1. Introduction
With the continuous expansion of the digital entertainment industry, the fine modeling of player behavior has become a key link to improve the game interaction experience and personalized content delivery. Aiming at the limitations of traditional modeling methods in the portrayal of temporal correlation and behavioral differences, this paper introduces a deep learning method to construct a behavioral recognition model, and optimizes the response mechanism of the interaction system on this basis.
In recent years, deep learning has demonstrated strong advantages in a variety of application domains. Ali et al. (2025) proposed a deep learning framework for solving fractional partial differential equations, showing its capacity to handle complex dynamic systems with nonlinearity and memory properties [
1]. Braun and Wulff (2025) explored the automation of agricultural subsidy processing using deep convolutional networks, highlighting the effectiveness of deep learning in decision-making systems driven by visual data [
2]. In the medical field, Yagmur et al. (2025) applied deep neural networks to the classification of EEG signals for Alzheimer’s detection, which confirmed the model's sensitivity to temporal sequence data with subtle variation [
3]. In terms of security applications, Basheer and P. R. (2025) developed an intrusion detection framework using graph convolutional networks, illustrating deep learning's robustness in processing irregular behavior patterns within large-scale systems [
4]. This study proposes a BiLSTM-Attention model to optimize game interactions through adaptive feedback.
2. Relevant Technology Base
In player behavior modeling, deep neural networks can effectively mine the potential laws in player operation data Taking convolutional neural network (CNN) as an example, it extracts spatial features through convolutional kernel, which is suitable for the recognition of player click heatmap and path trajectory; while recurrent neural network (RNN) and its variants LSTM and GRU are more suitable for the modeling of temporal behavior data, as shown in the following equation (1), the state transfer of LSTM controls the flow of information through the gating mechanism:
where
is the Oblivion Gate and
is the current cell state.
For large-scale behavioral data processing, the Transformer structure is advantageous in modeling long-distance dependencies with the self-attention mechanism defined as follows:
This study analyzes 20,000 operation records from a competitive game, where players average 87 interactions per minute with behavior sequences of length 136. After normalization and denoising, PCA shows the first three components retain 91.3% of the data. The modular game system supports real-time AI integration via API.
3. Design of Deep Learning-Based Player Behavior Modeling Approach
3.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
This study collects operation behavior data from 500 active players in a multiplayer competitive game, totaling 120 GB of raw logs. The data collection is based on client-side SDK injection and server log synchronization, ensuring millisecond-level event timestamp precision. After eliminating abnormal session records (3.7% of data), operation events are uniformly coded into time-sequence behavior vectors. A sliding window (30-second size, 5-second step) transforms continuous sequences into model inputs. Numerical features are normalized using Min-Max scaling, and categorical features are One-Hot encoded. Outliers are corrected with z-score, and missing values are controlled at 1.5%. The final dataset contains 280,000 sequences, ready for modeling.
3.2. Feature Extraction and Selection Strategy
Twelve primitive features, such as operation frequency and skill release intervals, were extracted from behavior logs, and higher-order semantic features were obtained using statistical methods combined with deep learning. PCA revealed that the first six components explained 87.6% of the variance, with "skill usage rhythm" and "interaction density" having the highest weights. A BiLSTM network, with 128 hidden units, ReLU activation, and Dropout=0.3, was used to capture temporal and nonlinear relationships in the data[
5].
3.3. Model Construction
A player behavior modeling model based on Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network to capture the backward and forward dependency properties in the behavioral sequences. The input feature vector dimension is
, where
is the time step and
is the filtered feature dimension [
6]. The BiLSTM network contains two layers, each containing 128 hidden units, and uses the ReLU activation function. The bi-directional structure is able to handle both historical and future states, and the hidden states are updated as follows:
The final output is a positive and negative hidden state splice:
. On that basis, the weight expressiveness of the key behavioral fragments is enhanced using the Attention mechanism, whose weights are computed as:
where
is the importance coefficient of the first
moment and
is the trainable parameter.
3.4. Model Training and Evaluation Indicator Design
In the model training phase, the BiLSTM-Attention model is parameter updated using the Adam optimizer, with the initial learning rate set to 0.001, combined with a dynamic learning rate decay strategy to avoid late oscillations [
7]. Meanwhile, in order to improve the model stability, the output of each layer is normalized using Batch Normalization, the training batch size is set to 64, and the maximum number of training rounds is 50. The loss function uses weighted cross-entropy to consider the imbalance problem of category distribution, which is defined as follows:
where,
is the sample weight,
is the true label, and
is the predicted value.
