| Table of Contents |
|
| List of Tables |
3 |
| List of Figures |
3 |
| 1. Introduction |
3 |
| 1.1. Introduction and Background of the Study |
3 |
| 1.2. Organisational Overview |
4 |
| 1.3. Problem Statement |
4 |
| 1.4. Aims, Objectives, Research Questions, Hypothesis, Propositions |
4 |
| 1.4.1. Research Objectives |
4 |
| 1.4.2. Research Questions |
4 |
| 1.5. Rationale/Importance of the Research |
4 |
| 1.6. Methodology |
5 |
| 1.7. Scope of the Study/Demarcation |
5 |
| 1.8. Structure of the Dissertation |
5 |
| 1.8.1. Chapter One |
5 |
| 1.8.2. Chapter Two |
5 |
| 1.8.3. Chapter Three |
5 |
| 1.8.4. Chapter Four |
5 |
| 1.8.5. Chapter Five |
5 |
| 2. Literature Review |
6 |
| 2.1. Introduction |
6 |
| 2.2. Base Theory of the Sub-Discipline/Different Background Aspects of the Concept |
6 |
| 2.2.1. Common Workplace Incentives |
6 |
| 2.2.2. Key Talent Retention Strategies |
7 |
| 2.3. Theoretical Frameworks/Models, and Related Research Issues |
7 |
| 2.3.1. Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory |
7 |
| 2.3.2. Vroom’s Expectancy Theory |
8 |
| 2.4. Previous Studies and Lessons Learnt |
8 |
| 2.5. Gaps Identified to Situate Own Research |
9 |
| 2.6. Summary of Chapter 2 |
9 |
| 3. Research Methodology |
9 |
| 3.1. Introduction |
9 |
| 3.2. Philosophical Position of the Research |
9 |
| 3.3. Paradigm Position of the Research |
10 |
| 3.4. Position of Research Approach |
10 |
| 3.5. Methodological Stance of the Research |
10 |
| 3.6. Stance of the Research Strategy and Design |
10 |
| 3.7. Research Sample and Population |
10 |
| 3.8. Data Collection and Data Analysis Tools/Techniques |
11 |
| 3.9. Ethical Consideration of the Research |
11 |
| 3.10. Summary of Chapter 3 |
11 |
| 4. Data Analysis and Discussions |
11 |
| 4.1. Introduction |
11 |
| 4.2. Analysis and Discussions |
12 |
| 4.2.1. Theme 1: Incentives and Recognition |
12 |
| 4.2.2. Theme 2: Work-Life Balance and Flexibility |
13 |
| 4.2.3. Theme 3: Career Growth and Development Opportunities |
13 |
| 4.2.4. Theme 4: Organisational Culture and Job Satisfaction |
14 |
| 4.3. Summary of Chapter 4 |
14 |
| 5. Conclusions, Limitations & Recommendations |
14 |
| 5.1. Conclusions on the Research Problem |
14 |
| 5.2. Summary of the Research Findings and Outcomes |
15 |
| 5.3. Original Contribution of the Research |
15 |
| 5.4. Limitations of the Research |
15 |
| 5.5. Recommendations/Areas for Further/Future Research |
16 |
| 5.6. Chapter Summary |
16 |
| References |
16 |
List of Tables
Table 3.7. Overall Resources Utilized…………………………………………………………….11
Table 4.2.1. %Change in Genders’ Gross Weekly earnings between 2022 and 2023……………..12
Table 4.2.2. Identified Gender Gaps in Hourly and Employee Bonuses in Apple UK between 2022-23 period……………………………………………………………………………………………13
List of Figures
Figure 2.3. Overview of Underpinning Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory………………………...8
Figure 4.2.1. Annual %Change to gross week pay for full-time workers in different UK regions for the 2023-24 Period……………………………………………………………………………….12
1. Introduction
1.1. Introduction and Background of the Study
Employees are among the key entities within the organisation whose influence extends beyond corporate performance as their expertise defines success, annual returns and other priority business areas today. Thus, maintaining skilled workers is essential but multiple employers across the globe face immense challenges due to high turnover rates. Here, the UK tech sector and global brands like Apple face similar issues in this competitive sector. While retaining the most skilled IT personnel is essential in this industry, high turnover rates introduce high costs and such multinationals often struggle due to disruptions in innovation. Researchers find that replacing an IT professional costs more than 50% of such workers' annual salaries (Mitrovska and Eftimov 2016). Moreover, the recent global COVID-19 pandemic intensified issues in maintaining a stable or top-performing workforce and environment, let alone in this sector. Therefore, it is essential to understand the key drivers of staff retention among UK employers who seek to boost operational continuity and financial performance. This study primarily explores employee retention factors that have influenced Apple’s UK operations and further highlights strategic measures that this employer can use to mitigate turnover rates in future.
1.2. Organisational Overview
Founded in early 1976 by Steve Jobs alongside Steve Wozniak, Apple Inc. is a global leader in the technology sector and offers multiple product or service categories ranging from the iPhone, and Apple Music digital platform to various accessories. The multinational's organisational structure blends both hierarchical and divisional models that support product-specific expertise while maintaining centralised oversight (AAPL 2022). This structure undoubtedly fosters the brand's innovation but Apple still significantly faces close competition. The key competitors include Samsung, Meta and Alphabet, among others, who are similarly striving for top talent that is needed in this sector. This crisis exposes vulnerabilities within Apple UK's retention strategies as the brand has been linked with senior executives' departure in the past. Thus, it is essential to reevaluate internal practices that will help Apple maintain market leadership in the UK and beyond.
1.3. Problem Statement
This research majors on the high turnover rates among the highly skilled IT personnel at Apple UK as failure to retain these professionals is a direct threat to operational efficiency, innovation and long-term profitability. This issue influences Apple and many UK firms’ operations and the rising competition primarily from rival tech firms introduces more challenges. In this case, the extra costs linked to recruitment, training new hires and the lost expertise can not be ignored. High turnover rates especially among some executives were also a key factor to Apple UK’s historic £1.5 billion post-Covid, which was a 61% revenue surge between 2021 and 2022 (AAPL 2022). Thus, it is essential to examine the underlying turnover causes to develop ideal targeted retention strategies that will sustain Apple UK’s competitive edge.
