Submitted:
24 April 2025
Posted:
24 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Neutrophils
3.1. Development
3.2. Interactions with Endothelium and Migration
3.3. Effector Mechanisms
3.4. Heterogeneity
3.5. Cell Death
4. Platelets
5. Neutrophil-Platelet Crosstalk
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drynda, A.; Padjas, A.; Wójcik, K.; Dziedzic, R.; Biedroń, G.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Włudarczyk, A.; Wilańska, J.; Musiał, J.; Zdrojewski, Z.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of EGPA Patients in Comparison to GPA Subgroup with Increased Blood Eosinophilia from POLVAS Registry. J. Immunol. Res. 2024, 2024, 4283928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcik, K.; Masiak, A.; Jeleniewicz, R.; Jakuszko, K.; Brzosko, I.; Storoniak, H.; Kur-Zalewska, J.; Wisłowska, M.; Madej, M.; Hawrot-Kawecka, A.; et al. Association of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) specificity with the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedroń, G.; Włudarczyk, A.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Wójcik, K.; Musiał, J.; Bazan-Socha, S.; Zdrojewski, Z.; Masiak, A.; Czuszyńska, Z.; Majdan, M.; et al. Respiratory involvement in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: a retrospective study based on POLVAS registry. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala A, Sharma PD, Jhaveri KD, Jain K, Geetha D. Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024 Nov 1;31(6):485–95.
- Iudici, M.; Puéchal, X.; Pagnoux, C.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Hamidou, M.; Blanchard-Delaunay, C.; Maurier, F.; Ruivard, M.; Quéméneur, T.; Aumaître, O.; et al. Significance of eosinophilia in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: data from the French Vasculitis Study Group Registry. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, M.V.; Frankel, S.K.; Maleki-Fischbach, M.; Tan, L.D. A rare case report of polyangiitis overlap syndrome: granulomatosis with polyangiitis and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasson, G.; Grayson, P.C.; Mahr, A.D.; LaValley, M.; Merkel, P.A. Value of ANCA measurements during remission to predict a relapse of ANCA-associated vasculitis--a meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2011, 51, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung SA, Langford CA, Maz M, Abril A, Gorelik M, Guyatt G, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;73(8):1366–83.
- Hellmich, B.; Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Schirmer, J.H.; Berti, A.; Blockmans, D.; Cid, M.C.; Holle, J.U.; Hollinger, N.; Karadag, O.; Kronbichler, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 83, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnoux, C.; Mahr, A.; Hamidou, M.A.; Boffa, J.-J.; Ruivard, M.; Ducroix, J.-P.; Kyndt, X.; Lifermann, F.; Papo, T.; Lambert, M.; et al. Azathioprine or Methotrexate Maintenance for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2790–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillevin, L.; Pagnoux, C.; Karras, A.; Khouatra, C.; Aumaître, O.; Cohen, P.; Maurier, F.; Decaux, O.; Ninet, J.; Gobert, P.; et al. Rituximab versus Azathioprine for Maintenance in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flossmann, O.; Berden, A.; de Groot, K.; Hagen, C.; Harper, L.; Heijl, C.; Höglund, P.; Jayne, D.; Luqmani, R.; Mahr, A.; et al. Long-term patient survival in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R. Complications of therapy for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, iii74–iii78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayer, M.; Chapman, G.B.; Thomas, M.; Dhaun, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Anti-neutrophil Cytoplasm Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2023, 26, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woywodt, A.; Streiber, F.; de Groot, K.; Regelsberger, H.; Haller, H.; Haubitz, M. Circulating endothelial cells as markers for ANCA-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Lancet 2003, 361, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, S.; Hafezi-Rachti, S.; Rupprecht, H.D. Thromboembolic events as a complication of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 55, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies with Specificity for Myeloperoxidase in Patients with Systemic Vasculitis and Idiopathic Necrotizing and Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. New Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niles, J.; Mccluskey, R.; Ahmad, M.; Arnaout, M. WEGENERS GRANULOMATOSIS AUTO-ANTIGEN IS A NOVEL NEUTROPHIL SERINE PROTEINASE. 1989, 74, 1888–1893.
