Submitted:
11 June 2025
Posted:
13 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
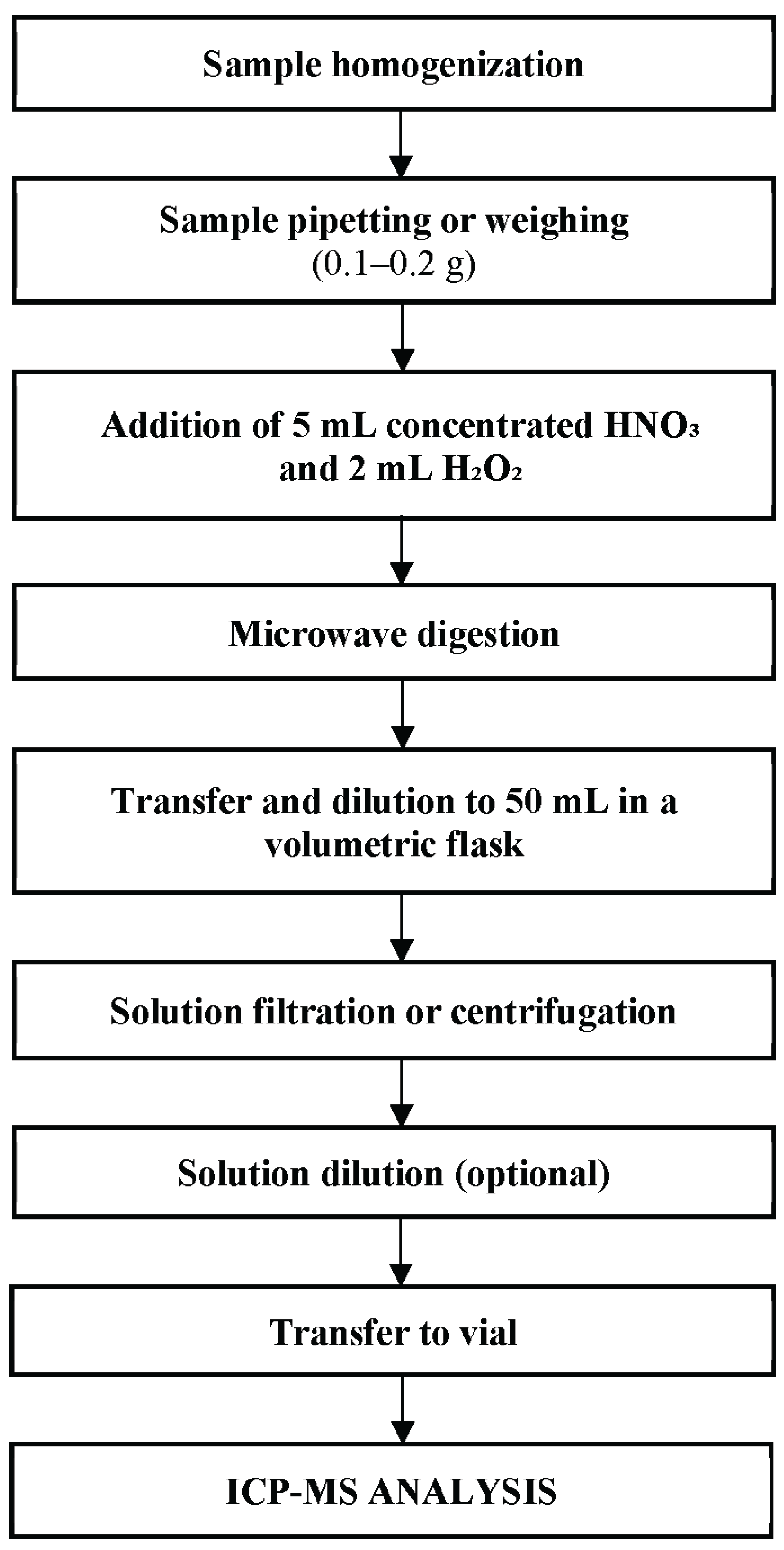
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
- Nitric acid (HNO₃) 65%, Merck (Germany).
- Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) 30%, Merck (Germany).
- Double-distilled water with conductivity < 18 MΩ.
- Single-element stock standards of Cr, Cd, Hg, and Sb at 100 µg/mL, purchased from AccuStandard.
- Stock standards of As, Cu, Pb, Mn, and Al at 1000 µg/mL, purchased from Inorganic Ventures.
- Working standard solutions with a concentration of 500 ng/mL were prepared by diluting the stock solutions.
- Internal standard mixture containing 10 µg/mL of each Bi, Ge, In, Sc, Tb, Y, and Li in 5% HNO₃.
- Tuning solution containing 10 ng/mL of each Ce, Co, Li, Mg, Tl, and Y in 2% HNO₃.
2.2. Instruments
- MARS 6 microwave digestion system (CEM, USA).
- Purelab Flex-3 ultrapure water purification system (ELGA, UK).
- UN110 drying oven (Memmert, Germany).
- ICP-MS 7900 system (Agilent Technologies).
2.3. Analytical Methods
Calibration Curve Preparation
Sample Collection and Storage
Analytical Procedure
ICP-MS Operating Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Digestion Volume
| Element | 3 mL HNO₃ + 2 mL H₂O₂ (%) |
5 mL HNO₃ + 2 mL H₂O₂ (%) |
7 mL HNO₃ + 2 mL H₂O₂ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 85.3 | 96.8 | 101.2 |
| Cr | 82.9 | 93.4 | 104.8 |
| Mn | 87.5 | 95.2 | 99.7 |
| Cu | 90.7 | 101.2 | 105.9 |
| As | 89.4 | 98.8 | 102.5 |
| Cd | 92.1 | 99.9 | 101.2 |
| Sb | 87.2 | 97.6 | 104.3 |
| Hg | 82.4 | 89.1 | 88.8 |
| Pb | 85.4 | 97.6 | 102.6 |
| Average | 82.4–92.1 | 89.1–101.2 | 88.8–105.9 |
3.2. Validation
| Element | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | LOD (mg/kg) | LOQ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 96.8 | 7.47 | 0.38 | 1.27 |
| Cr | 93.4 | 9.32 | 0.24 | 0.80 |
| Mn | 95.2 | 6.86 | 0.26 | 0.87 |
| Cu | 101.2 | 9.90 | 0.16 | 0.53 |
| As | 98.8 | 1.62 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Cd | 99.9 | 2.25 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Sb | 97.6 | 9.65 | 0.09 | 0.30 |
| Hg | 89.1 | 13.65 | 0.04 | 0.14 |
| Pb | 97.6 | 5.50 | 0.04 | 0.13 |
| Average | 89.1–101.2 | 1.62–13.65 | 0.01–0.38 | 0.03–1.80 |
3.3. Metals in Functional Foods
- Arsenic (As): The MoH allows up to 5 mg/kg. None of the samples exceeded this limit. As concentrations ranged from 0.01 to 0.89 mg/kg, with 11 samples below the LOD.
- Cadmium (Cd): Levels ranged from 0.01 to 0.06 mg/kg, with 11 samples below the LOD. The MoH limit is 1 mg/kg, indicating that Cd levels were relatively low in all cases.
- Mercury (Hg): The allowed limit is 0.1 mg/kg. Among the 27 samples, 22 had Hg concentrations below the detection limit. In the remaining 5 samples, Tinh bột nghệ vàng Phủ Quỳ and Tinh nghệ had relatively high levels, close to the regulatory threshold (0.08 and 0.09 mg/kg, respectively).
- Lead (Pb): Of the samples analyzed, 14 had Pb levels below the LOD, while 13 samples ranged from 0.04 to 0.59 mg/kg. The MoH limit for Pb is 3 mg/kg.
