Submitted:
21 June 2025
Posted:
23 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Assessing Cognitive Flexibility Deficits in Schizophrenia
3. Assessing Cognitive Flexibility Deficits in Rodents: Methodology, Neural Circuits and Neurotransmitters
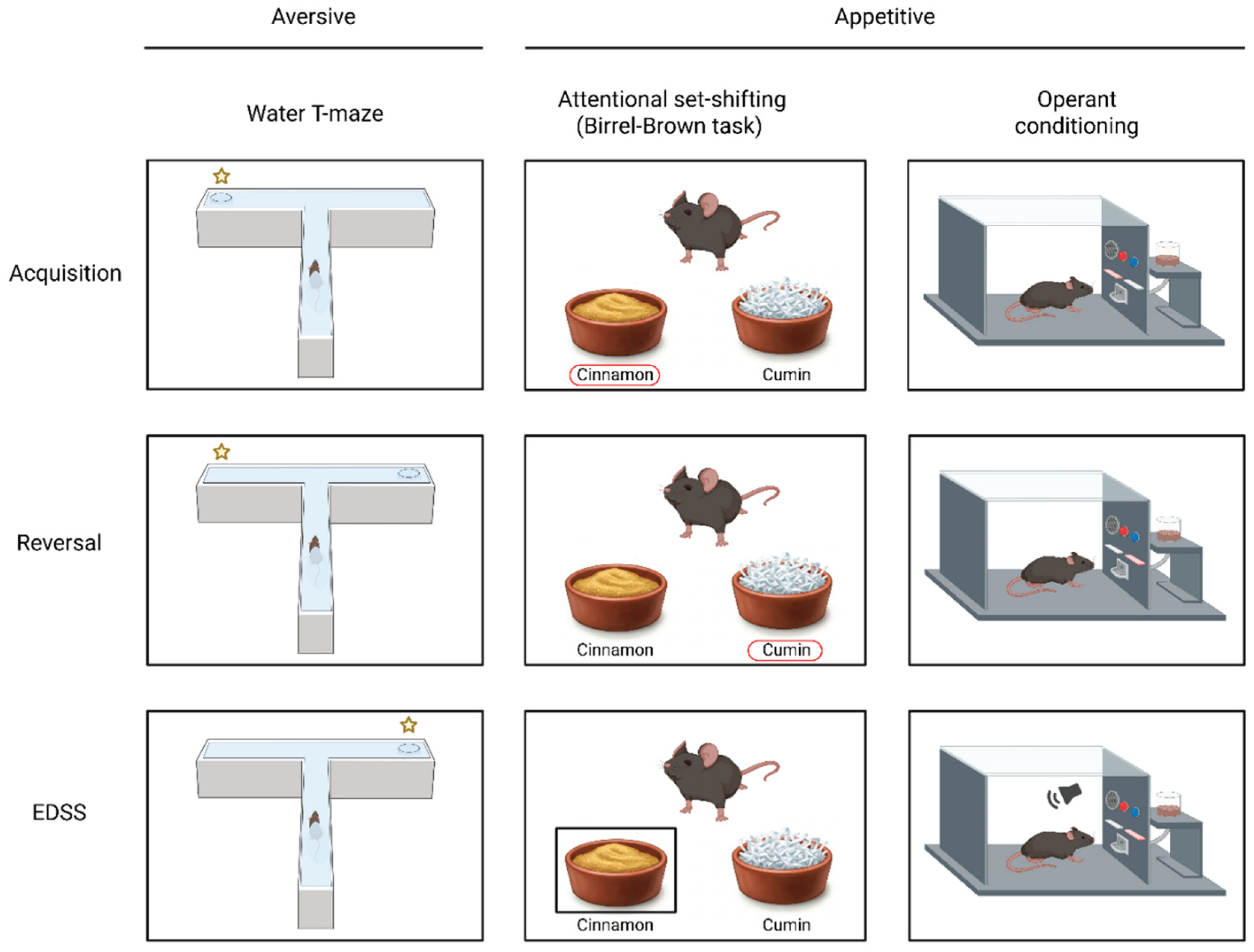
3.1. Aversive Learning Tasks
3.2. Appetitive Learning Tasks
4. The Neural Substrates of Cognitive Flexibility
4.1. Glutamate
4.2. GABA
4.3. Dopamine
4.4. Serotonin
4.5. Environmental Manipulations
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lange, F.; Seer, C.; Loens, S.; Wegner, F.; Schrader, C.; Dressler, D.; Dengler, R.; Kopp, B. Neural Mechanisms Underlying Cognitive Inflexibility in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropsychologia 2016, 93, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruner, P.; Pittenger, C. Cognitive Inflexibility in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Neuroscience 2017, 345, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumer, P.; Brandt, G.A.; Hirjak, D.; Bähner, F. Impaired Cognitive Flexibility in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review of Behavioral and Neurobiological Findings. Biomark Neuropsychiatry 2024, 11, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barch, D.M.; Braver, T.S.; Carter, C.S.; Poldrack, R.A.; Robbins, T.W. CNTRICS Final Task Selection: Executive Control. Schizophr Bull 2009, 35, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencz, T.; Smith, C.W.; McLaughlin, D.; Auther, A.; Nakayama, E.; Hovey, L.; Cornblatt, B.A. Generalized and Specific Neurocognitive Deficits in Prodromal Schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2006, 59, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, I.J.; Corley, J.; Gow, A.J.; Harris, S.E.; Houlihan, L.M.; Marioni, R.E.; Penke, L.; Rafnsson, S.B.; Starr, J.M. Age-Associated Cognitive Decline. Br Med Bull 2009, 92, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeste, D. V.; Wolkowitz, O.M.; Palmer, B.W. Divergent Trajectories of Physical, Cognitive, and Psychosocial Aging in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2011, 37, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, C.J.; Schmid, L.A.; Lässer, M.M.; Seidl, U.; Schröder, J. Cognitive Performance in Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia Across the Lifespan. GeroPsych (Bern) 2017, 30, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, E.C.; Marsh, A.A.; Mitchell, D.G.; Reid, M.E.; Sims, C.; Budhani, S.; Kosson, D.S.; Chen, G.; Towbin, K.E.; Leibenluft, E.; et al. Abnormal Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Function in Children With Psychopathic Traits During Reversal Learning. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008, 65, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, G.; Arguello, A.; Bari, A.; Brown, V.J.; Carter, C.; Floresco, S.B.; Jentsch, D.J.; Tait, D.S.; Young, J.W.; Robbins, T.W. Measuring the Construct of Executive Control in Schizophrenia: Defining and Validating Translational Animal Paradigms for Discovery Research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2013, 37, 2125–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crider, A. Perseveration in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1997, 23, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.O.; Kruppa, J.A.; Fink, G.R.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Konrad, K.; Schulte-Rüther, M. Developmental Differences in Probabilistic Reversal Learning: A Computational Modeling Approach. Front Neurosci 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, S.; Howlett, C.A.; Berryman, C.; Nedeljkovic, M.; Moseley, G.L.; Phillipou, A. Considerations for Using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test to Assess Cognitive Flexibility. Behav Res Methods 2021, 53, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilha, L.; Molnar, C.; Horner, M.D.; Anderson, B.; Forster, L.; George, M.S.; Nahas, Z. Neurocognitive Deficits and Prefrontal Cortical Atrophy in Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2008, 101, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, K.; Norman, R.; Théberge, J.; Densmore, M.; Schaefer, B.; Williamson, P. Glutamatergic Metabolite Correlations with Neuropsychological Tests in First Episode Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 2015, 233, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Xian, Z. Study Investigating Executive Function in Schizophrenia Patients and Their Unaffected Siblings. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0285034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, J.A.; Gold, J.M. Probabilistic Reversal Learning Impairments in Schizophrenia: Further Evidence of Orbitofrontal Dysfunction. Schizophr Res 2007, 93, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenzang, C.; Manoach, D.S.; Goff, D.C.; Barton, J.J.S. Task-Switching in Schizophrenia: Active Switching Costs and Passive Carry-over Effects in an Antisaccade Paradigm. Exp Brain Res 2007, 181, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffaber, P.D.; Kappenman, E.S.; Bodkins, M.; Shekhar, A.; O’Donnell, B.F.; Hetrick, W.P. Switch and Maintenance of Task Set in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2006, 84, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobellova, V.; Entlerova, M.; Svojanovska, B.; Hatalova, H.; Prokopova, I.; Petrasek, T.; Vales, K.; Kubik, S.; Fajnerova, I.; Stuchlik, A. Two Learning Tasks Provide Evidence for Disrupted Behavioural Flexibility in an Animal Model of Schizophrenia-like Behaviour Induced by Acute MK-801: A Dose–Response Study. Behavioural Brain Research 2013, 246, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badowska, D.M.; Brzózka, M.M.; Kannaiyan, N.; Thomas, C.; Dibaj, P.; Chowdhury, A.; Steffens, H.; Turck, C.W.; Falkai, P.; Schmitt, A.; et al. Modulation of Cognition and Neuronal Plasticity in Gain- and Loss-of-Function Mouse Models of the Schizophrenia Risk Gene Tcf4. Transl Psychiatry 2020, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asraf, K.; Zaidan, H.; Natoor, B.; Gaisler-Salomon, I. Synergistic, Long-Term Effects of Glutamate Dehydrogenase 1 Deficiency and Mild Stress on Cognitive Function and MPFC Gene and MiRNA Expression. Transl Psychiatry 2023, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvat, G.; Kimchi, T. Acetylcholine Elevation Relieves Cognitive Rigidity and Social Deficiency in a Mouse Model of Autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.A.; Tracy, B.A.; Gould, T.J.; Parikh, V. Effects of Chronic Low- and High-Dose Nicotine on Cognitive Flexibility in C57BL/6J Mice. Behavioural Brain Research 2013, 238, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshof, L.A.; Frajmund, L.A.; van Nuijs, D.; van der Heijden, D.C.N.; Middeldorp, J.; Hol, E.M. Both Male and Female APPswe/PSEN1dE9 Mice Are Impaired in Spatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility at 9 Months of Age. Neurobiol Aging 2022, 113, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Boom, B.J.G.; Mooij, A.H.; Misevičiūtė, I.; Denys, D.; Willuhn, I. Behavioral Flexibility in a Mouse Model for Obsessive-compulsive Disorder: Impaired Pavlovian Reversal Learning in SAPAP3 Mutants. Genes Brain Behav 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R. Developments of a Water-Maze Procedure for Studying Spatial Learning in the Rat. J Neurosci Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayalon, L.; Doron, R.; Weiner, I.; Joel, D. Amelioration of Behavioral Deficits in a Rat Model of Huntington’s Disease by an Excitotoxic Lesion to the Globus Pallidus. Exp Neurol 2004, 186, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, S.S.; Khan, U.; Lewandowski, N.; Chakraborty, D.; Provenzano, F.A.; Mingote, S.; Chornyy, S.; Frigerio, F.; Maechler, P.; Kaphzan, H.; et al. Glutamate Dehydrogenase–Deficient Mice Display Schizophrenia-Like Behavioral Abnormalities and CA1-Specific Hippocampal Dysfunction. Schizophr Bull 2019, 45, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Canabal, A.; López-Oropeza, G.; Sotres-Bayón, F. Hippocampal Neurogenesis Facilitates Cognitive Flexibility in a Fear Discrimination Task. Front Behav Neurosci 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.; Kim, E.; Jung, M.W. Enhanced Fear Limits Behavioral Flexibility in Shank2-Deficient Mice. Mol Autism 2022, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, A.; Jaggi, A.S. Electric Foot Shock Stress: A Useful Tool in Neuropsychiatric Studies. Rev Neurosci 2015, 26, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, K.C. Conditioned Taste Aversions. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2018, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouton, M.E.; Maren, S.; McNally, G.P. Behavioral and Neurobiological Mechanisms of Pavlovian and Instrumental Extinction Learning. Physiol Rev 2021, 101, 611–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, P.E.; Calton, M.A.; Mittleman, G. Performance of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J Mice on a Touchscreen-Based Attentional Set-Shifting Task. Behavioural Brain Research 2014, 261, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, M.E.; Detrick, S.; Kesner, R.P. Involvement of the Prelimbic–Infralimbic Areas of the Rodent Prefrontal Cortex in Behavioral Flexibility