Submitted:
07 May 2025
Posted:
08 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Method
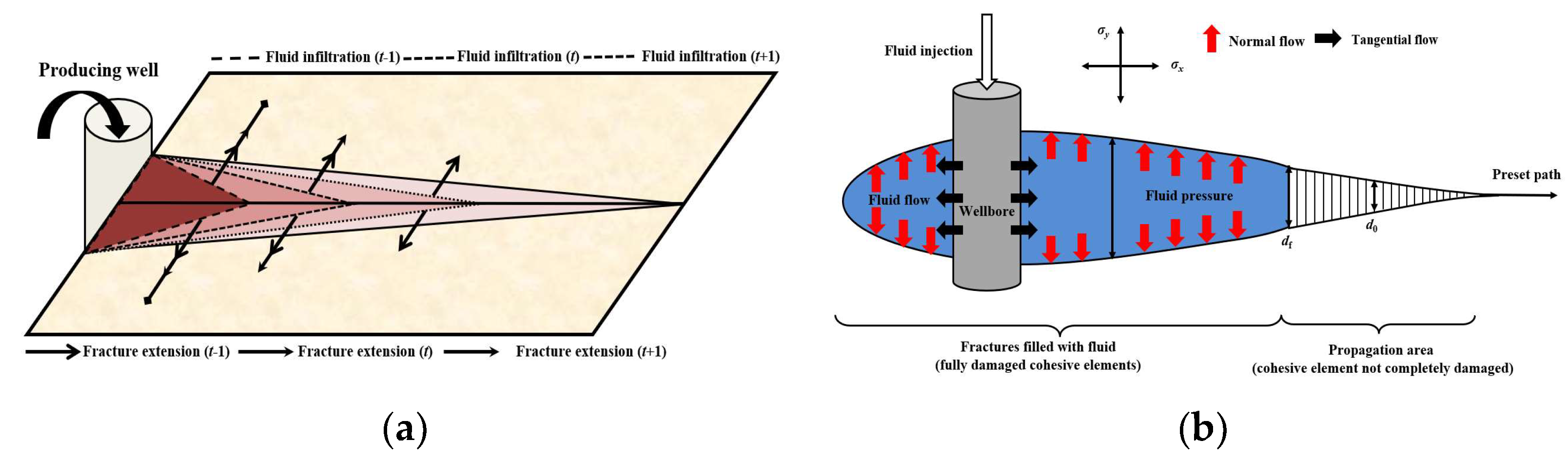
2.1. Physical Model and Assumptions
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.2.1. Rock Stress Equilibrium Equations
2.2.2. Pore Fluid Flow Equations
2.2.3. Fracture Initiation and Propagation Criteria
2.3. Grid Generation
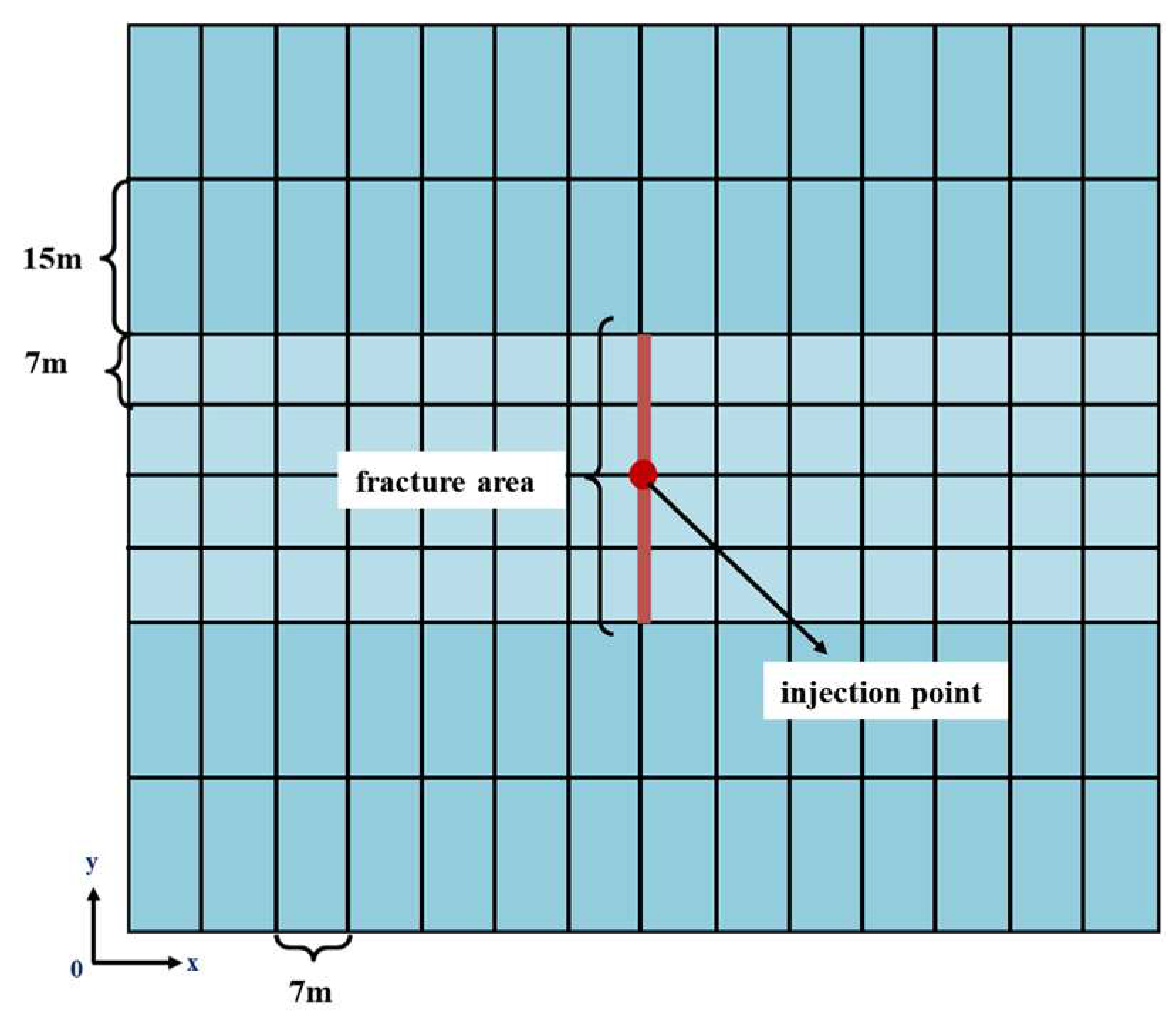
3. Application
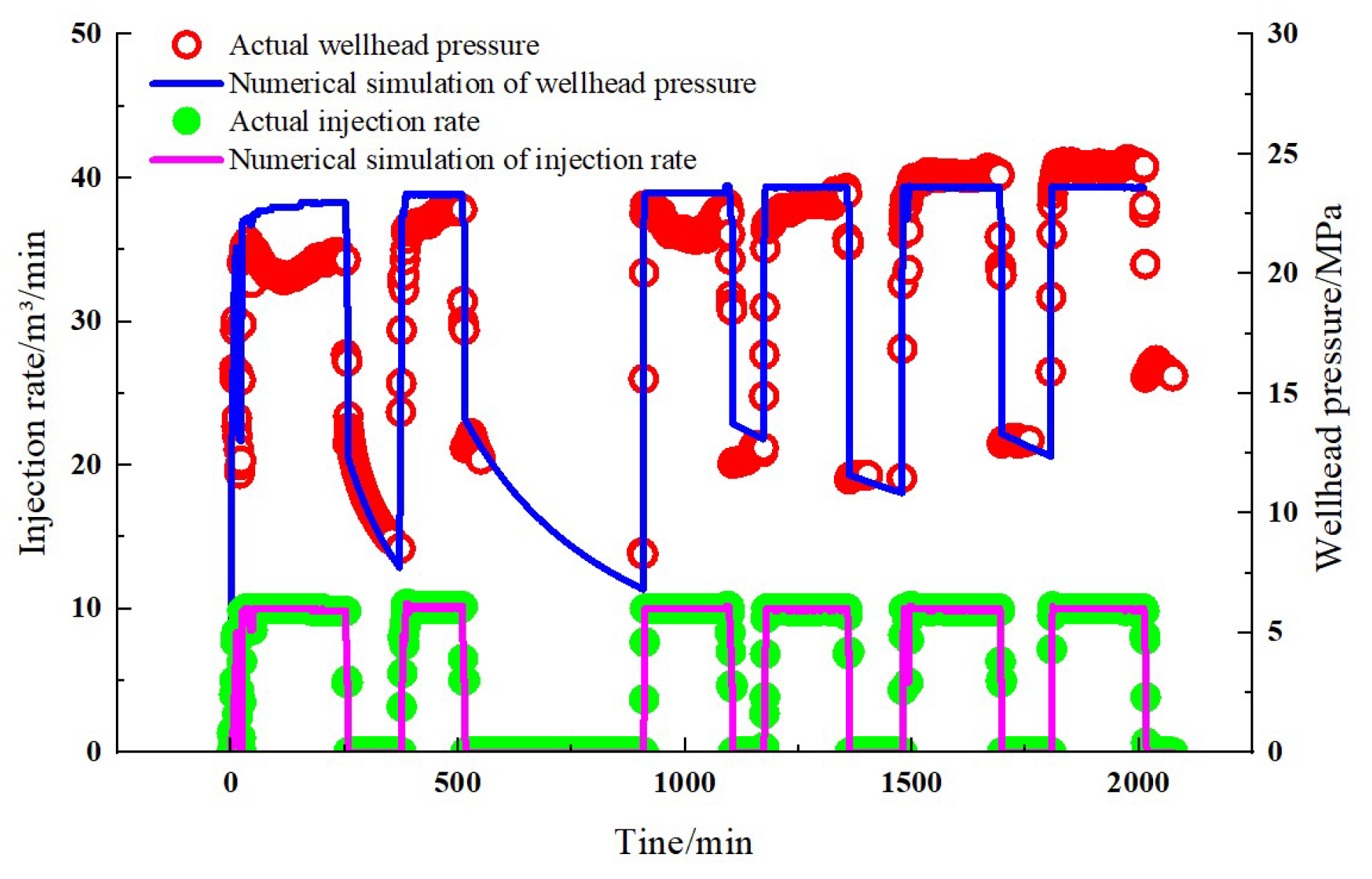
3.1. Validation
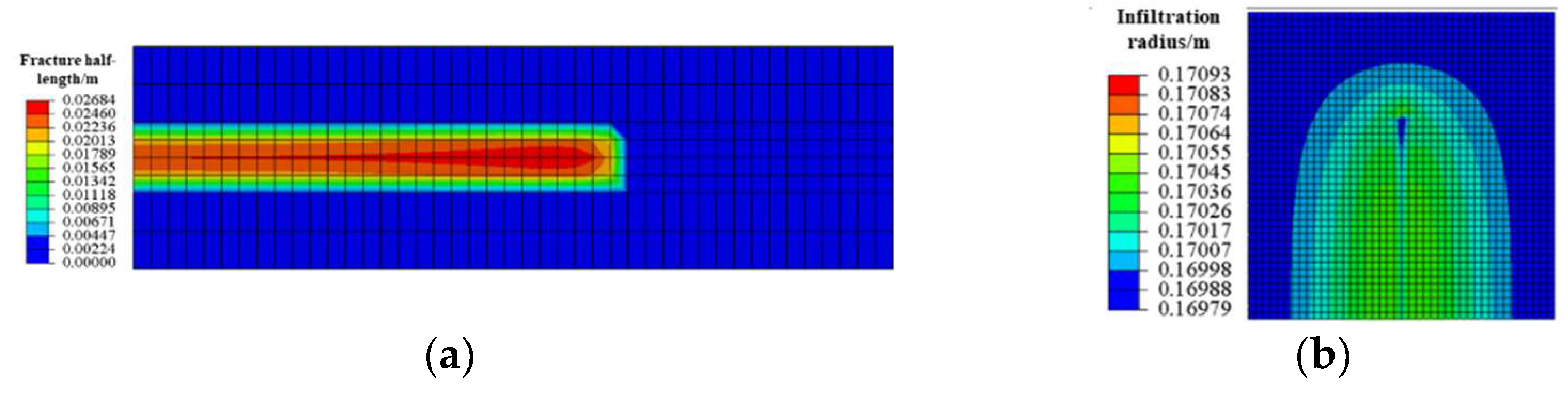
3.2. HFAOD Fracture Propagation and HFAOD Fluid Infiltration Law
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis
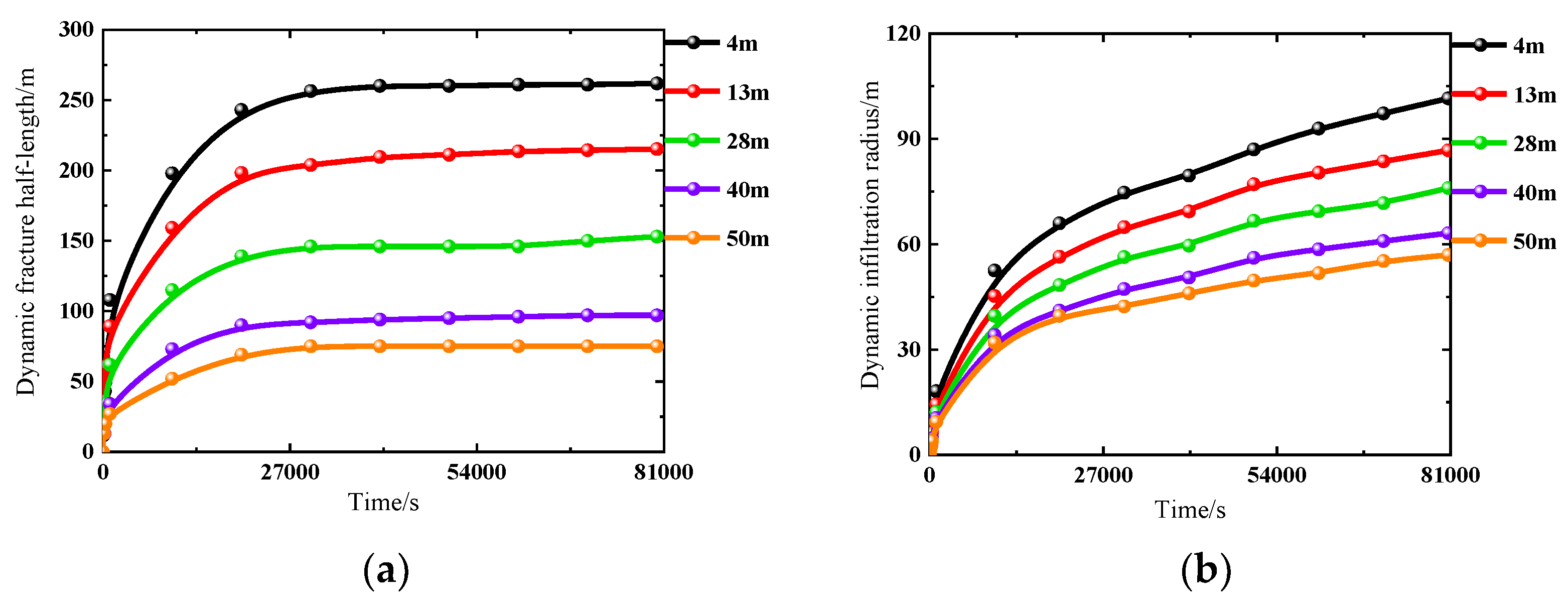
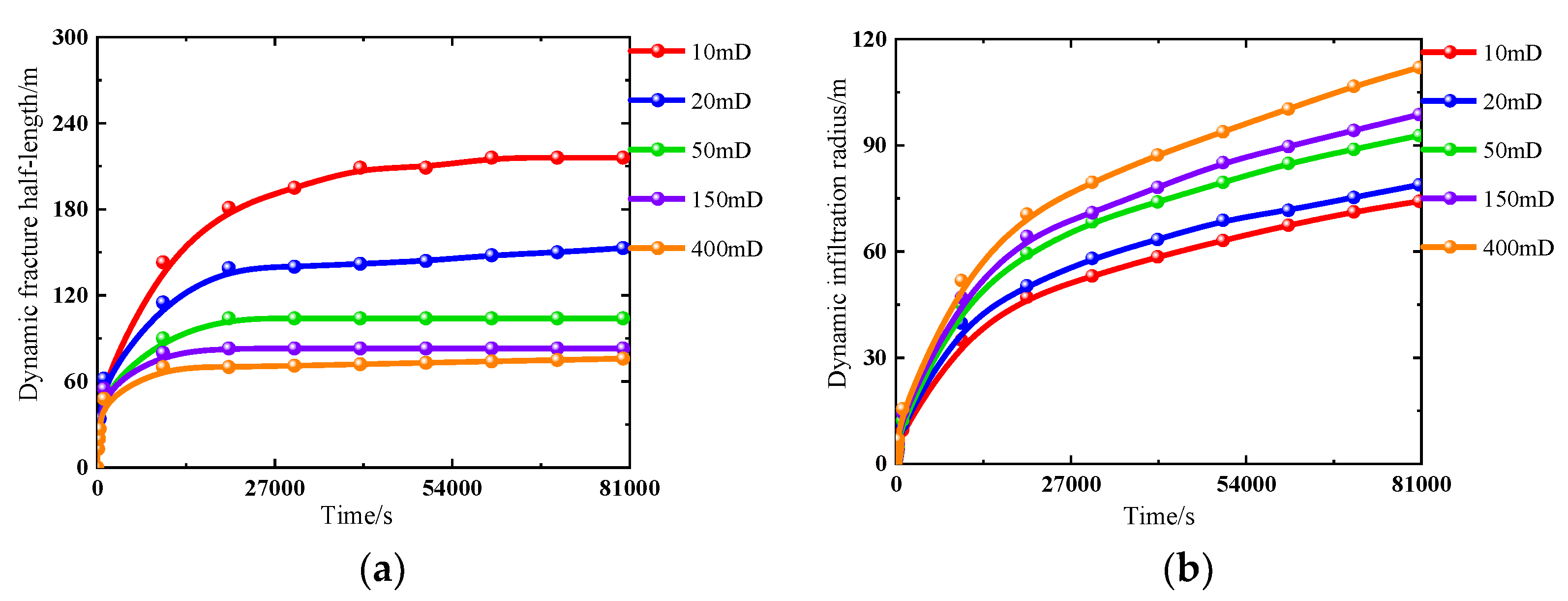
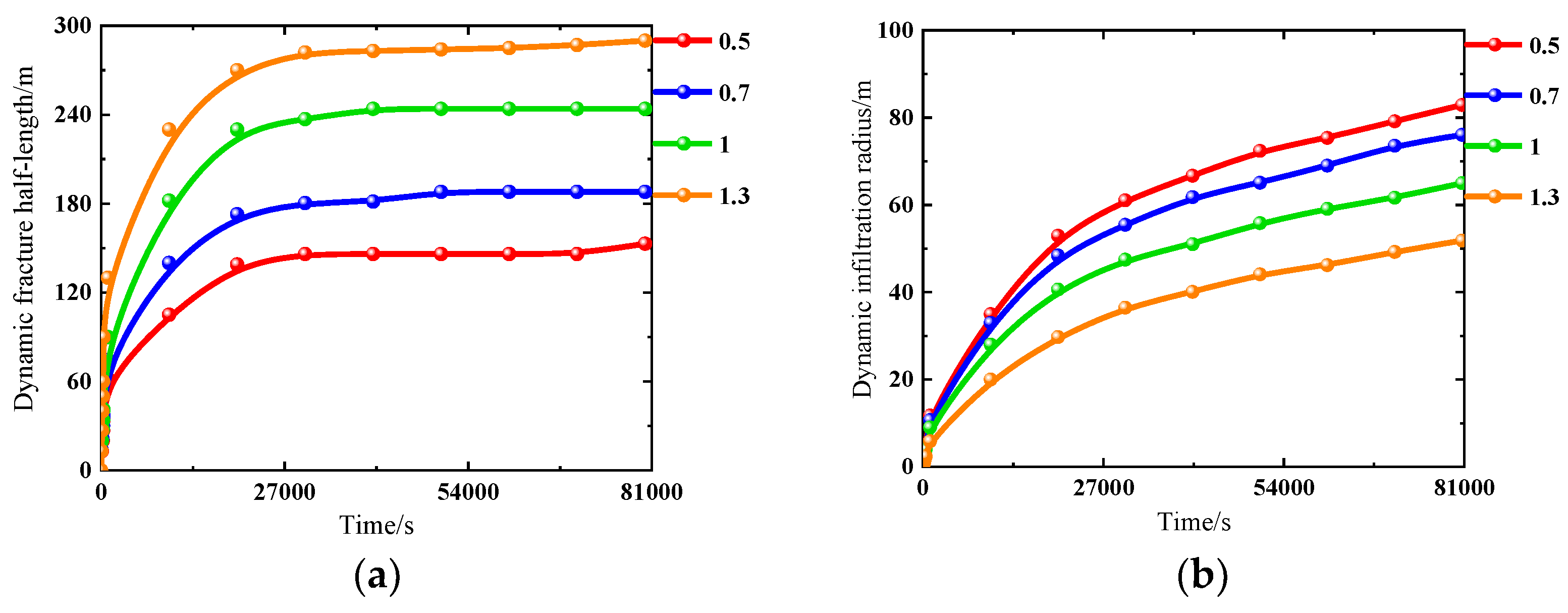
4.1.1. Geological Factors
