Submitted:
20 February 2025
Posted:
21 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
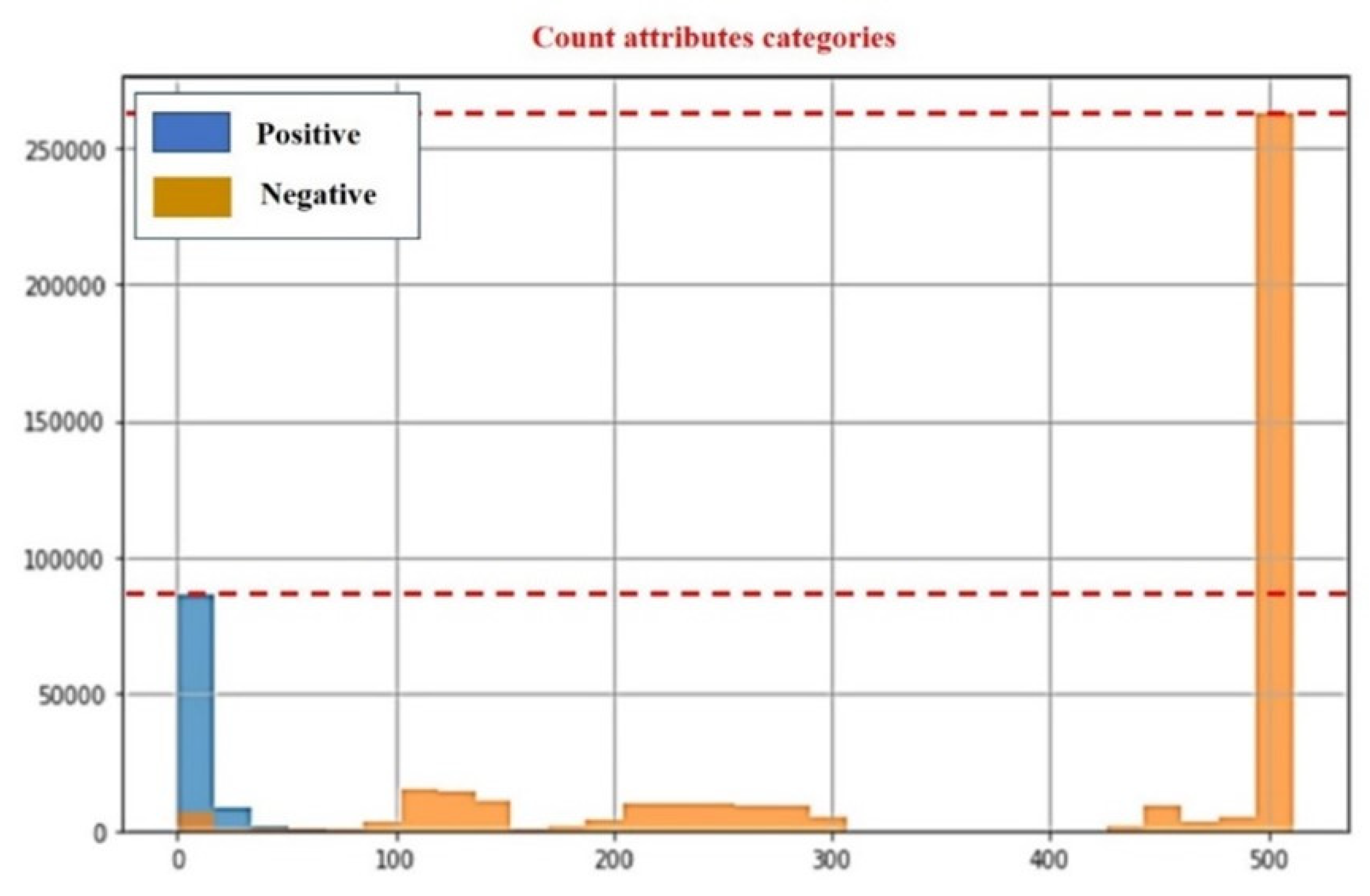
The fuzzy- logic (FL) based recommendation system is a research subject that studies and develops technological systems capable of solving complex tasks typically requiring human intelligence, as well as creating intelligent recommendation systems. Fuzzy logic (FL) and deep learning (DL) are techniques for handling variables that allow multiple values to be processed through the same variable. To resolve issues with an open, inexact spectrum of information that makes it feasible to obtain an array of specific. Our proposed model is a FL based recommendation system, characterized by a hybrid fuzzy detection (HFD) and loss computation model. Furthermore, the FL based model is developed using DL, along with a FL algorithm designed for detecting and preventing attacks. Configuration techniques results such as positive and negative attacks, which are attributed to the type of attack or normal behavior. The frequency results are attributed to the type of attack or normal behavior. Evolution analysis refers to the description and modeling of regularities or trends for objects whose count changes over time. The distribution includes a positive peak of 77 and a negative peak of over 100 categories, forming the foundation of the FL based recommendation system. In engineering finding the proposed FL and DL recommendation system has the potential to provide valuable support and help users achieve their financial goals.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Our proposed model is a FL based recommendation system, characterized by a hybrid fuzzy detection (HFD) and loss computation model.