1.4. Aims, Objectives, Research Questions, Hypothesis, Propositions
The main aim of this study is to investigate employee retention influences on performance and primarily focuses on Apple UK’s operations. The research objectives include:
1.4.1. Research Objectives
To assess the key aspects affecting employee retention.
To explore the impacts of retention on Apple UK’s annual performance.
To evaluate efficient staff retention strategies.
To examine the relation between employee retention and satisfaction levels.
1.4.2. Research Questions
- a)
What factors can UK organisations adopt to enhance employee retention?
- b)
How does employee retention influence business performance at Apple?
- c)
Why have previous methods to improve retention failed, and what recommendations can address these challenges
1.5. Rationale/Importance of the Research
The purpose of this study is to offer a valuable contribution to business practices through a deeper examination of retention challenges primarily within the UK IT sector. While multiple studies have significantly examined retention strategies across industries, it is essential to conduct content-specific research among multinationals within technology in the UK. The findings of this research are essential for modern business executives and human resource management as the insights will inform key business areas. More importantly, it should help in effective hiring and training, making informed decisions, especially within IT, creating innovative employee engagement programs and in business performance.
1.6. Methodology
This study relies mostly on peer-reviewed secondary research and annual performance reports to examine this context across the UK business setting.
1.7. Scope of the Study/Demarcation
This study focuses on employee retention within Apple's United Kingdom operations, specifically examining national-level challenges and strategies in the UK technology sector.
1.8. Structure of the Dissertation
The research is organized into five chapters that highlight further details regarding this business issue and major primarily on the case of Apple UK.
1.8.1. Chapter One
This chapter introduces the research context and examines the relevance of workforce retention within Apple and the UK technology sector. The highlighted sections include the research background, problem statement, study aims, objectives and questions. These sections lay the foundation for a deeper exploration of the influences of retention on corporate performance examined in the next chapters.
1.8.2. Chapter Two
This chapter mainly reviews underpinning theories and past research on employee retention to highlight the urgency of developing innovative strategies ideal for UK IT sector employers. To establish a solid foundation for investigating ideal retention methods, this chapter analyses common motivators, dissatisfaction factors and corporate practices that also appear in Apple UK's operations.
1.8.3. Chapter Three
This chapter details the overall philosophical, paradigmatic and methodological framework that is guiding this case study. This section justifies the use of interpretive, qualitative, induction and case study approaches in this study alongside multiple secondary resources. Other discussed aspects include the chosen data collection and analysis methods, sample and ethical considerations taken into account during research.
1.8.4. Chapter Four
This chapter mainly analyses qualitative and quantitative data obtained from various resources to investigate the influences of attrition on business performance in the UK alongside the Apple UK case study. Some of the major identified research themes include the role of incentives or employee recognition in turnover rates, work-life balance, career growth and corporate culture. These findings are precisely mapped onto the initial research objectives and questions. The results reveal that pre-existing retention initiatives have often failed due to impractical objectives that could lack tangible outcomes, especially in employee recognition and development programs. Nevertheless, Apple's current proactive strategies offer instructive lessons that could help UK employers strengthen further employee commitment and performance.
1.8.5. Chapter Five
This chapter offers remarks and recommendations based on the research to further affirm that employee retention plays an essential role in reshaping corporate performance. The research findings acknowledge that a combination of flexible work policies, fair employee compensation, ideal leadership and transparency are essential in retaining top talent. However, the research faces limitations due to scope and the methodology used but it makes meaningful contributions to theory and practice. The case study also opens avenues for future research that can help refine and enhance some of these conclusions using more performance metrics, turnover ratios and other aspects.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Introduction
Generally, employee turnover has become a modern-day business concern and multiple studies have heavily examined the main causes across diverse demographic or regional contexts. This study further offers an overview of core variables that are influencing retention rates primarily in the UK IT sector. To achieve the same, the study incorporates an extensive review of multiple scholarly articles sourced from reputable journal platforms like SAGE Journals, IEEE Xplore, Sabinet, Science Direct and others. These secondary resources offer valuable insights regarding the primary factors linked to employee turnover rates among IT professionals. The studies were chosen based on relevance to the case study and quality while those with overlapping content or insufficient have been excluded. Other utilized credible resources include government publications and annual performance reports from Apple or other relevant UK institutions. This literature review section mainly examines key notions like job satisfaction, motivation among IT employees, work dissatisfaction and optimal talent retention methods that will potentially bring changes within Apple UK's stores.
2.2. Base Theory of the Sub-Discipline/Different Background Aspects of the Concept
Employee retention remains a major business challenge affecting core business areas as employees are essential stakeholders redefining most firms' annual revenue (Khan 2020). Moreover, institutions’ ability to retain top talent often correlates with their capacity to perform well within competitive markets to ensure uninterrupted product or service delivery (Mazlan and Jambulingam 2023). A recent study further emphasizes the need to establish a positive relationship between retention and corporate success strategies as high retention has been directly linked to better business performance across industries (Kundu and Gahlawat 2016). The various workforce retention methods like adopting ideal incentive programs further often play an essential role in motivating employees to remain within the firm. Mazlan and Jambulingam (2023) find that reducing these turnover levels not only saves employers more on recruitment and training costs but also enhances productivity and operational efficiency. Thus, losing talented personnel is detrimental to profitability and beyond operations, which mandates addressing this context to identify long-term strategic solutions.
2.2.1. Common Workplace Incentives
While turnover has far-reaching influences across multiple business areas, losing specialised skills may have profound economic impacts and interruption, especially in the IT sector. To address this issue, organisations need to create reliable comprehensive incentive programs that can encourage staff retention. Turnover rates are impacted by both internal and multiple external factors. Some of the external influences may consist of the work settings or conditions and the work culture, while internal influences may be the incentivization structure, policies and salaries. These aspects directly define employee retention and most employers today strive to adopt the best programs comprising monetary rewards, profit sharing, performance-based employee bonuses or even stock options (Al-Suraihi et al. 2021). For instance, large firms like Apple, Vanguard UK and Walmart offer stock options and monthly dividends as an efficient compensation tool.
Incentives are important and capable of improving employees' willingness to remain within a firm in anticipation of substantial future returns. Additionally, pension schemes and other common long-term investments offer workers a sense of security that further encourages them to stay. Others like wellness programs, flexible job schedules, paid time off and career growth opportunities contribute to higher employee satisfaction levels (Tamers et al., 2024). These are core business aspects that influence work-life balance and apply also beyond the technology sector.
