Submitted:
13 June 2025
Posted:
16 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
High-Sensitivity FET Biosensors
Advanced Nanomaterial Synthesis and Integration
Gate-All-Around and Dual Gate Architectures
Techniques
Integration of CMOS and Real-Time Monitoring Techniques
Specialized Nanostructures and Nanoscale Fabrication Techniques
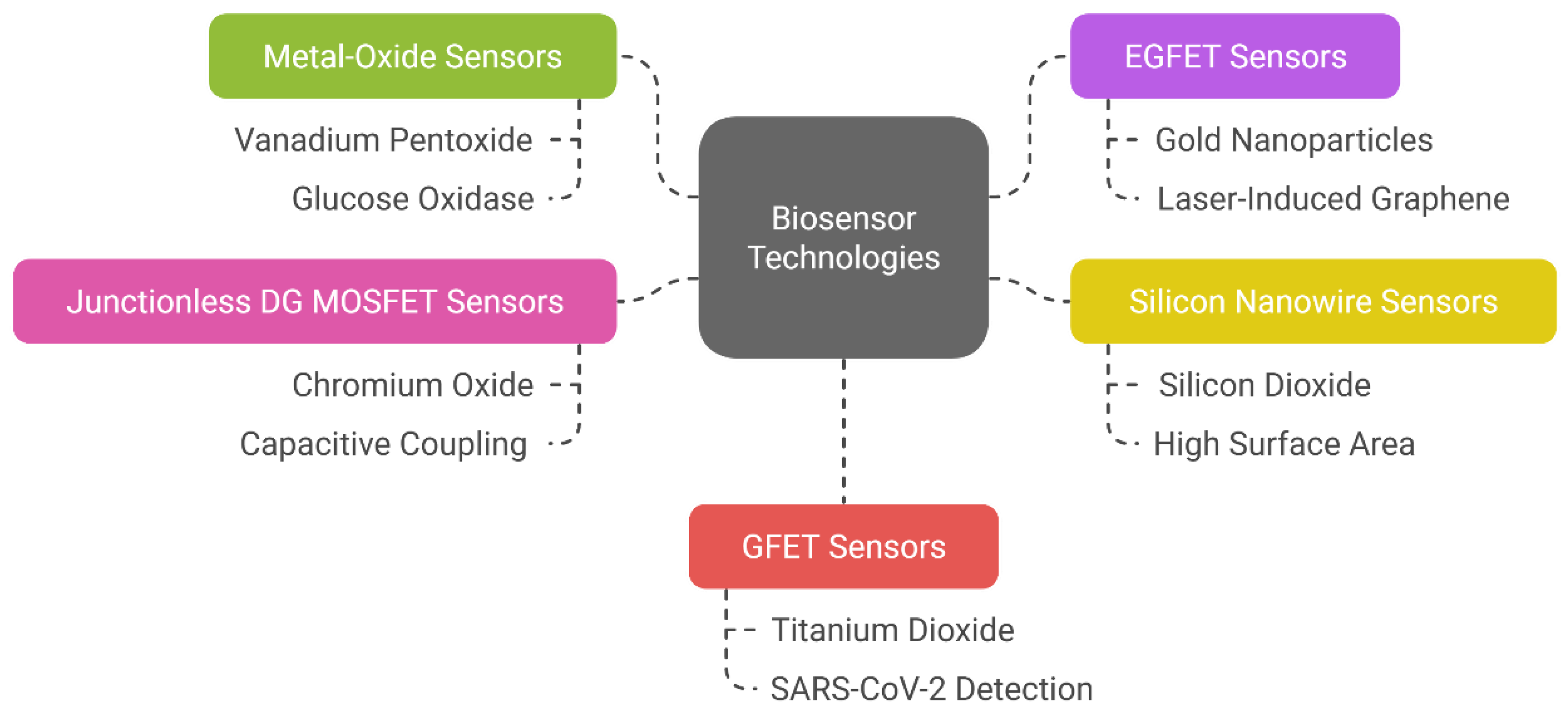
Advanced Sensor Material Types
High-K Dielectric Materials
High Mobility Semiconductors
Metal Oxides
Silicon-Based Sensors
Functionalized Surfaces and Biocompatible Coatings
Enzyme-Based Biosensors
Miscellaneous Sensors with Specific Functional Materials
Application of Electronic Sensor
Biomedical
Environment
Agriculture
Food
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mansouri, S., Recent developments of (bio)-sensors for detection of main microbiological and non-biological pollutants in plastic bottled water samples: A critical review. Talanta, 2024. 274: p. 125962. [CrossRef]
- Falina, S., et al., Ten years progress of electrical detection of heavy metal ions (hmis) using various field-effect transistor (fet) nanosensors: A review. Biosensors, 2021. 11(12): p. 478. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N., G. Pransu, and C. Adam Conte-Junior, Critical review and recent advances of 2D materials-Based gas sensors for food spoilage detection. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 2023. 63(30): p. 10536-10559. [CrossRef]
- Elli, G., et al., Field-effect transistor-based biosensors for environmental and agricultural monitoring. Sensors, 2022. 22(11): p. 4178. [CrossRef]
- Nisar, S., et al., 2D Materials in Advanced Electronic Biosensors for Point-of-Care Devices. Advanced Science, 2024. 11(31): p. 2401386.
