Submitted:
08 August 2025
Posted:
11 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Serious/Non Serious Suspected Adverse Reactions Percentage and Ratio
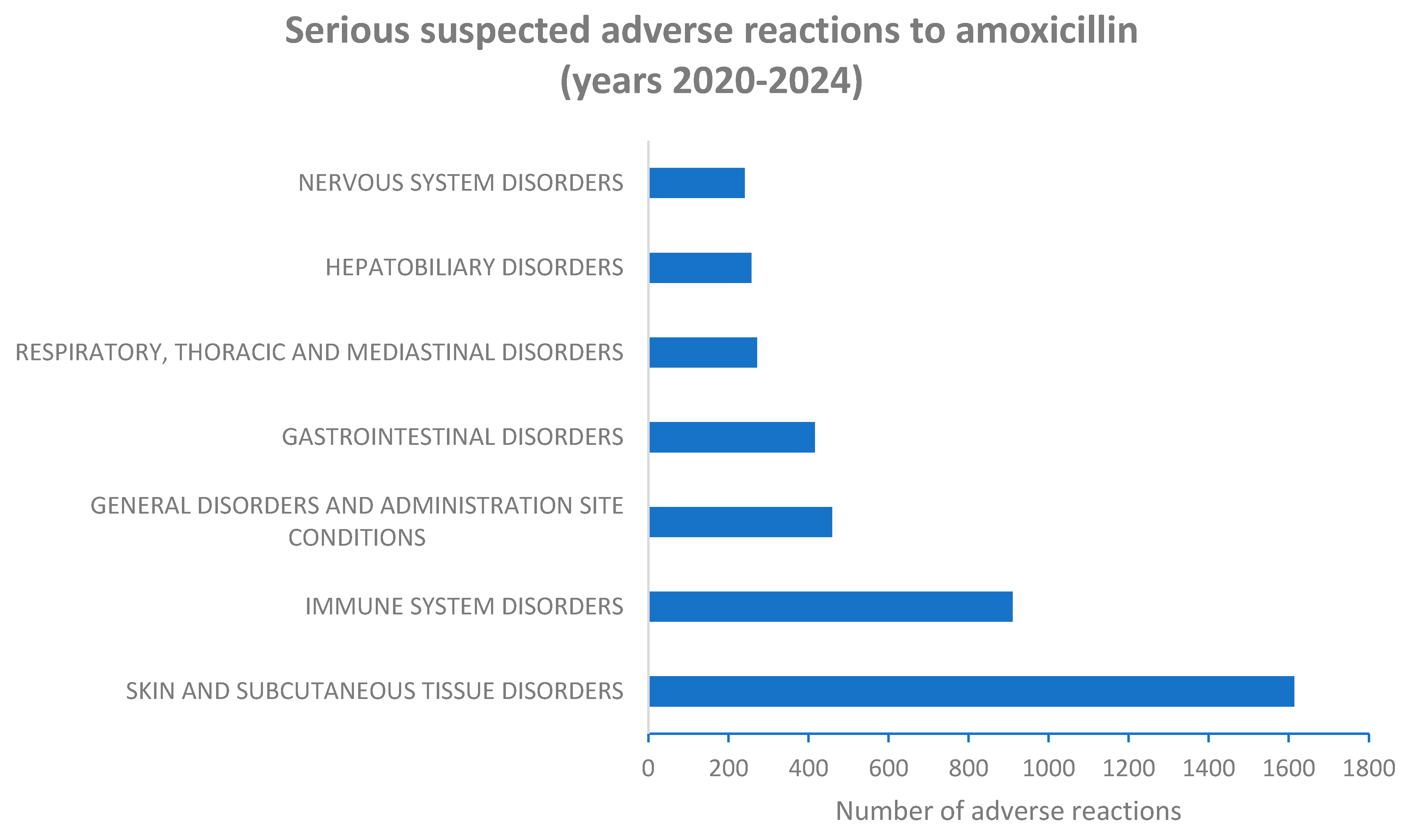
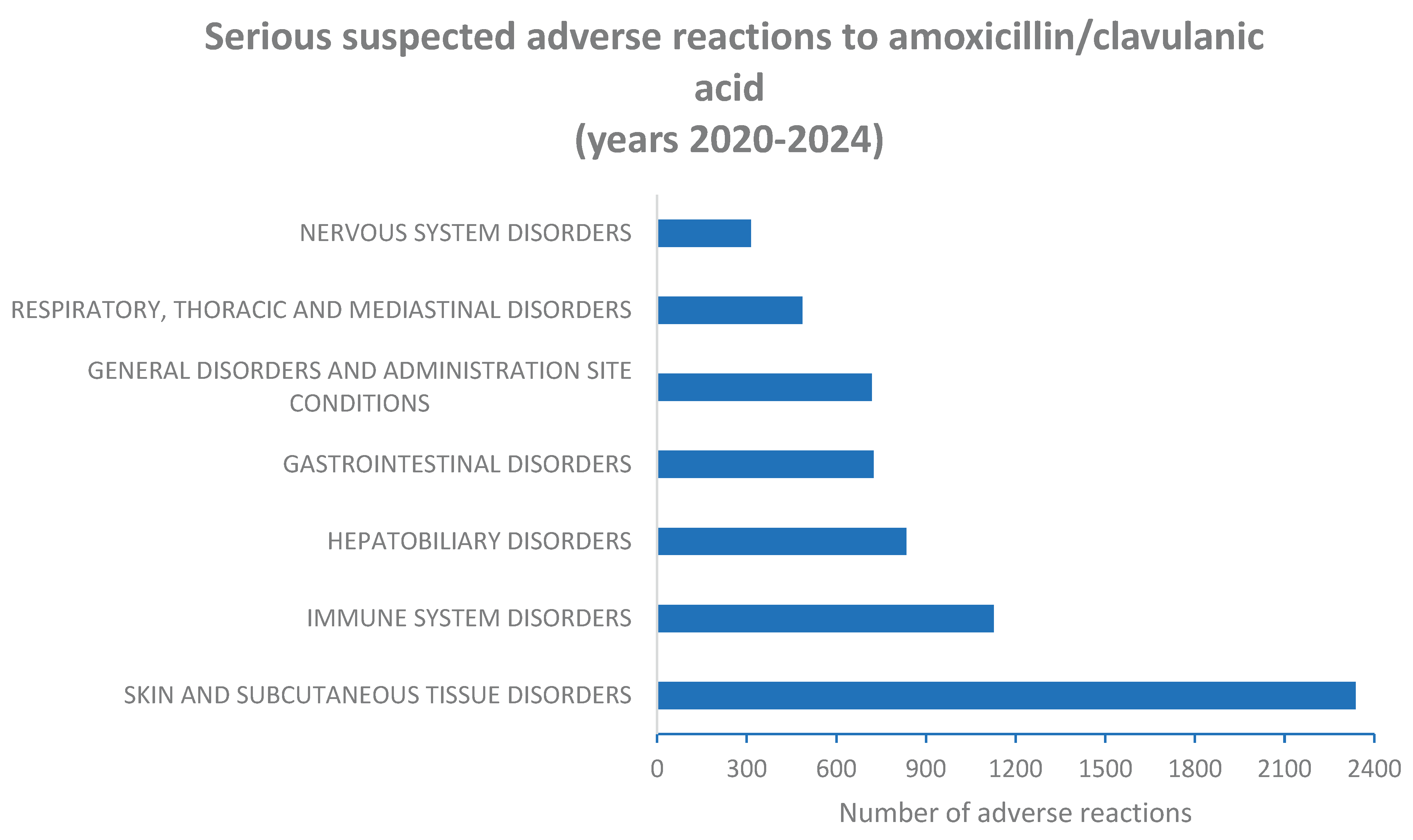
2.2. Serious Suspected Adverse Reactions to Amoxicillin and Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid Combination According to System Organ Class (SOC) Level
2.3. Sex Distribution of Cases Reporting Serious Suspected Adverse Reactions (SARs) to Amoxicillin and Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid Combination According to System Organ Class (SOC) Level
2.4. Evaluation of Adverse Reactions to Amoxicillin and Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid Signaled as “Hepatobiliary Disorders”
2.5. Evaluation of Adverse Reactions to Amoxicillin and Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid Signaled as “Drug Ineffective”
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Design of the Study
4.2. Data Analysis
4.3. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAR | Suspected adverse reaction |
| ICSR | Individual Case Safety Reports |
| SOC | System Organ Class |
| EEA | European Economic Area |
| ROR | Reporting Odds Ratio |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| C.I. | Confidence intervals |
| EU | European Union |
| MedDRA | Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities |
| PT | Preferred Term |
References
- Akhavan BJ, Khanna NR, Vijhani P. Amoxicillin. 2023 Nov 17. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. [PubMed]
- Huttner A, Bielicki J, Clements MN, Frimodt-Møller N, Muller AE, Paccaud JP, Mouton JW. Oral amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid: properties, indications and usage. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Jul;26(7):871-879. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodey GP, Nance J. Amoxicillin: in vitro and pharmacological studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):358-62. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Paterson DL, Bonomo RA. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: a clinical update. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005 Oct;18(4):657-86. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hsu CK, Lai CC. Different Indications Between Fluoroquinolone and Amoxicillin. Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 13;76(2):371. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu LY, Chang SC, Luh KT, Hsieh WC. Antibacterial activities of amoxicillin alone and in combination with clavulanic acid correlated with beta-lactamase production. Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1991 Aug;24(3):272-80. [PubMed]