- Falk, R.J.; Terrell, R.S.; A Charles, L.; Jennette, J.C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies induce neutrophils to degranulate and produce oxygen radicals in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1990, 87, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewert, B.H.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies stimulate neutrophils to damage human endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 1992, 41, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.; Davis, R.P.; Kim, S.-J.; Tse, M.; Esmon, C.T.; Kolaczkowska, E.; Jenne, C.N. Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice. Blood 2017, 129, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Yousef, G.M.; Ni, H. Cancer and platelet crosstalk: opportunities and challenges for aspirin and other antiplatelet agents. Blood 2018, 131, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.H.; Zharkova, O.; Lee, H.Y.; Toh, M.M.X.; Libau, E.A.; Celhar, T.; Narayanan, S.; Ahl, P.J.; Ong, W.Y.; Joseph, C.; et al. Platelet TLR7 is essential for the formation of platelet–neutrophil complexes and low-density neutrophils in lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2023, 63, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, N.; Baldini, M.; Ramirez, G.A.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Manfredi, A.A. Platelet-leukocyte deregulated interactions foster sterile inflammation and tissue damage in immune-mediated vessel diseases. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, D.; Li, D.-Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. Platelets are activated in ANCA-associated vasculitis via thrombin-PARs pathway and can activate the alternative complement pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 252–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Ma, T.-T.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. Platelets release proinflammatory microparticles in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Yasuoka, H.; Yoshimoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takeuchi, T. Platelet CXCL4 mediates neutrophil extracellular traps formation in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saverymuttu, S.H.; Peters, A.M.; Keshavarzian, A.; Reavy, H.J.; Lavender, J.P. The kinetics of 111Indium distribution following injection of 111Indium labelled autologous granulocytes in man. Br. J. Haematol. 1985, 61, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, J.; Braber, I.D.; Vrisekoop, N.; Kwast, L.M.; de Boer, R.J.; Borghans, J.A.M.; Tesselaar, K.; Koenderman, L. In vivo labeling with 2H2O reveals a human neutrophil lifespan of 5.4 days. Blood 2010, 116, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancey, J.T.; A Deubelbeiss, K.; A Harker, L.; A Finch, C. Neutrophil kinetics in man. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 58, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.K.; Liu, F.; Iwasaki, H.; Akashi, K.; Link, D.C. Pivotal role of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in the development of progenitors in the common myeloid pathway. Blood 2003, 102, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, S.M. The bone marrow: a site of neutrophil clearance. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, C.; Rankin, S.M.; Condliffe, A.M.; Singh, N.; Peters, A.M.; Chilvers, E.R. Neutrophil kinetics in health and disease. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, S.; Kotani, T.; Matsuda, S.; Nishioka, D.; Masuda, Y.; Unoda, K.; Hosokawa, T.; Ishida, S.; Takeuchi, T. Initial serum GM-CSF levels are associated with the severity of cerebral small vessel disease in microscopic polyangiitis patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 359, 577671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee-Wacker, M.C. Clearance of apoptotic neutrophils and resolution of inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, M.A.; Huo, Y.; Burcin, T.L.; Morris, M.A.; Olson, T.S.; Ley, K. Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils Regulates Granulopoiesis via IL-23 and IL-17. Immunity 2005, 22, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley K, Smith E, Stark MA. IL-17A-producing neutrophil-regulatory Tn lymphocytes. Immunol Res. 2006 Mar 1;34(3):229–42.
- Matsumoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Seki, N.; Tsujimoto, H.; Chiba, K.; Takeuchi, T. Significant association between clinical characteristics and immuno-phenotypes in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2019, 59, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.; Hamour, S.; Sawant, D.; Henderson, S.; Mansfield, N.; Chavele, K.-M.; Pusey, C.D.; Salama, A.D. Serum IL-17 and IL-23 levels and autoantigen-specific Th17 cells are elevated in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shen, C.; Zhong, Y.; Ooi, J.D.; Zhou, Y.-O.; Chen, J.-B.; Wu, T.; Meng, T.; Xiao, Z.; Lin, W.; et al. The association of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with all-cause mortality in Chinese patients with MPO-ANCA associated vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.S.; Jung, S.M.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio at diagnosis can estimate vasculitis activity and poor prognosis in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: a retrospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Ahn, S.S.; Jung, S.M.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Delta Neutrophil Index Is Associated with Vasculitis Activity and Risk of Relapse in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Yonsei Med J. 2018, 59, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbwachs, L.; Lesavre, P. Endothelium-Neutrophil Interactions in ANCA-Associated Diseases. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan-Socha, S.; Bukiej, A.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Musial, J. Integrins in Pulmonary Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, K.; Laudanna, C.; Cybulsky, M.I.; Nourshargh, S. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelliott, P.M.; Nishide, M.; Pavillon, N.; Okita, Y.; Shibahara, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Yoshimura, H.; Obata, S.; Kumanogoh, A.; I Smith, N. Cellular Adhesion Is a Controlling Factor in Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation Induced by Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies. ImmunoHorizons 2022, 6, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halai K, Whiteford J, Ma B, Nourshargh S, Woodfin A. ICAM-2 facilitates luminal interactions between neutrophils and endothelial cells in vivo. J Cell Sci. 2014 Feb 1;127(3):620–9.
- Bai, M.; Grieshaber-Bouyer, R.; Wang, J.; Schmider, A.B.; Wilson, Z.S.; Zeng, L.; Halyabar, O.; Godin, M.D.; Nguyen, H.N.; Levescot, A.; et al. CD177 modulates human neutrophil migration through activation-mediated integrin and chemoreceptor regulation. Blood 2017, 130, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, M.; Nojima, S.; Ito, D.; Takamatsu, H.; Koyama, S.; Kang, S.; Kimura, T.; Morimoto, K.; Hosokawa, T.; Hayama, Y.; et al. Semaphorin 4D inhibits neutrophil activation and is involved in the pathogenesis of neutrophil-mediated autoimmune vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, A.; Lovric, S.; Engel, A.; Beese, M.; Wyss, K.; Hertel, B.; Park, J.-K.; Becker, J.U.; Kegel, J.; Haller, H.; et al. Circulating ADAM17 Level Reflects Disease Activity in Proteinase-3 ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2860–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Song, D.; Huang, D. The emerging roles of semaphorin4D/CD100 in immunological diseases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2875–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li H, Zhou X, Huang Y, Liao B, Cheng L, Ren B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Pathogen Clearance: The Killing Mechanisms, the Adaption Response, and the Side Effects. Front Microbiol [Internet]. 2021 Feb 4;11.