- Yadav, S. and S. Rewari, Dual metal dual layer GAA NW–FET (DMDL–GAA–NW–FET) biosensor for label free SARS-CoV-2 detection. Microsystem Technologies, 2024. 30(5): p. 565-582. [CrossRef]
- Panahi, A. and E. Ghafar-Zadeh, Emerging Field-Effect Transistor Biosensors for Life Science Applications. 2023, MDPI. p. 793. [CrossRef]
- Du, M., et al., Direct, ultrafast, and sensitive detection of environmental pathogenic microorganisms based on a graphene biosensor. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2023. 1279: p. 341810. [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.C., et al., Advances in biosensors and diagnostic technologies using nanostructures and nanomaterials. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021. 31(44): p. 2104126. [CrossRef]
- Ji, H., et al., A Novel InSe-FET Biosensor based on Carrier-Scattering Regulation Derived from the DNA Probe Assembly-Determined Electrostatic Potential Distribution. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023. 33(14): p. 2213277. [CrossRef]
- Wasfi, A., F. Awwad, and M. Atef, DNA bases detection via MoS2 field effect transistor with a nanopore: first-principles modeling. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 2023. 114(2): p. 253-264. [CrossRef]
- Bahri, M., et al., Tungsten disulfide nanosheet-based field-effect transistor biosensor for DNA hybridization detection. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022. 5(4): p. 5035-5044. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M., et al., Bisphenol A Detection Using Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) Field-Effect Transistor Functionalized with DNA Aptamers. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2023. 8(11): p. 2201793. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S., A. Das, and S. Rewari, Dielectrically-modulated GANFET biosensor for label-free detection of DNA and avian influenza virus: proposal and modeling. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2024. 13(4): p. 047001. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., R. Chauhan, and M. Kumar, Sensitivity enhancement of dual gate FET based biosensor using modulated dielectric for Covid detection. Silicon, 2022. 14(17): p. 11453-11462. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., et al., Back-Gate Fully-Depleted Silicon-on-Insulator P-Channel Schottky Barrier MOSFET With Ultrahigh Voltage Sensitivity for Label-Free Virus RNA Detection. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Lavecchia di Tocco, F., et al., Detection of miR-155 using peptide nucleic acid at physiological-like conditions by surface plasmon resonance and bio-field effect transistor. Biosensors, 2024. 14(2): p. 79. [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.P., et al., Device-Physics Realization of ZnO–MWCNT Nanostructure-Based Field-Effect Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Simultaneous Genomic Detection of Foodborne Pathogens. Analytical Chemistry, 2023. 95(39): p. 14695-14701. [CrossRef]
- Li, K., et al., Ultrasensitive detection of exosomal miRNA with PMO-graphene quantum dots-functionalized field-effect transistor biosensor. Iscience, 2022. 25(7). [CrossRef]
- Majd, S.M., et al., Design of a novel aptamer/molecularly imprinted polymer hybrid modified Ag–Au@ Insulin nanoclusters/Au-gate-based MoS2 nanosheet field-effect transistor for attomolar detection of BRCA1 gene. Talanta, 2023. 257: p. 124394. [CrossRef]
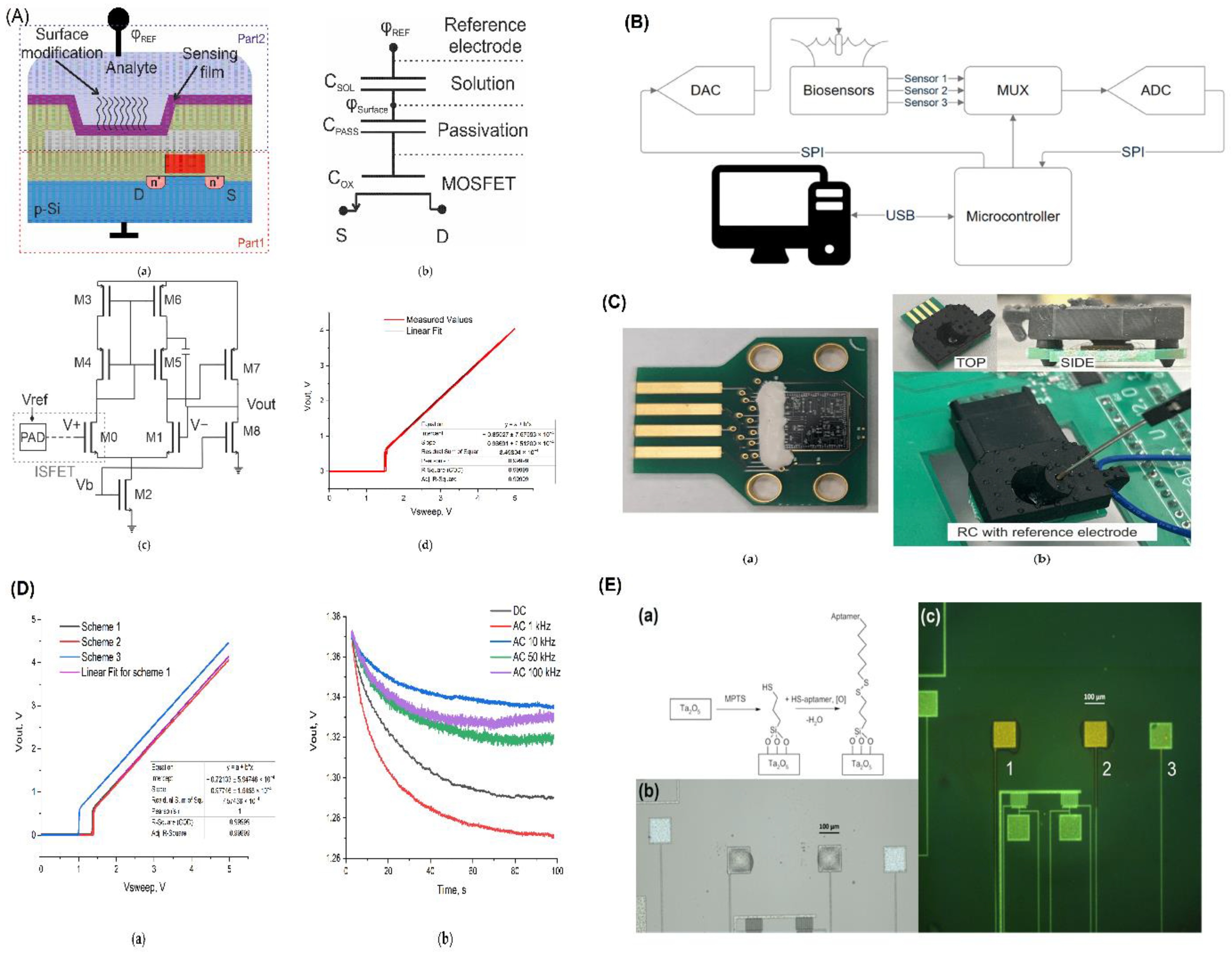