4.1.2. Construction Factors
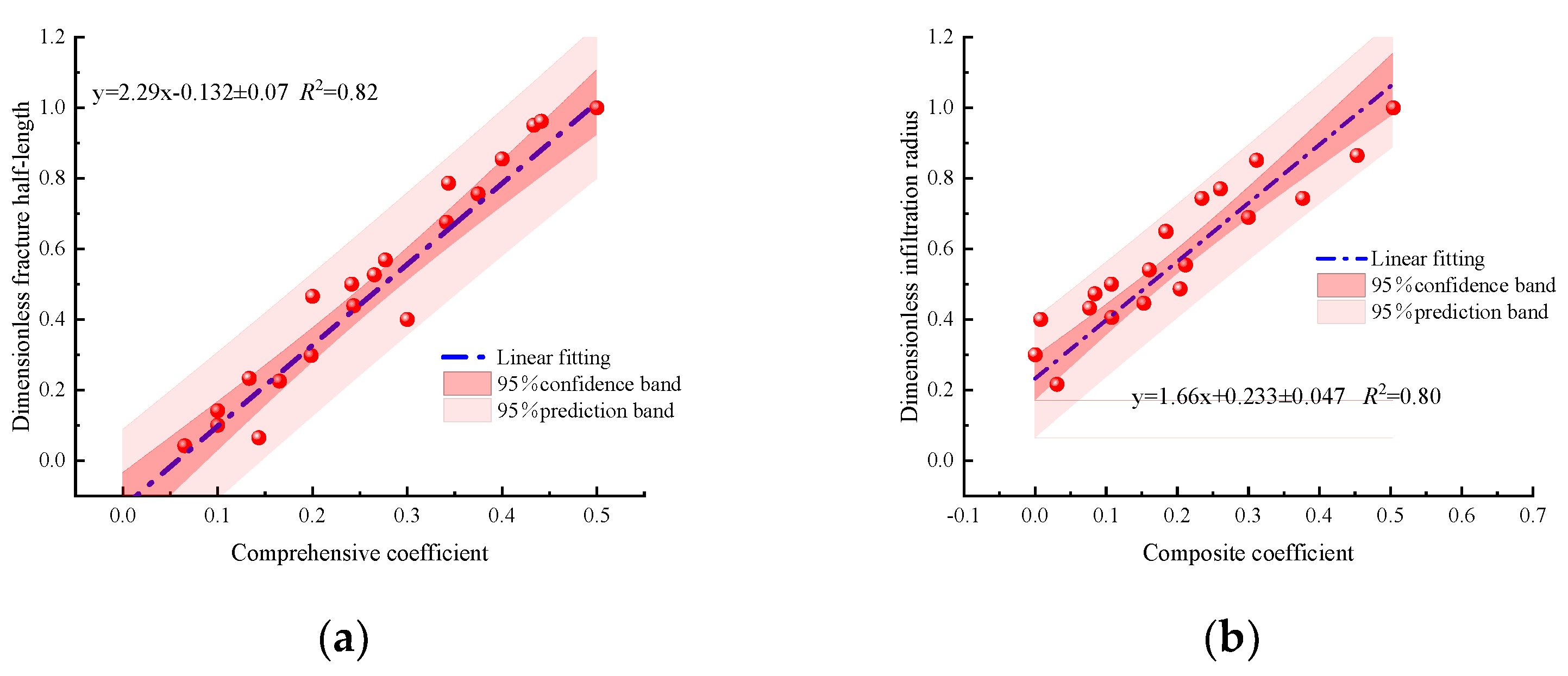
4.2. Dominant Controlling Factors
4.3. Prediction of Fracture Half-length and Infiltration Radius of HFAOD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y. C.; Wang, Y. M.; Yang, G. On the Application of hydraulic fracturing assisted oil displacement technology in Daqing Oilfield. China Petroleum and Chemical Standards and Quality 2017, 37, 163–164. [Google Scholar]
- Mud Logging Engineering. "Hydraulic Fracturing Assisted Oil Displacement Pilot Test Post-Polymer Flooding in Daqing Lamadian Oilfield Achieves Initial Success." Newsletter. Mud Logging Engineering 2017, 28, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y. J. Application of fracturing-flooding EOR technique in Type III oil reservoirs in Daqing Placanticline Oilfield. