Submitted:
19 February 2025
Posted:
20 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7), a member of the PDE superfamily, selectively catalyzes the hydrolysis of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP), thereby regulating the intracellular levels of this second messenger and influencing various physiological functions and processes. There are two subtypes of PDE7, PDE7A and PDE7B, which are encoded by distinct genes. PDE7 inhibitors have been shown to exert therapeutic potentials in neurological and respiratory diseases. However, FDA-approved drugs based on PDE7A inhibitor are still absent, highlighting the need for novel compounds to advance PDE7A inhibitor development. Methods: To address this urgent and important issue, we conducted a comprehensive chemical informatics analysis of compounds with potential PDE7A inhibition using a curated database to elucidate the chemical characteristics of highly active PDE7A inhibitors. Specific substructures that significantly enhance the activity of PDE7A inhibitors, including benzenesulfonamido, acylamino, and phenoxyl, were identified by interpretable machine learning analysis. Subsequently, a machine learning model employing the Random Forest-Morgan pattern was constructed for qualitative and quantitative prediction of PDE7A inhibitors. Results: As a result, 6 compounds with potential PDE7A inhibitory activity were screened out from the SPECS compound library. These identified compounds exhibited favorable molecular properties and potent binding affinities to the target protein, holding a promise as the candidates for further exploration in the development of potent PDE7A inhibitors. Conclusions: Results in the present study would advance the exploration of innovative PDE7A inhibitors and provide valuable insights for future endeavors in the discovery of novel PDE inhibitors.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