- Ryazantsev, D., et al., A Portable Readout System for Biomarker Detection with Aptamer-Modified CMOS ISFET Array. Sensors, 2024. 24(10): p. 3008. [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.-S., L.-S. Yu, and C.-H. Lin, Rapid Fluorescence-Free Detection of DNA Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification on Bare ITO Surface Under EG-FET Scheme. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023. 23(13): p. 13876-13881. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., et al., Au Nanoparticles/HfO₂/Fully Depleted Silicon-on-Insulator MOSFET Enabled Rapid Detection of Zeptomole COVID-19 Gene With Electrostatic Enrichment Process. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023. 70(3): p. 1236-1242. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S., S. Rewari, and R. Pandey, Physics-based analytical model for trap assisted biosensing in dual cavity negative capacitance junctionless accumulation mode FET. Microelectronics Journal, 2024. 143: p. 106032. [CrossRef]
- Wei, S., et al., A novel biosensor based on a bio-barcode for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Analytical Methods, 2023. 15(30): p. 3683-3691. [CrossRef]
- Tamersit, K., Dielectric-Modulated Junctionless Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor as a Label-Free DNA Nanosensor: Achieving Ultra-High Sensitivity in the Band-to-Band Tunneling Regime. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M., Performance analysis of electrochemical detection platform for DNA hybridization using TGN-based nanobiosensor. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2023. 12(12): p. 127001. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q., et al., Multi-Body Biomarker Entrapment System: An All-Encompassing Tool for Ultrasensitive Disease Diagnosis and Epidemic Screening. Advanced Materials, 2023. 35(46): p. 2304119. [CrossRef]
- Gubanova, O., et al., A novel extended gate ISFET design for biosensing application compatible with standard CMOS. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2024. 177: p. 108387. [CrossRef]
- Bitra, J. and G. Komanapalli, An Improved Z-Shaped Dual-Material-Gate DM-SDZ-TFET Biosensor for Label-Free Detection. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2024. 53(3): p. 1445-1460. [CrossRef]
- Felix, A.T., M. Mulato, and E.M. Guerra, Evaluation of sensitivity of Extended Gate Field Effect Transistor-biosensor based on V2O5/GOx for glucose detection. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2024. 177: p. 110428. [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M., G. Gopal, and T. Varma, Design and analysis of hetero-dielectric Junctionless-TFET (JL-TFET) with N+ pocket as label free biosensors. Physica Scripta, 2024. 99(4): p. 045405. [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, Z., Design and simulation of a nano biosensor based on amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide (a-IGZO) thin film transistor. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2024. 39(3): p. 035011. [CrossRef]
- Tomar, A., et al. AlN/β-Ga₂O₃ MOSHEMT as Biosensor. in 2024 IEEE Applied Sensing Conference (APSCON). 2024. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A., et al., Biomolecule detection using GaAs1− xSbX FET based dielectric modulated label-free biosensor. Physica Scripta, 2024. 99(2): p. 025020. [CrossRef]
- Sriramani, P., N. Mohankumar, and Y. Prasamsha, Drain current sensitivity analysis using a surface potential-based analytical model for AlGaN/GaN double gate MOS-HEMT. Micro and Nanostructures, 2024. 185: p. 207720. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. and K. Koley, Breast Cancer and Prostate Cancer Detection Considering Transconductance Generation Factor (g m/I DS) as a Sensing Metric for III-V Gate-all-around Tunnel FET Biosensor. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., et al., Ultrasensitive sensing urinary cystatin C via an interface-engineered graphene extended-gate field-effect transistor for non-invasive diagnosis of chronic kidney disease. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2024. 249: p. 116016. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. and S. Kale, Spacer-engineered reconfigurable silicon nanowire schottky barrier transistor as a label-free biosensor. Silicon, 2024. 16(5): p. 2023-2036. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. and R. Chauhan, Tweaking the Performance of Dielectric Modulated Junctionless Double Gate Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistor-Based Label-Free Biosensor. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2024. 171(1): p. 017503. [CrossRef]