- Furthermore, the FL based model is developed using DL, along with a FL algorithm designed for detecting and preventing attacks. Configuration techniques results such as positive and negative attacks, which are attributed to the type of attack or normal behavior. The frequency results are attributed to the type of attack or normal behavior.
- Evolution analysis refers to the description and modeling of regularities or trends for objects whose count changes over time. The distribution includes a positive peak of 77 and a negative peak of over 100 categories, forming the foundation of the FL based recommendation system. In engineering finding the proposed FL and DL recommendation system has the potential to provide valuable support and help users achieve their financial goals.
2. Experimental Designs
2.1. The FL-Based Recommendation System
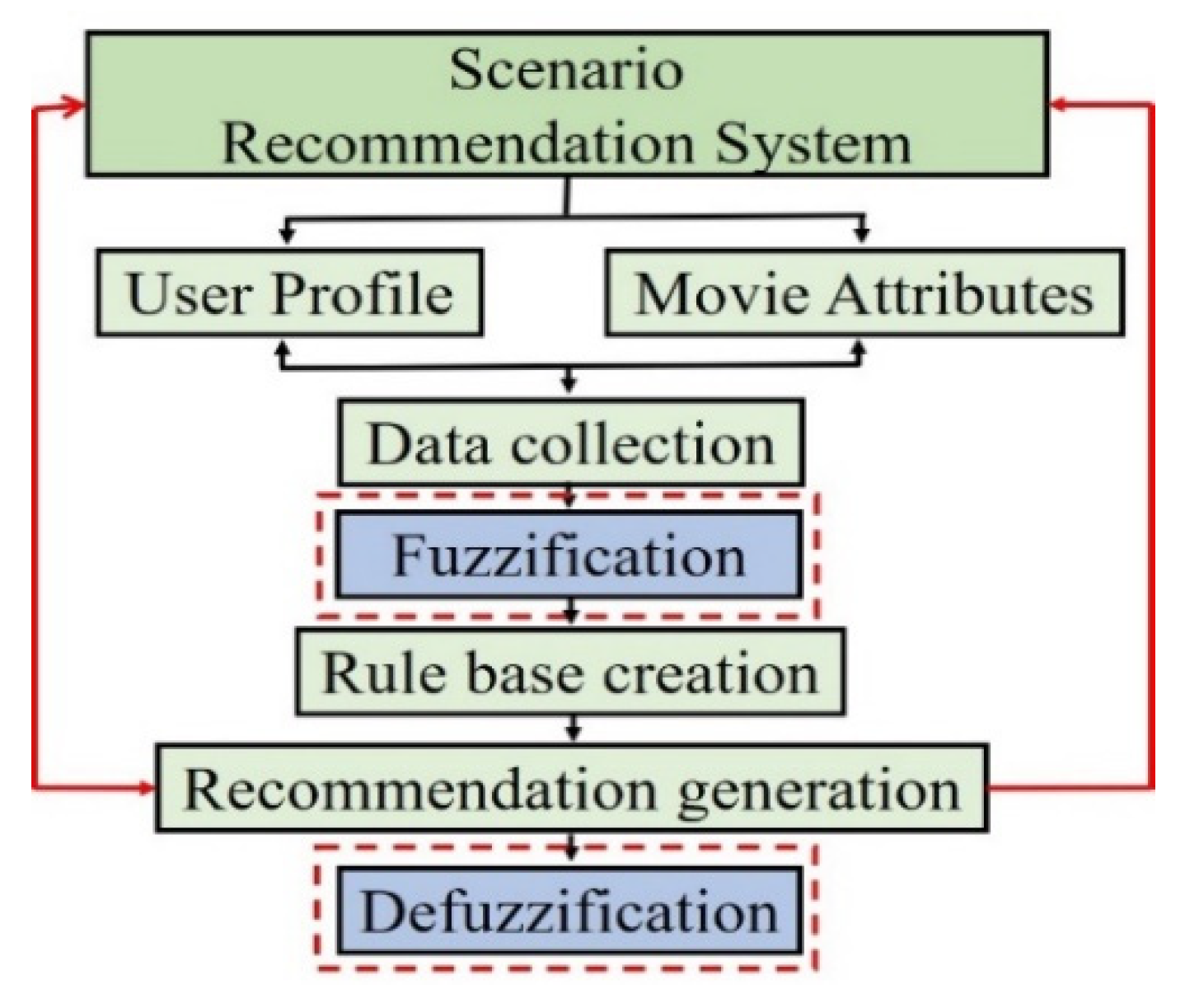
2.2. FL-Based Recommendation System
2.3. Using Deep Learning
| Total Attacks | Positive Attacks | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| 10000 | 50000 | 10000 |
| 5000 | 1000 | 2000 |
| 2500 | 500 | 250 |
| 1500 | 200 | 100 |
| 2000 | 1000 | 800 |
| 250 | 50 | 500 |
| 300 | 20 | 300 |
| 350 | 10 | 200 |
| 400 | 55 | 10 |
| 450 | 58 | 50 |
| 500 | 250 | 220 |
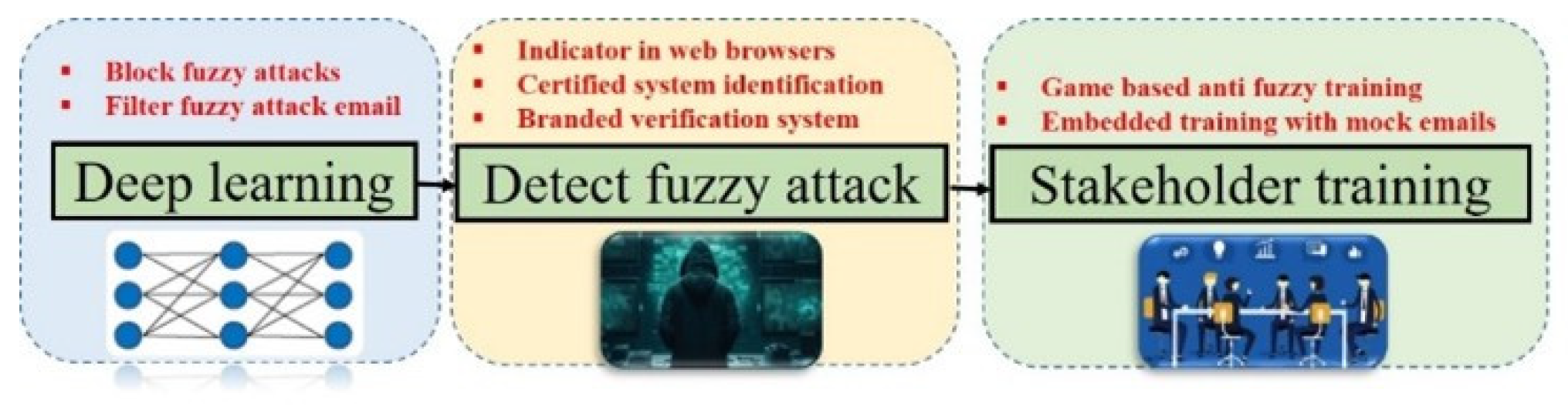
2.2. Algorithm for the Fuzzy Attacks
- [ x = 2^3 ]
