Submitted:
14 April 2025
Posted:
15 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
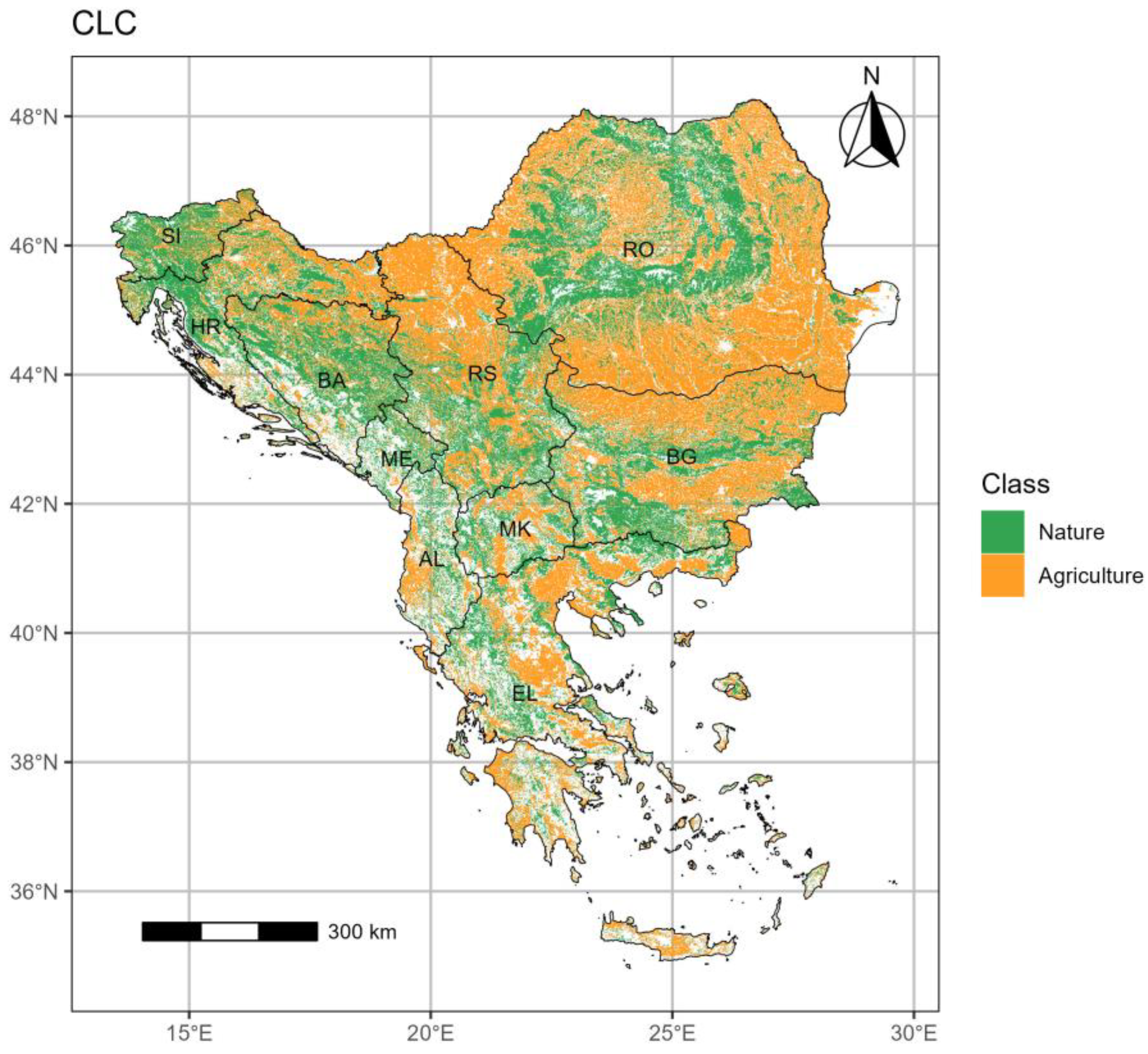
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
Johansson Continentality Index
Kerner Oceanity Index (KOI)
Pinna Combinative Index (PINNA)
3. Results
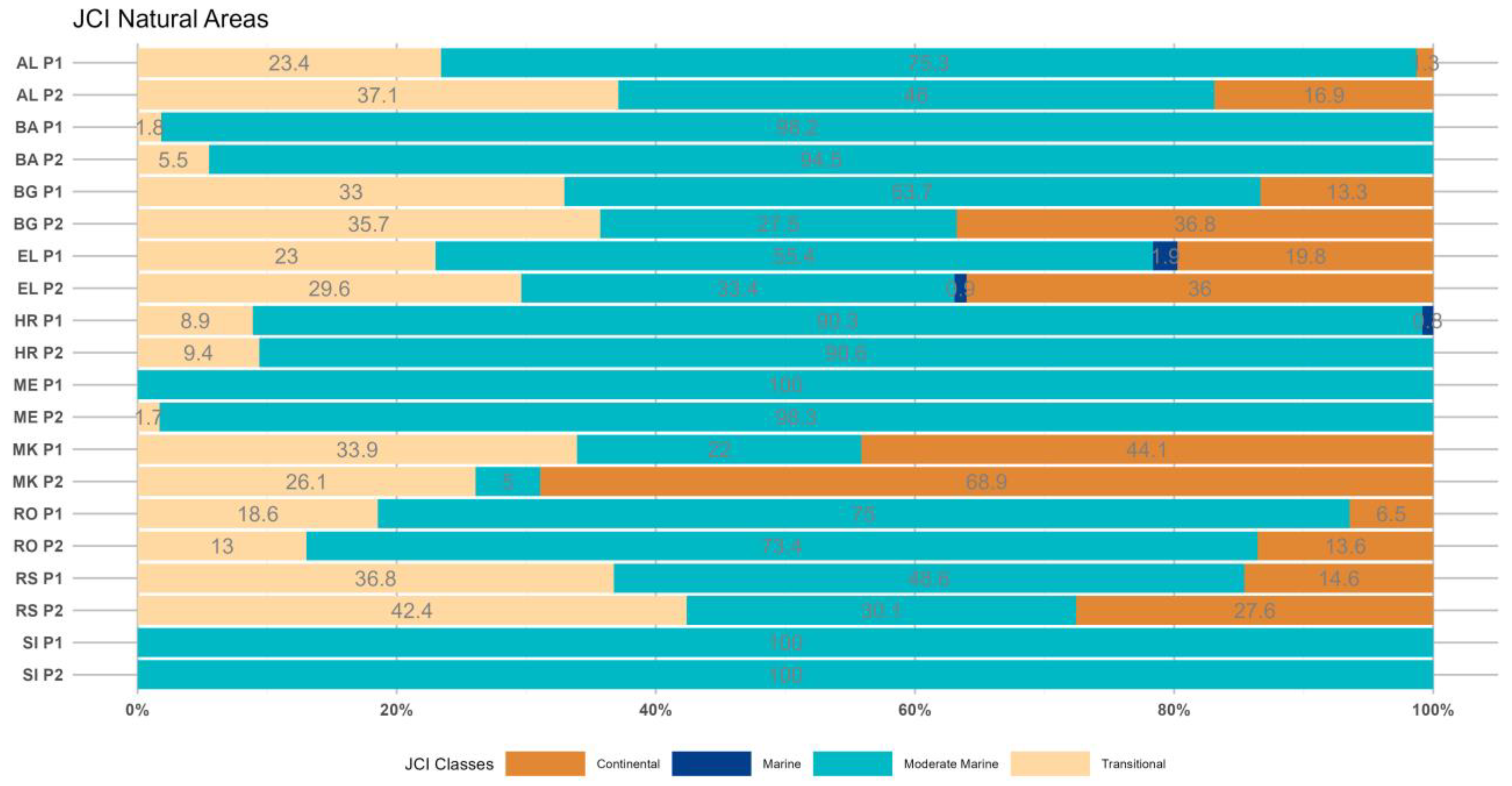
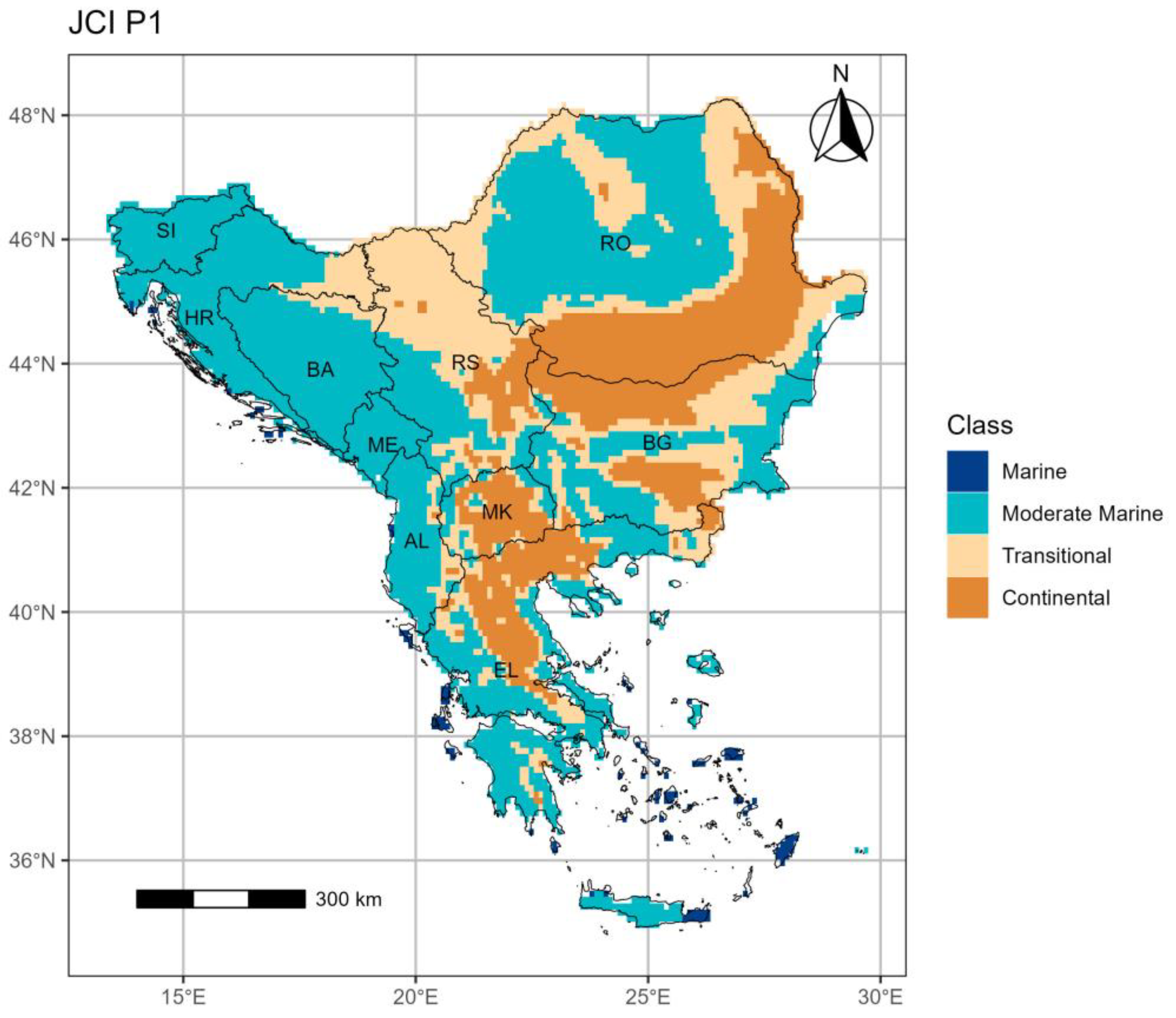
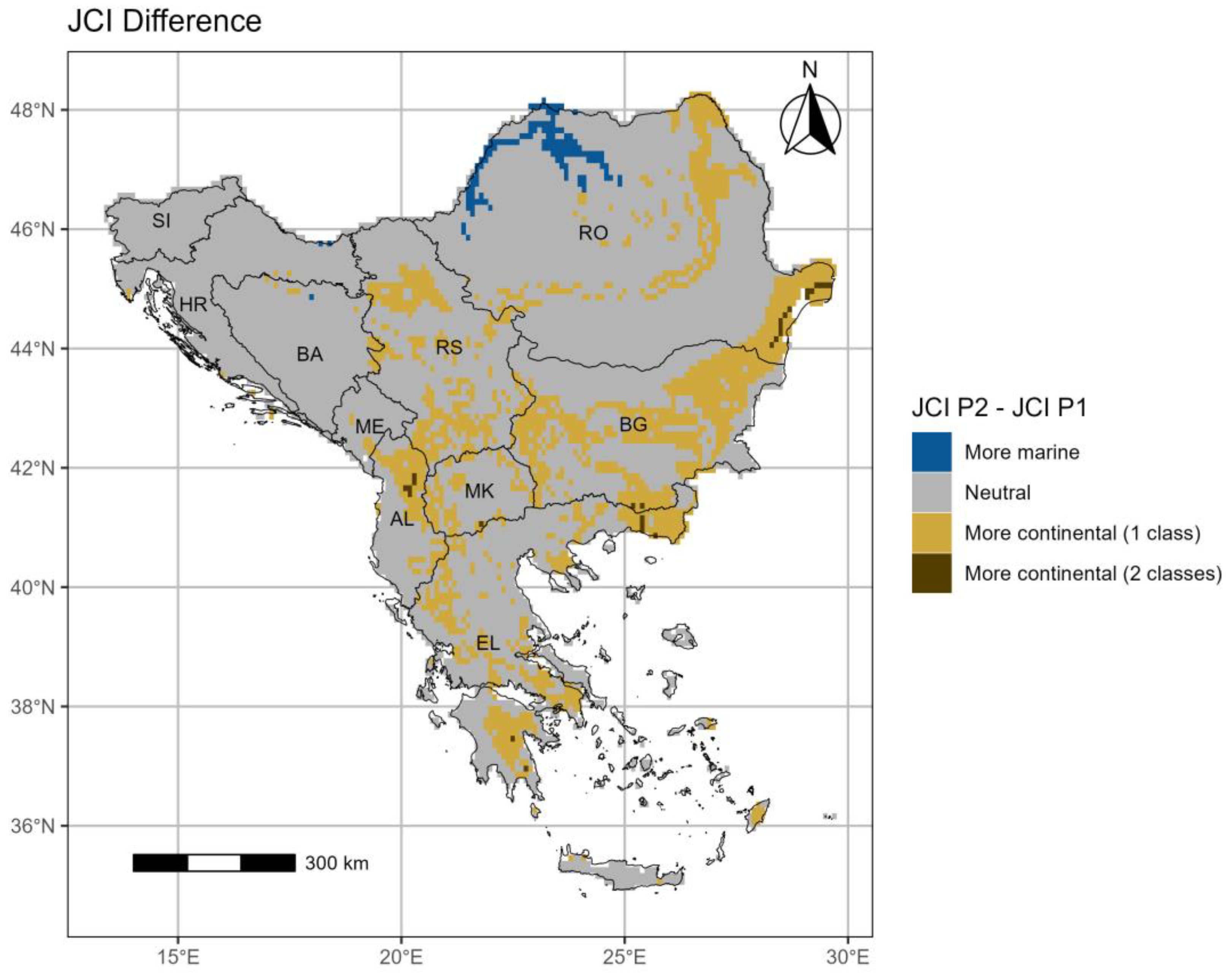
3.1. The Johansson Continentality Index (JCI)
3.1.1. Period 1 (p1: 1964–1993)
3.1.2. Period 2 (p2: 1994–2023)
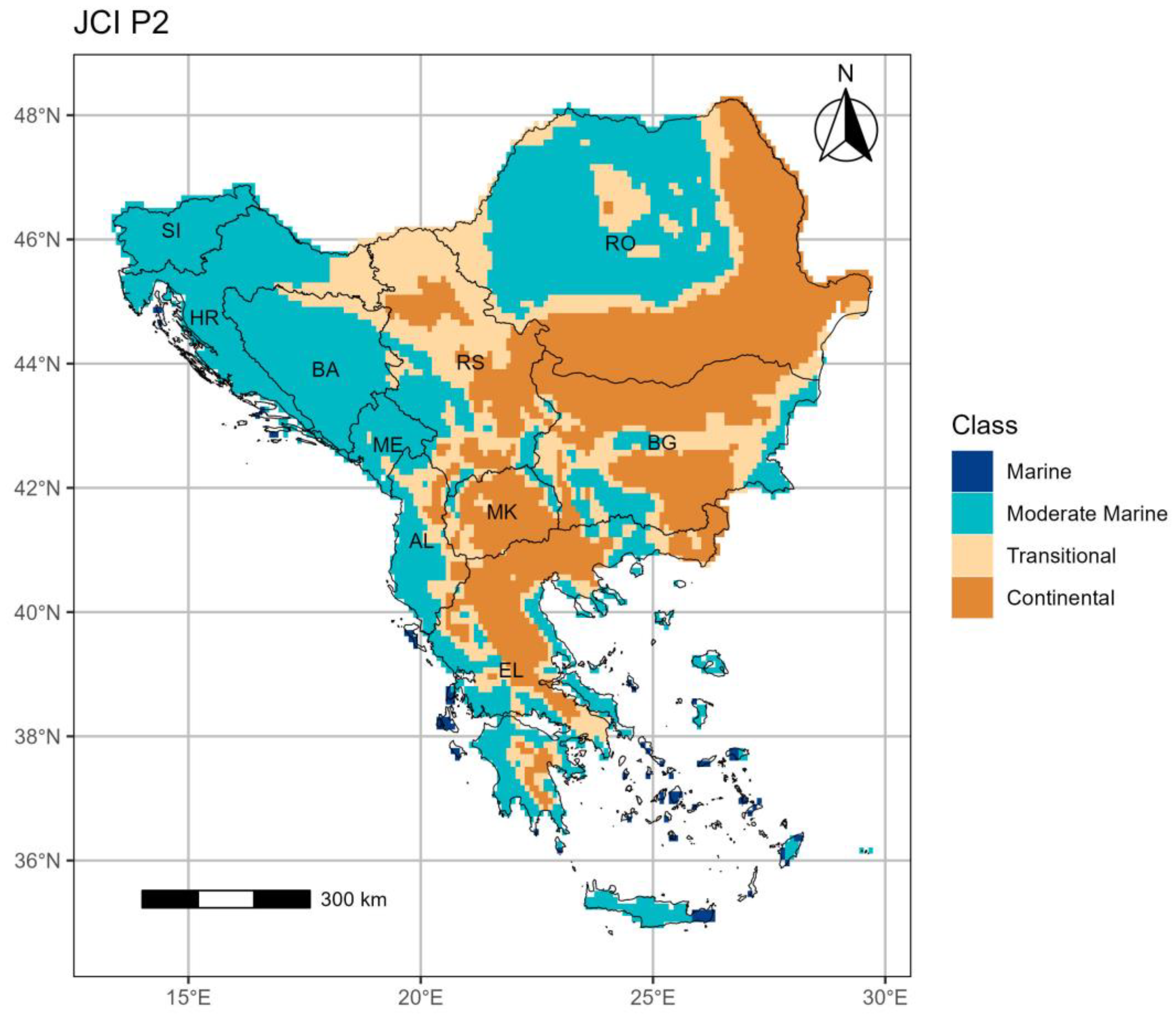

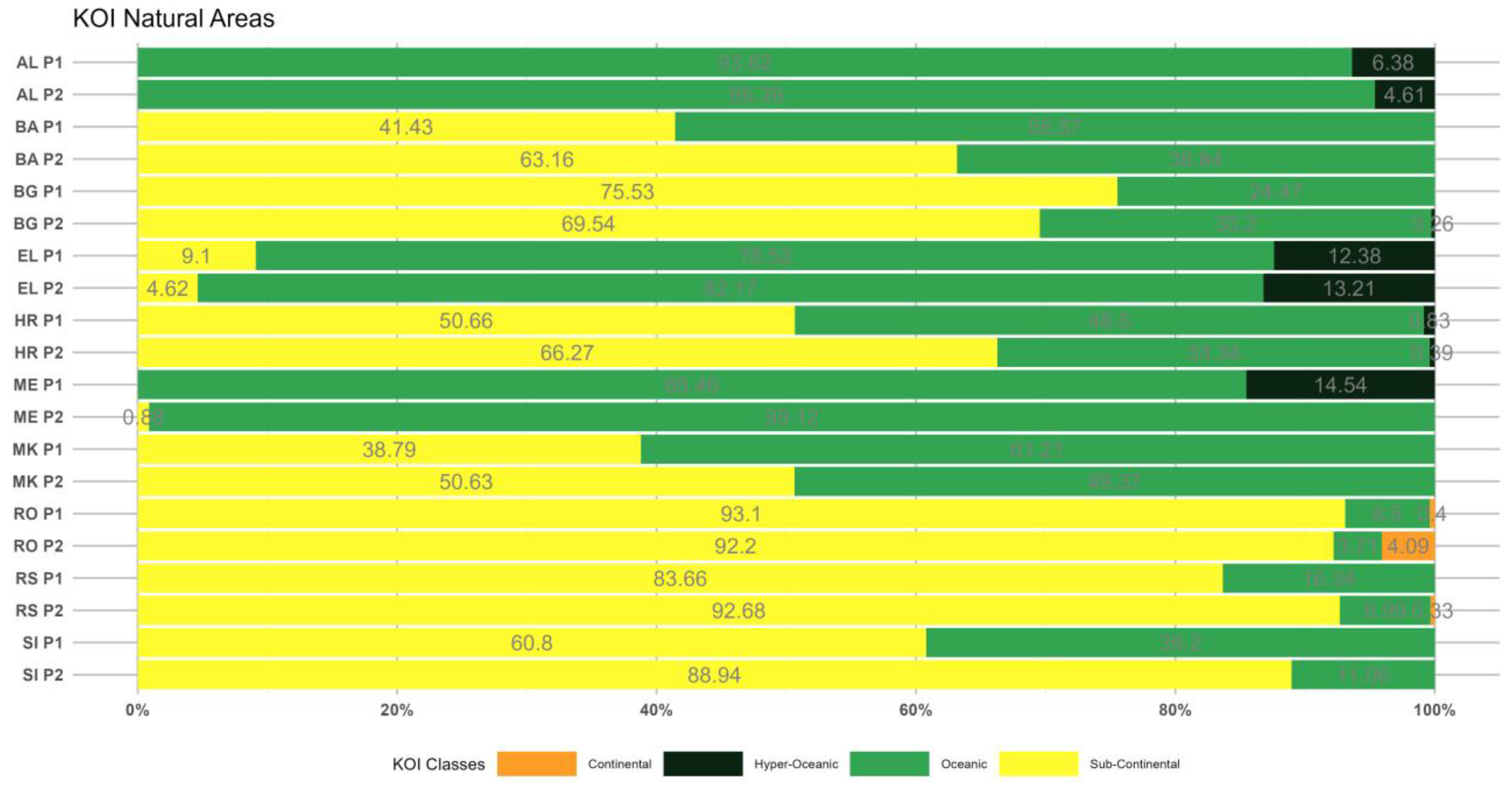
