1. Introduction
Headache is one of the most common neurological disorder in the pediatric population with an estimated prevalence of 88% [
1].
A recent meta-analysis reported that the prevalence of primary headache is 15% for migraine and 17% for tension type headache [
2].
However, there is a lack of extensive epidemiological research on the prevalence and incidence of primary headaches in the pediatric and adolescent populations and many studies often exhibit statistical heterogeneity. This variability arises from differences in study populations, including factors such as age range, sex, and socio-economic status, as well as from the different methodologies employed (e.g., school-based surveys, clinician interviews, telephone interviews) and the inconsistent application of diagnostic criteria, which are sometimes not specifically tailored to developmental age groups [
3].
In terms of disability, headache has a strong impact on everyday activities and quality of life, affecting children’s development and functioning in school, home or social environment, resulting in a severely debilitating condition [
4].
Despite the widespread disability produced by migraine, this disorder is still under-diagnosed and under-treated [
2].
Currently, clinical diagnosis is based on the criteria outlined in the 3rd edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3), which involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, family and social history, physical examination, and complete neurological examination. In cases where suspicious findings or red flags are present, additional investigations such as blood tests and neuroimaging may be conducted to differentiate primary headaches (e.g., migraine and tension-type headache) from secondary headaches (e.g., tumors, head trauma, infections, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, etc.).
Moreover, the ICHD-3 criteria primarily focus on adult headache phenotypes and do not fully account for potential differences in pediatric presentations, particularly in pre-pubertal children; therefore this limitation may contribute to delays in diagnosis and treatment. It has been suggested that pediatric migraines, especially in younger children, tend to have shorter attack durations [
5,
6] are less likely to be lateralized, compared to those in adults [
7,
8,
9].
Moreover, children’s migraines tend to be slightly associated with visual aura, while constitutional symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, flushing and pallor are more common.
Under the age of 18, migraine attacks typically last between 2 and 72 hours, with no evidence supporting untreated attacks of shorter duration. Migraines in this age group are more frequently bilateral compared to adults, with unilateral pain generally appearing in late adolescence or early adulthood. Migraine headaches are usually frontotemporal, while occipital localization in children is rare and warrants careful diagnostic evaluation. Additionally, in young children, photophobia and phonophobia are often inferred from behavioral observations rather than explicitly reported symptoms [
10].
The mentioned clinical differences between adults and children could be the result of differences in degree of brain maturation including myelination, new synapse formation and synaptic reorganization [
8].
Given the high prevalence of headaches in children and the lack of specific diagnostic criteria for this age group, there is a clear need for accurate clinical diagnostic guidelines [
11].
To enhance the sensitivity of the IHS criteria while preserving their high specificity for pediatric patients, several revisions to the original criteria have been proposed. These include reducing the minimum duration of an episode from 2 hours to 1 hour, decreasing the number of required episodes from 5 to 3, and removing the requirement for unilaterality [
12].
Given that attack duration and laterality are key diagnostic criteria for migraines, understanding these variations in children could provide insight into whether distinct diagnostic criteria are necessary for the pediatric population [
13].
Even though there are no specific diagnostic tests for migraine or tension-type headache,3an accurate diagnosis is essential to provide the best treatment approaches, that may differ between one type of headache to another.
The diagnosis is further complicated by children’s limited narrative abilities, particularly in those with underdeveloped or absent verbal expression. To address the challenge of defining the clinical phenotype of headaches, clinicians often rely on parent-reported medical histories. However, their responses may not always accurately reflect the child's condition and can sometimes exaggerate or deny the symptoms [
14].
Developing new strategies to overcome communication barriers is an ongoing challenge. In this context, drawings can serve as a valuable tool, especially since children are naturally expressive artists. For many, visual expression may prove more effective than verbal communication.2
Literature supports and encourages the use of drawings in clinical practice, both as part of the diagnostic process and during follow-up, highlighting their value as an effective, enjoyable, easy-to-use, and low-cost resource. However, only few studies have been conducted with the aim of appraising the utility of drawing in clinical diagnosis of pediatric headache, and most importantly, the subject is often approached from different perspectives in terms of research methods and objectives [
12].
In this context, we propose a narrative review accompanied by a collection of drawings, aimed at identifying and cataloguing specific correlations between graphic representations and clinical phenotypes. These include pain location, quality, intensity, and associations with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia, and types of migraine aura.
The primary goal is to establish a reference collection that helps clinicians in accurately interpreting children's drawings, enhancing diagnostic precision and patient care. In addition, headache drawings can be used to longitudinally track clinical progression and treatment response [
11,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20].
2. Review of Literature
Drawing is a valuable tool that provides access to a child’s psychological and emotional world, offering a direct window into their inner thoughts and feelings. It serves both as a genuine form of expression and an effective means of communication, often exceeding verbal methods in detail, clarity, and impact.
Unruh et al. were the firsts who explored the utility of children’s drawings as a diagnostic tool for evaluating pain, particularly in pediatric headaches. This method, grounded in the observation of visual and symbolic representation, provided an alternative for assessing pain where verbal communication was limited.
The authors analyzed a sample of 109 children aged 5 to 18 years, presenting with chronic or recurrent headaches. Each child was instructed to draw their pain and themselves experiencing pain, and the resulting illustrations were systematically analyzed for specific features, including the use of colors, line characteristics and symbolic elements. Statistical analysis revealed that 72% of the children used dark or aggressive imagery (e.g., storms, explosions, or jagged lines) to depict severe or pulsating headaches, correlating with clinical diagnoses of migraine (p < 0.01).
Additionally, 65% of the drawings included localized indications of pain, such as shading, or emphasizing the head region, aligning with self-reported pain locations (p < 0.05). Emotional content was also significant: 58% of children’s drawings displayed contextual elements such as distorted figures or somber backgrounds, which were associated with higher scores on anxiety scales (p < 0.05). The predominant colors were red and black, with no significant differences according to gender or age.
More specifically, children's illustrations of pain could be classified in 7 categories such as: actions and tools (32%), personification of pain (19%), physiological representation of pain (5%), perceptual disturbances (6%), abstract representation of pain (25%), localization (3%) and non-specific drawings (3%). Children's illustrations of themselves experiencing pain included: the recipient of pain (11%), an agent that relieves pain (44%), emotions resulting from pain (40%), localization (3%) and non-specific drawings (only 2%).
The non-invasive and basic nature of the method facilitated its application, requiring minimal preparation and yielding high compliance rates (95%).
In longitudinal follow-up, subsequent drawings showed changes in pain representation that correlated with reported clinical improvements, highlighting the method's value in assessing treatment efficacy
These findings indicate that children’s drawings serve not only as a reliable diagnostic complement, but also as a valuable tool for assessing both physical and emotional dimensions of pediatric headache. When integrated with clinical practice, this technique may improve diagnostic accuracy, particularly in younger populations, while providing a more holistic understanding of pain experiences. [
15]
Stafstrom et al. explored the diagnostic utility of children’s drawings as well in evaluating headaches, highlighting significant correlations between graphic representations and clinical phenotypes. 226 drawings were analyzed, recognizing the multitude of elements, information and details emerging from the images.
The study involved children aged 4 to 18 years, recruited from specialized pediatric neurology clinics. Participants met established diagnostic criteria for primary headache disorders, such as migraines and tension-type headaches, according to the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD)[
10].
Each child was guided to illustrate their headache experience, depicting pain location, intensity, and associated emotional or sensory features. These drawings were subsequently evaluated by a team of pediatric neurologists and psychologists. For instance, 90% of children diagnosed with migraines included precise indications of pain localization in their drawings, often using shading or intense markings in the head region (p < 0.01). Additionally, 78% of the drawings depicted emotional elements such as dark colors or negative contexts, closely associated with concurrent anxiety symptoms (p < 0.05). Metaphorical elements like lightning bolts or explosions, observed in 68% of drawings, were linked to pulsating pain characteristic of migraines. In contrast, tension-type headache sufferers drew elements such as bandages and head-binding material with fewer expressions of distress. The drawings were compared with the clinical diagnosis showing a sensitivity of 93.1%, a specificity of 82.7% and a positive predictive value of 87.1% for migraine, thus demonstrating significant associations between the graphic details and the children’s reported experiences.
The methodology's primary strength lay in its non-invasive nature, requiring minimal preparation while achieving excellent participant compliance (95%). In longitudinal follow-up, subsequent drawings provided valuable insights into the progression of the children’s conditions. For example, as treatment effectiveness increased, the drawings showed reduced emotional intensity and simplified pain representations. This dynamic evolution reinforced the utility of drawings in monitoring treatment efficacy over time. Moreover, pediatric neurologists collaborated with psychologists to interpret symbolic and emotional content, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the child's experience.
Through this study, Stafstrom highlighted the importance of creative approaches in pediatric neurology, offering a new dimension to symptom evaluation and patient care [
12].
Many studies have reinforced and validated the utility of distinctive drawings for various types of headache.
Wojaczynska-Stanek et al. explored the diagnostic potential of children’s drawings in understanding their perception and experience of headache. The research involved 68 girls aged 5-18 and 56 boys aged 7-18. Of the 124 children 40 had been clinically diagnosed with migraine, 47 with tension-type headache and 37 as the others. The authors analyzed the children’s pain drawings to uncover patterns that could enhance diagnostic precision and deepen insight into the subjective experience of pediatric headaches.
The findings revealed that 68% of the drawings included specific pain localization, with notable differences between migraine and tension type headache. Children with migraine commonly depicted pain as localized to one side of the head or around the eyes (78%), while those with tension type headache illustrated a diffuse or generalized pressure-like sensation across the entire head (64%). Additionally, 25% of the drawings featured symbolic elements, such as tears, lightning bolts or storm clouds, which underlined the emotional distress linked to their headaches, whereas 7% lacked specific pain-related depictions and instead showed a general sense of discomfort.
Color choice also emerged as a significant aspect of the drawings, reflecting the children’s emotional responses to their condition. Dark colors like black, gray, and dark blue predominated in 73% of the drawings, often symbolizing intense or negative feelings, while 27% incorporated brighter hues, suggesting a less distressing or neutral perception of the pain.
The study underscores the utility of children’s drawings as a complementary tool in the clinical assessment of headaches enhancing more targeted, empathetic care for pediatric headache disorders [
17].
Mosquera analyzed children’s and adolescent’s drawings to identify migraine in headache patients. The study involved 48 patients aged 5 to 19 years diagnosed with headache, who were asked to draw their perception of the pain, focusing on its location, intensity and associated symptoms. Each drawing was independently evaluated by two pediatric neurologists: one performing an artistic assessment, the other a clinical diagnosis. This protocol assessed the predictive accuracy of artistic evaluation relative to clinical findings.. The study revealed that 75% of the drawings depicted pain as unilateral, primarily in the orbital or temporal regions, consistent with the typical characteristics of migraines. In 20% of the cases, the drawings showed generalized or bilateral pain, often associated with less severe or atypical migraines, while 5% of the drawings lacked specific pain localization but included abstract or emotional elements to express discomfort. Symbolic elements, such as lightning bolts, dark clouds, or sharp lines, were present in 60% of the drawings, reflecting the intensity of the pain. Emotional imagery, including tears or exaggerated expressions, appeared in 30% of the cases, whereas 10% of the drawings were minimalistic but still conveyed the perception of pain. The color choice was another significant aspect, with dark colors (black, gray, dark blue) dominating 80% of the drawings, correlating with severe or distressing headache experiences. Bright colors appeared in 20% of the drawings, often associated with milder or less disabling headaches. The artistic diagnosis accurately predicted the clinical diagnosis of migraine with a sensitivity of 69.6%, specificity of 88%, positive predictive value of 84.2%, and a negative predictive value of 75.9%, demonstrating a strong concordance between the visual analysis of the drawings and the clinical evaluation based on IHS criteria. However, in 15% of the cases, the artistic diagnosis either underestimated or overestimated the severity of the migraine or failed to identify atypical features [
18].
A wider study conducted by Mazzotta et al. involved 67 children aged 6 to 14 years who experienced recurrent headaches, together with a control group of 90 healthy children.
Each child was asked to create a drawing representing their headache experience, which was analyzed by two child neuropsychiatrists blinded to clinical data, in order to differentiate migraine from tension type headache, through identifying patterns of pain localization, intensity, and associated symptoms.
78% of the drawings included specific pain localization, with 56% depicting unilateral or focal pain typically associated with migraines, and 22% illustrating bilateral or diffuse pain, more commonly linked to tension-type headaches. In 22% of the drawings, precise pain localization was absent, but these still provided valuable insights through symbolic or emotional representations. Almost half of the drawings (48%) contained symbolic imagery, such as lightning bolts, dark clouds, or tears, highlighting the intensity and emotional burden of the headaches. Additionally, 32% included visual cues like zigzag patterns or wavy lines, often indicative of migraine aura or light sensitivity. The use of dark colors (black, gray, or dark blue) was prevalent in 84% of the drawings, correlating with severe or distressing headache experiences, while brighter or neutral colors appeared in 16% of cases, typically reflecting milder symptoms.
Eventually, the artistic findings were then compared with clinical diagnoses.
The study found that 55% of the participants were clinically diagnosed with migraine, while 45% were classified with tension type headache. For migraine, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value (PPV) of the drawings were 85.71%, 81.48%, and 85.71%, respectively. For tension type headache, the sensitivity, specificity, and PPV were 81.48%, 85.71%, and 81.48%, respectively. The study demonstrated a high correspondence between artistic and clinical diagnoses, with an accuracy of 83%. For children with migraines, the artistic diagnosis was correct in 88% of cases, while for tension type headache it was accurate in 76%. However, 17% of the cases showed discrepancies, often due to atypical or overlapping headache features [
19].
Yilmaz (2019) explored how adolescents aged 14 to 18 diagnosed with migraine and visual aura could enhance the diagnostic process by depicting their symptoms through drawings. Five participants (three girls and two boys), selected based on the 2013 International Headache Society criteria, were included. Visual aura was observed in all participants, consistent with global estimates that 15–20% of migraine episodes involve such symptoms. The visual disturbances depicted included blurry vision, bright lights, zig-zag lines, and scotomas. These representations helped overcome communication barriers often encountered in pediatric neurology, providing clinicians with a more comprehensive understanding of the patients' experiences. The study emphasized that drawing symptoms could facilitate the diagnostic and follow-up processes, as visual descriptions are sometimes challenging for younger patients to articulate. The results align with prior research indicating that 76.3% of adults with migraines report visual aura, although previous studies primarily relied on verbal descriptions [
11].
Another transversal and descriptive study conducted by Garcia-Ron et al., assessed the concordance between the ‘artistic’ diagnosis of headache and the clinical diagnosis.
A neuropediatrician and two neurologists, experts in headache, were asked to review the patient’s drawing in order to formulate the artistic diagnosis, while the clinical diagnosis was made after a complete anamnesis and a clinical examination, by a different neuropediatrician.