4. Conclusions
References
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Anh, D.H.; Huong, P.T.T.; Thanh, N.V.; Trung, N.Q.; Cuong, T.V.; Mai, N.T.; Cuong, N.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; et al. Crinane, augustamine, and β -carboline alkaloids from Crinum latifolium. Phytochemistry Letters 2018, 24, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, T.H.; Phong, N.V.; Anh, L.N.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Secondary metabolites from a peanut-associated fungus Aspergillus niger IMBC-NMTP01 with cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities. Natural Product Research 2020, 36, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Hang, L.T.T.; Huong Giang, V.; Trung, N.Q.; Thanh, N.V.; Quang, T.H.; Cuong, N.X. Chemical constituents of Blumea balsamifera. Phytochemistry Letters 2021, 43, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Hang, L.T.T.; Huong, P.T.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Cuong, T.V.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Two new guaiane sesquiterpene lactones from the aerial parts of Artemisia vulgaris. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research 2017, 20, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, M.X.; Minh, T.N.; Anh, D.T.N.; Anh, H.N.; Anh, L.V.; Trung, N.Q.; Minh, B.Q.; Xuan, T.D. Protection and Rehabilitation Effects of Cordyceps militaris Fruit Body Extract and Possible Roles of Cordycepin and Adenosine. Compounds 2022, 2, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.N.; Anh, L.V.; Trung, N.Q.; Minh, B.Q.; Xuan, T.D. Efficacy of Green Extracting Solvents on Antioxidant, Xanthine Oxidase, and Plant Inhibitory Potentials of Solid-Based Residues (SBRs) of Cordyceps militaris. Stresses 2022, 3, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.N.; Minh, B.Q.; Duc, T.H.M.; Thinh, P.V.; Anh, L.V.; Dat, N.T.; Nhan, L.V.; Trung, N.Q. Potential Use of Moringa oleifera Twigs Extracts as an Anti-Hyperuricemic and Anti-Microbial Source. Processes 2022, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, T.H.; Phong, N.V.; Anh, D.V.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Oh, H.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Bioactive secondary metabolites from a soybean-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor IMBC-NMTP02. Phytochemistry Letters 2021, 45, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Hang, L.T.T.; Huong, P.T.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Cuong, T.V.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Two new guaiane sesquiterpene lactones from the aerial parts of Artemisia vulgaris. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research 2017, 20, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Anh, D.H.; Quang, T.H.; Trung, N.Q.; Thao, D.T.; Cuong, N.T.; An, N.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Kiem, P.V.; et al. Scutebarbatolides A-C, new neo-clerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don with cytotoxic activity. Phytochemistry Letters 2019, 29, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.; Vo, T.A.; Duong, M.T.; Pham, T.M.; Van Nguyen, Q.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Bui, M.Q.; Syrbu, N.N.; Van Do, M. Heavy metals in cultured oysters (Saccostrea glomerata) and clams (Meretrix lyrata) from the northern coastal area of Vietnam. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2022, 184, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Quang, T.; Bui-Quang, M.; Truong-Ngoc, M. Rapid Identification of Geographical Origin of Commercial Soybean Marketed in Vietnam by ICP-MS. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, M.Q.; Quan, T.C.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Tran-Lam, T.-T.; Dao, Y.H. Geographical origin traceability of Sengcu rice using elemental markers and multivariate analysis. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B 2022, 15, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Tran-Lam, T.-T.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Dao, Y.H.; Le, G.T. Assessment of organic and inorganic arsenic species in Sengcu rice from terraced paddies and commercial rice from lowland paddies in Vietnam. Journal of Cereal Science 2021, 102, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.N.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Janda, T.; Szalai, G.; Le, T.G. The potential health risks and environmental pollution associated with the application of plant growth regulators in vegetable production in several suburban areas of Hanoi, Vietnam. Biologia Futura 2020, 71, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-I.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, Y.-B.; Mok, J.H. Microwave-assisted sample preparation for screening of heavy metal elements in food additives by ICP-MS. LWT 2024, 208, 116708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.-M.