- Levy, O. Antimicrobial proteins and peptides of blood: templates for novel antimicrobial agents. Blood. 2000 Oct 15;96(8):2664–72.
- Pham, C.T.N. Neutrophil serine proteases: specific regulators of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurschou, M.; Borregaard, N. Neutrophil granules and secretory vesicles in inflammation. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xia, Y.; Su, J.; Quan, F.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lin, C.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Z. Neutrophil diversity and function in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowland, J.B.; Borregaard, N. Granulopoiesis and granules of human neutrophils. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordenfelt, P.; Tapper, H. Phagosome dynamics during phagocytosis by neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Gasim AH. Pathogenesis of ANCA Vasculitis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011 May;20(3):263–70.
- Hong, Y.; Eleftheriou, D.; Hussain, A.A.; Price-Kuehne, F.E.; Savage, C.O.; Jayne, D.; Little, M.A.; Salama, A.D.; Klein, N.J.; Brogan, P.A. Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Stimulate Release of Neutrophil Microparticles. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, E.; Böing, A. N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. , Classification, Functions, and Clinical Relevance of Extracellular Vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalli, J.; Montero-Melendez, T.; Norling, L.V.; Yin, X.; Hinds, C.; Haskard, D.; Mayr, M.; Perretti, M. Heterogeneity in Neutrophil Microparticles Reveals Distinct Proteome and Functional Properties. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soung, Y.H.; Ford, S.; Zhang, V.; Chung, J. Exosomes in Cancer Diagnostics. Cancers 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Gareev, I.; Yan, T.; Chen, X.; Ahmad, A.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, B.; Beylerli, O.; Yang, G.; et al. Exosomal miR-2276-5p in Plasma Is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Glioma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, L.; Sun, B.; Mustapic, M.; Chawla, S.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer’s disease. J. NeuroVirology 2019, 25, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Xie, L.; Qin, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Lv, F.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 835566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco C, Eldaboush A, Liu ML, Werth VP. Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Clinical Characterization, and Management of Dermatomyositis: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1967.
- Gasecka, A.; Böing, A.N.; Filipiak, K.J.; Nieuwland, R. Platelet extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for arterial thrombosis. Platelets 2016, 28, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antovic, A.; Mobarrez, F.; Manojlovic, M.; Soutari, N.; Baggemar, V.D.P.; Nordin, A.; Bruchfeld, A.; Vojinovic, J.; Gunnarsson, I. Microparticles Expressing Myeloperoxidase and Complement C3a and C5a as Markers of Renal Involvement in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–associated Vasculitis. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 47, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manojlovic, M.; Juto, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; Colic, J.; Vojinovic, J.; Nordin, A.; Bruchfeld, A.; Gunnarsson, I.; Mobarrez, F.; Antovic, A. Microparticles expressing myeloperoxidase as potential biomarkers in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitides (AAV). J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmiak, M.; Gielicz, A.; Stojkov, D.; Szatanek, R.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U.; Sanak, M. LTB4 and 5-oxo-ETE from extracellular vesicles stimulate neutrophils in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmiak, M.; Kosałka-Węgiel, J.; Polański, S.; Sanak, M. Endothelial cells response to neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles miRNAs in anti-PR3 positive vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 204, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmiak, M.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Kosałka-Węgiel, J.; Polański, S.; Sanak, M. Profile of circulating extracellular vesicles microRNA correlates with the disease activity in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 208, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glémain, A.; Néel, M.; Néel, A.; André-Grégoire, G.; Gavard, J.; Martinet, B.; Le Bloas, R.; Riquin, K.; Hamidou, M.; Fakhouri, F.; et al. Neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles induce endothelial inflammation and damage through the transfer of miRNAs. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 129, 102826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Collins, L.B.; Chen, T.-H.; Herr, N.; Takeda, S.; Sun, W.; Swenberg, J.A.; Nakamura, J. Oxidative stress at low levels can induce clustered DNA lesions leading to NHEJ mediated mutations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25377–25390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S. Role of oxidative stress and protein oxidation in the aging process1,2 1Guest Editor: Earl Stadtman 2This article is part of a series of reviews on “Oxidatively Modified Proteins in Aging and Disease.” The full list of papers may be found on the homepage of the journal. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, C.; Kouretas, D. Lipid peroxidation and tissue damage. Vivo Athens Greece 1999, 13, 295–309. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouz, D.; Khan, M.A.; Palaniyar, N. ROS induces NETosis by oxidizing DNA and initiating DNA repair. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.H.L.; Perdomo, J.; Ahmadi, Z.; Yan, F.; McKenzie, S.E.; Chong, B.H. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase blocks NETosis and reduces thrombosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5439–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilhorst, M.; Maria, A.T.; Kavian, N.; Batteux, F.; Borderie, D.; Le Quellec, A.; van Paassen, P.; Guilpain, P. Impact of MPO-ANCA-mediated oxidative imbalance on renal vasculitis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1769–F1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun R lan, Shang J chun, Han R hong, Xing G qun. Protective effect of astaxanthin on ANCA-associated vasculitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 May;132:111928.