- Now calculate ( 2^3 ):
- [ 2^3 = 2 times 2 times 2 = 8 ]
- [ x = 8 ]
- [1] Solve the logarithmic equation ( log_5(x) = 2 ).
- [2] Convert the exponential equation ( 10^4 = x ) to its logarithmic form.
- [3] Find the value of (x) in the equation ( log_{10}(x) = -1 ).
- The equation ( log_2(x) = 3 ) tells us that (x) is the number such that when 2 (the base of the logarithm) is raised to the power of 3, it equals (x). In other words, ( 2^3 = x ).
- : the set of rational numbers
- : the rational integers
- : a real algebraic integer of degree
- : The n-th integer square matrices
- : the n-th unimodular square matrix group
- Express respectively Energy consumption of storage, computation, communication and VMs resources.
- : The determinant of a matrix M.
- : isomorphisms which transfer to another conjugate of , where is the identify map
- a column vector of K, where and
- the n-square matrix which elements is
- the n square matrix of which element equals to where
- the square matrix of which element equals to where
- for
- : the set of rational numbers
- : the rational integers
- : a real algebraic integer of degree
- : The n-th integer square matrices
- : the n-th unimodular square matrix group
- Express respectively Energy consumption of storage, computation, communication and VMs resources.
- : The determinant of a matrix M.