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Zuo, Z.-T.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Jin, H. Comparison of Mineral Element Content in a Functional Food Maca (Lepidium meyeniiWalp.) from Asia and South America. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry 2015, 2015, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, E.P.; Evangelista, F.S.; Tormen, L.; Saint´Pierre, T.D.; Curtius, A.J.; Souza, S.S. de, Barbosa. The use of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for the determination of toxic and essential elements in different types of food samples. Food Chemistry 2009, 112, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokowski, l. V. V.; Sobrinho, R.B.; Armijo, C.J.V.; Dani, C.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Funchal, C. Method validation for determination of metals in Vitis labrusca L. grapevine leaf extracts by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Anais Da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 2016, 88, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Duc, N.; Nguyen-Quang, T.; Le-Minh, T.; Nguyen-Thi, X.; Tran, T.M.; Vu, H.A.; Nguyen, L.-A.; Doan-Duy, T.; Van Hoi, B.; Vu, C.-T.; et al. Multiresidue Pesticides Analysis of Vegetables in Vietnam by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography in Combination with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-Orbitrap MS). Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.D.; Tran-Lam, T.-T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Vu, N.D.; Ma, K.H.; Le, G.T. Acrylamide in daily food in the metropolitan area of Hanoi, Vietnam. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B 2019, 12, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.P.L.; Nguyen, V.T.A.; Do, T.T.T.; Nguyen Quang, T.; Pham, Q.L.; Le, T.T. Fatty Acid Composition, Phospholipid Molecules, and Bioactivities of Lipids of the Mud Crab Scylla paramamosain. Journal of Chemistry 2020, 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.H.T.; Tran-Lam, T.-T.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Quan, T.C.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Nguyen, D.T.; Dao, Y.H. A study on multi-mycotoxin contamination of commercial cashew nuts in Vietnam. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2021, 102, 104066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Hang, L.T.T.; Huong, P.T.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Cuong, T.V.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Two new guaiane sesquiterpene lactones from the aerial parts of Artemisia vulgaris. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research 2017, 20, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Cham, P.T.; Anh, D.H.; Cuong, N.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Quang, T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Dammarane-type triterpenoid saponins from the flower buds of Panax pseudoginseng with cytotoxic activity. Natural Product Research 2021, 36, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, Pc. P.; Ngo Van, H.; Quang, M.B.; Duong Thanh, N.; Nguyen Van, D.; Thanh, T.D.; Tran Minh, N.; Thi Thu, H.N.; Quang, T.N.; Thao Do, T.; Thanh, L.P.; et al. Stigmastane-type steroid saponins from the leaves of Vernonia amygdalina and their α -glucosidase and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities. Natural Product Research 2023, 38, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.H.; Lan, D.T.N.; Thu Minh, N.T.; Khanh, N.D.; Trang, D.T.; Cuong, P.V.; Hiep, N.T.; Nam, V.D.; Trung, N.Q.; Dat, N.T. Quassinoids and Alkaloids From the Roots of Eurycoma longifolia. Natural Product Communications 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, T.; Lejmel, M.A.; Molnár, A.B.; Majláth, I.; Pál, M.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Le, V.N.; Szalai, G. Interaction between elevated temperature and different types of Na-salicylate treatment in Brachypodium dystachion. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0227608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; Anh, L.N.; Trung, N.Q.; Quang, T.H.; Anh, D.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Van Minh, C. Cytotoxic phenolic glycosides from the seeds of Senna tora. Phytochemistry Letters 2021, 45, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.H.; Lan, D.T.N.; Thu Minh, N.T.; Khanh, N.D.; Trang, D.T.; Cuong, P.V.; Hiep, N.T.; Nam, V.D.; Trung, N.Q.; Dat, N.T. Quassinoids and Alkaloids From the Roots of Eurycoma longifolia. Natural Product Communications 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC - AOAC official method 2015.01. Heavy Metals in Food Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry First Action (2015).
- AOAC International, How to meet ISO 17025 requirements for method verification, USA (2007).
- Bộ Y tế - QCVN 8-2-2011/BYT: Quy chuẩn kỹ thuật quốc gia đối với các sản phẩm đồ uống không cồn.