- Todd PA, Benfield P. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. An update of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1990 Feb;39(2):264-307. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White AR, Kaye C, Poupard J, Pypstra R, Woodnutt G, Wynne B. Augmentin (amoxicillin/clavulanate) in the treatment of community-acquired respiratory tract infection: a review of the continuing development of an innovative antimicrobial agent. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004 Jan;53 Suppl 1:i3-20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habarugira JMV, Figueras A. Pharmacovigilance network as an additional tool for the surveillance of antimicrobial resistance. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2021 Aug;30(8):1123-1131. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulis G, Sommet A, Durrieu G, Bagheri H, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Montastruc JL; French Association of PharmacoVigilance Centres. Trends of reporting of 'serious'vs. 'non-serious' adverse drug reactions over time: a study in the French PharmacoVigilance Database. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Jul;74(1):201-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Edwards IR, Aronson JK. Adverse drug reactions: definitions, diagnosis, and management. Lancet. 2000;356:1255–9. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Salazar A, Rosales SP, Rangel-Frausto S, Criollo E, Archer-Dubon C, Orozco-Topete R. Epidemiology of adverse cutaneous drug reactions. A prospective study in hospitalized patients. Arch Med Res. 2006 Oct;37(7):899-902. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwamwitwa KW, Bukundi EM, Maganda BA, Munishi C, Fimbo AM, Buma D, Muro EP, Sabiiti W, Shewiyo DH, Shearer MC, Smith AD, Kaale EA. Adverse Drug Reactions Resulting From the Use of Chiral Medicines Amoxicillin, Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid, and Ceftriaxone: A Mixed Prospective-Retrospective Cohort Study. Inquiry. 2024 Jan-Dec;61:469580241273323. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mori F, Barni S, Pucci N, Rossi ME, de Martino M, Novembre E. Cutaneous adverse reactions to amoxicillin-clavulanic acid suspension in children: the role of sodium benzoate. Curr Drug Saf. 2012 Apr;7(2):87-91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antúnez C, Martín E, Cornejo-García JA, Blanca-Lopez N, R-Pena R, Mayorga C, et al. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions to peni- cillins and other betalactams. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(26):3327- 33. [CrossRef]
- Kulhas Celik I, Guvenir H, Hurmuzlu S, Toyran M, Civelek E, Kocabas CN, et al. The negative predictive value of 5-day drug provocation test in nonimmediate beta-lactam allergy in children. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124(5):494-9. [CrossRef]
- Fouhse JM, Yang K, More-Bayona J, Gao Y, Goruk S, Plastow G, Field CJ, Barreda DR, Willing BP. Neonatal Exposure to Amoxicillin Alters Long-Term Immune Response Despite Transient Effects on Gut-Microbiota in Piglets. Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 4;10:2059. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Miyata T, Shinohara M. Effect of antibiotics on rat leukocyte function. J Osaka Dent Univ. 1998 Apr;32(1):9-15. [PubMed]
