Submitted:
09 July 2025
Posted:
10 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
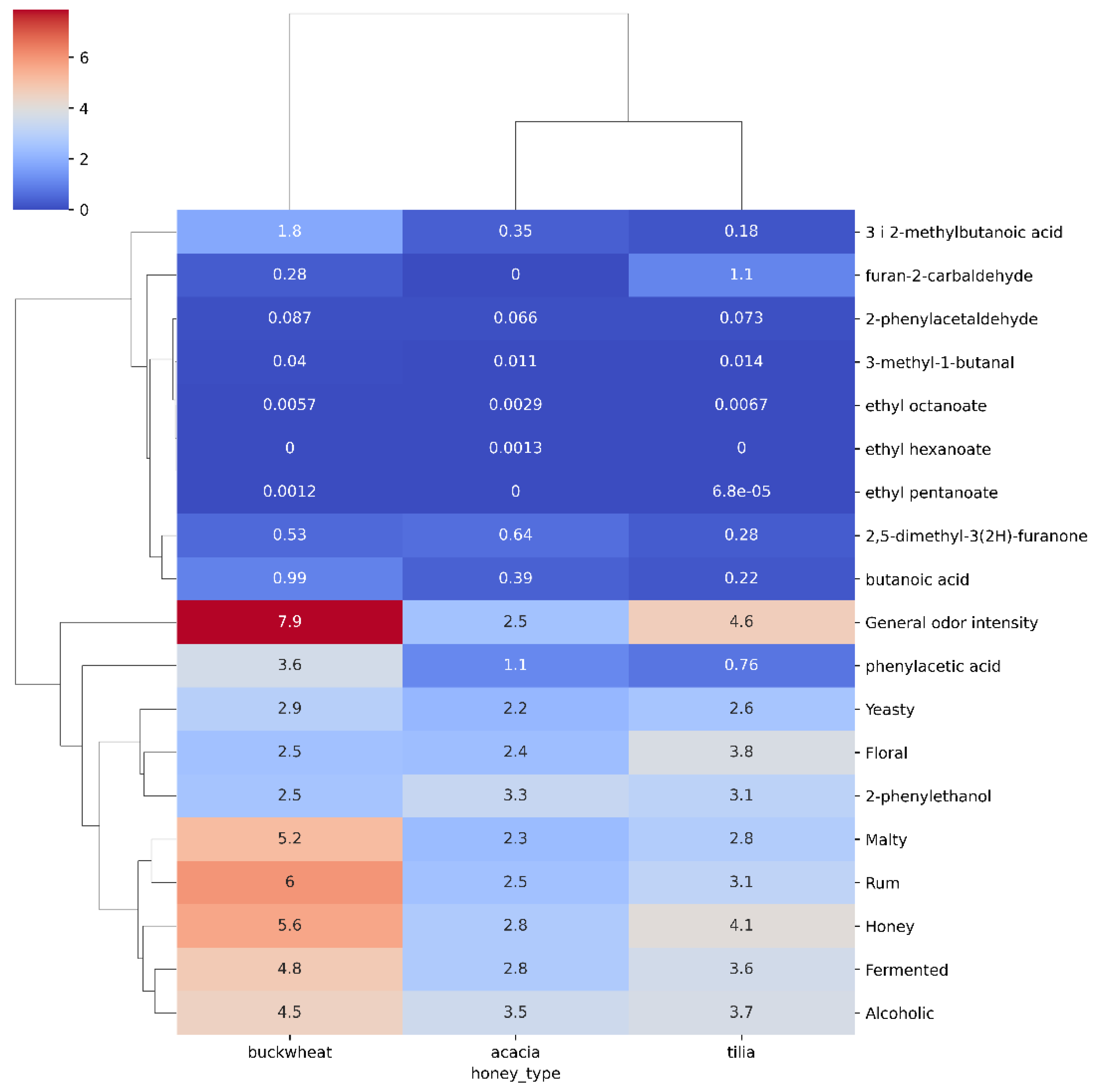
2.1. Hierarchical Analysis of Mead Aroma Compounds
2.2. Interpretation of K-Means of Honey Aroma Compounds
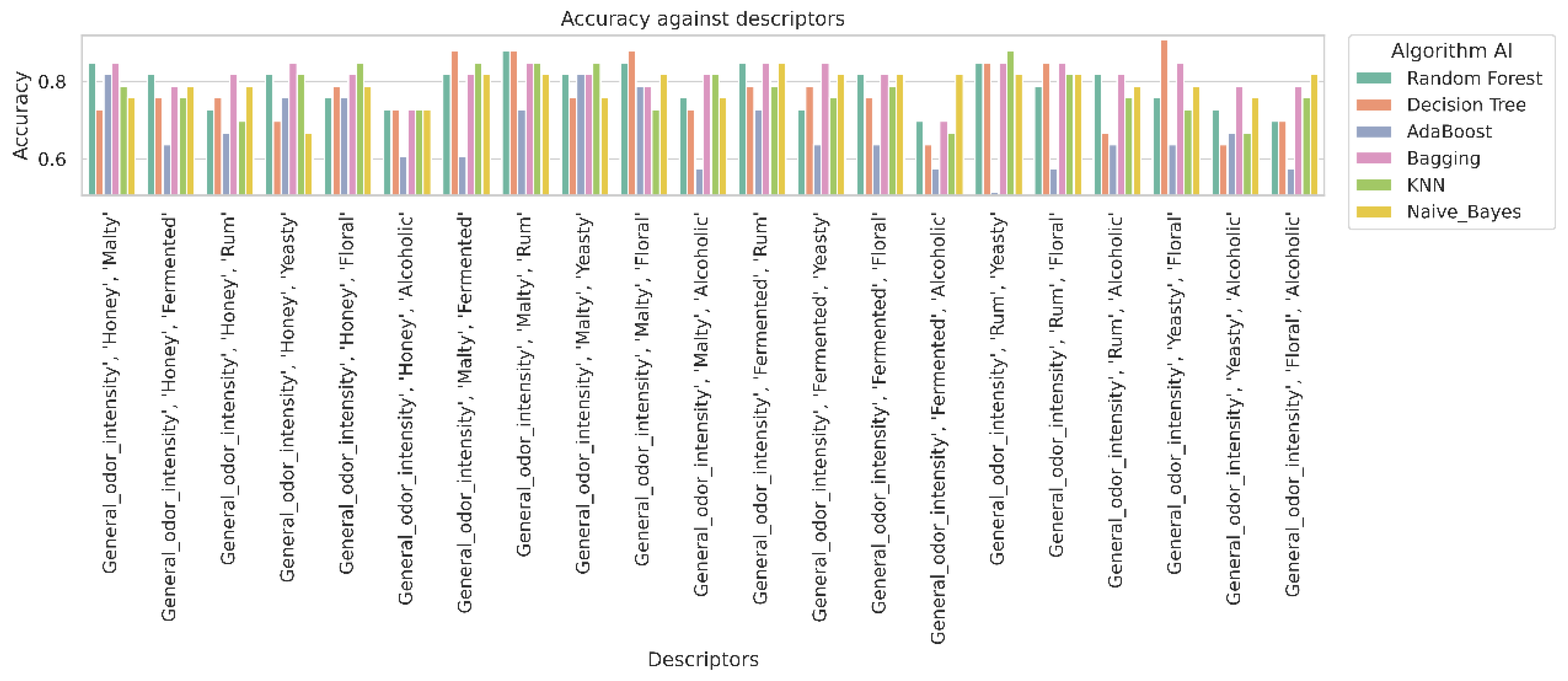
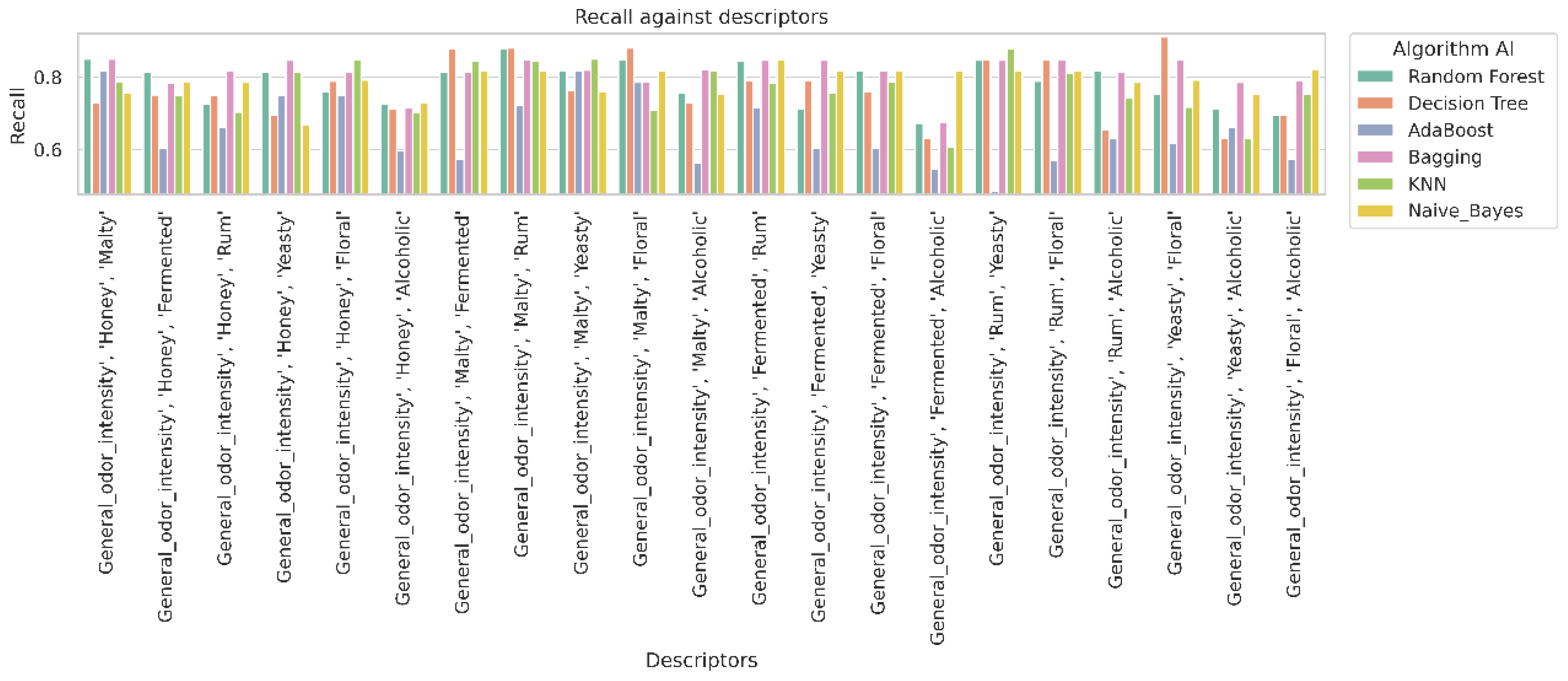
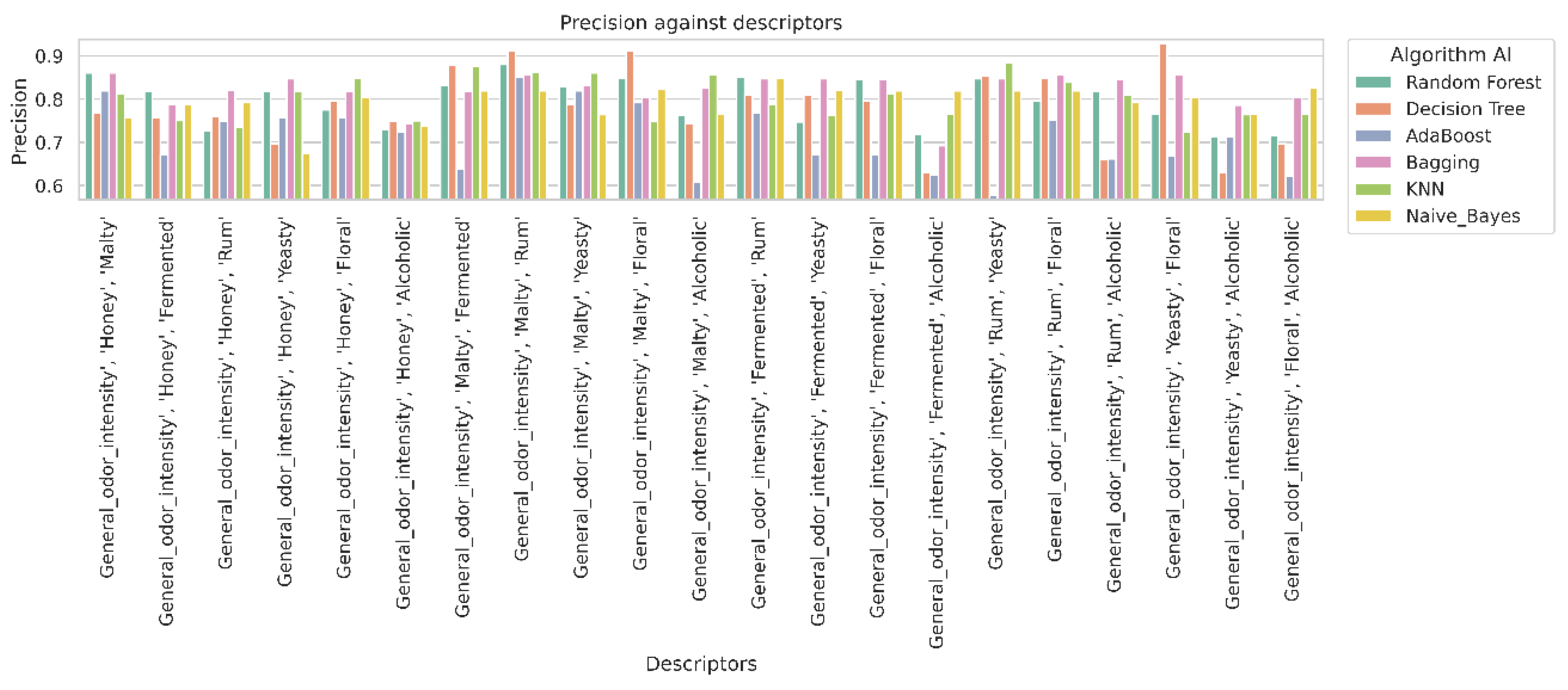
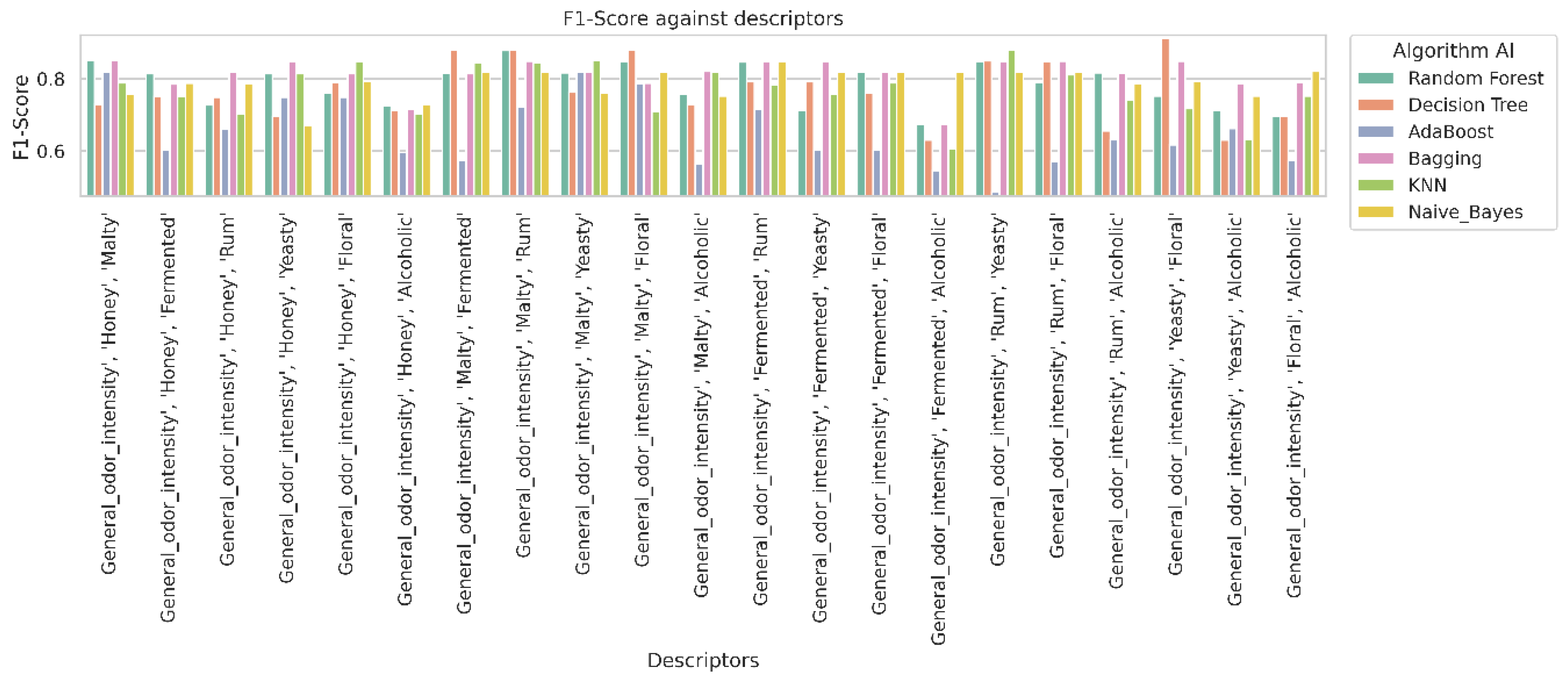
2.3. Machine Learning
2.4. Analysis of Classifier Performance Based on Confusion Matrix Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Parameter Selection for Classification Models
3.4. Model Training and Testing
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B.; Jung, C. Honey Bees and Their Brood: A Potentially Valuable Resource of Food, Worthy of Greater Appreciation and Scientific Attention. J Ecol Environ 2021, 45, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S. Honey as Nutrient and Functional Food : A Review. Bee Product Science 2015.
- Cicha-Wojciechowicz, D.; Drabińska, N.; Majcher, M.A. Influence of Honey Varieties, Fermentation Techniques, and Production Process on Sensory Properties and Odor-Active Compounds in Meads. Molecules 2024, 29, 5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.P.; Mendes-Ferreira, A.; Dias, L.G.; Oliveira, J.M.; Estevinho, L.M.; Mendes-Faia, A. Volatile Composition and Sensory Properties of Mead. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starowicz, M.; Granvogl, M. Effect of Wort Boiling on Volatiles Formation and Sensory Properties of Mead. Molecules 2022, 27, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviyanto, A.; Abdulla, W.H. Honey Botanical Origin Classification Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. J Food Eng 2020, 265, 109684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E. Detection of Honey Adulteration Using Machine Learning. PLOS Digital Health 2024, 3, e0000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulu, M.; Oertel, E.; Serra, R.; Farre, R.; Spano, N.; Caredda, M.; Malfatti, L.; Sanna, G. Classification of Unifloral Honeys from SARDINIA (Italy) by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Random Forest. Molecules 2020, 26, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Yang, W. An Improved Random Forest Algorithm. J Phys Conf Ser 2020, 1646, 012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitto, P.M.; Gasperi, F.; Biasioli, F.; Trainotti, E.; Furlanello, C. Modern Data Mining Tools in Descriptive Sensory Analysis: A Case Study with a Random Forest Approach. Food Qual Prefer 2007, 18, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybył, K.; Walkowiak, K.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Efficiency of Identification of Blackcurrant Powders Using Classifier Ensembles. Foods 2024, 13, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ÇUKUR, T.; ÇUKUR, F. Determining Factors Affecting Cooperative Membership of the Beekeepers Using Decision Tree Algorithms. Tarım Bilimleri Dergisi 2022, 28, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, Z.; Yücel, B.; Saner, G.; Takma, Ç. Investigating the Impact of Climate Parameters on Honey Yield under Migratory Beekeeping Conditions through Decision Tree Analysis: The Case of İzmir Province. ANADOLU Ege Tarımsal Araştırma Enstitüsü Dergisi 2023, 33, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, R.; Jain, D.; Patwardhan, M.; Puri, A.; Karande, S.; Rai, B. Data Based Predictive Models for Odor Perception. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, Y.; Nakamoto, T. Predictive Modeling for Odor Character of a Chemical Using Machine Learning Combined with Natural Language Processing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybył, K. Explainable AI: Machine Learning Interpretation in Blackcurrant Powders. Sensors 2024, 24, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Efficient Extraction of Deep Image Features Using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for Applications in Detecting and Analysing Complex Food Matrices. Trends Food Sci Technol 2021, 113, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischl, B.; Binder, M.; Lang, M.; Pielok, T.; Richter, J.; Coors, S.; Thomas, J.; Ullmann, T.; Becker, M.; Boulesteix, A.; et al. Hyperparameter Optimization: Foundations, Algorithms, Best Practices, and Open Challenges. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Castillo, C.; Astray, G.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. Random Forest, Artificial Neural Network, and Support Vector Machine Models for Honey Classification. eFood 2020, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahasneh, M.; Al-U’datt, M.; Rababah, T.; Al-Widyan, M.; Abu Kaeed, A.; Al-Mahasneh, A.J.; Abu-Khalaf, N. Classification and Prediction of Bee Honey Indirect Adulteration Using Physiochemical Properties Coupled with K-Means Clustering and Simulated Annealing-Artificial Neural Networks (SA-ANNs). J Food Qual 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Awadhi, M.A.; Deshmukh, R.R. Honey Classification Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 Smart Technologies, Communication and Robotics (STCR); IEEE, October 9 2021; pp. 1–5.
- Zuo, M.; Chen, X.; Sui, L. Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of Visual Stimulation-Induced EEG Signals in 2D and 3D VR Videos. Brain Sci 2025, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, F.; Tarazona, A.; Mateo, E.M. Comparative Study of Several Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of Unifloral Honeys. Foods 2021, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Razavi, S.; Choi, S.-M. Enhancing Flood-Prone Area Mapping: Fine-Tuning the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Algorithm for Spatial Modelling. Int J Digit Earth 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Xiao, K.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y. Automated Hyperparameter Optimization of Gradient Boosting Decision Tree Approach for Gold Mineral Prospectivity Mapping in the Xiong’ershan Area. Minerals 2022, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, J. A Fast Parameters Selection Method of Support Vector Machine Based on Coarse Grid Search and Pattern Search. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fourth Global Congress on Intelligent Systems; IEEE, December 2013; pp. 77–81.
- Pomme, L.-E.; Bourqui, R.; Giot, R.; Auber, D. Relative Confusion Matrix: Efficient Comparison of Decision Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference Information Visualisation (IV); IEEE, July 2022; Vol. 2022-July, pp. 98–103.
- Khan, M.M. Enhancing Honey Quality Control: A Machine Learning-Based Approach Using Hyperspectral Imaging. VFAST Transactions on Software Engineering 2025, 13, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHOU, M.; LONG, T.; ZHAO, Z.; CHEN, J.; WU, Q.; WANG, Y.; ZOU, Z. Honey Quality Detection Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Food Science and Technology 2023, 43, e98822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputro, A.H.; Aprichilia, C. Classification System of Honey Floral Origin Based on Visual Near-Infrared Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Information Engineering and Technology (SIET); IEEE, September 1 2019; pp. 125–129.