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing 2021, 40, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z. B.; Zeng, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, L. New effective energy-supplement development method of waterflood huff and puff for the oil reservoir with stimulated reservoir volume fracturing. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency 2017, 24, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. D.; Wu, Y. S.; Xiong, Q.; Pu, X. H.; Feng, J. S.; Yue, S. J. Status and development trend of fracturing-flooding technology in low permeability reservoirs. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field 2023, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F. Z.; Shao, Z. R.; Li, G.; Tang, L.; Yang, P.; Yan, B. F.; Chen, D.C.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, H. Application of dilatant pressure flooding technology in low permeability reservoir in Bonan Oilfield. Unconventional Oil & Gas 2023, 10, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S. M.; Cao, X. P.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. C.; Yu, C. L.; Sun, H. X. Practice and understanding of pressure drive development technology for low-permeability reservoirs in Shengli Oilfield. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency 2023, 30, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Bu, Y. H.; Sun, D. Practice and understanding of pressure-driven development technology in Shengli Oilfield. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency 2023, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. Q.; Liu, Z. G.; Shen, T. Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, W. L. Research and Practice on Efficient Development Technology for Tight Oil Reservoirs in Wuqi Oilfield. China Petroleum and Chemical Standards and Quality 2023, 43, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, Z. R.; Qiao, C. G.; Zhang, H. L.; Ma, W. Practice of pressure drive water injection technology in small fault block reservoir of low permeability in Jiangsu oilfield. Petrochemical Industry Application 2022, 41, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q. C. Mechanism and technological boundaries of fracturing displacement production enhancement in extra-low and ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoirs. Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, 2023.
