Submitted:
18 March 2025
Posted:
19 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease
2.1. Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System
2.2. Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System
2.3. Sialorrhea and Dysphagia
2.4. Constipation
2.5. Neurogenic Sexual Dysfunction
2.6. Urinary Symptoms
2.7. Cardiac Alterations
2.8. Orthostatic Hypotension
2.9. Seborrhoea and Seborrheic Dermatitis
2.10. Anhidrosis/Hyperhidrosis
2.11. Thermoregulatory Alterations
3. Sensory Alterations in Parkinson’s Disease
3.1. Hyposmia
3.2. Ageusia
3.3. Visual Disturbances
3.4. Pain
3.5. Paraesthesias
4. Sleep-Related Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease
5. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Parkinson’s Disease
5.1. Depression
5.2. Apathy
5.3. Anxiety
5.4. Visual Hallucinations
5.5. Phantosmia
6. Cognitive Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease
6.1. Inattention and Task-Switching Performance
6.2. Bradyphrenia
6.3. Dementia
6.4. Impulse Control Disorders and Impulsive-Compulsive Behaviours
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-syn | α-synuclein |
| CBT | Cognitive behavioural therapy |
| CPAP | Continuous positive airway pressure |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| CSP | Cortical silent period |
| DBS | Deep brain stimulation |
| DMV | Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus |
| DRT | Dopamine replacement therapy |
| EDS | Excessive daytime sleepiness |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| FOp | Frontal insular operculum |
| ICD | Impulse control disorder |
| MAO-B | Monoamine oxidase B |
| NBM | Nucleus basalis of Meynert |
| NPDs | Neuropsychiatric disorders |
| NSAID | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
| OB | Olfactory bulb |
| OFC | Orbitofrontal cortex |
| OH | Orthostatic hypotension |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnoea |
| PDD | Parkinson’s disease dementia |
| PFC | Prefrontal cortex |
| RBD | REM sleep behaviour disorder |
| REM | Rapid eye movement |
| RLS | Restless legs syndrome |
| SC | Spinal cord |
| SD | Seborrheic dermatitis |
| SN | Substantia nigra |
| SNRI | Serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor |
| SSRI | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| TCA | Tricyclic antidepressant |
| TMS | Transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor alpha |
| UPDRS | Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale |
| VTA | Ventral tegmental area |
References
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarsland, D.; Creese, B.; Politis, M.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Ffytche, D.H.; Weintraub, D.; Ballard, C. Cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2017, 13, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, K.R.; Healy, D.G.; Schapira, A.H.; National Institute for Clinical, E. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease: diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol 2006, 5, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Manuel Rojo-Abuin, J.; Rizos, A.; Rodriguez-Blazquez, C.; Trenkwalder, C.; Perkins, L.; Sauerbier, A.; Odin, P.; Antonini, A.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; et al. Distribution and impact on quality of life of the pain modalities assessed by the King's Parkinson's disease pain scale. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2017, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, A.; Jenner, P.; Ray Chaudhuri, K. Non-motor Parkinson's: integral to motor Parkinson's, yet often neglected. Pract Neurol 2014, 14, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Sastre, M.; Del Tredici, K. Development of alpha-synuclein immunoreactive astrocytes in the forebrain parallels stages of intraneuronal pathology in sporadic Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2007, 114, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, H.; Goldstein, D.S. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Handb Clin Neurol 2013, 117, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Q.; et al. Characteristics of Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease: A Large Chinese Multicenter Cohort Study. Front Aging Neurosci 2021, 13, 761044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, J. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: Implications for pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurobiol Dis 2020, 134, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.B.; Ledingham, D.; Foster, V.K.; Anderson, K.N.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Galley, D.; Pavese, N.; Pasquini, J. The longitudinal progression of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: A 7-year study. Front Neurol 2023, 14, 1155669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S. Multi-organ autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2011, 17, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Okamoto, L.E.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, C.N.; Park, K.W.; Baek, S.H.; Sung, J.H.; Jeon, N.; Koh, S.B.; Gamboa, A.; et al. Sympathetic dysfunction as an early indicator of autonomic involvement in Parkinson's disease. Clin Auton Res 2024, 34, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.A.; Chelimsky, T.C. Pure autonomic failure. Handb Clin Neurol 2019, 161, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isonaka, R.; Sullivan, P.; Goldstein, D.S. Pathophysiological Significance of alpha-Synuclein in Sympathetic Nerves: In Vivo Observations. Neurology 2025, 104, e210215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K. Where and how alpha-synuclein pathology spreads in Parkinson's disease. Neuropathology 2020, 40, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumimura, Y.; Ikemura, M.; Saito, Y.; Sengoku, R.; Kanemaru, K.; Sawabe, M.; Arai, T.; Ito, G.; Iwatsubo, T.; Fukayama, M.; et al. Analysis of the adrenal gland is useful for evaluating pathology of the peripheral autonomic nervous system in lewy body disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2007, 66, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.C.; Cuenca-Bermejo, L.; Fernandez-Villalba, E.; Martin-Balbuena, S.; da Silva Fernandes, M.J.; Scorza, C.A.; Herrero, M.T. Heart Matters: Cardiac Dysfunction and Other Autonomic Changes in Parkinson's Disease. Neuroscientist 2022, 28, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, T.; Hirayama, M.; Ueda, M.; Katsuno, M.; Sobue, G. Cardiac parasympathetic dysfunction in the early phase of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 2017, 264, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.A.; Kaufmann, H. Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies. Mov Disord 2018, 33, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wamelen, D.J.; Leta, V.; Johnson, J.; Ocampo, C.L.; Podlewska, A.M.; Rukavina, K.; Rizos, A.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Drooling in Parkinson's Disease: Prevalence and Progression from the Non-motor International Longitudinal Study. Dysphagia 2020, 35, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychronis, S.; Nasios, G.; Dardiotis, E.; Messinis, L.; Pagano, G. Pathophysiology and Symptomatology of Drooling in Parkinson's Disease. Healthcare (Basel) 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, J.; Patel, S.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Pagan, F. Sialorrhea in Parkinson's Disease. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Q.; Ge, N.N.; Zhu, H.H.; Sha, Z.T.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.D.; Tian, Y.Y. Dihydroergotoxine mesylate for the treatment of sialorrhea in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2019, 58, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttrup, I.; Warnecke, T. Dysphagia in Parkinson's Disease. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, G.; Furuya, H. Management of Dysphagia in Patients with Parkinson's Disease and Related Disorders. Intern Med 2020, 59, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeit, B.; Berkovich, E.; Claus, I.; Roderigo, M.; Schwake, A.L.; Izgelov, D.; Mimrod, D.; Ahring, S.; Oelenberg, S.; Muhle, P.; et al. Dysphagia for medication in Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, G.; Avenali, M.; Schindler, A.; Pizzorni, N.; Montomoli, C.; Abbruzzese, G.; Antonini, A.; Barbiera, F.; Benazzo, M.; Benarroch, E.E.; et al. A multinational consensus on dysphagia in Parkinson's disease: screening, diagnosis and prognostic value. J Neurol 2022, 269, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Liria, R.; Parra-Egeda, J.; Vega-Ramirez, F.A.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M.; Trigueros-Ramos, R.; Morales-Gazquez, M.J.; Rocamora-Perez, P. Treatment of Dysphagia in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Huang, J.P.; Tan, Y.C.