Submitted:
27 June 2025
Posted:
30 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
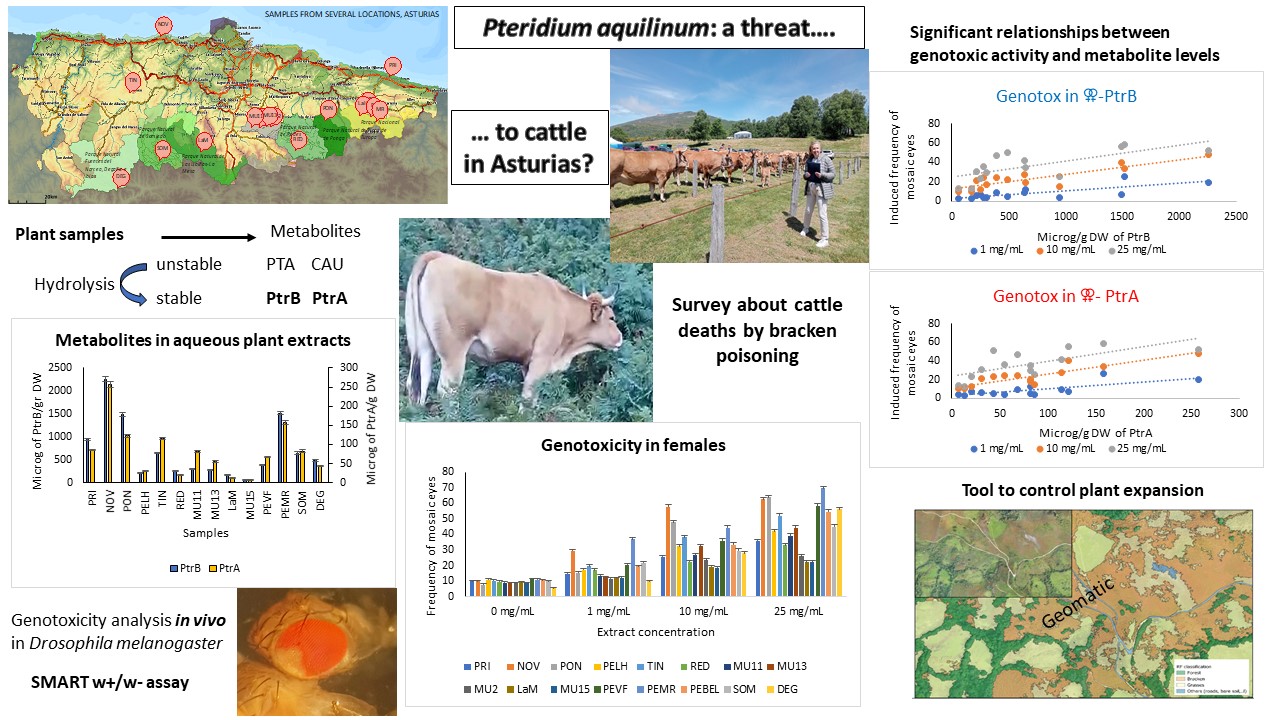
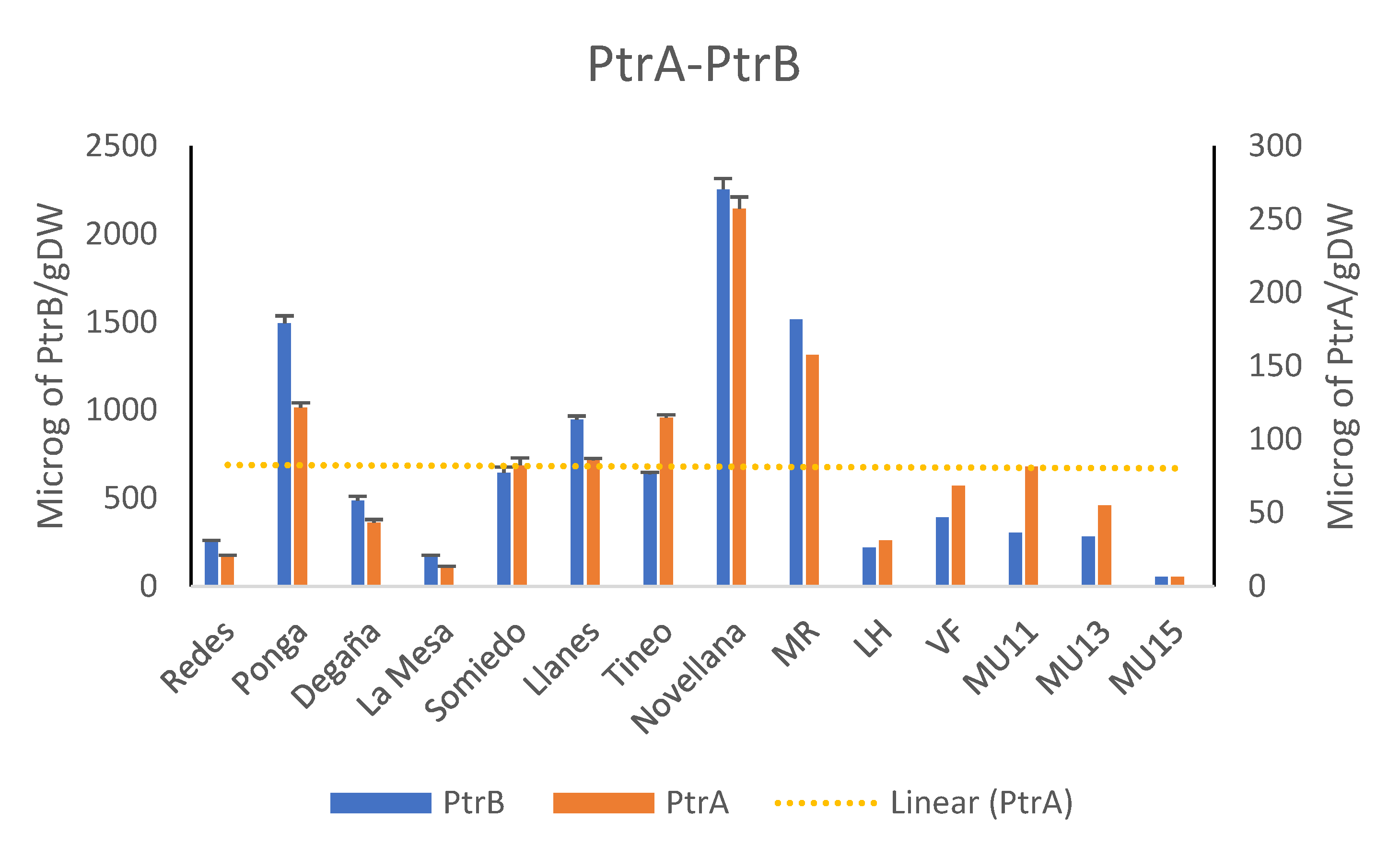
2.1. Quantification of Toxic Metabolites in Croziers Samples
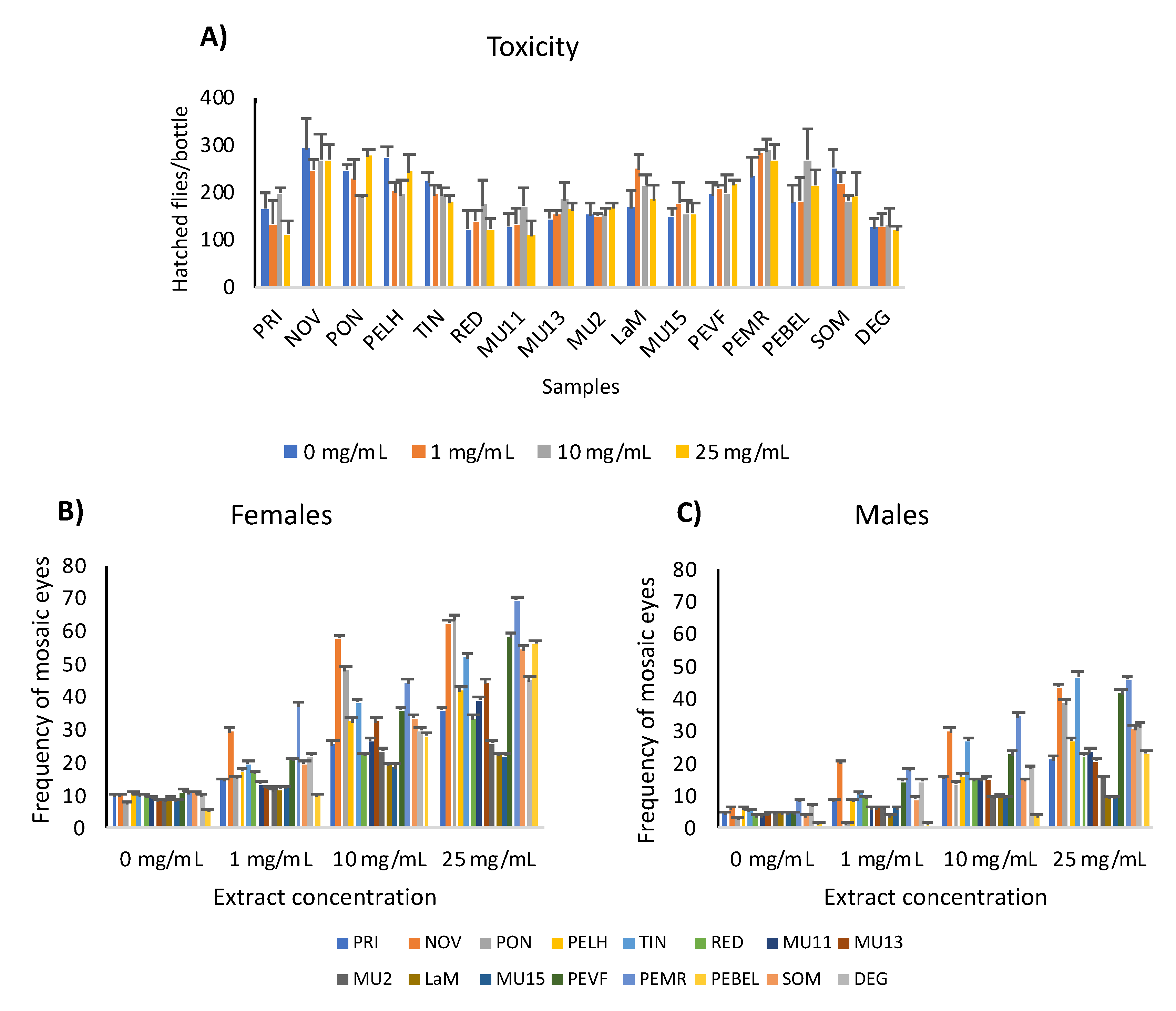
2.2. Genotoxicity Analysis of Aqueous Plant Extracts
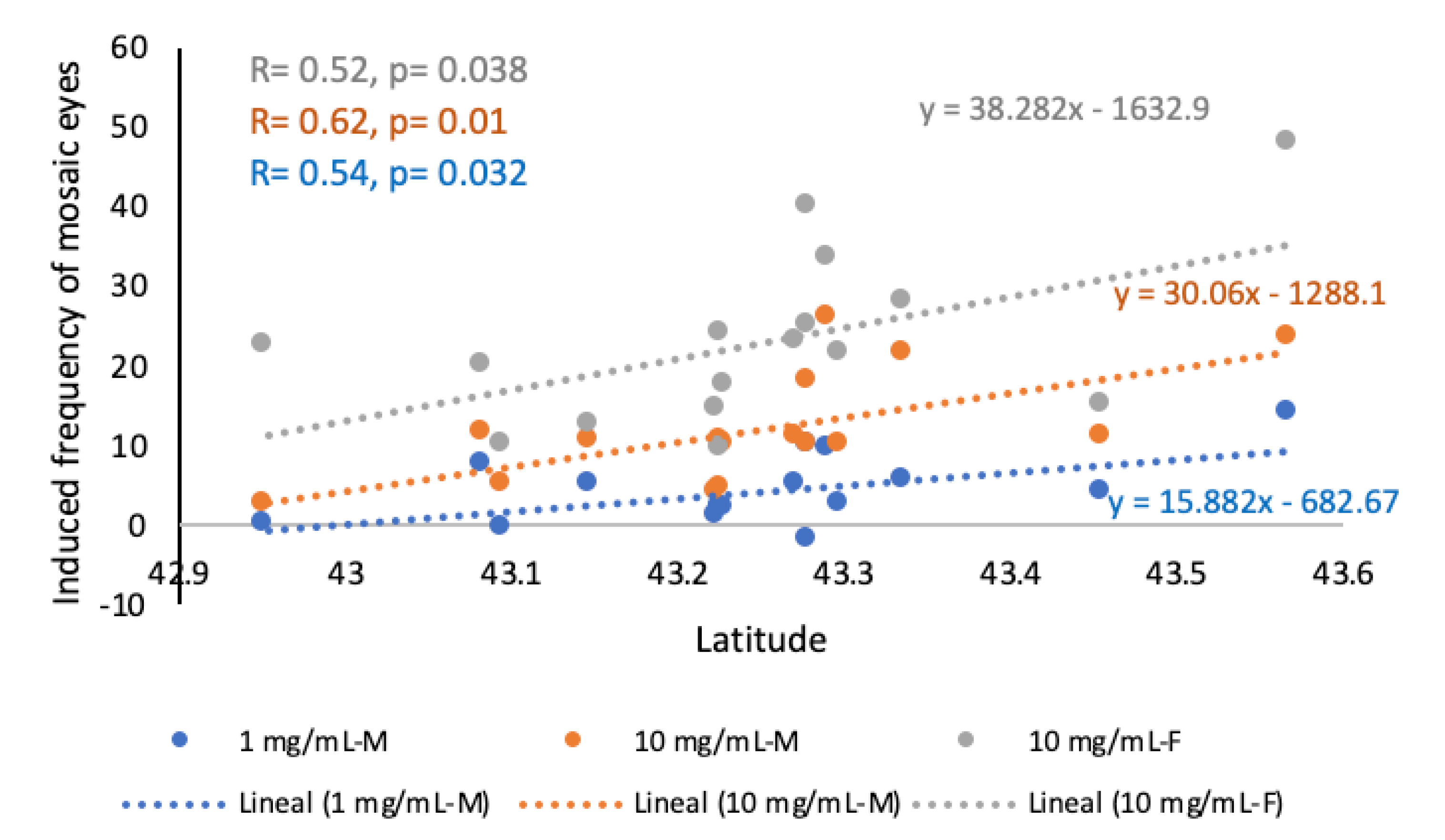
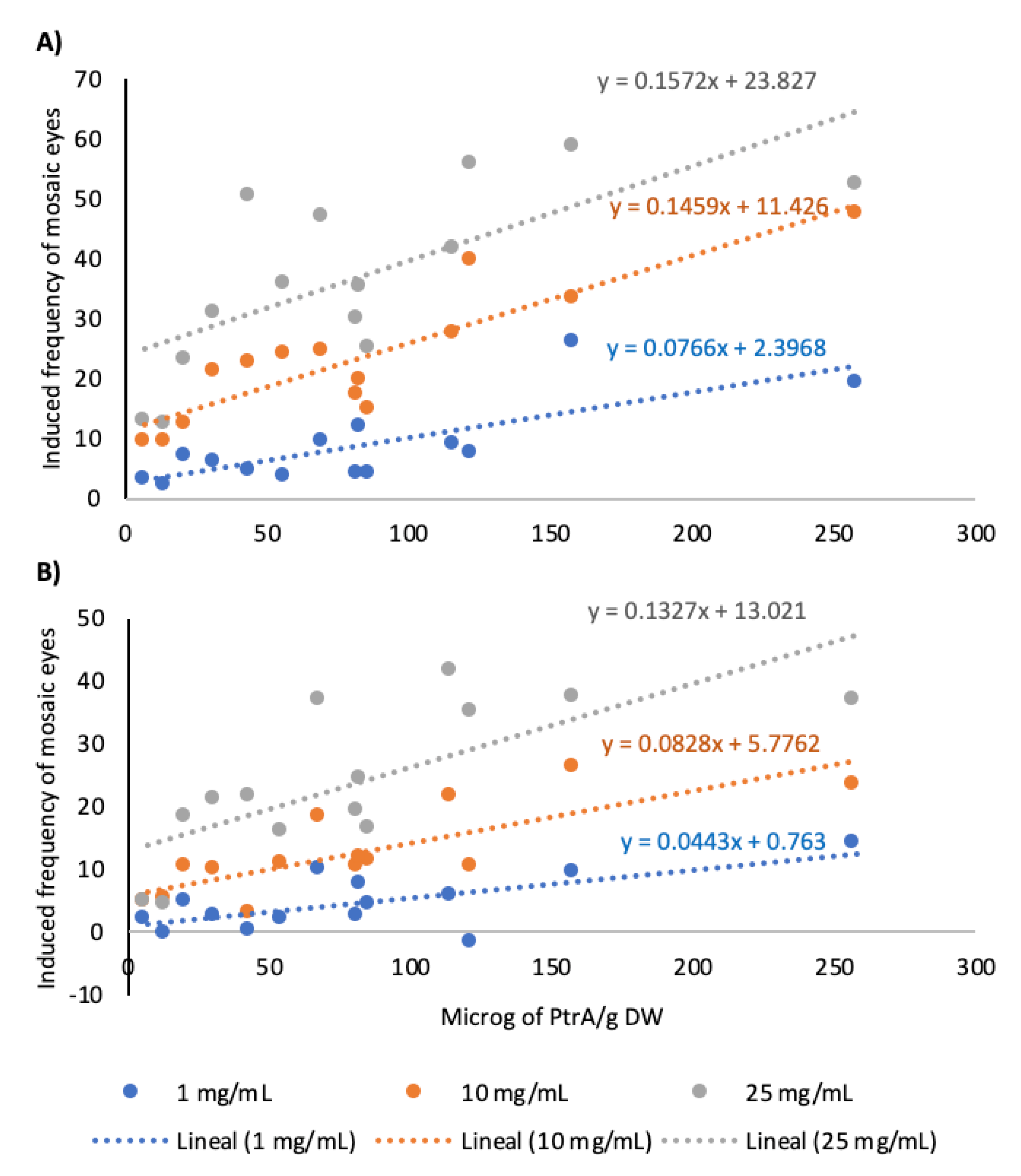
2.3. Relationships Between Pterosin Levels and Genotoxic Activities
2.4. Results of Farmer’s Surveys
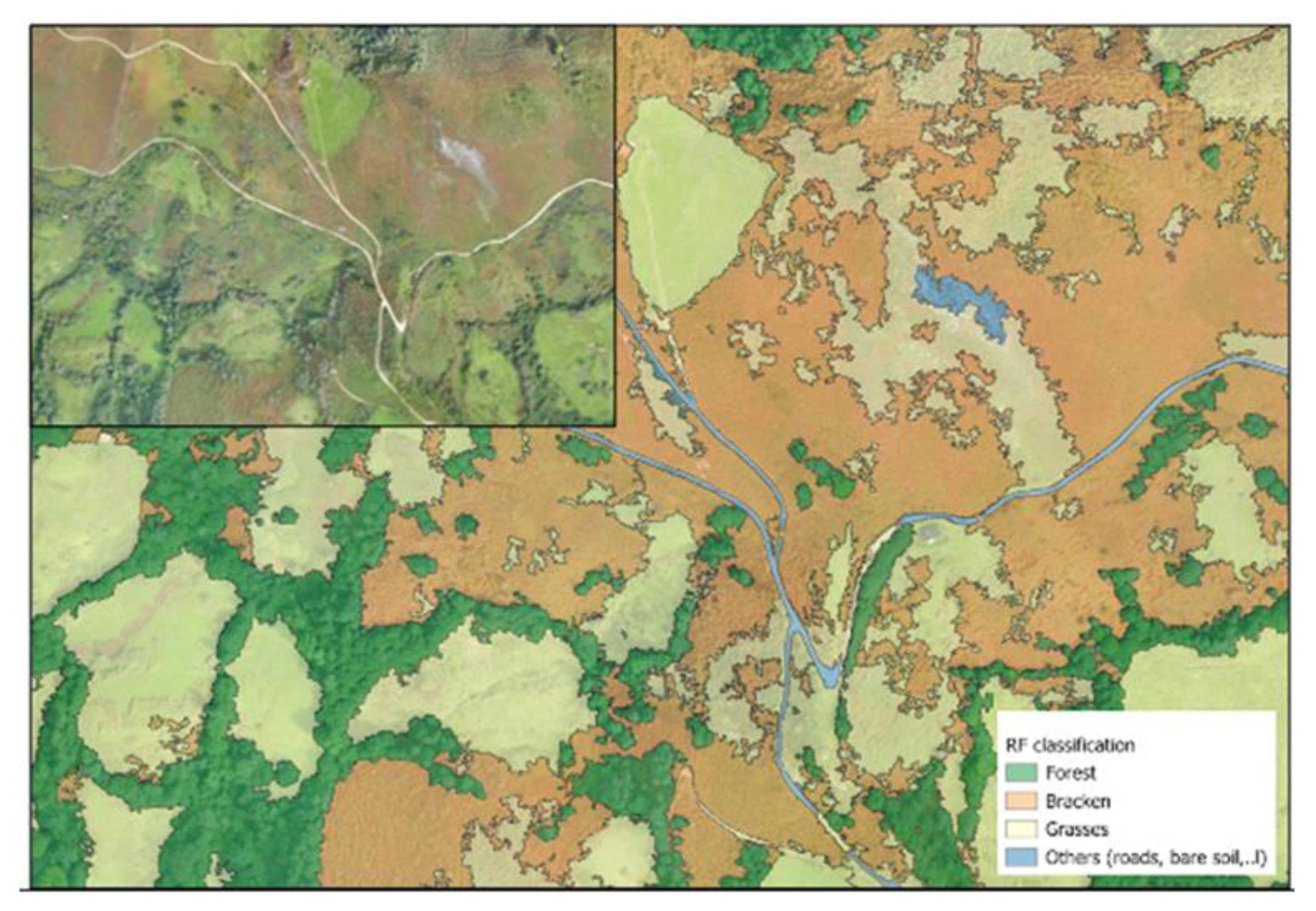
2.5. Implementing a Tool to Map Bracken
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Sites and Pteridium Plant Collection
4.2. Metabolite Analysis: Determination of Pterosins in Croziers from Brackens
4.3. Genotoxicity Analysis: SMART Assay
4.4. Surveys Obtained from Farmers
4.5. Implementing a Tool to Map Bracken
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuettpelz, E. , Schneider, H., Smith, A.R. et al. A community-derived classification for extant lycophytes and ferns. J. Syst. Evol. 2016, 54, 563–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L., Seawright, A.A. Bracken fern (Pteridium spp.). Carcinogenicity and human health—A brief review. Nat. Toxins, 1995, 3(1), 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Marrs, R.H., Watt, A.S. Biological Flora of