- Bộ Y tế - Quyết định 46/2007/QĐ-BYT “Quy định giới hạn tối đa ô nhiễm về sinh học và hóa học trong thực phẩm”.
| Stage | Temperature (°C) | Ramp Time (min) | Hold Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 180 | 15 | 15 |
| 2 | 30 | – | 15 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| RF power, W | ~1600 |
| Sampling depth, mm | ~3 |
| Carrier gas flow rate, L/min | ~0.7 |
| Auxiliary gas flow rate, L/min | ~0.3 |
| Nebulizer | MicroMist |
| Spray chamber temperature, °C | 2 |
| Vacuum pressure during analysis, Pa | 5 × 10⁻⁴ |
| Vacuum pressure in standby mode, Pa | 3 × 10⁻⁵ |
| Peristaltic pump speed, mL/min | 0.1 |
| Wash pump speed, rpm | 48 |
| Sample pump speed, rpm | 26 |
| Cooling water temperature, °C | 20 |
| Cooling water power, W | 1750 |
| Acquisition time per replicate, s | 5.8 |
| Wash time, s | 120 |
| Stabilization time, s | 30 |
| Cooling water flow rate, L/min | 2.4 |
| Number of replicates per point | 3 |
| Sample Type | Al | Cr | Mn | Cu | As | Cd | Sb | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lyver plus | 2.85 | 0.27 | 1.26 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.05 |
| Hewell | 34.15 | <0.24 | 8.41 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Newcalver | 5.72 | <0.24 | 47.83 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.04 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.05 |
| Diệp hạ châu | 12.85 | <0.24 | 86.43 | 0.66 | 0.28 | 0.03 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.05 |
| Vinagan | 4.84 | <0.24 | 5.21 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Nanogol | 44.64 | 0.93 | 8.46 | 0.93 | 0.18 | <0.01 | 0.10 | <0.04 | 0.04 |
| Ích tâm khang | 25.02 | 0.31 | 7.59 | 0.34 | 0.13 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.05 |
| Vương tâm thống | 15.44 | <0.24 | 92.11 | 0.56 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Ninh tâm vương | 17.77 | <0.24 | 6.23 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 0.01 | <0.09 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| An Mạch | 62.50 | 0.39 | 29.56 | 2.46 | 0.24 | 0.06 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.26 |
| Hanomax | 94.90 | 0.42 | 78.73 | 2.21 | 0.89 | 0.02 | 0.12 | <0.04 | 0.59 |
| BoniOxy 1 | 8.25 | 0.36 | 1.64 | 1.28 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Hộ tạng đường | 19.18 | 0.25 | 6.98 | 0.99 | 0.09 | 0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.15 |
| Diabetna | 7.68 | 0.27 | 26.52 | 3.84 | 0.29 | 0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Mega pro plus | 25.82 | 0.24 | 28.03 | 2.59 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| TD care | 45.07 | 0.57 | 26.20 | 3.73 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 0.11 | <0.04 | 0.12 |
| Thanh đường an | 22.92 | 0.40 | 25.95 | 2.96 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.05 |
| Tinh bột nghệ ngọc ý | 2.91 | <0.24 | 39.66 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Tinh bột nghệ Phủ Quỳ | 1.26 | 0.25 | 18.75 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | 0.08 | <0.04 |
| Tinh bột nghệ Nghệ An | 5.40 | 0.29 | 35.54 | <0.16 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | 0.05 | <0.04 |
| Tinh bột nghệ Út Em | 5.88 | 0.27 | 8.77 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Tinh bột nghệ Tân Nam | 20.37 | 0.20 | 65.31 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | 0.05 |
| Nghệ vàng | 4.89 | 0.24 | 59.78 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Tinh nghệ | 13.56 | 0.24 | 44.03 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | 0.09 | <0.04 |
| Tinh nghệ Sagamin | 8.50 | 0.33 | 2.08 | <0.16 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Curcumin | <0.38 | <0.24 | 1.53 | 0.65 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
| Tinh bột nghệ HV quân y | 0.39 | <0.24 | 0.38 | 0.17 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.09 | <0.04 | <0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