The study included 132 patients (61.1%, girls; mean age, 12 years) with clinical diagnoses of migraine (59.1%), tension-type headache (38.2%), and other headaches (trigeminal-autonomic and nummular) (2.7%). Each patient was asked to make a single drawing illustrating its own headache, without any suggestion nor additional instruction, and without any time limit.
The drawing showed, most frequently, symptoms related to the localization of pain, which was stressed as a black or red spot: bilateral (49/132 drawings, 37,1%), unilateral (43/132 drawings, 32,6%). The iconographic elements mostly associated with migraine were: unilaterality, bouncing quality, worsening with physical activity, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia and aura. Tension type headache was represented most frequently with bilateral pain, oppressive in quality and stress related. The concordance of the artistic and clinical diagnoses for migraine and tension-type headache was 78.5% and 78.6%, respectively, when the drawings were assessed by a neuropediatrician. This concordance was similar for migraine drawings assessed by both neurologists (76.3% and 83.6%), but not for tension-type headache (35.1% and 48.4%). The agreement between neurologists was moderate and similar for both types of headaches (migraine, k: 0.51; tension-type headache, k: 0.5). Among all the drawing elements, those previously associated with migraine found a massive correspondence with the clinical diagnosis of migraine; particularly, presence of aura, worsening with physical activity, nausea and vomiting showed a 100% concordance [
20].
Table 1 summarizes various studies that have analyzed the use of drawings as a tool for diagnosing headaches in children and adolescents. Overall, these studies highlight that drawings can be an effective method for understanding pain perception in young patients and supporting clinical diagnosis.
Table 1.
studies on drawings and headache diagnosis.
Table 1.
studies on drawings and headache diagnosis.
| |
Cohort |
Age and Gender |
Materials Methods |
Results |
| Unruh et al. (1983) |
109 |
5–18 years; 66 females, 43 males |
Children were asked to draw their pain and how they experience it. Drawings were analyzed for symbolic and emotional elements. |
32% of children depicted actions or instruments causing pain, 19% personified the pain, 25% used abstract representations, and 11% localized the pain on the body.
Children with migraine frequently depicted themselves relieving their pain (48%) compared to those with musculo-skeletal pain (31%).
Red and black were the most dominant colors. |
| Stafstrom et al. (2002) |
226 |
4–19 years; 105 males and 121 females |
Children created drawings depicting pain localization, intensity, and related emotions. 2 pediatric neurologists analyzed the drawings against clinical diagnosis. |
Headache drawings showed a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 83% compared to clinical diagnosis.
90% included precise pain localization; 78% showed emotional content; 68% included metaphorical elements like lightning bolts linked to migraines. |
| Mosquera et al. (2008) |
48 |
5–19 years; gender not specified |
Children drew their headache perceptions. Drawings were evaluated by a pediatric neurologist and compared with clinical findings. |
75% depicted unilateral pain, 60% used symbolic elements (lightning bolts, tears), 80% used dark colors, correlating with migraine characteristics. |
| Wojaczynska-Stanek et al. (2008) |
124 |
5–18 years; 68 females, 56 males |
124 children (40 migraines, 47 tension headaches, 37 others) provided pain drawings, analyzed for patterns in localization, color, and symbolic elements. |
Pain localization in 68% of drawings, symbolic elements in 25%, and 73% dark colors; migraines often had unilateral depictions. |
| Mazzotta et al. (2015) |
67 |
6–14 years; gender not specified |
67 children with headaches and 90 controls created drawings. Two child neuropsychiatrists blinded to clinical data analyzed the patterns. |
78% of drawings localized pain; 48% included symbolic imagery (e.g., lightning bolts). Sensitivity for migraines: 85.71%; tension headaches: 81.48%. |
| Yilmaz et al. (2019) |
5 |
14–18 years; 3 females, 2 males |
Adolescents with migraines and visual aura were asked to depict their symptoms, focusing on visual disturbances like zig-zag lines and scotomas. |
100% depicted visual aura symptoms, including zig-zag lines and scotomas, confirming their diagnostic value for adolescents. |
| Garcia-Ron et al. (2024) |
132 |
12 years (mean); 61.1% females |
Children with headaches drew their pain experiences without instructions. Neuropediatricians and neurologists assessed the drawings for diagnostic insights. |
78.5% concordance for migraines and 78.6% for tension headaches; migraine features like aura and nausea showed 100% diagnostic match. |
The studies involved groups of children and adolescents aged between 4 and 19 years, using drawings to gather information about pain localization, intensity, and symbolic characteristics. Analyses, often conducted by neurologists or neuropsychiatrists, revealed recurring elements such as:
High diagnostic sensitivity: the study by Stafstrom et al. (2002) [
12] reported a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 83% in using drawings for headache diagnosis.
Symbolic and chromatic elements: Drawings frequently included elements such as lightning bolts, tears, and dark colors associated with migraines. For instance, Mosquera et al. (2008) [
18] observed that 75% of children with migraines depicted unilateral pain, while 60% used symbolic elements like lightning bolts or tears. Similarly, Wojaczynska-Stanek et al. (2008) [
17] found that 73% of children with headaches used dark colors, suggesting a correlation between color tone and pain intensity.
Some studies differentiated between different types of headaches. For example, Unruh et al., (1983) found that children with migraines tended to depict themselves trying to relieve the pain (48%), a feature less common in children with musculoskeletal pain (31%). [
19] reported high diagnostic accuracy in distinguishing between migraines and tension-type headaches, with a sensitivity of 85.71% and 81.48%, respectively.
The studies vary in terms of evidence level, with some presenting highly reliable results (e.g. Stafstrom et al., 2002; Mosquera & Martino, 2008; Mazzotta et al., 2015) and others having smaller sample sizes and more limited evidence (e.g., Yilmaz et al., 2019). However, overall, research suggests that drawings can be a valuable tool to support clinical diagnosis, especially in children who may struggle to verbally describe their pain.
Despite some limitations, such as variability in interpreting the drawings and differences in analysis protocols, the results suggest that using drawings in the diagnosis of headaches in children and adolescents is a promising approach that can complement traditional clinical assessments, enhancing the understanding of pain experiences in young patients.
The use of the drawing has also been investigated in the adult population as a useful tool to assess the severity of headache as well as for making an appropriate differential diagnosis between headache, cluster headache and migraine, in the absence of specific biomarkers.
Buture et al. tested 150 healthy participants with 6 images portraying people with pain, asking them to rate the pictures as mild, moderate, severe or excruciating pain. During the second phase of the study 116 participants with headache (16 with Cluster Headache, 100 with migraine) were asked to assess the same images in the same manner. The latter were also requested to choose the image that most accurately illustrated their headache attacks. The results allowed the authors to develop a screening tool consisting of 6 images that was able to depict headache severity even though the images did not differentiate between cluster headache and migraine [
21].
That said, even though the usual focus in pain measurement is primarily pain intensity, it is also important to investigate other features such as frequency, duration and localization of pain.
Baeyer et al. explored the use of pain charts not only in the assessment of localization of pain but also to deepen other aspects such as severity and sensory quality, recurrent and chronic pain, using symbols, shading or colors. One of the main issues in using pain charts within multidimensional pediatric pain questionnaires and diaries is that many children below the age of 8 years often require adult assistance to complete them, which may bias their responses. Another challenge is posed by the definition of number and size of different locations or areas of pain that need to be differentiated. On the other hand, in clinical settings, pain charts provide significant flexibility, allowing the use of colors and symbols to represent not only the presence or absence of pain but also its quality and intensity, although these details must be developed collaboratively between individual patients and clinicians. Nevertheless, pain charts may not always be the most effective method for determining pain location. In certain cases, particularly when only a few areas are of concern, checklists focusing on specific body regions may be more appropriate.
Over the next decade, the authors expect to see a knowledge transfer and standardization, as those seen in the widespread adoption of the 0-10 metric in face, in visual analog and numerical scales for evaluation of pain intensity, in other aspects of assessment including pain location and quality.
These measures may play a crucial role in diagnosis, guiding treatment, and evaluating treatment effectiveness, especially in studies involving patients with pain in multiple areas [
22,
23].
Children’s Pain Perception and Expression
Children identify pain as originating from three primary sources: external, internal, and emotional. External pain is often visible and linked to injuries like cuts or burns, making it more comprehensible to children. [
24] Internal pain, associated with diseases, is harder for children to understand as they struggle to grasp its cause and implications. [
25] Emotional pain, often described as "pain in the heart," is linked to psychological distress from events such as losing a loved one [
26,
27].
Pain is closely associated with physical harm or physical discomfort in children's perception [
24]. Drawings and descriptions frequently depict pain through bodily injuries, often using colors like red and black to represent its severity. This association is particularly strong with external sources of pain but can also be linked to internal conditions. Children universally regard pain as an unpleasant experience. It is characterized by feelings of sadness, discomfort, and distress [
26]. The intensity of pain ranges from mild discomfort to extreme suffering, which can be described as unbearable or even life-threatening [
24]. Pain is also linked to both physical sensations (such as heat or pressure) and emotional distress (such as fear or anxiety). Pain is often perceived as a sign of danger or illness, leading to anxiety in children [
24,
26,
28,
29].
They associate pain with potential long-term harm, restrictions on daily activities, and medical interventions (such as injections). Some children view pain as a form of punishment, reinforcing feelings of guilt or distress [
30]. Hospitalization and medical procedures can further shape their understanding of pain, making it a source of fear and worry. Children’s descriptions of pain are influenced by their experiences, with healthy children focusing on physical aspects while chronically ill children emphasize emotional and psychological effects. Acute pain is often seen as severe but temporary, whereas chronic pain is associated with prolonged suffering and frustration. The colors red and black are commonly used to depict pain in drawings, representing distress and uncertainty [
27]. Some children express pain in self-centered ways, describing personal experiences rather than generalizing their understanding [
31,
32,
33].
3. Correlation Between the Clinical Phenotypes and the Graphic Representation of Pain
In IHS Classification - ICHD-3, migraine and tension-type headaches differ for the characteristics of pain. Migraine is more often unilateral, with a pulsating quality of pain, a moderate or severe pain intensity and aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity and associated with nausea and/or vomiting or photophobia and phonophobia.
On the other hand, the pain in tension-type headache is more often bilateral location, with a pressing or tightening (non-pulsating) quality, mild or moderate intensity, not aggravated by routine physical activity such as walking or climbing stairs and not associated with both nausea or vomiting and no more than one of photophobia or phonophobia.
According to ICHD-3 in children and adolescents (aged under 18 years), migraine headache is more often bilateral than is the case in adults; unilateral pain usually emerges in late adolescence or early adult life. Migraine headache is usually frontotemporal. Occipital headache in children is rare and calls for diagnostic caution. A subset of otherwise typical patients have facial location of pain, which is called “facial migraine” in the literature [
34]; there is no evidence that these patients form a separate subgroup of migraine patients. In young children, photophobia and phonophobia may be inferred from their behavior.
Considering the clinical differences between headaches in adults and those in children, effective diagnostic tools have recently been developed to support the diagnosis of headaches in individuals under 18 years of age. ID Migraine is an easy and quick to administer questionnaire that serves as a reliable screening and early diagnosis, already used in adults, which has recently been validated for children over the age of 6 and adolescents [
35].
All these instruments allow pediatric neurologists to make a clinical diagnosis together with a complete medical history and a neurological physical examination.
Alongside the various tools available for clinical diagnosis, the use of artistic diagnosis emerges as a complementary approach, supporting inferences drawn from official criteria and overcoming the limitations imposed by the limited descriptive and verbal abilities of pediatric patients.
We define the artistic diagnosis as the diagnosis that is issued after the evaluation of the drawings made by the patients by neuropediatricians and neurologists.
An accurate artistic diagnosis can be supported by the identification of specific, easily detectable graphic elements in children's drawings.
In terms of localization, pain can be differentiated in unilateral and bilateral.
In cases of unilateral pain, representations may include a hand placed on one side of the head, written descriptions explaining where the pain is felt, circles or arrows designating the exact area of discomfort, objects or lines positioned on one side of the head, or sparkles appearing on that side. For bilateral pain, images may show both hands covering each side of the head, circles or arrows indicating both painful areas, or bandages and circles around the head.