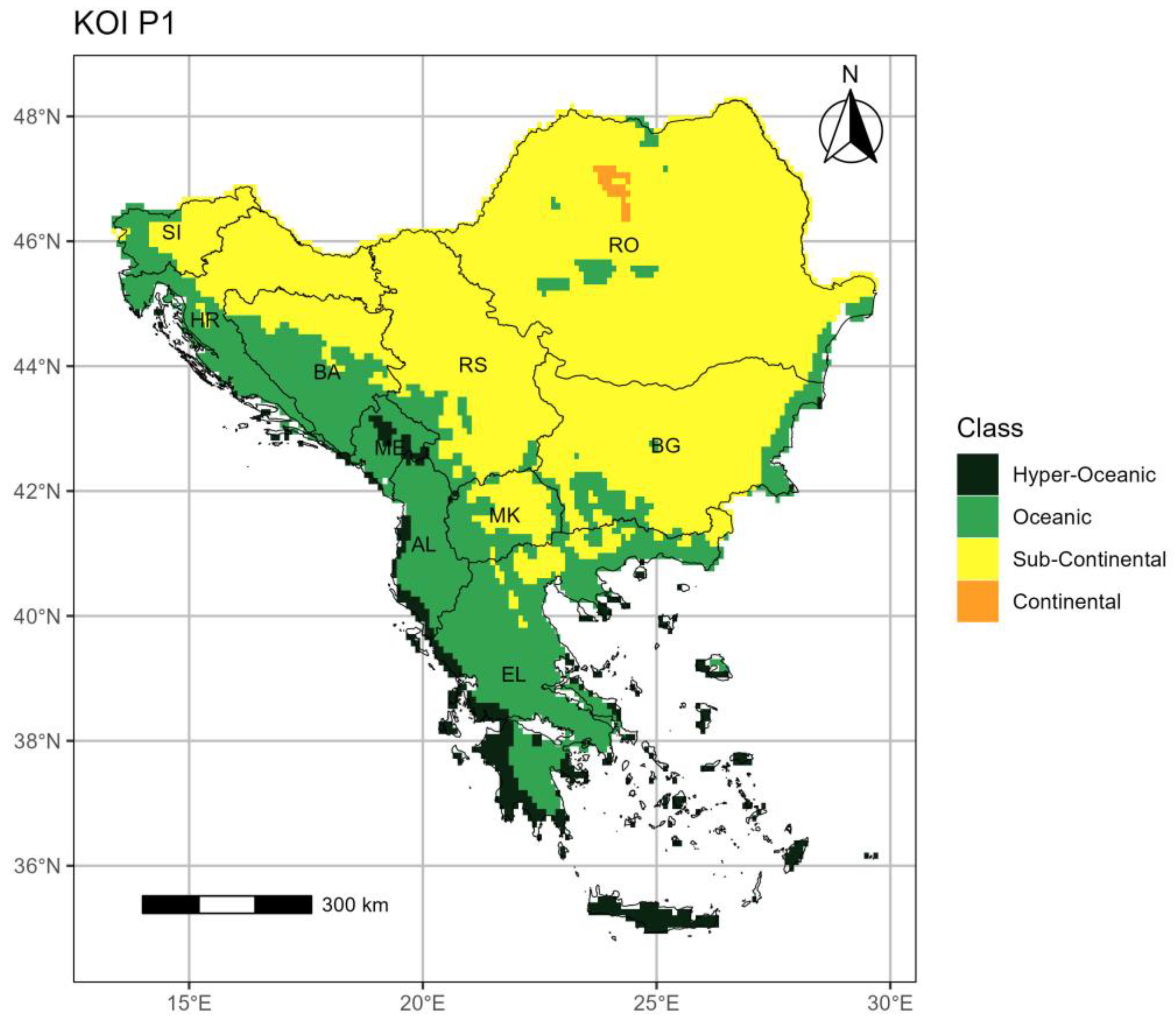
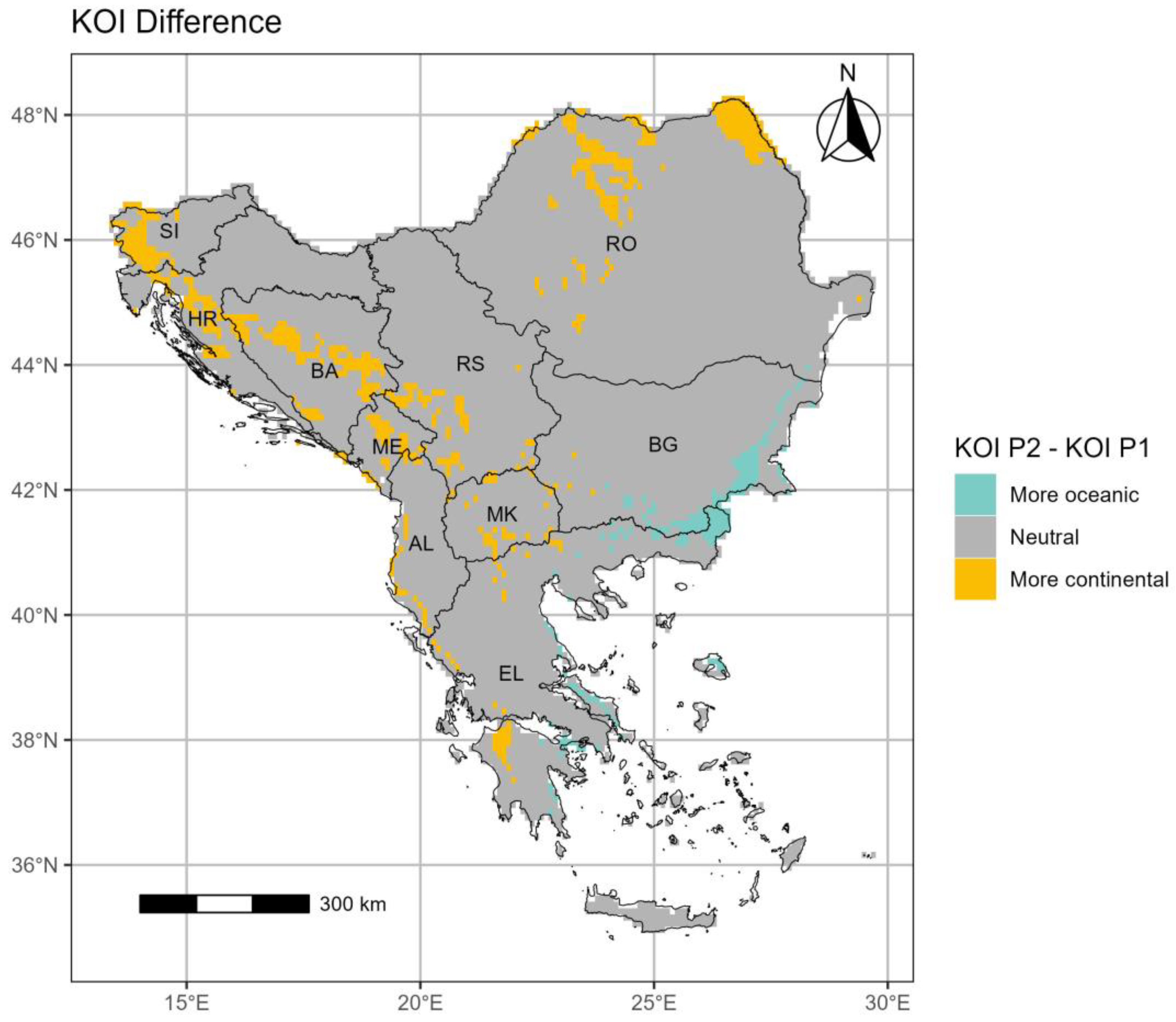
3.2. The Kerner Oceanicity index (KOI)
3.2.1. Period 1 (p1: 1964–1993)
3.2.2. Period 2 (p2: 1994–2023)
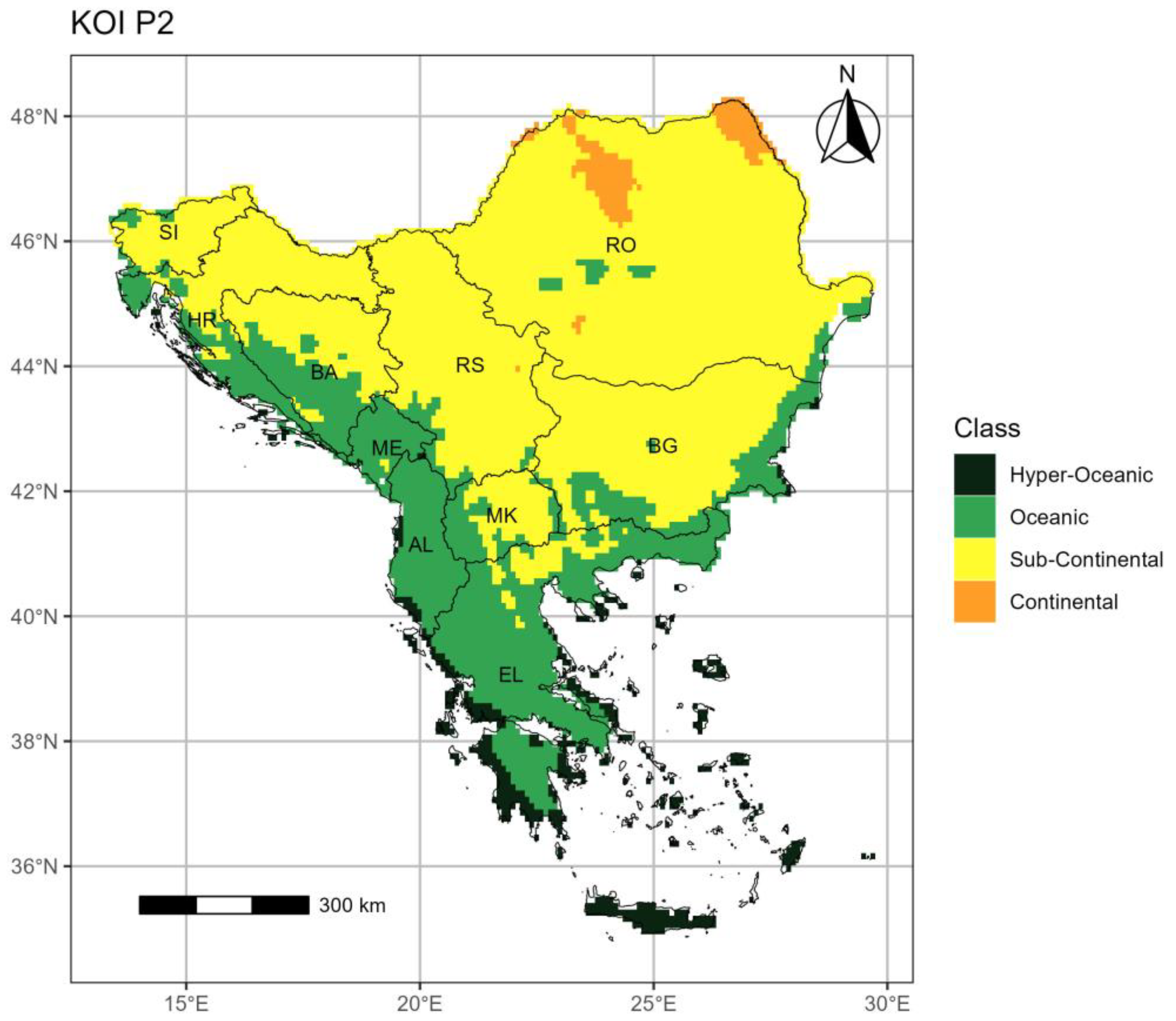
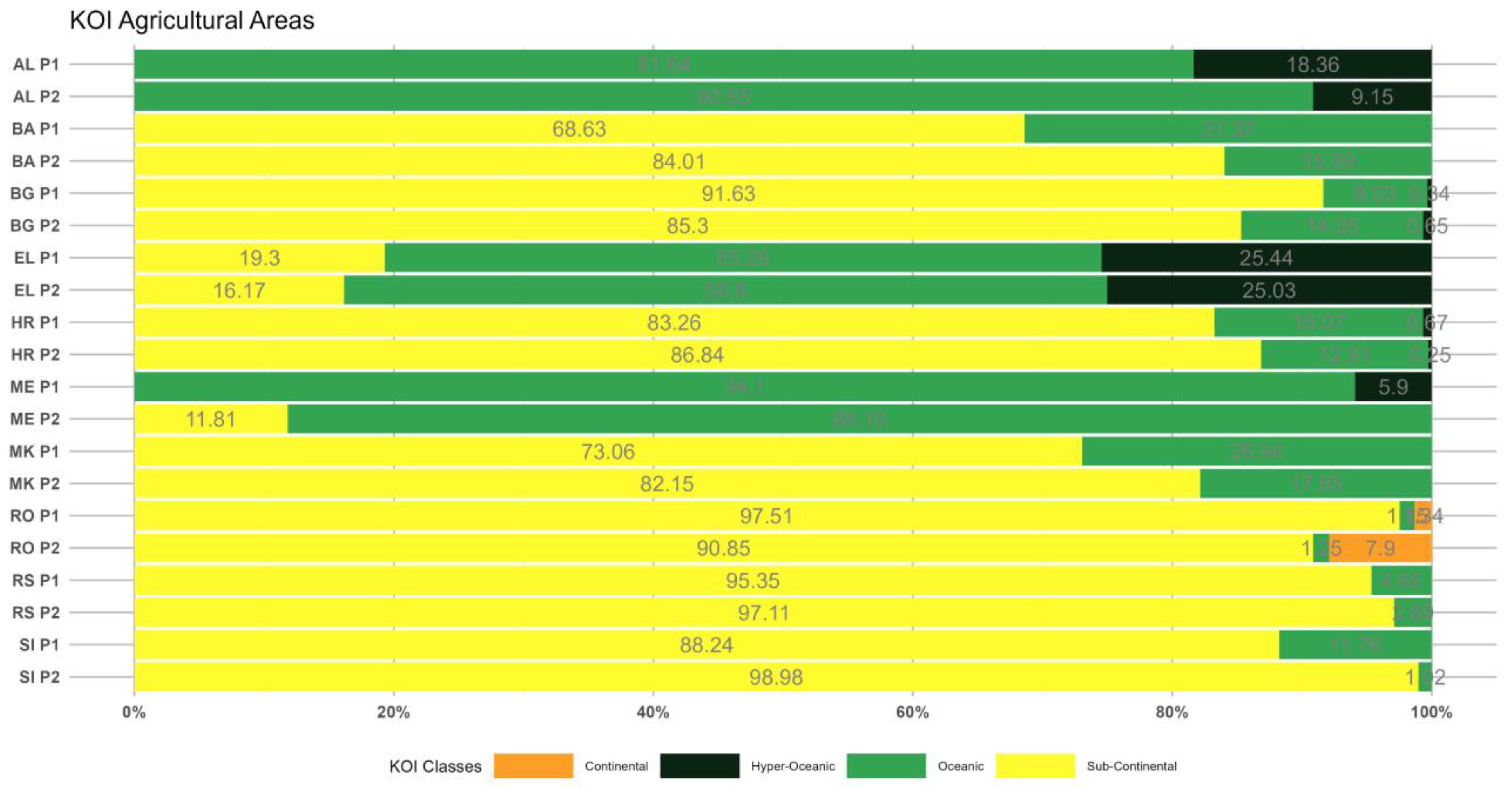
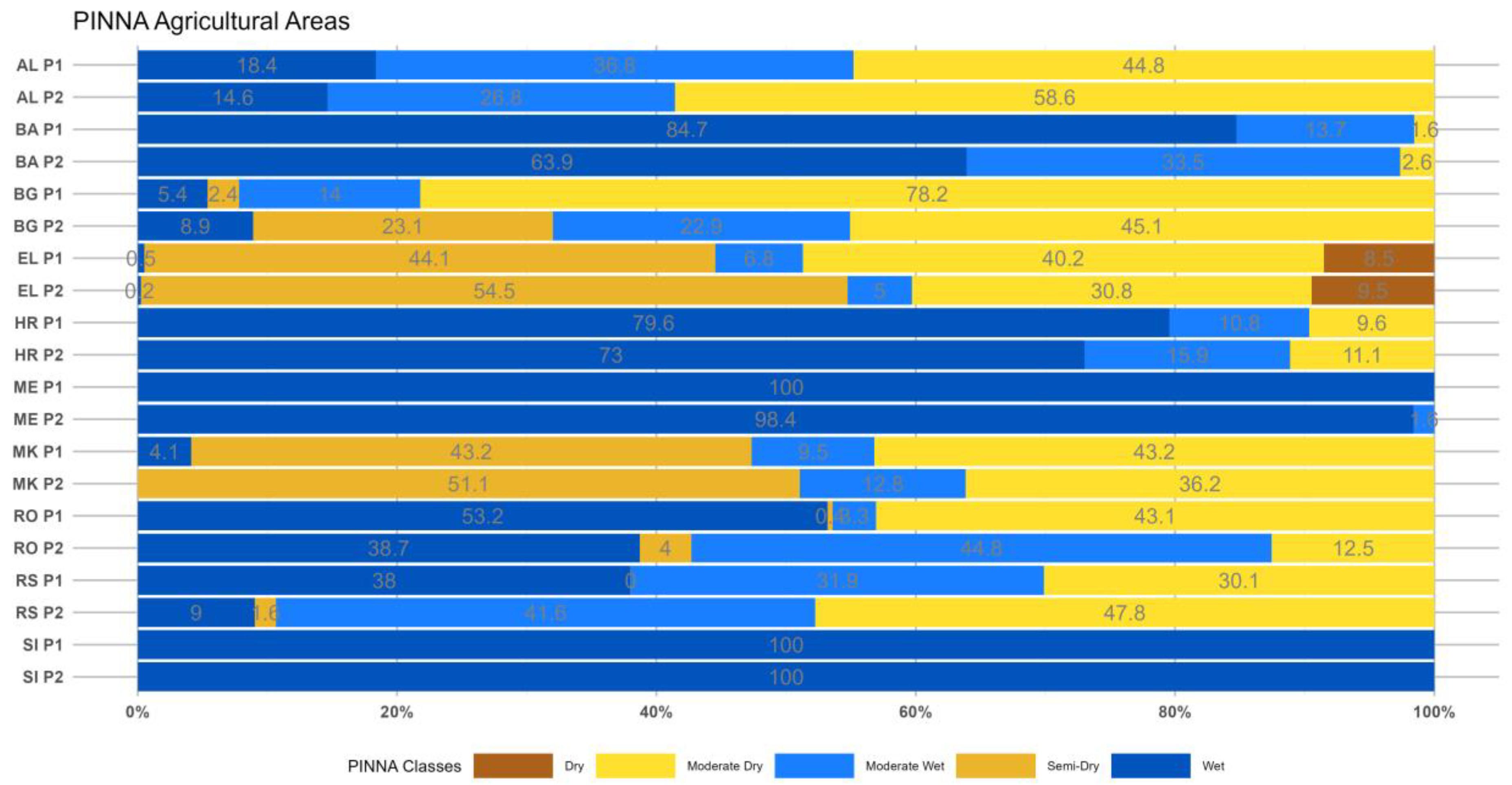
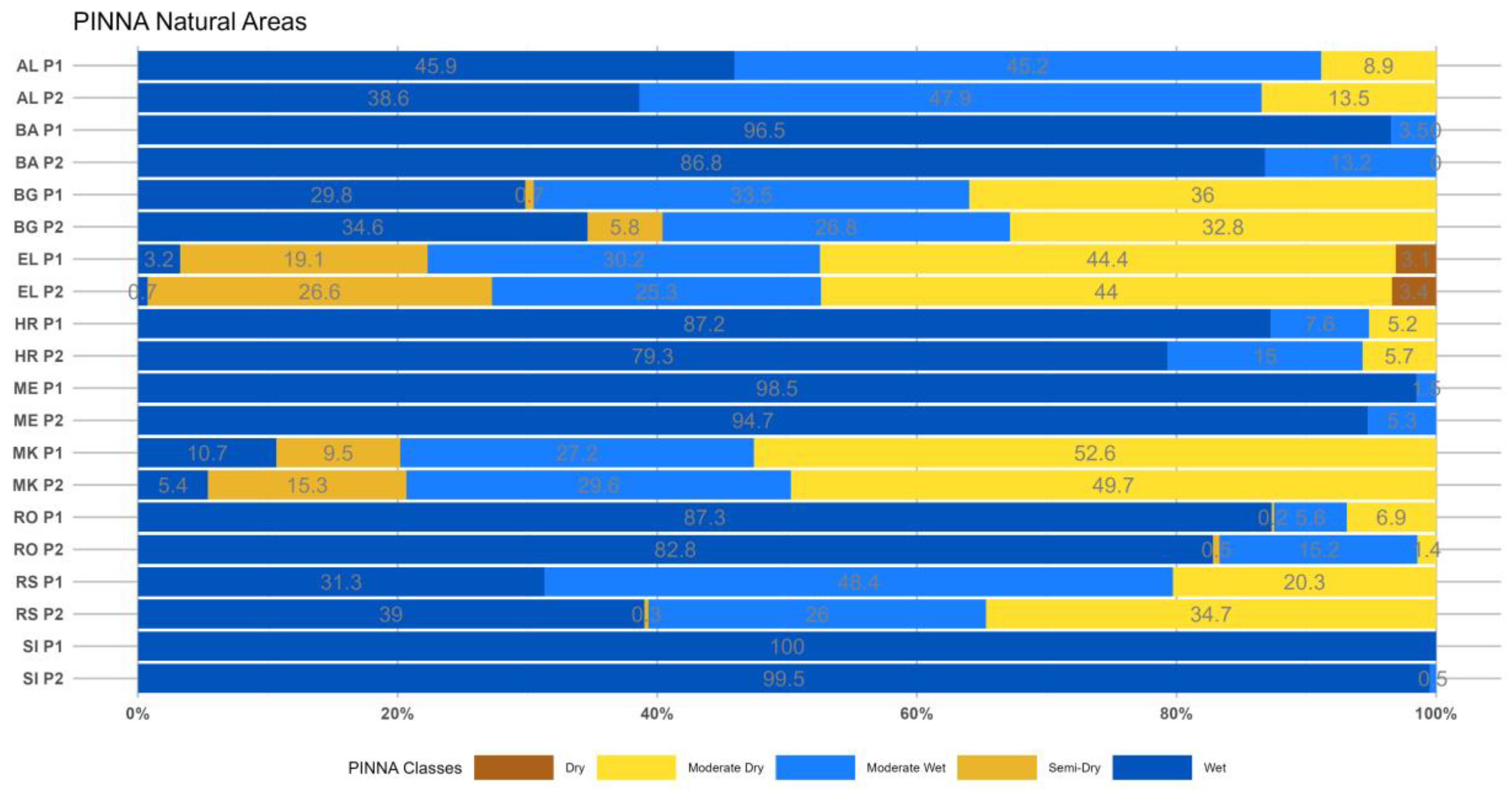
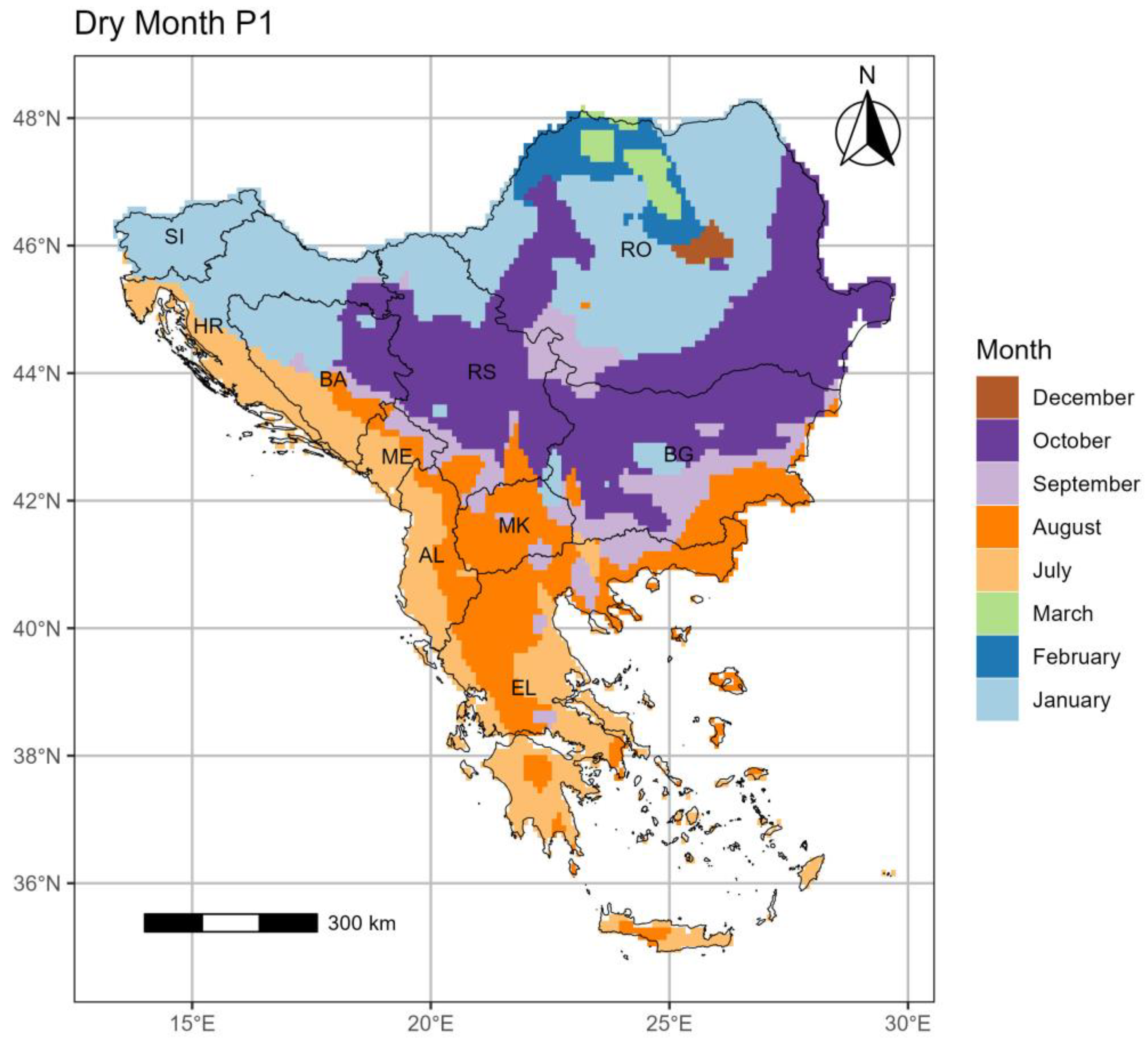
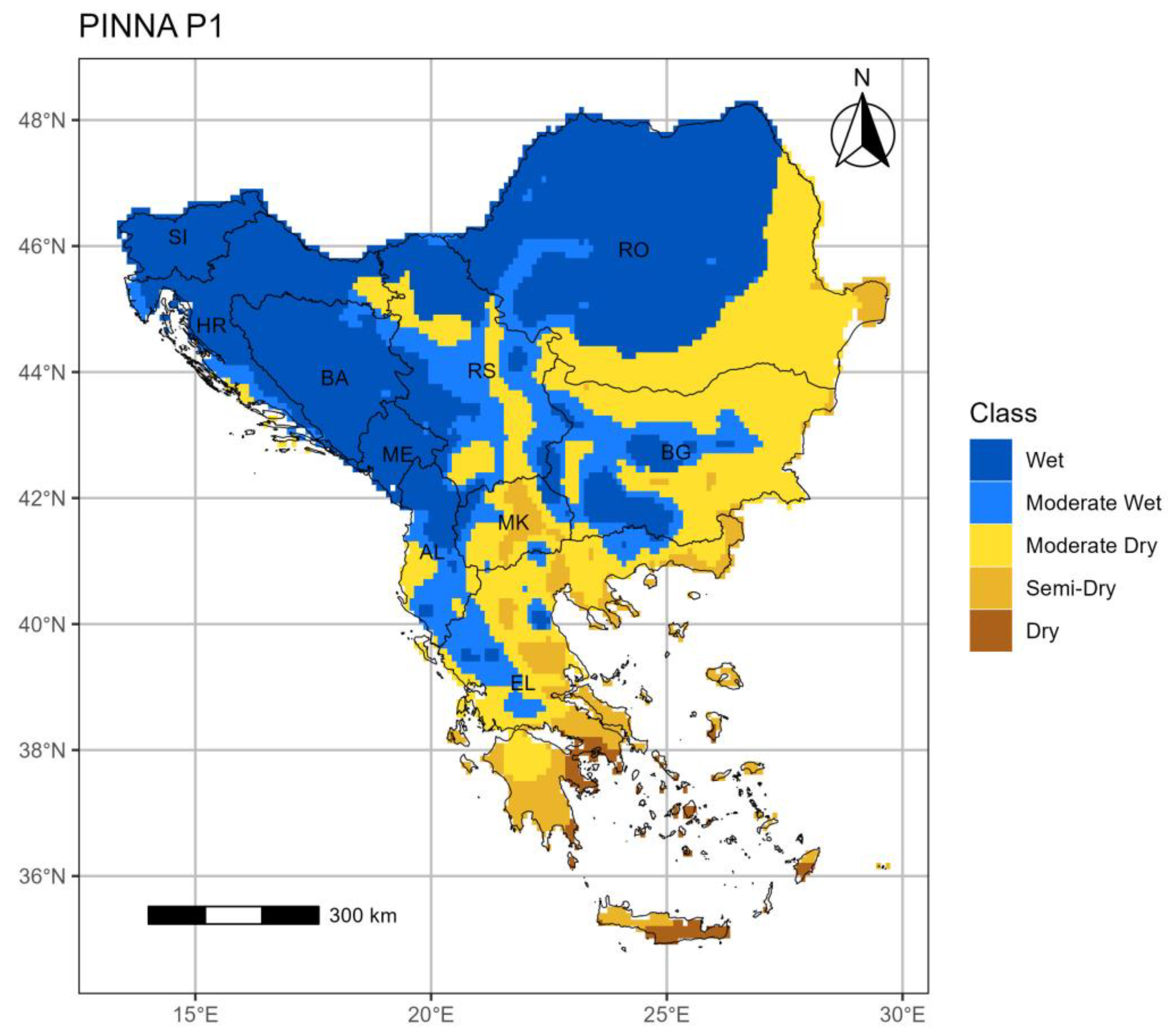
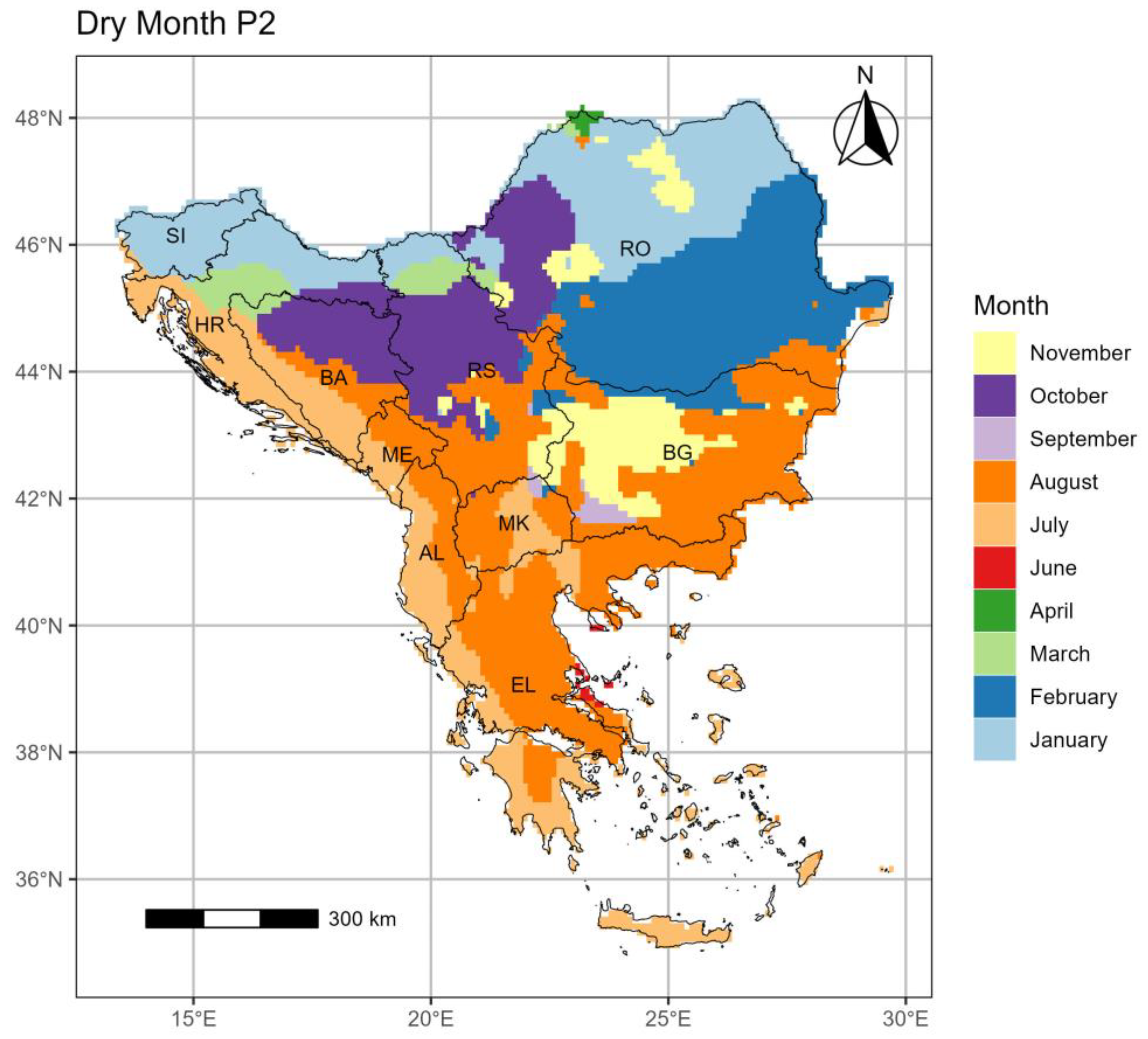
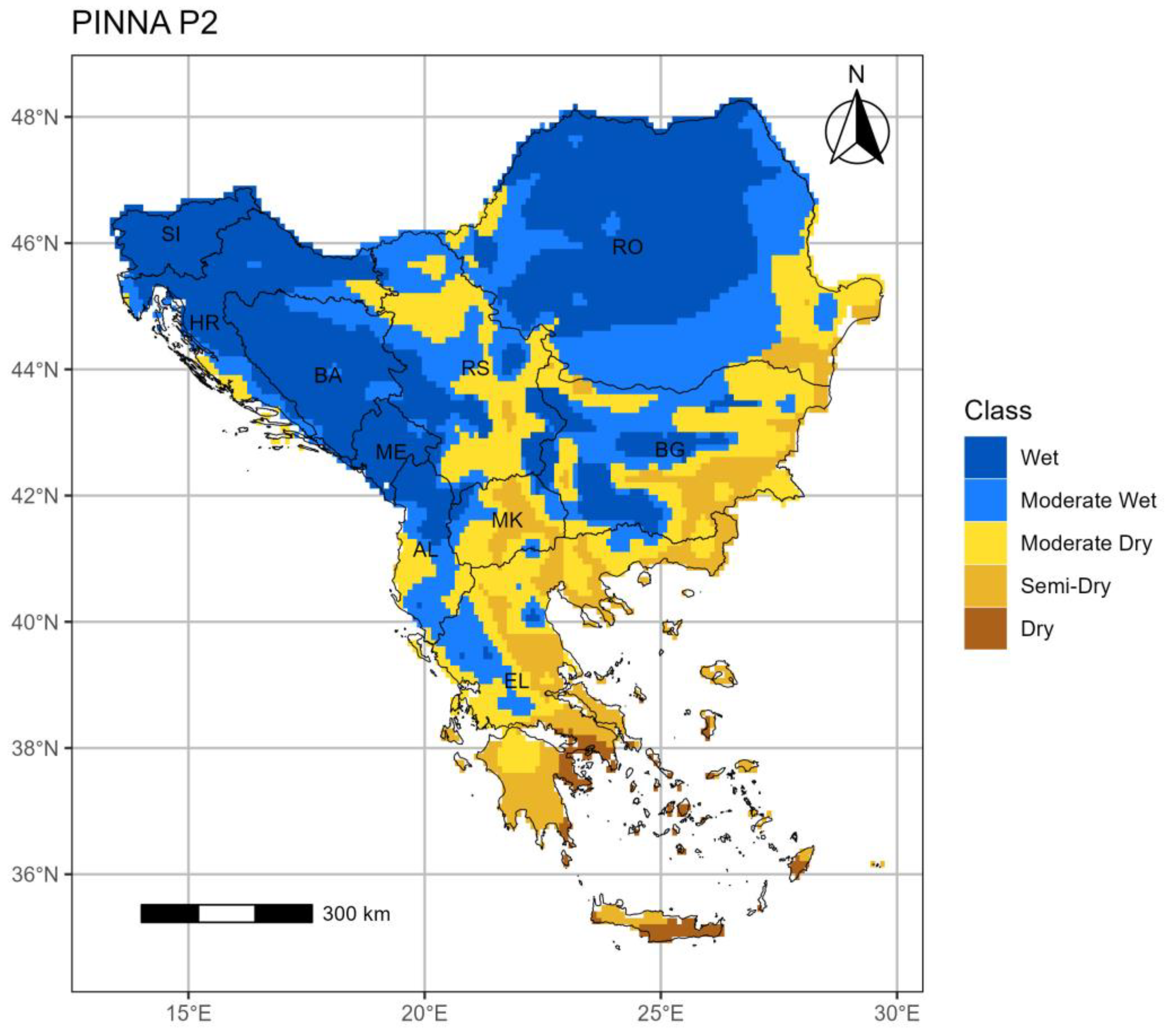
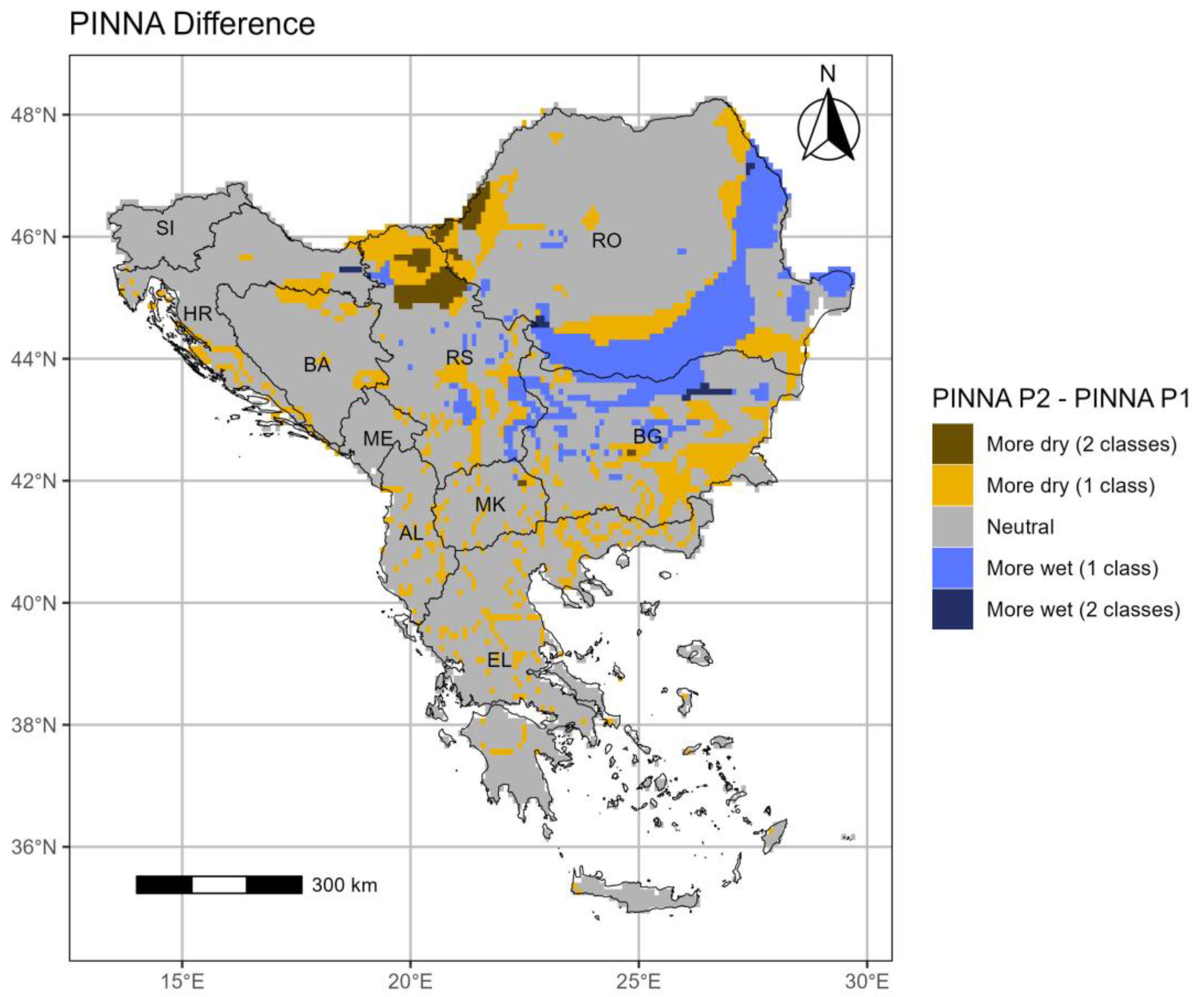
3.3. The Pinna Combinative index (PINNA)