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Zhou, F.; Peng, J.; Sun, M. Fast Classification of Geographical Origins of Honey Based on Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes Mantovani, R.; Horváth, T.; Rossi, A.L.D.; Cerri, R.; Barbon Junior, S.; Vanschoren, J.; Carvalho, A.C.P.L.F. de Better Trees: An Empirical Study on Hyperparameter Tuning of Classification Decision Tree Induction Algorithms. Data Min Knowl Discov 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Kumar, D.; Mittal, M. An Ensemble Approach for Classification and Prediction of Diabetes Mellitus Using Soft Voting Classifier. International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering 2021, 2, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catal, C.; Tufekci, S.; Pirmit, E.; Kocabag, G. On the Use of Ensemble of Classifiers for Accelerometer-Based Activity Recognition. Appl Soft Comput 2015, 37, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2011, 12. [Google Scholar]
- van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. Scikit-Image: Image Processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Ho, T.K. Machine Learning Made Easy: A Review of Scikit-Learn Package in Python Programming Language. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics 2019, 44, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python in a Nutshell - Alex Martelli, Anna Martelli Ravenscroft, Steve Holden, Paul McGuire - Google Książki. Available online: https://books.google.pl/books?hl=pl&lr=&id=2WSmEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT28&dq=python&ots=oUp1BWZF48&sig=kI8hqMTywjvESsgtVj8x9K1hr4U&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=python&f=false (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Kanungo, T.; Mount, D.M.; Netanyahu, N.S.; Piatko, C.D.; Silverman, R.; Wu, A.Y. An Efficient K-Means Clustering Algorithm: Analysis and Implementation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2002, 24, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
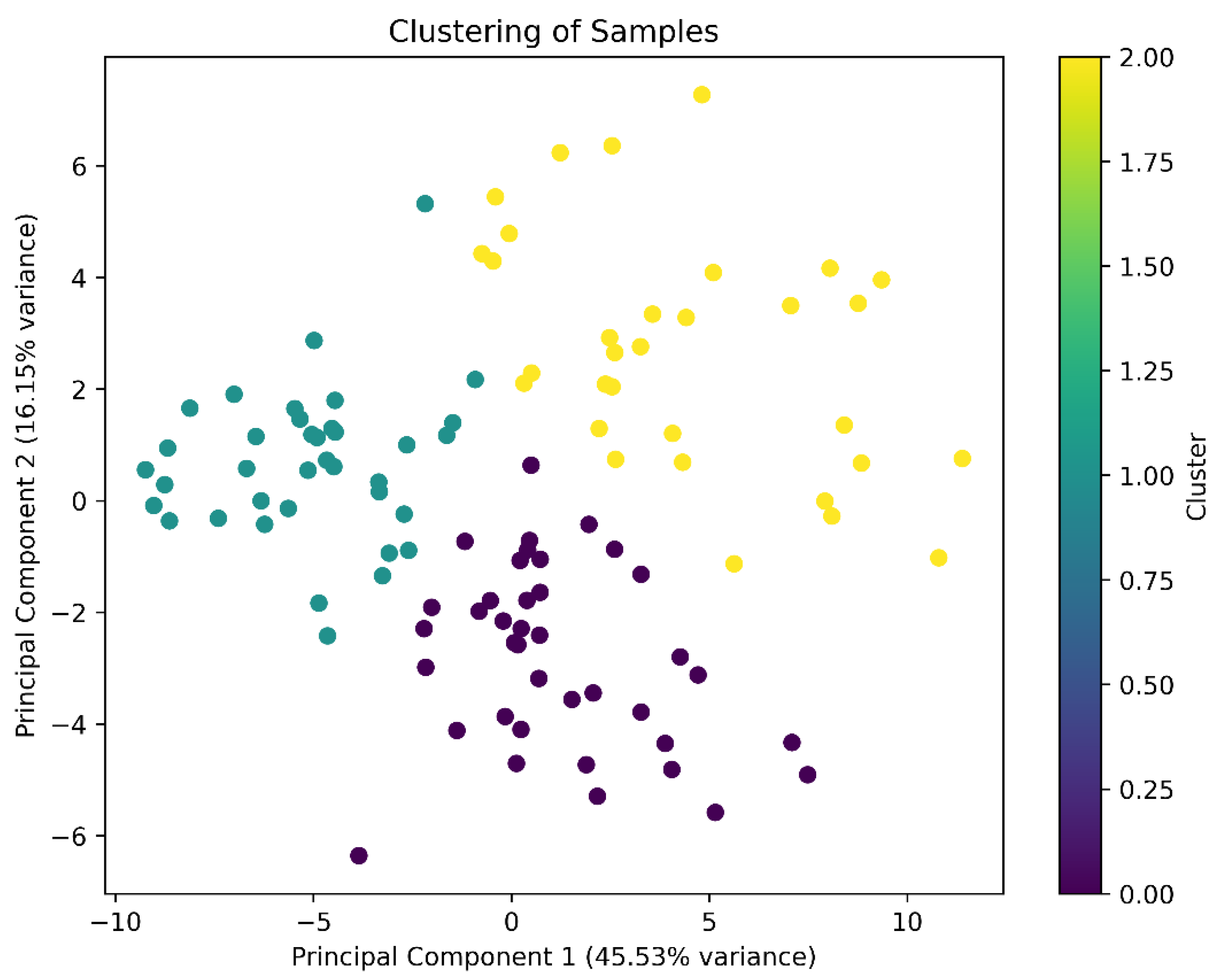
| CLUSTER | General_odor_intensity | Honey | Malty | Yeasty | Fermented | Alcoholic | Floral | Rum |
| 0 | 4.182051 | 4.125641 | 3.446154 | 4.164103 | 4.312821 | 4.997436 | 4.853846 | 4.164103 |
| 1 | 3.210811 | 2.435135 | 1.643243 | 0.943243 | 1.878378 | 2.097297 | 1.294595 | 1.513514 |
| 2 | 8.065625 | 6.165625 | 5.453125 | 2.468750 | 5.046875 | 4.656250 | 2.253125 | 6.203125 |
| No. | Descriptors | Alorithm AI | Best Hyperparameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Honey', 'Malty' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 500} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 5} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'chebyshev', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 2 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Honey', 'Fermented' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 6} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 5} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 3 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Honey', 'Rum' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 3, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 5} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 200} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 2} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 4 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Honey', 'Yeasty' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 3, 'n_estimators': 100} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 200} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'chebyshev', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 5 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Honey', 'Floral' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 50} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 6} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'euclidean', 'n_neighbors': 7} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 6 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Honey', 'Alcoholic' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 1000} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 5} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'minkowski', 'n_neighbors': 2} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 7 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Malty', 'Fermented' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 50} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 7} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 8 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Malty', 