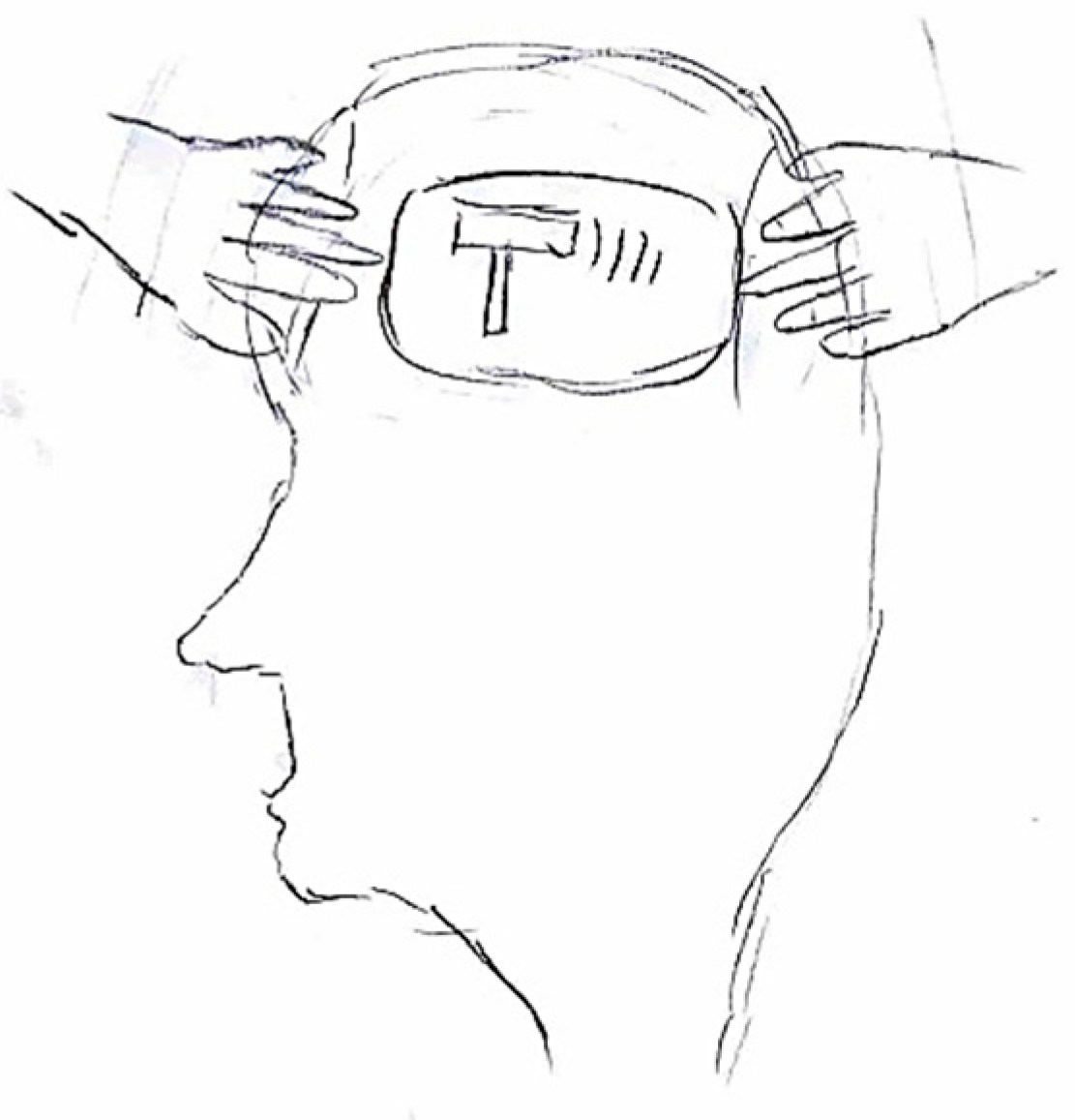
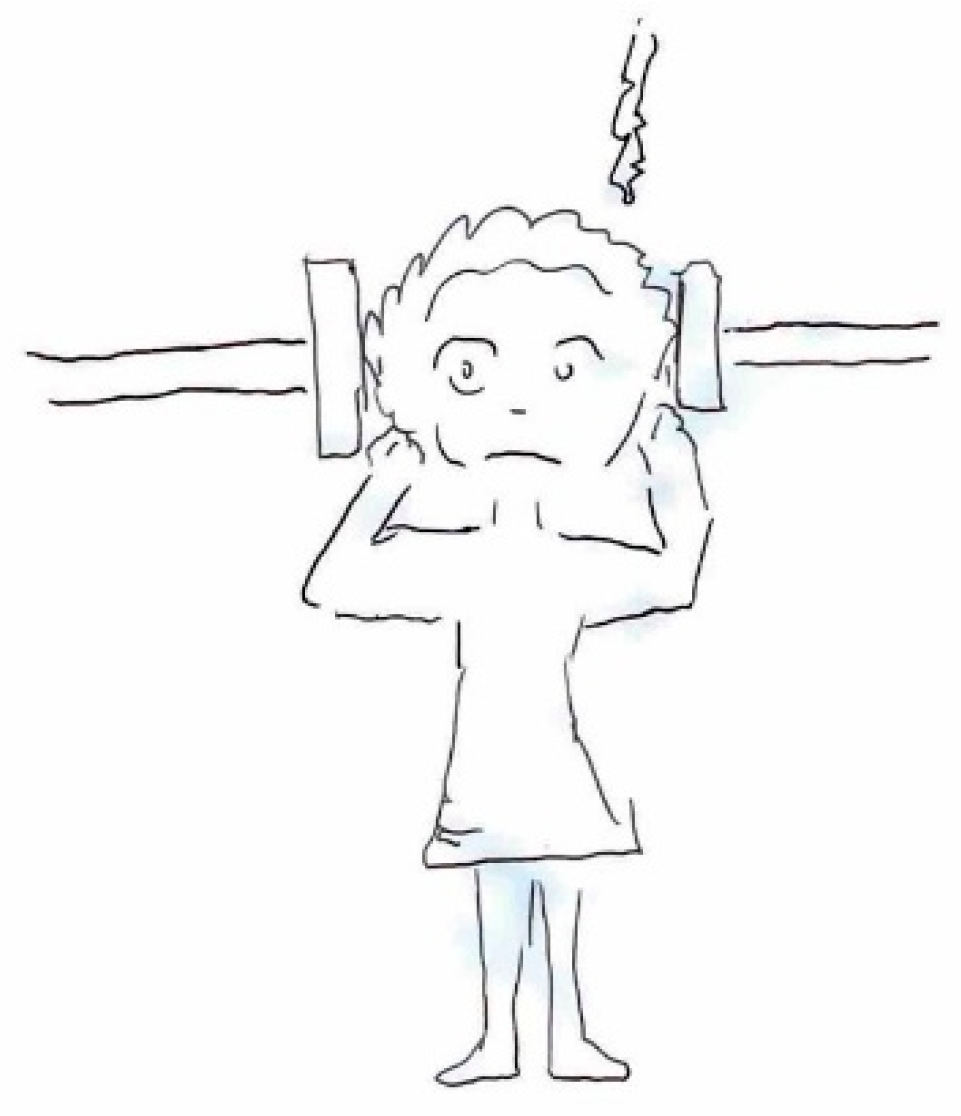
Different types of pain quality are also represented with specific symbols. Pulsating pain might be depicted using visuals like hearts, hammers, drums, pendulums, or with onomatopoeic words like “pum pum” or “bam bam.” On the other hand, pressing pain could be symbolized by images of stones or weights placed on the head, clamps, hands gripping the head, or gears. Pain that creates a sensation of tightness or constriction is often portrayed with bandages or knots squeezing the head. Stabbing pain is frequently illustrated with knives or drills, while burning pain is commonly represented with flames, candles, or fire.
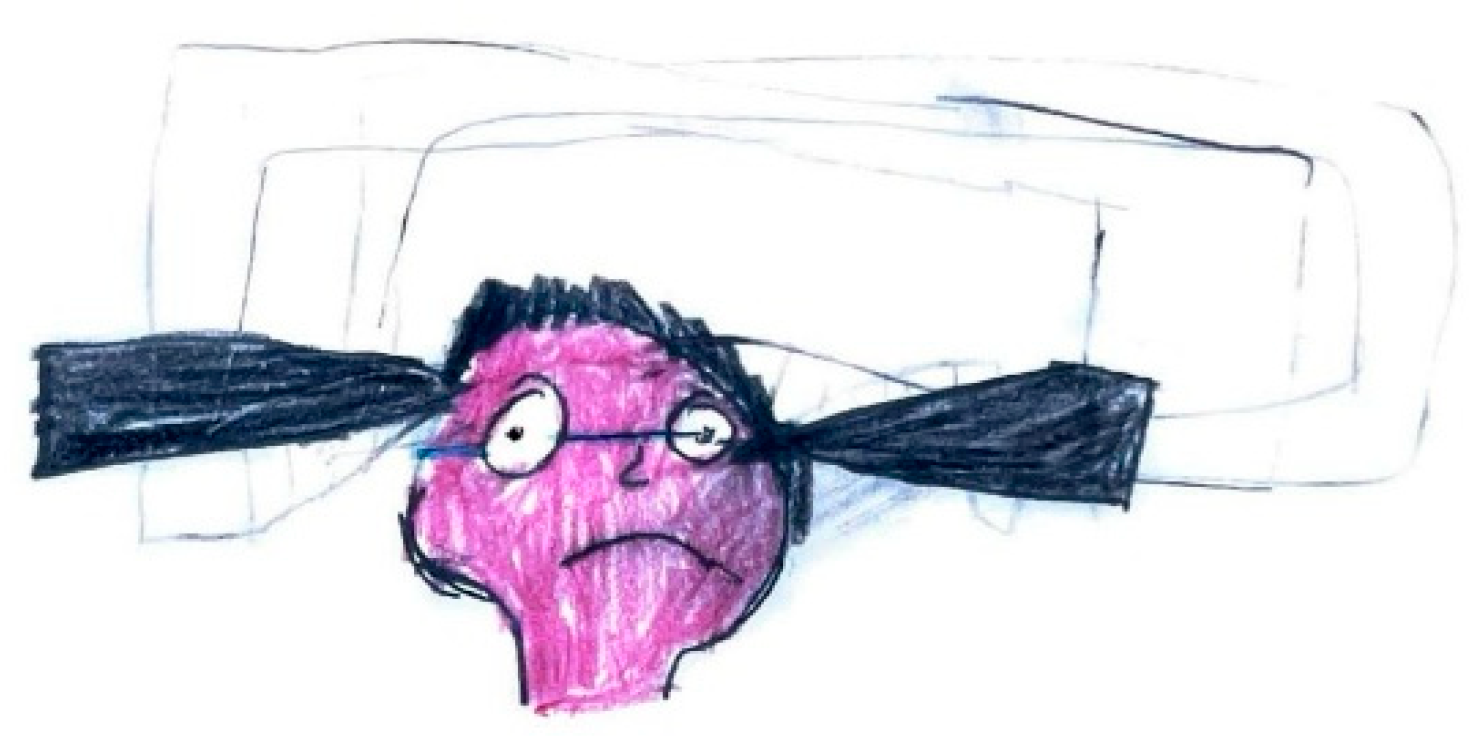
The intensity of pain is also shown through various graphic cues. Lower intensity pain might be represented with smaller drawings, pain located outside the head, bright and light images, and neutral or smiling facial expressions. Higher intensity pain, in contrast, could be depicted with larger illustrations, pain centered inside the head, darker images, the use of red or black, expressions of sadness or distress, tears, and a person lying down. Scripts or onomatopoeia may be added to further describe the intensity.
Other symptoms, such as the worsening of pain with physical activity or the urge to avoid it, can be visually shown by images of a person lying in bed or written descriptions explaining the avoidance of movement. Nausea is often symbolized by hands on the abdomen or mouth, while vomiting can be represented by visuals of a toilet, vomit, or hands clutching the stomach.
Sensitivity to light is often depicted by crossed-out light sources such as the sun or lamps, along with scripts describing the discomfort caused by light exposure. Phonophobia may be represented by crossed-out noise sources like voices, drums, musical notes, or horns, accompanied by scripts explaining the distress caused by sounds.
Lastly, visual aura can be represented with images of stars, colored spots, zigzag lines, half-objects or faces (hemianopsia), or fog. Other types of aura, like sensory, speech, language, motor, may not have specific visual representations but brainstem auras can include symbols such as double vision, fog, lines or circles around the head, or spirals.
We propose a complete list of iconographic elements of typical headache symptoms that are easily recognizable in the drawings of patients and control subjects. (
Table 2).
3.1. Migraine with Aura in Children
The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (ICHD-3) defines aura as a group of neurological symptoms that last between 5 and 60 minutes, typically preceding or occurring within an hour of a migraine headache. Diagnosis of migraine with aura (MA) requires a minimum of two episodes with completely reversible neurological symptoms, which may include visual, sensory, language-related, motor, brainstem, or retinal disturbances. Additionally, at least three of the following characteristics must be present:
The gradual appearance of a symptom over five minutes or more
At least two symptoms occurring sequentially
Each symptom persisting between 5 and 60 minutes
At least one unilateral symptom
At least one positive symptom (e.g., flickering lights, tingling)
The aura being followed by or coinciding with a headache within one hour
These criteria are applicable to both adults and children. ICHD-3 further categorizes migraine with aura into typical aura, brainstem aura, hemiplegic migraine (familial or sporadic), and retinal migraine. The hemiplegic and brainstem aura subtypes are considered more severe and can influence treatment decisions [
10,
37].
Approximately one-third of children and adolescents with migraines experience an aura phase. [
37] The most commonly reported aura in pediatric cases is visual aura, followed by somatosensory and language-related symptoms [
38].
Visual disturbances may manifest as:
Blurred vision
Zigzag lines
Scotomata (partial vision loss)
Scintillations (flashes of light)
Black dots
Kaleidoscopic patterns
Size perception distortions (micropsia/macropsia)
Other forms of aura include numbness or tingling (sensory disturbances), speech/language difficulties (aphasia, dysarthria), motor impairments (hemiparesis), and brainstem-related symptoms such as vertigo, tinnitus, and double vision [
39].
Aura symptoms can differ between episodes and may be challenging for young children to describe verbally. In clinical practice, children’s drawings are often utilized to communicate visual disturbances and differentiate migraines from other headache disorders [
40].
3.2. Neurological Mechanisms of Aura
The physiological foundation of aura is believed to involve cortical spreading depression (CSD), a wave of depolarization followed by hyperpolarization that slowly moves across the cerebral cortex [
41].
As CSD spreads over particular brain regions, temporary neurological symptoms emerge and then subside. This process disrupts ionic balance, neurotransmitter function, and blood circulation in the brain, all of which play a role in migraine pathophysiology [
42].
3.3. Differential Diagnosis Between Visual Hallucinations in Migraine with Aura and Epilepsy
Migraine and epilepsy share several clinical features, including episodic attacks with paroxysmal onset and distinct preictal, ictal, and post-ictal phases, characterized by changes in mood, behavior, consciousness, and sensory or motor functions. This overlap suggests shared mechanisms of neuronal hyperexcitability, modulated by subcortical pathways. Despite some well-established differences in clinical presentation, differential diagnosis can be challenging, particularly with atypical cases. Cortical spreading depression (CSD) is thought to be the mechanism behind aura in migraine and visual symptoms in occipital epilepsies.
Differentiating occipital lobe epilepsy from migraine can be challenging due to symptoms overlap, particularly simple visual hallucinations. Accurate diagnosis requires careful evaluation of the timing and characteristics of visual disturbances, especially in pediatric cases, where both conditions may co-occur. Epileptic ictal visual hallucinations are characterized by distinct attributes, including color, shape, size, movement, and duration.
The most reliable indicators of migaine visual aura are its accompanying symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia, and prolonged headache. A duration of more than 5 minutes strongly favors migraine aura (median duration of 20 minutes) over epilepsy aura (median duration of 56 seconds), with high diagnostic accuracy. However, some children with migraine may experience shorter or atypical auras, and in rare cases, visual aura can occur without headache, making diagnosis more complex. Common visual symptoms in children include black-and-white zig-zag patterns, peripheral visual disturbances, scintillating scotomas, and blurry vision. Less frequently, unusual colors, brightness, micropsia, teleopsia, and short-lasting visual snow may be present. Rarely, conditions such as palinopsia, visual snow syndrome, Alice in Wonderland syndrome, or complex visual hallucinations suggest alternative diagnoses.In this framework, drawing interpretation may significantly aid differential diagnosis by facilitating identification of pathognomonic aura characteristics [
43].
3.4. Migraine Triggers in Children
Patients with migraines often identify specific factors that increase the likelihood of an attack. These “trigger factors” refer to internal or external events or exposures that heighten the risk of migraines within a short timeframe. They fall into several categories, including behavioral, environmental, infectious, dietary, chemical, and hormonal factors, highlighting a hyperexcitable brain that reacts rapidly to various stimuli. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is essential for managing migraines effectively. Among pediatric patients, the most commonly reported migraine triggers include sleep deprivation, stress, warm climate, noise, and bright lights; stress is the most significant trigger, particularly stress from home and school environments. In children, the onset of migraines typically occurs within three hours of trigger exposure. Dietary factors also play a crucial role, with foods like chocolate, caffeine, milk, and cheese being frequently associated with migraine episodes. The impact of diet on migraines may involve alterations in serotonin and norepinephrine levels, changes in blood vessel function, or activation of critical brain pathways, further emphasizing the role of nutrition in migraine management for children and adolescents [
44].
4. Gallery
To systematically identify and categorize correlations between graphic representations and the clinical phenotypes of pediatric headache, we present a curated gallery of patient-generated drawings. These illustrations have been analyzed to classify iconographic features associated with the core characteristics of migraine—with and without aura—as well as tension-type headache. The visual elements observed are largely consistent with existing literature, although several novel and clinically relevant representational patterns have emerged.
