Submitted:
11 March 2025
Posted:
12 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Based on the background of digital transformation, this paper analyzes the influence mechanism of resource orchestration on the improvement of supply chain resilience from the perspective of resource orchestration theory, proposes a theoretical mechanism model, and explores the mechanism of resource orchestration motivation-resource orchestration under digital transformation (resource construction - capability transformation - value creation: supply chain resilience). Using a single case and proceduralized grounded method, the logical relationship with causality is effectively analyzed, and the mechanism and results of resource orchestration in different scenarios for improving supply chain resilience under digital transformation are accurately shown. The results show that supply chain resource construction (redundant resources, technical resources, internal resources and external resources) and capability transformation (manufacturing capabilities, digital platform capabilities and innovation capabilities) have positive effects on supply chain resilience (active and passive resiliency). Through resource construction and capacity transformation under the background of digital transformation, traditional manufacturing enterprises can help improve productivity, solve the contradiction between mass production and customization, expand the market and supply chain system, solve the supply shortage crisis and collaborative innovation, so as to improve the supply chain resilience. It provides a reference for traditional enterprise resource orchestration and optimization of supply chain resilience.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Supply Chain Resilience
2.2. Research on Related Resources That Affect Supply Chain Resilience
2.3. Research on the Relationship Between Enterprise Digital Transformation and Supply Chain Resilience
2.4. The Application of Resource Orchestration Theory
2.5. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Theory
3.2. Proceduralized Grounded Method
3.3. Case Selection and Collection
4. Data Analysis Process
4.1. Open Coding
4.2. Axial Coding
4.3. Selective Coding
- Motivation for resource orchestration. Compaks was established in 2014. Driven by factors such as internal supply chain problems, fierce external competitive environment, and national policy adjustments, traditional manufacturing enterprises face an urgent need for transformation. Digital transformation has become a necessary path to enhance supply chain resilience.
- Resource orchestration under digital transformation. Compaks strategically acquires and configures supply chain resources from its wider ecosystem based on organizational needs. The company then leverages these digital resources to optimize its management and production processes, developing distinctive capabilities in operations, digital platforms, and innovation. These enhanced capabilities result in improved supply chain resilience and value creation.
- Value creation. Based on the perspective of resource orchestration theory, Compaks Company improves supply chain resilience through digital transformation from the perspective of improving Supply chain active resilience and supply chain passive resilience.
4.4. Theoretical Saturation Test
5. Theoretical Model Construction
5.1. Resource Orchestration Motivation—Market Environment Risk Perception
5.1.1. Supply Side Risk Perception
5.1.2. Demand Side Risk Perception
5.2. Resource Orchestration Under Digital Transformation
5.2.1. resource Construction
5.2.2. Capability Transformation
5.2.3. Value Creation - Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
| categories | Supply chain active resilience | Supply chain passive resilience |
|---|---|---|
| trigger point | Intra-organizational active prevention |
Organize external contingencies to force |
| quality of performance | progressive | radical |
| space dimension | Business level (local) → Strategic level (overall) | Strategic level (overall) → Business level (local) |
| time dimension | time-slack | time-limited |
| Enhancing Resilient Paths | Select, acquire, and purchase the necessary digital resources, following established goals | Select, acquire, and purchase the necessary digital resources, dynamically adjust goals |
6. Discussion
6.1. Theoretical Contribution
6.2. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li,P. “Organizational resilience under VUCA conditions: analytical framework and practical insights”, Tsinghua Management Review, 2020,Vol. 6.
- Gu,M.H.; Huo,B.F. A review of supply chain resilience research: theory and impact mechanisms. Supply Chain Management, 2020,1, 11, 3.
- Fletcher, G.; Grifths, M. Digital transformation during a lockdown. Int J Inf Manage ,2020,55:102185.
- Badhotiya, G.K.; Soni, G.; Jain, V.; Joshi, R. and Mittal, S. Assessing supply chain resilience to the outbreak of COVID-19 in Indian manufacturing firms, Operations Management Research, 2022,No. 15, 1161-1180.
- Ozdemir, D.; Sharma, M.; Dhir, A. and Daim, T. Supply chain resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic, Technology in Society, 2022,Vol. 68, 101847.
- Li,W.A.; Chen,C.H.; Zhang,X.M.; Mao,J.Y et al. 《Construction of governance mechanisms and crisis management in the face of major public health emergencies -- ‘Responding to the New Crown Pneumonia Epidemic, expert commentary》, Economic Management,2020. No. 3.
