M30. Neurotox Res 2010, 17, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Weiner, L.M.; Bar-Am, O.; Epsztejn, S.; Cabantchik, Z.I.; Warshawsky, A.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Fridkin, M. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Novel Bifunctional Iron-Chelators as Potential Agents for Neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Bioorg Med Chem 2005, 13, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Gal, S.; Weiner, L.M.; Bar-Am, O.; Warshawsky, A.; Fridkin, M.; Youdim, M.B.H. Novel Multifunctional Neuroprotective Iron Chelator-monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases: In Vitro Studies on Antioxidant Activity, Prevention of Lipid Peroxide Formation and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition. J Neurochem 2005, 95, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Fridkin, M. Site-Activated Chelators Targeting Acetylcholinesterase and Monoamine Oxidase for Alzheimer’s Therapy. ACS Chem Biol 2010, 5, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Walt, M.M.; Terre’Blanche, G.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. The Adenosine Receptor Affinities and Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitory Properties of Sulfanylphthalimide Analogues. Bioorg Chem 2015, 59, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuder, K.J.; Załuski, M.; Schabikowski, J.; Latacz, G.; Olejarz-Maciej, A.; Jaśko, P.; Doroz-Płonka, A.; Brockmann, A.; Müller, C.E.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Novel, Dual Target-Directed Annelated Xanthine Derivatives Acting on Adenosine Receptors and Monoamine Oxidase B. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunschweiger, A.; Koch, P.; Schlenk, M.; Pineda, F.; Küppers, P.; Hinz, S.; Köse, M.; Ullrich, S.; Hockemeyer, J.; Wiese, M.; et al. 8-Benzyltetrahydropyrazino[2,1-f]Purinediones: Water-Soluble Tricyclic Xanthine Derivatives as Multitarget Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.; Akkari, R.; Brunschweiger, A.; Borrmann, T.; Schlenk, M.; Küppers, P.; Köse, M.; Radjainia, H.; Hockemeyer, J.; Drabczyńska, A.; et al. 1,3-Dialkyl-Substituted Tetrahydropyrimido[1,2-f]Purine-2,4-Diones as Multiple Target Drugs for the Potential Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Bioorg Med Chem 2013, 21, 7435–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Załuski, M.; Schabikowski, J.; Schlenk, M.; Olejarz-Maciej, A.; Kubas, B.; Karcz, T.; Kuder, K.; Latacz, G.; Zygmunt, M.; Synak, D.; et al. Novel Multi-Target Directed Ligands Based on Annelated Xanthine Scaffold with Aromatic Substituents Acting on Adenosine Receptor and Monoamine Oxidase B. Synthesis, in Vitro and in Silico Studies. Bioorg Med Chem 2019, 27, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabczyńska, A.; Schumacher, B.; Müller, C.E.; Karolak-Wojciechowska, J.; Michalak, B.; Pȩkala, E.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Impact of the Aryl Substituent Kind and Distance from Pyrimido[2,1-f]Purindiones on the Adenosine Receptor Selectivity and Antagonistic Properties. In Proceedings of the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry; Elsevier Masson SAS, April 1 2003; Vol. 38; pp. 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Drabczyńska, A.; Müller, C.E.; Lacher, S.K.; Schumacher, B.; Karolak-Wojciechowska, J.; Nasal, A.; Kawczak, P.; Yuzlenko, O.; Pekala, E.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Tricyclic Aryloimidazo-, Pyrimido-, and Diazepinopurinediones. Bioorg Med Chem 2006, 14, 7258–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabczyńska, A.; Müller, C.E.; Schiedel, A.; Schumacher, B.; Karolak-Wojciechowska, J.; Fruziński, A.; Zobnina, W.; Yuzlenko, O.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Phenylethyl-Substituted Pyrimido[2,1-f]Purinediones and Related Compounds: Structure-Activity Relationships as Adenosine A1 and A2A Receptor Ligands. Bioorg Med Chem 2007, 15, 6956–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabczyńska, A.; Yuzlenko, O.; Köse, M.; Paskaleva, M.; Schiedel, A.C.; Karolak-Wojciechowska, J.; Handzlik, J.; Karcz, T.; Kuder, K.; Müller, C.E.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Tricyclic Cycloalkylimidazo-, Pyrimido- and Diazepinopurinediones. Eur J Med Chem 2011, 46, 3590–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.; Brunschweiger, A.; Namasivayam, V.; Ullrich, S.; Maruca, A.; Lazzaretto, B.; Küppers, P.; Hinz, S.; Hockemeyer, J.; Wiese, M.; et al. Probing Substituents in the 1- and 3-Position: Tetrahydropyrazino-Annelated Water-Soluble Xanthine Derivatives as Multi-Target Drugs with Potent Adenosine Receptor Antagonistic Activity. Front Chem 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Han, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, S.; Hu, M.