1. Introduction
With the rapid development of e-commerce, the number of product images on online shopping platforms has grown exponentially. According to Statista, global retail e-commerce sales were estimated to reach about $6.3 trillion in 2023 and are projected to grow nearly $8.5 trillion by 2027, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of approximately 9%. To enhance user shopping experience and search efficiency, developing an effective and accurate image-text retrieval system has become increasingly important. Traditional product retrieval primarily relies on keyword matching, which not only requires merchants to manually add numerous tags but also often fails to accurately capture users’ visual needs and products’ visual characteristics.
In recent years, with the advancement of deep learning technology, particularly the breakthrough in multi-modal pre-trained models, new solutions have emerged for image-text retrieval tasks. Multi-modal pre-trained models can simultaneously understand the semantic information of images and text, establishing connections between the two modalities to achieve more precise image-text matching. This technology has broad application prospects in the e-commerce field, not only improving user shopping experience but also helping merchants better showcase products and increase sales efficiency.
In e-commerce scenarios, users often describe products they want to purchase using natural language, such as “a beige knit cardigan” or “a minimalist style desk.” Traditional keyword matching methods might miss many relevant products, while retrieval systems based on multi-modal pre-trained models can understand the semantic content of text descriptions and find the most matching product images in the visual space. This research aims to build such an intelligent image-text retrieval system to enhance the search experience on e-commerce platforms.
2. Literature Review
In recent years, multi-modal pre-trained models have made significant progress in image-text retrieval. Radford et al. [
1] proposed the CLIP model, which pioneered the approach of learning visual models through natural language supervision. Through large-scale image-text pair training, they achieved excellent zero-shot transfer capabilities. Subsequently, Li et al. [
2] introduced the BLIP model, which achieved breakthrough progress under a unified vision-language understanding and generation framework through an innovative bootstrapping language-image pre-training strategy.
In the field of multi-modal retrieval applications for e-commerce, Gu et al. [
3] were among the early explorers of multi-modal and multi-domain embedding learning in fashion product retrieval, proposing an embedding learning framework that comprehensively considers visual, textual, and attribute features. Jin et al. [
4] addressed the unique characteristics of e-commerce scenarios by proposing an instance-level multi-modal pre-training method for large-scale applications, significantly improving retrieval performance in e-commerce settings.
Regarding systematic research on cross-modal retrieval methods, Wang et al. [
5] conducted a comprehensive review of existing cross-modal retrieval methods, outlining the field’s research progress and indicating future directions. Yu et al. [
6] proposed the Heterogeneous Attention Network, effectively addressing the modal disparity issues in cross-modal retrieval and improving both retrieval efficiency and accuracy.
In terms of model optimization and practical deployment, Ji et al. [
7] introduced an online distillation-enhanced multi-modal Transformer model, optimizing model performance through sequential recommendation approaches to better suit practical application scenarios. This research not only improved model efficiency but also provided important references for deploying multi-modal models in real-world systems.
In summary, existing research has made significant progress in multi-modal pre-trained models, e-commerce applications, cross-modal retrieval methods, and model optimization, challenges persist in integrating these technolgoies effectively on e-commerce platforms. This research aims to build a more efficient and accurate image-text retrieval system for e-commerce platforms based on existing research achievements.
3. Data and Model Introduction
3.1. Data Introduction
This research utilizes a large-scale image-text dataset from the Kaggle platform, containing approximately 413,000 images and their corresponding text descriptions. The data is sourced from Google’s Conceptual Captions dataset, which is a high-quality dataset specifically designed for vision-language pre-training.
The dataset has the following characteristics: First, the image data covers a wide range, including various items, scenes, and people from daily life, alighning closely with the diverse product offerings on e-commerce platforms. Second, each image is paired with corresponding text descriptions that have been manually screened and cleaned, ensuring data quality. Third, the images in the dataset have moderate resolution, with most images sized between 224×224 pixels and 512×512 pixels, which is conducive to model training and practical application.