- Liu, Y. K.; Wang, F. J.; Wang, Y. M.; Li, H. B.; Zhang, D.; Yang, G.; Zhi, J. Q.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, Q. J.; Xu, H. The mechanism of hydraulic fracturing assisted oil displacement to enhance oil recovery in low and medium permeability reservoirs. Petroleum Exploration and Development 2022, 49, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, X. Study on stimulation technology of low permeability oilfield. Oil and Gas Production 2023, 49, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z. G.; Yu, C. L.; Sun, Q.; Bei, J. P. Physical simulation of fracturing-flooding and quantitative characterization of fractures in low-permeability oil reservoirs. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency 2022, 29, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. A New Method and Application of Full 3D Numerical Simulation for Hydraulic Fracturing Horizontal Fracture. Energies 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ca, L. M.; Feng, Q. H.; Wang, S.; Xu, S. Q.; Liu, G. W.; Huang, W. H. Numerical simulation of fracture-flooding with virtual element method in a continuous damage model. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics 2023, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F. Z.; Shao, Z. R.; Li, G.; Tang, L.; Yang, P.; Yan, B. F.; Chen, D.C.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, H. Application of dilatant pressure flooding technology in low permeability reservoir in Bonan Oilfield. Unconventional Oil & Gas 2023, 10, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H. Y.; Ma, Y. C.; Wang, Y. L.; Niu, J. L.; Liu, K.; He, Y. M. Application of pressure-drive integration technology of water injection well in tight sandstone reservoir. Petrochemical Industry Application 2023, 42, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T. Y.; Song, X. M.; Wu, S. H.; Li, Q. Y.; Wang, B. H.; Li, X. B.; Li, H.; Liu, H. L. A mathematical model and numerical simulation of waterflood induced dynamic fractures of low permeability reservoirs. Petroleum