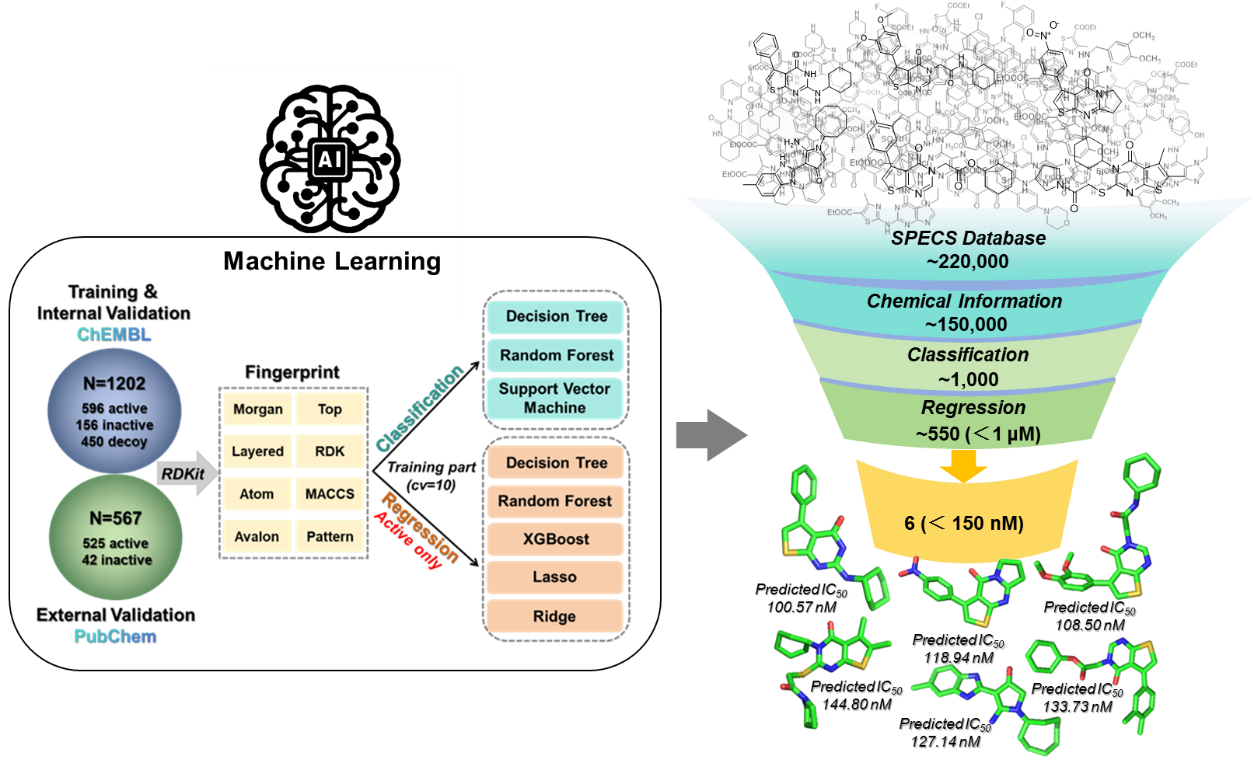
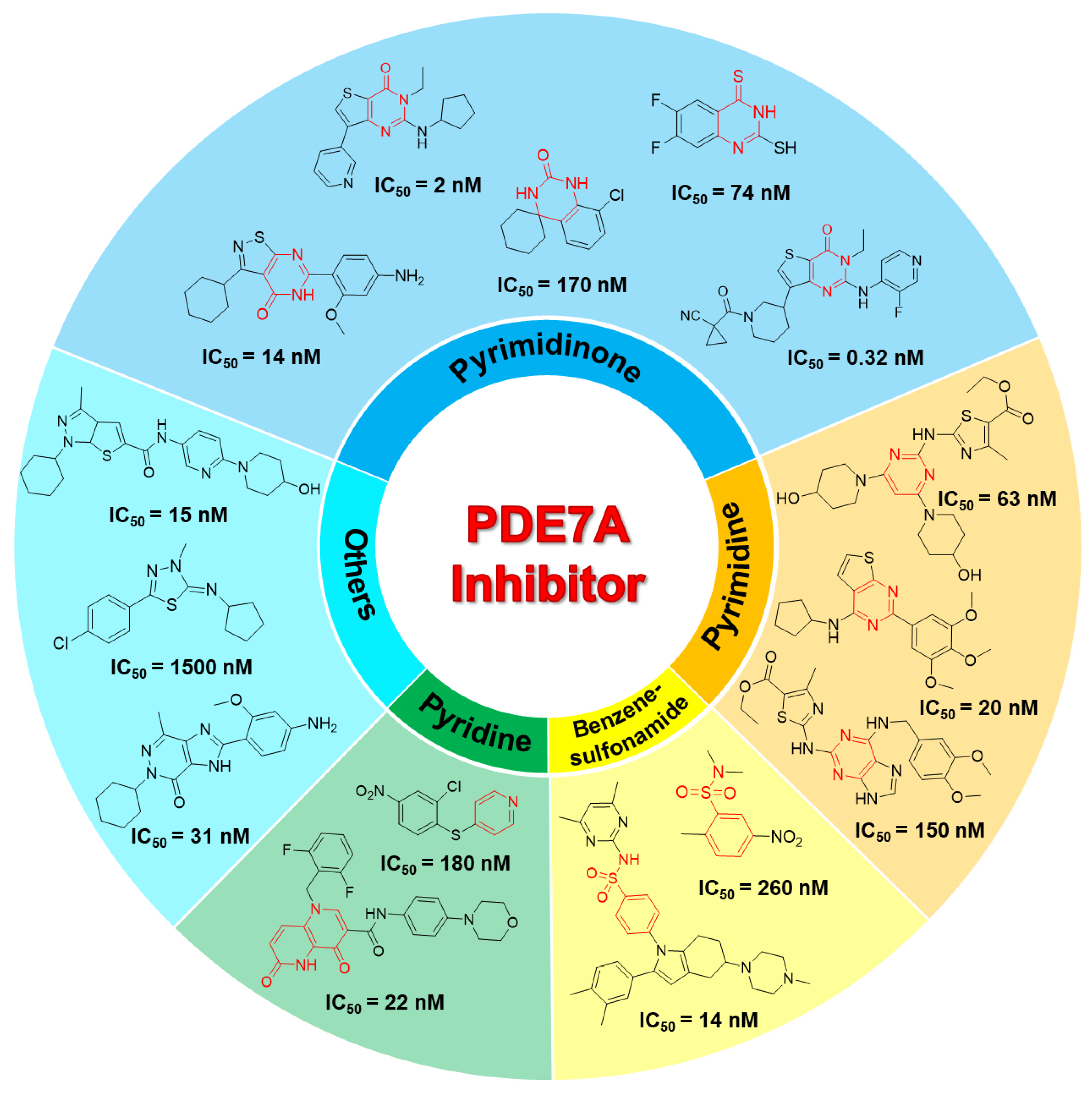
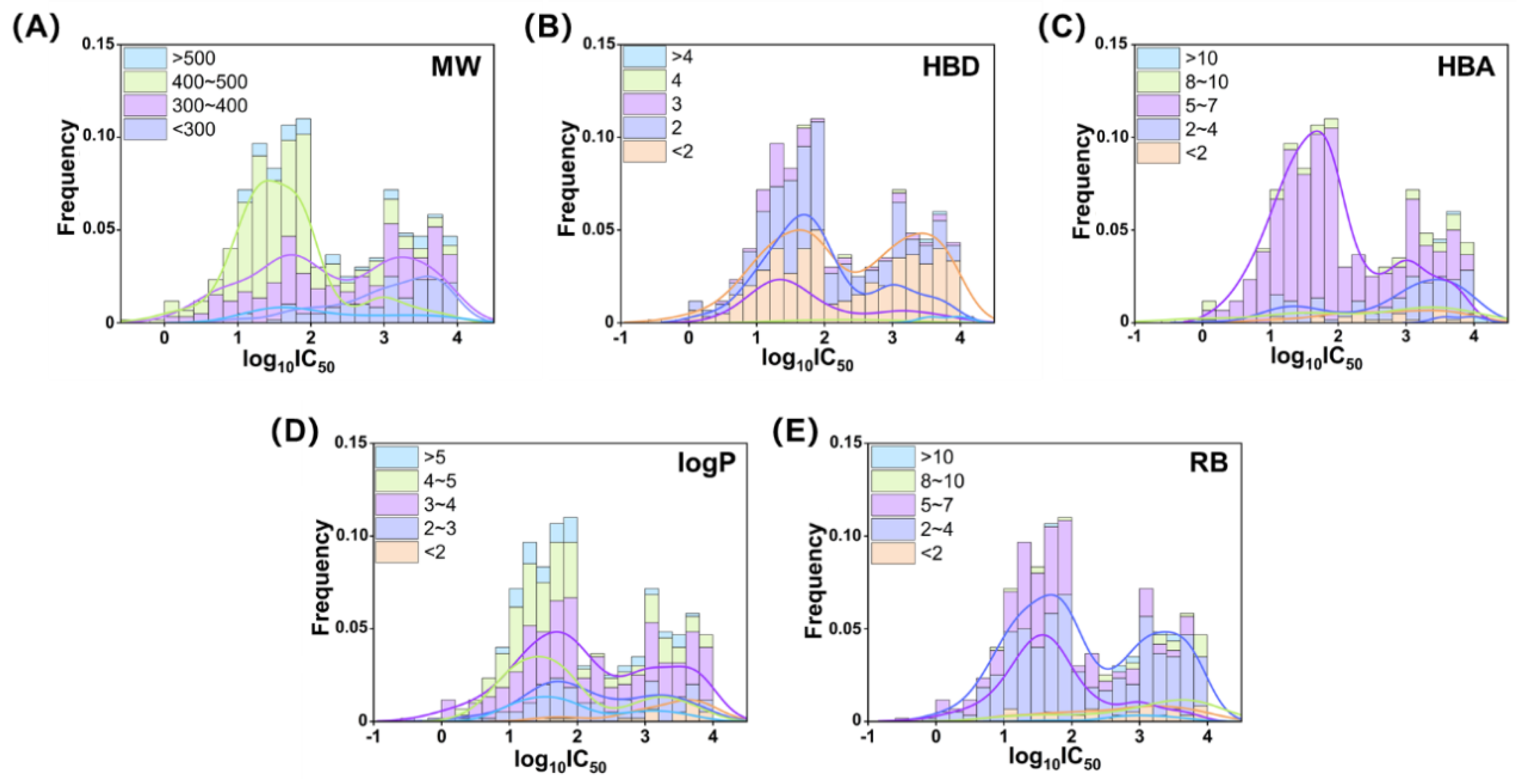
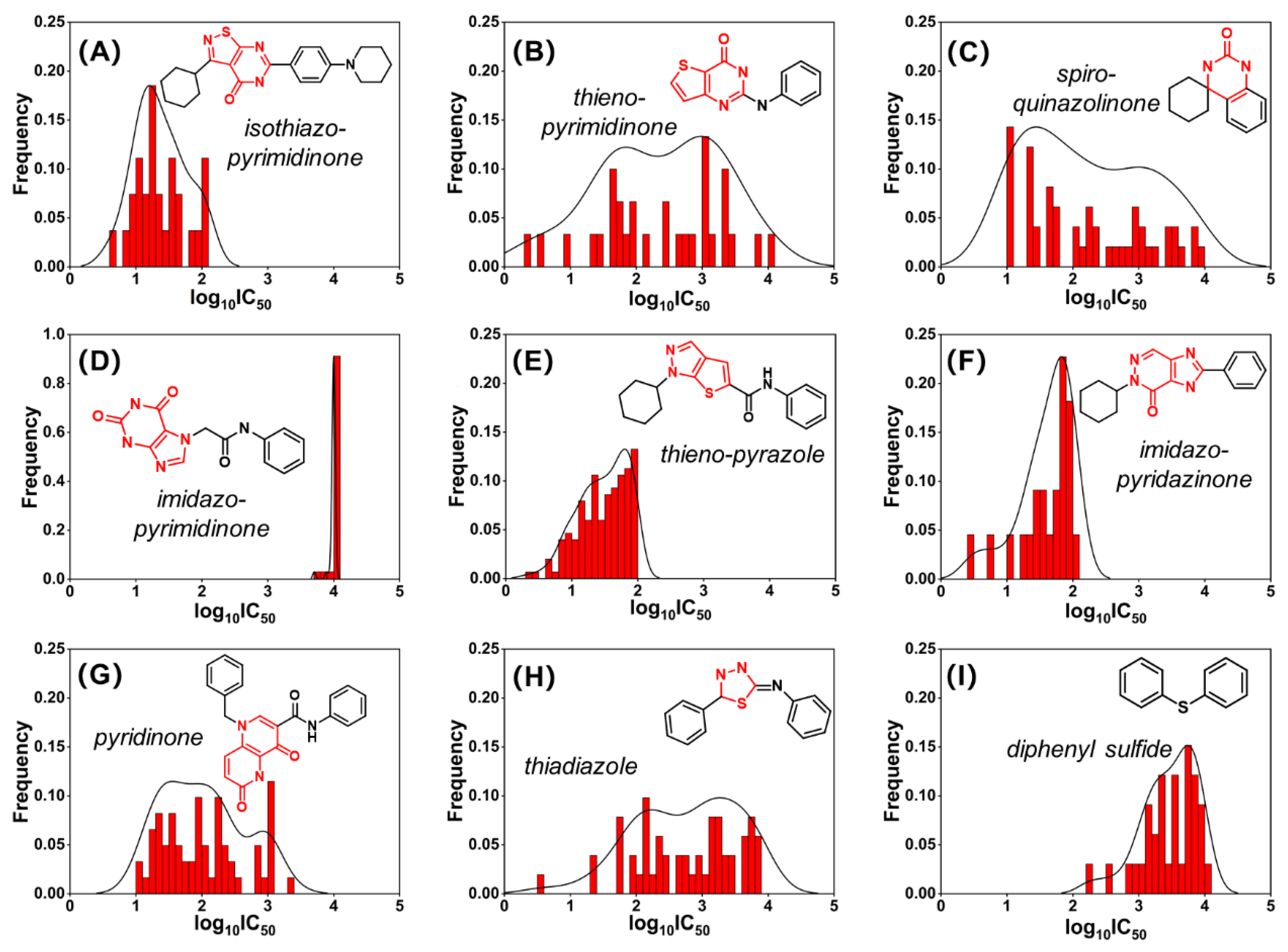
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Information Analysis
2.2. Murcko Scaffold Analysis
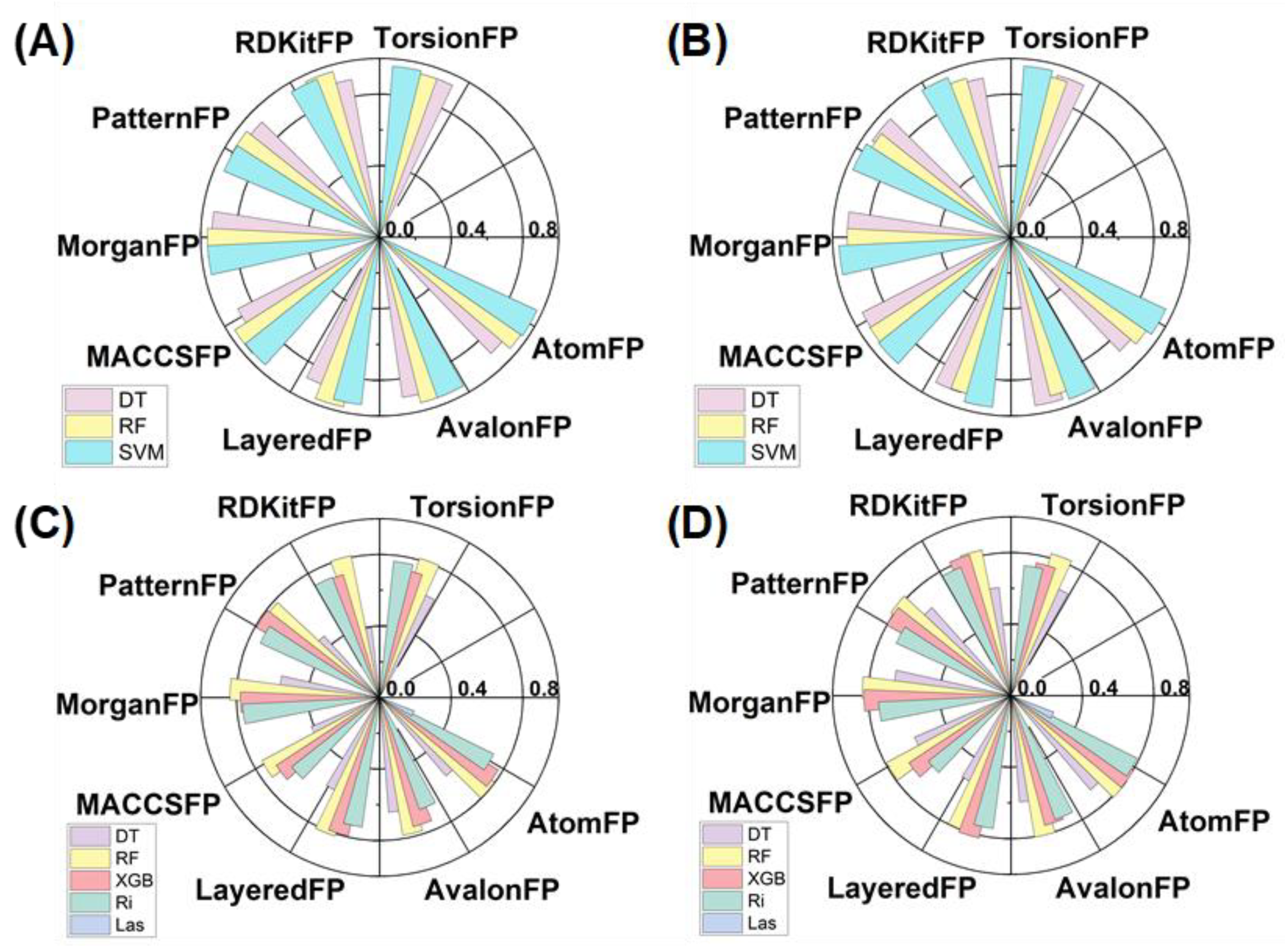
2.3. Development and Characterization of Machine Learning Models
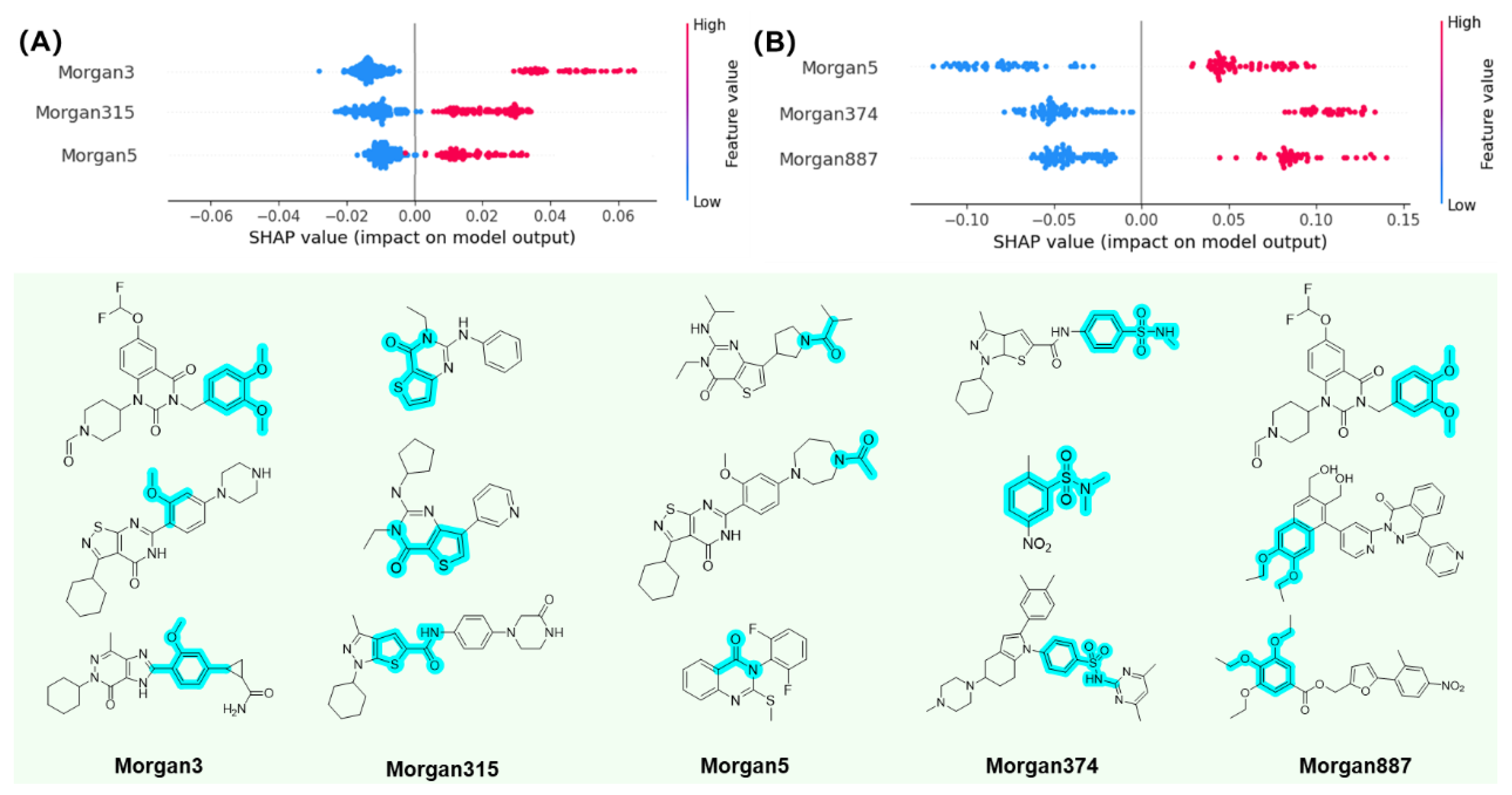
2.4. Interpretable Machine Learning Analysis
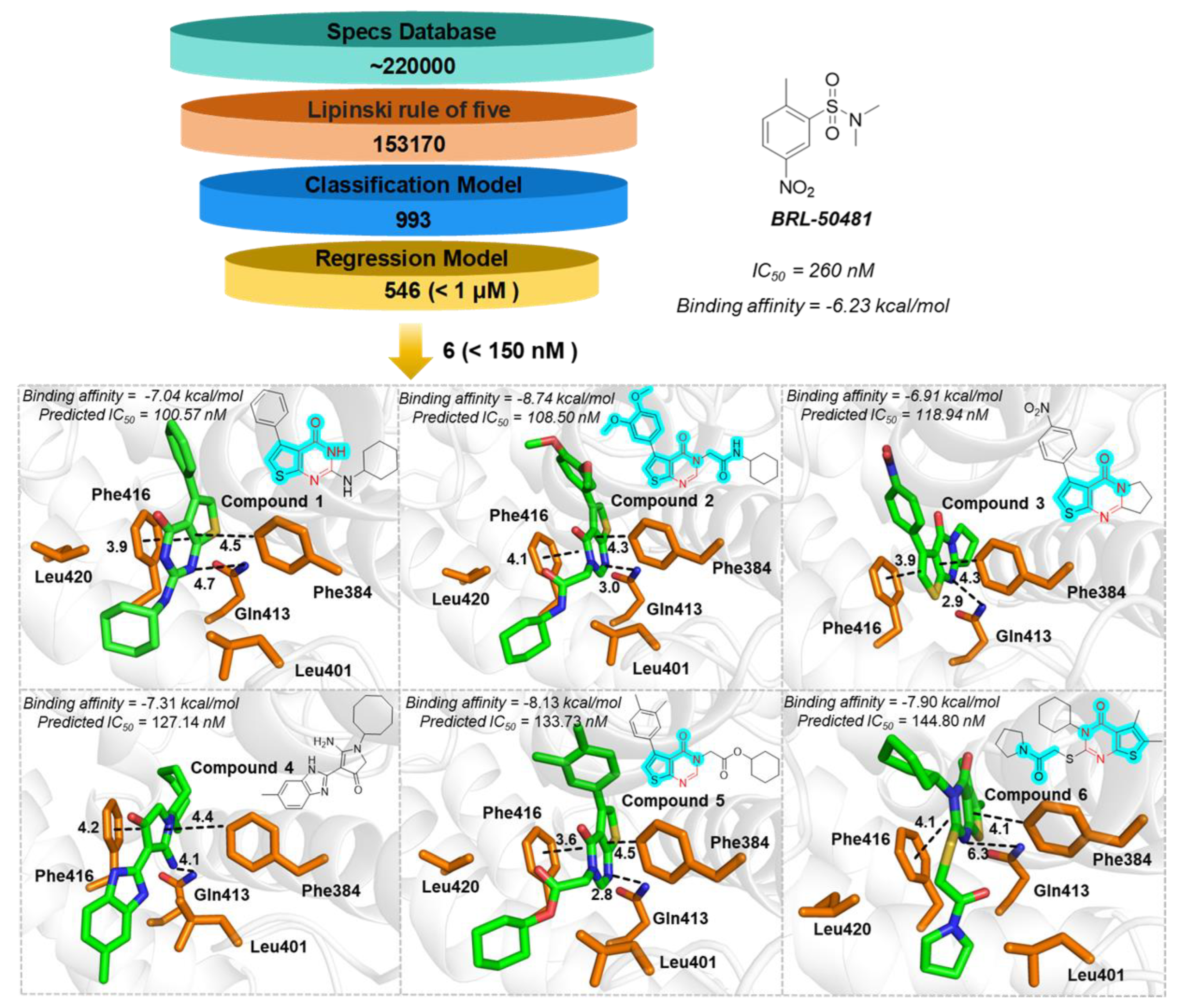
2.5. PDE7A Inhibitor Screening
3. Materials and Methods
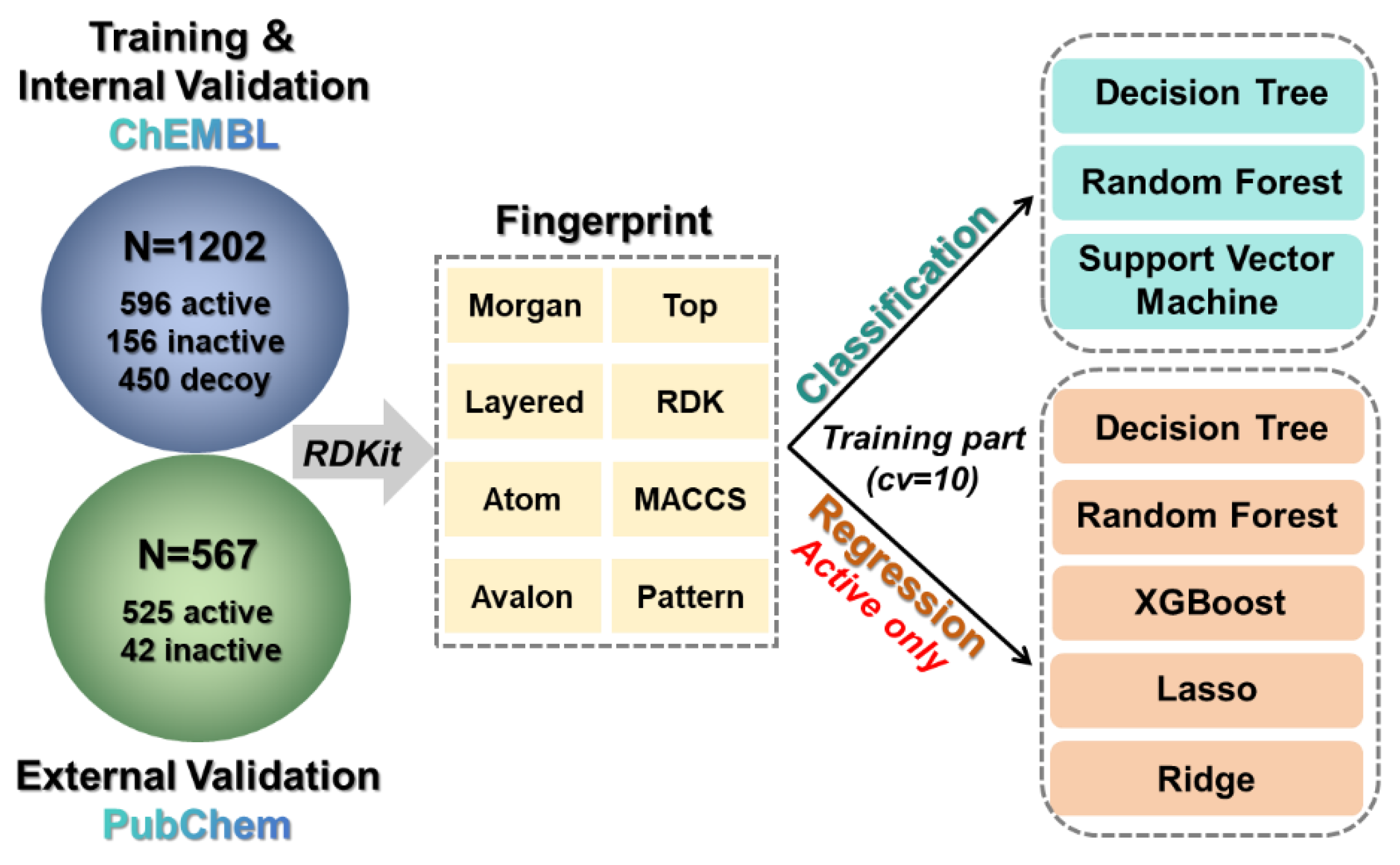
3.1. Data Preparation
3.2. Molecular Feature and Fingerprint Calculation
3.3. Machine Learning Model Construction
3.4. Model Evaluation
3.5. Feature Importance Analysis
3.6. Molecule Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bender, A.T.; Beavo, J.A. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacological reviews 2006, 58, 488–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.T. Targeting phosphodiesterases (PDEs) for treatment of CNS diseases. Current pharmaceutical design 2015, 21, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsien Lai, S.; Zervoudakis, G.; Chou, J.; Gurney, M.E.; Quesnelle, K.M. PDE4 subtypes in cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3791–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Gong, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, R.; Wei, X.; Bai, L.; Shi, J. Inhibitors of phosphodiesterase as cancer therapeutics. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2018, 150, 742–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, S.; Mauban, J.H.; Ward, C.W.; Bond, M. Phosphorylation of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) regulatory subunit modulates PKA-AKAP interaction, substrate phosphorylation, and calcium signaling in cardiac cells. The Journal of biological chemistry 2008, 283, 24145–24154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zuo, J.; Tang, W. Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Frontiers in pharmacology 2018, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.J.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Song, J.K.; Chun, K.H. A PDE1 inhibitor reduces adipogenesis in mice via regulation of lipolysis and adipogenic cell signaling. Experimental & molecular medicine 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Staubli, S.E.; Schneider, M.P.; Kessels, A.G.; Ivic, S.; Bachmann, L.M.; Kessler, T.M. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A trade-off network meta-analysis. European urology 2015, 68, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.D.; Long, M.; Li, F.; Hu, X.; Liao, X.X.; Du, Z.M. PDE5 inhibitor sildenafil in the treatment of heart failure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. International journal of cardiology 2014, 172, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.N.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, Y.D.; Xie, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Luo, H.B. Structure-based discovery of orally efficient inhibitors via unique interactions with H-pocket of PDE8 for the treatment of vascular dementia. Acta pharmaceutica Sinica. B 2022, 12, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, V.; Zhong, S.; Lin, H.; Xu, W.; Bradaia, A.; Steidl, E.; Gleyzes, M.; Wadel, K.; Buisson, B.; Padovan-Neto, F.E.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A Inhibition Improves Cortico-Basal Ganglia Function in Huntington's Disease Models. Neuron 2016, 92, 1220–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.Z.; Wang, D.; Skaggs, K.; Zhang, H.T. Phosphodiesterase 7(PDE7): A unique drug target for central nervous system diseases. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Qi, B.; He, J.; Ke, H.; Shi, J. Advances in the Development of Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2020, 63, 10594–10617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.M.; Brea, J.; Morales-García, J.A.; Perez, D.I.; González, A.; Alonso-Gil, S.; Gracia-Rubio, I.; Ros-Simó, C.; Conde, S.; Cadavid, M.I.; et al. Modulation of cAMP-specific PDE without emetogenic activity: New sulfide-like PDE7 inhibitors. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2014, 57, 8590–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño, T.; Wang, H.; Campillo, N.E.; Ballester, S.; González-García, C.; Hernández, J.; Pérez, C.; Cuenca, J.; Pérez-Castillo, A.; Martínez, A.; et al. Synthesis, structural analysis, and biological evaluation of thioxoquinazoline derivatives as phosphodiesterase 7 inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, M.; Brea, J.; Perez, D.I.; Soteras, I.; Val, C.; Perez, C.; Morales-García, J.A.; Alonso-Gil, S.; Paul-Fernandez, N.; Martin-Alvarez, R.; et al. Effect of phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) inhibitors in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Discovery of a new chemically diverse family of compounds. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2012, 55, 3274–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Yadav, P.S.; Bajpai, M.; Sangana, R.R.; Gullapalli, S.; Gudi, G.S.; Gharat, L.A. Isothiazole and isoxazole fused pyrimidones as PDE7 inhibitors: SAR and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2012, 22, 3223–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorthiois, E.; Bernardelli, P.; Vergne, F.; Oliveira, C.; Mafroud, A.K.; Proust, E.; Heuze, L.; Moreau, F.; Idrissi, M.; Tertre, A.; et al. Spiroquinazolinones as novel, potent, and selective PDE7 inhibitors. Part 1. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2004, 14, 4623–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempson, J.; Pitts, W.J.; Barbosa, J.; Guo, J.; Omotoso, O.; Watson, A.; Stebbins, K.; Starling, G.C.; Dodd, J.H.; Barrish, J.C.; et al. Fused pyrimidine based inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7): Synthesis and initial structure-activity relationships. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2005, 15, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewald, R.; Rueger, C.; Grunwald, C.; Egerland, U.; Hoefgen, N. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of dihydronaphthyridinediones as a novel structural class of potent and selective PDE7 inhibitors. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2011, 21, 6652–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Cieslinski, L.B.; Newton, R.; Donnelly, L.E.; Fenwick, P.S.; Nicholson, A.G.; Barnes, P.J.; Barnette, M.S.; Giembycz, M.A. Discovery of BRL 50481 [3-(N,N-dimethylsulfonamido)-4-methyl-nitrobenzene], a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 7: In vitro studies in human monocytes, lung macrophages, and CD8+ T-lymphocytes. Molecular pharmacology 2004, 66, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.X.; Huang, M.; Cui, W.; Feng, L.J.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liu, P.; Wan, Y.; et al. Discovery of a phosphodiesterase 9A inhibitor as a potential hypoglycemic agent. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2014, 57, 10304–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Tang, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Guan, G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; et al. PyCoCa:A quantifying tool of carbon content in airway macrophage for assessment the internal dose of particles. The Science of the total environment 2022, 851, 158103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, N.; Song, J.; Ren, C.; Tang, X.; Jiang, W. Effect of silica nanoparticles on cell membrane fluidity: The role of temperature and membrane composition. The Science of the total environment 2022, 838, 156552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Robinson, H.; Ke, H. Multiple