During the data preprocessing phase, we standardized the images through size adjustment and color space normalization. For text data, we conducted preprocessing steps such as tokenization and stop word removal to improve model training efficiency.
3.2. Model Architecture
This research employs three advanced pre-trained models as the system’s core components: BLIP, CLIP, and CLIP Interrogator. This multi-model fusion approach effectively utilizes the advantages of each model to improve the system’s overall performance.
BLIP is a powerful vision-language pre-trained model that adopts an innovative bootstrapping language-image pre-training method. The model uses ViT (Vision Transformer) as its image encoder, which better captures long-range dependencies in images through its Transformer-based architecture. For text processing, BLIP uses BERT as its text encoder, understanding text semantic information through multi-layer bidirectional Transformers. The model maps image and text features into the same semantic space through contrastive learning, achieving cross-modal feature alignment.
CLIP is a milestone multi-modal pre-trained model developed by OpenAI. Trained on 400 million image-text pairs, it demonstrates powerful zero-shot learning capabilities. CLIP adopts a dual-encoder architecture, processing image and text inputs separately, and trains the model to understand semantic connections between images and text through contrastive learning. In our system, CLIP primarily extracts high-level semantic features from images and text, providing a foundation for subsequent similarity calculations.
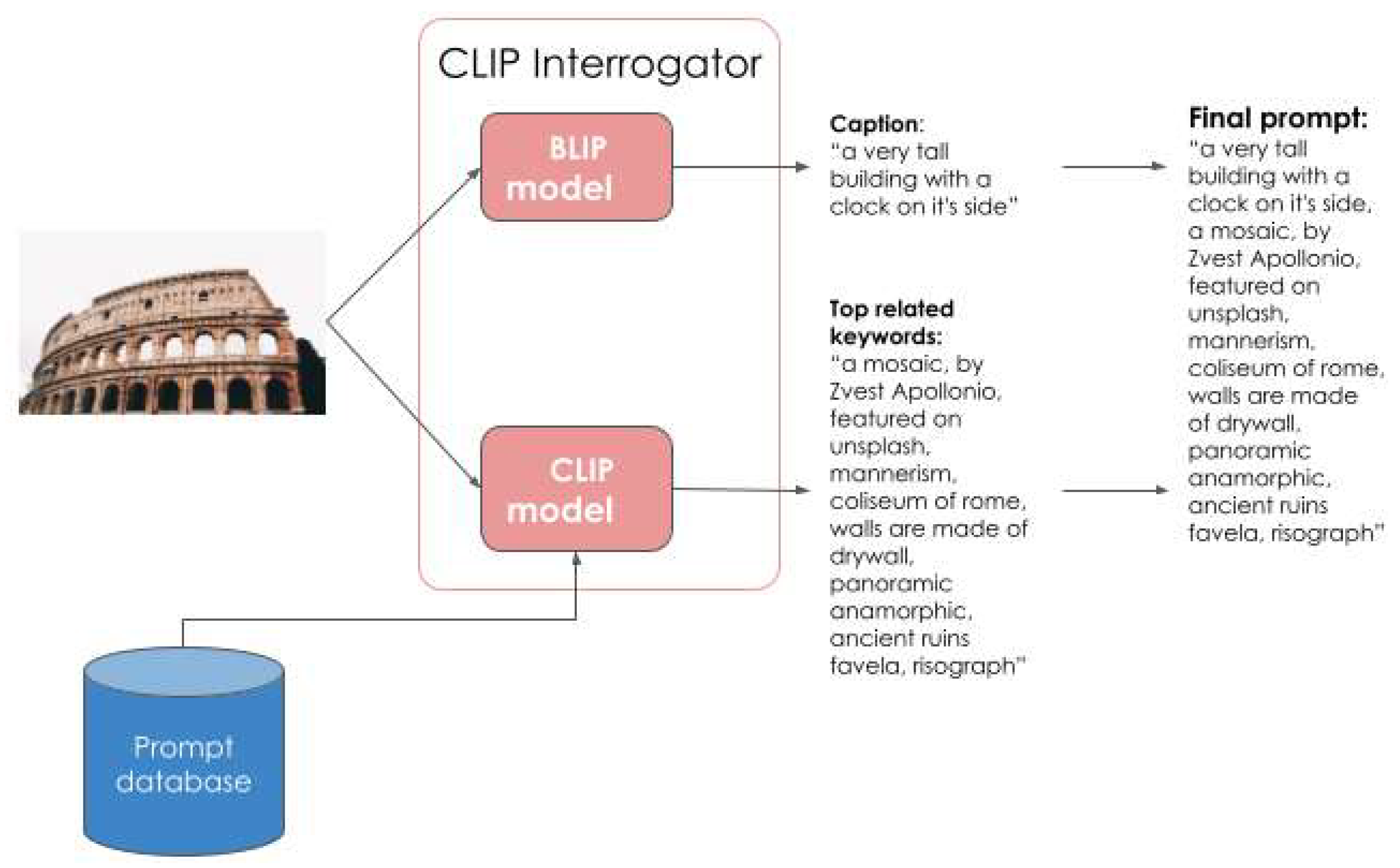
As shown in
Figure 1, the CLIP Interrogator combines both BLIP and CLIP models to generate comprehensive image descriptions by extracting captions and related keywords from the input image, which are then merged into a final detailed prompt.
CLIP Interrogator is an important extension based on the CLIP model, specifically designed for generating detailed image descriptions. This model can extract rich visual features from images, including information about objects, scenes, and styles across multiple dimensions. In our system, CLIP Interrogator serves as a bridge, converting visual features from images into text descriptions, thus providing additional semantic information for image-text matching.
For an input image I and text query T, the feature extraction process can be represented as:
where
,
are BLIP image and text features, and
,
are CLIP features, respectively.
and
represent their respective feature dimensions.
The CLIP Interrogator generates text description D from image I:
where wi represents words in the generated description.
The fusion of features from different models is achieved through:
where
denotes feature concatenation, and α,β,γ are learnable weights that satisfy:
The final similarity score between image and text is computed using:
During training, we optimize using a contrastive loss function:
wher, τ is the temperature parameter , N is the batch size,
represents other text samples in the batch.
The collaborative workflow of these three models operates as follows: First, when a user submits a text query, the system uses both BLIP and CLIP to extract semantic features from the text. In parallel, for product images in the database, the system uses CLIP Interrogator to generate detailed descriptions and combines these with image features extracted by BLIP and CLIP. Finally, the system computes similarity scores between the fused feature vectors of the text query and the product images, returning the most relevant matches. This multi-model fusion approach effectively capitalizes on the complementary strengths of each model, resulting in more precise and robust retrieval outcomes.
Consider briefly disucss key hyperparameters and how they are chosen or tuned.
4. Model Results Analysis
To validate the effectiveness of our proposed multi-modal retrieval system, we analyzed two representative test cases. As shown in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, the system demonstrates strong capabilities in image understanding and description generation across different scenarios.
Figure 2 showcases the system’s ability to comprehend everyday commercial scenarios. Given the original input describing a scene at a donut shop, the system-generated description accurately captures key elements of the scene, including “a man standing in front of a counter,” “digital rendering,” and “donut.” This demonstrates our system’s effectiveness in understanding visual elements and spatial relationships in commercial settings.
Figure 3 illustrates the system’s performance in handling artistic works. For this wooden rose carving, the system not only identifies basic physical attributes (“wooden object on a table”) but also understands artistic characteristics (“woodcut,” “op art”) and visual effects (“swirling around”). This indicates that our system is capable of processing complex visual content and can extract and describe multiple dimensional features of objects.
These test cases reveal several advantages of our proposed multi-modal retrieval system:
Strong Scene Adaptability: The system generates accurate descriptions for both everyday commercial scenes and artistic works;
Comprehensive Description: The system captures multiple key elements within scenes, including objects, spatial relationships, and detailed visual features -ensuring that no critical information is overlooked;
Deep Semantic Understanding: The generated descriptions go beyond surface features to include functional attributes and artistic characteristics, that providing a richer understanding of the visual content.