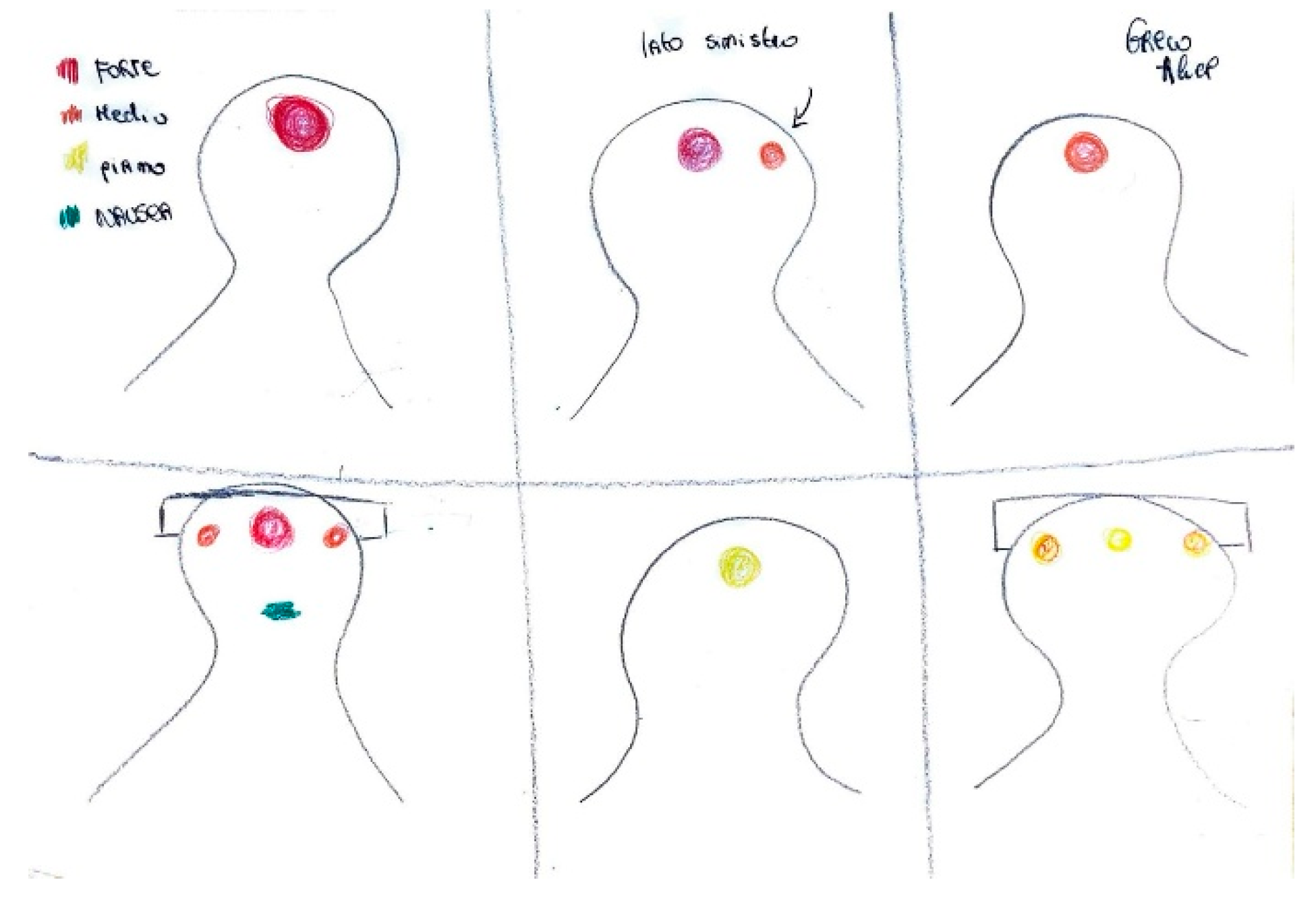
Pain
localization is frequently depicted through visual markers such as circles, directional arrows, or shaded regions. As shown in
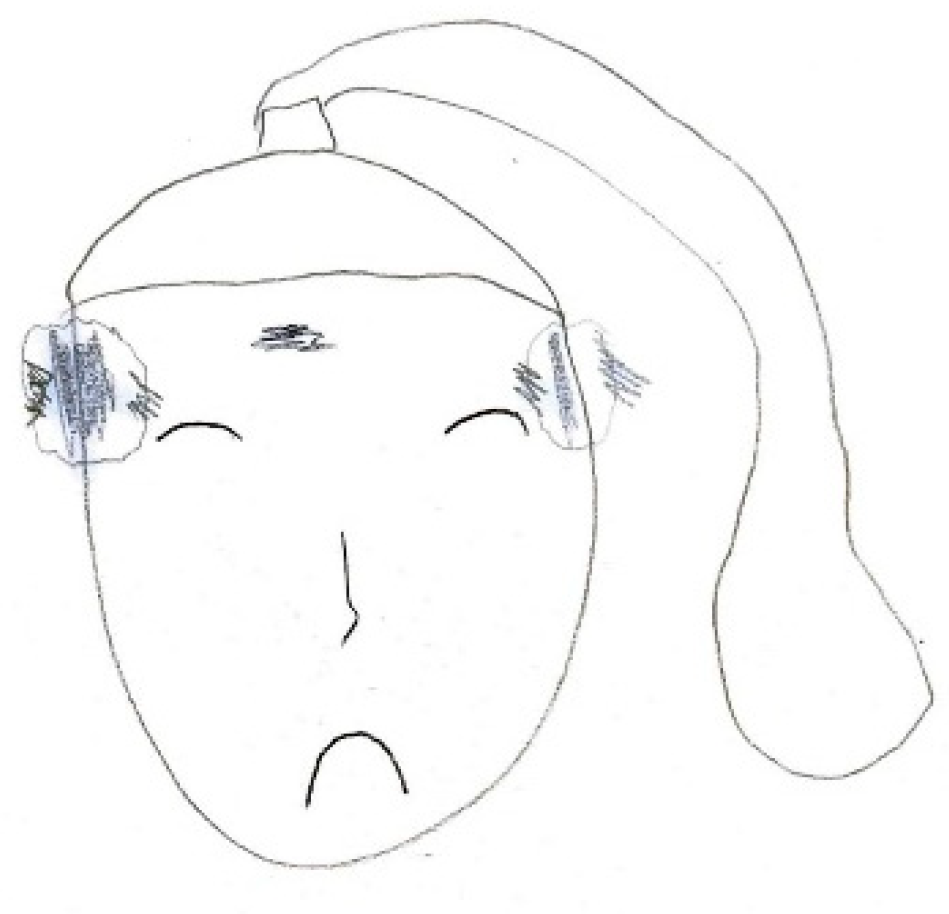
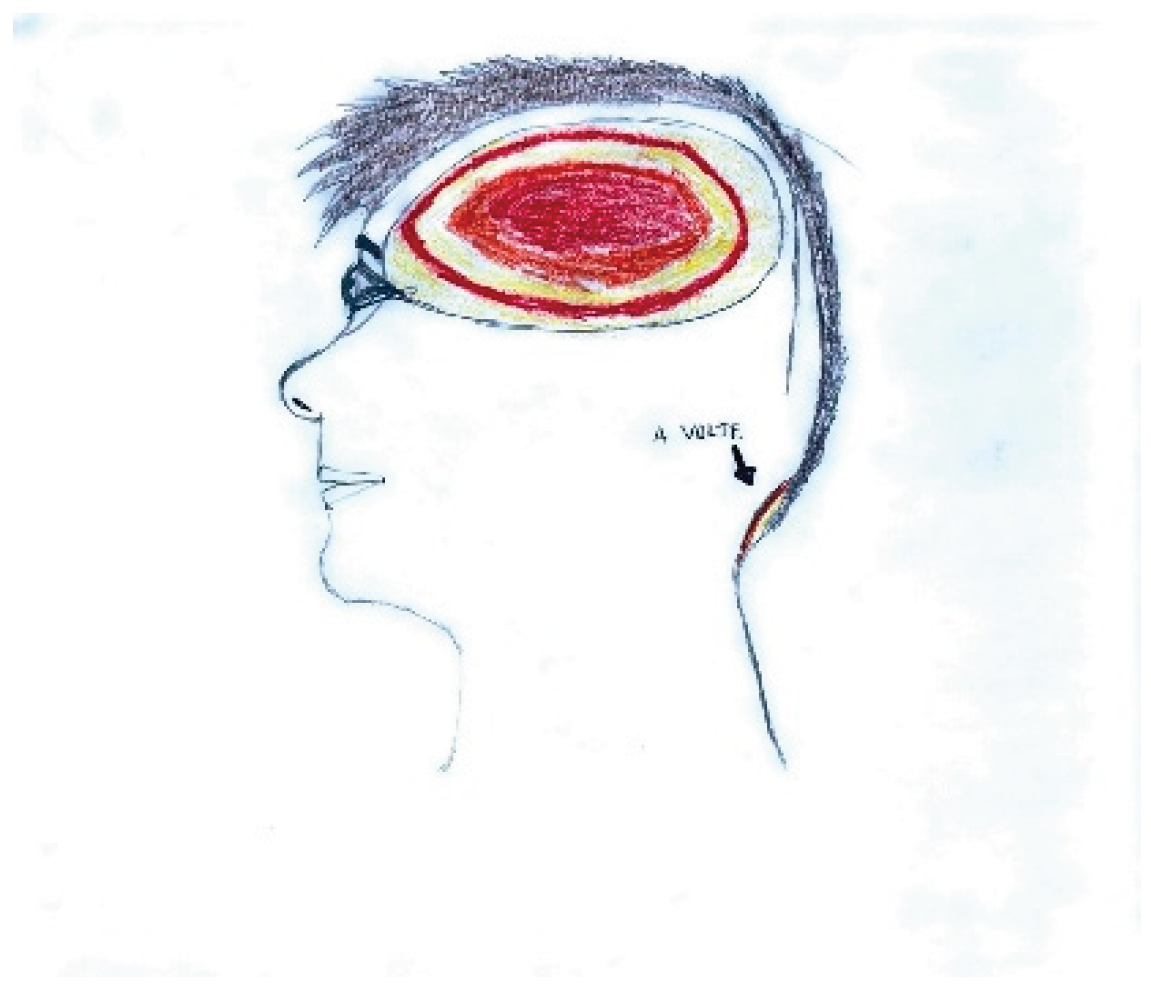
Figure 1, the parieto-temporal area is delineated with a red outline, highlighting the central focus of intense pain, while adjacent areas are shaded in lighter tones to indicate lesser involvement. The inclusion of an arrow pointing toward the occipital region, accompanied by the word “sometimes,” reflects the intermittent nature of pain in that area.
In
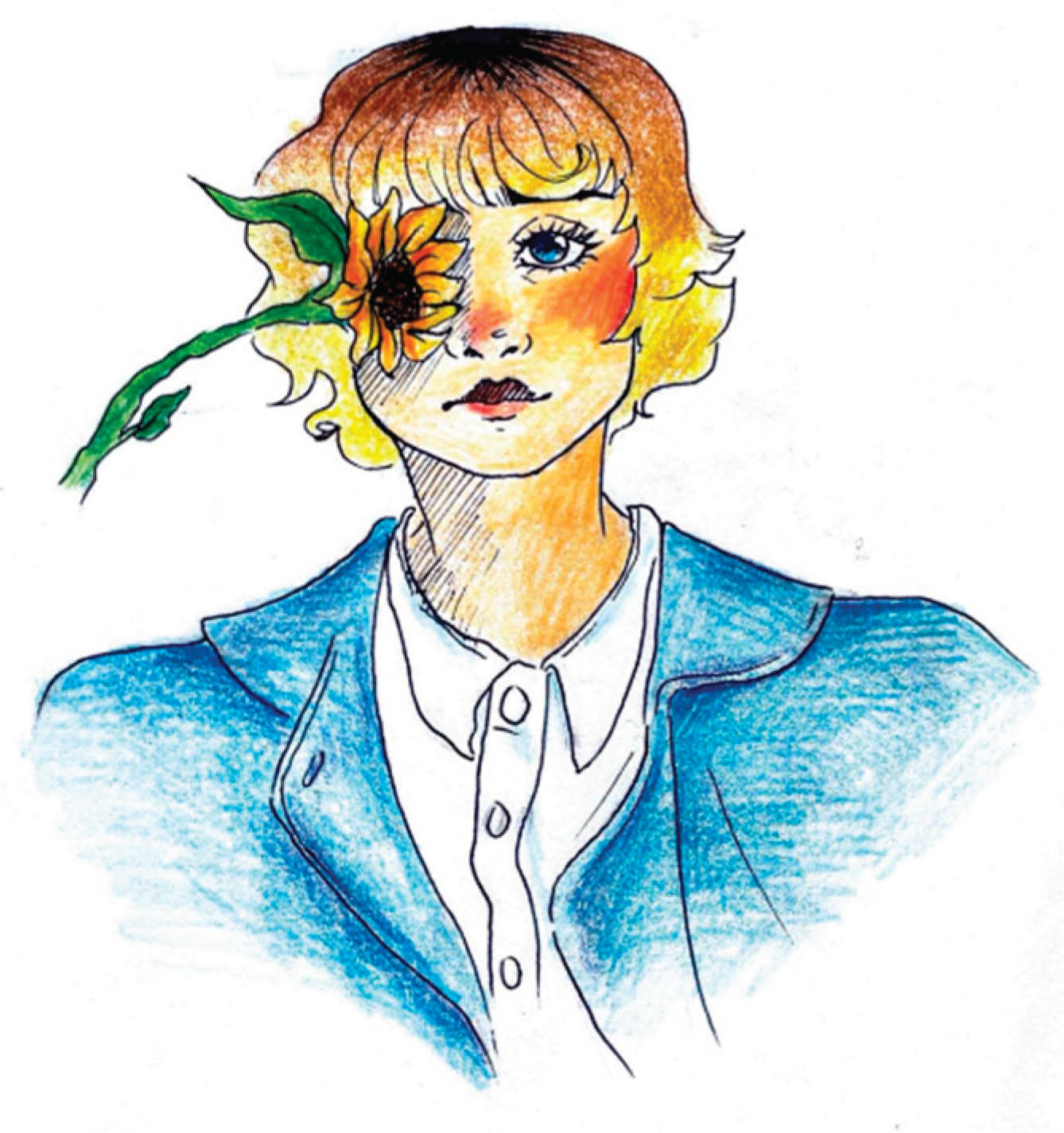
Figure 2, retro-orbital pain is rendered through bursts of color and flame-like patterns emanating from the eye, effectively conveying the burning and explosive quality of the discomfort.