- Michalski, R.; Zielonka, J.; Gapys, E.; Marcinek, A.; Joseph, J.; Kalyanaraman, B. Real-time Measurements of Amino Acid and Protein Hydroperoxides Using Coumarin Boronic Acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22536–22553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova-Acebes, M.; Pitaval, C.; Weiss, L.A.; Nombela-Arrieta, C.; Chèvre, R.; A-González, N.; Kunisaki, Y.; Zhang, D.; van Rooijen, N.; Silberstein, L.E.; et al. Rhythmic Modulation of the Hematopoietic Niche through Neutrophil Clearance. Cell 2013, 153, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, G.; Manwani, D.; Mortha, A.; Xu, C.; Faith, J.J.; Burk, R.D.; Kunisaki, Y.; Jang, J.-E.; Scheiermann, C.; et al. Neutrophil ageing is regulated by the microbiome. Nature 2015, 525, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca-Crevillén, A.; Adrover, J.M.; Hidalgo, A. Circadian Features of Neutrophil Biology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Wang, Y.; Chew, W.K.; Lima, R.; A-González, N.; Mattar, C.N.; Chong, S.Z.; Schlitzer, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Chew, S.; et al. Neutrophil mobilization via plerixafor-mediated CXCR4 inhibition arises from lung demargination and blockade of neutrophil homing to the bone marrow. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2321–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, F.; Robinson, J.; Phelan, M.; Bucknall, R.; Edwards, S. Receptor expression in synovial fluid neutrophils from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1993, 52, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, E.; Kazemier, K.M.; Grutters, J.C.; Koenderman, L.; Bosch, V.J.M.M.V.D. Human neutrophils switch to an activated phenotype after homing to the lung irrespective of inflammatory disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 155, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumagin, R. Phenotypic and Functional Diversity of Neutrophils in Gut Inflammation and Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 194, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, A.D.; Torell, A.; Popovic, J.; Stockfelt, M.; Jacobsson, B.; Rudin, A.; Christenson, K.; Lundell, A.-C.; Bylund, J. Pregnancy is associated with a simultaneous but independent increase in circulating CD177pos and immature low-density granulocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göhring K, Wolff J, Doppl W, Schmidt KL, Fenchel K, Pralle H, et al. Neutrophil CD177 (NB1 gp, HNA-2a) expression is increased in severe bacterial infections and polycythaemia vera. Br J Haematol. 2004 Jul;126(2):252–4.
- Abdgawad, M.; Gunnarsson, L.; A Bengtsson, A.; Geborek, P.; Nilsson, L.; Segelmark, M.; Hellmark, T. Elevated neutrophil membrane expression of proteinase 3 is dependent upon CD177 expression. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 161, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witko-Sarsat, V.; Lesavre, P.; Lopez, S.; Bessou, G.; Hieblot, C.; Prum, B.; Noël, L.H.; Guillevin, L.; Ravaud, P.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; et al. A Large Subset of Neutrophils Expressing Membrane Proteinase 3 Is a Risk Factor for Vasculitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smargianaki, S.; Elmér, E.; Lilliebladh, S.; Ohlsson, S.; Pettersson, Å.; Hellmark, T.; Johansson, Å.C. Disease Activity and Tendency to Relapse in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Are Reflected in Neutrophil and Intermediate Monocyte Frequencies. J. Immunol. Res. 2024, 2024, 6648265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, S.F.; Jerke, U.; Rolle, S.; Daumke, O.; Kettritz, R. Competitively disrupting the neutrophil-specific receptor–autoantigen CD177:proteinase 3 membrane complex reduces anti-PR3 antibody-induced neutrophil activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerke, U.; Rolle, S.; Dittmar, G.; Bayat, B.; Santoso, S.; Sporbert, A.; Luft, F.; Kettritz, R. Complement Receptor Mac-1 Is an Adaptor for NB1 (CD177)-mediated PR3-ANCA Neutrophil Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7070–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Kurasawa, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takeuchi, T. Identification of neutrophil β2-integrin LFA-1 as a potential mechanistic biomarker in ANCA-associated vasculitis via microarray and validation analyses. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, H.; Eichhorn, J.; Pieper, K.; Göbel, U.; Luft, F.C. Circulating leukocyte integrin expression in Wegener's granulomatosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Nishii, C.; Ohashi, A.; Tomita, M.; Nakai, S.; Murakami, K.; Nabeshima, K.; Fujita, Y.; Ishii, J.; Hiki, Y.; et al. Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors on Granulocytes in Patients with Myeloperoxidase Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Vasculitis. Nephron Clin. Pr. 2009, 113, c222–c233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacbarth, E.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A. Low density neutrophils in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute rheumatic fever. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaver, C.; Nana, F.A.; Delhez, N.; Luyckx, M.; Hirsch, T.; Bayard, A.; Houbion, C.; Dauguet, N.; Brochier, A.; van der Bruggen, P.; et al. Immunosuppressive low-density neutrophils in the blood of cancer patients display a mature phenotype. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 7, e202302332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, B. Dysfunction of low-density neutrophils in peripheral circulation in patients with sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.L.; A Makki, F.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Low-density granulocytes: functionally distinct, immature neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis with altered properties and defective TNF signalling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 101, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Qin, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Shi, Y. A Distinct Immature Low-Density Neutrophil Population Characterizes Acute Generalized Pustular Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 2831–2835.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, C.; Chen, J.; Fan, C.; He, J. Elevated circulating pro-inflammatory low-density granulocytes in adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny MF, Yalavarthi S, Zhao W, Thacker SG, Anderson M, Sandy AR, et al. A Distinct Subset of Proinflammatory Neutrophils Isolated from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induces Vascular Damage and Synthesizes Type I IFNs. J Immunol. 2010 Mar 15;184(6):3284–97.