2.2.2. Key Talent Retention Strategies
Most widely used employee retention methods constitute enhancing job satisfaction, work-life balance, career growth opportunities and positive work culture in various ways. Job satisfaction is primarily the positive feelings or attitude that workers have towards their work and this aspect is a central element in employee turnover (Dziuba et al. 2020). Unfortunately, employers may not easily find a universal solution or model to reinvent their workers' satisfaction levels as this is a multi-faceted business context. Research finds that younger employees are twice as likely to leave their work roles than their older counterparts and modern institutions need to adapt their retention strategies to the younger demographics' needs (Kanchana and Jayathilaka, 2023). Fortunately, some of the commonly used motivators like personnel recognition, incentives and the nature of work can effectively boost satisfaction levels.
On the other hand, investing heavily in employees' career growth through updated and personalized training programs can reduce turnover rates. Employers understand these programs' integral role in reducing turnover rates and in fostering brand loyalty. Shiri et al. (2023) similarly find reliable evidence from over 7000 publications that development and training programs highly enhance employees' intention to stay in a current role and lower early retirement instances. More often, proper training equips workers with the needed skills to excel in their work and their productivity is a direct benefit to the firm's overall performance.
It is also integral to maintain a strong work-life balance today for the workers' well-being. A poor work-life balance contributes to burnout, fatigue and dissatisfaction which are all key elements in high-turnover workplaces (Mendis and Weerakkody, 2017). In this case, the tech sector is more demanding as most roles can be fairly practical. Thus, prioritising offering this balance is vital and can potentially lower turnover rates. Thus, any UK employer invested in flexible work schedules and personal well-being is well-positioned towards creating a more satisfying work setting. Other strategies like enhancing job happiness are also key determinants of retention levels. Employees who are emotionally fulfilled may be less likely to abandon their employers than the latter. Thus, businesses need to create the best work environment that ensures workers feel valued and supported as their input also influences profitability. Recent research also acknowledges that the most satisfied workforce often has lower turnover rates and higher productivity (Gazi et al. 2024). Also. Ideal organisational leadership and communication strategies may not be ignored as they are essential in fostering a positive work culture, job satisfaction and ultimately higher retention.
2.3. Theoretical Frameworks/Models, and Related Research Issues
Various theoretical models can be used to explain the key factors involved in employee retention and turnover intentions. This research relies on Vroom’s Expectancy Theory and Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory as these frameworks highlight the relevance of key aspects like incentives and job satisfaction.
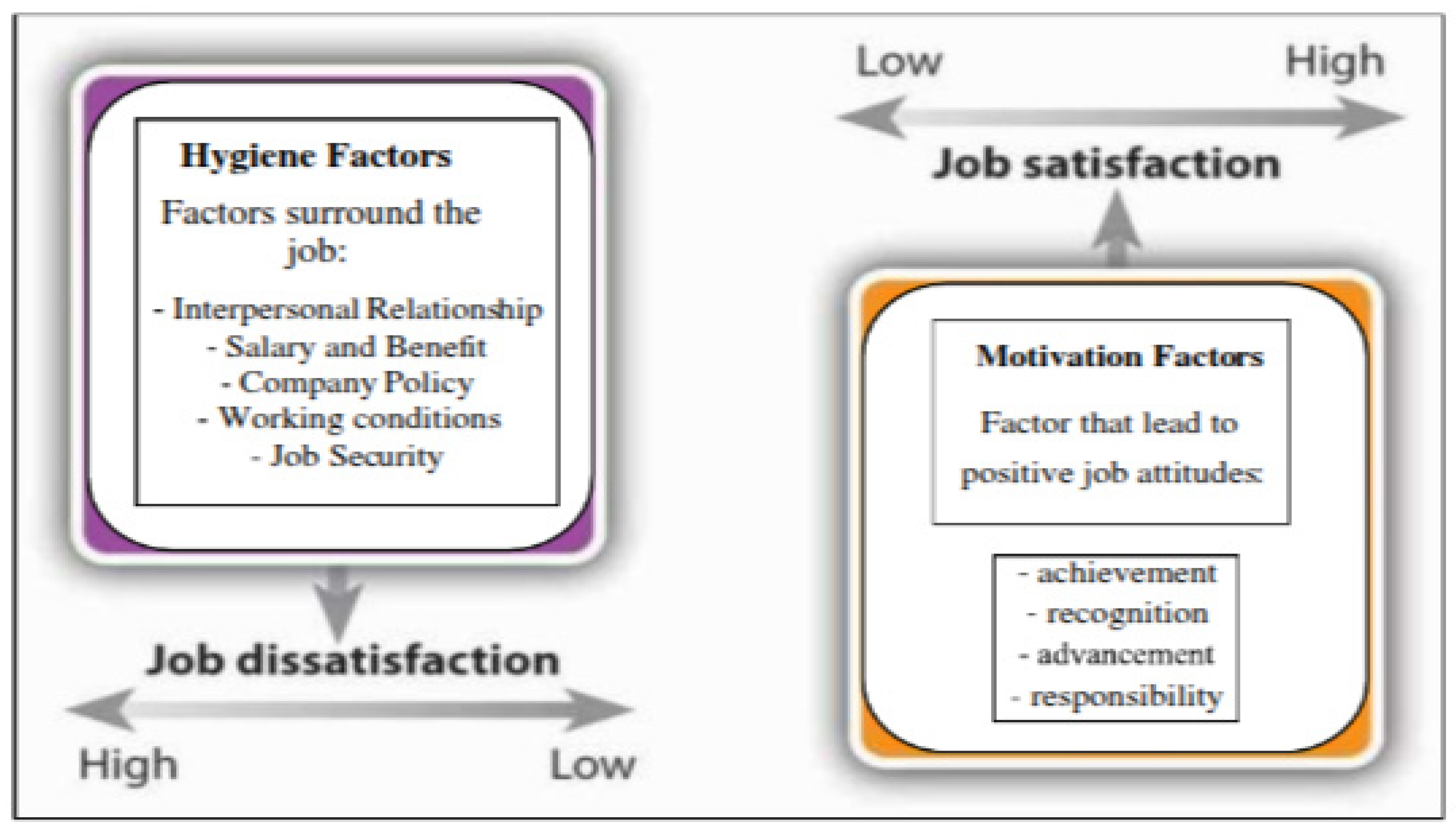
2.3.1. Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
The two-factor theory states that several factors in the work environment affect an employee's efficiency. According to Bexheti and Bexheti (2016), these categorised as dissatisfaction and work satisfiers are also motivation or drive and hygiene variables, respectively. These two elements as depicted in
Figure 2.3 are entirely independent of one another. This approach prioritises the advantages and overall health of the employees. More precisely, both elements belong to the group of motivators, which contains common characteristics including work-related challenges, participation in decision-making, responsibilities, recognition of achievements, and a sense of community inside the organisation (Bexheti and Bexheti 2016). According to Lee et al. (2022), this promotes the sense of fulfilment that comes from one's growth and progress.