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y.; Ye, F. Synthesis and Evaluation of Phenylxanthine Derivatives as Potential Dual A2AR Antagonists/MAO-B Inhibitors for Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivara, S.; Piersanti, G.; Bartoccini, F.; Diamantini, G.; Pala, D.; Riccioni, T.; Stasi, M.A.; Cabri, W.; Borsini, F.; Mor, M.; et al. Synthesis of (E)-8-(3-Chlorostyryl)Caffeine Analogues Leading to 9-Deazaxanthine Derivatives as Dual A2A Antagonists/MAO-B Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2013, 56, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stößel, A.; Schlenk, M.; Hinz, S.; Küppers, P.; Heer, J.; Gütschow, M.; Müller, C.E. Dual Targeting of Adenosine A2A Receptors and Monoamine Oxidase B by 4H-3,1-Benzothiazin-4-Ones. J Med Chem 2013, 56, 4580–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, I.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A. Nitrocatechol Derivatives of Chalcone as Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Catechol-O-Methyltransferase. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 2018, 18, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitge, R.; Smit, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Evaluation of Nitrocatechol Chalcone and Pyrazoline Derivatives as Inhibitors of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase and Monoamine Oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Beer, A.D.; Legoabe, L.J.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. The Inhibition of Catechol O-Methyltransferase and Monoamine Oxidase by Tetralone and Indanone Derivatives Substituted with the Nitrocatechol Moiety. Bioorg Chem 2021, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarria, D.; Benfeito, S.; Soares, P.; Lima, C.; Garrido, J.; Serrão, P.; Soares-da-Silva, P.; Remião, F.; Oliveira, P.J.; Borges, F. Boosting Caffeic Acid Performance as Antioxidant and Monoamine Oxidase B/Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem 2022, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavari, M.; Malan, S.F.; Joubert, J. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of Sulfonyl Isatin Derivatives as Monoamine Oxidase and Caspase-3 Inhibitors. Medchemcomm 2016, 7, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Inhibitor | IC50 MAO-A (nM) |
IC50 MAO-B (nM) |
SI | Inhibitory profile | LogP | TPSA | BBB penetration | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15a | >10,000 | 0.586 ± 0.087 | 17,064 | Rev/Comp | 3.60 | 57.8 | - | - |
| 15b | >10,000 | 0.386 ± 0.052 | 25,906 | - | 2.67 | 57.8 | - | - |
| 15c | >10,000 | 1.59 ± 0.16 | 6,289 | - | 3.72 | 46.9 | - | - |
| 17 | >10,000 | 0.612 ± 0.065 | 16,339 | - | 4.38 | 41 | - | - |
| 18a | >10,000 | 0.662 ± 0.059 | 15,105 | - | - | 46.92 | Yes | - |
| 43a | 87,900 ± 4,780 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 19,977 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 47b | 6,470 ± 1250 | 2.5 ± 0.15 | 2,588 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 63 | 3,920 ± 827 | 4.0 ± 1 | 980 | Rev/Comp | - | - | - | - |
| 66c | 25,2200 ± 20,400 | 270 ± 20 | 934 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 66d | 436,500 ± 40,300 | 480 ± 4 | 909 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 73b | 15,370 | 11.35 | 1,354 | Rev | - | - | - | - |
| 76a | 5820 ± 720 | 6.2 ± 0.9 | 938,7 | Rev/Comp | - | - | - | - |
| 87a | 218,000 | 25 | 8,720 | Rev | - | - | - | - |
| 96 | - | 47.4 | >211 | Rev/Comp | - | 68.55 | - | Low |
| 102a | NA | 0.31 ± 0.02 | >333,333 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 102b | NA | 0.80 ± 0.05 | >125,000 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 102c | NA | 0.74 ± 0.02 | >135,870 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 108 | 99,999 ± 0.53 | 0.37 ± 40 | >270,270 | Rev/Comp | - | 35.53 | Yes | Low |
| 114 | NA | 0.67 ± 0.13 | >149,254 | Rev/Comp | 3.69 | 59.31 | Yes | Low |
| 127a | 28,900 ± 4,220 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 20,643 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 127b | >100,000 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | >40,000 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 140 | >100,000 | 9 ± 1 | 110,000 | Comp | - | - | - | - |
| 141 | >100,000 | 12.34 ± 1.62 | >8,104 | - | 3.66 | 35.53 | Yes | Low |
| 147 | - | 3.9 ± 0.7 | >25,641 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 148a | 50,700 ± 4,450 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 17,482 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 148b | 17,700 ± 2,940 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 13,615 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 148c | 38,200 ± 3,130 | 4 ± 1 | 9,550 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 154 | 46,200 ± 11,200 | 2.7 ± 0.64 | 17,111 | Rev | - | - | - | - |
| 164 | NA | 11.97 ± 0.37 | >8,354 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 172 | >100,000 | 60 ± 4 | 1,666.67 | Rev | - | - | Yes | - |
| 175a | >40,000 | 110 ± 24 | >363 | Rev/Comp | - | - | - | - |
| 180 | 15,220 ± 3,400 | 32 ± 2 | 475 | - | - | - | - | Low |
| 189b | 2660 ± 51 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 501 | Rev/Comp | - | - | Yes | - |
| 189c | 29,100 ± 2,520 | 7.2 ± 1.8 | 4,041 | - | - | - | Yes | - |
| 213 | >10,000 | 34.9 ± 2.5 | 286 | Rev/Comp | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





