Submitted:
27 February 2025
Posted:
28 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Many public PyTorch repositories implement Local Normalized Cross-Correlation Loss (LNCC) using five sequential convolution operations. This implementation is, however, slow, failing to utilize modern hardware's performance potential fully. By simply replacing these convolutions with one single group convolution, we found the training time of LNCC-based deep registration models can be halved without affecting the numerical results, leading to notable cost savings. We hope that this simple approach will be beneficial to the community. An example code is available at \url{https://github.com/xi-jia/FastLNCC}.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Algorithm 1: LNCC loss calculation with five sequential convolutions |
Require:I (input image), J (reference image), w (window size)
|
2. Implementation
2.1. Pseudo Code
| Algorithm 2: LNCC loss calculation with one group convolution |
Require:I (input image), J (reference image), w (window size)
|
2.2. Runtime Analysis
- Data: 403 training pairs from the IXI dataset (https://brain-development.org/ixi-dataset/) pre-processed by TransMorph [9] are selected as training data.
- Training: Each one of the five models is trained in five epochs using the Algorithm 1 and the new Algorithm 2, respectively.
- Results: The training time required for each epoch is reported to compare the difference between the two algorithms.
- Others: The batch size of all networks is set to 1. The sub-window of LNCC is fixated at . All models are trained on the same Nvidia A100-40G GPU with Pytorch. (More experiments are in the Appendix A.)
3. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Appendix A
| GPU | Quadro-rtx8000-48g | P100-sxm2-16gb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm1 | Algorithm2 | Reduced(%) | Algorithm1 | Algorithm2 | Reduced(%) | |
| VM-1 | 669.5427791 | 395.2477166 | 40.97 | 1002.45329 | 640.9769462 | 36.06 |
| VM-2 | 701.1765172 | 426.4876567 | 39.18 | 1079.542767 | 716.4298012 | 33.64 |
| 731.4320591 | 455.3439657 | 37.75 | 1160.251004 | 797.7661547 | 31.24 | |
| 1022.4765293 | 748.9222134 | 26.75 | 1616.234878 | 1254.400603 | 22.39 | |
| TM | 878.5947878 | 603.5537508 | 31.30 | 1241.964152 | 880.458546 | 29.11 |
References
- Cachier, P.; Bardinet, E.; Dormont, D.; Pennec, X.; Ayache, N. Iconic feature based nonrigid registration: the PASHA algorithm. Computer vision and image understanding 2003, 89, 272–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical image analysis 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, M.; Ayache, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Pennec, X.; (ADNI, A.D.N.I.; et al. LCC-Demons: a robust and accurate symmetric diffeomorphic registration algorithm. NeuroImage 2013, 81, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Zhao, A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Guttag, J.; Dalca, A.V. An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018, pp.
- Balakrishnan, G.; Zhao, A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Guttag, J.; Dalca, A.V. VoxelMorph: a learning framework for deformable medical image registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2019, 38, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Brown, N.M.; Saeed, S.U.; Casamitjana, A.; Baum, Z.M.C.; Delaunay, R.; Yang, Q.; Grimwood, A.; Min, Z.; Blumberg, S.B.; et al. DeepReg: a deep learning toolkit for medical image registration. Journal of Open Source Software 2020, 5, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.C.; Chung, A.C. Fast Symmetric Diffeomorphic Image Registration with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, C.; Huang, H.; Luo, Z. Learning deformable image registration from optimization: perspective, modules, bilevel training and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2021, 44, 7688–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Frey, E.C.; He, Y.; Segars, W.P.; Li, Y.; Du, Y. TransMorph: Transformer for unsupervised medical image registration. Medical Image Analysis, 1026. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Bartlett, J.; Zhang, T.; Lu, W.; Qiu, Z.; Duan, J. U-net vs transformer: Is u-net outdated in medical image registration? In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. Springer; 2022; pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Li, W.; Brown, R.; Ma, N.; Kerfoot, E.; Wang, Y.; Murrey, B.; Myronenko, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, D.; et al. Monai: An open-source framework for deep learning in healthcare. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.02701, arXiv:2211.02701 2022.
