Submitted:
12 June 2025
Posted:
12 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
The Importance of Integration
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Integration allows for real-time sharing of quality-related data between the lab and production environments. This ensures that any deviations from quality standards are immediately communicated, enabling prompt corrective actions.
- Streamlined Workflows: By connecting SAP QM with lab systems and shop floors, organizations can streamline workflows, reducing manual intervention and the risk of errors. Automated data transfers and notifications enhance operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: The pharmaceutical industry is subject to stringent regulations, and maintaining compliance is critical. Integration helps ensure that all quality data is accurately captured, documented, and reported, thus facilitating audits and regulatory inspections.
- Improved Decision-Making: Access to real-time quality data empowers decision-makers to make informed choices regarding production processes, material usage, and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Ultimately, the integration of SAP QM with laboratory systems and shop floors contributes to improved product quality, which is essential for patient safety and company reputation.
Key Challenges in Integration
- Data Silos: Many organizations operate with legacy systems that do not communicate effectively with SAP QM. These data silos hinder the flow of information, making it challenging to achieve seamless integration.
- Change Management: Integrating new systems often requires significant changes to existing workflows and processes. Resistance to change from employees can impede successful implementation.
- Technical Complexity: The technical aspects of integration, including data mapping, interface development, and system configuration, can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Compliance Concerns: Ensuring that the integration meets regulatory requirements can be challenging, particularly in an industry where compliance is paramount. Organizations must prioritize validation and documentation.
- Cost Considerations: The costs associated with integration projects can be significant. Organizations must weigh the potential benefits against the investment required for successful implementation.
Best Practices for Implementation
- Conduct a Thorough Needs Assessment: Before initiating integration, organizations should conduct a comprehensive assessment to identify specific quality management needs and gaps in current processes.
- Involve Stakeholders Early: Engaging stakeholders from laboratory, production, and IT departments early in the process is crucial for understanding requirements and addressing concerns.
- Invest in Training: Providing adequate training to employees on the new integrated system is essential for ensuring user adoption and minimizing resistance to change.
- Utilize Middleware Solutions: Middleware can facilitate communication between SAP QM and laboratory systems, helping to bridge any gaps and streamline data transfers.
- Ensure Compliance and Validation: Organizations must prioritize compliance with regulatory requirements during the integration process. Thorough validation and documentation of the integrated system are critical.
Connecting SAP QM with Lab Systems
- Key Benefits of Integrating SAP QM with Lab Systems
| Benefit | Description |
| Real-Time Data Access | Immediate access to lab results for production decisions. |
| Automated Workflows | Reduction of manual entry and error potential. |
| Compliance Tracking | Enhanced ability to track compliance with quality standards. |
| Improved Traceability | Better traceability of materials and processes. |
| Faster Issue Resolution | Quicker identification and resolution of quality issues. |
Connecting SAP QM with Shop Floors
- Key Benefits of Integrating SAP QM with Shop Floors
| Benefit | Description |
| Enhanced Quality Control | Integration allows for real-time monitoring of production quality. |
