Submitted:
05 May 2025
Posted:
06 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Participant Selection Criteria
- -
- Healthy children aged 2 to 6 years who attended childcare facilities, having completed a full vaccination course of PCV10 (3 + 1 doses).
- -
- Healthy children aged 5 months to 6 years who did not attend childcare facilities but had received at least one of the mandatory doses of PCV10.
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Detection of S. pneumoniae
2.4.1. Classical Detection Method
2.4.2. Molecular Methods
2.4.3. Typing of S. pneumoniae Isolates
- Band A: 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 6C, 6D, 7F/7A, 9A/9V, 14, 18A, 18B/18C, 18F, 19A, 19F, 23A, 23B, 23F.
- Band B: 2, 8, 9N/9L, 10A, 10B, 10F/C, 11A/D, 11B, 11C, 11F, 12A/46, 12B/44, 12F, 15B/15C, 17F, 20, 22F/22A, 33F/33A, 37.
- Band C: 7B, 7C/40, 15A, 15F, 16F, 19B/19C, 21, 25A/25F, 38, 24A, 24B/24F, 31, 32A/32F, 33B/33D, 33C, 35A, 35C, 35F, 47F, 41A, 41F.
- LytA and cpsA were also identified as control genes during the hybrid analysis.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Tested Group
3.2. S. pneumoniae Serotypes
3.3. Vaccine Serotypes
3.4. The Dynamics of the Spread of S. pneumoniae
3.4.1. The Dynamics of the Spread of S. pneumoniae Serotypes
3.4.2. Age Distribution of Detected S. pneumoniae Serotypes
| Capsulated StPn/serotypes | < 12 mo, n(%) (total n=28) | 12-35 mo, n(%) (total n=39) | 36-59 mo n(%) (total n=60) | 5-6 years (total n=59) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3 (10.7) | 1 (2.56) | 3 (5) | 6 (10.2) |
| 4 | 0 (0) | 1 (2.56) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 5 | 0 (0) | 1 (2.56) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 14 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) |
| 20 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (1.7) |
| 21 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0) |
| 31 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| 38 | 0 (0) | 1 (2.56) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 10A | 4 (14.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (5) |
| 10B | 0 (0) | 1 (2.56) | 5 (8.3) | 6 (10.2) |
| 10F/C | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.3) | 9 (15.3) |
| 11A/D | 3 (10.7) | 5 (12.8) | 5 (8.3) | 2 (3.4) |
| 12А/46 | 1 (3.6) | 1 (2.56) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 15A/15F | 0 (0) | 1 (2.56) | 2 (3.3) | 3 (5) |
| 15B/15C | 3 (10.7) | 6 (15.4) | 9 (15) | 5 (8.5) |
| 19A | 1 (3.6) | 6 (15.4) | 4 (6.7) | 6 (10.2) |
| 19B/19C | 3 (10.7) | 2 (5.1) | 16 (26.7) | 19 (32.2) |
| 19F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) |
| 22F/22A | 1 (3.6) | 1 (2.56) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 23A | 0 (0) | 1 (2.56) | 6 (10) | 5 (8.5) |
| 23B | 0 (0) | 5 (12.8) | 7 (11.6) | 4 (6.8) |
| 23F | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 24A | 1 (3.6) | 1 (2.56) | 3 (5) | 2 (3.4) |
| 24B/24F | 1 (3.6) | 1 (2.56) | 3 (5) | 4 (6.8) |
| 33F/33A | 1 (3.6) | 1 (2.56) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| 35C | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| 35F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (1.7) |