Exploration and Development 2015, 42, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X. A Novel Continuous Fracture Network Model: Formation Mechanism, Numerical Simulation, and Field Application. Geofluids 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ji, G.; Li, K. A new pseudo 3D hydraulic fracture propagation model for sandstone reservoirs considering fracture penetrating height. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 2022, 264, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. W.; Liu, X. J.; Xiong, J.; Liang, L. X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Fracture propagation law and main controlling factors of conglomerate hydraulic fracturing based on discrete element method. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing 2023, 42, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Z. G.; Bai, X. J.; Zhao, Y. Distribution characteristics and main controlling factors of hydraulic fracturing fractures of coalbed methane in the southwestern margin of Qinshui Basin. Coal Engineering 2023, 55, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Wang, F.; Huang, H.; Sun, X.; Mu, J. F. Fluid loss model for dynamic propagation of hydraulic fractures. Petroleum Geology and Engineering 2020, 34, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. L.; Lin, X.B.; Leng, J. Y.; Zhou, C. J.; Ma, Z. G.; Xiao, Y. X. Quantitative prediction of fracturing fluid leak-off in shale gas reservoirs based on spontaneous imbibition model of fracturing fluid. Natural Gas Industry 2024, 44, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, H. B.; Li, F. X.; He, B.; Zhou, T.; Li, N. Influence mechanism of fracturing fluid filtration on fracture initiation and dynamic closure process. Natural Gas Industry 2023, 43, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. H.; Ding, W. L.; Wang, Z.; Lan, B. F.; Zhao, J. L.; Zhao, D. Main Controlling Factor of Fracture Network Formation of Volume Fracturing in Shale Reservoirs and Its Evaluation Method. Geological Science and Technology Information 2015, 34, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