3.3.1. Period 1 (p1: 1964–1993)
3.3.2. Period 2 (p2: 1994–2023)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Independently of the employed index (JCI, KOI or PINNA), the climatic footprint of the SEEu reveals spatiotemporal increasing continentality and aridity trends.
- The exploited indices seriously contribute to realizing and comprehending the overall alterations of the climate undergone territorially and regionally.
- The JCI demonstrates an increasing continentality trend mostly over the southern and eastern regions of the SEEu. This trend is basically shown by the spatiotemporal expansion of the Continental category over both the AgrA and NatA majorly of BG followed by RS, RO and EL. This is exhibited also over the NatA of AL and MK. The changing climate towards intense continentality arises at the expense mostly of the Moderate Marine conditions. The latter remain spatiotemporally stable over the SI.
- The KOI outcomes illustrate decreasing oceanicity (or increasing continentality) over most of the SEEu attributed to the spatial increase of the Sub-Continental and Continental regimes in the western and northern areas and the concomitant decrease of the Oceanic and Hyper-Oceanic categories over time. The Sub-Continantal expansion is evident over both AgrA and NatA of BA, MK, SI but also over the NatA of HR and RS. The spatiotemporal expansion of the Continental category is exhibited over the AgrA and NatA of RO. On the contrary, oceanicity trends are shown over the AgrA and NatA of BG and to a lesser extent over the AgrA of EL.
- The PINNA climate categories’ distribution displays an increasing aridity trend over the SEEu which appears more intense in the central and eastern regions. This evolution is attributed to the spatiotemporal increase of the Semi-Dry and Moderate Wet climate types at the cost of the Wet conditions in most cases. The higher distribution of the Semi-Dry is majorly apparent over the AgrA and NatA of BG and on a smaller scale over both areas of MK and EL and the AgrA of RO. A remarkable expansion of the Moderate Wet climate is demonstrated over the AgrA and NatA of RO and BA and to a less degree over the respective areas of HR and MK and the AgrA of BG and RS. Slight increase of the Dry is shown over EL, while the Wet regime over SI remains spatiotemporally unmodified.