| Data-Driven Decisions | Production teams can make informed decisions based on quality data. |
| Compliance Documentation | Automatic documentation of quality checks enhances compliance efforts. |
| Streamlined Operations | Improved communication between quality and production teams. |
| Predictive Analytics | Ability to analyze data for trends and potential issues. |
The Integration of SAP QM with Lab Systems and Shop Floors
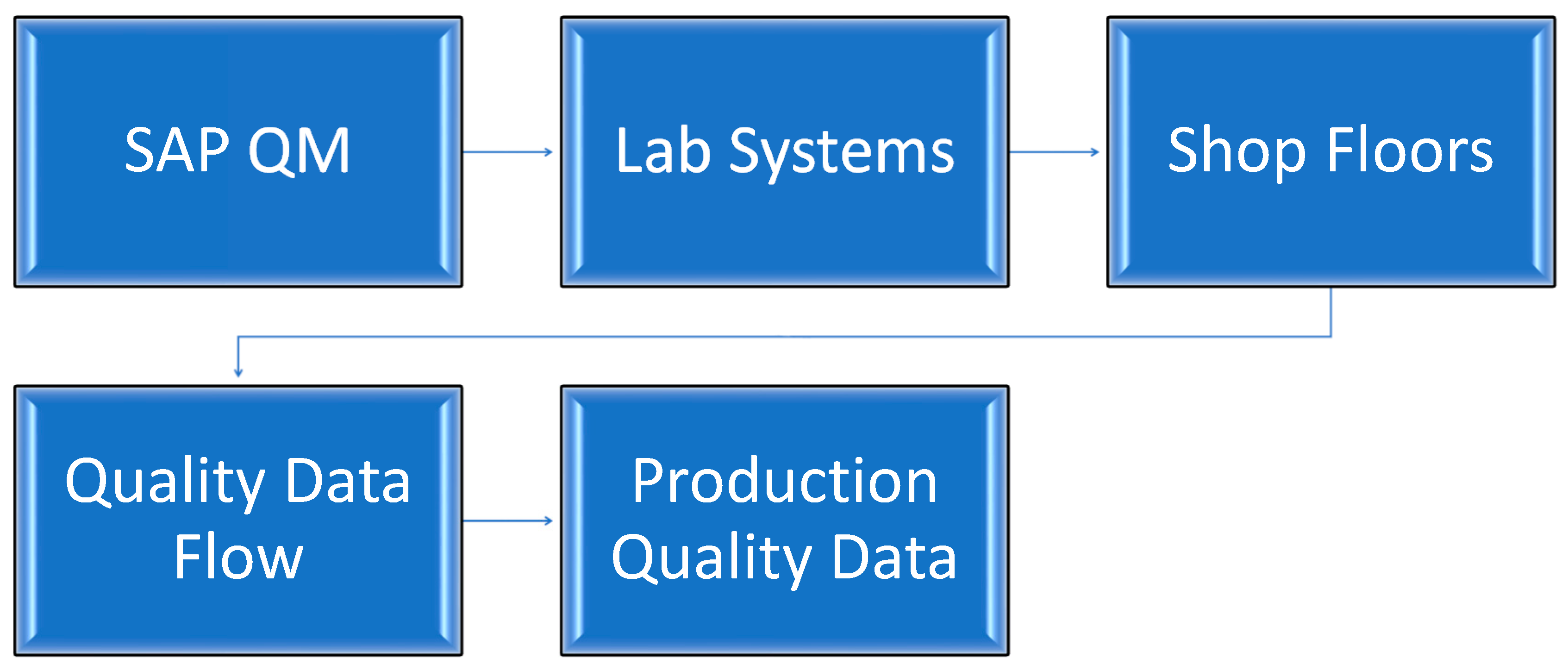
Further Considerations for Integration
Change Management and Cultural Shift
- Leadership Engagement: Leadership must actively support the integration process and communicate its importance to all employees. This can help in gaining buy-in and minimizing resistance to change.
- Continuous Training and Support: Regular training sessions should be conducted to ensure that employees are comfortable using the integrated system. This could include workshops, webinars, and access to online resources.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing channels for employees to provide feedback on the integration process can help identify potential issues early and foster a sense of ownership among staff.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
- Modular Integration: Implementing a modular approach to integration allows organizations to adapt and expand their systems as needed without overhauling the entire infrastructure. This flexibility is critical in a rapidly changing industry.
- Adoption of Emerging Technologies: Exploring the integration of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), can enhance the capabilities of SAP QM. These technologies can help in predictive analytics, allowing organizations to anticipate quality issues before they arise.
Regulatory Compliance and Validation
- Validation Protocols: Developing robust validation protocols for the integrated system is essential to meet regulatory standards. This involves comprehensive testing and documentation of all processes to demonstrate compliance during audits.
- Audit Readiness: Organizations should maintain an audit-ready posture by ensuring that all quality data is accessible and accurately documented. This can facilitate smoother inspections by regulatory bodies.
Measuring Success
- Reduction in Non-Conformance Reports (NCRs): Monitoring the number of NCRs can provide insight into the effectiveness of quality management processes.
- Cycle Time for Quality Checks: Tracking the time taken for quality checks can help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement in workflows.
- Training Compliance Rates: Ensuring that employees complete necessary training on the integrated system can be a measure of readiness and engagement.
- Customer Complaints and Returns: Analyzing customer feedback and product returns can indicate overall product quality and highlight areas needing attention.
Implementation Steps for Integrating SAP QM with Lab Systems and Shop Floors
1. Assessing Current Systems and Needs
- Mapping Existing Workflows: Understand current laboratory and shop floor workflows to identify potential inefficiencies and areas that require enhancement.
- Identifying Stakeholders: Engage with key stakeholders from various departments, including quality assurance, production, and IT, to gather insights and expectations.
- Defining Integration Objectives: Establish clear goals for what the integration aims to achieve, such as improved data accuracy, faster reporting, or enhanced compliance.
2. Selecting Appropriate Integration Tools
- Middleware Solutions: Evaluate middleware platforms that can facilitate communication between SAP QM and lab systems. These tools can help bridge compatibility gaps and enable seamless data flow.
- APIs: Utilize Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for real-time data exchange. APIs can enhance connectivity between different systems, ensuring that quality data is always up to date.
- Custom Development: In some cases, custom solutions may be necessary to meet specific organizational needs. Collaborating with IT experts can help develop tailored applications for better integration.