- Melnyk, S.A.; Davis,E.W.; Spekman,R.E.;Sandor,J.Outcome-driven supply chains. MIT Sloan Management Review, 2010,51,32–38.
- Zhu, S.J.; Luo, Y.; Duan, W.J. Service oriented manufacturing, markup rate distribution, and resource allocation efficiency [J] China Industrial Economy, 2021 (4): 62-80.
- Yu, Y.G.; Zheng, S.M.; Huo, B.F. Frontier Topics in Platform Supply Chain Management Theory and Methods [J] Management Science, 2021, 34 (6): 60-66.
- Zhang, H.P.; Hu, S.X. Research on the Promotion Strategy of "Internet plus Government Affairs Service" Cross departmental Data Sharing, Intelligence Magazine, 2018, Issue 12.
- Zheng, L. "Fill in the blanks and leave blank spaces in digital governance", People's Forum Academic Frontiers, 2021,Issue 23.
- Karimi J.; Walter Z. The role of dynamic capabilities in responding to digital disruption: a factorbased study of the newspaper industry. J Manag Inf Syst ,2015,32(1):39–81.
- Cha KJ.; Hwang T.; Gregor S.An integrative model of IT-enabled organizational transformation: a multiple case study. Management Decision, 2015,Vol. 53( 8), pp. 1755-1770.
- Yeow A.; Soh C.; Hansen R. Aligning with new digital strategy: a dynamic capabilities approach. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 2017:43-58. [CrossRef]
- Resca A.; Za S.; Spagnoletti P. Digital platforms as sources for organizational and strategic transformation: a case study of the Midblue project. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 2013, 8(2):71-84. [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, S.; Reinhard Prügl. Digital transformation: a review, synthesis and opportunities for future research. Management Review Quarterly, 2020,1-109.
- Wang, J.G, .; Feng, Q.Q .; Kai, Qi.A study of supply chain competitiveness under supply disruption and demand perturbation. Industrial Engineering, 2021,24(3), 9.
- Lei, Cheng.; Xinyu,Ai. Factor Marketized Allocation, Supply Chain Elasticity and Distribution Firm Performance [J]. Research on Business Economics, 2022(5).
- Heckmann, I.; Comes, T.; Nickel, S. A critical review on supply chain risk - definition, measure and modeling. Omega-International Journal of Management Science 2015, 52, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, S.; Grosse, E.; Ivanov, D. Supply chain resilience: A tertiary study. International Journal of Integrated Supply Management,2022,16(1), 52. [CrossRef]
- Pettit,T J.; Croxton,K L.; Fiksel J. The evolution of resilience in supply chain management: A retrospective on ensuring supply chain resilience[J]. Journal of Business Logistics, 2019, 40(1). [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, E.M.A.C.; Shen ,G.Q.; Kumaraswamy, M. Supply chain resilience: Mapping the knowledge domains through a bibliometric approach. Built Environment Project and Asset Management, 2021,11(4), 705–721.
- ALI, A.; MAHFOUZ, A.; ARISHA, A.Analyzing supply chain resilience:integrating the constructs in a concept mapping framework via a systematic literature review[J]. Supply chain management- an international journal,2017(1), 16-39.
- Kamalahmadi, M.; Parast, M. A review of the literature on the principles of enterprise and supply chain resilience:Major findings and directions for future research[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2016, 171(1), 116–133.
- Johnson, N.; Elliott, D.; Drake, P. Exploring the role of social capital in facilitating supply chain resilience. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal,2013, 18(3), 324–336. [CrossRef]
- Hohenstein, N. O.; Feisel, E.; Hartmann, E.; Giunipero, L.; Maria Jesus Saenz, P.; Xenophon Koufteros, D. Research on the phenomenon of supply chain resilience a systematic review and paths for further investigation. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 2015.45(1/2), 90–117. [CrossRef]
- SEOK, H.; KIM, K.; NOF S, Y. Intelligent contingent multi - sourcing model for resilient supply networks[J]. Expert systems with applications, 2016, 51, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.P. Research on the Relationship between Supply Chain Capability, Supply Chain Flexibility and the Performance of Commerce and Distribution Enterprises [J]. Research on Business Economy,2020,(21).
- Cheng K L.Enhancing effects of supply chain resilience: insights from trajectory and resource - based perspectives [J]. Supply chain management - an international journal,2017,22(4),329 - 340.