Figure 3 illustrates localized, shaded areas in the temporal and frontal regions, accompanied by a facial expression indicative of significant distress, highlighting the severity of the pain. In contrast,
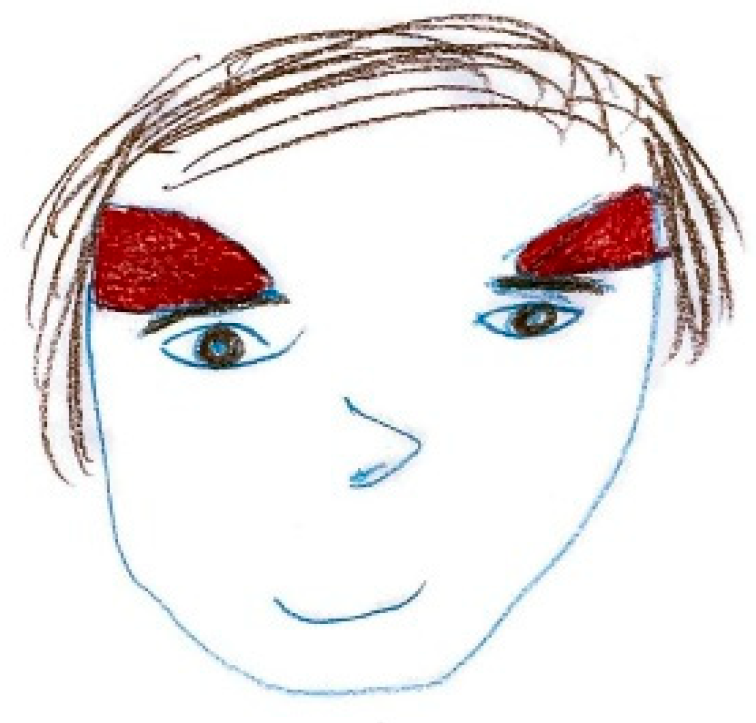
Figure 4 exemplifies bilateral pain presentation, with symmetrical red markings on both sides of the head.
The
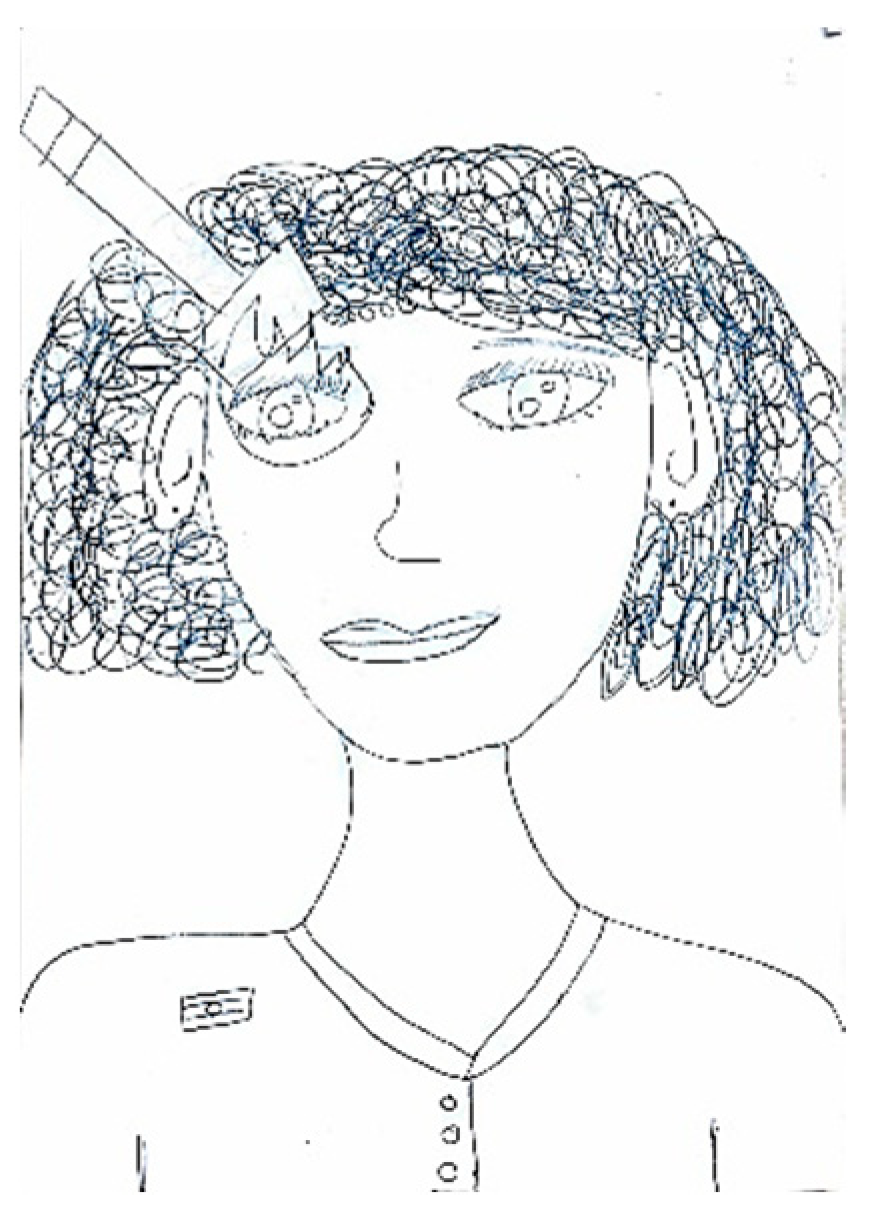
quality of pain is often symbolized by various objects offering insights into its distinctive characteristics. For instance, a pressing pain is typically represented by an object constricting the head, such as a press (
Figure 5), while the stabbing pain is often suggested using sharp objects such as knives or spikes (
Figure 6).
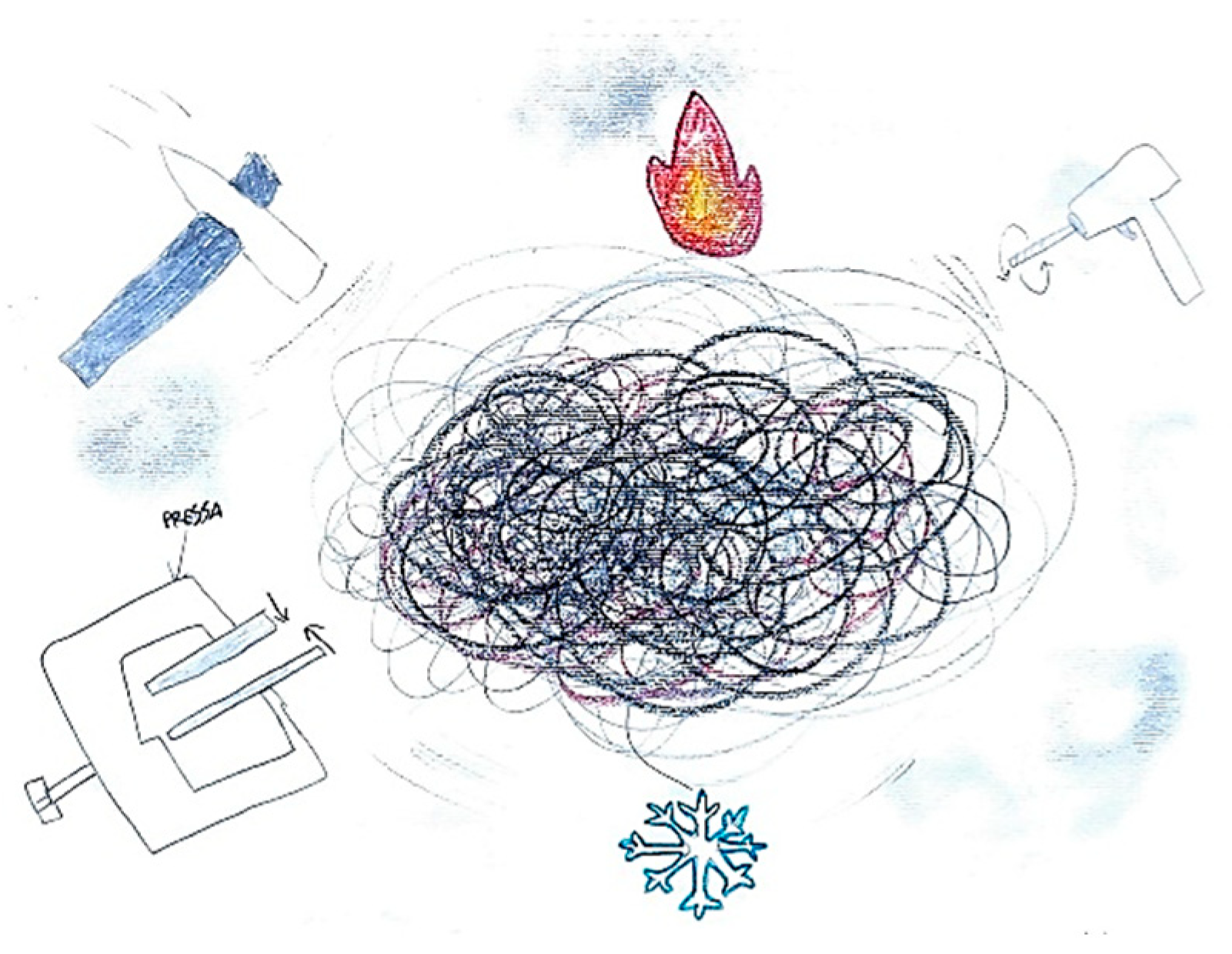
It is not uncommon for pediatric patients to simultaneously perceive and depict multiple pain qualities within a single illustration. For example, in
Figure 7, the image of a hammer striking the temporal region symbolizes the pulsating nature of the headache, while the presence of a flame in the ocular area conveys the burning sensation characteristic of retro-orbital pain. Similarly,
Figure 8 illustrates the coexistence of diverse pain modalities: a hammer indicating pulsating pain, a drill representing stabbing sensations, and a press suggesting a compressive or pressing quality. These elements are further enriched by visual cues associated with thermal sensations, such as representations of heat and cold. Collectively, these illustrations underscore the multidimensional and complex nature of pain perception in children, highlighting the utility of drawing as a nuanced diagnostic tool.
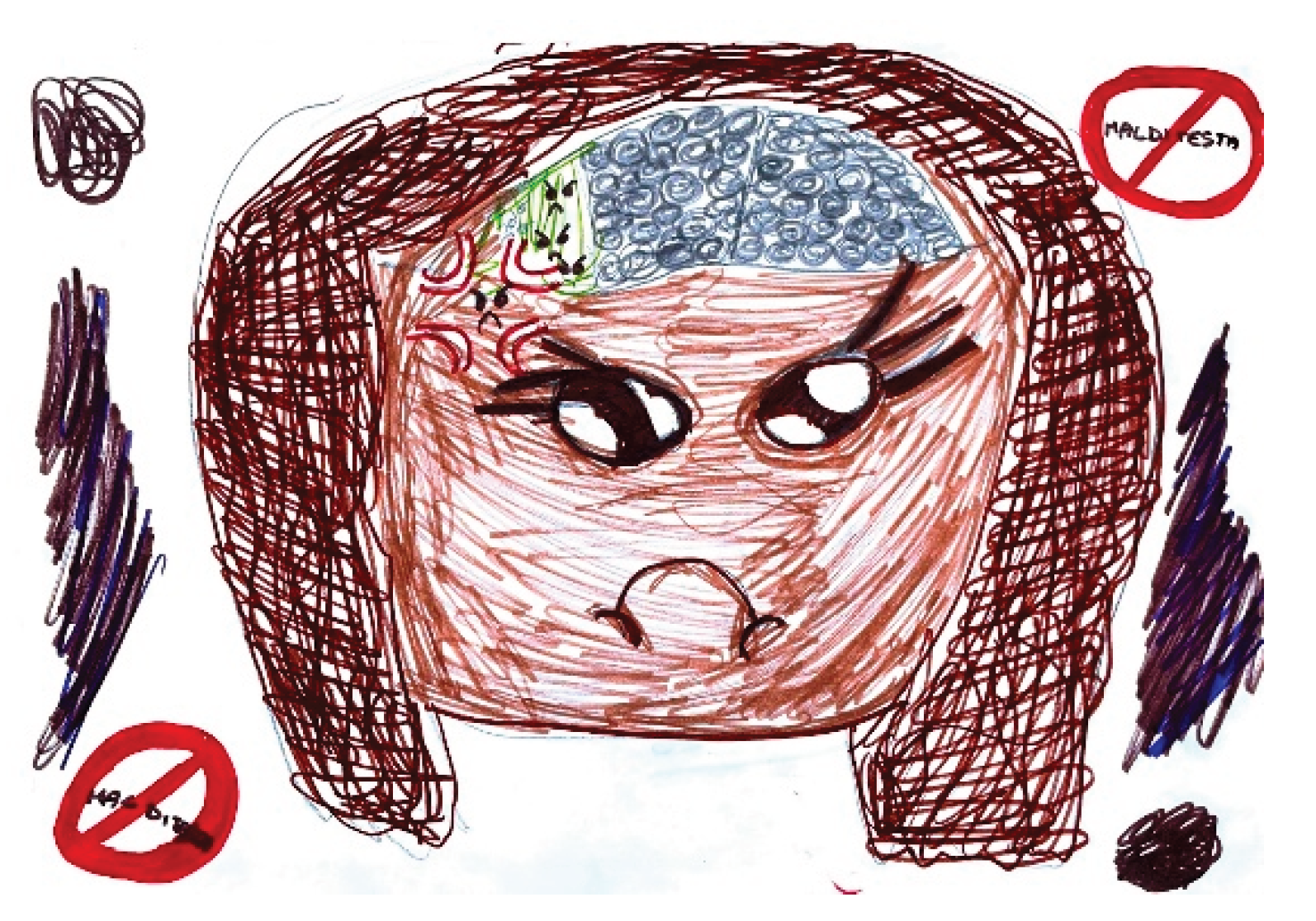
4.1. Intensity of Pain
In children, the numerical concept related to pain intensity scales is often not yet acquired. Additionally, rather than quantifying pain intensity using adjectives, children prefer to express it through color scales and by representing the degree of associated disability.
It is also possible to observe that pain representations outside the head are more frequently associated with lower pain intensity, while severe pain is more often depicted inside the head.
Red and black are preferentially chosen to represent very strong pain and severe distress is often reflected in depictions of faces with sad expressions, frequently accompanied by tears.
Figure 9.
Female, 10 years old.
Figure 9.
Female, 10 years old.
Figure 10.
Female, 8 years old.
Figure 10.
Female, 8 years old.
Figure 11.
Female, 12 years old.
Figure 11.
Female, 12 years old.