Research finds is a link between hygiene another aspect and the worker's pay and well-being (Bexheti and Bexheti 2016). This aspect is categorised as "Hygiene" in Herzberg's model since it has a direct connection to maintenance and outside variables related to the job. Along with their pay in the form of incentives or salary, it might also cover the organization's practices and general well-being (Bexheti and Bexheti 2016). This implies that employees might not be able to perform their duties in the absence of particular conditions. Lastly, this model suggests that while enhancing hygiene factors may eliminate dissatisfaction, employee motivation requires mostly offering achievement and personal development opportunities. Thus, any institution that balances both hygiene and motivation factors should be well-positioned towards fostering a satisfied and committed workforce that could mitigate turnover issues.
2.3.2. Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
According to Vroom's Expectancy Theory, employees act in a way that maximises their pleasure and minimises their distress (Baakeel, 2018). In this model, employees are driven by the anticipated correlation between their input (effort) and output or rewards. Thus, employees will remain with a company longer if they think their efforts will result in the rewards they want. Managers need to know what employees value to ensure that the rewards they deliver match their expectations. In this approach, elements like instrumentality, anticipation, and valence are crucial, especially in modern workplaces. To accomplish their goals, managers need to ascertain what motivates their staff, make sure they have the tools they need, and fulfil their incentive commitments (Lokman et al., 2022).
2.4. Previous Studies and Lessons Learnt
Many industries are significantly developing and the need for a larger IT workforce is attributed to the rising globalisation rate, technology and solutions to competitiveness in such environments (Aničić and Nestorović 2020). Subsequently, the UK companies' potential for success relies primarily on their capacity to function properly, adaptability and innovation in such settings. Researchers highlight that such outcomes are also reliant on trained IT personnel who are assets in the modern competitive environment (Hameed et al., 2021). Unfortunately, employee turnover primarily in the technology sector, let alone in the UK, is a global concern that imposes significant financial and operational burdens. Al-Suraihi, Samikon and Ibrahim (2021) find that the cost of replacing an IT professional amounts to around 50-150% of their annual salary mainly due to added hiring, training and productivity loss costs. Thus, UK employers need to prioritise strategic retention methods that will mitigate some of these impacts effectively.
2.5. Gaps Identified to Situate Own Research
Despite the evident need to focus on employee retention strategies, a research gap in understanding specific interventions that would be revolutionary in the technology sector and among UK companies like Apple. Current studies arguably lack more data that directly correlates to certain business outcomes, which can limit actionable insights. As a result, employers in the tech sector may struggle to develop specialised strategies that will align with broader performance and corporate objectives. This research is focused on these issues and strives to offer tailored or evidence-based solutions.
2.6. Summary of Chapter 2
This chapter mainly reviews underpinning theories and past research on employee retention to highlight the urgency of developing innovative strategies ideal for UK IT sector employers. To establish a solid foundation for investigating ideal retention methods, this chapter analyses common motivators, dissatisfaction factors and corporate practices that also appear in Apple UK's operations.
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Introduction
This chapter outlines the overall methodology used in this research to investigate the influences of employee turnover on UK companies’ performance and focuses primarily on the case of Apple UK. This section discusses the study’s philosophical stance, research paradigm, approaches, methodological position, strategies and the adopted design. To generate actionable insights, secondary data from multiple reputable resources have been utilized to further identify key patterns linked to attrition today. Also, this chapter further discusses the targeted population and research sample alongside ethical considerations taken into account during the study.
3.2. Philosophical Position of the Research
This study adopts an interpretive philosophical stance or a qualitative approach to address this attrition crisis. Interpretivism is primarily a research approach that majors on understanding how people behave and their experiences by often examining these behaviors' meaning and relevant social phenomena (Pervin and Mokhtar, 2022). In this case study, this approach is used to identify the causes and influences of staff turnover based on employer and employee perspectives. More specifically, this study focuses on how individuals perceive certain corporate practices and the immediate impacts on their decision to leave or stay. Unlike the positivism method which primarily seeks quantifiable and generalised facts, using this qualitative model supports a more in-depth exploration of some of these complex human behaviours. It should also allow the study to capture rich and nuanced insights from multiple secondary data resources.
3.3. Paradigm Position of the Research
Generally, this research mainly follows a qualitative research paradigm. A qualitative paradigm is often ideal in such contexts as the model supports in-depth investigation of key social and corporate phenomena instead of simply relying on numerical measurement (Lim, 2024). Here, a qualitative model should be suitable as employee turnover can be associated with intricate human behaviours, motivations and different emotions that will be best captured qualitatively. This paradigm allows this study to adopt flexibility primarily in examining varied perspectives that have been drawn from secondary research. These resources offer a context-based understanding of deeper issues that are the underlying reasons and impacts of turnover rates in the UK.
3.4. Position of Research Approach
This study adopts an inductive approach and this bottom-up method often allows theories to emerge from different identified or observed research patterns that can form new explanations (Sileyew, 2019). Thus, it seems more appropriate here and helps uncover evolving employee turnover trends and some of the immediate responses among UK employers like Apple. This approach is also more flexible and open to various unexpected findings that could arise from secondary resources. Thus, the study does not necessarily confirm preset assumptions but rather builds theoretical insights regarding effective employee performance and retention strategies.
3.5. Methodological Stance of the Research
The qualitative research approach used allows this study to rely on a broad range of existing data regarding staff turnover rates, trends and business performance without the constraints of primary data collection. Qualitative research is often efficient and ethical primarily when examining sensitive and broad topics like dissatisfaction factors among workers (Abuhamda, Ismail and Bsharat, 2021). This case study benefits from already validated insights instead of conducting primary research that was arguably impractical especially due to time or resource constraints. These insights are past findings, recent statistical data, trends, contradictions and knowledge gaps that may be linked to this topic.