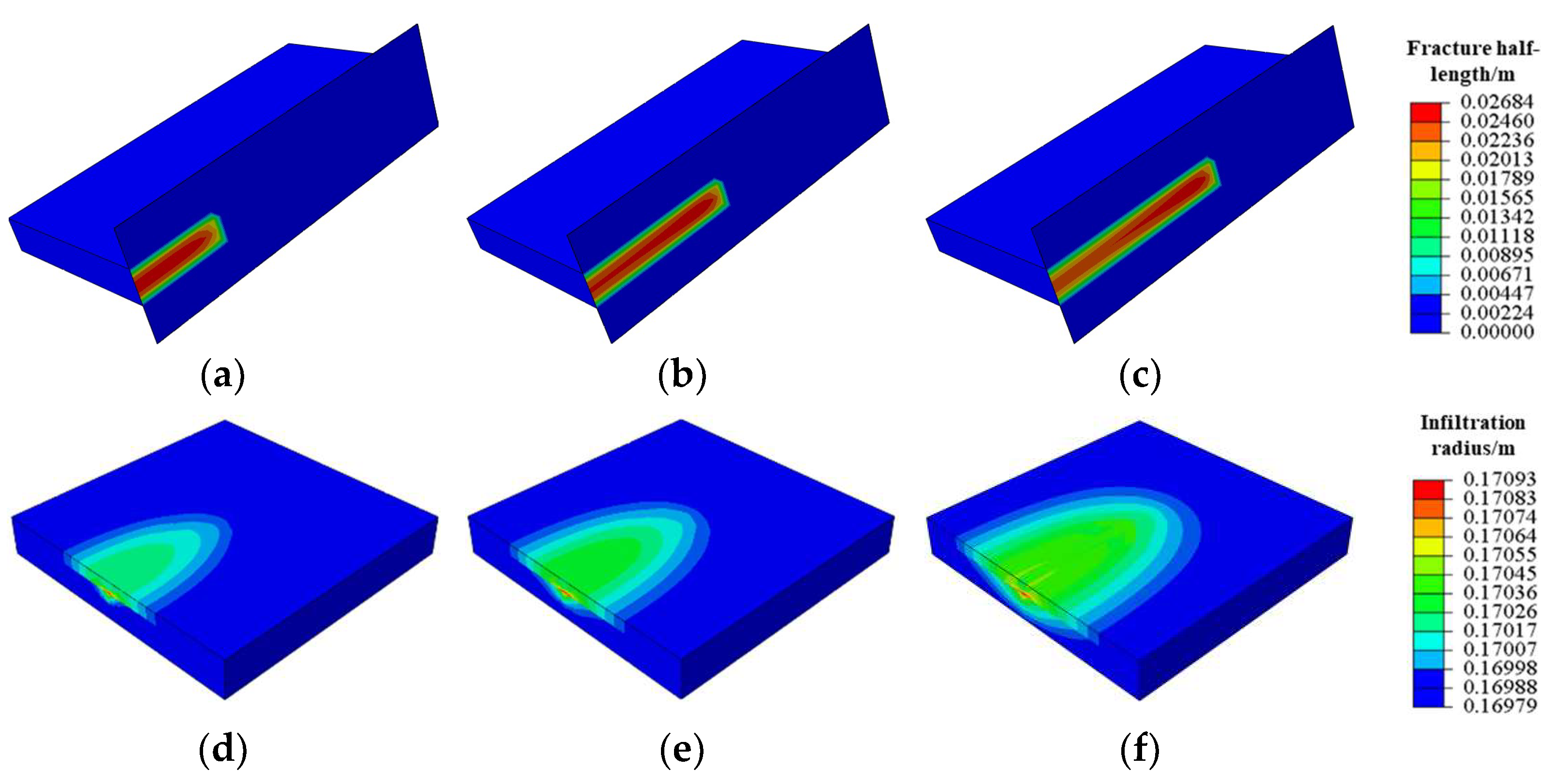
| Parameters | Reservoir | Interlayer |
|---|---|---|
| Young's modulus/(GPa) | 26 | 18 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.24 | 0.32 |
| Tensile strength/(MPa) | 5 | 6 |
| Fluid infiltration coefficient/(m∙s1/2) | 2.56E-13 | 2.56E-14 |
| Formation stress/(MPa) | 41,50 | 45,54 |
| HFAOD fluid viscosity/(Pa∙s) | 0.001 | |
| Injection rate/(m3/s) | 0.08 | |
| Influencing factors | Scheme | Parameters | Fracture half - length/(m) | Infiltration radius/(m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geological factors | Thickness/(m) | 1 | 4 | 262 | 102 |
| 2 | 13 | 215 | 87 | ||
| 3 | 28 | 153 | 76 | ||
| 4 | 40 | 97 | 63 | ||
| 5 | 50 | 75 | 57 | ||
| Permeability/(mD) | 6 | 10 | 216 | 74 | |
| 7 | 20 | 153 | 79 | ||
| 8 | 50 | 104 | 93 | ||
| 9 | 150 | 83 | 99 | ||
| 10 | 400 | 76 | 112 | ||
| Formation pressure coefficient before HFAOD | 11 | 0.5 | 153 | 79 | |
| 12 | 0.7 | 188 | 73 | ||
| 13 | 1 | 244 | 65 | ||
| 14 | 1.3 | 290 | 52 | ||
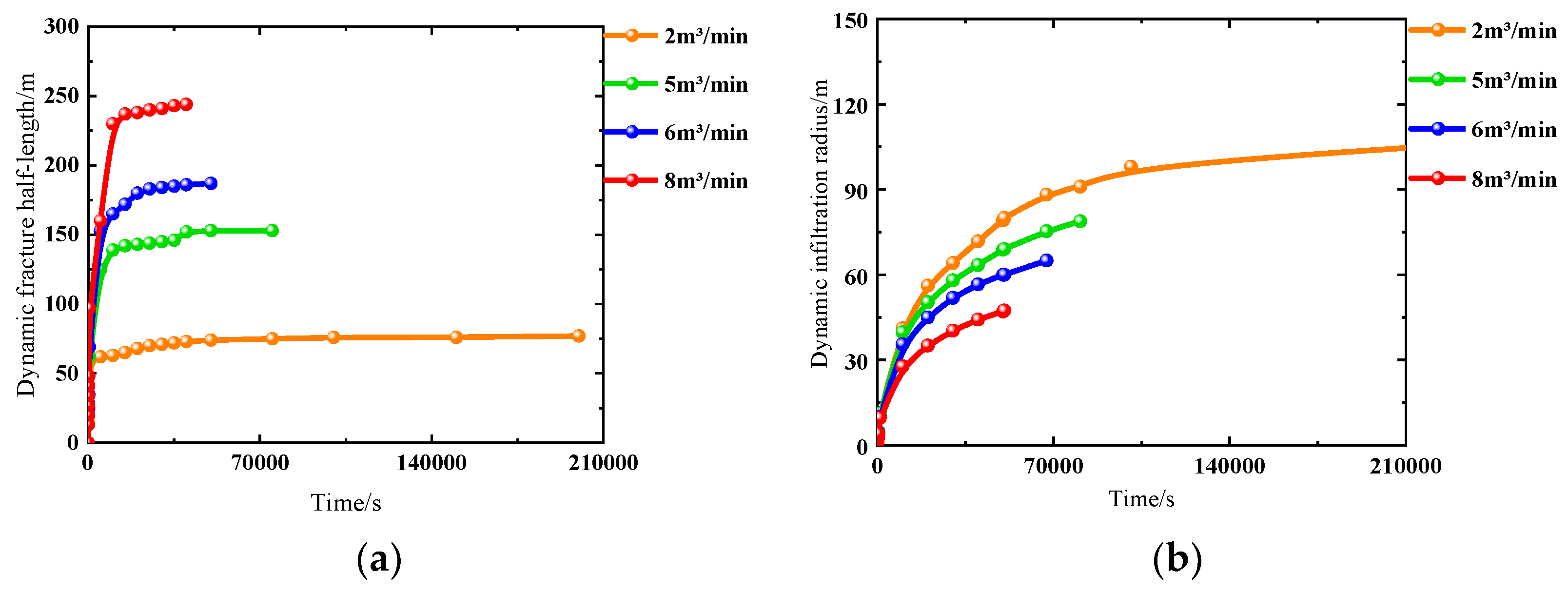
| Construction factors | Injection rate/(m3/min) | 15 | 2 | 77 | 105 |
| 16 | 5 | 153 | 79 | ||
| 17 | 6 | 187 | 65 | ||
| 18 | 8 | 244 | 47 | ||
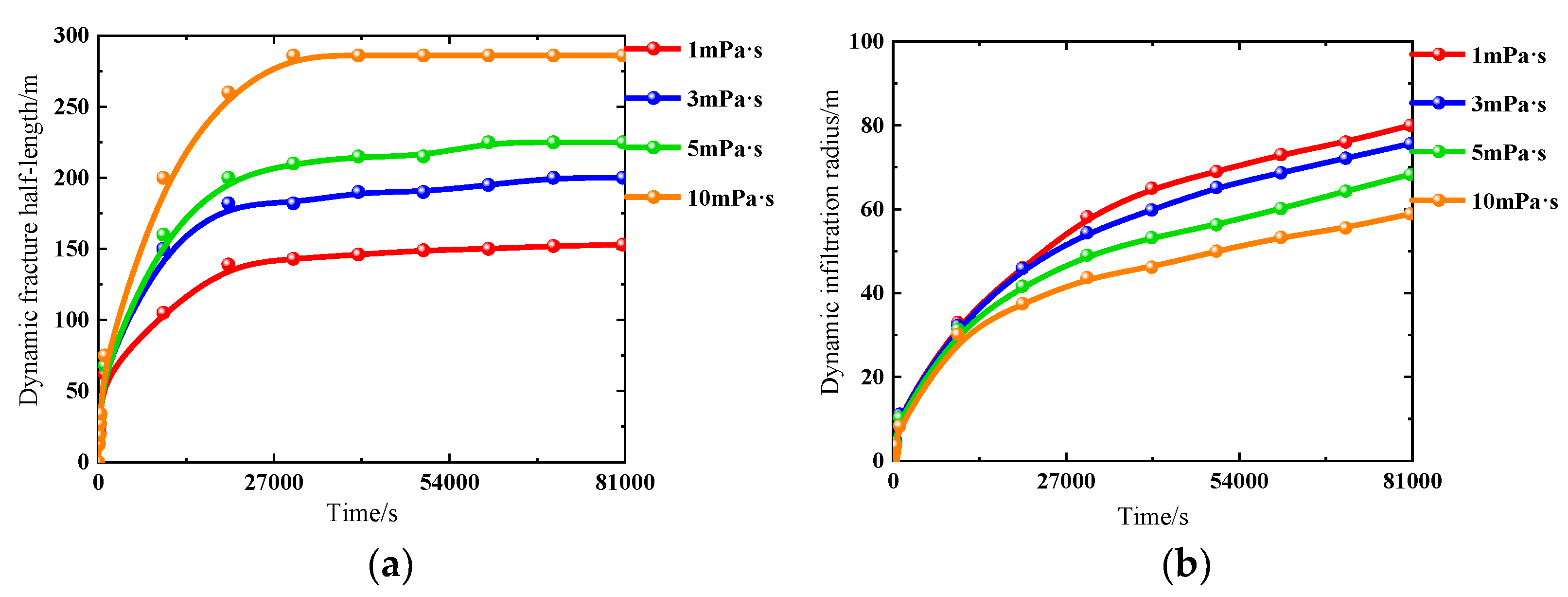
| Viscosity/(mPa·s) | 19 | 1 | 153 | 79 | |
| 20 | 3 | 200 | 76 | ||
| 21 | 5 | 225 | 68 | ||
| 22 | 10 | 286 | 59 | ||
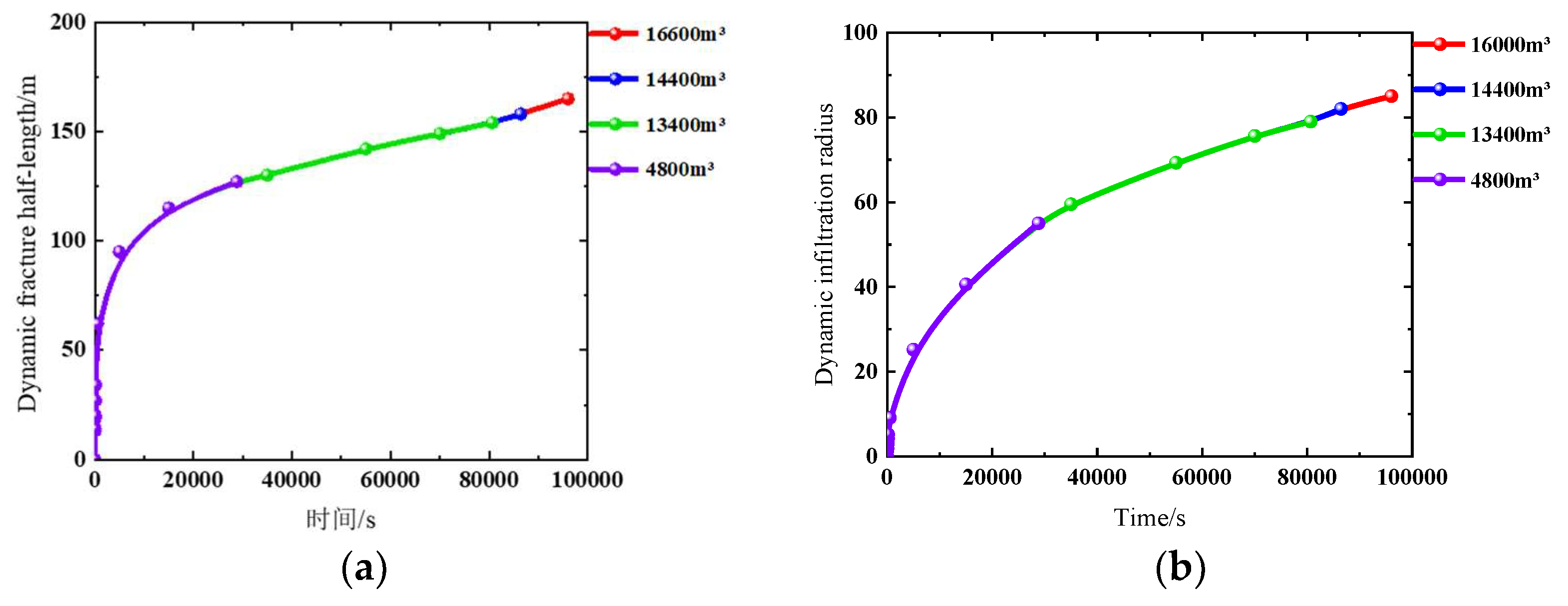
| Cumulative injection volume/(m3) | 23 | 4800 | 125 | 55 | |
| 24 | 13440 | 153 | 79 | ||
| 25 | 14400 | 158 | 82 | ||
| 26 | 16000 | 165 | 85 |
| Parameters | Cumulative injection volume (m3) | Thickness (m) | Injection rate (m3/min) | Formation pressure coefficient | Permeability (mD) | Viscosity (mPa∙s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weigh of fracture half-length | 0.1329 | 0.2462 | 0.2046 | 0.1621 | 0.1364 | 0.1579 |
| Weigh of infiltration radius | 0.1199 | 0.0975 | 0.1642 | 0.2038 | 0.2999 | 0.1145 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