- Lee, WM. Drug-induced acute liver failure. Clin Liver Dis. 2013 Nov;17(4):575-86, viii. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Larrey D, Pageaux GP. Drug-induced acute liver failure. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Feb;17(2):141-3. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrajolo C, Verhamme KM, Trifirò G, 't Jong GW, Giaquinto C, Picelli G, Oteri A, de Bie S, Valkhoff VE, Schuemie MJ, Mazzaglia G, Cricelli C, Rossi F, Capuano A, Sturkenboom MC. Idiopathic acute liver injury in paediatric outpatients: incidence and signal detection in two European countries. Drug Saf. 2013 Oct;36(10):1007-16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortland I, Mirjalili M, Kullak-Ublick GA, Peymani P. Drug-induced liver injury in Switzerland: an analysis of drug-related hepatic disorders in the WHO pharmacovigilance database VigiBase™ from 2010 to 2020. Swiss Med Wkly. 2021 May 12;151:w20503. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Rodríguez LA, Stricker BH, Zimmerman HJ. Risk of acute liver injury associated with the combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Jun 24;156(12):1327-32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucena MI, Molokhia M, Shen Y, Urban TJ, Aithal GP, Andrade RJ, Day CP, Ruiz-Cabello F, Donaldson PT, Stephens C, Pirmohamed M, Romero-Gomez M, Navarro JM, Fontana RJ, Miller M, Groome M, Bondon-Guitton E, Conforti A, Stricker BH, Carvajal A, Ibanez L, Yue QY, Eichelbaum M, Floratos A, Pe'er I, Daly MJ, Goldstein DB, Dillon JF, Nelson MR, Watkins PB, Daly AK; Spanish DILI Registry; EUDRAGENE; DILIN; DILIGEN; International SAEC. Susceptibility to amoxicillin-clavulanate-induced liver injury is influenced by multiple HLA class I and II alleles. Gastroenterology. 2011 Jul;141(1):338-47. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Abajo FJ, Montero D, Madurga M, García Rodríguez LA. Acute and clinically relevant drug-induced liver injury: a population based case-control study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;58(1):71-80. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Habarugira JMV, Figueras A. Antimicrobial stewardship: can we add pharmacovigilance networks to the toolbox? Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 May;77(5):787-790. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong L, Liu X, Wang X, de Leeuw W, Jonker M, Brul S, Ter Kuile B. Driving factors for beta-lactam resistance gene amplification during de novoresistance evolution in E. coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Jul 23:e0044125. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benninger, MS. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium extended release tablets: a new antimicrobial for the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis and community-acquired pneumonia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003 Oct;4(10):1839-46. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader MS, Loeb M, Brooks AA. An update on the management of urinary tract infections in the era of antimicrobial resistance. Postgrad Med. 2017 Mar;129(2):242-258. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Moreno MO, Centelles-Serrano MJ, Cortell-Ortolá M, Fort-Gallifa I, Ruiz J, Llovet-Lombarte MI, Picó-Plana E, Jardí-Baiges AM. Molecular epidemiology and resistance mechanisms involved in reduced susceptibility to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from a chronic care centre. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 May;37(5):462-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauben M, Zhou X. Quantitative methods in pharmacovigilance: focus on signal detection. Drug Saf. 2003;26(3):159-86. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo F, De Sarro A, Caputi AP, Polimeni G. Amoxicillin and amoxicillin plus clavulanate: a safety review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2009 Jan;8(1):111-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammendolia I, Mannucci C, Cardia L, Calapai G, Gangemi S, Esposito E, Calapai F. Pharmacovigilance on cannabidiol as an antiepileptic agent. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1091978. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sportiello L, Capuano A. Sex and gender differences and pharmacovigilance: a knot still to be untied. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 17;15:1397291. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- MedDRA and pharmacovigilance: a complex and little-evaluated tool. Prescrire Int. 2016 Oct;25(175):247-250. [PubMed]
- Hauben, M. Signal detection in the pharmaceutical industry: integrating clinical and computational approaches. Drug Saf. 2007;30(7):627-30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bate A, Evans SJ. Quantitative signal detection using spontaneous ADR reporting. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2009 Jun;18(6):427-36. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faillie, JL. Case-non-case studies: Principle, methods, bias and interpretation. Therapie. 2019 Apr;74(2):225-232. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Medicinal Product |
Total number of ICSRs | Serious ICSRs |
Non serious ICSRs | Serious/non serious ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 7900 | 3685 | 4215 | 0.87 |
| Amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid |
10329 | 5114 | 5215 | 0.98 |
| SOC | Male cases (N = 1658) |
Female cases (N = 2032) |
Male and female cases |
% of all serious cases | Significance level (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 655 (40.6%) |
959 (59.4%) |
1614 | 43.7% | 0.0034* |
| Immune system disorders | 383 (42.1%) |
527 (57.9%) |
910 | 24.7% | 0.1226 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 186 (40.5%) |
273 (59.5%) |
459 | 12.4% | 0.0737 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 161 (38.7%) |
255 (61.3%) |
416 |
11.3% | 0.0158* |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 98 (36.2%) |
173 (63.8%) |
271 | 7.3% | 0.0054* |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 124 (48.2%) |
133 (51.8%) |
257 | 7.0% | 0.3017 |
| Nervous system disorders | 99 (41.2%) |
141 (58.8%) |
240 | 6.5% | 0.2669 |
| SOC | Males (N = 2238) |
Females (N = 2579) |
Male and female cases |
% of all serious cases | Significance level (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 1189 (50.8%) |
1149 (49.2%) |
2338 | 48.5% | 0.0005* |
| Immune system disorders | 547 (48.5%) |
580 (51.5%) |