- Overall, the tendency towards increased continentality and aridity initiates great concern involving the conservation, sustainability and development of the agricultural and natural ecosystems. The increasing temperature and decreasing precipitation expected to comprise more intense phenomena in the future, particularly over the SEEu, may be evaluated as serious risk features and furthermore maybe labeled as threats to sustainability mainly regarding water availability.
- It is moreover highlighted that more agricultural areas are impacted by the Semi-Dry and Continental regimes and depend on irrigation or need supplementary water inputs for the achievement of sustainability goals. Expanded natural formations are influenced by the evolved more xerothermic climates and are therefore already more susceptive to adverse conditions.
- This reality bequeaths the obligation for the implementation of mitigation plans and adaptation measures by considering the gradual spatiotemporal evolution of a dry-thermal trend which appears to be continually increasing up to present but also in the future particularly of the Southeastern European territory.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEEu | South-Eastern Europe |
| AL | Albania |
| BA | Bosnia Herzegovina |
| BG | Bulgaria |
| SI | Croatia |
| EL | Greece |
| ME | Montenegro |
| MK | North Macedonia |
| RO | Romania |
| RS | Serbia |
| SI | Slovenia |
| JCI | Johansson Continentality Index |
| KOI | Kerner Oceanity Index |
| PINNA | Pinna Combinative Index |
| AgrA | Agricultural Areas |
| NatA | Natural Areas |
| p1 | First period (1964–1993) |
| p2 | Second period (1994–2023) |
References
- Hernández-Morcillo, M.; Burgess, P.; Mirck, J.; Pantera, A.; Plieninger, T. Scanning Agroforestry-Based Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 80, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Global and European Temperatures (2024) Available online:. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/global-and-european-temperatures (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Naumann, G.; Vogt, J.V. Pan-European Seasonal Trends and Recent Changes of Drought Frequency and Severity. Glob. Planet. Change 2017, 148, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, J.; D’Andrea, F.; Drobinski, P.; Muller, C. Regimes of Precipitation Change Over Europe and the Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2024, 129, e2023JD040413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berényi, A.; Bartholy, J.; Pongrácz, R. Analysis of Precipitation-Related Climatic Conditions in European Plain Regions. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 42, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F.; Tsiros, I.X. Projecting Bioclimatic Change over the South-Eastern European Agricultural and Natural Areas via Ultrahigh-Resolution Analysis of the de Martonne Index. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelebek, M.B.; Batibeniz, F.; Önol, B. Exposure Assessment of Climate Extremes over the Europe–Mediterranean Region. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markonis, Y.; Kumar, R.; Hanel, M.; Rakovec, O.; Máca, P.; AghaKouchak, A. The Rise of Compound Warm-Season Droughts in Europe. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabb9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, V.; Markonis, Y.; Rakovec, O.; Svoboda, M.; Trnka, M.; Kumar, R.; Hanel, M. Europe under Multi-Year Droughts: How Severe Was the 2014–2018 Drought Period? Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakovec, O.; Samaniego, L.; Hari, V.; Markonis, Y.; Moravec, V.; Thober, S.; Hanel, M.; Kumar, R. The 2018–2020 Multi-Year Drought Sets a New Benchmark in Europe. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, G.; Cammalleri, C.; Mentaschi, L.; Feyen, L. Increased Economic Drought Impacts in Europe with Anthropogenic Warming. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Anchukaitis, K.J.; Touchan, R.; Meko, D.M.; Cook, E.R. Spatiotemporal Drought Variability in the Mediterranean over the Last 900 Years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2016, 121, 2060–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistor, M.-M. High-Resolution Projections of the Aridity in Europe under Climate Change. In Climate and Land Use Impacts on Natural and Artificial Systems. Mitigation and Adaptation.; Nistor, M.-M., Ed.; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 73–90 ISBN 978-0-12-822184-6.
- Dascălu, S.; Gothard, M.; Bojariu, R.; Birsan, M.-V.; Cică, R.; Vintila, R.; Adler, M.-J.; Chendeş, V.; Mic, R.-P. Drought-Related Variables over the Bârlad Basin (Eastern Romania) under Climate Change Scenarios. Catena 2016, 141, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Giorgi, F. Increased Aridity in the Mediterranean Region under Greenhouse Gas Forcing Estimated from High Resolution Simulations with a Regional Climate Model. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 62, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltas, E. Spatial distribution of climatic indices in northern Greece. Meteorol. Appl. 2007, 14, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.M. Spatial Distribution of Climate Indices in the Emilia-Romagna Region. Meteorol. Appl. 2016, 23, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheval, S.; Dumitrescu, A.; Birsan, M.-V. Variability of the Aridity in the South-Eastern Europe over 1961–2050. CATENA 2017, 151, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.-M. Climate Change Effect on Groundwater Resources in South East Europe during 21st Century. Quat. Int. 2019, 504, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltas, E.A. Climatic Conditions and Availability of Water Resources in Greece. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2008, 24, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droulia, F.; Charalampopoulos, I. Future Climate Change Impacts on European Viticulture: A Review on Recent Scientific Advances. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droulia, F.; Charalampopoulos, I. A Review on the Observed Climate Change in Europe and Its Impacts on Viticulture. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, G.; Fontana, N.; Mishra, A.K. Investigating Drought in Apulia Region, Italy Using SPI and RDI. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltineanu, C.; Mihailescu, I.F.; Seceleanu, I.; Dragota, C.; Vasenciuc, F. Using Aridity Indices to Describe Some Climate and Soil Features in Eastern Europe: A Romanian Case Study. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007, 90, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corduneanu, F.; Țopa, D.-C.; Balan, I.-E.; Balan, I.; Boți, I.; Pricop, C.; Crețu, A.; Bucur, D. Northeast Romania Water Resources Management in the Context of Climate Change Issue - Iaşi County Case Study. Romanian Agric. Res. 2021, 38, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aridity - American Meteorological Society (AMS) - Glossary of Meteorology Available online:. Available online: https://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Aridity (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Charalampopoulos, I. Agrometeorological Conditions and Agroclimatic Trends for the Maize and Wheat Crops in the Balkan Region. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F. Frost Conditions Due to Climate Change in South-Eastern Europe via a High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution Dataset. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straffelini, E.; Tarolli, P. Climate Change-Induced Aridity Is Affecting Agriculture in Northeast Italy. Agric. Syst. 2023, 208, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şmuleac, L.; Rujescu, C.; Șmuleac, A.; Imbrea, F.; Radulov, I.; Manea, D.; Ienciu, A.; Adamov, T.; Pașcalău, R. Impact of Climate Change in the Banat Plain, Western Romania, on the Accessibility of Water for Crop Production in Agriculture. Agriculture 2020, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Polychroni, I.; Droulia, F.; Nastos, P.T. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Growing Degree Days Agroclimatic Index for Viticulture over the Northern Mediterranean Basin. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Dimopoulos, P. Future Bioclimatic Change of Agricultural and Natural Areas in Central Europe: An Ultra-High Resolution Analysis of the De Martonne Index. Water 2023, 15, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F.; Evans, J. The Bioclimatic Change of the Agricultural and Natural Areas of the Adriatic Coastal Countries. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Dimopoulos, P. Projections on the Spatiotemporal Bioclimatic Change over the Phytogeographical Regions of Greece by the Emberger Index. Water 2024, 16, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Jing, H.; Zheng, Z.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F. Aridification Weakens Ecosystem Services by Reducing Complexity and Stability of Socio-Ecological Networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, V.; El Moçayd, N.; Seker, M.; Seaid, M. Future Projection of Droughts in Morocco and Potential Impact on Agriculture. J. Environ. Manage. 2024, 367, 122019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Salvia, R.; Quaranta, G.; Cudlín, P.; Salvati, L.; Gimenez-Morera, A. Climate Aridity and the Geographical Shift of Olive Trees in a Mediterranean Northern Region. Climate 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F. The Agro-Meteorological Caused Famines as an Evolutionary Factor in the Formation of Civilisation and History: Representative Cases in Europe. Climate 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lickley, M.; Solomon, S. Drivers, Timing and Some Impacts of Global Aridity Change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.; Graciano, C.; Hughes, A.C.; Farré-Armengol, G.; Peñuelas, J. Impact of Aridity Rise and Arid Lands Expansion on Carbon-Storing Capacity, Biodiversity Loss, and Ecosystem Services. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheyruri, Y.; Sharafati, A.; Neshat, A. The Socioeconomic Impact of Severe Droughts on Agricultural Lands over Different Provinces of Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, A.B.; Gebreyohannes, T.; Kahsay, G.H. Modelling Climate Change and Aridity for Climate Impact Studies in Semi-Arid Regions: The Case of Giba Basin, Northern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2025, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronidis, D. ; Theofanous Nikolaos Changes in Climatic Patterns and Tourism and Their Concomitant Effect on Drinking Water Transfers into the Region of South Aegean, Greece. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 35, 1725–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebremedhin, M.A.; Abraha, A.Z.; Fenta, A.A. Changes in Future Climate Indices Using Statistical Downscaling Model in the Upper Baro Basin of Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, M.A.; Kahsay, G.H.; Fanta, H.G. Assessment of Spatial Distribution of Aridity Indices in Raya Valley, Northern Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.-M.; Mîndrescu, M. Climate Change Effect on Groundwater Resources in Emilia-Romagna Region: An Improved Assessment through NISTOR-CEGW Method. Quat. Int. 2019, 504, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Vogt, J.; Naumann, G.; Carrao, H.; Barbosa, P. Towards Identifying Areas at Climatological Risk of Desertification Using the Köppen-Geiger Classification and FAO Aridity Index. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2210–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prăvălie, R.; Bandoc, G. Aridity Variability in the Last Five Decades in the Dobrogea Region, Romania. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Sateriano, A.; Zitti, M. Long-Term Land Cover Changes and Climate Variations – A Country-Scale Approach for a New Policy Target. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, M.B.; An, W.; Xu, C.; Radaković, M.G.; Hao, Q.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z.; Perić, Z.; Gavrilov, G.; Marković, S.B. Independent Aridity and Drought Pieces of Evidence Based on Meteorological Data and Tree Ring Data in Southeast Banat, Vojvodina, Serbia. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bešt́áková, Z.; Strnad, F.; Vargas Godoy, M.R.; Singh, U.; Markonis, Y.; Hanel, M.; Máca, P.; Kyselý, J. Changes of the Aridity Index in Europe from 1950 to 2019. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2023, 151, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, M.B.; Radaković, M.G.; Sipos, G.; Mezősi, G.; Gavrilov, G.; Lukić, T.; Basarin, B.; Benyhe, B.; Fiala, K.; Kozák, P.; et al. Aridity in the Central and Southern Pannonian Basin. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milentijević, N.; Martić-Bursać, N.; Gocić, M.; Ivanović, M.; Strålman, S.O.; Pantelić, M.; Milošević, D.; Stričević, L. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aridity and Humidity Indices in Bačka (Serbia). Pure Appl. Geophys. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, G.; Alexandru, A.-M.; Nita, I.-A.; Birsan, M.-V. Climate Change in the Provenance Regions of Romania over the Last 70 Years: Implications for Forest Management. Forests 2022, 13, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, N.; Yanakiev, D. Climate Aridity in Southern Bulgaria for the Period 1961-2015. Forum Geogr. 2020, 19, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Sachindra, D.A.; Nowosad, M.; Ullah, W.; Bhatti, A.S.; Jin, Z.; Ali, A. Spatiotemporal Changes in Global Aridity in Terms of Multiple Aridity Indices: An Assessment Based on the CRU Data. Atmospheric Res. 2022, 268, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrnjak, I.; Gavrilov, M.; Markovic, S.; Lukic, T.; Tošić, I.; Unkašević, M. Special Software for Aridity Indices Calculation (AICS); Vojvodina, Serbia Case Study. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic 2013, 63, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbac-Cotoara-Zamfir, R. Changes in Agricultural Water Demands for Western Romania. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 42nd international symposium on agricultural engineering.