- Villanueva, E.; Yalavarthi, S.; Berthier, C.C.; Hodgin, J.B.; Khandpur, R.; Lin, A.M.; Rubin, C.J.; Zhao, W.; Olsen, S.H.; Klinker, M.; et al. Netting Neutrophils Induce Endothelial Damage, Infiltrate Tissues, and Expose Immunostimulatory Molecules in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ruiz, J.M.; Carrillo-Vázquez, D.A.; Leal-Alanis, A.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Tapia-Rodríguez, M.; Maravillas-Montero, J.L.; Nuñez-Álvarez, C.A.; Carazo-Vargas, E.R.; Romero-Hernández, I.; Juárez-Vega, G.; et al. Low-Density Granulocytes and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps as Biomarkers of Disease Activity in Adult Inflammatory Myopathies. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 28, e480–e487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z.-G.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yi, H.; Yang, Y.-G. Arginase-1–dependent promotion of T H 17 differentiation and disease progression by MDSCs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 331ra40–331ra40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaonaigh, A.U.; Coughlan, A.M.; Dwivedi, A.; Hartnett, J.; Cabral, J.; Moran, B.; Brennan, K.; Doyle, S.L.; Hughes, K.; Lucey, R.; et al. Low Density Granulocytes in ANCA Vasculitis Are Heterogenous and Hypo-Responsive to Anti-Myeloperoxidase Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Gou, S.-J.; Huang, J.; Hao, J.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. C5a and its receptors in human anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R140–R140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, P.C.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Xu, L.; Lim, N.; Gao, Z.; Asare, A.L.; Specks, U.; Stone, J.H.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.F.; et al. Neutrophil-Related Gene Expression and Low-Density Granulocytes Associated With Disease Activity and Response to Treatment in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Camarillo, C.; Alemán, O.R.; Rosales, C. Low-Density Neutrophils in Healthy Individuals Display a Mature Primed Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre-Roig, C.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Glogauer, M.; Scapini, P. Neutrophil Diversity in Health and Disease. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardisty, G.R.; Llanwarne, F.; Minns, D.; Gillan, J.L.; Davidson, D.J.; Findlay, E.G.; Gray, R.D. High Purity Isolation of Low Density Neutrophils Casts Doubt on Their Exceptionality in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Figueroa, E.; Álvarez-Carrasco, P.; Ortega, E.; Maldonado-Bernal, C. Neutrophils: Many Ways to Die. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdgawad, M.; Pettersson, Å.; Gunnarsson, L.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Geborek, P.; Nilsson, L.; Segelmark, M.; Hellmark, T. Decreased Neutrophil Apoptosis in Quiescent ANCA-Associated Systemic Vasculitis. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e32439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmiak, M.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Musiał, J.; Sanak, M. Delayed neutrophil apoptosis in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: dysregulation of neutrophil gene signature and circulating apoptosis-related proteins. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 49, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahilog, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Alam, A.; Eguchi, S.; Weng, H.; Ma, D. The Role of Neutrophil NETosis in Organ Injury: Novel Inflammatory Cell Death Mechanisms. Inflammation 2020, 43, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmiak, M.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Szczeklik, W.; Musiał, J.; Brzozowski, T.; Sanak, M. Neutrophil-related and serum biomarkers in granulomatosis with polyangiitis support extracellular traps mechanism of the disease. . 2016, 34, S98–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraaij, T.; Kamerling, S.W.; van Dam, L.S.; Bakker, J.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Page, T.; Brunini, F.; Pusey, C.D.; Toes, R.E.; Scherer, H.U.; et al. Excessive neutrophil extracellular trap formation in ANCA-associated vasculitis is independent of ANCA. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Krumbholz, M.; Schönermarck, U.; Back, W.; Gross, W.L.; Werb, Z.; Gröne, H.-J.; Brinkmann, V.; Jenne, D.E. Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aendekerk, J.P.; Ysermans, R.; Busch, M.H.; Theunissen, R.O.; Bijnens, N.; Potjewijd, J.; Damoiseaux, J.G.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; van Paassen, P. Assessment of longitudinal serum neutrophil extracellular trap–inducing activity in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis and glomerulonephritis in a prospective cohort using a novel bio-impedance technique. Kidney Int. 2023, 104, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmiak, M.P.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Szczeklik, W.; Musiał, J.; Sanak, M. Circulating mitochondrial DNA in serum of patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, S.L.; O’sullivan, K.M.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Gan, P.Y.; Summers, S.A. Toll-like Receptor 9 Induced Dendritic Cell Activation Promotes Anti-Myeloperoxidase Autoimmunity and Glomerulonephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Mihalache, C.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Simon, H.U. Viable neutrophils release mitochondrial DNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury MK, Gupta K, Franco SR, Liu B. Necroptosis in the Pathophysiology of Disease. Am J Pathol. 2020 Feb;190(2):272–85.