1127 | 23.4% | 0.2087 |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 453 (54.3%) |
381 (45.7%) |
834 | 17.3% | 0.0001* |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 300 (41.4%) |
425 (58.6%) |
725 |
15.0% | 0.0107* |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 322 (44.8%) |
397 (55.2%) |
719 | 14.9% | 0.4007 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 202 (41.6%) |
284 (58.4%) |
486 | 10.1% | 0.0395* |
| Nervous system disorders | 147 (46.8%) |
167 (53.2%) |
314 | 6.5% | 0.9028 |
|
SOC |
Cases of SARs to amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid |
All other cases of SARs to amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid |
Cases of SARs to amoxicillin |
All other cases of SARs to amoxicillin |
ROR of cases of SARs to amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid vs amoxicillin (95% C.I.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 2338 | 7991 | 1614 | 6286 | 1.13 (1.06-1.22) |
| Immune system disorders | 1127 | 9202 | 910 | 6990 | 0.94 (0.86-1.03) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 719 | 9610 | 459 | 7441 | 1.21 (1.07-1.37) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 725 | 9604 | 416 | 7484 | 1.36 (1.20-1.54) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 486 | 9843 | 271 | 7629 | 1.39 (1.19-162) |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 834 | 9495 | 257 | 7643 | 2.61 (2.26-3.01) |
| Nervous system disorders | 314 | 10015 | 240 | 7660 | 1.00 (0.84-1.19) |
|
Medicinal product |
Total number of serious cases |
Male cases |
Female cases |
Cases reporting “Hepatobiliary disorders” |
Male cases reporting “Hepatobiliary disorders” |
Female cases reporting “Hepatobiliary disorders” |
Significance level P |
| Amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid |
10329 | 4558 | 5771 | 834 | 453 |
381 |
0.00001 |
| Amoxicillin | 7900 | 3219 | 4681 | 257 | 124 |
133 |
0.02211 |
| Medicinal product |
Serious cases of “Hepatobiliary disorders” |
All other serious cases |
ROR of serious cases of “Hepatobiliary disorders” to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid vs amoxicillin (95% C.I.) |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid | 834 | 3983 | 2.78 (2.41-3.24) |
| Amoxicillin | 45 | 3433 |
| Medicinal product |
Total number of cases (serious and non serious) | Male serious and non serious cases |
Female serious and non serious cases | Cases reporting “Drug ineffective” as adverse reaction |
Male cases reporting “Drug ineffective” as adverse reaction |
Female cases reporting “Drug ineffective” as adverse reaction |
Significance level P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid |
10329 | 4558 | 5771 | 156 | 80 | 76 | 0.00001 |
| Amoxicillin | 7900 | 3219 | 4681 | 45 | 16 | 29 | N.S. |
| Medicinal product | Cases of “Drug ineffective” |
All other cases | ROR of cases of “Drug ineffective” to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid vs amoxicillin (95% C.I.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid | 156 | 10173 | 2.68 (1.92-3.73) |
| Amoxicillin | 45 | 7855 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