3.6. Stance of the Research Strategy and Design
In general, this research applies a case study strategy by focusing mainly on Apple’s operations in the UK. More often, case studies are reliable in examining real-life contemporary issues and ensuring the same remains within context (Hancock et al., 2021). Using this design, this study majors on the impacts of turnover rates on corporate perception and uses different insights to offer talent retention strategies. Other strategies like ethnography or phenomenological research seemed unsuitable as they focused more on cultural immersion and individual experiences instead of business practices. On the contrary, this case study facilitates a more holistic examination of Apple's internal and external practices that should offer applicable lessons to other UK employers facing high turnover.
3.7. Research Sample and Population
Arguably, the research sample used in this case study includes a broad variety of secondary data and resources primarily from peer-reviewed journal articles, company reports, industry whitepapers, and credible online databases. Some of the used databases are Semantic Scholar, Science Direct and the Cite Them Right platform, among others. To ensure relevance and accuracy in this research, only materials published within the past ten years have been used and all the resources are summarised in
Table 3.7.
3.8. Data Collection and Data Analysis Tools/Techniques
All the used data was collected from reputable and open-access databases based on relevance, and credibility alongside the publication date to ensure no resource is older than ten years. Also, more attention was paid to the resources that discuss turnover trends, data, employee satisfaction, corporate performance metrics primarily at Apple and retention strategies. This data is analysed using a thematic model to identify any recurring themes including turnover causes, retention methods and key performance outcomes. This data analysis approach is also aligned with Braun and Clarke’s six-phase model, which suggests beginning with familiarisation with the data, codes' generation and searching for themes (Peel, 2020). The researcher can then review the thematic patterns, and define and name them before producing the final report. Other included descriptive statistics, especially from annual reports from companies are necessary to complement the qualitative findings.
3.9. Ethical Consideration of the Research
In general, strict ethical standards were maintained in this case study and the secondary sources used throughout are properly cited using the Harvard referencing style to eliminate plagiarism instances. The used data is also publicly available and no confidential or personal information was breached in this research. The research is also conducted based on the academic integrity guidelines of the University of East London. The list of references further includes DOI and hyperlinks to some of the non-academic sources to ensure transparency and intellectual honesty.
3.10. Summary of Chapter 3
This chapter details the overall philosophical, paradigmatic and methodological framework that is guiding this case study. This section justifies the use of interpretive, qualitative, induction and case study approaches in this study alongside multiple secondary resources. Other discussed aspects include the chosen data collection and analysis methods, sample and ethical considerations taken into account during research.
4. Data Analysis and Discussions
4.1. Introduction
This chapter presents this study's findings based on insights from multiple secondary resources on the influences of attrition on UK companies' performance by paying attention to Apple UK. Based on the research objectives, these findings are assessed and categorized into specific themes that can answer the initial research questions. The identified retention factors or thematic patterns are generalised into key employee retention strategies, retention impacts on Apple UK's performance in the recent past, and the relation between retention and employee satisfaction, among other aspects. These findings draw on selected qualitative and quantitative data collected from Apple UK's performance reports and other sources offering UK labour market information. To contextualize the study results, other theoretical frameworks are applied including Herzberg's Hygiene factors and Vroom's expectancy model to further support interpretation.
4.2. Analysis and Discussions
4.2.1. Theme 1: Incentives and Recognition
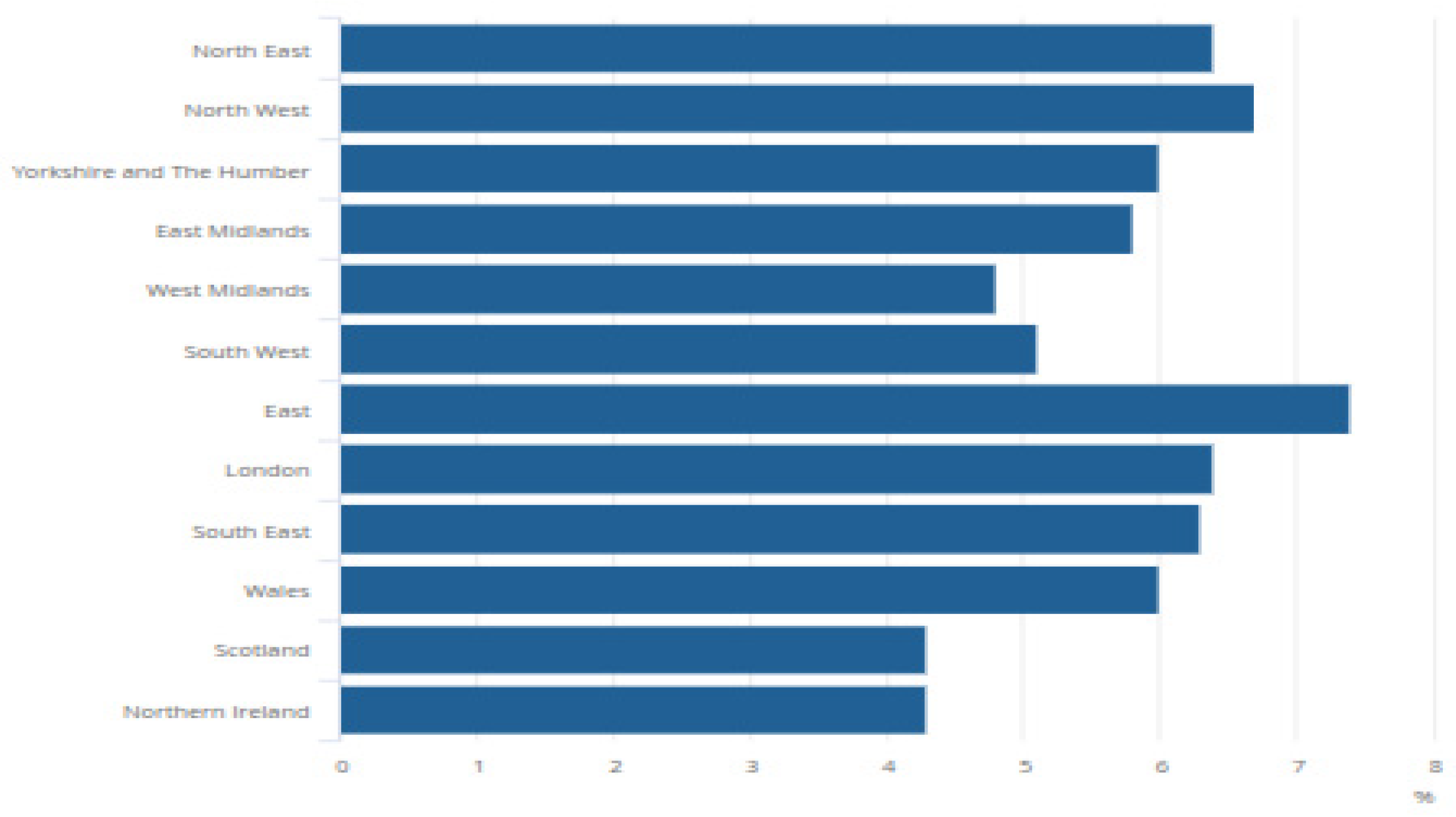
Generally, personnel recognition and common financial incentives are critical drivers of employee retention. According to Hassan (2016), significant evidence suggests that an appropriately structured incentive program can enhance commitment and productivity among workers significantly. However, certain discrepancies within these incentives' distribution often persist, let alone in the UK, primarily as regional and gender-based payment gaps. For instance, UK employers' incentive tendencies show that male workers in the nation's capital often get higher performance-based remuneration percentages in the final years of their careers (White 2023). White (2023) also notes that the full-time employees' weekly pay across all the UK sectors fell by around 1.5% in 2023 alone. Such discrepancies shown in
Figure 4.2.1 across the UK industries are striking. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) similarly notes that the full-time employees within London alone receive an average of triple the incentives paid to professionals in other regions in the country (Stansbury, 2023). Such discrepancy in incentives among genders worsens this problem. Recent data represented in
Table 4.2.1 and
Figure 4.2.1 for the 2022-24 period show specific gender and regional disparities respectively across the UK for the full-time and part-time workers based on the ONS statistical reports.