The model training introduces Dropout (set to 0.3) with L2 regularization term to effectively mitigate the overfitting risk, which is defined as the regularization term:
where,
is the model parameter and
is the regularization coefficient, set to 0.01[
8].
4. Optimization Design of Game Interaction System
The optimized game interaction system adopts a modular design, including a front-end interface, behavior perception module, predictive control engine, and feedback scheduler. It uses a client SDK to collect real-time player data, and the perception module identifies behavior types The control engine adjusts interaction parameters and supports Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA). Feedback is adapted in real time to enhance immersion[
9]. The system is decoupled via RESTful API, enabling quick deployment and updates in engines like Unity, achieving personalized, adaptive interaction for an enhanced game experience.
5. System Implementation and Experimental Analysis
5.1. System Architecture and Module Design
The system follows a decoupled front-end and back-end design with four core modules: interaction acquisition, behavioral modeling, optimization control, and feedback rendering [
10]. The front-end, built on Unity, uses a lightweight SDK for real-time data collection and uploading. The back-end, using Python and TensorFlow, performs classification predictions on behavioral sequences. The control module adjusts game interaction parameters based on model outputs, while the feedback module updates the UI and responses in real time. Modules communicate via RESTful APIs for efficient system performance in a high-concurrency environment.
5.2. Data Set Construction and Experimental Environment
The dataset comprises operation logs from 500 players in an online competitive game, capturing interactions such as clicks, movements, and skill releases[
11]. It includes approximately 280,000 behavioral sequences with 30 time steps and 8 feature dimensions per step. Behavior labels are categorized into 4 patterns based on expert annotation. After cleaning and normalization, the data is formatted as sequence tensors for model training. The experimental environment uses an Intel i9-13900K processor, 32GB RAM, NVIDIA RTX 3080 GPU, Ubuntu 22.04, Python 3.9, TensorFlow 2.14, and Jupyter Notebook for model management. Flask API and Unity interface are used for system deployment testing.
5.3. Model Training Results and Analysis
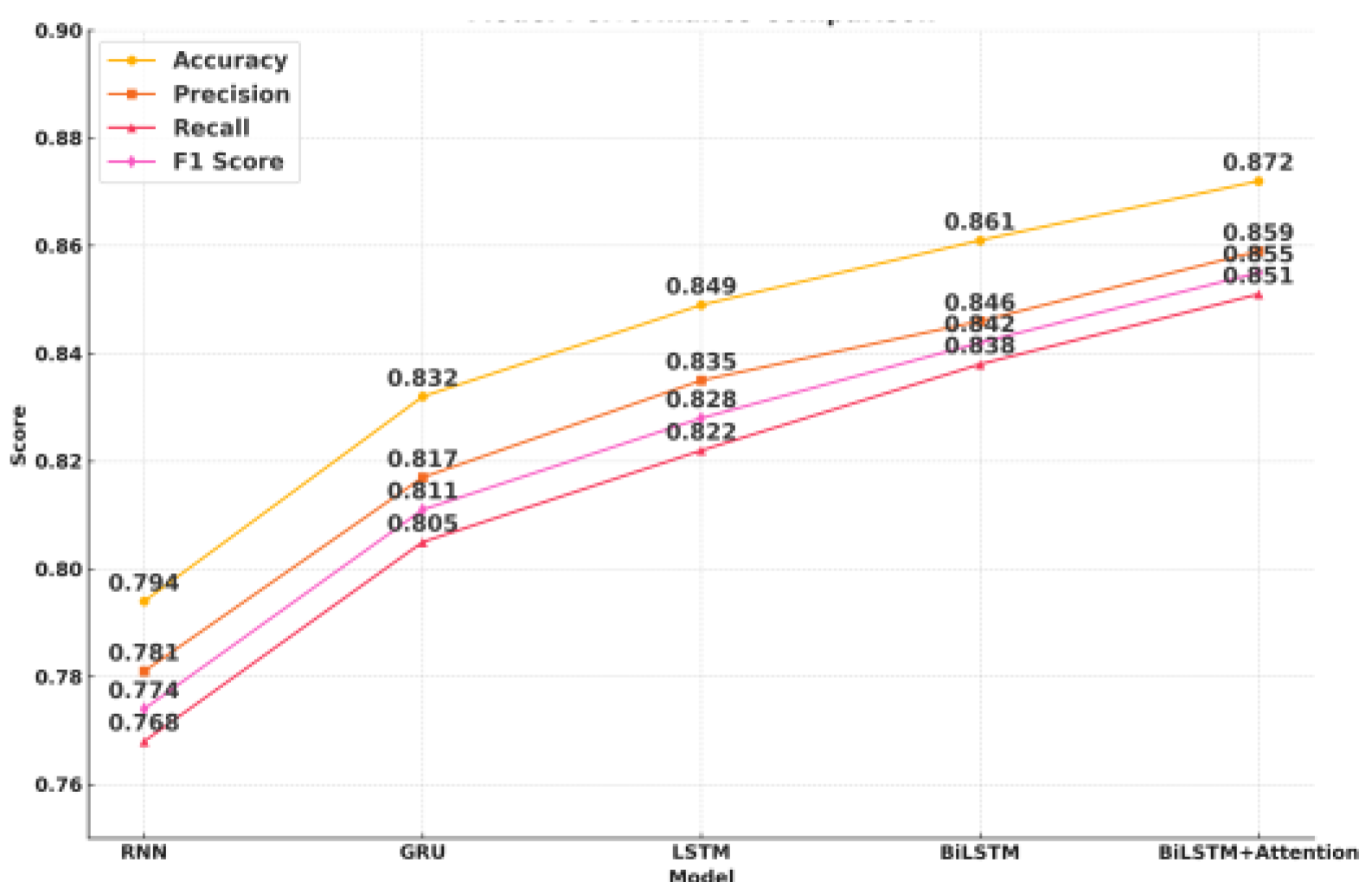
Five deep learning models are compared using Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1 Score for comprehensive performance evaluation.