| 39F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) |
| 41A/41F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| 6A | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 3 (5) |
| 6C | 7 (25) | 4 (10.3) | 9 (15) | 5 (8.5) |
| 6D | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0) |
| 7B | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.4) |
| 7C/40 | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 4 (6.7) | 5 (8.5) |
| 9A/9V | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) |
| 9N/9L | 0 (0) | 2 (5.1) | 0 (0) | 3 (5) |
3.5. Mono- and Co-Detection of S. pneumoniae Serotypes
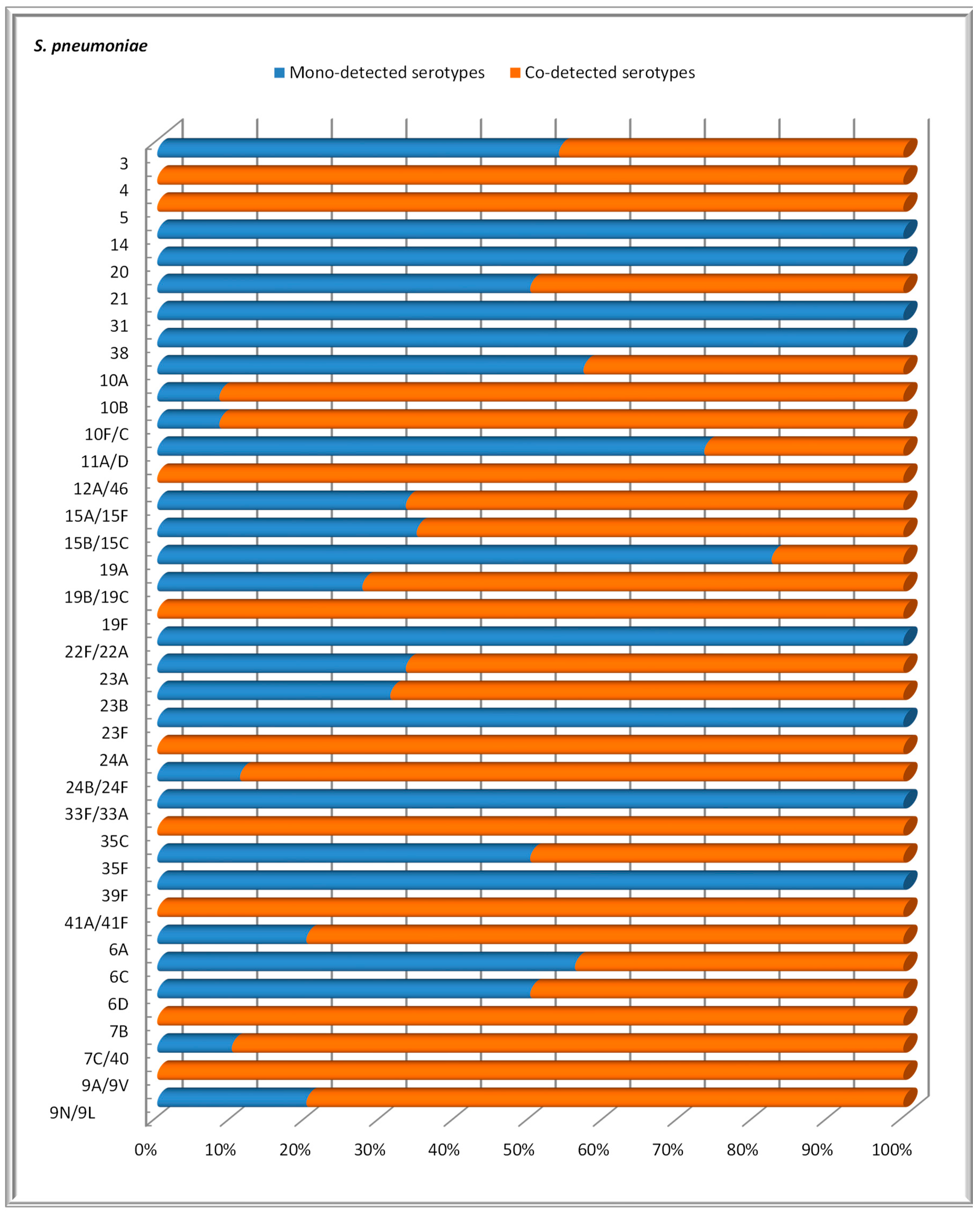
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiser, J. N.; Ferreira, D. M.; Paton, J. C. (2018). Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nature reviews. Microbiology 2018, 16(6), 355–367. [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan, M.; Ozsurekci, Y.; Aykac, K.; Hacibedel, B.; Ozbilgili, E.. Economic burden of pneumococcal infections in children under 5 years of age. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics 2018, 14(1), 106–110. [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, D.; De Groot, R.; Hermans, P. W.. Streptococcus pneumoniae colonisation: the key to pneumococcal disease. The Lancet. Infectious diseases 2004, 4(3), 144–154. [CrossRef]
- van der Poll, T.;Opal, S. M. Pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet (London, England) 2009, 374(9700), 1543–1556. [CrossRef]
- Brooks, L. R. K., & Mias, G. I. Streptococcus pneumoniae's Virulence and Host Immunity: Aging, Diagnostics, and Prevention. Frontiers in immunology,2018, 9, 1366. [CrossRef]
- Morimura, A.; Hamaguchi, S.; Akeda, Y.;Tomono, K.. Mechanisms Underlying Pneumococcal Transmission and Factors Influencing Host-Pneumococcus Interaction: A Review. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2021, 11, 639450. [CrossRef]
- Loughran, A. J.; Orihuela, C. J.;Tuomanen, E. I.. Streptococcus pneumoniae: Invasion and Inflammation. Microbiology spectrum 2019, 7(2). 10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0004-2018. [CrossRef]
- Weight, C. M.; Venturini, C.; Pojar, S.; Jochems, S. P.; Reiné, J.;Nikolaou, E.; Solórzano, C.; Noursadeghi, M.; Brown, J. S.; Ferreira, D. M.; Heyderman, R. S.. Microinvasion by Streptococcus pneumoniae induces epithelial innate immunity during colonisation at the human mucosal surface. Nature communications 2019, 10(1), 3060. [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Salmen, A.; Aebi, S.; de Gouveia, L.; von Gottberg, A.;Hathaway, L. J. Pneumococcal serotype determines growth and capsule size in human cerebrospinal fluid. BMC microbiology 2020, 20(1), 16. [CrossRef]