According to ONS (2024), the UK private sector is yet to recover from recent crises like the recent global epidemic and the typical full-time worker still earns less in incentives compared to 2008's statistics. However, such data may be skewed as some individuals primarily the top executives especially at Apple and similar private industry employers often receive more generous benefits than others. Nevertheless, research finds that most workers seek recognition and any form of remuneration for diligent efforts or achievements at work, regardless of type as even a verbal recognition can be effective (Faisal Ahammad et al. 2015). Similarly, Apple UK acknowledges the need to create ideal payment and incentive programs as they influence the worker's decision to resign. Unfortunately, Apple UK also has evident but minor bonus and employees' hourly pay gaps based on recent annual gender pay gap and performance reports as summarised in
Table 4.2.2. Nevertheless, Apple UK and the entire organisation primarily use multiple remuneration strategies that include handshakes, personnel recognition cards, vouchers, Beer Bash parties and also stock dividends (Apple, 2022).
4.2.2. Theme 2: Work-Life Balance and Flexibility
Work-life balance also emerged as a major aspect influencing retention rates and research demonstrates that the most flexible work arrangements today tend to promote more loyalty among skilled workers (Estanio et al., 2023). Also, the younger generations among most employers today mostly seek workplaces that value certain flexible work schedules (Lee, Chong, and Ojo 2024). In this case study, Apple UK has been implementing more hybrid workplace models like many employers in the tech sector and offers workers remote work alternatives at least two days per week (Smite et al. 2023). However, full telework policies are yet to be fully adopted at Apple UK, which reflects the existing hesitation to implement the same industrial-wide despite the modern workers' flexibility demands. Further research indicates that around 40% of workers in many workplaces often consider leaving employment if the employer forces them to have full-time work attendance (Smite et al. 2023). According to the International Labor Office (ILO), teleworking is among the increasingly endorsed EU policies and can be categorised as a hygiene factor essential towards job satisfaction based on Herzberg's model (Hee et al. 2018). Thus, fostering flexibility in work routines is essential as it addresses direct employee needs and it should support Apple's ability to maintain the most stable or skilled workforce.
4.2.3. Theme 3: Career Growth and Development Opportunities
Also, career growth opportunities are pivotal towards retaining talented workers and research acknowledges that employers without any clear development programs often face high attrition (Urme, 2023). Hirschi and Spurk (2021) acknowledge that the most ambitious workers regularly seek opportunities externally when the internal promotion prospects seem stagnant. Apple's strategy primarily supports internal promotions for the upper-level roles and this approach reflects a more retention-focused model aligned with Maslow's hierarchy of needs (Apple, 2022). More specifically, supporting these self-actualization needs through promotions and professional growth should arguably foster higher loyalty levels among workers. However, any comprehensive career development program can be costly but research suggests that investment in career growth may potentially yield more returns due to reduced turnover rates alongside better employee performance (Infuehr and Kronenberger, 2023). Thus, Apple and UK firms' retention strategies need to offer more than training as it is essential to ensure the programs can be linked to visible and practical career progression.
4.2.4. Theme 4: Organisational Culture and Job Satisfaction
Lastly, an organisation’s culture and job satisfaction critically influence the turnover rates and annual performance in various ways. Lee et al. (2022) identify job satisfaction as a key predictor of voluntary employee turnover and highlight the need to foster positive work cultures today. In this case, study, Apple UK's business model integrates a more competitive remuneration program, an inclusive work environment and unique recognition events like the 'Beer Bash' to strengthen internal culture (AAPL, 2022). These are essential business aspects and Herzberg's theory similarly underscores how a poor work setting or hygiene factors often breed dissatisfaction among workers and, thus, high turnover. Lee et al. (2022) also find a significant correlation between operational efficiency, employee satisfaction and favourable corporate reputation. Thus, to sustain better business performance within some of these dynamic industries like the technology sector, Apple and UK firms need to continuously invest in nurturing job satisfaction using the most tangible and intangible methods.
4.3. Summary of Chapter 4
This chapter mainly analyses qualitative and quantitative data obtained from various resources to investigate the influences of attrition on business performance in the UK alongside the Apple UK case study. Some of the major identified research themes include the role of incentives or employee recognition in turnover rates, work-life balance, career growth and corporate culture. These findings are precisely mapped onto the initial research objectives and questions. The results reveal that pre-existing retention initiatives have often failed due to impractical objectives that could lack tangible outcomes, especially in employee recognition and development programs. Nevertheless, Apple's current proactive strategies offer instructive lessons that could help UK employers strengthen further employee commitment and performance.