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Y. The effectiveness and safety of botulinum toxin injections for the treatment of sialorrhea with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 2023, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, D.; Stover, N.; Shprecher, D.R.; Hamedani, A.G.; Pfeiffer, R.F.; Parkman, H.P.; Quigley, E.M.; Cloud, L.J.; Other Non-motor Features Working Group of the Parkinson Study, G. Consensus practice recommendations for management of gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2024, 124, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savica, R.; Boeve, B.F.; Mielke, M.M. When Do alpha-Synucleinopathies Start? An Epidemiological Timeline: A Review. JAMA Neurol 2018, 75, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchi, F.; Torti, M. Constipation in Parkinson's Disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 2017, 134, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.J.; Yu, S.Y.; Zuo, L.J.; Lian, T.H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.D.; Piao, Y.S.; Guo, P.; Liu, L.; Jin, Z.; et al. Parkinson disease with constipation: clinical features and relevant factors. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzitta, G.; Ferrazzoli, D.; Folini, A.; Palamara, G.; Maestri, R. Severe Constipation in Parkinson's Disease and in Parkinsonisms: Prevalence and Affecting Factors. Front Neurol 2019, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa Carrasco, A.J.; Timmermann, L.; Pedrosa, D.J. Management of constipation in patients with Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2018, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raciti, L.; De Cola, M.C.; Ortelli, P.; Corallo, F.; Lo Buono, V.; Morini, E.; Quattrini, F.; Filoni, S.; Calabro, R.S. Sexual Dysfunction in Parkinson Disease: A Multicenter Italian Cross-sectional Study on a Still Overlooked Problem. J Sex Med 2020, 17, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigno, M.D.S.; Amaral Domingues, C.; Araujo Leite, M.A. Sexual Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review of the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale Sexual Dysfunction in Parkinson Disease: A Systematic Review of the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 2023, 36, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haktanir, D.; Yilmaz, S. Sexual Dysfunction and Related Factors in Patients With Parkinson's Disease. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv 2023, 61, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codling, D.; Shaw, P.; David, A.S. Hypersexuality in Parkinson's Disease: Systematic Review and Report of 7 New Cases. Mov Disord Clin Pract 2015, 2, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, W.H. Autonomic dysfunctions in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 2003, 250 Suppl 1, I28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.W.; Mishkin, M. Penile erection evoked from forebrain structures in Macaca mulatta. Arch Neurol 1968, 19, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, Y.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Ackermans, L.; Beuls, E.A. Thalamus and penile erection. Int J Impot Res 2004, 16, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavy-Le Traon, A.; Cotterill, N.; Amarenco, G.; Duerr, S.; Kaufmann, H.; Lahrmann, H.; Tison, F.; Wenning, G.K.; Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; et al. Clinical Rating Scales for Urinary Symptoms in Parkinson Disease: Critique and Recommendations. Mov Disord Clin Pract 2018, 5, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Cui, Y.S.; Yan, R.; Cao, S.S.; Feng, T. Prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms, urinary incontinence and retention in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 977572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, F.; Bartolotta, T.V.; Cosentino, G.; Mastrilli, S.; Arnao, V.; Aridon, P.; Scurria, S.; Pavone, A.; Pavone, C.; D'Amelio, M. Urological dysfunctions in patients with Parkinson's disease: clues from clinical and non-invasive urological assessment. BMC Neurol 2018, 18, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanis, L. alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012, 2, a009399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.; Seol, W.; Son, I.; Ho, D.H. Detection and Assessment of alpha-Synuclein Oligomers in the Urine of Parkinson's Disease Patients. J Parkinsons Dis 2020, 10, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Cui, X.; Yoshimura, N.; Mao, W.; Xu, E.; Wang, Q.; Ou, T. Assessment and Management of Urinary Dysfunction in 187 Patients with Parkinson's Disease. J Parkinsons Dis 2020, 10, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, L.; Singh, R.; Gundeti, M.; Barua, J.M.; Masood, J. Urinary tract dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: a review. Int Urol Nephrol 2012, 44, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.T.; Dendi, R.; Holmes, C.; Goldstein, D.S. Progressive loss of cardiac sympathetic innervation in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 2002, 52, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Bermejo, L.; Almela, P.; Navarro-Zaragoza, J.; Fernandez Villalba, E.; Gonzalez-Cuello, A.M.; Laorden, M.L.; Herrero, M.T. Cardiac Changes in Parkinson's Disease: Lessons from Clinical and Experimental Evidence. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, F.A.; Fiorini, A.C.; Scorza, C.A.; Finsterer, J. Cardiac abnormalities in Parkinson's disease and Parkinsonism. J Clin Neurosci 2018, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Serita, T.; Seto, M.; Tomita, I.; Satoh, H.; Iwanaga, K.; Takashima, H.; Tsujihata, M. Loss of 123I-MIBG uptake by the heart in Parkinson's disease: assessment of cardiac sympathetic denervation and diagnostic value. J Nucl Med 1999, 40, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orimo, S.; Uchihara, T.; Nakamura, A.; Mori, F.; Kakita, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H. Axonal alpha-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson's disease. Brain 2008, 131, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denfeld, Q.E.; Turrise, S.; MacLaughlin, E.J.; Chang, P.S.; Clair, W.K.; Lewis, E.F.; Forman, D.E.; Goodlin, S.J.; American Heart Association Cardiovascular Disease in Older Populations Committee of the Council on Clinical, C. ; Council on, C.; et al. Preventing and Managing Falls in Adults With Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2022, 15, e000108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, R.F. Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamotte, G.; Lenka, A. Orthostatic Hypotension in Parkinson Disease: What Is New? Neurol Clin Pract 2022, 12, e112–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutsforth-Gregory, J.K.; Low, P.A. Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension in Parkinson Disease: A Primer. Neurol Ther 2019, 8, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, Y.Y.; Jonker, A.J.; Oudejans, E.; de Jong, F.J.J.; van Dam, A.W.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; van de Berg, W.D.J. Differential insular cortex subregional vulnerability to alpha-synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2019, 45, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, E.; Zeng, J.; Li, Q.; Mei, S.; Hua, Y. Impaired Cerebral Autoregulation in Parkinson's Disease: An Orthostatic Hypotension Analysis. Front Neurol 2022, 13, 811698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.S. Dysautonomia in Parkinson's disease: neurocardiological abnormalities. Lancet Neurol 2003, 2, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Ogaki, K.; Shiina, T.; Sakuramoto, H.; Nozawa, N.; Suzuki, K. Impact of autonomic symptoms on the clinical course of Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci 2024, 45, 3799–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velseboer, D.C.; de Haan, R.J.; Wieling, W.; Goldstein, D.S.; de Bie, R.M. Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2011, 17, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, S.; Kuric, I.; Kuric, T.G.; Popovic, Z.; Kragujevic, J.; Zubonja, T.M.; Rajkovaca, I.; Matosa, S. Seborrheic Dermatitis Is Related to Motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease. J Clin Neurol 2022, 18, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, M.; Benito-Leon, J.; Calon, F. Malassezia and Parkinson's Disease. Front Neurol 2019, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, V.; et al. Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, E.; Trivedi, D.K.; Sarkar, D.; Walton-Doyle, C.; Milne, J.; Kunath, T.; Rijs, A.M.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Goodacre, R.; Silverdale, M.; et al. Metabolomics of sebum reveals lipid dysregulation in Parkinson's disease. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.W.; Pope, S.M.; Jaboori, K.A. Diagnosis and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Am Fam Physician 2015, 91, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa, E.; Garrido, A.; Scholz, S.W.; Poewe, W. Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2021, 20, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolano, M.; Provitera, V.; Estraneo, A.; Selim, M.M.; Caporaso, G.; Stancanelli, A.; Saltalamacchia, A.M.; Lanzillo, B.; Santoro, L. Sensory deficit in Parkinson's disease: evidence of a cutaneous denervation. Brain 2008, 131, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haehner, A.; Hummel, T.; Reichmann, H. Olfactory loss in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011, 2011, 450939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.A.; Johnson, A. Olfactory function in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Chronic Dis 1975, 28, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L. Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2012, 8, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haehner, A.; Boesveldt, S.; Berendse, H.W.; Mackay-Sim, A.; Fleischmann, J.; Silburn, P.A.; Johnston, A.N.; Mellick, G.D.; Herting, B.; Reichmann, H.; et al. Prevalence of smell loss in Parkinson's disease--a multicenter study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2009, 15, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, E.J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Ciesielski-Jones, A.J.; Justice, M.A.; Cousins, D.S.; Peddada, S. Meta-analyses on prevalence of selected Parkinson's nonmotor symptoms before and after diagnosis. Transl Neurodegener 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, M.E.; Morley, J.F.; Duda, J.E. Olfactory Dysfunction as an Early Biomarker in Parkinson's Disease. Neurosci Bull 2017, 33, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Li, F. Hyposmia as a Predictive Marker of Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019, 3753786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.S.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Raijmakers, P.; Doty, R.L.; Berendse, H.W. Hyposmia as a marker of (non-)motor disease severity in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2019, 126, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; et al. Olfactory Dysfunction Predicts Disease Progression in Parkinson's Disease: A Longitudinal Study. Front Neurosci 2020, 14, 569777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.C.; Chang, M.H.; Yang, C.P.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, C.H. The Association of Olfactory Dysfunction With Depression, Cognition, and Disease Severity in Parkinson's Disease. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 779712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Shiina, T.; Sakuramoto, H.; Nozawa, N.; Ogaki, K.; Suzuki, K. Sleep and Autonomic Manifestations in Parkinson's Disease Complicated With Probable Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder. Front Neurosci 2022, 16, 874349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengoku, R.; Matsushima, S.; Bono, K.; Sakuta, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Miyagawa, S.; Komatsu, T.; Mitsumura, H.; Kono, Y.; Kamiyama, T.; et al. Olfactory function combined with morphology distinguishes Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2015, 21, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Park, S.I.; Yim, Y. Clinical significance of MRI-measured olfactory bulb height as an imaging biomarker of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 2024, 19, e0312728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, A.; Iranzo, A.; Holzknecht, E.; Perra, D.; Bongianni, M.; Gaig, C.; Heim, B.; Serradell, M.; Sacchetto, L.; Garrido, A.; et al. Alpha-synuclein seeds in olfactory mucosa of patients with isolated REM sleep behaviour disorder. Brain 2021, 144, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Wang, Q.; Orru, C.D.; Fernandez, M.; Compta, Y.; Ghetti, B.; Zanusso, G.; Zou, W.Q.; Caughey, B.; Beauchemin, C.A.A. Enhanced quantitation of pathological alpha-synuclein in patient biospecimens by RT-QuIC seed amplification assays. PLoS Pathog 2024, 20, e1012554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.H.; Ye, B.S.; Sohn, Y.H.; Yun, M.; Lee, P.H. Clinical and Dopamine Depletion Patterns in Hyposmia- and Dysautonomia-Dominant Parkinson's Disease. J Parkinsons Dis 2021, 11, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.K.; Zhang, Y.; Lim, K.L.; Tanaka, Y.; Huang, H.; Gao, J.; Ross, C.A.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Parkin ubiquitinates the alpha-synuclein-interacting protein, synphilin-1: implications for Lewy-body formation in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 2001, 7, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Nie, W.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X. Olfactory dysfunction and its related molecular mechanisms in Parkinson's disease. Neural Regen Res 2024, 19, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Deeb, J.; Fernando, M.; Noyce, A.; Visentin, E.; Findley, L.J.; Hawkes, C.H. Abnormality of taste and smell in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2009, 15, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashihara, K.; Hanaoka, A.; Imamura, T. Frequency and characteristics of taste impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease: results of a clinical interview. Intern Med 2011, 50, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, G.; Melis, M.; Sarchioto, M.; Melis, M.; Melis, M.; Morelli, M.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I. 6-n-propylthiouracil taste disruption and TAS2R38 nontasting form in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2018, 33, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagota, P.; Chotechuang, N.; Anan, C.; Kitjawijit, T.; Boonla, C.; Bhidayasiri, R. Umami and Other Taste Perceptions in Patients With Parkinson's Disease. J Mov Disord 2022, 15, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppo, V.; Melis, M.; Melis, M.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.; Cossu, G. "Smelling and Tasting" Parkinson's Disease: Using Senses to Improve the Knowledge of the Disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2020, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.J.; Kanel, P.; Roytman, S.; Bohnen, N.I.; Hampstead, B.M. Basal forebrain integrity, cholinergic innervation and cognition in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Brain 2024, 147, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, E.; Zanini, A.; Cecchini, M.P.; Tamburin, S. The Association Between Neurocognitive Disorders and Gustatory Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 2024, 34, 192–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Schluter, A.; Carmona, M.; Moreno, J.; Ansoleaga, B.; Torrejon-Escribano, B.; Gustincich, S.; Pujol, A.; Ferrer, I. Functional genomics reveals dysregulation of cortical olfactory receptors in Parkinson disease: novel putative chemoreceptors in the human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2013, 72, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Lijn, I.; de Haan, G.A.; Huizinga, F.; van der Feen, F.E.; Rutgers, A.W.F.; Stellingwerf, C.; van Laar, T.; Heutink, J. Self-Reported Visual Complaints in People with Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review. J Parkinsons Dis 2022, 12, 785–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Lijn, I.; de Haan, G.A.; van der Feen, F.E.; Huizinga, F.; Stellingwerf, C.; van Laar, T.; Heutink, J. Prevalence and nature of self-reported visual complaints in people with Parkinson's disease-Outcome of the Screening Visual Complaints questionnaire. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0283122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Kanel, P.; Griggs, A.; Carli, G.; Vangel, R.; Albin, R.L.; Bohnen, N.I. Regional cerebral cholinergic vesicular transporter correlates of visual contrast sensitivity in Parkinson's disease: Implications for visual and cognitive function. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2025, 131, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hely, M.A.; Reid, W.G.; Adena, M.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Morris, J.G. The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson's disease: the inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov Disord 2008, 23, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, T.G.; Carew, J.; Serrano, G.; Adler, C.H.; Shill, H.A.; Sue, L.I.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Akiyama, H.; Cuenca, N.; Arizona Parkinson's Disease, C. Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive retinal neuronal elements in Parkinson's disease subjects. Neurosci Lett 2014, 571, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuno-Lizaran, I.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Walker, D.G.; Adler, C.H.; Cuenca, N. Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in the retina is a biomarker of Parkinson's disease pathology severity. Mov Disord 2018, 33, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuno-Lizaran, I.; Sanchez-Saez, X.; Lax, P.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Cuenca, N. Dopaminergic Retinal Cell Loss and Visual Dysfunction in Parkinson Disease. Ann Neurol 2020, 88, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Z.; He, R.; Chu, H.; Tang, Y.; Liu, P.; Lu, X. Retinopathy in Parkinson's disease: A potential biomarker for early diagnosis and clinical assessment. Neuroscience 2025, 565, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, F.; Ghiasian, M.; Mohamadrahimi, B.; Jiriaee, N.; Eslamighayour, A. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) findings in patients with Parkinson's disease presenting to Farshchian Hospital (Sina) in 2019 compared to the normal population. J Fr Ophtalmol 2025, 48, 104379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, S.; Uysal, H.A.; Bilgin, S.; Yaka, E.C.; Kusbeci, O.Y.; Sener, U. Assessment of Changes in Vascular Density in the Layers of the Eye in Patients With Parkinson's Disease. Ann Neurosci, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, M.; Soker, E.B.; Ozdogru, D.; Balal, M.; Ciloglu, E. Evaluation of retinal microvascular changes with OCT-A in Parkinson disease and essential tremor. Medicine (Baltimore) 2024, 103, e40752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedani, A.G.; Abraham, D.S.; Maguire, M.G.; Willis, A.W. Visual Impairment Is More Common in Parkinson's Disease and Is a Risk Factor for Poor Health Outcomes. Mov Disord 2020, 35, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylius, V.; Perez Lloret, S.; Cury, R.G.; Teixeira, M.J.; Barbosa, V.R.; Barbosa, E.R.; Moreira, L.I.; Listik, C.; Fernandes, A.M.; de Lacerda Veiga, D.; et al. The Parkinson disease pain classification system: results from an international mechanism-based classification approach. Pain 2021, 162, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, A.C.R.; Pereira, K.C.; Rodrigues, V.F.; Alves, D.P.A.; Marques, J.B.; Monteiro, E.R.; Jesus, I.R.T. Pain characterization in patients with Parkinson's disease. Pain Pract 2024, 24, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalash, A.; Mohamed, S.R.; Badr, M.Y.; Elgamal, S.; Elaidy, S.A.; Elhamrawy, E.A.; Abdel-Tawab, H.; Elshebawy, H.; Abdelraheem, H.S.; Roushdy, T.; et al. Pain Characteristics of Parkinson's Disease Using Validated Arabic Versions of the King's Parkinson's Disease Pain Scale and Questionnaire: A Multicenter Egyptian Study. J Mov Disord 2024, 17, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, D.; Gambioli, F.; De Bartolo, M.I.; Mancinelli, R.; Biagioni, F.; Carotti, S.; Falato, E.; Leodori, G.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Vivacqua, G.; et al. Pain in Parkinson's disease: a neuroanatomy-based approach. Brain Commun 2024, 6, fcae210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.T.; Lin, C.H. Pain in early-stage Parkinson's disease: Implications from clinical features to pathophysiology mechanisms. J Formos Med Assoc 2017, 116, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.C.; Lin, C.H. An overview of pain in Parkinson's disease. Clin Park Relat Disord 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.; Jost, W.H. Pain in Parkinson's Disease: Pathophysiology, Classification and Treatment. J Integr Neurosci 2023, 22, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.; Geroin, C.; Antonini, A.; Smania, N.; Tinazzi, M. Understanding and Treating Pain Syndromes in Parkinson's Disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 2017, 134, 827–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roversi, K.; Callai-Silva, N.; Roversi, K.; Griffith, M.; Boutopoulos, C.; Prediger, R.D.; Talbot, S. Neuro-Immunity and Gut Dysbiosis Drive Parkinson's Disease-Induced Pain. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 759679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zou, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Yu, T.; et al. Activation of locus coeruleus-spinal cord noradrenergic neurons alleviates neuropathic pain in mice via reducing neuroinflammation from astrocytes and microglia in spinal dorsal horn. J Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T.; Gallop, K.; Correll, C.U.; Carvalho, A.F.; Veronese, N.; Wright, E.; Stubbs, B. Pain perception in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental studies. Ageing Res Rev 2017, 35, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corra, M.F.; Vila-Cha, N.; Sardoeira, A.; Hansen, C.; Sousa, A.P.; Reis, I.; Sambayeta, F.; Damasio, J.; Calejo, M.; Schicketmueller, A.; et al. Peripheral neuropathy in Parkinson's disease: prevalence and functional impact on gait and balance. Brain 2023, 146, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, C.H.; Garcia, J.; Wang, N.; Shih, L.C.; Freeman, R. The diagnostic discrimination of cutaneous alpha-synuclein deposition in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2016, 87, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doppler, K.; Jentschke, H.M.; Schulmeyer, L.; Vadasz, D.; Janzen, A.; Luster, M.; Hoffken, H.; Mayer, G.; Brumberg, J.; Booij, J.; et al. Dermal phospho-alpha-synuclein deposits confirm REM sleep behaviour disorder as prodromal Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2017, 133, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Bejarano, F.; Mendez, M.O.; Alba, A.; Rodriguez-Leyva, I.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Rodriguez-Aranda, M.D.C.; Guevara, E.; Guirado-Lopez, R.A.; Ramirez-Elias, M.G. Raman Spectroscopy Study of Skin Biopsies from Patients with Parkinson's Disease: Trends in Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation from the Amide I Region. Appl Spectrosc 2022, 76, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, S.; Yang, J.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Z.; Luo, H.; et al. Detection of skin alpha-synuclein using RT-QuIC as a diagnostic biomarker for Parkinson's disease in the Chinese population. Eur J Med Res 2024, 29, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Sun, L.; Zhi, Y.; Ding, J.; Yuan, Y.S.; Shen, F.F.; Li, X.; Ji, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein deposits in sural nerve deriving from Schwann cells: A biomarker for Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2019, 60, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolano, M.; Provitera, V.; Manganelli, F.; Iodice, R.; Stancanelli, A.; Caporaso, G.; Saltalamacchia, A.; Califano, F.; Lanzillo, B.; Picillo, M.; et al. Loss of cutaneous large and small fibers in naive and l-dopa-treated PD patients. Neurology 2017, 89, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, E.; Senese, C.; Chiaro, G.; Disanto, G.; Pinton, S.; Morandi, S.; Bertaina, I.; Bianco, G.; Staedler, C.; Galati, S.; et al. Alpha-synuclein oligomers and small nerve fiber pathology in skin are potential biomarkers of Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2021, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melli, G.; Vacchi, E.; Biemmi, V.; Galati, S.; Staedler, C.; Ambrosini, R.; Kaelin-Lang, A. Cervical skin denervation associates with alpha-synuclein aggregates in Parkinson disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2018, 5, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Carrion, O.; Ortega-Robles, E.; Ortuno-Sahagun, D.; Ramirez-Bermudez, J.; Hamid, A.; Shalash, A. Sleep-Related Disorders in Parkinson's Disease: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Approaches. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2025, 24, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q.; Kuang, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, D.; et al. Insomnia in Parkinson's Disease: Causes, Consequences, and Therapeutic Approaches. Mol Neurobiol 2025, 62, 2292–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, A.; Hogl, B. Sleep in Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Zu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Cui, G.; Xu, C. Association between serum neurofilament light chain levels and sleep disorders in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 2023, 812, 137394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchill, E.; Watson, C.J.; Fanshawe, J.B.; Badenoch, J.B.; Rengasamy, E.; Ghanem, D.A.; Holle, C.; Conti, I.; Sadeq, M.A.; Saini, A.; et al. The impact of psychiatric comorbidity on Parkinson's disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Reg Health Eur 2024, 39, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, D.; Sousa, M.; Maradan-Gachet, M.E.; Debove, I.; Lhommee, E.; Krack, P. Psychiatric and cognitive symptoms of Parkinson's disease: A life's tale. Rev Neurol (Paris), 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Garcia, P.; Rashid-Lopez, R.; Cruz-Gomez, A.J.; Lozano-Soto, E.; Sanmartino, F.; Espinosa-Rosso, R.; Gonzalez-Rosa, J.J. Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Clinically Defined Parkinson's Disease: An Updated Review of Literature. Behav Neurol 2022, 2022, 1213393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Cong, S. Prevalence and clinical aspects of depression in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 129 studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2022, 141, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Quan, W.; Song, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Risk of Parkinson's disease and depression severity in different populations: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Brain Behav 2024, 14, e3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenoch, J.B.; Paris, A.; Jacobs, B.M.; Noyce, A.J.; Marshall, C.R.; Waters, S. Neuroanatomical and prognostic associations of depression in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2024, 95, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, J.; Ceravolo, R.; Brooks, D.J.; Bonuccelli, U.; Pavese, N. Progressive loss of raphe nuclei serotonin transporter in early Parkinson's disease: A longitudinal (123)I-FP-CIT SPECT study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2020, 77, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazdis, R.M.; von Zimmermann, C.; Lenz, B.; Kornhuber, J.; Muhle, C. Peripheral Upregulation of Parkinson's Disease-Associated Genes Encoding alpha-Synuclein, beta-Glucocerebrosidase, and Ceramide Glucosyltransferase in Major Depression. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Rincon, M.; Saenz-Farret, M.; Miguel-Puga, A.; Micheli, F.; Arias-Carrion, O. Rational pharmacological approaches for cognitive dysfunction and depression in Parkinson's disease. Front Neurol 2015, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Brok, M.G.; van Dalen, J.W.; van Gool, W.A.; Moll van Charante, E.P.; de Bie, R.M.; Richard, E. Apathy in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord 2015, 30, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Song, E.; Zhu, M.; Appel-Cresswell, S.; McKeown, M.J. Apathy scores in Parkinson's disease relate to EEG components in an incentivized motor task. Brain Commun 2024, 6, fcae025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, N.; Kandiah, N.; Acharyya, S.; Chander, R.J.; Ng, A.; Au, W.L.; Tan, L.C. Baseline predictors of worsening apathy in Parkinson's disease: A prospective longitudinal study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2016, 23, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.; MacAskill, M.; Pascoe, M.; Anderson, T.; Heron, C.L. Dimensions of apathy in Parkinson's disease. Brain Behav 2023, 13, e2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, P.; Lanctot, K.L.; Aguera-Ortiz, L.; Aalten, P.; Bremond, F.; Defrancesco, M.; Hanon, C.; David, R.; Dubois, B.; Dujardin, K.; et al. Is it time to revise the diagnostic criteria for apathy in brain disorders? The 2018 international consensus group. Eur Psychiatry 2018, 54, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Lin, J.; Liu, K.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, B.; Zhao, B.; Song, W.; et al. Evolution of Apathy in Early Parkinson's Disease: A 4-Years Prospective Cohort Study. Front Aging Neurosci 2020, 12, 620762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Heron, C.; Horne, K.L.; MacAskill, M.R.; Livingstone, L.; Melzer, T.R.; Myall, D.; Pitcher, T.; Dalrymple-Alford, J.; Anderson, T.; Harrison, S. Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Association of Clinical and Neurocognitive Factors With Apathy in Patients With Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2024, 102, e209301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, L.; Gan, C.; Sun, H.; Shan, A.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K. Association between the functional connectivity of ventral tegmental area-prefrontal network and pure apathy in Parkinson's disease: a cross-sectional study. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2024, 14, 4735–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas-Jimenez, O.; Ojeda, N.; Pena, J.; Cabrera-Zubizarreta, A.; Diez-Cirarda, M.; Gomez-Esteban, J.C.; Gomez-Beldarrain, M.A.; Ibarretxe-Bilbao, N. Apathy and brain alterations in Parkinson's disease: a multimodal imaging study. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2018, 5, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Horta, S.; Sampedro, F.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Fernandez-Bobadilla, R.; Marin-Lahoz, J.; Riba, J.; Kulisevsky, J. Non-demented Parkinson's disease patients with apathy show decreased grey matter volume in key executive and reward-related nodes. Brain Imaging Behav 2017, 11, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, S.Y.; Zuo, L.J.; Cao, C.J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.J.; Piao, Y.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, S.D.; et al. Excessive Iron and alpha-Synuclein Oligomer in Brain are Relevant to Pure Apathy in Parkinson Disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 2016, 29, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.P.; McDonald, K.R.; Allsop, D.; Diggle, P.J.; Leroi, I. Apathy as a behavioural marker of cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: a longitudinal analysis. J Neurol 2020, 267, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, B.; Van, S.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.; Ismail, Z.; Pringsheim, T.; Goodarzi, Z. Diagnosis, treatment and management of apathy in Parkinson's disease: a scoping review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broen, M.P.; Narayen, N.E.; Kuijf, M.L.; Dissanayaka, N.N.; Leentjens, A.F. Prevalence of anxiety in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord 2016, 31, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wu, K. Early identification of Parkinson's disease with anxiety based on combined clinical and MRI features. Front Aging Neurosci 2024, 16, 1414855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, G.; Lopes, R.; Viard, R.; Betrouni, N.; Kuchcinski, G.; Devignes, Q.; Defebvre, L.; Leentjens, A.F.G.; Dujardin, K. Anxiety in Parkinson's disease is associated with changes in the brain fear circuit. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2020, 80, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.R.S.; Stanojlovic, M.; Zelikowsky, M.; Bonsberger, J.; Hean, S.; Mulligan, C.; Baldauf, L.; Fleming, S.; Masliah, E.; Chesselet, M.F.; et al. Alpha-synuclein pathology, microgliosis, and parvalbumin neuron loss in the amygdala associated with enhanced fear in the Thy1-aSyn model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2021, 158, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Arkin, E.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, T. Erythrocytic alpha-Synuclein Species for Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis and the Correlations With Clinical Characteristics. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 827493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Guo, P.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Guan, H.; Zhang, W.; Luo, D.; et al. Parkinson's disease with anxiety: clinical characteristics and their correlation with oxidative stress, inflammation, and pathological proteins. BMC Geriatr 2024, 24, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Dobkin, R.; Weintraub, D.; Cho, H.R.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Bock, M.; Brown, E.; Aarsland, D.; Dahodwala, N. Association of Baseline Depression and Anxiety with Longitudinal Health Outcomes in Parkinson's Disease. Mov Disord Clin Pract 2024, 11, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, N.; Shek-Kwan Chang, R.; Cheung, C.; Pang, S.; Lau, K.K.; Suckling, J.; Rowe, J.B.; Yu, K.; Ka-Fung Mak, H.; Chua, S.E.; et al. The default mode network is disrupted in Parkinson's disease with visual hallucinations. Hum Brain Mapp 2014, 35, 5658–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, B.J.; Duncan, G.W.; Khoo, T.K.; Barker, R.A.; Burn, D.J.; Yarnall, A.J.; Lawson, R.A. Categorising Visual Hallucinations in Early Parkinson's Disease. J Parkinsons Dis 2018, 8, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenelon, G.; Mahieux, F.; Huon, R.; Ziegler, M. Hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain 2000, 123 ( Pt 4) Pt 4, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; Killen, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Graziadio, S.; Rochester, L.; Firbank, M.; Baker, M.R.; Allan, C.; Collerton, D.; Taylor, J.P.; et al. Exploring Bottom-Up Visual Processing and Visual Hallucinations in Parkinson's Disease With Dementia. Front Neurol 2020, 11, 579113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatavicius, A.; Matar, E.; Lewis, S.J.G. Visual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: spotlight on central cholinergic dysfunction. Brain 2025, 148, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shen, B.; Lu, L.; Lan, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L. Prevalence and risk factors for visual hallucinations in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci 2017, 372, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d'Angremont, E.; van der Zee, S.; Slingerland, S.; Slomp, A.C.; de Vries, E.F.J.; van Laar, T.; Sommer, I.E. Cholinergic deficiency in Parkinson's disease patients with visual hallucinations. Brain 2024, 147, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firbank, M.J.; Parikh, J.; Murphy, N.; Killen, A.; Allan, C.L.; Collerton, D.; Blamire, A.M.; Taylor, J.P. Reduced occipital GABA in Parkinson disease with visual hallucinations. Neurology 2018, 91, e675–e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.E.C.; Zeidman, P.; Sultana, T.; Zarkali, A.; Razi, A.; Weil, R.S. Changes in both top-down and bottom-up effective connectivity drive visual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease. Brain Commun 2023, 5, fcac329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkali, A.; McColgan, P.; Leyland, L.A.; Lees, A.J.; Weil, R.S. Longitudinal thalamic white and grey matter changes associated with visual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2022, 93, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzakis, M.E.; Christian, L.M.; Moran, L.B.; Graeber, M.B.; Pearce, R.K.; Gentleman, S.M. Dementia and visual hallucinations associated with limbic pathology in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2009, 15, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Ikeda, T.; Ishida, C.; Komai, K.; Yamada, M. Delusions and visual hallucinations in a patient with Parkinson's disease with dementia showing pronounced Lewy body pathology in the nucleus basalis of Meynert. Neuropathology 2019, 39, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.R.; Warren, J.D.; Lees, A.J. Using the presence of visual hallucinations to differentiate Parkinson's disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008, 79, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, B.; Reid, J.A.; Shermetaro, C. Phantosmia. In StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL), 2025.