- Geno, K. A.; Gilbert, G. L.; Song; J. Y.; Skovsted, I. C.; Klugman, K. P.; Jones, C.; Konradsen, H. B.; Nahm, M. H. Pneumococcal Capsules and Their Types: Past, Present, and Future. Clinical microbiology reviews, 2015, 28(3), 871–899. [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, A. L.; Wijmenga-Monsuur, A. J.; van Houten, M. A.; Bosch, A. A. T. M.; Groot, J. A.; van Engelsdorp Gastelaars, J.; Bruin, J. P.; Bogaert, D.; Rots, N. Y.; Sanders, E. A. M.; Trzciński, K. Molecular surveillance of nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae in children vaccinated with conjugated polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccines. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 23809. [CrossRef]
- Ganaie, F.; Saad, J. S.; McGee, L.; van Tonder, A. J.; Bentley, S. D.; Lo, S. W.; Gladstone, R. A.; Turner, P.; Keenan, J. D.; Breiman, R. F.; Nahm, M. H. A New Pneumococcal Capsule Type, 10D, is the 100th Serotype and Has a Large cps Fragment from an Oral Streptococcus. mBio 2020, 11(3), e00937-20. [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, F.; Moiane, B.; Gertz, R. E.; Jr, Chochua, S.; Snippes Vagnone, P. M.; Lynfield, R.; Sigaúque, B.; Carvalho, M. D. G.,;Beall, B. New Pneumococcal Serotype 15D. Journal of clinical microbiology 2021, 59(5), e00329-21. [CrossRef]
- Savrasova, L.; Villerusa, A.; Zeltina, I.; Krumina, A.; Cupeca, H.;Balasegaram, S.; Greve, M.; Savicka, O.; Selderina, S.; Galajeva, J.; Dushacka, D. Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes and factors associated with antimicrobial resistance in Invasive pneumococcal disease cases in Latvia, 2012-2022. Frontiers in public health 2025, 13, 1501821. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, J.; Yu, Z.;Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H. . Epidemiological characteristics and antibiotic resistance mechanisms of Streptococcus pneumoniae: An updated review. Microbiological research 2023, 266, 127221. [CrossRef]
- Musher, D. M; Anderson, R.;Feldman, C. The remarkable history of pneumococcal vaccination: an ongoing challenge. Pneumonia (Nathan Qld.) 2022, 14(1), 5. [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.; Mantero, M.; Mirsaeidi, M.; Blasi, F. The role of vaccination in preventing pneumococcal disease in adults. Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 20 Suppl 2014, 5(0 5), 52–58. [CrossRef]
- The poly Rodgers, G. L., Whitney, C. G., & Klugman, K. P. (2021). Triumph of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines: Overcoming a Common Foe. The Journal of infectious diseases, 224(12 Suppl 2), S352–S359. [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J. C.; Deloria Knoll, M.; Kagucia, E. W.; Garcia Quesada, M.; Zeger, S. L.; Hetrich, M. K;, Yang, Y.; Herbert, C.; Ogyu, A.; Cohen, A. L.; Yildirim, I.; Winje, B. A.; von Gottberg, A.; Viriot, D.; van der Linden, M.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Suga, S.; Steens, A.; Skoczynska, A.; Sinkovec Zorko, N.; … PSERENADE Team. Global impact of ten-valent and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on invasive pneumococcal disease in all ages (the PSERENADE project): a global surveillance analysis. The Lancet. Infectious disease 2025s, 25(4), 457–470. [CrossRef]
- Malcheva, M. Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype distribution after the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. PROBLEMS of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases 2019, 47(1), 5-8.