'Rum' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 5} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 5} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 9 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Malty', 'Yeasty' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 50} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 6} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 200} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'minkowski', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 10 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Malty', 'Floral' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 4} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'chebyshev', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 11 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Malty', 'Alcoholic' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 4} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 12 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Fermented', 'Rum' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 5, 'n_estimators': 50} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 6} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 500} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'euclidean', 'n_neighbors': 2} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 13 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Fermented', 'Yeasty' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 6} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'euclidean', 'n_neighbors': 5} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 14 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Fermented', 'Floral' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 5} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 15 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Fermented', 'Alcoholic' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 3, 'n_estimators': 100} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'euclidean', 'n_neighbors': 2} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 16 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Rum', 'Yeasty' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 50} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 7} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 1.0, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 5} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 17 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Rum', 'Floral' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 500} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 500} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'chebyshev', 'n_neighbors': 2} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 18 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Rum', 'Alcoholic' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 5, 'n_estimators': 100} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'euclidean', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 19 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Yeasty', 'Floral' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 6} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'chebyshev', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 20 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Yeasty', 'Alcoholic' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 3, 'n_estimators': 50} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'chebyshev', 'n_neighbors': 2} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09} | ||
| 21 | 'General_odor_intensity', 'Floral', 'Alcoholic' | Random Forest | {'max_depth': 7, 'n_estimators': 10} |
| Decision Tree | {'max_depth': 3} | ||
| AdaBoost | {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators': 100} | ||
| Bagging | {'n_estimators': 50} | ||
| KNN | {'metric': 'manhattan', 'n_neighbors': 3} | ||
| Naive_Bayes | {'var_smoothing': 1e-09 |
| Machine learning algorithm type | Hyperparameters used | Value |
|---|---|---|
| DecisionTree | max_depth | 3,4,5,6,7 |
| RandomForest | max_depth | 3,4,5,6,7 |
| RandomForest | n_estimators | 10, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 |
| AdaBoost | n_estimators | 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 |
| AdaBoost | learning_rate | 0.01, 0.1, 1.0 |
| KNN | n_neighbors | 2,3,5,7 |
| KNN | metric | euclidean, manhattan, chebyshev, minkowski |
| KNN | weights | 'uniform', 'distance' |
| Bagging | n_estimators | 50,100,200 |
| Naive_Bayes | var_smoothing | 1e-9, 1e-8, 1e-7, 1e-6, 1e-5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