- : isomorphisms which transfer to another conjugate of , where is the identify map
- a column vector of K, where and
- the n-square matrix which elements is
- the n square matrix of which element equals to where
- the square matrix of which element equals to where
- for
3. Model Design
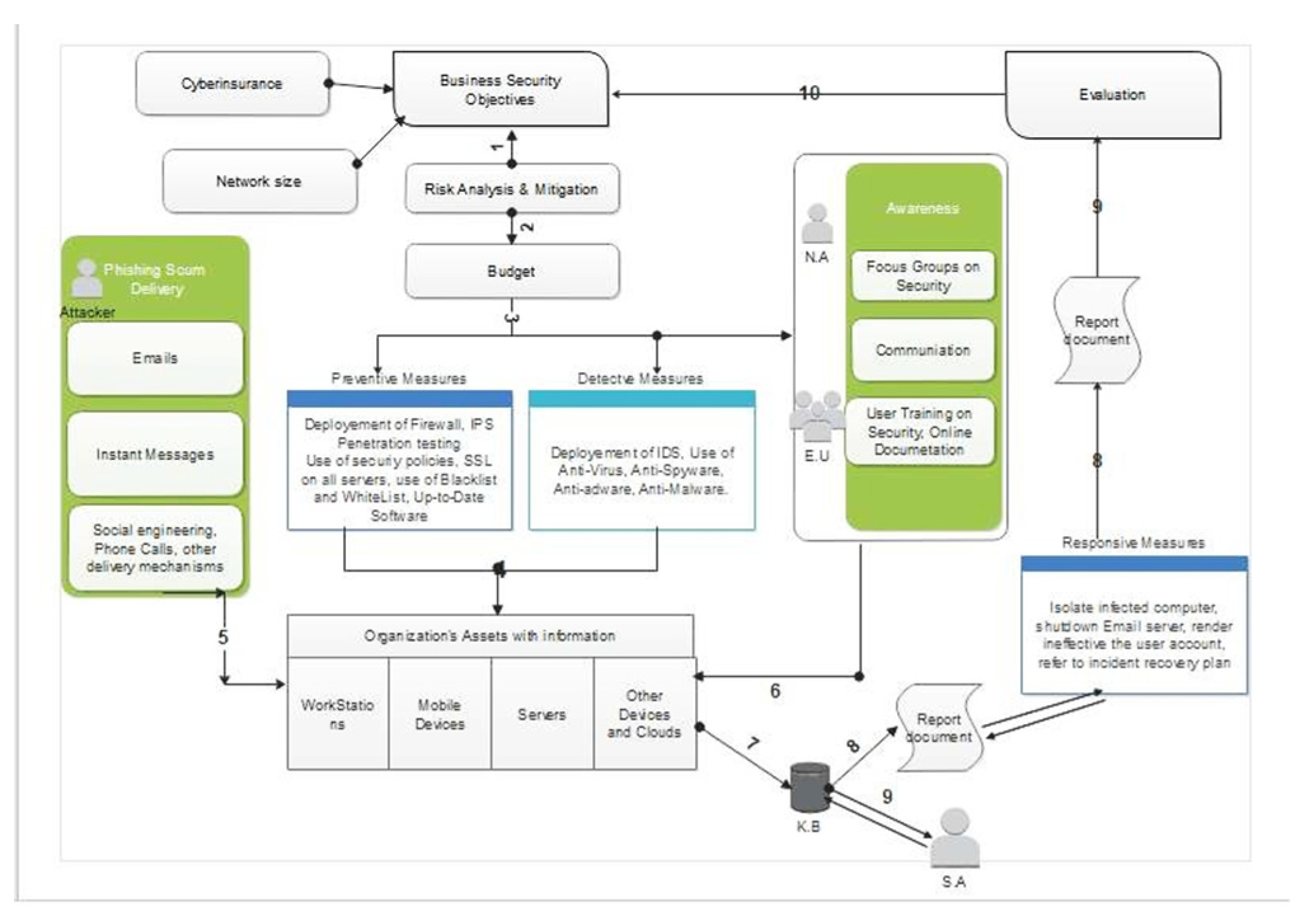
3.1. Fuzzy Attacks Steps
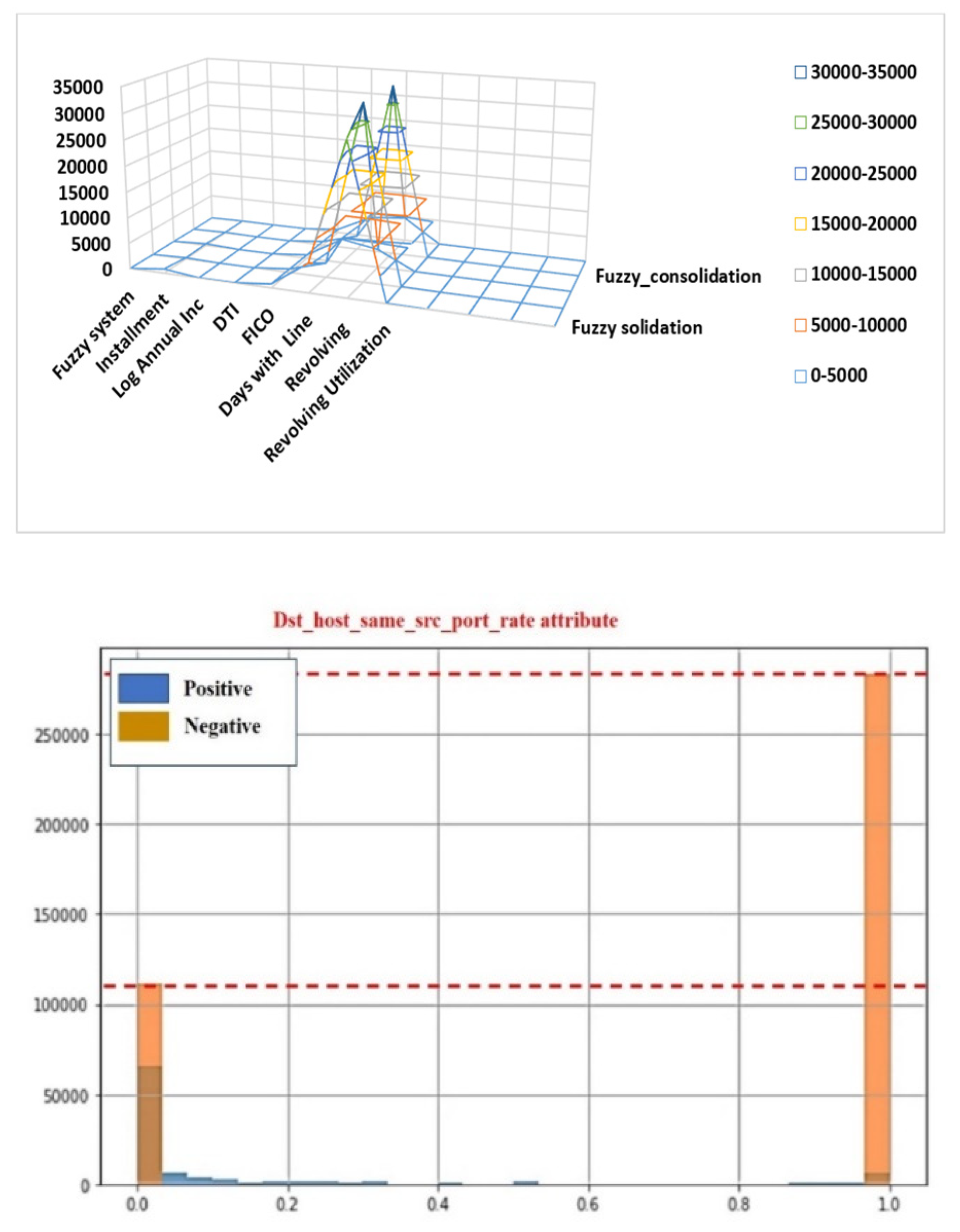