- BRUSSET, X.; TELLER, C. Supply chain capabilities,risks,and resilience [J]. International journal of production economics 2017, 184, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- LEE S M.; RHA J S. Ambidextrous supply chain as a dynamic capability: building a resilient supply chain [J]. Management decision,2016,54(1), 2 - 23.
- HAZEN B T.; BYRD T A. Toward creating competitive advantage with logistics information technology [J]. International journal of physical distribution & logistics management,2012,42(1) ,8 - 35.
- ROBERTA PEREIRA C.; CHRISTOPHER M.; DA SILVA A L. Achieving supply chain resilience: the role of procurement [J]. Supply chain management - an international journal,2014,19(5- 6), 626 - 642.
- ZHU, X.Q. How big data analytic capability affects supply chain performance-an analysis based on supply chain resilience perspective[J]. China Circulation Economy,2021, 35(06),84-93. [CrossRef]
- LAM J S, L.; BAI X, W.A. quality function deployment approach to improve maritime supply chain resilience[J]. Transportation research part E - logistics and transportation review 2016, 92, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- CHOWDHURY M M H.; QUADDUS M. Supply chain readiness,response and recovery for resilience [J].Supply chain management - an international journal,2016,21(6),709 - 731.
- BRIDGETTE S - T.; BRANICKI L. Creating resilient smes: why one size might not fit all [J]. International journal of production research, 2011,49 ( 18) : 5565 - 5579.
- Yao, W.X.; Chen, Q. Post processing of Supply Chain Stress Testing: A Perspective of Elastic Supply Chain [J] Research on Technology Management, 2015, (4): 193-197.
- Yin, Q.Q.; Xu, J. The Impact of Elastic Supply Network on Enterprise Development and Implementation Strategies [J] Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University (Social Sciences Edition), 2013, (1): 61-66.
- KHALILI S M.; JOLAI F.; TORABI S A. Integrated production - distribution planning in two - echelon systems: a resilience view [J]. International journal of production research,2017,55 ( 4) : 1040 - 1064.
- PONOMAROV S Y.; HOLCOMB M C. Understanding the concept of supply chain resilience[J]. International journal of logistics management,2009,20 ( 1) : 124 - 143.
- Ge, X.T.; Xie, J.G.; Yang, H.N. Digital Transformation and Enterprise Supply Chain Resilience: Evidence from Chinese Listed Companies and Suppliers [J] Journal of Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, 2024, (03): 136-150. [CrossRef]
- TUKAMUHABWA B.; STEVENSON M.; BUSBY J. Supply chain resilience in a developing country context: a case study on the interconnectedness of threats,strategies and outcomes[J]. Supply chain management - an international journal,2017,22 ( 6) : 486 - 505.
- JAARON A A M.; BACKHOUSE C J. Service organisations resilience through the application of the vanguard method of systems thinking: a case study approach [J]. International journal of production research,2014,52 ( 7) : 2026 - 2041.
- DATTA P. Supply network resilience: a systematic literature review and future research [J]. International journal of logistics management,2017,28 ( 4) : 1387 - 1424.
- BLACKHURST J.; DUNN K S.; CRAIGHEAD C W. An empirically derived framework of global supply resiliency [J]. Journal of business logistics,2011,32 ( 4) : 374 - 391.
- CARVALHO H.; DUARTE S.; MACHADO V C. Lean,agile,resilient and green: divergencies and synergies[J]. International journal of lean six sigma,2011,2 ( 2) : 151 - 179.
- ALI I.; NAGALINGAM S.; GURD B. Building resilience in SMEs of perishable product supply chains: enablers,barriers and risks [J]. Production planning & control,2017,28 ( 15) : 1236 - 1250.
- GABLER C B.; RICHEY R G.; STEWART G T . Disaster resilience through public - private short - term collaboration [J]. Journal of business logistics,2017,38 ( 2) : 130 - 144.
- JAIN V.; KUMAR S.; SONI U,et al. Supply chain resilience: model development and empirical analysis [J]. International journal of production research,2017,55 ( 22) : 6779 - 6800.
- Yin, W. Identifying the pathways through digital transformation to achieve supply chain resilience: an fsqca approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023,30(4), 10867-10879.