- Krieg, Noel R.;and John, G. Holt. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. Yi Hsien Publishing Co., 1984.
- de Lamballerie, X.; Zandotti, C.; Vignoli, C.; Bollet, C.; de Micco, P. A one-step microbial DNA extraction method using "Chelex 100" suitable for gene amplification. Research in microbiology 1992, 143(8), 785–790. [CrossRef]
- Lang, A. L. S.;McNeil, S. A.; Hatchette, T. F.; Elsherif, M.; Martin, I.; LeBlanc, J. J. . Detection and prediction of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes directly from nasopharyngeal swabs using PCR. Journal of medical microbiology 2015, 64(8), 836–844. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Pan, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H. Epidemiology Characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae From Children With Pneumonia in Shanghai: A Retrospective Study. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2019, 9, 258. [CrossRef]
- Candeias, C.; Almeida, S. T.; Paulo, A. C.; Simões, A. S.; Ferreira, B.; Cruz, A. R.; Queirós, M.; Touret, T.; Brito-Avô, A., de Lencastre, H.; Sá-Leão, R.. Streptococcus pneumoniae carriage, serotypes, genotypes, and antimicrobial resistance trends among children in Portugal, after introduction of PCV13 in National Immunization Program: A cross-sectional study. Vaccine 2024, 42(22), 126219. [CrossRef]
- Warda, K.; Amari, S.; Boureddane, M.; Elkamouni, Y.; Arsalane, L.; Zouhair, S.; Bouskraoui, M.. Changes in pneumococcal serotypes distribution and penicillin resistance in healthy children five years after generalization of PCV10. Heliyon 2024, 10(4), e25741. [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E;, Van Heirstraeten, L.; Willen, L.; Desmet, S.; Wouters, I.; Vermeulen, H.; Lammens, C.; Goossens, H.; Van Damme, P.;Verhaegen, J.; Beutels, P.; Theeten, H.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; NP Carriage Study Group. Serotype 19A and 6C Account for One-Third of Pneumococcal Carriage Among Belgian Day-Care Children Four Years After a Shift to a Lower-Valent PCV. Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 2023, 12(1), 36–42. [CrossRef]
- Desmet, S.; Lagrou, K.; Wyndham-Thomas, C.; Braeye, T.; Verhaegen, J.; Maes, P.; Fieuws, S.; Peetermans, W. E.; Blumental, S.. Dynamic changes in paediatric invasive pneumococcal disease after sequential switches of conjugate vaccine in Belgium: a national retrospective observational study. The Lancet. Infectious diseases 2021, 21(1), 127–136. [CrossRef]
- Desmet, S.; Wouters, I.; Heirstraeten, L. V.; Beutels, P.; Van Damme, P.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Maes, P.; Verhaegen, J.; Peetermans, W. E.; Lagrou, K.; Theeten, H. In-depth analysis of pneumococcal serotypes in Belgian children (2015-2018): Diversity, invasive disease potential, and antimicrobial susceptibility in carriage and disease. Vaccine 2021, 39(2), 372–379. [CrossRef]
- Alexandrova, A. S.; Setchanova, L. P.; Pencheva, D. R.; Mitov, I. G. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of serogroup 6 Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates collected during 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine era in Bulgaria. Acta microbiologica et immunologica Hungarica 2020, 67(2), 91–99. [CrossRef]