- Schreiber, A.; Rousselle, A.; Becker, J.U.; von Mässenhausen, A.; Linkermann, A.; Kettritz, R. Necroptosis controls NET generation and mediates complement activation, endothelial damage, and autoimmune vasculitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, 201708247–E9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan H fa, Zou T, Tuo Q zhang, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi AA, et al. Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Feb 3;6(1):1–16.
- Rousselle, A.; Lodka, D.; Kling, L.; Kettritz, R.; Schreiber, A. Endothelial Cell Ferroptosis Promotes Renal Damage in ANCA-Induced Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 481–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminita, E.; Becker, I.C.; Italiano, J.E. What It Takes To Be a Platelet: Evolving Concepts in Platelet Production. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalloussi, D.; Dhenge, A.; Bergmeier, W. New insights into cytoskeletal remodeling during platelet production. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willeke, P.; Kümpers, P.; Schlüter, B.; Limani, A.; Becker, H.; Schotte, H. Platelet counts as a biomarker in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCL5 derived from platelets increases megakaryocyte proplatelet formation - PubMed [Internet].
- Lee, L.E.; Ahn, S.S.; Pyo, J.Y.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Pan-immune-inflammation value at diagnosis independently predicts all-cause mortality in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuk, H.; Tecer, D.; Goker, B.; Varan, O.; Babaoglu, H.; Guven, S.C.; Ozturk, M.A.; Haznedaroglu, S.; Tufan, A. Platelet/lymphocyte ratio and mean platelet volume in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Hortic. Bras. 2019, 60, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Jung, S.M.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Platelet to lymphocyte ratio is associated with the current activity of ANCA-associated vasculitis at diagnosis: a retrospective monocentric study. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, F.; Tang, J.; Luo, L.; Huang, L.; Zhou, F.; Qi, E.; Hu, X.; Deng, S.; Ge, H.; et al. Low platelet count at diagnosis of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis is correlated with the severity of disease and renal prognosis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L H, C S, Y Z, Jd O, Yo Z, Jb C, et al. Risk factors for treatment resistance and relapse of Chinese patients with MPO-ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Med [Internet]. 2020 May;20(2).
- Flad, H.-D.; Brandt, E. Platelet-derived chemokines: pathophysiology and therapeutic aspects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2363–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, O.; Sonmez, M. Role of platelets in immune system and inflammation. Porto Biomed. J. 2017, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen H, van der Sluijs P. Platelet secretory behaviour: as diverse as the granules … or not? J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Dec 1;13(12):2141–51.
- Berger, M.; Maqua, H.; Lysaja, K.; Mause, S.F.; Hindle, M.S.; Naseem, K.; Dahl, E.; Speer, T.; Marx, N.; Schütt, K. Platelets from patients with chronic inflammation have a phenotype of chronic IL-1β release. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 8, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemetson KJ, Clemetson JM, Proudfoot AEI, Power CA, Baggiolini M, Wells TNC. Functional expression of CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CXCR4 chemokine receptors on human platelets. Blood. 2000 Dec 15;96(13):4046–54.
- Worth, R.G.; Chien, C.D.; Chien, P.; Reilly, M.P.; McKenzie, S.E.; Schreiber, A.D. Platelet FcγRIIA binds and internalizes IgG-containing complexes. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 34, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark SR, Ma AC, Tavener SA, McDonald B, Goodarzi Z, Kelly MM, et al. Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat Med. 2007 Apr;13(4):463–9.
- Vik, D.P.; Fearon, D.T. Cellular distribution of complement receptor type 4 (CR4): expression on human platelets. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peerschke, E.I.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Platelet Receptors for the Complement Component C1q: Implications for Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Immunobiology 1998, 199, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Conde, I.; Crúz, M.A.; Zhang, H.; López, J.A.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. Platelet activation leads to activation and propagation of the complement system. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heras Benito, M. Complement in vasculitis associated with anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies with renal involvement: pathogenic, prognostic and therapeutic implications. Med Clin (Barc). 2023 Aug 25;161(4):160–5.
- Aslan, J.E. Platelet Proteomes, Pathways, and Phenotypes as Informants of Vascular Wellness and Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, M.G.; El Bannoudi, H.; Luttrell-Williams, E.; Engel, A.; Barrett, T.J.; Myndzar, K.; Izmirly, P.; Belmont, H.M.; Clancy, R.; Ruggles, K.V.; et al. Modeling of clinical phenotypes in systemic lupus erythematosus based on the platelet transcriptome and FCGR2a genotype. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, H.; Sakata, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Takeuchi, T. Phenotype of Platelets Are Altered and Activated in Circulation of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Blood 2018, 132, 3732–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.E.; Levis, J.E.; Schneider, D.J.; Bambace, N.M.; Sharma, D.; Lal, I.; Wood, M.E.; Muss, H.B. Platelet phenotype changes associated with breast cancer and its treatment. Platelets 2016, 27, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massberg, S.; Grahl, L.; von Bruehl, M.-L.; Manukyan, D.; Pfeiler, S.; Goosmann, C.; Brinkmann, V.; Lorenz, M.; Bidzhekov, K.; Khandagale, A.B.; et al. Reciprocal coupling of coagulation and innate immunity via neutrophil serine proteases. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Savchenko, A.S.; Thomas, G.M.; Martinod, K.; DE Meyer, S.F.; Bhandari, A.A.; Wagner, D.D. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote deep vein thrombosis in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 10, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M. Promotion of Hypercoagulability in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis by C5a-Induced Tissue Factor–Expressing Microparticles and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2780–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bont CM, Boelens WC, Pruijn GJM. NETosis, complement, and coagulation: a triangular relationship. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019 Jan;16(1):19–27.