elements jointly determine inhibitor selectivity of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases 4 and 7. The Journal of biological chemistry 2005, 280, 30949–30955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, M.J.; Cooper, N.; Davenport, R.J.; Dyke, H.J.; Galleway, F.P.; Galvin, F.C.; Gowers, L.; Haughan, A.F.; Lowe, C.; Meissner, J.W.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of guanine analogues as phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) inhibitors. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2001, 11, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, W.J.; Vaccaro, W.; Huynh, T.; Leftheris, K.; Roberge, J.Y.; Barbosa, J.; Guo, J.Q.; Brown, B.; Watson, A.; Donaldson, K.; et al. Identification of purine inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7). Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2004, 14, 2955–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Kawai, K.; Asano, T.; Amano, S.; Asanuma, Y.; Sawada, K.; Onodera, Y.; Ueo, N.; Takahashi, N.; Sonoda, Y.; et al. 2-(Isopropylamino)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives as selective phosphodiesterase 7 inhibitors with potent in vivo efficacy. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2015, 25, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Endo, Y.; Asano, T.; Amano, S.; Sawada, K.; Ueo, N.; Takahashi, N.; Sonoda, Y.; Nagai, M.; Kamei, N.; et al. Discovery of 2-(Cyclopentylamino)thieno 3,2-d pyrimidin-4(3H)-one Derivatives as a New Series of Potent Phosphodiesterase 7 Inhibitors. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2014, 57, 9844–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic acids research 2017, 45, D945–d954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Suzek, T.O.