- Zheng, J.Q.; Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Lim, N.H.; Papież, B.W. Residual Aligner-based Network (RAN): Motion-separable structure for coarse-to-fine discontinuous deformable registration. Medical Image Analysis 2024, 91, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Jia, X.; Lu, W.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.; Krull, A.; Duan, J. WiNet: Wavelet-based Incremental Learning for Efficient Medical Image Registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer; 2024; pp. 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, B.; Pan, J.; Ghahremani, M.; Rueckert, D.; Wachinger, C.; Wiestler, B. Mamba? In Catch The Hype Or Rethink What Really Helps for Image Registration. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration. Springer; 2024; pp. 86–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, A.; Hansen, L.; Mok, T.C.; Chung, A.C.; Siebert, H.; Häger, S.; Lange, A.; Kuckertz, S.; Heldmann, S.; Shao, W.; et al. Learn2Reg: comprehensive multi-task medical image registration challenge, dataset and evaluation in the era of deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2022, 42, 697–712. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 |
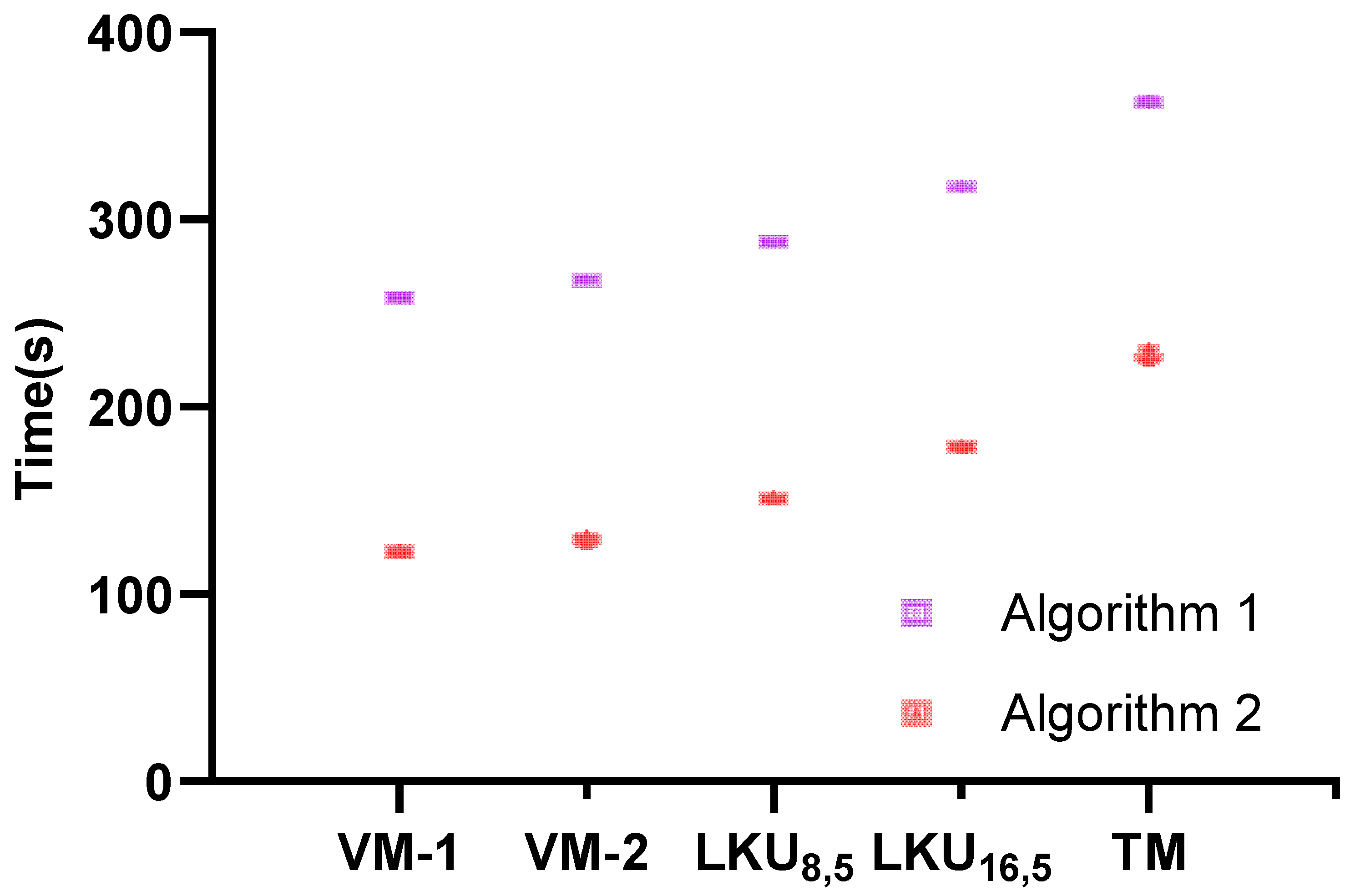
| Models | Epoch1 | Epoch2 | Epoch3 | Epoch4 | Epoch5 | Avg | Epoch1 | Epoch2 | Epoch3 | Epoch4 | Epoch5 | Avg | |
| VM-1 | 258.95 | 258.07 | 257.69 | 258.02 | 257.62 | 258.07 | 123.37 | 122.31 | 122.40 | 122.52 | 122.46 | 122.61 | |
| VM-2 | 267.78 | 267.57 | 267.64 | 267.67 | 267.90 | 267.71 | 131.07 | 129.66 | 129.66 | 129.10 | 126.77 | 129.25 | |
| 288.10 | 287.61 | 287.95 | 287.90 | 287.67 | 287.84 | 152.01 | 150.71 | 150.85 | 150.70 | 150.72 | 151.00 | ||
| 319.11 | 316.98 | 316.94 | 316.97 | 317.01 | 317.40 | 179.67 | 178.49 | 178.47 | 178.71 | 178.28 | 178.72 | ||
| TM | 364.44 | 362.00 | 361.99 | 361.95 | 362.01 | 362.48 | 231.30 | 224.78 | 224.59 | 225.09 | 225.08 | 226.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