5. Conclusions, Limitations & Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions on the Research Problem
This study aims to investigate employee retention challenges and influences on performance by focusing on the case of Apple UK's operations. The findings show the need to adopt more modern retention strategies that are aligned with highly competitive environments like the IT sector. Most employees now value work-life balance, remote work and flexibility as well as inclusion at work. This study establishes that high turnover has undeniable consequences beyond financial losses as this issue can affect operational stability, workforce morale and innovation in the IT sector. For IT-based employers like Apple, retaining the most skilled professionals is essential and directly linked to sustained business performance or competitiveness. The study results firmly show that, while fair remuneration is essential, it may not be the sole factor often driving employee retention or turnover rates. Some of the identified sub-patterns include the organisational climate, leadership styles and communication framework that all play equally important roles in these aspects.
Also, employees who feel valued at work and involved in decision-making may be more likely to commit to their roles. This research offers a further explanation regarding the same using Herzberg's two-factor model that is based on intrinsic and extrinsic motivation factors. For instance, intrinsic motivators may constitute meaningful work and personal growth while extrinsic motivation factors can be an employee's salary and job security. Adopting a similar multi-faceted strategy and remuneration model blends financial incentives with strong leadership or employee recognition effectively. Multiple resources utilized in the study further acknowledge that investing in better training programs, and clearer and honest recruitment processes are linked to high retention rates. However, the latter and misaligned job expectations, let alone in the IT sector, can lead to frustration and employee dissatisfaction. This study uncovers that Apple and other UK employers should heavily benefit from strategic retention plans, inclusive work cultures and practices. These insights suggest that modern business leaders need to look beyond traditional HR roles. Instead, it is essential to adopt more holistic approaches or views of the employees' experience to encourage their willingness to stay.
5.2. Summary of the Research Findings and Outcomes
The research findings primarily show that employee retention strategies hugely influence corporate performance within and beyond the IT sector. Some of the prominently identified retention strategies include maintaining work-life balance at work, flexibility in work policies, fair compensation and inclusion in management practices. Most resources used highlight that modern employees respond positively to remote work and leadership styles that favour personal expression, collaboration and a better culture. On the other hand, rigid work schedules, unclear job expectations and unfair compensation were linked to high turnover rates. The research highlights the rising relevance towards transparency in hiring and training practices. Furthermore, competitive compensation models emerge as essential but do not necessarily guarantee to create the sufficient work environment for high retention rates. Most workers' demands are also heavily aligned with professional and personal growth. Thus, it is essential for employers to regularly consider the best upskilling opportunities, and recognise top contributors and other benefits.
5.3. Original Contribution of the Research
This research fairly contributes new insights to both academic and business communities by offering a detailed qualitative analysis of talent retention within the UK and the IT sector, let alone at Apple. While most of the existing and used literature is quantitative in nature, this case study strives to fill a critical gap by exploring some of the key employee motivations and business responses to the same using a qualitative approach. For business managers and UK HR practitioners, this research offers a practical framework that can be used to enhance retention by aligning corporate policies with the modern employee's expectations. Other aspects like the emphasis on interpersonal relationships and corporate culture as modern retention tools further represent the evident shift from transactional approaches to more transformative human-centred management strategies.
5.4. Limitations of the Research
While these insights are undoubtedly valuable, this research has limitations as it is geographically confined to the UK business environment. Thus, the conclusions of the study may not necessarily apply to some regions with different labour laws and cultural values. Also, the primary focus on Apple UK's operations limits the generalisation of certain findings to other sectors and organisations. Despite being rich in context and depth, this case study also majorly relies on qualitative methods and this approach arguably limits the ability to statistically analyse some broader patterns across a larger population. These aspects highlight the need to use broader sampling and mixed research methods that could build on these findings.
5.5. Recommendations/Areas for Further/Future Research
Based on the research findings, it is recommended that UK business leaders prioritise more flexible working arrangements, involve workers in decision-making, and create more immersive leadership programs that focus on emotional intelligence and better communication. More importantly, the remuneration programs may need regular readjustment to reflect inflation, national policy changes, responsibility and additional benefits. This approach may be an added step towards building loyalty and recognising contribution more effectively. It is also advisable to emphasize transparent and realistic hiring practices that can ensure there is a better match between advertised roles and potential candidates.
5.6. Chapter Summary
This chapter offers remarks and recommendations based on the research to further affirm that employee retention plays an essential role in reshaping corporate performance. The research findings acknowledge that a combination of flexible work policies, fair employee compensation, ideal leadership and transparency are essential in retaining top talent. However, the research faces limitations due to scope and the methodology used but it makes meaningful contributions to theory and practice. The case study also opens avenues for future research that can help refine and enhance some of these conclusions using more performance metrics, turnover ratios and other aspects.
References
- AAPL, (2022). Annual Report under Section 13 Or 15(D) Of The Securities Exchange Act Of 1934 For The Fiscal Year Ended September 24, 2022 form 10-K [Online]. Apple. [ 25 April 2025]. Available at: https://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReports/PDF/NASDAQ_AAPL_2022.pdf.
- Abuhamda, E., Ismail, I.A. and Bsharat, T.R., 2021. Understanding quantitative and qualitative research methods: A theoretical perspective for young researchers. International Journal of Research, 8(2), pp.71-87.
- Al-Suraihi, W.A., Samikon, S.A., Al-Suraihi, A.H.A. and Ibrahim, I., 2021. Employee turnover: Causes, importance and retention strategies. European Journal of Business and Management Research, 6(3), pp.1-10. [CrossRef]
- Aničić, D. and Nestorović, O., 2020. Globalization's influence on the competitiveness of the national economy. Journal of process management and new technologies, 8(1). [CrossRef]
- Apple (2022) Apple UK gender pay gap report 2022-2023, Apple UK. Available at: https://www.apple.com/legal/more-resources/docs/uk-gender-pay-gap-report-2022.pdf (Accessed: 28 April 2025).
- Baakeel, O.A., 2018. Using Expectancy Theory to Explain Performance Appraisal Elements and Employees' Motivation. Journal of Fundamental & Applied Sciences, 10.