- My, L.; Di Bacco, M.; Scorzini, A.R. On the Use of Gridded Data Products for Trend Assessment and Aridity Classification in a Mediterranean Context: The Case of the Apulia Region. Water 2022, 14, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, A.; Toros, H.; Incecik, S. Spatial Variations of Climate Indices in Turkey. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Continentality - American Meteorological Society (AMS) - Glossary of Meteorology Available online:. Available online: https://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Continentality (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Stine, A.R.; Huybers, P. Changes in the Seasonal Cycle of Temperature and Atmospheric Circulation. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7362–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balybina, A.S.; Osipova, O.P. Climate Continentality in Cisbaikalia in Different Circulation Epochs. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2024, 45, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschi, J.; Sinha, B.; Josey, S. Global Warming and Changes of Continentality since 1948. Weather 2007, 62, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonevicius, E.; Stankunavicius, G.; Rimkus, E. Continentality and Oceanity in the Mid and High Latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere and Their Links to Atmospheric Circulation. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 5746191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó-Takács, B.; Farda, A.; Zahradníček, P.; Stepanek, P. Continentality in Europe According to Various Resolution Regional Climate Models with A1B Scenario in the 21st Century. Időjárás 2015, 119, 515–535. [Google Scholar]
- Ciaranek, D. Variability of the Thermal Continentality Index in Central Europe. In Proceedings of the ”Air and Water, Components of the Environment”; Cluj-Napoca, Romania, March 21 2014; pp. 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Brázdil, R.; Chromá, K.; Dobrovolný, P.; Tolasz, R. Climate Fluctuations in the Czech Republic during the Period 1961–2005. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilček, J.; Jaroslav, S.; Vido, J.; Nalevanková, P.; Kandrík, R.; Škvareninová, J. Minimal Change of Thermal Continentality in Slovakia within the Period 1961–2013. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2016, 7, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlăduţ, A. Ștefania Thermal Continentality in Romania (Period 1961–2018). Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriano, C.; Gutiérrez, E.; Colangelo, M.; Gazol, A.; Sánchez-Salguero, R.; Tumajer, J.; Shishov, V.; Bonet, J.A.; Martínez de Aragón, J.; Ibáñez, R.; et al. Seasonal Precipitation and Continentality Drive Bimodal Growth in Mediterranean Forests. Dendrochronologia 2023, 78, 126057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Corte-Real, J.A. Spatial Distribution of Climate Indices in the Iberian Peninsula. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1648, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, A.M.E.; McCabe, M.F.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Robaa, S.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. Recent Changes in Continentality and Aridity Conditions over the Middle East and North Africa Region, and Their Association with Circulation Patterns. Clim. Res. 2016, 69, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ols, C.; Gschwantner, T.; Schadauer, K.; Bontemps, J.-D. Unexpected Negative Effect of Available Water Capacity Detected on Recent Conifer Forest Growth Trends Across Wide Environmental Gradients. Ecosystems 2022, 25, 404–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlăduţ, A.; Nikolova, N.; Licurici, M. Evaluation of Thermal Continentality within Southern Romania and Northern Bulgaria (1961-2015). Geofizika 2018, 35, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oceanicity - American Meteorological Society AMS) - Glossary of Meteorology Available online:. Available online: https://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Oceanicity (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Gavilán, R. The Use of Climatic Parameters and Indices in Vegetation Distribution. A Case Study in the Spanish Sistema Central. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2005, 50, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschi, P.; Cosentino, C.; Mallia, E.; Trocchi, V. Fertility of the European Brown Hare Across Plain, Hill and Mountain Environments in the Italian Peninsula. Animals 2024, 14, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaisarje, G.K.; Chaudhari, H.S. Influence of Continentality and Oceanity Over India During 1981–2010 and Its Teleconnections to ENSO and IOD. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 2443–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachur, A.N.; Skrylnik, G.P. Continentality and Oceanicity as Indicators of the Current Ecological State of the Russian Far East. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2022, 43, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, I.; Droulia, F. A Pathway towards Climate Services for the Agricultural Sector. Climate 2024, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.H.; Alexander, L.V.; Donat, M.G.; Zhang, X.; Bador, M.; Herold, N.; Lippmann, T.; Allan, R.; Aguilar, E.; Barry, A.A.; et al. Development of an Updated Global Land In Situ-Based Data Set of Temperature and Precipitation Extremes: HadEX3. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2020, 125, e2019JD032263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Stalhandske, Z.; Fischer, E.M. Detection of a Climate Change Signal in Extreme Heat, Heat Stress, and Cold in Europe From Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 8363–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A State-of-the-Art Global Reanalysis Dataset for Land Applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Guardia, L.; de Miranda, J.H.; dos Santos Luciano, A.C. Assessment of Irrigation Water Use for Dry Beans in Center Pivots Using ERA5 Land Climate Variables and Sentinel 2 NDVI Time Series in the Brazilian Cerrado. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, D.; Meili, N.; Fatichi, S. Satellite-Based Evidence Highlights a Considerable Increase of Urban Tree Cooling Benefits from 2000 to 2015. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3085–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pacheco-Labrador, J.; Migliavacca, M.; Miralles, D.; Hoek van Dijke, A.; Reichstein, M.; Forkel, M.; Zhang, W.; Frankenberg, C.; Panwar, A.; et al. Widespread and Complex Drought Effects on Vegetation Physiology Inferred from Space. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.I.; Conradi, T.; Muhoko, E. Shifts in Vegetation Activity of Terrestrial Ecosystems Attributable to Climate Trends. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, L.A.; Portela, M.M.; Moreira Freitas, L.M.; Gharbia, S. Addressing the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Heatwaves in Portugal with a Validated ERA5-Land Dataset (1980–2021). Water 2023, 15, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltas, E. Spatial distribution of climatic indices in northern Greece. Meteorol. Appl. 2007, 14, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheval, S.; Dumitrescu, A.; Birsan, M.-V. Variability of the Aridity in the South-Eastern Europe over 1961–2050. CATENA 2017, 151, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Bivand, R.; Forner, K.; Ooms, J.; Pebesma, E.; Sumner, M.D. Terra: Spatial Data Analysis Available online:. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=terra (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing Available online:. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Apostol, L.; Sirghea, L. Thermal Continentalism in Europe. In Air & Water Components of the Environment; 2015; pp. 49–55.
- Wypych, A. Variability of the European Climate on the Basis of Differentiation of Indicators of Continentalism. In The Polish Climate in the European Context: An Historical Overview; Przybylak, R., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2010; ISBN 978-90-481-3167-9. [Google Scholar]
- Croitoru, A.-E.; Piticar, A.; Imbroane, A.M.; Burada, D.C. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Aridity Indices Based on Temperature and Precipitation in the Extra-Carpathian Regions of Romania. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.-M.; Dezsi, Ş.; Cheval, S.; Baciu, M. Climate Change Effects on Groundwater Resources: A New Assessment Method through Climate Indices and Effective Precipitation in Beliş District, Western Carpathians. Meteorol. Appl. 2016, 23, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlăduţ, A.; Nikolova, N.; St. Kliment Ohridski University of Sofia, Faculty of Geology and Geography; Licurici, M.; University of Craiova, Faculty of Sciences, Geography Department Aridity Assessment within Southern Romania and Northern Bulgaria. Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. Geogr. Bull. 2017, 79, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlăduţ, A. Ștefania; Licurici, M. Aridity Conditions within the Region of Oltenia (Romania) from 1961 to 2015. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 140, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremija, S.; Brasanac-Bosanac, L.; Ćirković-Mitrović, T.; Stajic, S. Climate Characteristics of Mountain Beech Forests Belt (Fagetum Montanum Illyricum Fuk. et Stef. 1958) on Manjača. Sustain. For. 2019, 79–80, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrnjak, I.; Lukić, T.; Gavrilov, M.B.; Marković, S.B.; Unkašević, M.; Tošić, I. Aridity in Vojvodina, Serbia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, M.B.; Lukić, T.; Janc, N.; Basarin, B.; Marković, S.B. Forestry Aridity Index in Vojvodina, North Serbia. Open Geosci. 2019, 11, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaković, M.G.; Tošić, I.; Bačević, N.; Mladjan, D.; Gavrilov, M.B.; Marković, S.B. The Analysis of Aridity in Central Serbia from 1949 to 2015. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bačević, N.; Vukoičić, D.; Nikolić, M.; Janc, N.; Milentijević, N.; Gavrilov, M. Aridity in Kosovo and Metohija, Serbia. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 12, 563–570. [Google Scholar]
- Gocić, M.; Milentijević, N.; Ivanović, M.; Tošić, I.; Živanović, S.; Bursać, N.M.; Stričević, L. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Aridity Indices in the Region of Southern and Eastern Serbia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2025, 156, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burić, D.; Mihajlović, J.; Ducić, V.; Milenković, M.; Anđelković, G. Contribution to the Study of Climate Change in Serbia Using Continentality, Oceanity, and Aridity Indices. IDŐJÁRÁS 2023, 127, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luković, J.; Burić, D.; Mihajlović, J.; Pejović, M. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Aridity-Humidity Indices in Montenegro. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 4553–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buric, D.; Ivanovic, R.; Milenkovic, M. Indicators of Specificity of Climate: The Example of Podgorica (Montenegro). J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2018, 68, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burić, D.; Milenković, M.; Ducić, V. The Specificities of the Climate of Danilovgrad (Montenegro). Glas Srp Geogr Dru 2019, 99, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanova, H.; Nedkov, S.; Petrov, G. GIS-Based Modelling of Landscape Patterns in Mountain Areas Using Climate Indices and Regression Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 180, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappas, I.; Zorapas, V. ; K. In , K. Estimation and Surface Distribution of Climate Indices in the Water District of Central – Eastern Greece. In Proceedings of the 10th International Hydrogeological Congress of Greece; Thessaloniki, October 8 2014; pp. 397–406. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrakis, A. Climatic Classification of an Industrial Area of Eastern Mediterranean (Thriassio Plain: Greece). In Advances in Meteorology, Climatology and Atmospheric Physics; Helmis, C.G., Nastos, P.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013; ISBN 978-3-642-29172-2. [Google Scholar]
| JCI | Climate classification |
|---|---|
| >20 | Marine |
| [20,32) | Moderate marine |
| [32-34] | Transitional |
| >34 | Continental |
| KOI | Climate classification |
|---|---|
| >20 | Hyper - Oceanic |
| (10,20] | Oceanic |
| (0,10] | Sub-Continental |
| (-10,0] | Continental |
| PINNA | Climate classification |
|---|---|
| >40 | Wet |
| (30,40] | Moderate Wet |
| (20,30] | Moderate Dry |
| (10,20] | Semi-Dry |
| (2.5,10] | Dry |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