- Rufino, F.C., et al., Non-Functionalized Graphene Ribbons FET Biosensor Platform: SARS-CoV-2 Detection on TiO 2 Gate Dielectric Windows. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024. 24(12): p. 18791-18804. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. and A. Vohra, Sensitivity enhancement using triple metal gate work function engineering of junctionless cylindrical gate all around SiNW MOSFET based biosensor for neutral biomolecule species detection for upcoming sub 14 nm technology node. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2024. 306: p. 117459. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P., et al., Design and Analysis of Junctionless-Based Gate All Around N+ Doped Layer Nanowire TFET Biosensor. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2024. 13(1): p. 017002. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S., S.S. Mohanty, and G.P. Mishra, Gate electrode stacked source/drain SON trench MOSFET for biosensing application. Physica Scripta, 2023. 98(12): p. 125027. [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, A., et al., Design and Simulation of Dielectrically Modulated Dual Material Gate-Stack Double-Gate FinFET Biosensor. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2024. 13(5): p. 057002. [CrossRef]
- Raj, A. and S.K. Sharma, Exploring the Potential of Dielectric Modulated SOI Junctionless FinFETs for Label-Free Biosensing. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2024. 53(2): p. 766-772. [CrossRef]
- Richardson, H., et al., Towards monitoring of critical illness via the detection of histones with extended gate field-effect transistor sensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X, 2024. 19: p. 100501. [CrossRef]
- Nigam, K.K., P. Yadav, and V.A. Tikkiwal, Performance analysis of dual material control gate cavity on source electrically doped TFET biosensor for biomedical applications. Micro and Nanostructures, 2024. 191: p. 207844. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.S., N. Mohankumar, and S.K. Singh, Sensitivity improvement in gate engineered technique dielectric modulated GaN MOSHEMT with InGaN notch for label-free biosensing. Engineering Research Express, 2024. 6(2): p. 025309. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V., et al., Dielectric modulated negative capacitance heterojunction TFET as biosensor: proposal and analysis. Silicon, 2024: p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A., et al., Detection of α-Galactosidase A Reaction in Samples Extracted from Dried Blood Spots Using Ion-Sensitive Field Effect Transistors. Sensors, 2024. 24(11): p. 3681. [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M., P. Parthasarathy, and U.A. Kumar, Surface potential analysis of dual material gate silicon-based ferroelectric TFET for biosensing application. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2024. 13(1): p. 017001. [CrossRef]