for Place and Response Learning. The Journal of Neuroscience 1999, 19, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragozzino, M.E. The Effects of Dopamine D(1) Receptor Blockade in the Prelimbic-Infralimbic Areas on Behavioral Flexibility. Learning & Memory 2002, 9, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinalli, D.A.; Cohen, S.J.; Calubag, M.; Oz, G.; Zhou, L.; Stackman, R.W. DREADD-Inactivation of Dorsal CA1 Pyramidal Neurons in Mice Impairs Retrieval of Object and Spatial Memories. Hippocampus 2023, 33, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, E.; Moser, M.; Andersen, P. Spatial Learning Impairment Parallels the Magnitude of Dorsal Hippocampal Lesions, but Is Hardly Present Following Ventral Lesions. The Journal of Neuroscience 1993, 13, 3916–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I.; Forrest, E.; Andersen, P.; Morris, R.G. Spatial Learning with a Minislab in the Dorsal Hippocampus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1995, 92, 9697–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooge, R.; De Deyn, P.P. Applications of the Morris Water Maze in the Study of Learning and Memory. Brain Res Rev 2001, 36, 60–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, J.P.C.; Sánchez-Santed, F.; Heinsbroek, R.P.W.; Donker, A.; Postmes, P. A Behavioural Analysis of Rats with Damage to the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Using the Morris Water Maze: Evidence for Behavioural Flexibility, but Not for Impaired Spatial Navigation. Brain Res 1994, 652, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissonette, G.B.; Powell, E.M. Reversal Learning and Attentional Set-Shifting in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, J.-P.; Goulet, S.; Doré, F.Y. Neonatal Ventral Hippocampus Lesions Disrupt Extra-Dimensional Shift and Alter Dendritic Spine Density in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex of Juvenile Rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2008, 90, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.A.; McGaughy, J. Attentional Effects of Lesions to the Anterior Cingulate Cortex: How Prior Reinforcement Influences Distractibility. Behavioral Neuroscience 2011, 125, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonette, G.B.; Martins, G.J.; Franz, T.M.; Harper, E.S.; Schoenbaum, G.; Powell, E.M. Double Dissociation of the Effects of Medial and Orbital Prefrontal Cortical Lesions on Attentional and Affective Shifts in Mice. The Journal of Neuroscience 2008, 28, 11124–11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulougouris, V.; Dalley, J.W.; Robbins, T.W. Effects of Orbitofrontal, Infralimbic and Prelimbic Cortical Lesions on Serial Spatial Reversal Learning in the Rat. Behavioural Brain Research 2007, 179, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods-Sharifi, S.; Haluk, D.M.; Floresco, S.B. Differential Effects of Inactivation of the Orbitofrontal Cortex on Strategy Set-Shifting and Reversal Learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2008, 89, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, M.E. The Contribution of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex, Orbitofrontal Cortex, and Dorsomedial Striatum to Behavioral Flexibility. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007, 1121, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.J. Evidence for a Specialized Role of the Locus Coeruleus Noradrenergic System in Cortical Circuitries and Behavioral Operations. Brain Res 2016, 1641, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janitzky, K.; Lippert, M.T.; Engelhorn, A.; Tegtmeier, J.; Goldschmidt, J.; Heinze, H.-J.; Ohl, F.W. Optogenetic Silencing of Locus Coeruleus Activity in Mice Impairs Cognitive Flexibility in an Attentional Set-Shifting Task. Front Behav Neurosci 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaughy, J.; Ross, R.S.; Eichenbaum, H. Noradrenergic, but Not Cholinergic, Deafferentation of Prefrontal Cortex Impairs Attentional Set-Shifting. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscher, C.; Malenka, R.C. NMDA Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression (LTP/LTD). Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012, 4, a005710–a005710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, Y.; Coyle, J.T. Glutamate Hypothesis in Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2019, 73, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, S.; Bhat, A.A.; Masoodi, T.; Hashem, S.; Akhtar, S.; Ali, T.A.; Amjad, S.; Chawla, S.; Bagga, P.; Frenneaux, M.P.; et al. Genetics of Glutamate and Its Receptors in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2380–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardgett, M.E.; Boeckman, R.; Krochmal, D.; Fernando, H.; Ahrens, R.; Csernansky, J.G. NMDA Receptor Blockade and Hippocampal Neuronal Loss Impair Fear Conditioning and Position Habit Reversal in C57Bl/6 Mice. Brain Res Bull 2003, 60, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadman, K.K.; Watson, D.J.; Stanton, M.E. NMDA Receptor Antagonism Impairs Reversal Learning in Developing Rats. Behavioral Neuroscience 2006, 120, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.L.; Neill, J.C.; Idris, N.F.; Marston, H.M.; Wong, E.H.F.; Shahid, M. Effects of Asenapine, Olanzapine, and Risperidone on Psychotomimetic-Induced Reversal-Learning Deficits in the Rat. Behavioural Brain Research 2010, 214, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Monim, Z.; Reynolds, G.P.; Neill, J.C. The Effect of Atypical and Classical Antipsychotics on Sub-Chronic PCP-Induced Cognitive Deficits in a Reversal-Learning Paradigm. Behavioural Brain Research 2006, 169, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrono, E.; Hrůzova, K.; Svoboda, J.; Stuchlík, A. The Role of Optogenetic Stimulations of Parvalbumin-Positive Interneurons in the Prefrontal Cortex and the Ventral Hippocampus on an Acute MK-801 Model of Schizophrenia-like Cognitive Inflexibility. Schizophr Res 2023, 252, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-T.; Su, Y.-A.; Wang, H.-L.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Liao, X.-M.; Wang, X.-D.; Si, T.-M. Repeated Blockade of NMDA Receptors During Adolescence Impairs Reversal Learning and Disrupts GABAergic Interneurons in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Front Mol Neurosci 2016, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonnard, D.; Dreesen, E.; Callaerts-Vegh, Z.; D’Hooge, R. NMDA Receptor Dependence of Reversal Learning and the Flexible Use of Cognitively Demanding Search Strategies in Mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2019, 90, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.J.; Stanton, M.E. Medial Prefrontal Administration of MK-801 Impairs T-Maze Discrimination Reversal Learning in Weanling Rats. Behavioural Brain Research 2009, 205, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Gong, B.; Howland, J.G.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.T. Hippocampal Long-Term Depression Mediates Spatial Reversal Learning in the Morris Water Maze. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, S.; Labrie, V.; Roder, J.C. D-Serine Augments NMDA-NR2B Receptor-Dependent Hippocampal Long-Term Depression and Spatial Reversal Learning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, M.R.; Groth, K.; Moghaddam, B. Glutamate Receptors in the Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex Regulate Set-Shifting Ability. Behavioral Neuroscience 2003, 117, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipina, T.; Men, X.; Blundell, M.; Salahpour, A.; Ramsey, A.J. Abnormal Sensory Perception Masks Behavioral Performance of Grin1 Knockdown Mice. Genes Brain Behav 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, D.J.; Bannerman, D.M. The Role of Habituation in Hippocampus-dependent Spatial Working Memory Tasks: Evidence from GluA1 AMPA Receptor Subunit Knockout Mice. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvas, M.; Palmiter, R.D. Specific Contributions of N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors in the Dorsal Striatum to Cognitive Flexibility. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, K.; Saha, M.; Mishina, M.; Young, J.W.; Brigman, J.L. Loss of GluN2A-containing NMDA Receptors Impairs Extra-dimensional Set-shifting. Genes Brain Behav 2014, 13, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigman, J.L.; Daut, R.A.; Wright, T.; Gunduz-Cinar, O.; Graybeal, C.; Davis, M.I.; Jiang, Z.; Saksida, L.M.; Jinde, S.; Pease, M.; et al. GluN2B in Corticostriatal Circuits Governs Choice Learning and Choice Shifting. Nat Neurosci 2013, 16, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrie, V.; Duffy, S.; Wang, W.; Barger, S.W.; Baker, G.B.; Roder, J.C. Genetic Inactivation of D-Amino Acid Oxidase Enhances Extinction and Reversal Learning in Mice. Learning & Memory 2009, 16, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterlis, I.; Holmes, S.E.; Sharma, P.; Krystal, J.H.; DeLorenzo, C. Metabotropic Glutamatergic Receptor 5 and Stress Disorders: Knowledge Gained From Receptor Imaging Studies. Biol Psychiatry 2018, 84, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, Y.