- lmeida, S. C. G.; Lemos, A. P. S.; Bierrenbach, A. L.; Moraes, J. C.; Brandileone, M. C. C. Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Streptococcus pneumoniae in COVID-19 Pandemic Era in Brazil. Microorganisms 2024, 12(2), 401. [CrossRef]
- Naucler, P.; Galanis, I.; Morfeldt, E.; Darenberg, J.; Örtqvist, Å.; Henriques-Normark, B. . Comparison of the Impact of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine 10 or Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine 13 on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Equivalent Populations. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2017, 65(11), 1780–1789. [CrossRef]
- Antibiotic Resistance and Clonal Spread. Pneumonia 2014, 3, 204–221. [CrossRef]
- Neves, F. P. G.; Cardoso, N. T.; Souza, A. R. V.; Snyder, R. E.; Marlow, M. M.; Pinto, T. C. A.; Teixeira, L. M.; Riley, L. W. Population structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae colonizing children before and after universal use of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Brazil: emergence and expansion of the MDR serotype 6C-CC386 lineage. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy 2018, 73(5), 1206–1212. [CrossRef]
- Duval, D.; Evans, B.; Sanders, A.; Hill, J.; Simbo, A.; Kavoi, T.; Lyell, I.; Simmons, Z.; Qureshi, M.; Pearce-Smith, N.; Arevalo, C. R.; Beck, C. R.; Bindra, R.; Oliver, I. Non-pharmaceutical interventions to reduce COVID-19 transmission in the UK: a rapid mapping review and interactive evidence gap map. Journal of public health (Oxford, England) 2024, 46(2), e279–e293. [CrossRef]
- Bertran, M.; D'Aeth, J. C.; Abdullahi, F.; Eletu, S.; Andrews, N. J.; Ramsay, M. E.; Litt, D. J.; Ladhani, S. N. . Invasive pneumococcal disease 3 years after introduction of a reduced 1 + 1 infant 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunisation schedule in England: a prospective national observational surveillance study. The Lancet. Infectious diseases 2024, 24(5), 546–556. [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J. C.; de Luis, R.; Del Río, S.; Gamen, S.; Cercenado, E.; Orellana, M. A.;Yuste, J. Direct identification of pneumococcal serotypes in blood cultures by a PCR-reverse-hybridisation technique. Enfermedades infecciosas y microbiologia clinica (English ed.) 2020, 38(4), 170–173. [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Morimoto, K.; Konosuke. Global distribution and characteristics of pneumococcal serotypes in adults. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 2025, 21.1: 2469424. [CrossRef]
- Korona-Glowniak, I.; Malm, A.. Characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae strains colonizing upper respiratory tract of healthy preschool children in Poland. TheScientificWorldJournal 2012 ,732901. [CrossRef]
- Torén, K; Albin, M.; Alderling, M.; Schiöler, L.; Åberg, M.. Transmission factors and exposure to infections at work and invasive pneumococcal disease. American journal of industrial medicine 2023, 66(1), 65–74. [CrossRef]
- Parker, A. M.; Jackson, N.; Awasthi, S.; Kim, H., Alwan, T.; Wyllie, A. L.; Kogut, K.; Holland, N.; Mora, A. M.; Eskenazi, B.; Riley, L. W.; Lewnard, J. A. (2024). Upper respiratory Streptococcus pneumoniae colonization among working-age adults with prevalent exposure to overcrowding. Microbiology spectrum 2024, 12(8), e0087924. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Tina Q. Pediatric invasive pneumococcal disease in the United States in the era of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. Clinical microbiology reviews 2012 vol. 25,3: 409-19. [CrossRef]