- Paulose, A.K., et al., Rapid Escherichia coli cloned DNA detection in serum using an electrical double layer-gated field-effect transistor-based DNA sensor. Analytical Chemistry, 2023. 95(17): p. 6871-6878. [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-Y., et al., Rapid and sensitive LAMP/CRISPR-powered diagnostics to detect different hepatitis C virus genotypes using an ITO-based EG-FET biosensing platform. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2023. 394: p. 134278. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K., et al., SARS-CoV-2 Detection in COVID-19 Patients' Sample using Wooden Quoit Conformation Structural Aptamer (WQCSA)-Based Electronic Bio-sensing System. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2024: p. 116506. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-R., et al., A self-driven, microfluidic, integrated-circuit biosensing chip for detecting four cardiovascular disease biomarkers. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2024. 249: p. 115931. [CrossRef]
- Dou, C., et al., Au-functionalized wrinkle graphene biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Interleukin-6. Carbon, 2024. 216: p. 118556. [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C., et al., Rapid and Direct Detection of Trimethylamine N-oxide Using an Off-Chip Capacitance Biosensor with Readout SoC for Early-Stage Thrombosis and Cardiovascular Disease. ACS sensors, 2024. 9(2): p. 638-645. [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C., et al., An Off-Chip Capacitance Biosensor Based on Improved Cole-Cole Model for the Detection of Trimethylamine N-Oxide in Early Cardiovascular Disease. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. and R.K. Chauhan, A novel dielectric modulated misaligned double-gate junctionless MOSFET as a label-free biosensor. Engineering Proceedings, 2023. 35(1): p. 8. [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, H.R., et al., Bridged EGFET Design for the Rapid Screening of Sorbents as Sensitisers in Water-Pollution Sensors. Sensors, 2023. 23(17): p. 7554. [CrossRef]
- Maity, A., et al., Scalable graphene sensor array for real-time toxins monitoring in flowing water. Nature Communications, 2023. 14(1): p. 4184. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X., et al. Silicon-based High-Gain Photodetector with A Strong 254-nm Response for Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Monitoring in City Sewage Water. in 2023 7th IEEE Electron Devices Technology & Manufacturing Conference (EDTM). 2023. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L., et al., Fabrication of Aptamer-based Field Effect Transistor Sensors for Detecting Mercury Ions. ECS Transactions, 2023. 111(3): p. 63. [CrossRef]
- Benslimane, O., et al., Nitrate measurement of Moroccan soil through Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistor (ISFET). Measurement: Sensors, 2023. 29: p. 100879. [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N., et al. Electrochemical EGFET pH Sensing Performance using ZnO-based Composite Thin Films Sensing Electrode. in 2023 IEEE Regional Symposium on Micro and Nanoelectronics (RSM). 2023. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.H., et al., Aptamer-Based Electric-Double-Layer (EDL) Extended-Gated FET Biosensor for Detection of Cadmium Ion. ECS Transactions, 2023. 111(3): p. 3. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S., et al., Enhanced pH Sensing Capability by Platinum Adsorption onto Titanium Dioxide Nanorods. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Jung, G., et al., Energy efficient artificial olfactory system with integrated sensing and computing capabilities for food spoilage detection. Advanced Science, 2023. 10(30): p. 2302506. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R., et al., Label-free detection of Cu (II) in fish using a graphene field-effect transistor gated by structure-switching aptamer probes. Talanta, 2022. 237: p. 122965. [CrossRef]