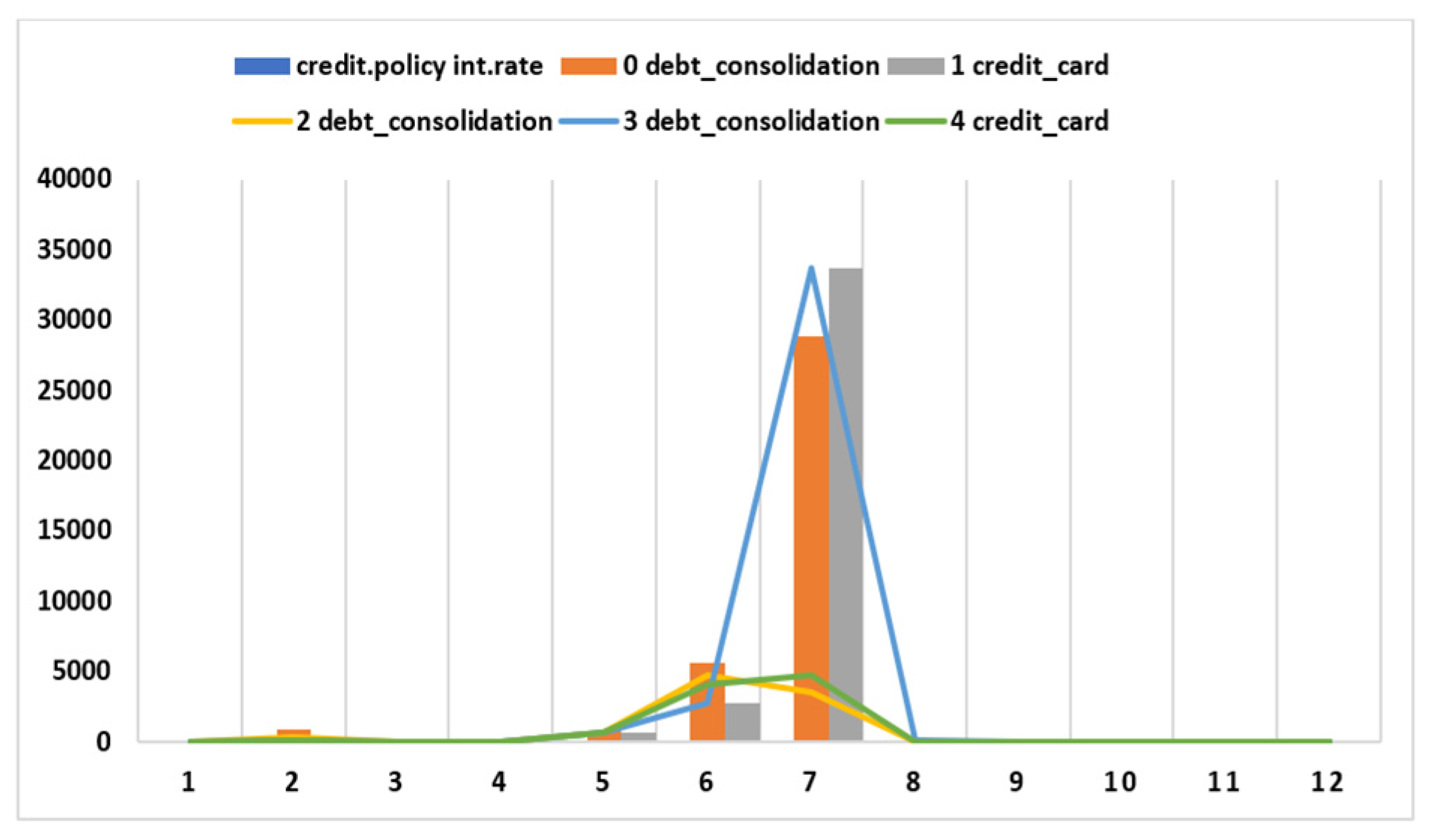
| Fuzzy state | Fuzzy system | Installment | Log Annual Inc | DTI | FICO | Days with Line | Revolving | Revolving Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy sulfidation | 0.1189 | 829.1 | 11.3504 | 19.48 | 737 | 5639.958 | 28854 | 52.1 |
| Fuzz card | 0.1071 | 228.22 | 11.0821 | 14.29 | 707 | 2760 | 33623 | 76.7 |
| Fuzzy consolidation | 0.1357 | 366.86 | 10.3735 | 11.63 | 682 | 4710 | 3511 | 25.6 |
| Fuzzy consolidation | 0.1008 | 162.34 | 11.3504 | 8.1 | 712 | 2699.958 | 33667 | 73.2 |
| Fuzzy_ditcard | 0.1426 | 102.92 | 11.2997 | 14.97 | 667 | 4066 | 4740 | 39.5 |
3.2. Conversion Leverages the Definition of Logarithms
- [ log_b(a) = c if a = b^c ]
- So, for ( log_2(x) = 3 ):
- [ x = 2^3 ]
- Next, we calculate ( 2^3 ):
- [ 2^3 = 2 times 2 times 2 = 8 ]
- Thus, ( x = 8 ).