3. Data Standardization and Migration
- Data Mapping: Create a data mapping plan to define how data from lab systems will correspond to fields in SAP QM. Consistency in data formats is essential.
- Data Cleansing: Before migration, cleanse the data to remove duplicates, errors, and irrelevant information. This ensures that only high-quality data is transferred to the new system.
- Testing Migration: Conduct thorough testing of data migration processes to identify any issues before going live. This may involve pilot testing with smaller datasets.
4. Training and Change Management
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop tailored training sessions for different user groups to ensure they understand the new processes and systems. This may involve hands-on workshops and e-learning modules.
- Continuous Support: Provide ongoing support and resources to help employees navigate the new system post-implementation. A dedicated help desk or support team can be beneficial.
- Change Champions: Identify change champions within the organization who can advocate for the integration and assist their colleagues in adapting to the new processes.
5. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
- Performance Metrics: Utilize KPIs established during the planning phase to assess the effectiveness of the integration. Regularly review these metrics to identify areas for improvement.
- Feedback Loops: Implement mechanisms for collecting feedback from users about the new system. This can help identify pain points and areas needing refinement.
- Iterative Improvements: Adopt an iterative approach to enhancements. Regularly assess the system and make adjustments based on user feedback and evolving industry requirements.
| KPI | Description | Target Level |
| Non-Conformance Reports | Number of quality issues reported per month | Decrease by 20% |
| Cycle Time for Checks | Average time taken for quality checks (in hours) | Reduce to < 1 hour |
| Training Completion Rate | Percentage of employees trained on new systems | 100% |
| Customer Complaints | Number of complaints received per quarter | Decrease by 15% |
| Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
| Data Silos | Implement middleware solutions for data integration |
| Resistance to Change | Engage stakeholders early and provide comprehensive training |
| Compliance Concerns | Develop robust validation protocols during integration |
| System Compatibility Issues | Conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems prior to integration |
Future Trends in SAP QM Integration with Lab Systems and Shop Floors
1. Enhanced Automation and AI Integration
- Automated Data Capture: Integrating IoT devices within lab systems and shop floors can facilitate real-time data capture, reducing manual entry errors and improving data accuracy. For example, sensors can automatically collect temperature and humidity data in storage facilities, feeding this information directly into SAP QM for compliance monitoring.
- Predictive Analytics: Leveraging AI algorithms, organizations can analyze historical data to predict potential quality issues before they occur. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, minimizing non-conformance incidents and ensuring regulatory compliance.
2. Cloud-Based Solutions
- Scalability: Cloud-based SAP solutions allow organizations to scale their operations easily, accommodating growth or changes in production without significant upfront investments in IT infrastructure.
- Remote Access and Collaboration: With cloud technologies, teams can access critical quality data and collaborate from anywhere. This is particularly advantageous in global organizations, facilitating quicker decision-making and enhanced compliance across different regions.
3. Blockchain for Enhanced Traceability
- Immutable Record Keeping: Using blockchain, organizations can create tamper-proof records of all quality-related data, ensuring that any changes or updates are documented transparently. This is crucial for compliance and can enhance stakeholder trust.
- Improved Traceability: Blockchain enables better tracking of products throughout the supply chain, allowing companies to quickly identify and address quality issues, ultimately ensuring patient safety.
4. Advanced Data Analytics and Visualization Tools
- Facilitate Data-Driven Decisions: Integrating SAP QM with advanced analytics platforms can provide valuable insights into quality trends and potential areas of concern. Data visualization tools enable stakeholders to understand complex data sets easily, making it easier to identify trends and make informed decisions.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced analytics can support real-time monitoring of quality metrics, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to potential issues. Dashboards that visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) can help teams stay informed and proactive.
5. Emphasis on Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
- Integrated Compliance Frameworks: SAP QM will increasingly support integrated compliance frameworks that align with global regulations, enabling companies to navigate the complexities of various markets more effectively.
- Risk-Based Approaches: Organizations will adopt more sophisticated risk management practices, utilizing SAP QM to assess and mitigate quality risks across all stages of production. This proactive stance helps maintain compliance and ensures product safety.
Conclusion
References
- ISO. (2022). ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems. International Organization for Standardization.
- McKinsey & Company. (2023). Cloud in Life Sciences: The Future of Pharmaceutical Operations. Retrieved from McKinsey.
- Sinha, R., & Joshi, S. (2021). Blockchain Applications in Pharmaceuticals: Enhancing Quality and Traceability. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 110(5), 1620-1628.
- Zaborowski, J. (2022). The Future of Quality Management in Pharma: Harnessing AI and Automation. Pharmaceutical Executive, 42(1), 40-45.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