- Wang, L.S.; PANG, Z.Q.; Xing, Q. Innovation spillover effect of enterprise digital transformation: Based on the perspective of industrial chain and supply chain resilience [J/OL]. Soft Science,2024, (11) : 1-12.
- Gao, Y.; Leng, Y.B.; Shan,B.A. Control Supply Chain Risks in Digital Transformation: A New Way to Improve Supply Chain Resilience. J. Organ. End User Comput. 2022,34, 7, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; XIAO, Y.; WANG, N.H. Study on the resilience of international trade supply chain in the process of digital transformation: from the perspective of network structure under the impact of uncertain events [J/OL]. Journal of Management,2021, 11 (08), 1-19 https://cfffgc1d129f57bb244a4h0fonb699fkbx6pcofgfy.eds.tju.edu.cn/kcms/detail/41.1408.F.20241014.1122.012.html.
- Song, D.L.; Liu,F.J.; Ding,W.L. Enterprise and supply chain resilience: digital transformation based on social network analysis perspective [J]. Journal of southeast university (philosophy and social sciences e dition), 2024, 26 (5) ,47-60 + 149 + 2.
- Yuan,Y.H.; Wu, D.D. Enterprise digital transformation and supply chain resilience: from the perspective of supply chain spillover [J/OL]. Systems Engineering Theory and Practice, 2019, 11 (08), 1-22. https://cfffgc1d129f57bb244a4h0fonb699fkbx6pcofgfy.eds.tju.edu.cn/kcms/detail/11.2267.N.20240905.1101.002.html.
- Faruquee, M.; Paulraj, A.; Irawan, CA. Strategic supplier relationships and supply chain resilience: is digital transformation that precludes trust benefcial? Int J Oper Prod Manag, 2021, 41, 1192–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin,W.; Ran,W. Supply Chain Diversification, Digital Transformation, and Supply Chain Resilience: Configuration Analysis Based on fsQCA. Sustainability. 2022, 14(13), 7690.
- Zeng, H.Y.; Yu, Y.B. Study on the impact of supply chain elasticity on innovation performance in the context of digital transformation [J]. Logistics Technology, 2019,47(08),100-103+107. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.L.; Li, H.C. The influence of duality on supply chain Resilience under digital transformation: A configuration study based on fsQCA [J]. The circulation economy, 2024, (17) : 113-116. The.
- Feng, D.; Zhang, H.J.The impact of digital transformation on supply chain resilience - A moderated mediation model. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum University (Social Science Edition) ,2024,(02), 1-8+16.
- Liu, X.H. Digital transformation, supply chain resilience and distribution firms' business performance. Research on Business Economics,2023,(2), 161-164.
- Ye, F .; Liu, K .; Li, L.X et al. Digital supply chain management in the COVID-19 crisis: An asset orchestration perspective [J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2022, 245: 108396.
- Sirmon,D. G. ,M. A. Hitt,and R. D. Ireland. Managing Firm Resources in Dynamic Environments to Create Value: Looking Inside the Black Box[J]. Academy of Management Review,2007,32,( 1) : 273 - 292.
- Wang, H.H .; Du, M. International research hotspots and evolution of digital innovation: a visual analysis [J]. Science and Technology Progress and Countermeasures, 2021, 38(21):9. (in Chinese).
- Liu,H. F.; S. B. Wei,and W. L. Ke,et al. The Configuration between Supply Chain Integration and Information Technology Competency: A Resource Orchestration Perspective[J]. Journal of Operations Management,2016,( 44) : 13 - 29.
- Zhang,C. , L,X., J. Dhaliwal. Alignments between the Depth and Breadth of Inter-organizational Systems Deployment and Their Impact on Firm Performance[J]. Information & Management,2016,53,( 1) : 79 - 90.
- Miao,F.; G. P. Wang., P. Jiraporn. Key Supplier Involvement in IT-enabled Operations: When Does it Lead to Improved Performance? [J]. Industrial Marketing Management,2018,( 75) : 134 - 145.
- Gong,Y.; F,Jia.; S. Brown,et al. Supply Chain Learning of Sustainability in Multi-tier Supply Chains[J]. International Journal of Operations & Production Management,2018,38,( 4) : 1061 - 1090.
- Burin,R. G.; M. N. Perez-Arostegui.; J. Llorens-Montes. Ambidexterity and IT Competence Can Improve Supply Chain Flexibility? A Resource Orchestration Approach[J]. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 2020,26,( 2) : 1 - 15.