the British Isles: Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn, J. Ecol. 2006, 4(6), 1272-1321. [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H., Donnelly, E., Strobel, B.W., Holm, P.E., Hansen, H.C.B. Land management of bracken needs to account for bracken carcinogens. A case study from Britain, J. Env. Man. 2015, 151, 258-266. [CrossRef]
- Pakeman R.J., Marrs R.H., Howard D.C., Barr C.J., Fuller R.M. The bracken problem in Great Britain: Its present extent and future changes. Appl. Geogr 1996, 16, 65-86. [CrossRef]
- Pakeman, R.J., Le Duc, M.G., Marrs, R. A review of current bracken control and associated vegetation strategies in Great Britain. Web Ecol. 2002. 3, 6-11. https://doi.org/10.5194/we-3-6-2002 Alonso Amelot, M.E., Avendaño, M. Possible association between gastric cancer and bracken fern in Venezuela. An epidemiological study. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 252-259. [CrossRef]
- Holland, J., Aplin, P. Super-resolution image analysis as a means of monitoring bracken (Pteridium aquilinum) distributions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 75, 48-63. [CrossRef]
- Cao, H., Chai, T.T., Wang, X., Morais-Braga, M.F.B., Yang, J.H., Wong, F.C., Wang, R., Yao, H., Cao, J., Cornara, L., Burlando, B., Wang, Y., Xiao, J., Coutinho, H.D.M. 2017. Phytochemicals from fern species: potential for medicine applications. Phytochem Rev: pPSE, 2017, 16: 379-440. [CrossRef]