As shown in
Table 1, BiLSTM+Attention outperforms others in all metrics, highlighting its effectiveness in modeling complex player behaviors. See
Figure 1 for details.
Observe the convergence trend and stability performance of the model during the training process, record the accuracy and loss value changes of BiLSTM+Attention model during 10 rounds of training, and construct the following training process data table.
Table 2 shows stable training and validation accuracy, with minimal loss difference, indicating high model stability and robustness.
5.3. Assessment of the Effectiveness of System Optimization
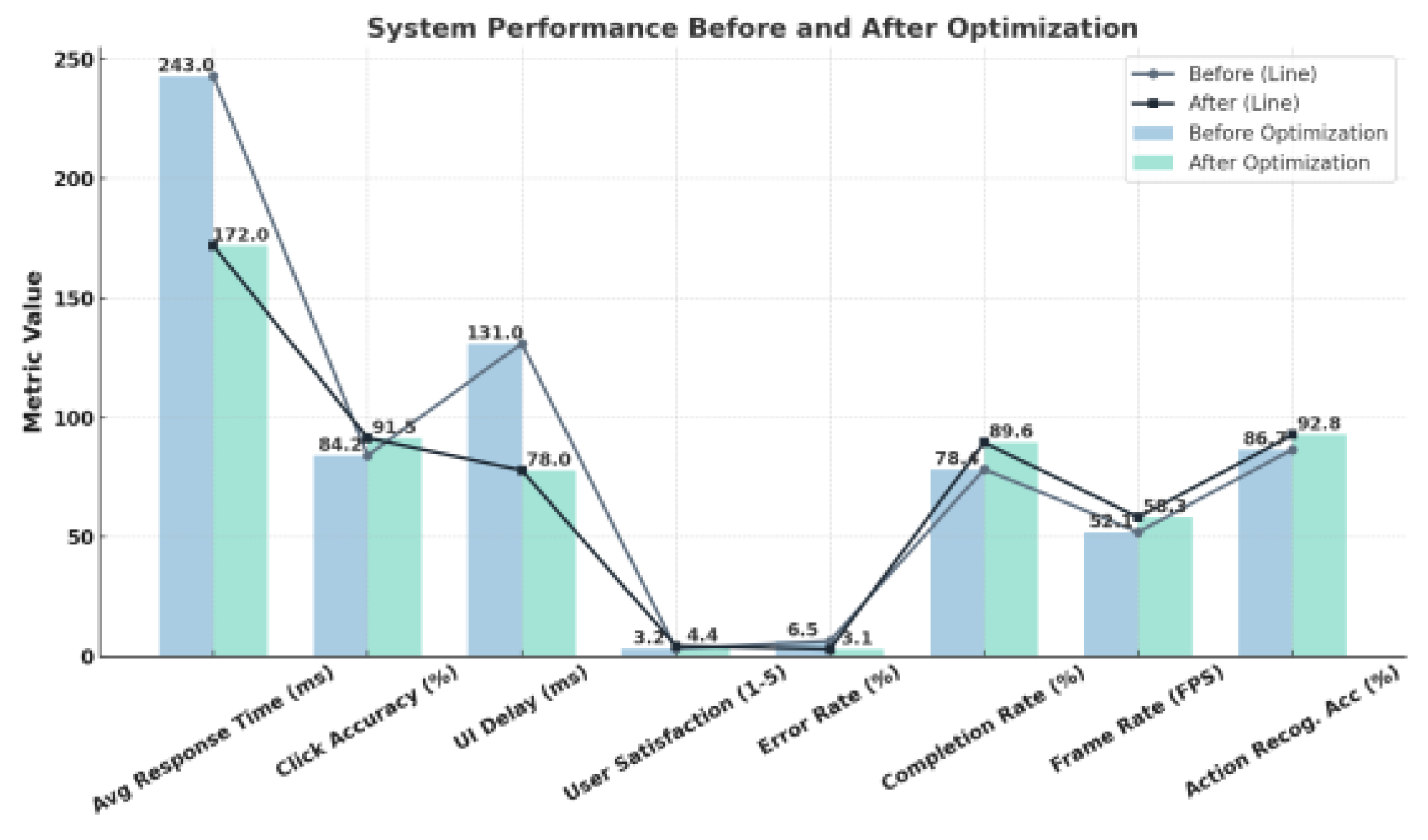
The experimental comparison of the system before and after optimisation is detailed in
Table 3.