-J.I.; O’Malley, K.L. Mechanisms Associated with Activation of Intracellular Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGluR5. Neurochem Res 2017, 42, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeleznikow-Johnston, A.M.; Renoir, T.; Churilov, L.; Li, S.; Burrows, E.L.; Hannan, A.J. Touchscreen Testing Reveals Clinically Relevant Cognitive Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of Schizophrenia Lacking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 16412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Kim, E.; Noh, H.J.; Kang, S.; Phillips, B.U.; Kim, D.G.; Bussey, T.J.; Saksida, L.; Heath, C.J.; Kim, C.H. Assessment of MGluR5 KO Mice under Conditions of Low Stress Using a Rodent Touchscreen Apparatus Reveals Impaired Behavioural Flexibility Driven by Perseverative Responses. Mol Brain 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kraniotis, S.; He, Q.; Marshall, J.J.; Nomura, T.; Stauffer, S.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Conn, P.J.; Contractor, A. Potentiating MGluR5 Function with a Positive Allosteric Modulator Enhances Adaptive Learning. Learning & Memory 2013, 20, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastambide, F.; Cotel, M.-C.; Gilmour, G.; O’Neill, M.J.; Robbins, T.W.; Tricklebank, M.D. Selective Remediation of Reversal Learning Deficits in the Neurodevelopmental MAM Model of Schizophrenia by a Novel MGlu5 Positive Allosteric Modulator. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, M.E.; Santiago, C.I.; Stansley, B.J.; Maksymetz, J.; Gogliotti, R.G.; Engers, J.L.; Nicoletti, F.; Lindsley, C.W.; Conn, P.J. Mechanisms Underlying Prelimbic Prefrontal Cortex MGlu3/MGlu5-Dependent Plasticity and Reversal Learning Deficits Following Acute Stress. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Sherry, D.M.; Liu, X.; Fremeau, R.T.; Seal, R.P.; Edwards, R.H.; Copenhagen, D.R. Vesicular Glutamate Transporter 3 Expression Identifies Glutamatergic Amacrine Cells in the Rodent Retina. Journal of Comparative Neurology 2004, 477, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneault, É.; Poirel, O.; Riad, M.; Prud’homme, J.; Dumas, S.; Turecki, G.; Fasano, C.; Mechawar, N.; El Mestikawy, S. Distribution of Vesicular Glutamate Transporters in the Human Brain. Front Neuroanat 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balschun, D.; Moechars, D.; Callaerts-Vegh, Z.; Vermaercke, B.; Van Acker, N.; Andries, L.; D’Hooge, R. Vesicular Glutamate Transporter VGLUT1 Has a Role in Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation and Spatial Reversal Learning. Cerebral Cortex 2010, 20, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granseth, B.; Andersson, F.K.; Lindström, S.H. The Initial Stage of Reversal Learning Is Impaired in Mice Hemizygous for the Vesicular Glutamate Transporter (VGluT1). Genes Brain Behav 2015, 14, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, S.S.; Chornyy, S.; Safory, H.; Gross, A.; Wolosker, H.; Gaisler-Salomon, I. Glutamate Dehydrogenase Deficiency Disrupts Glutamate Homeostasis in Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex and Impairs Recognition Memory. Genes Brain Behav 2020, e12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morellini, F.; Sivukhina, E.; Stoenica, L.; Oulianova, E.; Bukalo, O.; Jakovcevski, I.; Dityatev, A.; Irintchev, A.; Schachner, M. Improved Reversal Learning and Working Memory and Enhanced Reactivity to Novelty in Mice with Enhanced GABAergic Innervation in the Dentate Gyrus. Cerebral Cortex 2010, 20, 2712–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, S.A.; Dillon, D.G.; Young, J.W.; Thomas, M.L.; Faget, L.; Yoo, J.H.; Der-Avakian, A.; Hnasko, T.S.; Geyer, M.A.; Ramanathan, D.S. Modulation of Ventromedial Orbitofrontal Cortical Glutamatergic Activity Affects the Explore-Exploit Balance and Influences Value-Based Decision-Making. Cerebral Cortex 2023, 33, 5783–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüsch, N.; Tebartz van Elst, L.; Valerius, G.; Büchert, M.; Thiel, T.; Ebert, D.; Hennig, J.; Olbrich, H.-M. Neurochemical and Structural Correlates of Executive Dysfunction in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2008, 99, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirayama, Y.; Obata, T.; Matsuzawa, D.; Nonaka, H.; Kanazawa, Y.; Yoshitome, E.; Ikehira, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Iyo, M. Specific Metabolites in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Are Associated with the Neurocognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia: A Preliminary Study. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.-K.; Werner, A.; Kuntke, P.; Petasch, M.-S.; Bensmann, W.; Zink, N.; Koyun, A.H.; Quednow, B.B.; Beste, C. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Glutamate Concentrations in the Striatum and Anterior Cingulate Cortex Not Found to Be Associated with Cognitive Flexibility. Brain Sci 2023, 13, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, L.; Huang, M.; Michael, E.; Kwon, S.; Meltzer, H.Y. TPA-023 Attenuates Subchronic Phencyclidine-Induced Declarative and Reversal Learning Deficits via GABAA Receptor Agonist Mechanism: Possible Therapeutic Target for Cognitive Deficit in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonette, G.B.; Bae, M.H.; Suresh, T.; Jaffe, D.E.; Powell, E.M. Astrocyte-Mediated Hepatocyte Growth Factor/Scatter Factor Supplementation Restores GABAergic Interneurons and Corrects Reversal Learning Deficits in Mice. The Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 30, 2918–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonette, G.B.; Schoenbaum, G.; Roesch, M.R.; Powell, E.M. Interneurons Are Necessary for Coordinated Activity During Reversal Learning in Orbitofrontal Cortex. Biol Psychiatry 2015, 77, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigman, J.L.; Padukiewicz, K.E.; Sutherland, M.L.; Rothblat, L.A. Executive Functions in the Heterozygous Reeler Mouse Model of Schizophrenia. Behavioral Neuroscience 2006, 120, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausrat, T.J.; Muhia, M.; Gerrow, K.; Thomas, P.; Hirdes, W.; Tsukita, S.; Heisler, F.F.; Herich, L.; Dubroqua, S.; Breiden, P.; et al. Radixin Regulates Synaptic GABAA Receptor Density and Is Essential for Reversal Learning and Short-Term Memory. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, M.T.; Piantadosi, P.T.; Floresco, S.B. Prefrontal Cortical Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Transmission and Cognitive Function: Drawing Links to Schizophrenia from Preclinical Research. Biol Psychiatry 2015, 77, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, N.; Yoshimura, R.; Kakeda, S.; Moriya, J.; Hayashi, K.; Ikenouchi-Sugita, A.; Umene-Nakano, W.; Hori, H.; Ueda, N.; Korogi, Y.; et al. Associations between Plasma Levels of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG) and Negative Symptoms or Cognitive Impairments in Early-stage Schizophrenia. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental 2009, 24, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayano, G. Dopamine: Receptors, Functions, Synthesis, Pathways, Locations and Mental Disorders: Review of Literatures. Journal of Mental Disorders and Treatment 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, G.R. Dopamine Transporter: Basic Science and Human Variation of a Key Molecule for Dopaminergic Function, Locomotion, and Parkinsonism. Movement Disorders 2003, 18, S71–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Taylor, E.M.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Chong, T.T.-J.; Coxon, J.P. Dopamine D2 Receptor Modulates Exercise Related Effect on Cortical Excitation/Inhibition and Motor Skill Acquisition. The Journal of Neuroscience 2024, 44, e2028232024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, D.; Mapelli, L. Dopaminergic Modulation of Prefrontal Cortex Inhibition. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, D.; Taylor, E.M.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Chong, T.T.-J.; Coxon, J.P. D2 Receptor Blockade Eliminates Exercise-Induced Changes in Cortical Inhibition and Excitation. Brain Stimul 2023, 16, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulougouris, V.; Castañé, A.; Robbins, T.W. Dopamine D2/D3 Receptor Agonist Quinpirole Impairs Spatial Reversal Learning in Rats: Investigation of D3 Receptor Involvement in Persistent Behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2009, 202, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, A.; Wiedholz, L.; Millstein, R.; Yang, R.; Bussey, T.; Saksida, L.; Holmes, A. Genetic and Dopaminergic Modulation of Reversal Learning in a Touchscreen-Based Operant Procedure for Mice. Behavioural Brain Research 2006, 171, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, N.P.; Gomez-Serrano, M. D4 Dopamine Receptor-Specific Antagonist Improves Reversal Learning Impairment in Amphetamine-Treated Male Rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 2014, 22, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSteno, D.A.; Schmauss, C. A Role for Dopamine D2 Receptors in Reversal Learning. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruzich, P.J.; Grandy, D.K. Dopamine D2receptors Mediate Two-Odor Discrimination and Reversal Learning in C57BL/6 Mice. BMC Neurosci 2004, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruzich, P.J.; Mitchell, S.H.; Younkin, A.; Grandy, D.K. Dopamine D2 Receptors Mediate Reversal Learning in Male C57BL/6J Mice. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2006, 6, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Wang, Y.; Sasaoka, T.; Okada, K.; Niwa, M.; Sawa, A.; Hikida, T. Dopamine D2L Receptor Is Required for Visual Discrimination and Reversal Learning. Complex Psychiatry 2016, 2, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellendonk, C.; Simpson, E.H.; Polan, H.J.; Malleret, G.; Vronskaya, S.; Winiger, V.; Moore, H.; Kandel, E.R. Transient and Selective Overexpression of Dopamine D2 Receptors in the Striatum Causes Persistent Abnormalities in Prefrontal Cortex Functioning. Neuron 2006, 49, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselinović, T.; Vernaleken, I.; Janouschek, H.; Cumming, P.; Paulzen, M.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Gründer, G. The Role of Striatal Dopamine D2/3 Receptors in Cognitive Performance in Drug-Free Patients with Schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2018, 235, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.L.M.; Amsbaugh, H.M.; Reilly, J.L.; Rosen, C.; Marvin, R.W.; Ragozzino, M.E.; Bishop, J.R.; Sweeney, J.A.; Hill, S.K. Beneficial and Adverse Effects of Antipsychotic Medication on Cognitive Flexibility Are Related to COMT Genotype in First Episode Psychosis. Schizophr Res 2018, 202, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad-Zadeh, L.F.; Moses, L.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.M. Serotonin: A Review. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2008, 31, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spies, M.; Knudsen, G.M.; Lanzenberger, R.; Kasper, S. The Serotonin Transporter in Psychiatric Disorders: Insights from PET Imaging. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.-J.; Xue, Y.-R.; Shao, H.; Wei, C.; Liu, T.; He, J.; Yang, Y.-H.; Wang, H.-M.; Li, N.; Ren, S.-Q.; et al. Hippocampal Excitation-Inhibition Balance Underlies the 5-HT2C Receptor in Modulating Depressive Behaviours. Brain 2024, 147, 3764–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos-Lima, E.; Higa, G.S.V.; Viana, F.J.C.; Tamais, A.M.; Cruvinel, E.; Borges, F. da S.; Francis-Oliveira, J.; Ulrich, H.; De Pasquale, R. Serotonergic Modulation of the Excitation/Inhibition Balance in the Visual Cortex. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 25, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigman, J.L.; Mathur, P.; Harvey-White, J.; Izquierdo, A.; Saksida, L.M.; Bussey, T.J.; Fox, S.; Deneris, E.; Murphy, D.L.; Holmes, A. Pharmacological or Genetic Inactivation of the Serotonin Transporter Improves Reversal Learning in Mice. Cerebral Cortex 2010, 20, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odland, A.U.; Sandahl, R.; Andreasen, J.T. Sequential Reversal Learning: A New Touchscreen Schedule for Assessing Cognitive Flexibility in Mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2021, 238, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodeo, D.A.; Hassan, O.; Klein, L.; Halberstadt, A.L.; Powell, S.B. Acute Serotonin 2A Receptor Activation Impairs Behavioral Flexibility in Mice. Behavioural Brain Research 2020, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulougouris, V.; Glennon, J.C.; Robbins, T.W. Dissociable Effects of Selective 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C Receptor Antagonists on Serial Spatial Reversal Learning in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 2007–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulougouris, V.; Robbins, T.W. Enhancement of Spatial Reversal Learning by 5-HT 2C Receptor Antagonism Is Neuroanatomically Specific. The Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 30, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üçok, A.; Alpsan, H.; Çakır, S.; Saruhan-Direskeneli, G. Association of a Serotonin Receptor 2A Gene Polymorphism with Cognitive Functions in Patients with Schizophrenia. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics 2007, 144B, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosia, M.; Anselmetti, S.; Pirovano, A.; Ermoli, E.; Marino, E.; Bramanti, P.; Smeraldi, E.; Cavallaro, R. HTTLPR Functional Polymorphism in Schizophrenia: Executive Functions vs. Sustained Attention Dissociation. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2010, 34, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, W.; Xue, X.; Shao, F.; Li, N. Brief Social Isolation in Early Adolescence Affects Reversal Learning and Forebrain BDNF Expression in Adult Rats. Brain Res Bull 2011, 86, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, S.S.; Linder-Shacham, D.; Gaisler-Salomon, I. Differential Effects of Social Isolation in Adolescent and Adult Mice on Behavior and Cortical Gene Expression. Behavioural Brain Research 2017, 316, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butts, K.A.; Floresco, S.B.; Phillips, A.G. Acute Stress Impairs Set-Shifting but Not Reversal Learning. Behavioural Brain Research 2013, 252, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, C.A.; Zhang, Y.; Howland, J.G. Effects of Acute Restraint Stress on Set-Shifting and Reversal Learning in Male Rats. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2013, 13, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwill, H.L.; Manzano-Nieves, G.; LaChance, P.; Teramoto, S.; Lin, S.; Lopez, C.; Stevenson, R.J.; Theyel, B.B.; Moore, C.I.; Connors, B.W.; et al. Early Life Stress Drives Sex-Selective Impairment in Reversal Learning by Affecting Parvalbumin Interneurons in Orbitofrontal Cortex of Mice. Cell Rep 2018, 25, 2299–2307.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munarriz-Cuezva, E.; Meana, J.J. Poly (I:C)-induced Maternal Immune Activation Generates Impairment of Reversal Learning Performance in Offspring. J Neurochem 2025, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodeo, D.A.; Lai, C.-Y.; Hassan, O.; Mukamel, E.A.; Behrens, M.M.; Powell, S.B. Maternal Immune Activation Impairs Cognitive Flexibility and Alters Transcription in Frontal Cortex. Neurobiol Dis 2019, 125, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Yoshino, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Yamamuro, K.; Kimoto, S.; Noriyama, Y.; Makinodan, M.; Yamashita, M.; Saito, Y.; Kishimoto, T. Maternal Immune Activation Affects Hippocampal Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Transmission in Offspring From an Early Developmental Period to Adulthood. Front Cell Neurosci 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lian, J.; Hodgson, J.; Zhang, W.; Deng, C. Prenatal Poly I:C Challenge Affects Behaviors and Neurotransmission via Elevated Neuroinflammation Responses in Female Juvenile Rats. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 25, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, M.; Frau, R.; Pistis, M. Transgenerational Sex-Dependent Disruption of Dopamine Function Induced by Maternal Immune Activation. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleznikow-Johnston, A.; Burrows, E.L.; Renoir, T.; Hannan, A.J. Environmental Enrichment Enhances Cognitive Flexibility in C57BL/6 Mice on a Touchscreen Reversal Learning Task. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Nishikawa, K.; Noda, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Fujisaku, T.; Ohno-Shosaku, T. Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Exploratory Behavior, Win-Stay and Lose-Shift Performance, Motor Sequence Learning, and Reversal Learning during the Three-Lever Operant Task in Mice. Behavioural Brain Research 2022, 429, 113904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro-Piquero, P.; Zancada-Menendez, C.; Begega, A. Housing Condition-Related Changes Involved in Reversal Learning and Its c-Fos Associated Activity in the Prefrontal Cortex. Neuroscience 2015, 307, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.S.; Meyer, U. Maternal Immune Activation and Neuropsychiatric Illness: A Translational Research Perspective. American Journal of Psychiatry 2018, 175, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socrates, A.J.; Mullins, N.; Gur, R.C.; Gur, R.E.; Stahl, E.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Reichenberg, A.; Jones, H.; Zammit, S.; Velthorst, E. Polygenic Risk of Social Isolation Behavior and Its Influence on Psychopathology and Personality. Mol Psychiatry 2024, 29, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.S.; Trainor, B.C.; Lam, J.C.W.; Yonelinas, A.P. Acute Stress Impairs Cognitive Flexibility in Men, Not Women. Stress 2016, 19, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarde, S.M.; Genner, R.M.; Hrncir, H.; Arnold, A.P.; Jentsch, J.D. Sex Chromosome Complement Affects Multiple Aspects of Reversal-learning Task Performance in Mice. Genes Brain Behav 2021, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Flexibility requirement | Valence | Implicated Brain Structures | Neurotransmitters Involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID Shift | Aversive | Hippocampus, mPFC | Glutamate, GABA |
| Appetitive | OFC, mPFC, Striatum | Glutamate, GABA, Serotonin, Dopamine | |
| EDSS | Aversive | mPFC | Glutamate, GABA |
| Appetitive | mPFC, Ventral Hippocampus, ACC | Glutamate, GABA, Serotonin, Noradrenaline |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