- Matongera, T.N. , Mutanga O., Dube T., Sibanda M. Detection and mapping the spatial distribution of bracken fern weeds using the Landsat 8 OLI new generation sensor. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G., Booth, K.E., Cox, E.S., Pakeman, R.J., Le Duc, M.G., Connor, L., Blackbird, S., Marrs, R.H. Change to ecosystem properties through changing the dominant species: Impact of Pteridium aquilinum- Control and heathland restoration treatments on selected soil properties. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.C. Bracken fern invasion in southern yucatán: A case for land-change science. Geograph. Rev. 2004, 94, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Ouden, J. The role of bracken (Pteridium aquilinum) in forest dynamics. Doctoral Thesis. Wageningen University and Research. 2000. https://edepot.wur.nl/197082.
- Senyanzobe, J.M.V. , Mulei, J.M., Bizuru, E., Nsengimuremyi, C. Impact of Pteridium aquilinum on vegetation in Nyungwe forest, Rwanda. Heliyon, 2020, 6, e04806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, J. A biological hazard of our age: Bracken fern [Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn]. A review. Acta Vet. Hungarica, 2009, 57, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil da Costa, R.M., Bastos, M.M.S.M., Oliveira, P.A., Lopes, C. Bracken-associated human and animal health hazards: Chemical, biological and pathological evidence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012a, 203-204, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Aranha, P.C. R, Rasmussen, L.H., Wolf-Jäckel, G.A., Elvang Jensen, H.M., Bruun Hansen, H.C., Christian Frits, C. Fate of ptaquiloside—A bracken fern toxin—In cattle. PLoS One, 2019, 14, e0218628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malík, M., Mika, O.J., Navrátilová, Z., Killi, U.K., Tlustoš, P., Patočka, J. Health and environmental hazards of the toxic Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn (bracken fern). Plants, 2023, 13 (1), 18. [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E., Avendaño, M. Human carcinogenesis and bracken fern: a review of the evidence. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 675-686. [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H. , Kroghsbo S., Frisvad, J.C., Hansen, H.C.B. Occurrence of the carcinogenic bracken constituent ptaquiloside in fronds, topsoils and organic soil layers in Denmark. Chemosphere, 2003, 51, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, M.T. , Hayes, P.Y., Somerville, M.J., De Voss, J.J. Ptesculentoside, a novel sesquiterpene glucoside from the australian bracken fern Pteridium esculentum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 5, 1997–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, A. , Potter, D., O’Connor, P. 32P-Post-labelling analysis of DNA adducts formed in the upper gastrointestinal tissue of mice fed bracken extract or bracken spores. Brit. J. Cancer, 1996, 74, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M., Smith, B.L., Prakash, A.S. Bracken carcinogens in the human diet. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 1999, 44, 69-79. [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.M., Baird, M.S. Carcinogenic effects of ptaquiloside in bracken fern and related compounds. Br. J. Cancer, 2000, 83, 914-920. [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.N., O’Connor, P.J., Prakash, A.S., Shahin, M., Povey, A.C. Bracken (Pteridium aquilinum)-Induced DNA adducts in mouse tissues are different from the adduct induced by the activated form of the bracken carcinogen ptaquiloside. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 2001, 281, 589-594. [CrossRef]
- Dawra, R.K., Kurade, N.P., Sharma, O.P. Carcinogeniciy of the fern Pteridium aquilinum collected from an enzootic bovine haematuria-free hilly area in India. Curr. Sci. 83, 2002, 1005-1009. https://www.jstor.org/stable/24106927.