- Luo, S., et al., Breath alcohol sensor based on hydrogel-gated graphene field-effect transistor. Biosensors and bioelectronics, 2022. 210: p. 114319. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R., et al., Ammonium ion detection in solution using vertically grown ZnO nanorod based field-effect transistor. RSC advances, 2016. 6(60): p. 54836-54840. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., et al., A micro-carbon nanotube transistor for ultra-sensitive, label-free, and rapid detection of Staphylococcal enterotoxin C in food. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023. 449: p. 131033. [CrossRef]
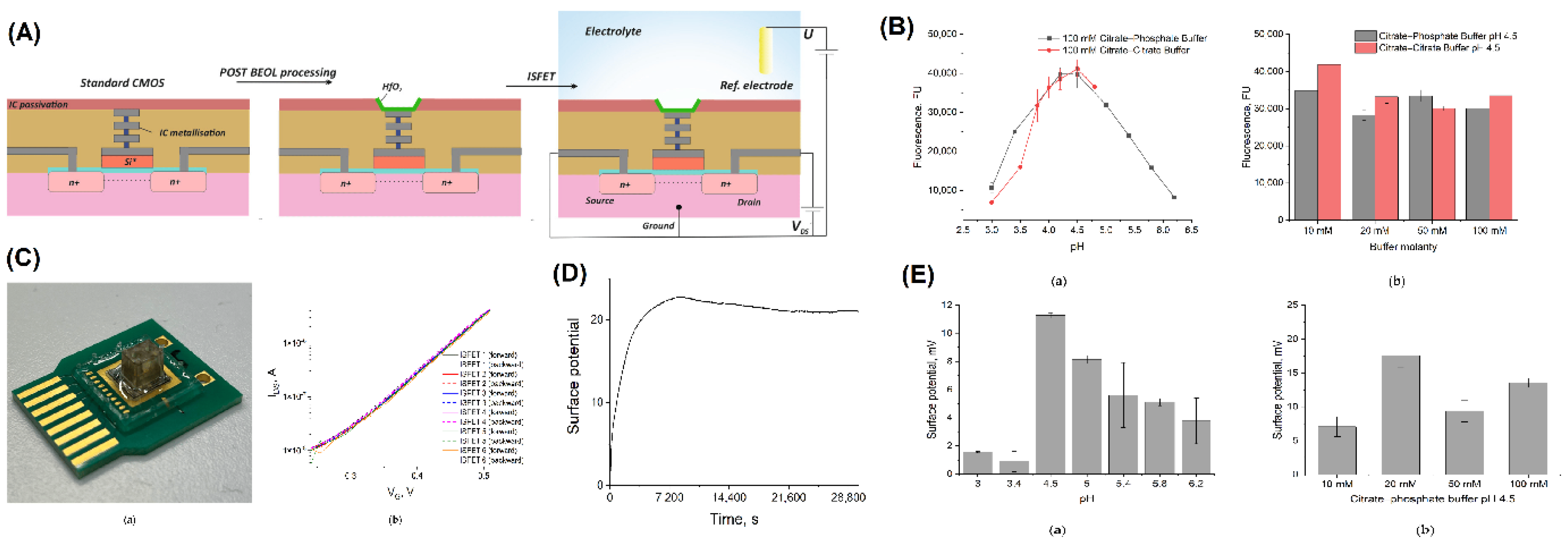
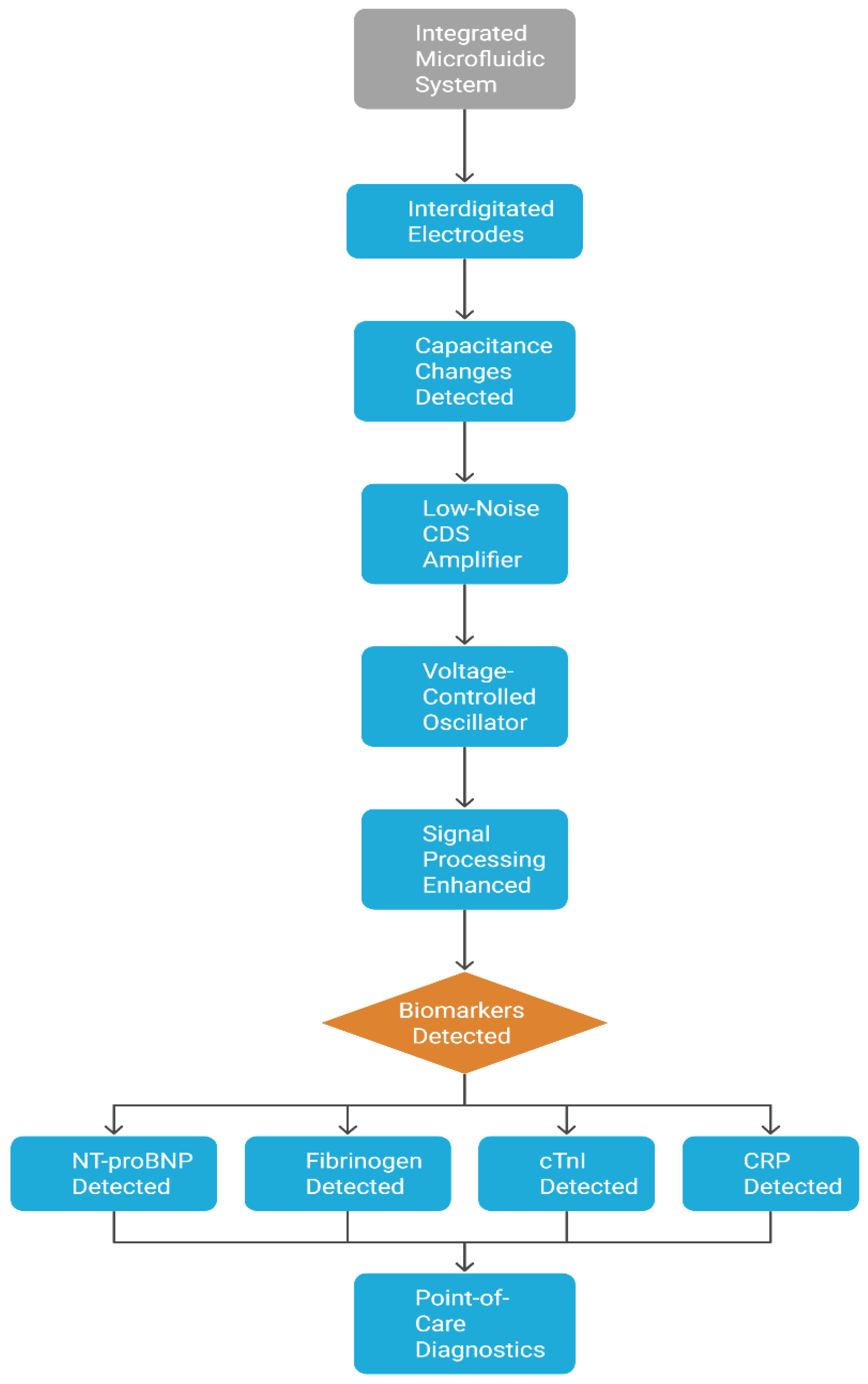
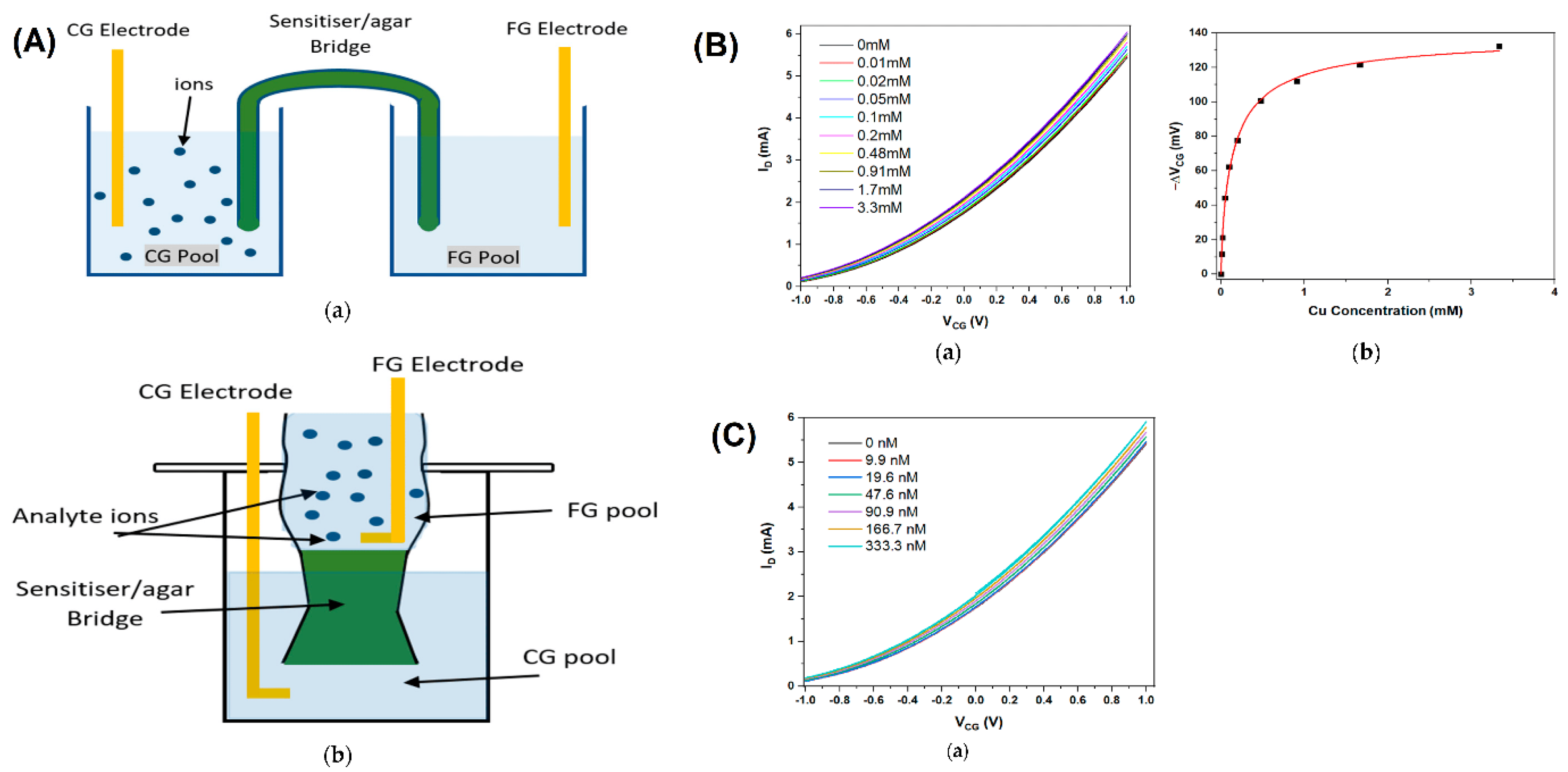
| Title | Summary | Unique Features | Materials Used | Sensitivity Metrics | Specificity Methods | Fabrication Techniques | Applications | Ref |
| GAAE-GANFET Biosensor | High sensitivity and specificity for detecting DNA and avian influenza virus. | Gate-all-around structure, strong gate-channel coupling, graded doping, oxide stacking | Al2O3, HfO2, silica-binding proteins | Threshold voltage sensitivity: 318.2 mV for AI-ab, enhanced drain current and transconductance sensitivity | Specific bioreceptors, targeted immobilization | Advanced engineering, strong gate-channel coupling | Detection of DNA, avian influenza virus | [14] |
| RNAFET Biosensor | Detection of RNA using complementary DNA probe with high sensitivity and specificity. | FDSOI technology, double-gate structure, strong capacitive coupling | HfO2, AuNPs, NiSi | Back-gate threshold voltage sensitivity: 1.765 V/log[RNA], dynamic range: 1 pM to 100 pM | DNA probe hybridization, precise patterning, Au-S bonds with thiol groups | UV lithography, reactive ion etching, self-assembly of probe DNA | Medical diagnostics, viral RNA detection | [16] |
| DMDL-GAA-NW-FET Biosensor | Detection of SARS-CoV-2 using protein and DNA targets. | Dual metal gate structure, nanowire structure, high surface-to-volume ratio, nanocavity | HfO2, SiO2, dual metal gates | VTH sensitivity: 7.08 times higher for S-protein, ION sensitivity: 2.38 times higher | Immobilization of S-protein and DNA specific to SARS-CoV-2 | Precise tuning of threshold voltage, dielectric modulation | SARS-CoV-2 detection | [6] |
| PNA-based bioFET for miRNA Detection | Detection of miR-155 with high sensitivity and specificity using PNAs. | PNA probes, thiol-gold chemistry, passivation with MCH | PNA, AuNPs | LOD: ~5 nM, dynamic range: 10–150 nM | PNA probes, passivation with MCH | Liquid-UVPO, self-assembly of PNA, passivation with MCH | Clinical diagnostics, miRNA detection | [17] |
| DC–NC–JAM-FET Biosensor | Detection of biomolecules using dual cavity and negative capacitance for high sensitivity. | Negative capacitance, dual cavities, JAM structure | HfO2, HZO | Enhanced threshold voltage, on-state current, subthreshold swing sensitivity | Dual cavities for specific detection, high surface-to-volume ratio | Simplified fabrication, JAM structure, subthreshold operation | Various biosensing applications | [24] |
| ISFET Aptasensor for Troponin I Detection | Uses DNA aptamers to detect troponin I, a biomarker for acute myocardial infarction (AMI). | AC mode with sine wave reference voltage, molecular printing technique, platinum reference electrode | Ta₂O₅, platinum, high-quality discrete components | DC mode: LOD: 15.77 ng/mL, Range: 31.25-625 ng/mL. AC mode: LOD: 3.27 ng/mL | Selective DNA aptamer binding, non-response to myoglobin and NT-proBNP | Ta₂O₅-gated ISFET, CMOS readout circuits, precise molecular printing | AMI diagnosis | [21] |
| MOSFET-Based Biosensor for COVID-19 Detection | Au nanoparticles/HfO2/FDSOI MOSFET for detecting COVID-19 ORF1ab gene. | Planar double gate MOSFET, electrostatic enrichment | Au nanoparticles, HfO2, silicon | LOD: 67 zM (~0.04 copy/μL), Range: 200 zM - 100 fM | Specific probe DNA immobilization, minimal non-specific binding | Selective immobilization of probe DNA, controlled hybridization environment | COVID-19 screening and diagnostics | [23] |