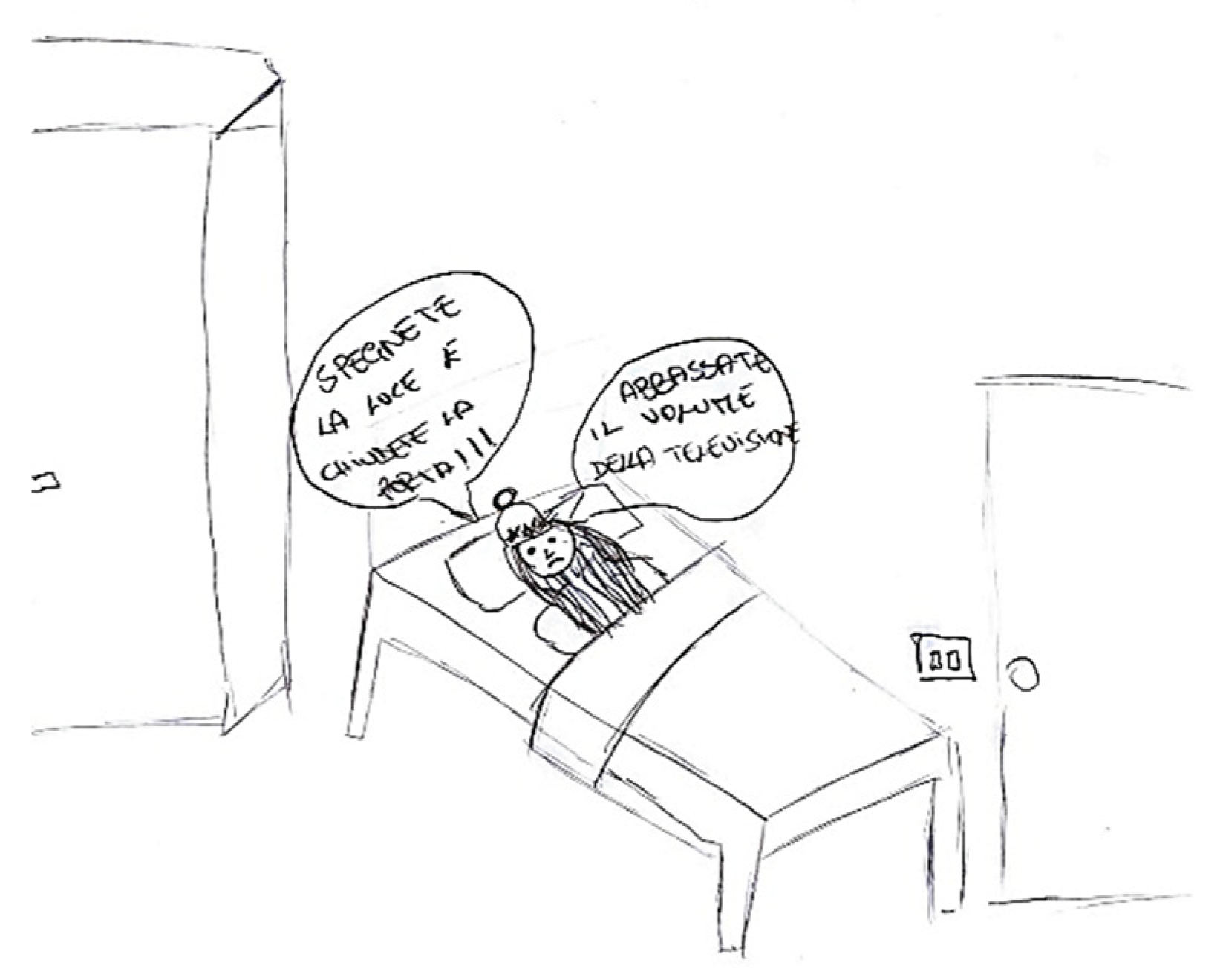
4.2. Related Symptoms and Behaviors
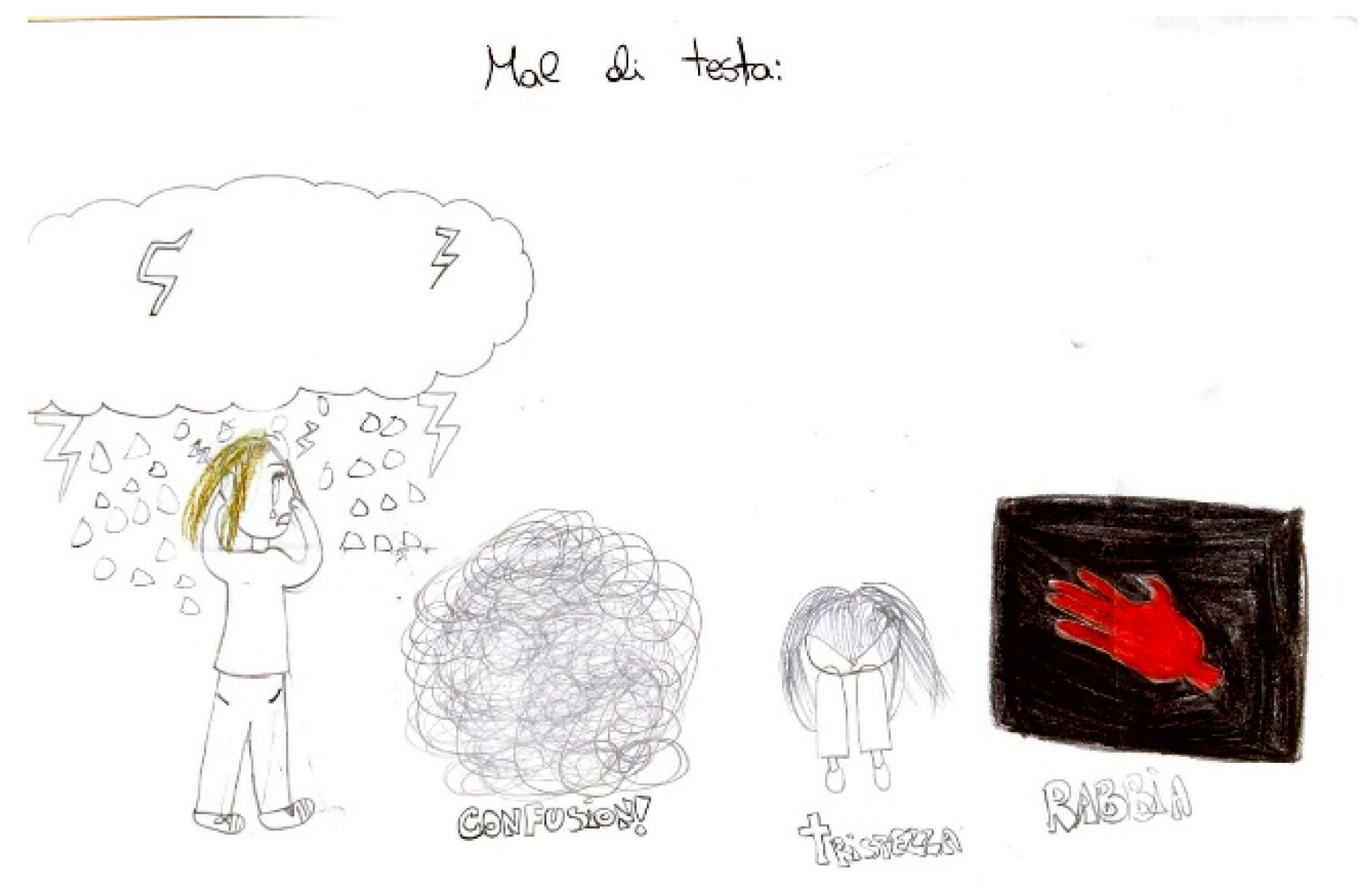
Headache is frequently accompanied by a range of symptoms and behavioral changes, including confusion and mood alterations. Classical manifestations
typically include, phonophobia and photophobia,
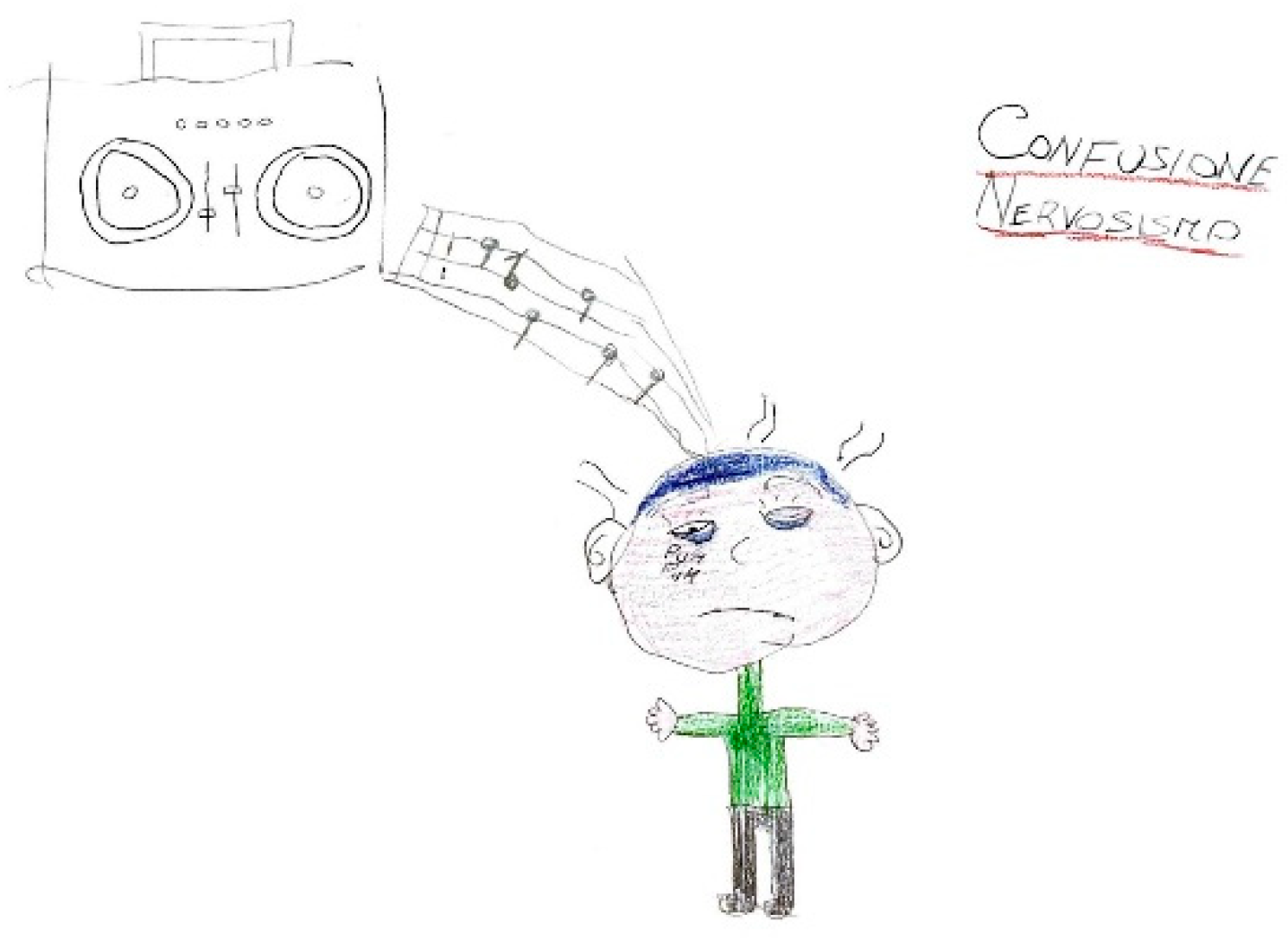
which patients frequently depict using symbolic representations of light or sound. For instance, in
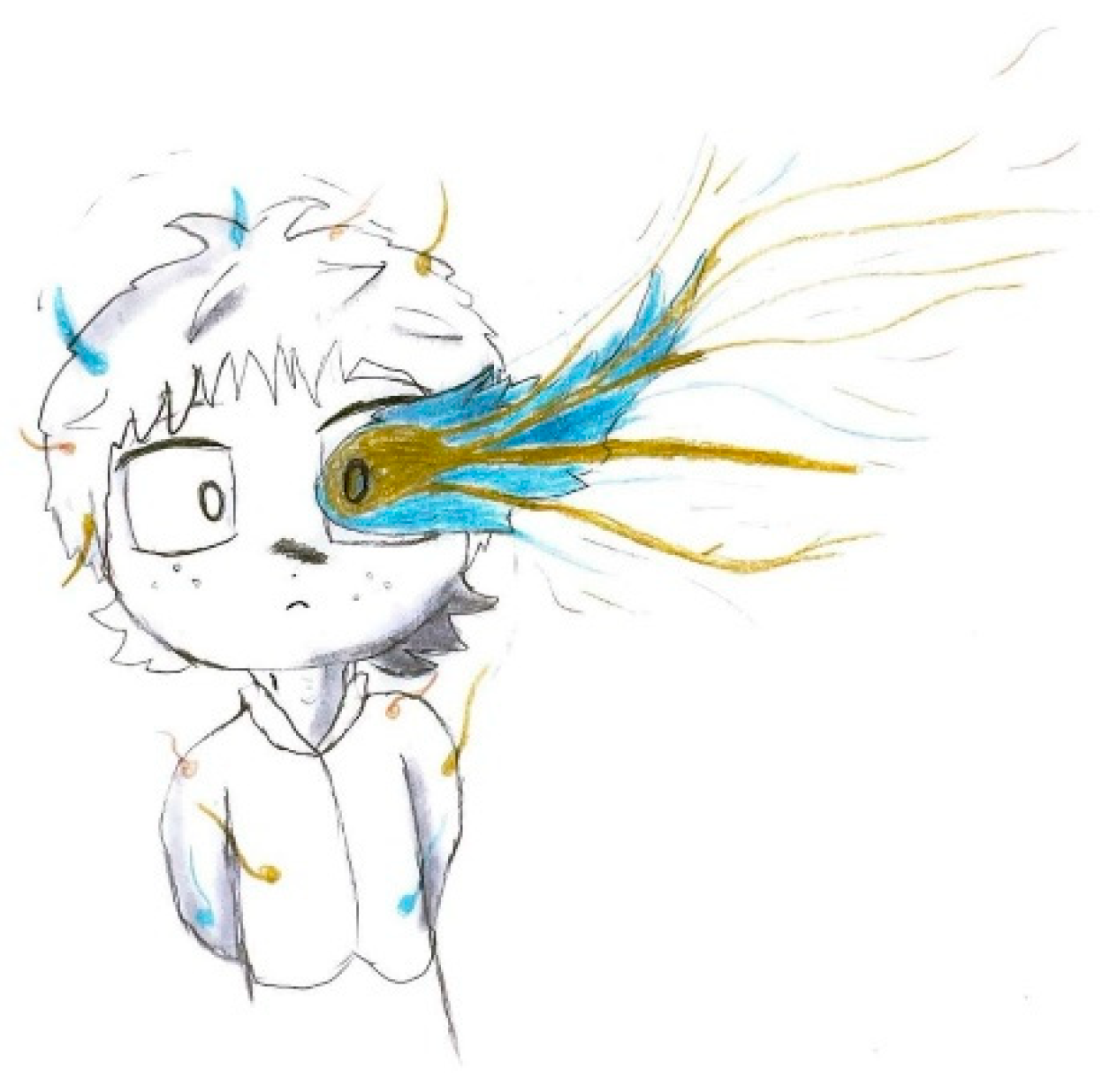
Figure 12, auditory stimuli are symbolized by musical notes that induce discomfort, emphasized by distressed facial expressions and onomatopoeic words like "pum-pum," underscoring the pulsatile and intense nature of the pain. Nausea and vomiting are common features associated with migraines, often clearly depicted, such in
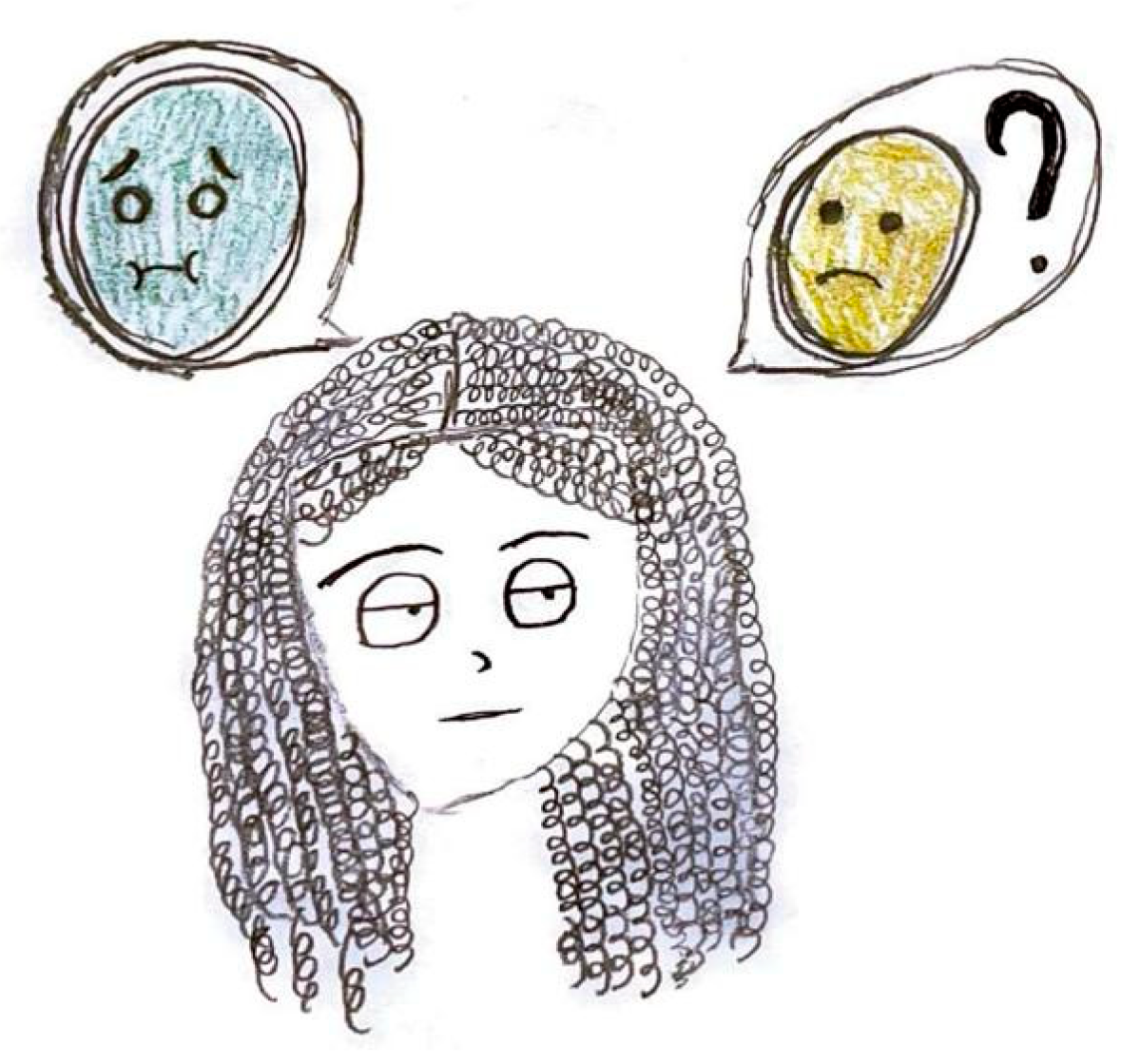
Figure 13 or evoked through blurred colors or shades of green and yellow to represent physical illness. Mental confusion, which can occur before, during, or after a migraine episode, is also commonly portrayed. In
Figure 13, nausea is conveyed through an expression of disgust, while confusion is symbolized by a bewildered expression and a question mark.