- Gligor,D.; M. Holcomb.; M. J. Maloni,et al. Achieving Financial Performance in Uncertain Times: Leveraging Supply Chain Agility[J]. Transportation Journal,2019,58,( 4) : 247 - 279.
- Gligor,D. Performance Implications of the Fit Between Suppliers’Flexibility and Their Customers’ Expected Flexibility: A Dyadic Examination[J]. Journal of Operations Management,2018,( 58 - 59) : 73 - 85.
- Karimi J.; Walter Z. The role of dynamic capabilities in responding to digital disruption: a factorbased study of the newspaper industry. Journal of Management Information Systems, 2015, 32(1):39-81. [CrossRef]
- Resca A.; Za S.; Spagnoletti P. Digital platforms as sources for organizational and strategic transformation: a case study of the Midblue project. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 2013, 8(2):71-84. [CrossRef]
- Fan,B.; Chen,L. "Research on the Big Data Capability of Government Departments - From an Organizational Perspective", Public Administration Review, 2017,Issue 1.
- Helfat,C.E.; S.Finkelstein.; W. Mitchell,et al. Dynamic Capabilities: Understanding Strategic Change in Organizations[M]. Malden,MA: Blackwell,2007.
- Sirmon,D. G.; M. A. Hitt.; R. D. Ireland. Managing Firm Resources in Dynamic Environments to Create Value: Looking Inside the Black Box[J]. Academy of Management Review,2007,32,( 1) : 273 - 292.
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, Z.B. Review of Resource Scheduling Theory and Its Research Progress [J] Economic Management, 2020,42 (09): 193-208. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.Q.; Xu,J.F. Compilation of the Theoretical Framework of Resource View [J]. Foreign Economics and Management, 2002, 24 (7): 6-13.
- Wu, Q.; Yao,Y.X. Enterprise digital transformation and supply chain configuration: centralization or diversification. China Industrial Economy, 2023 (8): 99-117.
- Gioia, D.A.; Corley, K.G.; Hamilton, A.L.,”Seeking Qualitative Rigor in Inductive Research: Notes on the Gioia Methodology”,Organizational Research Methods,2013,16(1),pp. 15~31.
- Jia, X. D.; Liang, H. The 'jungle' of rooted theory, past and future. Research Management, 2020,(05), 151-163. [CrossRef]
- GLASERB G.; STRAUSS AL.The discovery of grounded theory: strategies for qualitative research[M].Chicago: Aldine,1967, 40-136.
- Jia, X. D.; Liang, H. A preliminary study on the paradigm of Chinese local management theory construction based on the “rooted spirit”[J]. Journal of Management, 2016, 13(3),11. [CrossRef]
- Kamez K. Constructing a rooted theory: a practical guide to qualitative research [M]. Bian, G.Y. Translation. Chongqing:Chongqing University Press,2009.
- EISENHARDT K M.Theory building from cases: opportunities and challenges[J]. Academy of Management Journal,2007,50(1), 25-32.
- LI,L,; TAO,H.Y. Dynamic Mechanism of Shanzhai Mode Formation and Its Implications for Domestic Brands[J]. Research Management,2013,34(2),112-119.
- MILESMB.; HUBERMANA,M.Qualitative data analysis: an expanded source book[M].Thousand Oaks:Sage Publications,1994,119-123.
- YongJian,Li.; KL,Xue.; W,Wang.A Review of Research on Supply Chain Disruption Management. Nankai University Business School, China Institute of Corporate Governance,2016, Tianjin 300071, China.
- Parast,M.M.; Subramanian,N. An Examination of The Effect of Supply Chain Disruption Risk Drivers on Organizational Performance: Evidence from Chinese Supply Chains[J]. Supply Chain Management an International Journal,2021,26(4), 548—562.
- Weifeng,XU.; Qingsong,RUAN.; Guodong,GUANG. Private entrepreneurs' external environment risk perception and corporate innovation investment[J]. Research Management,2021, 42(03), (pp.160-171). [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer T., Leiponen A., Schilling M, et al. Platform ecosystems as meta-organizations: Implications for platform strategies[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 2022, 43(3): 405-424.
- Cui, M., Pan, S. L. Developing focal capabilities for e-commerce adoption: A resource orchestration perspective. Information Management,2015, 52(2), 200–209.
- Cutolo, D., Kenney, M. Platform-Dependent Entrepreneurs: Power Asymmetries, Risks, and Strategies in the Platform Economy. ERPN: Start-Up & Small Business Finance (Sub-Topic), 2019.