- [ x = 8 ]
- - Base (b) = 2
- - Exponent (c) = 3
- - Result (a) = (x)
- Solve the logarithmic equation ( log_5(x) = 2 ).**
- - Convert to exponential form: ( x = 5^2 )
- - Calculate: ( 5^2 = 25 )
- - Final answer: ( x = 25 )
- Convert the exponential equation ( 10^4 = x ) to its logarithmic form.**
- - Using the definition: ( log_{10}(x) = 4 )
- - Final answer: ( log_{10}(x) = 4 )
- Find the value of (x) in the equation ( log_{10}(x) = -1 ).**
- - Convert to exponential form: ( x = 10^{-1} )
- - Calculate: ( 10^{-1} = 0.1 )
- - Final answer: ( x = 0.1 )
4. Results

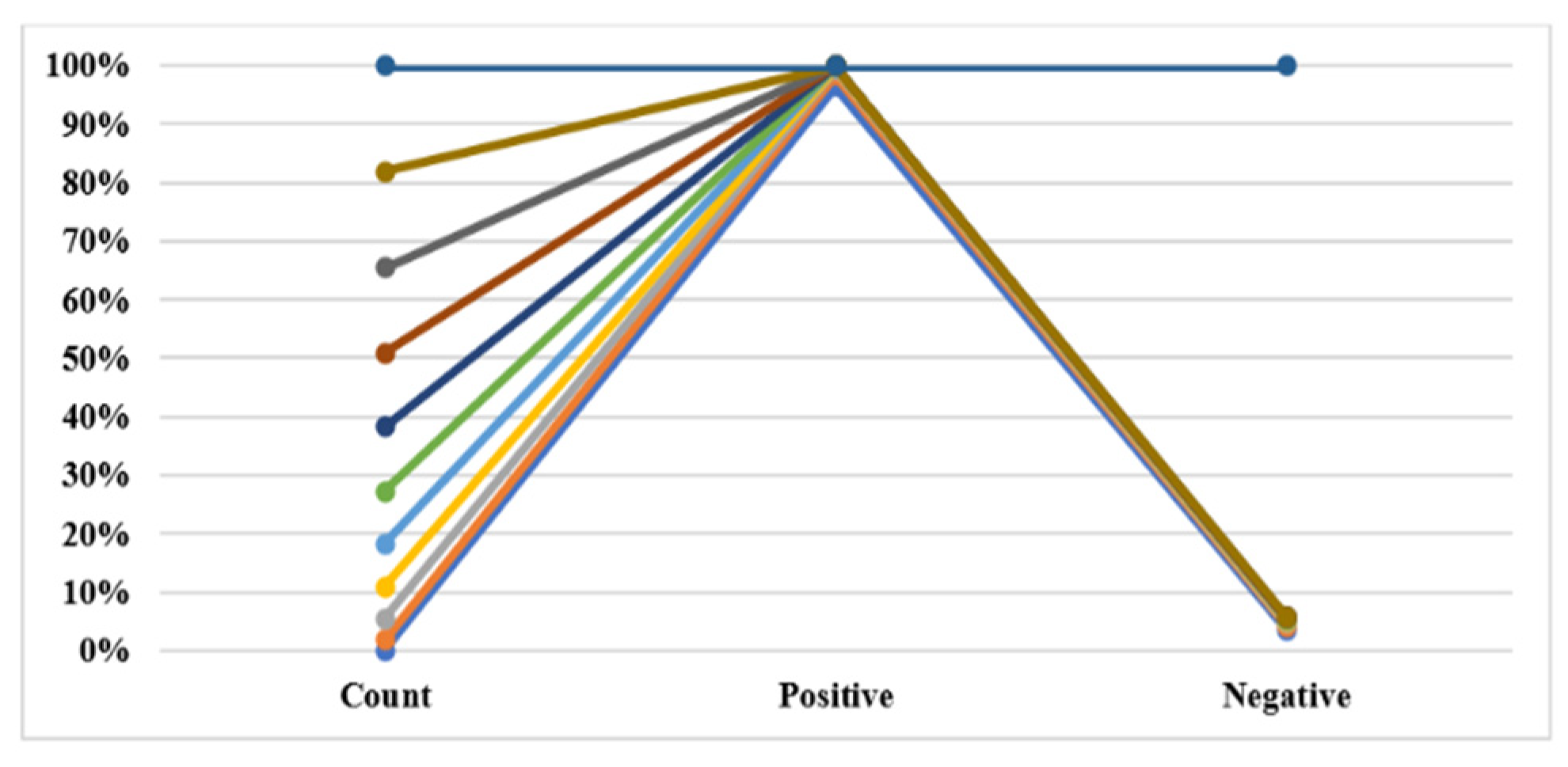
| Count | Positive | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50000 | 10000 |
| 50 | 1000 | 2000 |
| 100 | 500 | 1500 |
| 150 | 200 | 1000 |
| 200 | 100 | 800 |
| 250 | 50 | 500 |
| 300 | 20 | 300 |
| 350 | 10 | 200 |
| 400 | 5 | 100 |
| 450 | 2 | 50 |
| 500 | 1 | 270000 |
5. Conclusion
References
- Jiang, Yiming, Chenguang Yang, and Hongbin Ma. "A Review of Fuzzy Logic and Neural Network Based Intelligent Control Design for Discrete-Time Systems." Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society 2016, no. 1 (2016): 7217364. [CrossRef]
- Cherroun, Lakhmissi, and Mohamed Boumehraz. "Intelligent systems based on reinforcement learning and fuzzy logic approaches," Application to mobile robotic"." In 2012 International Conference on Information Technology and e-Services, pp. 1-6. IEEE, 2012.