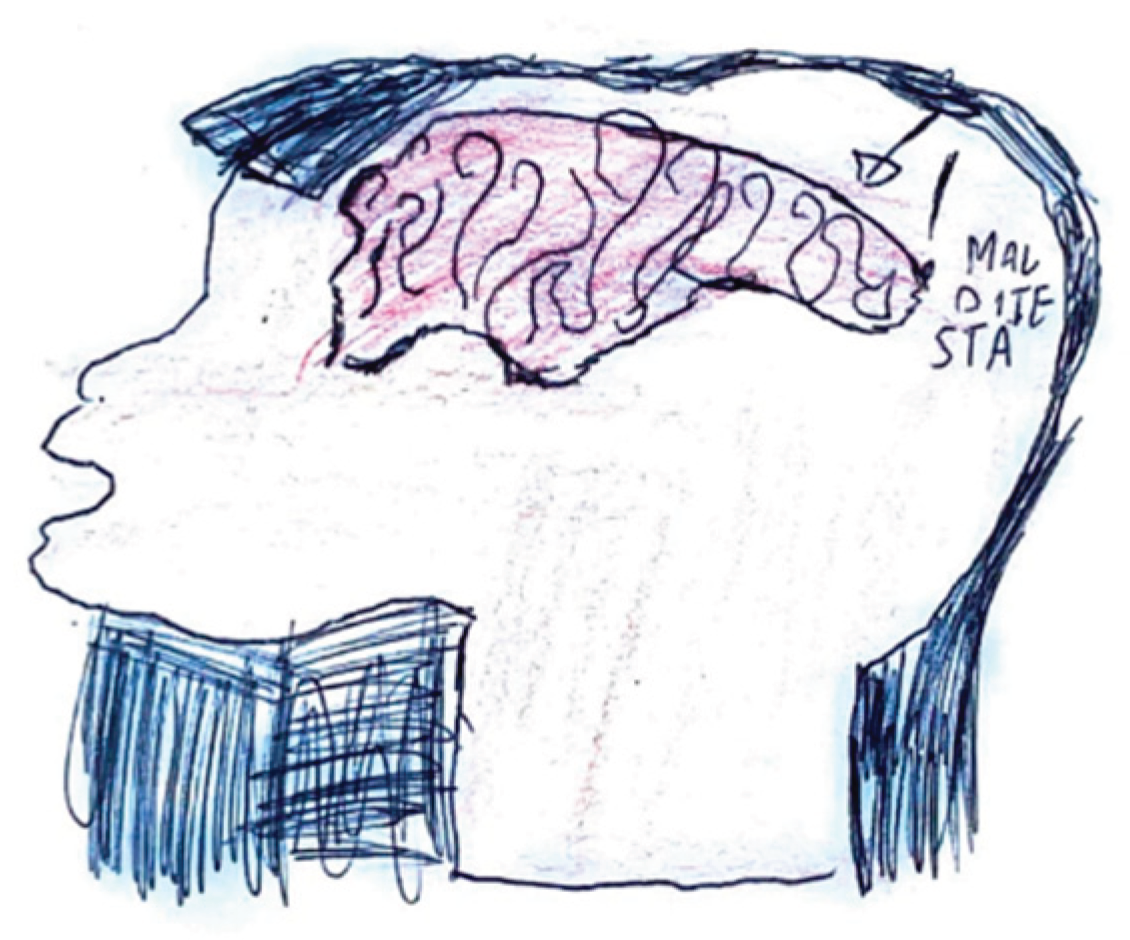
Figure 15 illustrates the "brain fog" phenomenon, represented by a cloud, alongside the emotional impact of the headache itself, which becomes a source of sadness and anger.
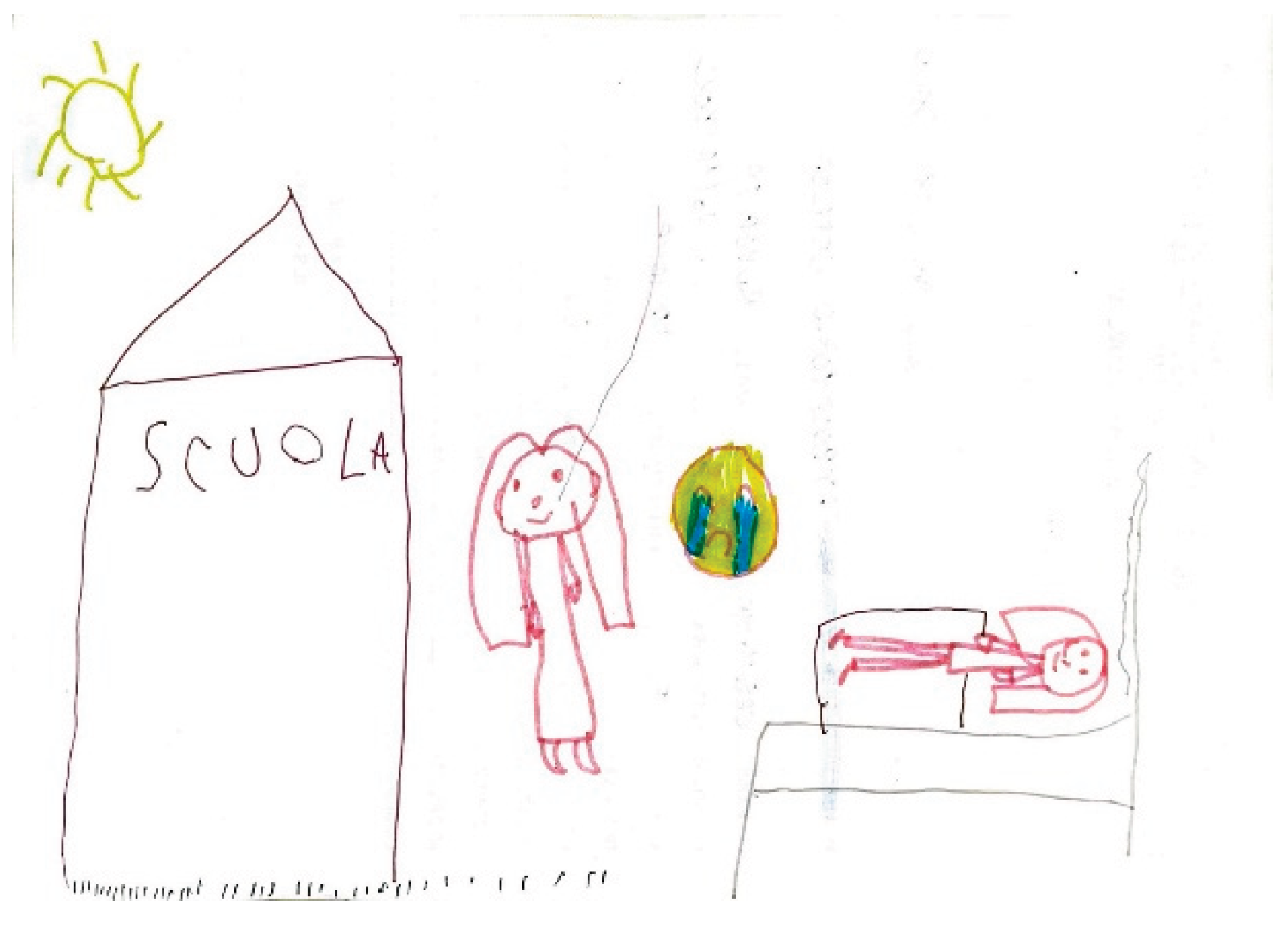
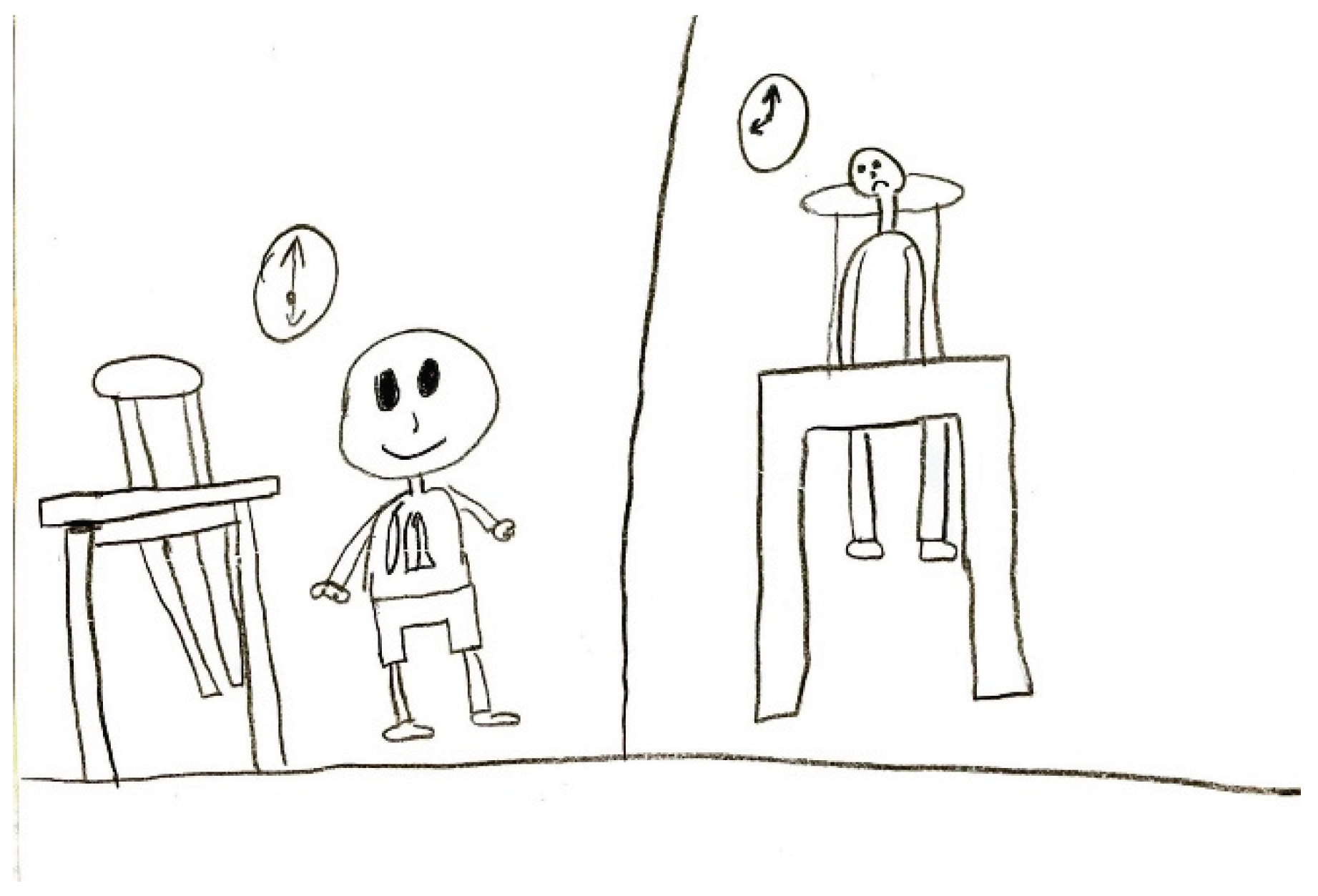
Occasionally, the discomfort linked to a headache manifest as a change in the child’s behavior, such as retreating to bed or being unable to engage in regular daily activities, including scholastic tasks (
Figure 16 and
Figure 17).