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E. The chemistry and toxicology of bioactive compounds in bracken fern (Pteridium ssp) with special reference to chemical ecology and carcinogenesis. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry, Atta-Uhr-Rahman, Ed. Elsevier Science. Amsterdam, 2002, 26, 685–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil da Costa, R.M., Coelho, P., Sousa, R., Bastos, M.M.S.M., Porto, B., Teixeira, J.P., Malheiro, I., Lopes, C. Multiple genotoxic activities of ptaquiloside in human lymphocytes: Aneugenesis, clastogenesis and induction of sister chromatid exchange. Mutat. Res. 2012b, 747(1), 77-81. [CrossRef]
- Oliveros-Bastidas, A. , Calcagno-Pissarelli, M.P., Naya, M., Ávila-Núñez, J.L., Alonso-Amelot, M.E. Human gastric cancer, Helicobacter pylori and bracken carcinogens: A connecting hypothesis. Med. Hypoth. 2016, 88, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P.J., Alonso-Amelot, M.E., Roberts, S.A., Povey, A.C. The role of bracken fern iludanes in bracken fern-induced toxicities. Mut. Res.-Rev. Mut. Res. 2019, 782, 108276. [CrossRef]
- Kisielius, V. , Markusen, B., Hansen, H.C.B., Rasmussen, L.H. Geographical distribution of caudatoside and ptaquiloside in bracken ferns in northern europe. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E., Avendaño, M. Possible association between gastric cancer and bracken fern in Venezuela: an epidemiologic study. Int J Cancer. 2001. [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.N. , Brasileiro-Filho, G., Silva, M.E., Pena, S.D.J. Bracken fern-induced malignant tumours in rats: Absence of mutations in p53, h-ras and k-ras and no microsatellite instability. Mutat. Res. 2002, 499, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, B. , Rasmussen, L.H., Svendsen, G.W., Ingerslev, F., Hansen, H.C.B. Genotoxic activity and inhibition of soil respiration by ptaquiloside, a bracken fern carcinogen. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2751–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida Santos, M. , Dórea, J., Luna, H. Bracken fern can be clastogenic or aneugenic depending on the tissue cell assay. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1845–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum) and some of its constituents. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risk Chem. Hum, 1986, 40, 47-65.
- Niwa, H. , Ojika, M., Wakamatsu, K., Yamada, K., Hirono, I., Matsushita, K. Ptaquiloside, a novel norsesquiterpene glucoside from bracken, var. latiusculum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 4117–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoeven, J.C.M. , Lagerweij, W.J., Posthumus, M.A., van Veldhuizen, A., Holterman, H.A.J. Aquilide A, a new mutagenic compound isolated from bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn). Carcinogenesis, 1983, 4, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojika, M. , Wakamatsu, K., Niwa, H., Yamada, K. Ptaquiloside, a potent carcinogen isolated from bracken fern var. latiusculum: Structure elucidation based on chemical and spectral evidence, and reactions with amino acids, nucleosides, and nucleotides. Tetrahedron, 1987, 43, 5261–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, A., Hirosawa, A., Natori, S., Iwasaki, S., Sofuni, T., Ishidate Jr, M. Mutagenicity of ptaquiloside, the carcinogen in bracken, and its related iludane-type sesquiterpenes. II. Chromosomal aberration tests with cultured mammalian cells. Mutat. Res. 1989, 215. 179-185. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K. , Ojika, M., Kigoshi, H. Ptaquiloside, the major toxin of bracken, and related terpene glycosides: Chemistry, Biology and Ecology. Nat. Prod. Rep., 2007, 24, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, T., Uesugi, M., Sugiura, Y., Kigoshi, H., Tanaka, H., Hirokawa, J., Ojika, M., Yamada, K. DNA damage by ptaquiloside, a potent bracken carcinogen: Detection of selective strand breaks and identification of DNA cleavage products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 479-486. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H., Chang, F.-R., Lu, M.-C., Hsieh, P.-W., Wu, M.-J., Du, Y.-C., Wu, Y.-C. New benzoyl glucosides and cytotoxic pterosin sesquiterpenes from Pteris ensiformis Burm. Molecules, 2008, 13, 255-266. [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H. , Bruun Hansen, H.C., Lauren, D. Sorption, degradation and mobility of ptaquiloside, a carcinogenic bracken (Pteridium sp.) Constituent, in the soil environment. Chemosphere, 2005, 58, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H. , Lauren, D.R., Smith, B.L. Variation in ptaquiloside content in bracken (Pteridium esculentum (Forst. F) Cockayne) in New Zealand. New Zeal. Vet. J. 2008, 56, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.H. , Schmidt, B., Sheffield, E. Ptaquiloside in bracken spores from Britain. Chemosphere, 2013, 90, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siman, S.E., Povey, A.C., Ward, T.H., Margison, G.P., Sheffield, E. Fern spore extracts can damage DNA. Br. J. Cancer, 2000, 63, 69-73. [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E. , Avendaño, M. Conglomerados de cáncer gástrico en el estado de Mérida, Venezuela. Interciencia, 2009, 34, 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, L.H. Presence of the carcinogen ptaquiloside in fern-based food products and traditional medicine: Four cases of human exposure. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Amelot, M. , Castillo, U., De Jongh, F. Passage of the bracken fern carcinogen ptaquiloside into bovine milk. Le Lait, 1993, 73, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galpin, O.P., Whitaker, C.J., Whitaker, R., Kassab, J.Y. Gastric cancer in Gwynedd. Possible links with bracken. Br. J. Cancer, 1990, 61, 737-740. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H., Jacobsen, O.S., Hansen, H.C.B., Juhler, R.K. Quantification of ptaquiloside and pterosin b in soil and groundwater using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9848-54. [CrossRef]