- Solla, P.; Masala, C.; Pinna, I.; Ercoli, T.; Loy, F.; Orofino, G.; Fadda, L.; Defazio, G. Frequency and Determinants of Olfactory Hallucinations in Parkinson's Disease Patients. Brain Sci 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannier, S.; Berdague, J.L.; Rieu, I.; de Chazeron, I.; Marques, A.; Derost, P.; Ulla, M.; Llorca, P.M.; Durif, F. Prevalence and phenomenology of olfactory hallucinations in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2012, 83, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, B.N.; Burkhard, P.R. Phantosmias and Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 2008, 65, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, T.; Bagella, C.F.; Frau, C.; Ruiu, E.; Othmani, S.; Gusinu, G.; Masala, C.; Sechi, L.A.; Solla, P.; Defazio, G. Phantosmia in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review of the Phenomenology of Olfactory Hallucinations. Neurol Int 2023, 16, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, E.R.; Segerstrom, S.C.; van Horne, C.G.; Schmitt, F.A.; Koehl, L.M. Meta-Analysis of Cognition in Parkinson's Disease Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia Progression. Neuropsychol Rev 2022, 32, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanni, K.E.; Ross, J.M.; Higginson, C.I.; Dressler, E.M.; Sigvardt, K.A.; Zhang, L.; Malhado-Chang, N.; Disbrow, E.A. Perceived and performance-based executive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2014, 36, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirnberger, G.; Frith, C.D.; Jahanshahi, M. Executive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease is associated with altered pallidal-frontal processing. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R.; Cote, L. Reaction time and vigilance in Parkinson's disease. Possible role of altered norepinephrine metabolism. Arch Neurol 1984, 41, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehagia, A.A.; Barker, R.A.; Robbins, T.W. Cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: the dual syndrome hypothesis. Neurodegener Dis 2013, 11, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, R.D.; Ren, X.; Ellis, T.D.; Toraif, N.; Barthelemy, O.J.; Neargarder, S.; Cronin-Golomb, A. Dual tasking in Parkinson's disease: Cognitive consequences while walking. Neuropsychology 2017, 31, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proud, E.; Morris, M.E.; Bilney, B.; Miller, K.J.; Nijkrake, M.J.; Munneke, M.M.; McGinley, J.L. Effects of dual-task interference on dexterity performance in people with mild to moderately severe Parkinson's disease: An observational analysis. J Hand Ther 2025, 38, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, K.R.; Uc, E.Y. Real-life consequences of cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Prog Brain Res 2022, 269, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focker, J.; Cole, D.; Beer, A.L.; Bavelier, D. Neural bases of enhanced attentional control: Lessons from action video game players. Brain Behav 2018, 8, e01019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, G.; Parris, B.A. Inattention and task switching performance: the role of predictability, working memory load and goal neglect. Psychol Res 2020, 84, 2090–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ou, R.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H.; Hou, Y.; Wei, Q.; Song, W.; Cao, B.; Chen, Y.; Shang, H. Executive dysfunctions and behavioral changes in early drug-naive patients with Parkinson's disease. J Affect Disord 2019, 243, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pont-Sunyer, C.; Hotter, A.; Gaig, C.; Seppi, K.; Compta, Y.; Katzenschlager, R.; Mas, N.; Hofeneder, D.; Brucke, T.; Bayes, A.; et al. The onset of nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson's disease (the ONSET PD study). Mov Disord 2015, 30, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melugin, P.R.; Nolan, S.O.; Kandov, E.; Ferrara, C.F.; Farahbakhsh, Z.Z.; Siciliano, C.A. Medial prefrontal dopamine dynamics reflect allocation of selective attention. bioRxiv, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Carrion, O.; Poppel, E. Dopamine, learning, and reward-seeking behavior. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2007, 67, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, T.S.; Bub, D.N.; Hunter, M.A. Task switching deficits associated with Parkinson's disease reflect depleted attentional resources. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Yousaf, J.; Ahmad, H. Frontal-subcortical defects correlate with task switching deficits in Parkinson;s disease. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 2017, 22, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Yoo, H.; Concha, E.O.; De Ridder, D.; Pickut, B.A.; Vanneste, S. The Functional Alterations in Top-Down Attention Streams of Parkinson's disease Measured by EEG. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, F.; Constantinidis, C. Bottom-up and top-down attention: different processes and overlapping neural systems. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasi, G.; Fiorio, M.; Yelnik, J.; Krack, P.; Sala, F.; Schmitt, E.; Fraix, V.; Bertolasi, L.; Le Bas, J.F.; Ricciardi, G.K.; et al. Disentangling the Role of Cortico-Basal Ganglia Loops in Top-Down and Bottom-Up Visual Attention: An Investigation of Attention Deficits in Parkinson Disease. J Cogn Neurosci 2015, 27, 1215–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquillon, P.; Bourriez, J.L.; Palmero-Soler, E.; Destee, A.; Defebvre, L.; Derambure, P.; Dujardin, K. Role of basal ganglia circuits in resisting interference by distracters: a swLORETA study. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulaer, B.; Kunisawa, K.; Tanabe, M.; Yanagawa, A.; Saito, K.; Mouri, A.; Nabeshima, T. Pharmacological blockade of dopamine D1- or D2-receptor in the prefrontal cortex induces attentional impairment in the object-based attention test through different neuronal circuits in mice. Mol Brain 2021, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Moscovitch, M.; Alain, C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of memory-guided attention: Frontal and parietal activation suggests involvement of fronto-parietal networks. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci 2021, 12, e1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehagia, A.A.; Barker, R.A.; Robbins, T.W. Revisiting the effects of Parkinson's disease and frontal lobe lesions on task switching: the role of rule reconfiguration. J Neuropsychol 2014, 8, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R.; Stern, Y.; Sano, M.; Cote, L.; Williams, J.B. Clinical and biochemical correlates of bradyphrenia in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 1987, 37, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peavy, G.M. Mild cognitive deficits in Parkinson disease: where there is bradykinesia, there is bradyphrenia. Neurology 2010, 75, 1038–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, A.; Lange, F.; Seer, C.; Hendel, M.K.; Kopp, B. Computational Modeling for Neuropsychological Assessment of Bradyphrenia in Parkinson's Disease. J Clin Med 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letanneux, A.; Velay, J.L.; Viallet, F.; Pinto, S. Altered Inhibitory Mechanisms in Parkinson's Disease: Evidence From Lexical Decision and Simple Reaction Time Tasks. Front Hum Neurosci 2021, 15, 624026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, R.M.; Cummings, J.L. Frontal-subcortical dementias. Neurologist 2008, 14, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Baker, K.; Umamahesan, C.; Gilmour, S.; Charlett, A.; Taylor, D.; Young, A.H.; Dobbs, R.J.; Dobbs, S.M. Bradyphrenia and Tachyphrenia in Idiopathic Parkinsonism Appear, in Part, Iatrogenic: An Observational Study with Systematic Review Background. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.L.; Weintraub, D.; Lemmen, R.; Perera, G.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Svenningsson, P.; Aarsland, D. Risk of Dementia in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov Disord 2024, 39, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, M.; Aarsland, D.; Brown, R.; Burn, D.J.; Duyckaerts, C.; Mizuno, Y.; Broe, G.A.; Cummings, J.; Dickson, D.W.; Gauthier, S.; et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2007, 22, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Pathobiology of Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson Disease: Challenges and Outlooks. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrom, D.O.; Simonsen, J.; Raket, L.L.; Sgarbi, S.; Hellsten, J.; Hagell, P.; Norlin, J.M.; Kellerborg, K.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Odin, P. High risk of developing dementia in Parkinson's disease: a Swedish registry-based study. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 16759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.; Drozdova, A.; Wang, W.; Thomas, M. The impact of dementia development concurrent with Parkinson's disease: a new perspective. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballol, N.; Marti, M.J.; Tolosa, E. Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 2007, 22 Suppl 17, S358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, M. Dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2003, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, A.; Hampshire, A.; Barker, R.A.; Owen, A.M. Normal aging and Parkinson's disease are associated with the functional decline of distinct frontal-striatal circuits. Cortex 2017, 93, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, N.I.; Brazhnik, E.S.; Kitchigina, V.F. Pathological Correlates of Cognitive Decline in Parkinson's Disease: From Molecules to Neural Networks. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2023, 88, 1890–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, L.; Odlaug, B.L.; Grant, J.E. Impulse control disorders: updated review of clinical characteristics and pharmacological management. Front Psychiatry 2011, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, H.; Prange, S.; Bischof, G.N.; Hoenig, M.C.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Timmermann, L.; Fink, G.R.; Drzezga, A.; Eggers, C.; van Eimeren, T. Impulsive-compulsive behaviour in early Parkinson's disease is determined by apathy and dopamine receptor D3 polymorphism. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2023, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Behavioral disorders in Parkinson disease: current view. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2025, 132, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcano, P.; Jacobson, J.; Ghoniem, K.; Mullan, A.; Camerucci, E.; Stang, C.; Piat, C.; Bower, J.H.; Savica, R. Impulse control disorders and use of dopamine agonists in early onset Parkinson's disease. Front Neurol 2024, 15, 1404904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletti, M.; Logi, C.; Lucetti, C.; Del Dotto, P.; Baldacci, F.; Vergallo, A.; Ulivi, M.; Del Sarto, S.; Rossi, G.; Ceravolo, R.; et al. A single-center, cross-sectional prevalence study of impulse control disorders in Parkinson disease: association with dopaminergic drugs. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2013, 33, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joutsa, J.; Martikainen, K.; Vahlberg, T.; Voon, V.; Kaasinen, V. Impulse control disorders and depression in Finnish patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2012, 18, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Violante, M.; Gonzalez-Latapi, P.; Cervantes-Arriaga, A.; Camacho-Ordonez, A.; Weintraub, D. Impulse control and related disorders in Mexican Parkinson's disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2014, 20, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, D.; Claassen, D.O. Impulse Control and Related Disorders in Parkinson's Disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 2017, 133, 679–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, E.; van der Werf, Y.D.; van den Heuvel, O.A. Parkinson's disease-related disorders in the impulsive-compulsive spectrum. J Neurol 2008, 255 Suppl 5, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, V.; Mehta, A.R.; Hallett, M. Impulse control disorders in Parkinson's disease: recent advances. Curr Opin Neurol 2011, 24, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napier, T.C.; Corvol, J.C.; Grace, A.A.; Roitman, J.D.; Rowe, J.; Voon, V.; Strafella, A.P. Linking neuroscience with modern concepts of impulse control disorders in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2015, 30, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfschlag, M.; Cedergren Weber, G.; Weintraub, D.; Odin, P.; Hakansson, A. Impulse control disorders in Parkinson's disease: a national Swedish registry study on high-risk treatments and vulnerable patient groups. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, D.; Mamikonyan, E. Impulse Control Disorders in Parkinson's Disease. Am J Psychiatry 2019, 176, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
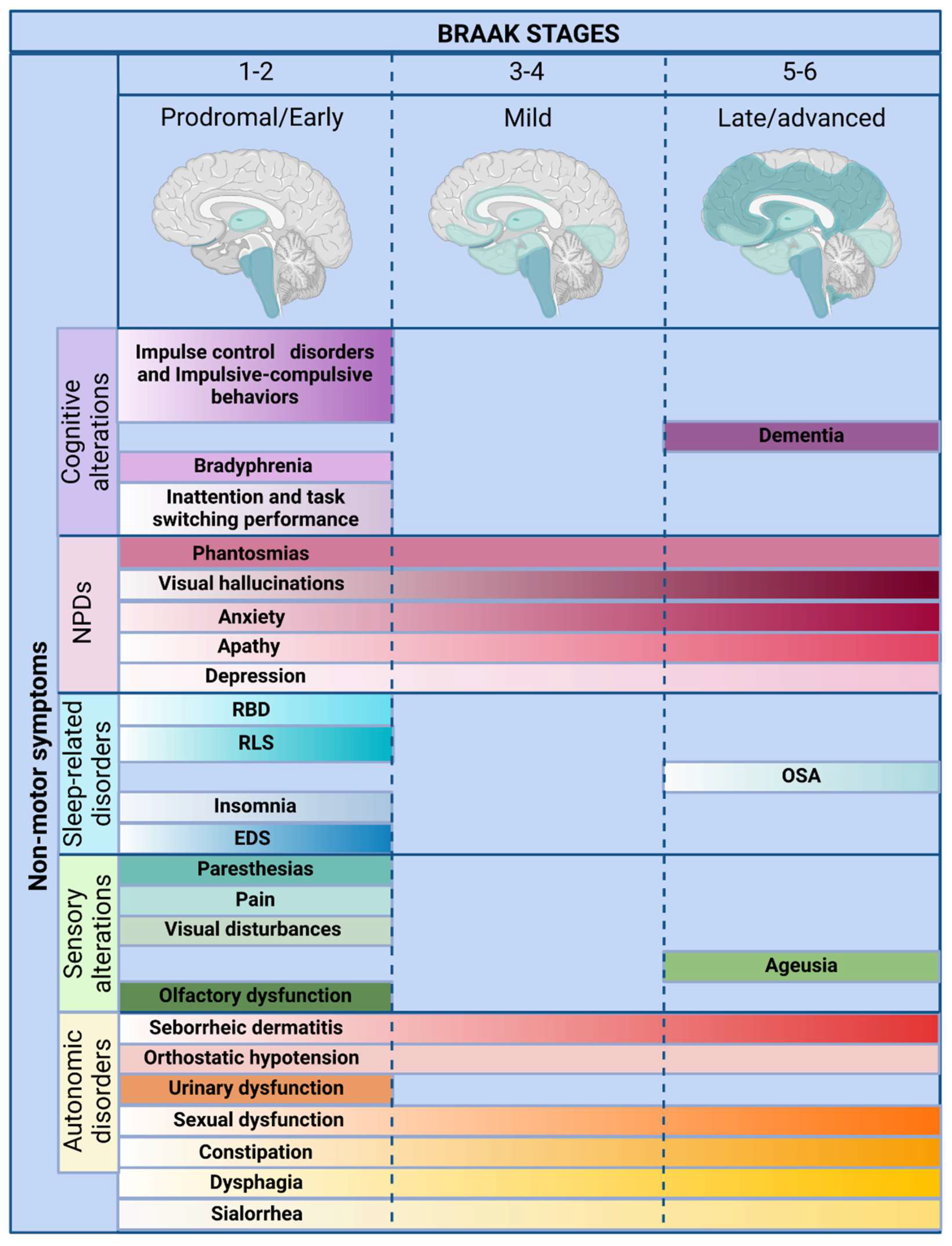
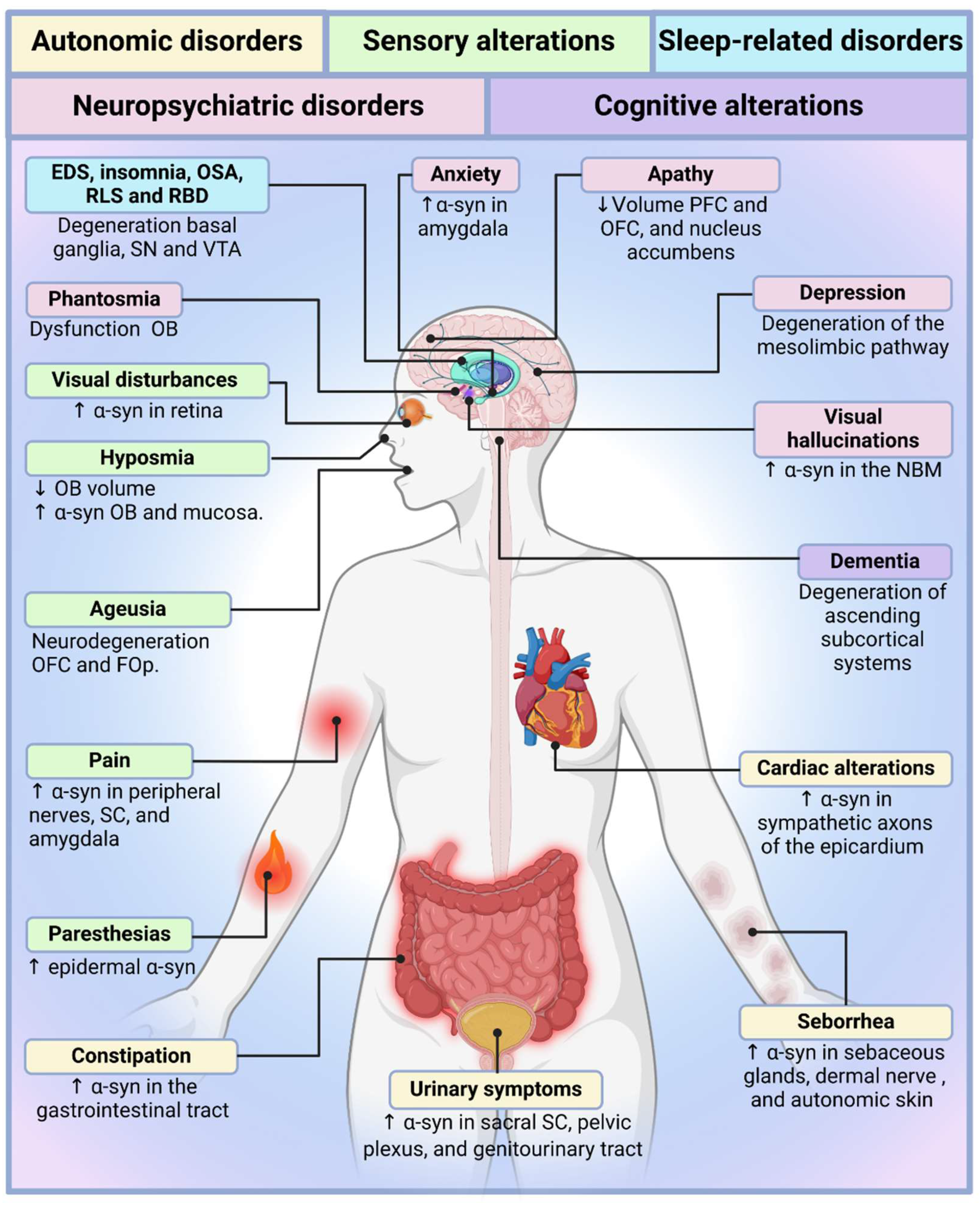
| Symptom | Prevalence & Stage | Biomarkers | Pharmacological Treatment |
Non-pharmacological Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sialorrhea | ↑ 37-84%, early | ↑ α-synuclein (basal ganglia) | Botulinum toxin, glycopyrrolate | Speech therapy, postural adjustments |
| Dysphagia | ↑ 40-87%, early | ↑ α-synuclein (enteric nervous system) | Botulinum toxin, Levodopa | Swallowing therapy, neuromodulation |
| Constipation | ↑ 40-63%, Prodromal | ↑ α-synuclein (sacral nuclei) | Lubiprostone, Prokinetics | Dietary fibre |
| Sexual dysfunction | ↑ 65-90%, Early | No α-synuclein correlation | Sildenafil, Hormone therapy | Psychotherapy, Couples therapy |
| Urinary dysfunction | ↑ 25-61%, 5-6 years post-motor onset | ↑ α-synuclein (pelvic plexus) | Antimuscarinics, Beta-3 agonists | Bladder training, Pelvic floor exercises |
| Orthostatic hypotension | ↑ 30-50%, Early/Late | ↑ α-synuclein (autonomic nervous system) | Droxidopa, midodrine, fludrocortisone | ↑ Salt/fluids, compression stockings |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | ↑ 52-59%, early & progressive | ↑ α-synuclein (sebaceous glands, dermal nerves) | Ketoconazole, cannabidiol | Skincare, microbiome modulation |
| Symptom | Prevalence & Stage | Biomarkers | Pharmacological Treatment |
Non-pharmacological Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olfactory dysfunction | ↑ 90%, prodromal | ↑ α-synuclein (olfactory bulb, mucosa), ↓ functional activity | Intranasal insulin, DBS | Olfactory training |
| Ageusia | ↑ 4-54%, mild-advanced | ↓ Taste receptor gene expression, neurodegeneration | No specific treatment | Dietary adjustments |
| Visual disturbances | ↑ 90%, prodromal | ↑ α-synuclein (retina), ↓ dopamine, retinal atrophy | Dopaminergic therapy, artificial tears | Prism glasses, vision therapy |
| Pain | ↑ 20-98%, prodromal | ↑ α-synuclein (spinal cord, nerves), ↓ dopamine, ↑ neuroinflammation | NSAIDs, anticonvulsants, opioids | Physical therapy, CBT, DBS |
| Paresthesias | ↑ 40%, prodromal | ↑ α-synuclein (epidermal nerves), ↓ nerve fiber density | Dopaminergic meds, anticonvulsants | Sensory retraining |
| Symptom | Prevalence & Stage | Biomarkers | Pharmacological Treatment |
Non-pharmacological Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS | ↑ 21-76%, early | ↓ Hypocretin-1, ↑ Tau, ↑ α-synuclein | Modafinil, istradefylline, melatonin | Sleep hygiene, CBT, exercise |
| Insomnia | ↑ 60-80%, early | ↑ α-synuclein, associated with motor & cognitive symptoms | Melatonin, benzodiazepines | CBT-I, neuromodulation |
| OSA | ↑ 45-66%, advanced | ↑ Leptin, ghrelin, IL-6 | Clonazepam, melatonin | CPAP therapy, sleep hygiene |
| RLS | ↑ 20-40%, early | ↓ Dopamine & serotonin, ↑ iron in brain | Dopaminergic agents, gabapentin | Exercise, thermotherapy |
| RBD | ↑ 33-58%, preclinical | ↑ Cognitive impairment risk, α-synuclein | Clonazepam, melatonin | Sleep safety modifications |
| Symptom | Prevalence & Stage | Biomarkers | Pharmacological Treatment |
Non-pharmacological Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | ↑ 35-45%, prodromal-late | ↓ Thalamus & amygdala function | SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs | CBT, TMS, ECT |
| Apathy | ↑ 40-52%, early-late | ↓ Mesocortical activity, VTA dysfunction | Dopamine agonists, rivastigmine | DBS, TMS |
| Anxiety | ↑ 31%, prodromal-late | ↑ TNF-α, ↓ nitric oxide | SSRIs, benzodiazepines | CBT, meditation |
| Visual Hallucinations | ↑ 27-50%, early-advanced | ↓ Acetylcholine, cognitive decline | Rivastigmine, clozapine | CBT, music therapy |
| Phantosmias | ↑ 0.5-18.2%, early-late | Correlation with hallucinations | Antiseizure, antipsychotics | Surgical intervention |
| Symptom | Prevalence & Stage | Biomarkers | Pharmacological Treatment |
Non-pharmacological Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inattention & Task-Switching | ↑ 20%, Preclinical | EEG alterations, gene mutations | Atomoxetine, methylphenidate | Cognitive training, physical activity |
| Bradyphrenia | ↑ 25%, Early | ↑ CSF metabolites, linked to constipation & bradykinesia | Levodopa, MAO-B inhibitors | Processing speed training |
| Dementia | ↑ 80%, Late | ↑ Cortical atrophy, ↑ α-synuclein, ↓ Amyloid-β | Donepezil, memantine, emerging therapies | Exercise, non-invasive brain stimulation |
| Impulse Control Disorders | ↑ 20%, Early | ↑ Dopamine tone, ↑ OFC metabolism | Adjust DRT, antipsychotics | CBT, DBS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