- Bexheti, L. and Bexheti, A., 2016. The impact of Herzberg's two-factor theory and efficiency at work. European Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 1(2), pp.378-385. [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, S.T., Ingaldi, M. and Zhuravskaya, M., 2020. Employees' job satisfaction and their work performance as elements influencing work safety. System Safety: Human-Technical Facility-Environment, 2(1). [CrossRef]
- Estanio, M., Losbanes, M.G., Vigonte, F. and Abante, M.V., 2023. Flexible Work Arrangement: Its Significance to Employees' Performance and Productivity. Available at SSRN 4602059. [CrossRef]
- Gazi, M.A.I., Yusof, M.F., Islam, M.A., Amin, M.B. and bin S Senathirajah, A.R., 2024. Analyzing the impact of employee job satisfaction on their job behaviour in the industrial setting: An analysis from the perspective of job performance. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10(4), p.100427. [CrossRef]
- Faisal Ahammad, M., Mook Lee, S., Malul, M. and Shoham, A., 2015. Behavioural ambidexterity: The impact of incentive schemes on productivity, motivation, and performance of employees in commercial banks. Human Resource Management, 54(S1), pp.s45-s62. [CrossRef]
- Hancock, D.R., Algozzine, B. and Lim, J.H., 2021. Doing case study research: A practical guide for beginning researchers. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R., 2016. The role of human capital management in enhancing engagement and retention among the top talent in the organization: A critical literature review. Journal of Emerging Economies and Islamic Research, 4(4), pp.1-14.
- Hameed, K., Arshed, N., Yazdani, N. and Munir, M., 2021. On globalization and business competitiveness: A panel data country classification. Studies of Applied Economics, 39(2). [CrossRef]
- Hee, O.C., Yan, L.H., Rizal, A.M., Kowang, T.O. and Fei, G.C., 2018. Factors influencing employee job satisfaction: A conceptual analysis. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(6), pp.331-340.
- Hirschi, A. and Spurk, D., 2021. Ambitious employees: Why and when ambition relates to performance and organizational commitment. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 127, p.103576. [CrossRef]
- Infuehr, J. and Kronenberger, S., 2023. The Impact of Job Similarity Along the Career Path on the Firm’s Promotion Strategy. Schmalenbach Journal of Business Research, 75(2), pp.149-172.
- Kanchana, L. and Jayathilaka, R., 2023. Factors impacting employee turnover intentions among professionals in Sri Lankan startups. Plos one, 18(2), p.e0281729. [CrossRef]
- Khan, U., 2020. Effect of employee retention on organizational performance. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management, and Innovation, 2(1), pp.52-66. [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.C. and Gahlawat, N., 2016. Effects of employee retention practices on perceived firm and innovation performance. International Journal of Innovation and Learning, 19(1), pp.25-43. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H., Chong, C.W. and Ojo, A.O., 2024. Influence of workplace flexibility on employee engagement among young generation. Cogent Business & Management, 11(1), p.2309705.
- Lee, B., Lee, C., Choi, I. and Kim, J., 2022. Analyzing determinants of job satisfaction based on two-factor theory. Sustainability, 14(19), p.12557. [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M., 2024. What is qualitative research? An overview and guidelines. Australasian Marketing Journal, p.14413582241264619. [CrossRef]
- Lokman, A., Hassan, F., Ustadi, Y.A., Rahman, F.A.A., Zain, Z.M. and Rahmat, N.H., 2022. Investigating motivation for learning via Vroom’s Theory. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 12(1), pp.504-530. [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, M.R.M. and Jambulingam, M., 2023. Challenges of talent retention: a review of literature. Journal of Business and Management Review, 4(2), pp.078-091. [CrossRef]
- Mendis, M.D.V.S. and Weerakkody, W.A.S., 2017. The impact of work-life balance on employee performance concerning telecommunication industry in Sri Lanka: a mediation model. Kelaniya Journal of Human Resource Management, 12(1), pp.72-100. [CrossRef]
- Mitrovska, S. and Eftimov, L., 2016. Calculating the cost for employee turnover in the IT industry in Macedonia by using a web calculator. Journal of HRM, 19(1). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312597439_Calculating_the_cost_for_employee_turnover_in_the_IT_industry_in_Macedonia_by_using_a_web_calculator [Accessed 25 March 2025].
- ONS (2024) Employee earnings in the UK: 2024, Employee earnings in the UK - Office for National Statistics. Available at: https://www.ons.gov.uk/employmentandlabourmarket/peopleinwork/earningsandworkinghours/bulletins/annualsurveyofhoursandearnings/2024#toc (Accessed: 27 April 2025).
- Peel, K.L., 2020. A beginner’s guide to applied educational research using thematic analysis. Practical Assessment Research and Evaluation, 25(1). [CrossRef]
- Pervin, N. and Mokhtar, M., 2022. The interpretivist research paradigm: A subjective notion of a social context. International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development, 11(2), pp.419-428. [CrossRef]
- Shiri, R., El-Metwally, A., Sallinen, M., Pöyry, M., Härmä, M. and Toppinen-Tanner, S., 2023, November. The role of continuing professional training or development in maintaining current employment: A systematic review. In Healthcare (Vol. 11, No. 21, p. 2900). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Sileyew, K.J., 2019. Research design and methodology (Vol. 7). Cyberspace.
- Stansbury, A., Turner, D. and Balls, E., 2023. Tackling the UK’s regional economic inequality: Binding constraints and avenues for policy intervention. Contemporary Social Science, 18(3-4), pp.318-356.
- Smite, D., Moe, N.B., Hildrum, J., Gonzalez-Huerta, J. and Mendez, D., 2023. Work-from-home is here to stay: Call for flexibility in post-pandemic work policies. Journal of Systems and Software, 195, p.111552.
- Tamers, S.L., Chosewood, L.C., Childress, A., Hudson, H., Nigam, J. and Chang, C.C., 2019. Total Worker Health® 2014–2018: the novel approach to worker safety, health, and well-being evolves. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), p.321. [CrossRef]
- Urme, U.N., 2023. The impact of talent management strategies on employee retention. International Journal of Science and Business, 28(1), pp.127-146. [CrossRef]
- White, N. (2023) Employee earnings in the UK: 2023, Employee earnings in the UK - Office for National Statistics. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/employee-earnings-in-the-uk-2023 (Accessed: 26 April 2025).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).