- Singh, Harpreet, Madan M. Gupta, Thomas Meitzler, Zeng-Guang Hou, Kum Kum Garg, Ashu MG Solo, and Lotfi A. Zadeh. "Real-life applications of fuzzy logic." Advances in Fuzzy Systems 2013 (2013): 3-3. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Hui, Danning Zhang, Yiheng Shu, and Guibing Guo. "Deep learning for sequential recommendation: Algorithms, influential factors, and evaluations." ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS) 39, no. 1 (2020): 1-42. [CrossRef]
- Jameson, Anthony, Martijn C. Willemsen, Alexander Felfernig, Marco De Gemmis, Pasquale Lops, Giovanni Semeraro, and Li Chen. "Human decision making and recommender systems." Recommender systems handbook (2015): 611-648. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, Siddhartha, Basudeb Mukhopadhyay, and Soumen Shaw. "Rayleigh surface wave propagation in orthotropic thermoelastic solids under three-phase-lag model." Journal of Thermal Stresses 40, no. 4 (2017): 403-419. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, Siddhartha, Basudeb Mukhopadhyay, and Soumen Shaw. "Thermal shock response in magneto-thermoelastic orthotropic medium with three-phase-lag model." Journal of Electromagnetic waves and Applications 31, no. 9 (2017): 879-897. [CrossRef]
- Yung –nien Sun, Yi-Ying Wang, Shao-Chien Chang, Li-wha Wu, and Sen – tien Tsai, "Color-based tumor segmentation for the automated estimation of oral cancer parameters", Microscopy Research and Technique, Vol. 73, Issue. 1, pp 5- 13, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Ranjan Rashmi Paul, Anirban Mukherjee, Pranab K. Dutta, Swapna Banerjee, Mousumi, Pal, Jyotirmoy Chatterjee, and Keya Chaudhuri, "A novel wavelet neural network-based pathological stage detection technique for an oral, precancerous condition", Journal of Clinical Pathology, Vol.58, Issue.9, pp 932 – 938,2024. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B., & Mukhopadhyay, A. (2017). Phishing Detection and Loss Computation Hybrid Model A Machine-learning Approach. ISACA JOURNAL, 20-29.
- Ding, J., & Sun, S. (2019). Integrative analysis of gene expression and methylation data for breast cancer cell lines. Biodata mining, 11(1), 13. [CrossRef]
- Kim, I., Choi, S., & Kim, S. (2019). BRCA-Pathway: a structural integration and visualization system of TCGA breast cancer data on KEGG pathways. BMC bioinformatics, 19(1), 42. [CrossRef]
- Li, C., Lee, J., Ding, J., & Sun, S. (2019). Integrative analysis of gene expression and methylation data for breast cancer cell lines. Biodata mining, 11(1), 13. [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y., Yang, J. P., Lang, Y. H., Peng, L. X., Yang, M. M., Liu, Q., ... & Li, C. Z. (2018). Global expression profiling and pathway analysis of mouse mammary tumor reveals strain and stage specific dysregulated pathways in breast cancer progression. Cell Cycle, 1-11.
- Kim, I., Choi, S., & Kim, S. (2019). BRCA-Pathway: a structural integration and visualization system of TCGA breast cancer data on KEGG pathways. BMC bioinformatics, 19(1), 42. [CrossRef]
- Li, C., Lee, J., Ding, J., & Sun, S. (2019). Integrative analysis of gene expression and methylation data for breast cancer cell lines. Biodata mining, 11(1), 13. [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y., Yang, J. P., Lang, Y. H., Peng, L. X., Yang, M. M., Liu, Q., ... & Li, C. Z. (2018). Global expression profiling and pathway analysis of mouse mammary tumor reveals strain and stage specific dysregulated pathways in breast cancer progression. Cell Cycle, 1-11.
- Kim, I., Choi, S., & Kim, S. (2019). BRCA-Pathway: a structural integration and visualization system of TCGA breast cancer data on KEGG pathways. BMC bioinformatics, 19(1), 42. [CrossRef]
- Li, C., Lee, J., Ding, J., & Sun, S. (2019). Integrative analysis of gene expression and methylation data for breast cancer cell lines. Biodata mining, 11(1), 13. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z Zhang, Z Li, and Y Qiao, “Joint Face Detection and Alignment Using Multi-Task Cascaded Convolutional Networks,” IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2016.
- J Su, L Gao, W Li, Y Xia, N Cao, and R Wang, “Fast face tracking-by-detection algorithm for secure monitoring,” Appl Sci, 2019. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