| DGDMFET Biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 Detection | Dual gate dielectric modulated FET biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 proteins and DNA. | Dual gate configuration, high dielectric constant of Cr2O3 | Cr2O3, SiO2, gold, tungsten | Enhanced sensitivity with 12% increase in threshold voltage sensitivity | Differentiation of target virus proteins using specific probes | Photolithography, ion implantation, precise nanogap formation | Virus detection, High sensitivity applications | [15] |
| InSe-FET Biosensor for RNA Detection | Field-Effect Transistor biosensor using 2D InSe for DNA-based RNA target detection. | High electron mobility InSe, microfluidic integration | InSe | Sensitivity: 13.5253/decade, LOD: 0.22 fM, Range: 1 fM - 10 nM | Selective binding to target miRNA (miR155) | High-purity, defect-free crystalline InSe, precise DNA probe immobilization | Clinical diagnostics, Disease screening | [10] |
| EDL-Gated BioFET for E. coli O157 | Biosensor using ssDNA probes for detecting E. coli O157 | ssDNA probes, EDL gating, Extended gate design | High-quality ssDNA probes, Gold electrodes, Thiol-modified DNA, MOSFET components | LOD: 1 fM; Dynamic range: 1 fM to 1 pM; R² = 0.996 | Specific binding to complementary DNA sequences, minimizing non-specific binding | Precision ssDNA immobilization, Surface functionalization, High-precision microfabrication | Rapid diagnostic tool for E. coli O157 | [53] |
| Detection | with high specificity and sensitivity. | |||||||
| MoS2-Based FET for Bisphenol A Detection | MoS2 FET biosensor functionalized with ssDNA and dsDNA for detecting BPA. | MoS2, AuNPs, ssDNA, dsDNA, PDMS-based microfluidic channel | MoS2, AuNPs, ssDNA, dsDNA | LOD: 1 pg/mL; Dynamic range: 1 pg/mL to 1 µg/mL; Sensitivity: ssDNA (4.27% to 24.48%), dsDNA (2.17% to 26.59%) | DNA functionalization ensures high affinity for BPA molecules, reducing cross-reactivity | Electron-beam evaporation, Annealing, Oxygen plasma treatment | Biomedical and environmental applications | [13] |
| ITO-EG-FET for Hepatitis C Detection | ITO-EG-FET biosensor using CRISPR/Cas12a for HCV detection with high specificity. | CRISPR/Cas12a-induced cleavage, Extended gate design | ITO, ssDNA, APTES/GA coating | LOD: 1 genomic copy/reaction; Dynamic range: 10610^6106 to 1 genomic copy/reaction | CRISPR/Cas12a ensures highly specific target recognition and cleavage | Surface modification with APTES/GA, Loop-mediated isothermal amplification | Hepatitis C detection | [54] |
| EG-FET for DNA Detection | EG-FET sensor using LAMP for detecting lambda phage DNA with high sensitivity. | LAMP, Extended gate design, Hydrogen ion detection | ITO, PMMA, Epoxy resin, Ag/AgCl reference electrode | LOD: 10 genomic copies/reaction; Hydrogen ion detection: -80.1 ± 0.03 mV/pH; R² = 0.998 | LAMP technique amplifies target DNA sequences specifically, reducing false positives | PID controller, Epoxy resin encapsulation, Integrated PCB, Solid-state Ag/AgCl reference electrode | Real-time and fluorescence-free LAMP detection | [22] |
| SiNW FET for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Detection | SiNW FET biosensor combining magnetic separation, urease catalysis, and FET detection for M.T. DNA. | Magnetic separation, Urease catalysis, High-resolution patterning | SiNWs, MNPs, SiO2NPs, Urease | LOD: 78.541 fM; Dynamic range: 1 pM to 1 µM | Magnetic separation selectively captures target DNA, reducing interference from other bacteria | Magnetic separation, Urease catalysis | Clinical diagnostics for tuberculosis | [25] |