As seen in
Table 3, After optimization, the system's performance improved significantly. The average response time decreased by 29.2%, from 243ms to 172ms. Click accuracy increased from 84.2% to 91.5%, and interface interaction delay dropped from 131ms to 78ms. User satisfaction rose from 3.2 to 4.4, and error rate reduced from 6.5% to 3.1%. The session success rate improved to 89.6%, and action recognition accuracy increased to 92.8%, demonstrating the effectiveness of behavior modeling for optimization. See
Figure 2 for details.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we conduct a systematic research on player behavior modeling and interaction system optimization, construct a time-series modeling framework based on BiLSTM-Attention structure, and design an optimization strategy for the interaction mechanism to enhance the responsiveness and adaptability of the game experience. The experimental results verify the effective improvement of the proposed method in multiple dimensions such as accuracy, response speed, and user satisfaction. Future work can further integrate multimodal sensory signals, such as speech, facial expression and eye movement trajectory, to achieve higher accuracy behavior recognition and contextual response, and explore real-time reasoning capabilities and resource scheduling strategies under cross-platform deployment.
References
- Ali A,Senu N,Ahmadian A, et al. A deep learning framework for solving fractional partial differential equations [J]. Physica Scripta, 2025, 100 (4): 046012-046012. [CrossRef]
- Braun T D K,Wulff N J. Pioneering automation in agricultural subsidy processing through deep learning for computer vision [J]. Journal of Business Analytics, 2025, 8 (2): 93-115.
- Yagmur S S,Karabiber O C,Cosku G Y, et al. Classification of Alzheimer’s dementia EEG signals using deep learning [J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2025, 47 (7): 1353-1365. [CrossRef]
- Basheer L,P R. A deep learning framework for intrusion detection system in smart grids using graph convolutional network [J]. Engineering Research Express, 2025, 7 (1): 015257-015257.
- Koziel S,Dabrowska P A. Cost-efficient behavioral modeling of antennas by means of global sensitivity analysis and dimensionality reduction [J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15 (1): 3778-3778. [CrossRef]
- Wen X,Chen X. A New Breakthrough in Travel Behavior Modeling Using Deep Learning: A High-Accuracy Prediction Method Based on a CNN [J]. Sustainability, 2025, 17 (2): 738-738.
- Sorensen D I,Leany A H,Wonnacott A, et al. Modeling Viscoelastic Behavior of Piezoresistive Nanocomposite Strain Gauges [J]. Mechanics of Composite Materials, 2025, 60 (6): 1-16.
- Ana V N,C. S M,Lucia B P, et al. A narrative video game for adults with subjective and objective cognitive impairment. Design and preliminary results on user-interaction and efficacy [J]. Behaviour & Information Technology, 2024, 43 (8): 1518-1530. [CrossRef]
- Matoska T,Patel M,Liu H, et al. Review of Deep Learning Based Autosegmentation for Clinical Target Volume: Current Status and Future Directions [J]. Advances in Radiation Oncology, 2024, 9 (5): 101470-.
- Sudhir S,Sandesh T,Kishor K B, et al. An Efficient and Secure Authentication Protocol with Deep Learning Based Key Generation toward Securing Healthcare Data in IoT [J]. Cybernetics and Systems, 2024, 55 (4): 848-871. [CrossRef]
- Danhong Z,Shaohua H,Junwei W. A study of experiencing flow through online games interaction exercise [J]. Current Psychology, 2023, 43 (14): 12522-12534.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).