- Jullien, S.; Sharma, R.; Lhamu Mynak, M.; Henares, D.; Muñoz-Almagro, C.; Bassat, Q. 2020. Pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage among Bhutanese children hospitalized with clinical pneumonia: serotypes and viral co-infection. BMC infectious diseases 2020, 20(1), 940. [CrossRef]
- Dhoubhadel, B. G.; Suzuki, M.; Ishifuji, T.; Yaegashi, M.; Asoh, N.; Ishida, M.; Hamaguchi, S.; Aoshima, M.; Yasunami, M.; Ariyoshi, K.; Morimoto, K.; Adult Pneumonia Study Group-Japan (APSG-J) (2022). High prevalence of multiple serotypes of pneumococci in patients with pneumonia and their associated risk factors. Thorax 2022, 77(11), 1121–1130. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
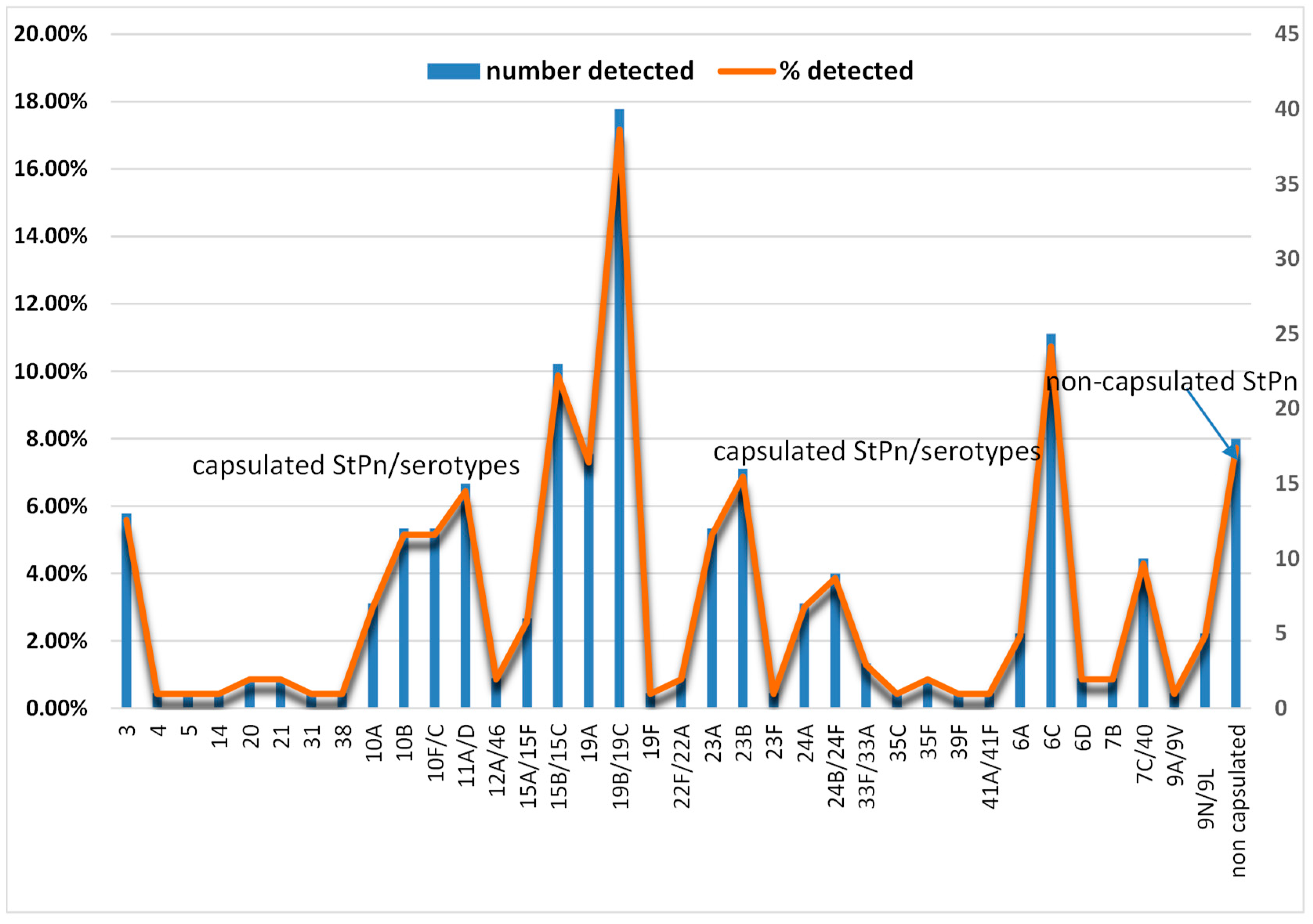

| StPn serotypes | Number of detections | P resence in vaccine (vaccine generation) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 13 (2.3) | PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 4 | 1 (0.2) | PCV7; PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 5 | 1 (0.2) | PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 14 | 1 (0.2) | PCV7; PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 20 | 2 (0.4) | not present |
| 21 | 2 (0.4) | not present |
| 31 | 1 (0.2) | not present |
| 38 | 1 (0.2) | not present |
| 10A | 7 (1.2) | PCV20 |
| 10B | 12 (2.1) | not present |
| 10F/C | 12 (2.1) | not present |
| 11A/D | 15 (2.6) | PCV20 ( 11A) |
| 12A/46 | 2 (0.4) | not present |
| 15A/15F | 6 (1.1) | not present |
| 15B/15C | 23 (4) | PCV20 ( 15B) |
| 19A | 17 (2.9) | PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 19B/19C | 40 (7) | not present |
| 19F | 1 (0.2) | PCV7; PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 22F/22A | 2 (0.35) | PCV15, PCV20 ( 22F) |
| 23A | 12 (2.1) | not present |
| 23B | 16 (2.8) | not present |
| 23F | 1 (0.2) | PCV7; PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 24A | 7 (1.2) | not present |
| 24B/24F | 9 (1.5) | not present |
| 33F/33A | 3 (0.5) | PCV15, PCV20 ( 33F) |
| 35C | 1 (0.2) | not present |
| 35F | 2 (0.35) | not present |
| 39F | 1 (0.2) | not present |
| 41A/41F | 1 (0.2) | not present |
| 6A | 5 (0.9) | PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 |
| 6C | 25 (4.4) | not present |
| 6D | 2 (0.35) | not present |
| 7B | 2 (0.35) | not present |
| 7C/40 | 10 (1.8) | not present |
| 9A/9V | 1 (0.2) | PCV7;PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20 (9V) |
| 9N/9L | 5 (0.9) | not present |
| Co-detected serotypes | Serotypes | < 12 mo, n(%) (total n=28) |
12-35 mo, n(%) (total n=39) | 36-59 mo n(%) (total n=60) | 5-6 years n(%) (total n=59) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 10A;12A/46 | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 10B;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 10F/C;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 10F/C;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (5) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 15A/15F;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 15B/15C;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 19A;21 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 19A;6C | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 19B/19C;15A/15F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 19B/19C;24B/24F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 19B/19C;7C/40 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 23A;12A/46 | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 23A;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 23A;23B | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 23B;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 3;10В | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.4) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 3;11A/D | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 3;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 3;19B/19C | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6A;19B/19C | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6C;10B | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6C;10F/C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6C;15A/15F | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6C;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6C;19A | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6C;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (3.3) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 6D;7C/40 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 7C/40;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 7C/40;35C | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with two serotypes | 7В;7В/40 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 11A/D;24A;24B/24F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 19B/19C;24A;24B/24F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 23A;10F;C19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 9N/9L;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 7С/40;24А;24В/24F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 24A;24B/24F;9N/9L | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 10F/C;7C/40;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 10F/C;7C/40;7B | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 15В/15С;10А;10В | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 23B;10B;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 2 (3.4) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 23B;19B/19C;35F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 3;23A;11A/11D | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 6A;10F/C;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 6A;15A/15F;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with three serotypes | 9N/9L;10F/C;11A/D | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with four serotypes | 19B/19C;24A;24B/24F;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with four serotypes | 23A;23B;10B;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with four serotypes | 19F;23A;9A/9V;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with four serotypes | 23B;10A;10F/C;19B/19C | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.69) |
| Co-detected with four serotypes | 6A;7C/40;19B/19C;41A/41F | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with five serotypes | 6C;23A;23B;10B;15B/15C | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Co-detected with six serotypes | 4;5;6C;9N/9L;24A;24B/24F | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