- Tomasson, G.; Lavalley, M.; Tanriverdi, K.; Finkielman, J.D.; Davis, J.C.; Hoffman, G.S.; McCUNE, W.J.; Clair, E.W.S.; Specks, U.; Spiera, R.; et al. Relationship Between Markers of Platelet Activation and Inflammation with Disease Activity in Wegener’s Granulomatosis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Gorzelanny, C.; Schneider, S.W. Platelets in Skin Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferroni, P.; Martini, F.; Riondino, S.; La Farina, F.; Magnapera, A.; Ciatti, F.; Guadagni, F. Soluble P-selectin as a marker of in vivo platelet activation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 399, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanowska-Grabowska, R.; Wallace, K.; Field, J.J.; Chen, L.; Marshall, M.A.; Figler, R.; Gear, A.R.; Linden, J. P-Selectin–Mediated Platelet-Neutrophil Aggregate Formation Activates Neutrophils in Mouse and Human Sickle Cell Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2392–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etulain, J.; Martinod, K.; Wong, S.L.; Cifuni, S.M.; Schattner, M.; Wagner, D.D. P-selectin promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation in mice. Blood 2015, 126, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadie, J.-M.; Bae, H.-B.; Jiang, S.; Park, D.W.; Bell, C.P.; Yang, H.; Pittet, J.-F.; Tracey, K.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; et al. HMGB1 promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation through interactions with Toll-like receptor 4. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L342–L349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchfeld, A.; Wendt, M.; Bratt, J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Chavan, S.; Tracey, K.J.; Palmblad, K.; Gunnarsson, I. High-Mobility Group Box-1 Protein (HMGB1) Is Increased in Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmatic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis with Renal Manifestations. Mol. Med. 2010, 17, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliyev, B.K.; Menshikov, M. Comparative evaluation of the role of the adhesion molecule CD177 in neutrophil interactions with platelets and endothelium. Eur. J. Haematol. 2012, 89, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
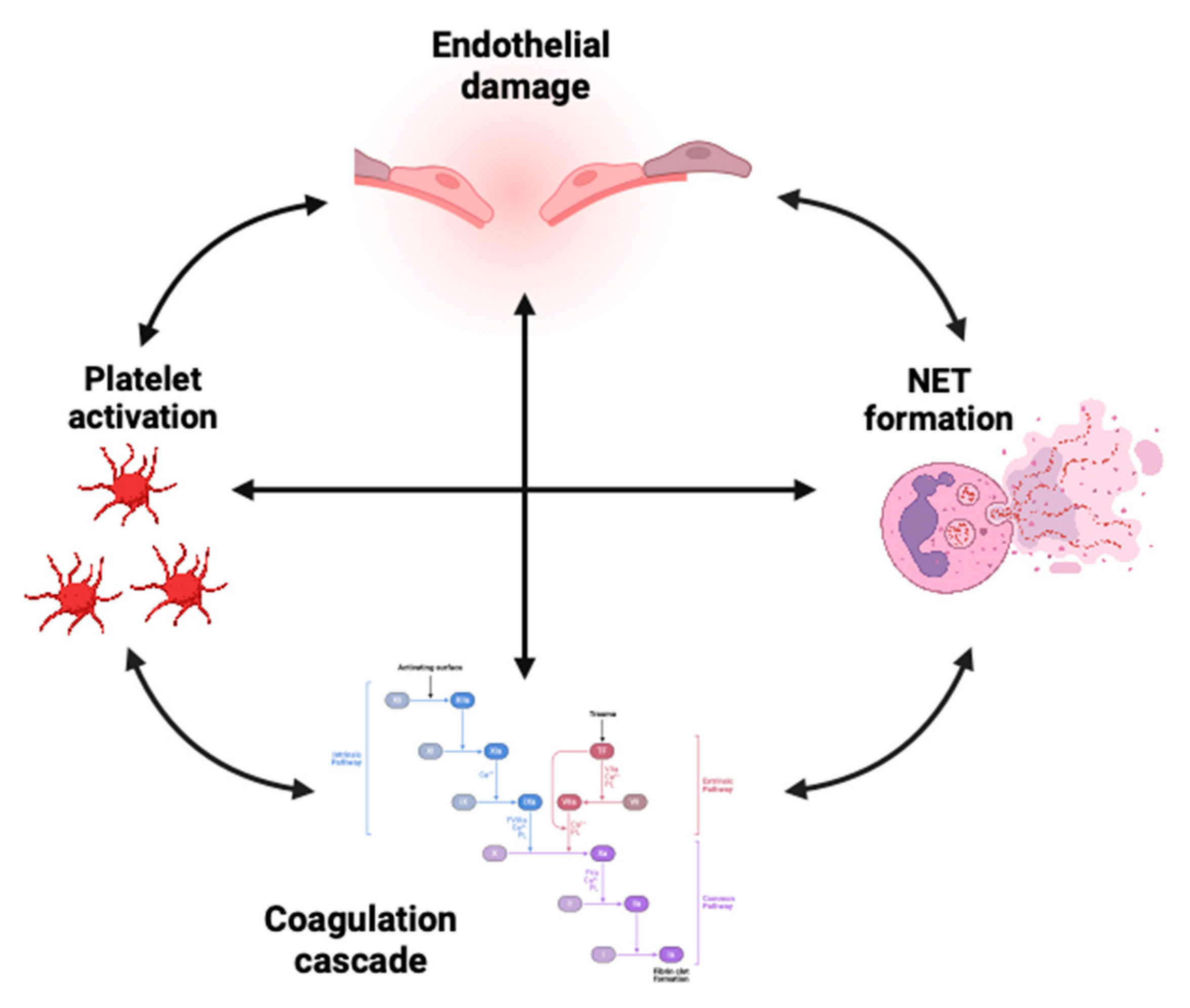
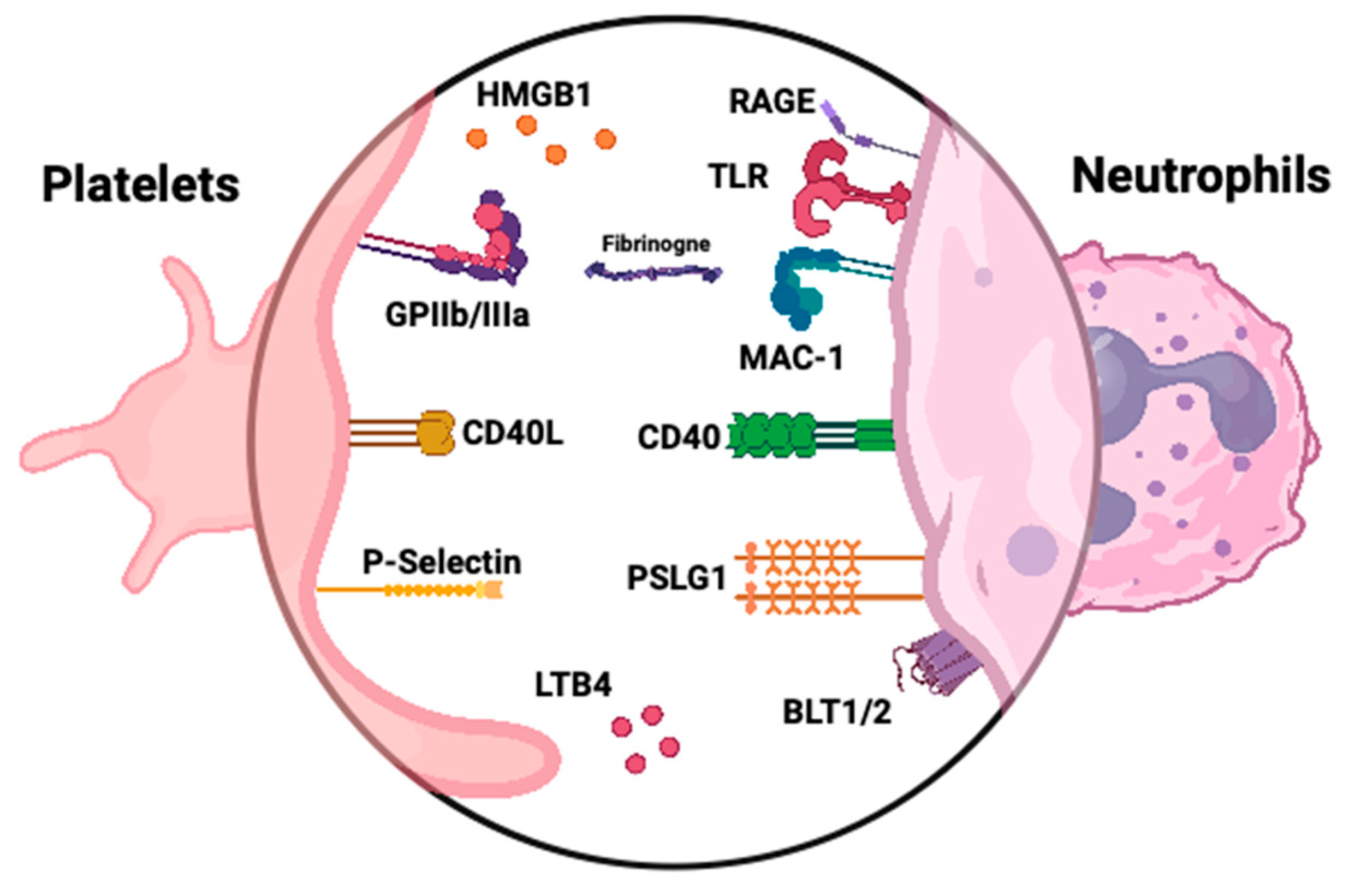
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