Figure 12.
Male, 13 years old.
Figure 12.
Male, 13 years old.
Figure 13.
Male, 10 years old.
Figure 13.
Male, 10 years old.
Figure 14.
Female, 11 years old.
Figure 14.
Female, 11 years old.
Figure 15.
Female, 11 years old.
Figure 15.
Female, 11 years old.
Figure 16.
Female, 7 years old.
Figure 16.
Female, 7 years old.
Figure 17.
Male, 9 years old.
Figure 17.
Male, 9 years old.
4.3. Aura
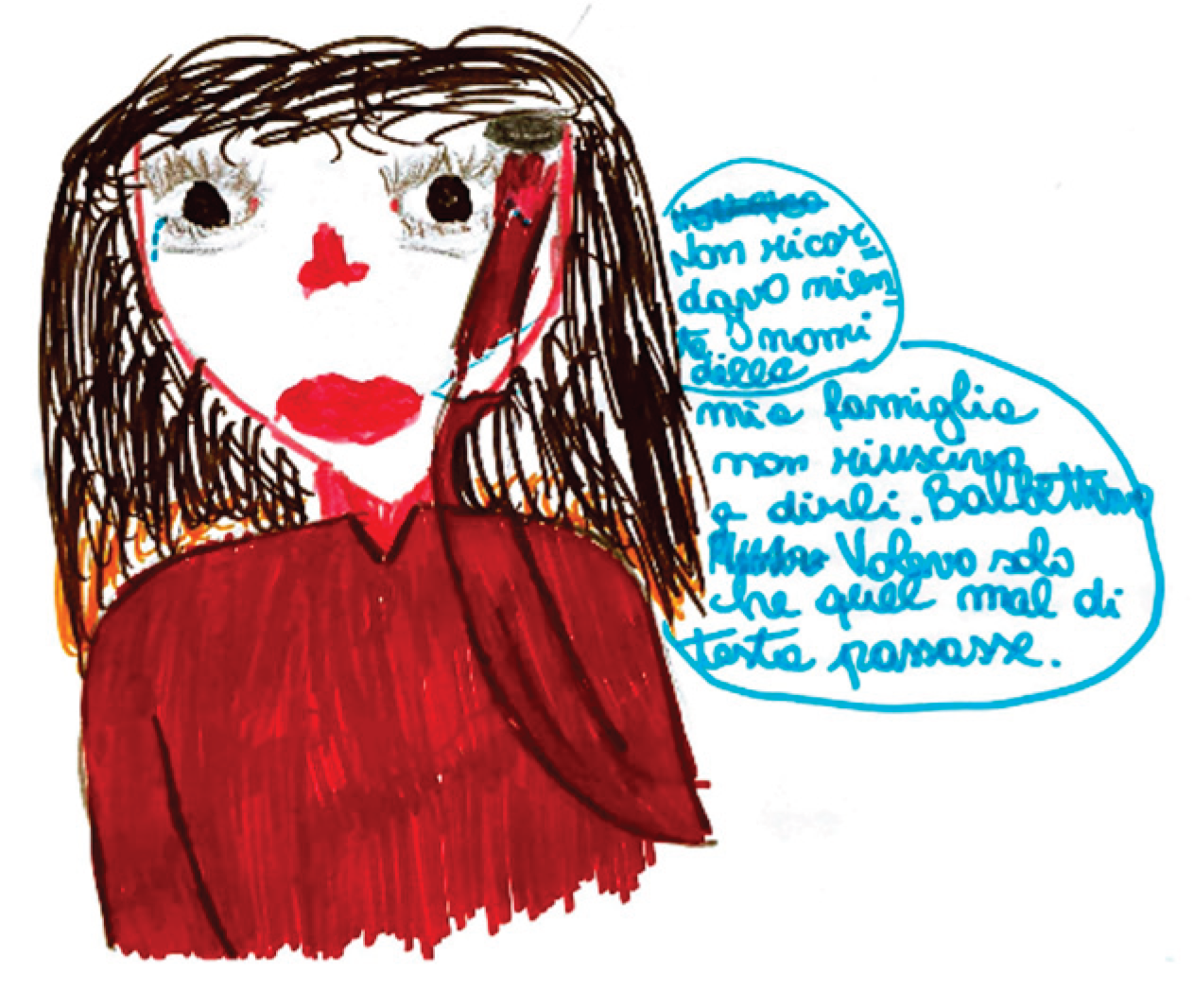
Migraine aura is often represented visually as stars, dots, zigzag lines, vision loss, or fog. Hemianopia is depicted with half-figures, such as a television screen half-obscured. Diplopia is drawn with a doubling of observed figures.
In one of the analyzed drawings, aphasia is represented with an explanatory speech bubble: 'I couldn't say the names of my family members, I stuttered.'
Figure 18.
Female, 8 years old.
Figure 18.
Female, 8 years old.
Figure 19.
Female, 9 years old.
Figure 19.
Female, 9 years old.
Figure 20.
Female, 9 years old.
Figure 20.
Female, 9 years old.
4.4. Alleviating Factors and Therapies
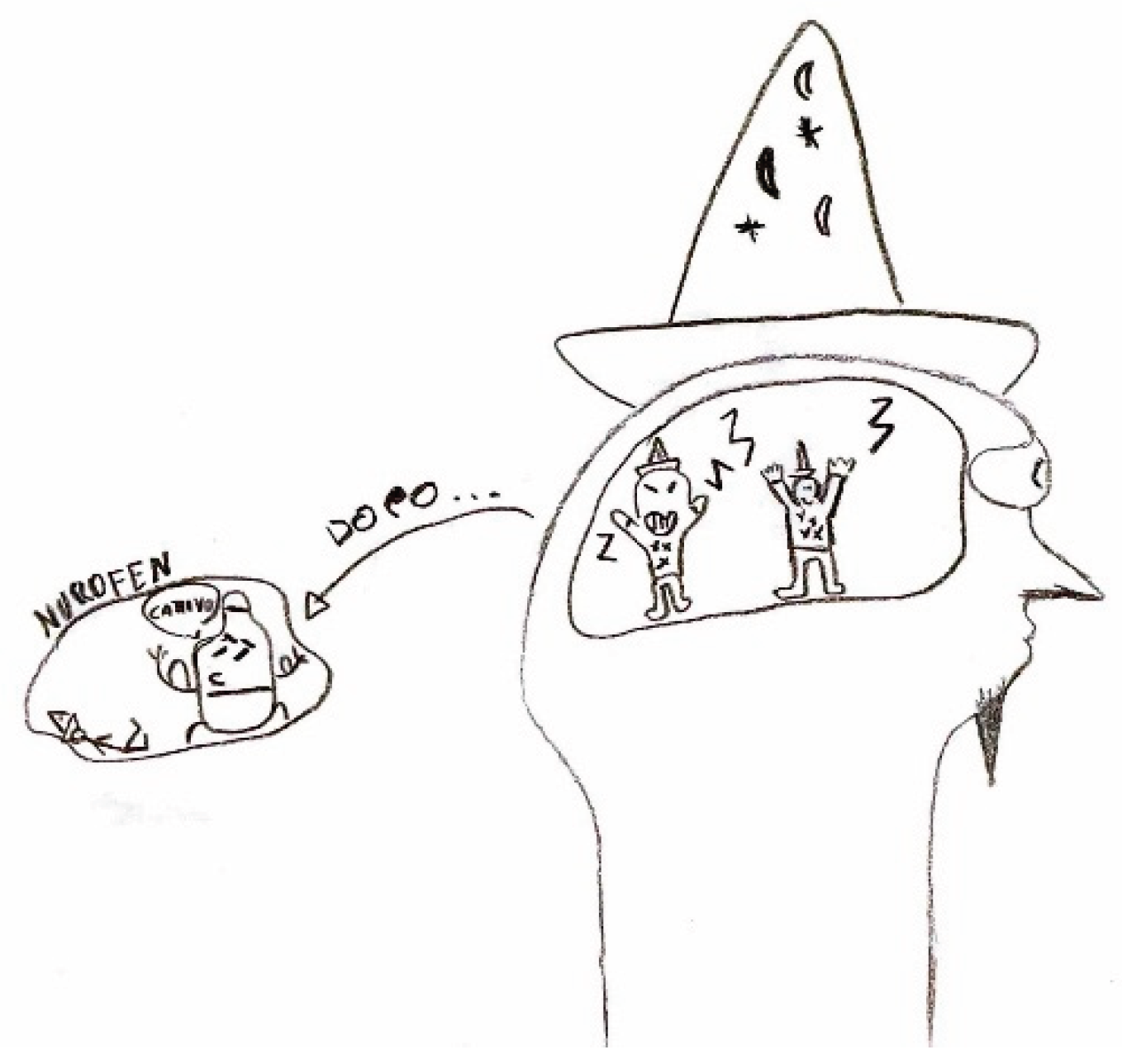
In some cases, the focus of the graphic representation shifts toward certain pain-relieving approaches, both in terms of action and behaviors, as well as pharmacological interventions. In the first instance, habitual self-administered maneuvers include head massages or compression, along with complete rest in bed away from lights or sounds. In the latter case, illustrating the action of medication may provide the physician with greater insight into the effectiveness of the symptomatic treatment.
Figure 21.
Male, 11 years old.
Figure 21.
Male, 11 years old.
Figure 22.
Female, 14 years old.
Figure 22.
Female, 14 years old.
4.5. Expression of Pain
The expression of pain in children occurs in different ways, but it is possible to highlight some characteristics common to many drawings. Headaches are frequently represented as a round geometric figure, a mass, or a stone placed where the brain should be. Brain fog takes on the characteristics of a grey fog or cloud. In children who have learned to write, spontaneous writing of captions and explanations is often associated, elaborating on how pain varies and the emotions associated with it. High-intensity pain is generally represented with expressions of sadness and tears.
Figure 23.
Female, 10 years old.
Figure 23.
Female, 10 years old.
Figure 24.
Female, 7 years old.
Figure 24.
Female, 7 years old.
Figure 25.
Female, 8 years old.
Figure 25.
Female, 8 years old.
4.6. Representation of Pain in Adolescents
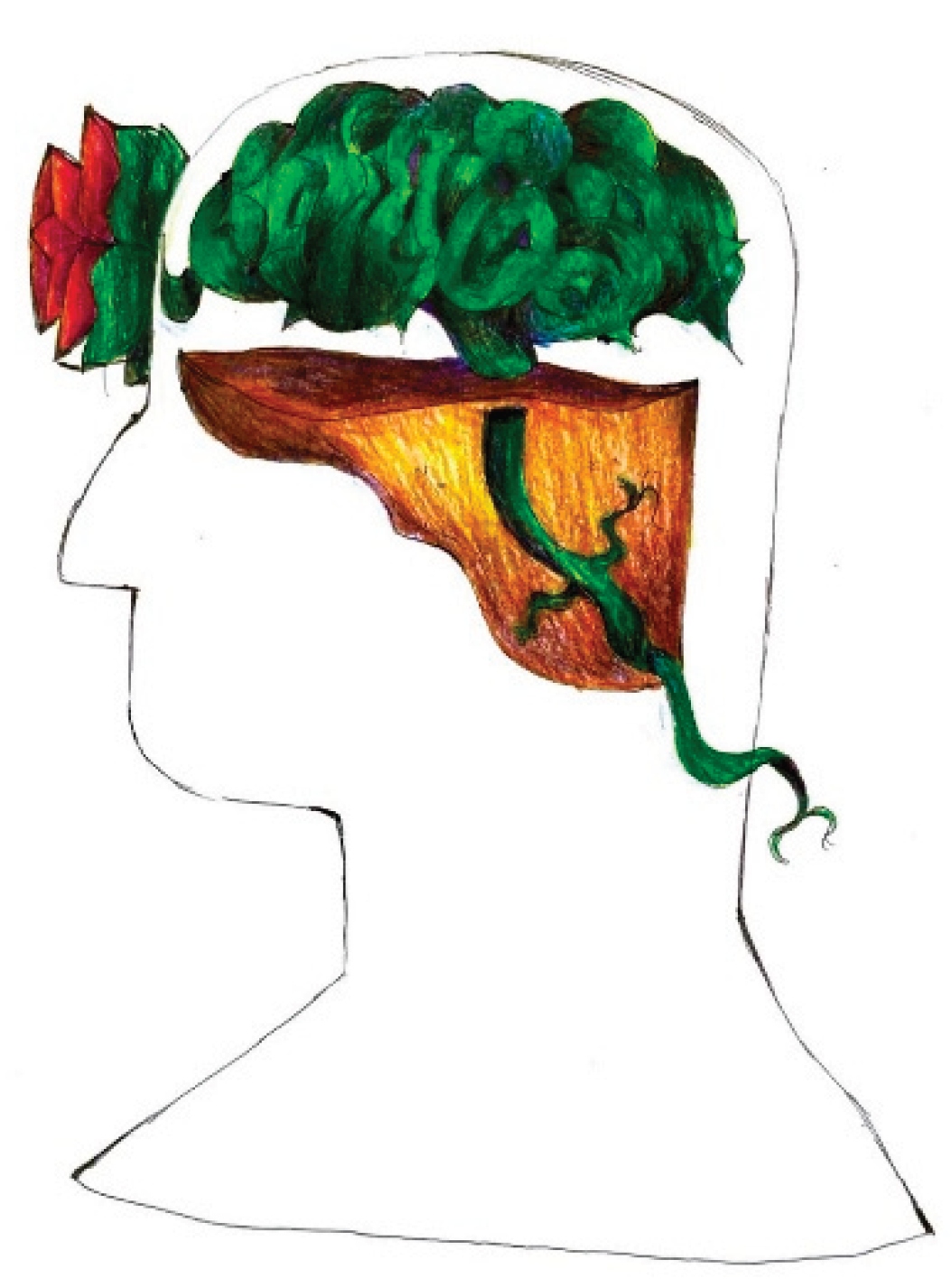
As descriptive and abstraction abilities mature in this population, their drawings show increasing complexity, elaboration, and often abstraction. Rather than elementary geometric shapes, migraine pain sometimes becomes a thorny plant tightly rooted in the young patient's head, and the areas where this manages to make its way outside the head correspond to those where the pain is perceived as better localized and more intense (for example the nape of the neck and the forehead).
Figure 26.
Female, 15 years old.
Figure 26.
Female, 15 years old.
Figure 27.
Female, 16 years old.
Figure 27.
Female, 16 years old.
Additional illustrations categorized according to clinical phenotype of pediatric headache are provided as supplementary materials.