These results suggest that our system has significant potential for practical applications in e-commerce. By providing accurate image-text matching services, the system can enhance user search experiences, reduce reliance on manual tagging, and improve overall conversion rates. The system’s ability to generate detailed and context-aware descriptions demonstrates its effectiveness in bridging the gap between visual content and textual queries, making it particularly valuable for online shopping scenarios where precise product matching is essential.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented a multi-modal retrieval system for e-commerce platforms that leverages advanced pre-trained models. Through the innovative integration of BLIP, CLIP, and CLIP Interrogator, our research has successfully developed a comprehensive solution that effectively bridges the gap between textual queries and visual content in online shopping scenarios This system helps users to retrieve matching accuracy during the shopping process, improve the shopping experience, and reduce search abandonment, retention, etc.
Our research makes several significant contributions to the field of multi-modal retrieval. We have proposed a novel multi-model fusion approach that effectively combines the strengths of three state-of-the-art pre-trained models, leveraging BLIP’s powerful vision-language understanding, CLIP’s zero-shot learning capabilities, and CLIP Interrogator’s detailed description generation abilities. The feature fusion mechanism we developed achieves more comprehensive and accurate representations of both images and text, enabling better cross-modal understanding and matching through the weighted combination of features from different models.
The experimental results have validated the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating that the system can successfully generate accurate and detailed descriptions of product images, understand complex visual features, and provide reliable image-text matching for e-commerce applications. Our system shows strong adaptability across diverse e-commerce scenarios, from everyday products to artistic items, generating detailed, context-aware descriptions that facilitate accurate product matching.
Looking forward, several promising directions for future research emerge from this work. While our current system demonstrates strong performance, there is potential for further efficiency optimization to reduce computational complexity while maintaining performance, making the system more suitable for large-scale deployment. Future work will explore techniques such as model pruning and knowledge distillation to streamline computational demands, as well as targeted fine-tuning using domain-specific datasets for categories like fashion and electronics. Additionally, improving real-time performance also remains an important consideration for enhancing user experience in real-world applications.
Our research contributes significantly to the advancement of multi-modal retrieval systems in e-commerce, providing a practical solution for improving online shopping experiences through better image-text understanding and matching. By integrating our system with personalized recommendation engines and emerging AR/VR technologies, the potential exists to further transform the online shopping experience through immersive and tailored interactions. The proposed system not only addresses current challenges in e-commerce image retrieval but also lays a solid foundation for future developments in intelligent e-commerce platforms. As online shopping continues to evolve, the importance of accurate and efficient multi-modal retrieval systems will only grow, making our contributions particularly relevant for the future of e-commerce.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Fujian Province Young and Middle-aged Teacher Education Research Project (Science and Technology Category) under Grant No. JAT220471, titled “Design of Intelligent Image Search System.” We express our gratitude for the financial support provided, which has been instrumental in the successful completion of this study.
References
- Radford A, Kim J W, Hallacy C, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]//International conference on machine learning. PmLR, 2021: 8748-8763.
- Li J, Li D, Xiong C, et al. Blip: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training for unified vision-language understanding and generation[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2022: 12888-12900.
- Gu X, Wong Y, Shou L, et al. Multi-modal and multi-domain embedding learning for fashion retrieval and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 21(6): 1524-1537.
- Jin Y, Li Y, Yuan Z, et al. Learning instance-level representation for large-scale multi-modal pretraining in e-commerce[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 11060-11069.
- Wang T, Li F, Zhu L, et al. Cross-modal retrieval: a systematic review of methods and future directions[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2025.
- Yu T, Yang Y, Li Y, et al. Heterogeneous attention network for effective and efficient cross-modal retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the 44th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval. 2021: 1146-1156.
- Ji W, Liu X, Zhang A, et al. Online distillation-enhanced multi-modal transformer for sequential recommendation[C]//Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. 2023: 955-965.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).