- Ovesen, R.G. , Rasmussen, L.H., Hansen, H.C.B. Degradation kinetics of ptaquiloside in soil and soil solution. Env. Tox. Chem. 2008, 27, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauson-Kaas, F. , Ramwell, C., Hansen, H.C.B., Strobel, B.W. Ptaquiloside from bracken in stream water at base flow and during storm events. Water Res. 2016, 106, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrbic, N., Kisielius, V., Pedersen, A.K., Christensen, S.C.B., Hedergaad, M.J., Hansen, H.C.B., Rasmussen, L.H. Occurrence of carcinogenic iludane glycosides in drinking water wells. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 44. [CrossRef]
- Kisielius, V., Lindqvist, D.N., Thygesen, M.B., Rodamer, M., Hansen, H.C.B., Rasmussen, L.H. Fast LC-MS. Quantification of ptesculentoside, caudatoside, ptaquiloside and corresponding pterosins in bracken ferns. J. Chromatogr. B: Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1138, 121966. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Pescador, A. , Gutiérrez Romero, L., Blanco-González, E., Montes-Bayón, M., Sierra, L.M. Intracellular biotransformation of ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles and their effect in cultured human cells and in Drosophila larvae in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, E.W., Nivard, M.J.M. Performance of 181 chemicals in a Drosophila assay predominantly monitoring interchromosomal mitotic recombination. Mutagenesis, 1993, 8, 57-81. [CrossRef]
- Marcos, R., Sierra, L.M., Gaivão, I. The SMART assays of Drosophila: Wings and eyes as target tissues. In Genotoxicity and DNA repair: A practical approach, 2014, Sierra, L.M., Gaivão, I., Eds., Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 283-295. ISBN 978-1-4939-1068-7. [CrossRef]
- Gaivão, I., Ferreira, J., Sierra, L.M. The w/w + somatic mutation and recombination test (smart) of Drosophila melanogaster for detecting antigenotoxic activity in genotoxicity and mutagenicity - mechanisms and test methods. In Genotoxicity and Mutagenicity -Mechanisms and Test Methods, Soloneski, S., Larramendy M.L., Eds., IntechOpen, 2021. ISBN: 978-1-83880-042-0. [CrossRef]
- Vogel, E.W. , Nivard, M.J.M. A novel method for the parallel monitoring of mitotic recombination and clastogenicity in somatic cells in vivo. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1999, 431, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Sar, D. , Aguado, L., Montes Bayón, M., Comendador, M.A., Blanco González, E., Sanz-Medel, A., Sierra, L.M. Relationships between cisplatin-induced adducts and DNA strand-breaks, mutation and recombination in vivo in somatic cells of Drosophila melanogaster, under different conditions of nucleotide excision repair. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 741, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen L.H., Hansen H.C.B. Growth of bracken in Denmark and the content of ptaquiloside in fronds, rhizomes and roots. In Poisonous Plants and Related Toxins, 2004. Stewart C.S., Pennycott T.W., Acamovic T., Wallingford, Eds. CABI Publishing, pp. 354-360. [CrossRef]
- Vetter, J. Toxicological and medicinal aspects of the most frequent fern species, Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn. In Working with Ferns: Issues and Applications, 2011, Fernández H, Revilla MA, Kumar A Eds. Springer New York, pp. 361–375. ISBN 978-1-4419-7161-6. [CrossRef]
- Rincón, D.F. , Díaz, G.J., Gardner, D.R. Detección de ptaquilósido en diferentes estados fenológicos de “helecho macho” (Pteridium aquilinum) y análisis de muestras de leche en granjas con hematuria en Tolima, Colombia. CES Med. Vet. Zootecnia, 2016, 11, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, M.T., Brock, I. J., Reichmann, K.G., McKenzie, R.A., Blaney, B.J. Norsesquiterpene glycosides in bracken ferns (Pteridium esculentum and Pteridium aquilinum subsp. wightianum) from eastern Australia: Reassessed poisoning risk to animals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1, 2011, 59(9), 5133–5138. [CrossRef]
- García-Jorgensen, D.B., Diamantopoulos, E., Kisielius, V., Rosenfjeld, M., Rasmussen, L.H., Strobel, B.W., Hansen, H.C.B. Bracken growth, toxin production and transfer from plant to soil: a 2-year monitoring study. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 45. [CrossRef]
- Gil da Costa, R.M., Povey, A., Medeiros-Fonseca, B., Ramwell, C., O’Driscoll, C., Williams, D., Hansen, H.C.B., Rasmussen, L.H., Fletcher, M.T., O’Connor, P., Bradshaw, R.H.W., Robinson, R., Mason, J. Sixty years of research on bracken fern (Pteridium spp.) toxins: Environmental exposure, health risks and recommendations for bracken fern control. Environ. Res. 2024. 257, 119274. [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J., Curt, M.D., Aguado, P.L., Esteban, B., Sánchez, J., Checa, M., Mosquera, F., Romero, L. Principado de Asturias, Tomo 7. In Caracterización de las comarcas agrarias de España. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Medio Rural y Marino, 2011, ISBN: 978-84-491-1175-4. https://comarcasagrarias.chil.me/post/tomo-7-Principado-de-Asturias-93415.