- Ma, H.J., Wang,J.J., Su, Z.F. How small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises can allocate resources and utilize digital opportunities under the background of digital transformation: a study on fsQCA based on resource allocation theory [J]. Nankai Management Review, 2024, 27 (4): 90-100. [CrossRef]
- Avenyo E K.; Tregenna F.; Kraemer-Mbula E. Do productive capabilities affect export performance? Evidence from African firms[J]. The European Journal of Development Research, 2021, 33(2), 304-329.
- Sheng, W.Z.; Chen,J. Research on Measurement Indicators of Innovation Capability of Small and Medium sized Manufacturing Enterprises [J]. Journal of Management Engineering, 2015, 29 (04), 49-55.
- Ben Arfi W.; Hikkerova L. Corporate entrepreneurship, product innovation, and knowledge conversion: the role of digital platforms[J]. Small Business Economics, 2021, 56(3), 1191-1204.
- Li L.; Su F.; Zhang W, et al. Digital transformation by SME entrepreneurs: A capability perspective[J]. Information Systems Journal, 2018, 28(6), 1129-1157.
- Hosseini, S.; Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. Review of quantitative methods for supply chain resilience analysis. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2019, 125, 285–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, R. The role of risk management in buyer-supplier relationships with a preferred customer status for total quality management. TQM Journal. 2020, 32, 959–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| development logic | Case Information | conceptualization | categorization |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Motivation for the organization of resources orchestration |
Compaks -Australian caravan dealers: the industry started late, the development is slow; caravan enterprises are many but not strong, it is difficult to form a scale, the production is subject to the dealer's orders, and the profit of the product is also slow to go up. Small scale, low production, few customers, Compass wants to get orders, can only rely on product quality. The caravanning industry is backward in terms of manufacturing process and efficiency, the quality of caravanning modification is not uniform, the caravan leasing and traveling supporting services are not perfect, and the user experience is poor, and many other problems. In China, the caravanning industry and caravanning tourism is still in its infancy, and caravanning enterprises generally have problems such as fragmented procurement of parts, difficult to find accessories, poor communication with users, weak technical foundation and financing difficulties. The Compaks' head of customs Li Longlong said, parts varieties, brands, specifications are complicated, customers delete parts or even cancel the order occurs from time to time, “high-priced with all the parts that do not need to be used, not to mention the occupation of funds, but also affects the implementation of the company's production plan.” Wang Weiyuan, chairman of the board, said, “Affected by the epidemic, the shortage of materials, raw material prices, poor shipping logistics and other factors impact, personalized customization on the industrial chain, supply chain put forward higher requirements.” |
a1. Lack of user communication a2. Subject to dealer orders a3. Weak technical foundation a4. Over-reliance on exports a5. Financing difficulties a6. Hard to find accessories a7. Procurement fragmentation a8. The industry is backward a9. Weak anti-risk ability a10. Impact of the epidemic a11. Market changes |
A1. Supply-side risk perception(a2, a3, a5, a6, a7, a9) A2.Demand-side risk perception(a1, a4, a8, a10, a11) |
|
Resource orchestration under digital transformation (resource building - capacity transformation - value creation) |