| MoS2 Nanoscale Bioelectronic FET for DNA Base Identification | MoS2-based FET sensor with nanopore for identifying DNA bases with high sensitivity and specificity. | Nanopore integration, Gate terminal enhancement | MoS2 | LOD: femtomolar to picomolar range; Broad dynamic range; Enhanced sensitivity with gate terminal | Unique electronic signatures for each DNA base reduce non-specific interactions | Nanoscale precision, Electron beam lithography | DNA sequencing and base identification | [11] |
| MoS2 FET Aptasensor | Label-free aptasensor integrated with MoS2 FET for detecting BRCA1 ssDNA. | Pentagonal design with partial ground plane for enhanced surface area, integrated Ag–Au nanoclusters for improved electron transfer | MoS2, Ag–Au nanoclusters, aptamers | LOD: 3.0 aM (buffer), 6.4 aM (serum); Sensitivity: 0.4851 μA/decade (buffer), 0.3718 μA/decade (serum) | High affinity binding of aptamers, use of MIP for specific binding sites | Electropolymerization, MIP, electrolyte-gated FET | Early breast cancer diagnosis | [20] |
| CNT Transistor-Based Biosensor | CNT transistor-based biosensor with tetrahedral DNA nanostructure and antibodies for detecting ERβ, monkeypox virus, and ctDNA. | Tetrahedral DNA nanostructure scaffold for optimized recognition site spacing, dual patch elements for multiband capability | CNTs, pyrene derivatives, TDNs | LOD: 6.74 aM (ERβ), 991 aM (A35R), 0.21 aM (ctDNA); Sensitivity: 0.07 M^-1 (ERβ) | Dual recognition sites in Y-shaped BioES, cross-linking reactions ensuring strong attachment | Precise lithography, non-covalent coupling, self-assembly of TDNs | Clinical diagnostics, population-wide screening | [28] |
| Lg-TGNFET DNA Biosensor | Liquid gate trilayer graphene nanoribbon FET for DNA detection. | Trilayer graphene nanoribbons for higher current and improved performance, liquid gate setup for consistent environment | Trilayer graphene nanoribbons (TGN) | Detects DNA concentrations as low as 0.01 nM; significant current decrease and gate voltage shift with increasing DNA concentrations | Controlled doping, π-π interactions with DNA bases | High-resolution lithography, controlled doping, SAMs, Ag/AgCl wire | DNA detection | [27] |
| JL CNTFET DNA Nanosensor | Label-free DNA nanosensor using junctionless CNTFET operating in BTBT regime. | Junctionless design for simplified manufacturing, coaxial gating for enhanced electrostatic control | CNTs | Significant modulation in tunneling current in response to DNA | Use of high-k dielectrics, single-stranded DNA probes for selective binding | Junctionless design, laterally open cavities, coaxial gating, CVD, EBL, ALD | DNA sequence detection | [26] |
| ZnO-MWCNT Composite Biosensor | Electrical biosensor for detecting DNA sequences of foodborne pathogens | Combines ZnO stability with MWCNT mobility, strong linear response | ZnO, MWCNT, ss-DNA probes | LOD: 1 fg/μL; Dynamic range: 1 fg/μL to 10 ng/μL | Custom-designed ss-DNA probes for specific DNA sequences | Hydrothermal synthesis, SAM formation, EDC-NHS cross-linking, drop-casting | Detection of Proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli, Clostridium botulinum | [18] |
| WS2 FET DNA Biosensor | FET biosensor for DNA detection | High-quality, uniform monolayer WS2, minimal defects | WS2 | LOD: 3 aM; Dynamic range: 10^-16 M to 10^-9 M | Blocking non-specific sites with poly-C | Chemical vapor deposition, PMMA-assisted transfer, thermal annealing, photolithography, stepwise functionalization | Early disease diagnosis | [12] |
| PMO-GQDs on RGO FET Biosensor | FET biosensor for miRNA detection | High probe density, strong linear relationship (R² = 0.99) | RGO, GQDs, PMOs, PLL | LOD: 85 aM; Dynamic range: 100 aM to 1 nM | Use of neutrally charged PMOs to reduce non-specific interactions | PLL film, hybridization optimization, 3D structure formation | Detection of target miRNA21 | [19] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