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Han, L.; Karapetyan, K.; Dracheva, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem's BioAssay Database. Nucleic acids research 2012, 40, D400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Nan, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, C.; Xin, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Combining multi-dimensional molecular fingerprints to predict the hERG cardiotoxicity of compounds. Computers in biology and medicine 2022, 144, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Shan, M.; Qin, L.P.; Cheng, G. Reliable prediction of cannabinoid receptor 2 ligand by machine learning based on combined fingerprints. Computers in biology and medicine 2023, 152, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Sun, X.; Hu, F.; Tang, X.; Wang, K. Molecular determinants for the chemical activation of the warmth-sensitive TRPV3 channel by the natural monoterpenoid carvacrol. The Journal of biological chemistry 2022, 298, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.X.; Zhu, B.L.; Xu, J.P.; Zhou, Z.Z. Advances in the development of phosphodiesterase 7 inhibitors. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2023, 250, 115194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliokoski, T.; Kramer, C.; Vulpetti, A.; Gedeck, P. Comparability of mixed IC50 data - a statistical analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, T.; Yang, P.; Zhao, J.; Arkin, I.T.; Liu, H. Predicting the reproductive toxicity of chemicals using ensemble learning methods and molecular fingerprints. Toxicology letters 2021, 340, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Caldwell, G.W. Metabolism profiling, and cytochrome P450 inhibition & induction in drug discovery. Current topics in medicinal chemistry 2001, 1, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysinger, M.M.; Carchia, M.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Directory of Useful Decoys, Enhanced (DUD-E): Better Ligands and Decoys for Better Benchmarking. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2012, 55, 6582–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemis, G.W.; Murcko, M.A. The properties of known drugs. 1. Molecular frameworks. Journal of medicinal chemistry 1996, 39, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, S.; Lin, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, X. Hepatotoxicity assessment investigations on PFASs targeting L-FABP using binding affinity data and machine learning-based QSAR model. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety 2023, 262, 115310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speybroeck, N. Classification and regression trees. International journal of public health 2012, 57, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedaie, A.; Najafi, A.A. Support vector machine with Dirichlet feature mapping. Neural networks : The official journal of the International Neural Network Society 2018, 98, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.Q.; Guestrin, C.; Assoc Comp, M. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13-17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. The lasso method for variable selection in the Cox model. Statistics in medicine 1997, 16, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A.N. Solution of incorrectly formulated problem and the regularization method. (trans.). 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Swami, A.; Jain, R.J.J.o.M.L.R. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of machine Learning research 2013, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, D.; Catal, C.; Tekinerdogan, B. Precision nutrition: A systematic literature review. Computers in biology and medicine 2021, 133, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4--9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of computational chemistry 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