The person in charge, Yu Hui, introduced that after resuming work on February 8th, due to the impact of the epidemic, the original board supplier was unable to start work. The enterprise resumption and production increase service platform on the COSMOPlat platform quickly solved the procurement needs. Wang Weiyuan has decided to cooperate with COSMOPlat to jointly create a sub platform for the RV industry based on user experience, hoping to promote the transformation of old and new driving forces of Kangpaisi and accelerate the transformation and upgrading of enterprise intelligent manufacturing. The enterprise has invested approximately 80 million yuan to purchase new equipment, upgrade production lines, and implement digital management systems such as ERP and PLM. Pei Zhanbao stated that he has deep cooperation with the Haier Group team, conducting remote collaborative production through video, providing training to newly hired employees, and improving production efficiency; Campaigner will go to the "cloud" to seek solutions from the industrial Internet and carry out intelligent digital transformation. In 2019, the headquarters of Compaks Company acquired cross-border supply chain platform products from the COSMOPlat platform. The platform utilizes an integrated supply chain management system deployed in the cloud to streamline a series of tedious operations related to sea freight exports, including orders, booking, dispatching vehicles, and customs clearance. Two overseas warehouses have been established in South Korea and Australia, with a total storage area of over 7000 square meters, and there are continuous orders for RV exports. Compaks has purchased technology from the COSMOPlat platform for digital and intelligent transformation. The entire production process has been optimized, making Compaks the first intelligent manufacturing and interconnected factory in the RV industry in China. Traditional RVs have been upgraded to intelligent RVs, achieving shared and interconnected product design and development, production and manufacturing, iterative upgrades, and other links. Compaks has partnered with universities such as Tsinghua University, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Shandong University of Technology to launch a new round of patent research and development. The company has established a technical team of over 150 people and invests 5% of its annual sales revenue into technology research and development. On the Compaks car, more than 120 invention patents and utility model patents are loaded. In 2018, with the help of Sindar, an ecological brand in the camping industry, "Compaks RV" transformed from enterprise led to user led, linking connected factories, smart appliances, connected vehicles, RV campsites, and travel enthusiasts into an ecosystem, upgrading traditional houses and vehicles into mobile smart homes and enhancing user experience. |
a12. Data Interworking - Structured capital a.13 Multi-Source Procurement a14 Business leadership support a15 Cooperation with Internet platforms a.16 Co-building - Cognitive Capital a17 Purchase the device a18. Buy digital technology a19. Training digital talent a.20. Establishment of relationship resource a21. Organizational changes a22. Management model change a23. Management model innovation a24. Solution change a25. Changes in production patterns a26. Enterprise intelligent manufacturing upgrade a27. Production process optimization a28. Research and development in cooperation with universities a29. R&d in cooperation with the platform a30. Based on the user perspective. a31. Establishment of new production patterns a32. Product innovation |