- Zaccone, C., Cavoski, I., Costi, R., Sarais, G., Caboni, P., Traversa, A., Miano, T.M. Ptaquiloside in Pteridium aquilinum subsp. aquilinum and corresponding soils from the South of Italy: Influence of physical and chemical features of soils on its occurrence. Sci. Total Env. 2014, 496, 365–372. [CrossRef]
- Skrbic, N. , Pedersen, A.-K., Christensen, S.C.B., Hansen, H.C.B., Rasmussen, L.H. A Novel method for determination of the natural toxin ptaquiloside in ground and drinking water. Water, 2852; 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, J. The norsesquiterpene glycoside ptaquiloside as a poisonous, carcinogenic component of certain ferns. Molecules, 2022, 27, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-da-Paz, M. , Pereira, L.O., Bicalho, L.S., Dorea, J.G., Pocas-Fonseca, M.J., Santos, M.de F. Interaction of bracken-fern extract with vitamin C in human sub-mandibular gland and oral epithelium cell lines. Mutat. Res.- Genet. Toxicol. Environ, Mutagen. 2008, 652, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.O., Bicalho, L.S., Campos-da-Paz Lopes, M., de Sousa, T.M., Báo, S.N., de Fátima Menezes Almeida Santos, M., Fonseca, M.J. DNA damage and apoptosis induced by Pteridium aquilinum aqueous extract in the oral cell lines HSG and OSCC-3. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2009. 38, 441-447. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J. , Magalhães, A., Michel, V., Amado, I.F., Aranha, P., Ovesen, R.G., Hansen, H.C.B., Gärtner, F., Reis, C.A., Touati, E. Pteridium aquilinum and its ptaquiloside toxin induce DNA damage response in gastric epithelial cells, a link with gastric carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, J.W., Stocco dos Santos, R.C., Dagli, M.L., D’Angelino, J.L., Birgel, E.H., Becak, W. Chromosome aberrations in cattle raised on bracken fern pasture. Experientia, 1988, 44, 785-788. [CrossRef]
- Lioi, M.B., Barbieri, R., Borzacchiello, G., Dezzi, S., Roperto, S., Santoro, A., Russo, V., Roperto, F. Chromosome aberrations in cattle with chronic enzootic haematuria. J. Comp. Pathol, 2004, 131(2), 233-236. [CrossRef]
- Peretti, V., Ciotola, E., Albarella, S., Russo, V., Di Meo, G.P., Iannuzzi, L., Roperto, F., Barbieri, V. Chromosome fragility in cattle with chronic enzootic haematuria. Mutagenesis, 2007, 22, 317-320. [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M., Smith, B.L., Worral, S., Moore, M.R., Seawright, A.A., Prakash, A.S. Bracken fern carcinogenesis: Multiple intravenous doses of activated ptaquiloside induce DNA adducts, monocytosis, increased TNF alpha levels, and mammary gland carcinoma in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998a, 244, 192-197. [CrossRef]
- Matoba, M., Saito, E., Saito, K., Koyama, K., Natori, S., Matsushima, T., Takimoto, M. Assay of ptaquiloside, the carcinogenic principle of bracken, Pteridium aquilinum, by mutagenicity testing in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutagenesis, 1987, 2, 419-423. [CrossRef]
- Nagao, T., Saito, K., Hirayama, E., Uchikoshi, K., Koyama, K., Natori, S., Morisaki, N., Iwasaki, S., Matsushima, T. 1989. Mutagenicity of ptaquiloside, the carcinogen in bracken, and its related iludane-type sesquiterpenes. I. Mutagenicity in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat. Res. 1989, 215, 173-178. [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.S. , Pereira, T.N., Smith, B.L., Shaw, G., Seawright, A.A. Mechanism of bracken fern carcinogenesis: Evidence for H-ras activation via initial adenine alkylation by ptaquiloside. Nat. Toxins, 1996, 4, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M. , Moore, M.R., Worrall, S., Smith, B.L., Seawright, A.A., Prakash, A.S. H-ras activation is an early event in the ptaquiloside-induced carcinogenesis: Comparison of acute and chronic toxicity in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998a, 250, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardón, D. , de la Fuente, I., Calonge E., Pérez-Alenza, M.D., Castaño, M., Dunner, S., Peña, L. H-ras. Immunochemical expression and molecular analysis of urinary bladder lesions in grazing adult cattle exposed to bracken fern. J. Comp. Pathol. 2005, 132, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasani, F., Baghban, F., Brujeni, G.H.N., Kazemi, M. Tp53 intronic mutations in bovine enzootic hematuria-associated urinary bladder tumours. Vet. Pathol., 2012, 50, 543-547. [CrossRef]
- Wong, K., Abascal, F., Ludwig, L., Aupperle-Lellbach, H., Grassinger, J., Wright, C.W., Allison, S.J., Pinder, E., Phillips, R.M., Romero, L.P., et al. Cross-Species oncogenomics offers insight into human muscle- invasive bladder cancer. Genome Biol., 2023, 24, 191. [CrossRef]
- Kisielius, V., Drejer, M., Dornhoff, J.K., Mrkajic, N.S., Lindqvist, D.N., Hansen, H.C.B., Rasmussen, L.H. Occurrence and stability of ptesculentoside, caudatoside and ptaquiloside in surface waters. Environ. Sci.: Process. Impacts, 2022, 24, 277–289. [CrossRef]
- Sheaves, B.J., Brown, R.W. Densities of Ixodes ricinus ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on moorland vegetation communities in the UK. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1995, 19, 489–497. [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.S. The Development and Seasonal Activity of the Tick Ixodes ricinus: a vector of Lyme borreliosis and other tick-borne diseases. Rev. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1991, 79, 323-333.
- Madison-Antenucci, S., Kramer, L.D., Gebhardt, L.L., Kauffman, E. Emerging tick-borne diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33. [CrossRef]
- Matongera, T.N., Mutanga, O., Dube, T., Lottering, R.T. Detection and mapping bracken fern weeds using multispectral data: A review of progress and challenges. Geocarto Int. 2016, 33, 209-224. [CrossRef]
- Takeshige, R., Onishi, M., Aoyagi, R., Sawada, Y., Imai, N., Ong, R., Kitayama, K. Mapping the spatial distribution of fern thickets and vine-laden forests in the landscape of bornean logged-over tropical secondary rainforests. Remote Sens. 2022. 14, 3354. [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.K. , Sharma, R., Kumari, A., Rasmussen, L.H., Patil, R.D., Bhar, R. Survey of ferns and clinic-pathological studies on the field cases of enzootic bovine haematuria in Himachal Pradesh, a North-western Himalayan state of India. Toxicon, 2017, 138, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, V. IDB - Index-Database, Development of a database for remote sensing indices. ZFL-Colloquium, Bonn 2012. https://www.50northspatial.org.ua/idb-remote-sensing-indices-database/.


| Chemical | µgL-1 Min | µgL-1 Max | R2 | LOD (µgL-1) | LOQ (µgL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PtrB | 5 | 160 | 0.998 | 2.5 | 5 |
| PtrA | 0.75 | 80 | 0.994 | 0.046 | 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