AA3. Redundant Resources (a13) A4. Organizational Resources (a13) A5. Technical Resources (a14,a15) A6. Human Resources (a19) A7. Cooperation Resources (a15,a16) A8.Relationship resources (a12,a16,a.18) A9. Manufacturing Capacity (a21-a24) A10. Digital platform capability (a25,a26, a27) A11. Innovation ability (a28-a32) |
|
value creation |
On the manufacturing side, COSMOPlat RV Industry Intensive Purchasing Service provides a stable supply chain solution for Compaks. The procurement module has reduced the purchase price of galvanized sheet, one of the main materials for RV production, by 12% and the overall cost of module procurement by 7.3% ...... During the epidemic, Compaks relied on the resources of the COSMOPlat platform to realize a 3-day solution for lightweight panels for caravans and a 1-day solution for the supply of sandwich panels. Under the influence of the epidemic, customs inspection and quarantine is difficult, there is no fixed place, and the sampling environment is poor, Compaks relies on the resources of the COSMOPlat platform, and creates the inspection and quarantine square cabin in just 15 days, which provides the inspection and quarantine work with a stable, comfortable, and safe place with the functions of intelligent air management and disinfection of the square cabin. The User Interaction module enables companies to get designs and orders directly from users,the car body color, engine power and other personalized customization are realized, realizing a 63% product premium and a 62% increase in orders. The caravan enterprises also take the policy wind to set up “overseas warehouse” in foreign countries. Under this mode, enterprises can prepare goods for export in advance according to the historical order situation, compared with the traditional “order - production - export” mode, faster delivery, better customer experience, but also to facilitate the enterprise according to the maritime logistics, container and other conditions to flexibly adjust the delivery and Reduce costs. |
a33. Improved procurement efficiency a34. Flexible supply and demand a35. Disruptive innovation a36. Personalized customization a37. Operational flexibility a38. Reduce costs and increase efficiency a39. Production flexibility |
A12. Supply chain proactive flexibility improvement (a33, a36, a37,a38,a39) A13. Supply chain passive resilience improvement (a34,a35) |
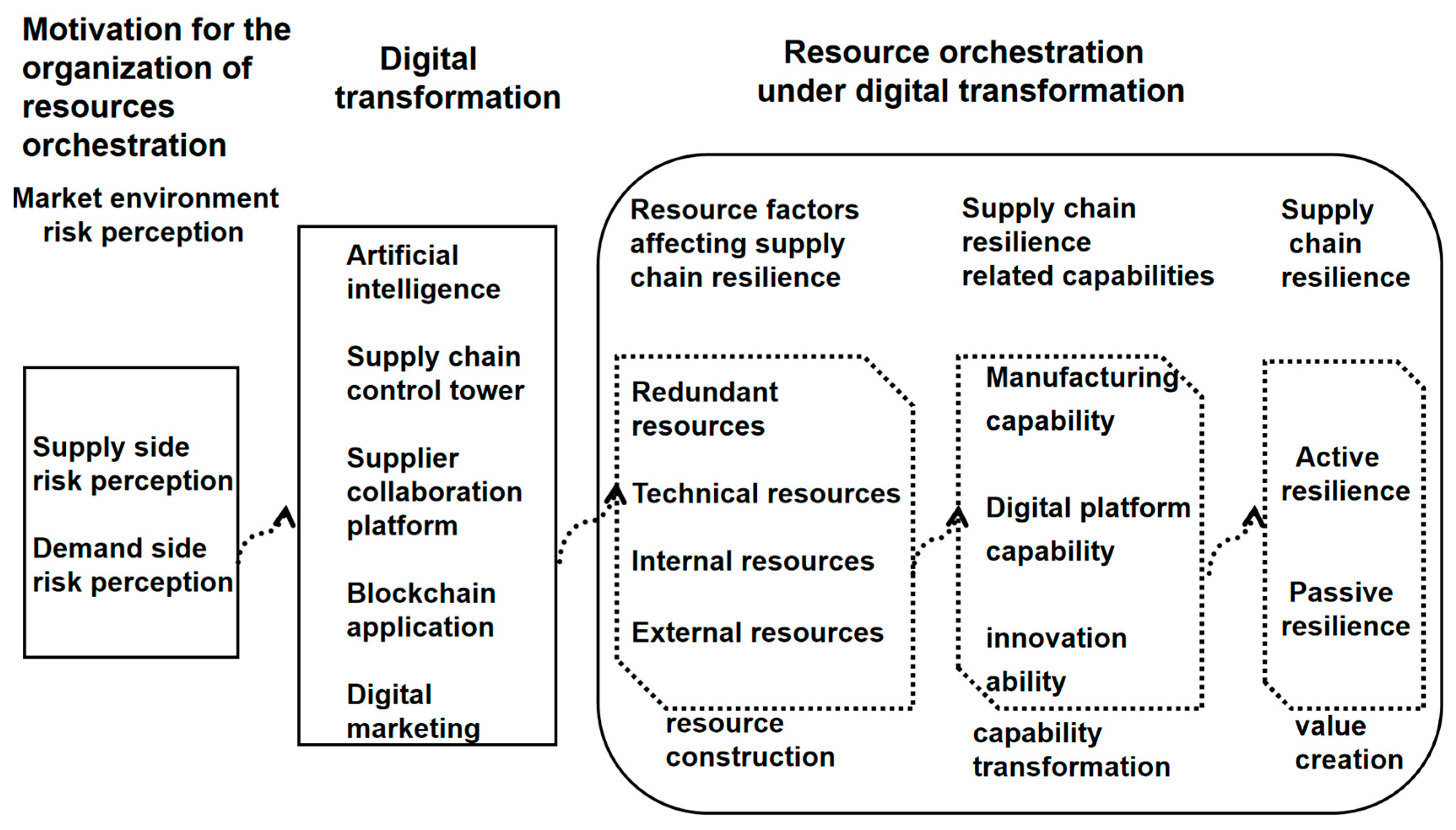
| main category | support category | connotation of category |
|---|---|---|
| Market environment risk perception (Motivation for resource orchestration) Resource factors affecting supply chain resilience (Resource Construction) Capability related to supply chain resilience (Ability Conversion) Improvement of supply chain resilience (Value creation) |
Supply side risk perception Demand side risk perception Redundant resources Technical resources Internal resources External resources Manufacturing capability Digital platform capability Innovation capability Supply chain active resilience improvement Supply chain passive resilience improvement |
Driven by internal problems and a fiercely competitive external environment, traditional manufacturing companies need to rely on resource orchestration to deal with Obtain and purchase relevant resources that the enterprise lacks from the social resource pool, and construct resources by combining them with existing resources according to its own needs Enterprises utilize orchestration resources to enhance their manufacturing, digital platform, and innovation capabilities Resource orchestration under digital transformation can improve procurement efficiency, personalize customization, achieve cost reduction and efficiency improvement, and disruptive innovation, while expanding new markets. Improved the active and passive resilience of the supply chain, and continued to analyze its own risks and needs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





