Submitted:
01 February 2025
Posted:
03 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Importance
1.2. Evolution of Fake News Detection
1.3. Role of Large Language Models (LLMs)
1.4. Purpose of the Review
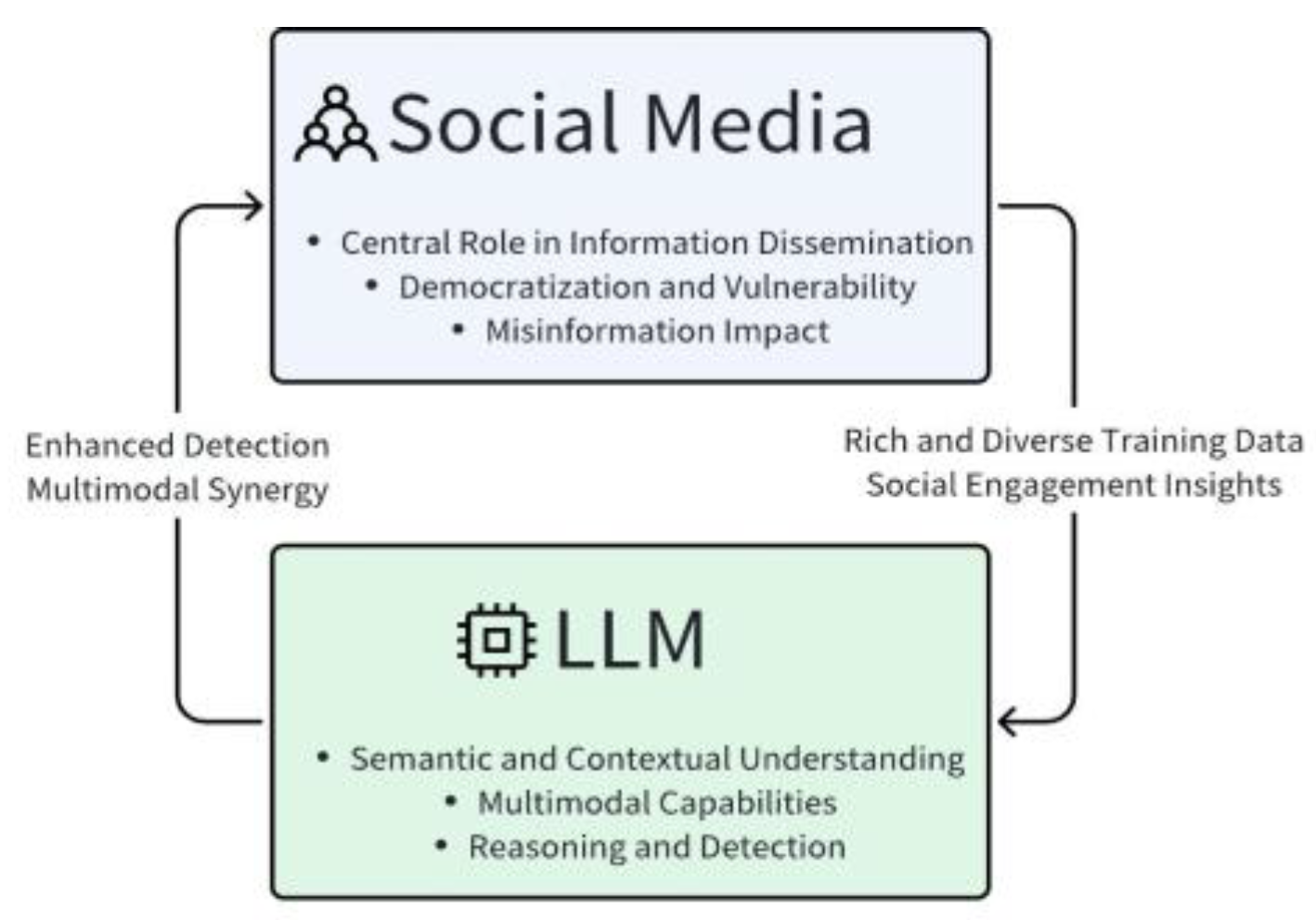
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Core Concepts in Fake News Detection
2.1.1. Definition and Characteristics of Fake News.
2.1.2. Multimodal Nature of Fake News.
2.1.3. Role of Semantics and Contextual Features.
2.2. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Knowledge Graphs
2.2.1. Integration with LLMs for Enhanced Representation Learning.
3. Current State of Research
3.1. Logical Development of Models
3.1.1. Early Approaches: Feature-Based and Machine Learning Models.
3.1.2. Neural Networks and Pre-Trained Models.
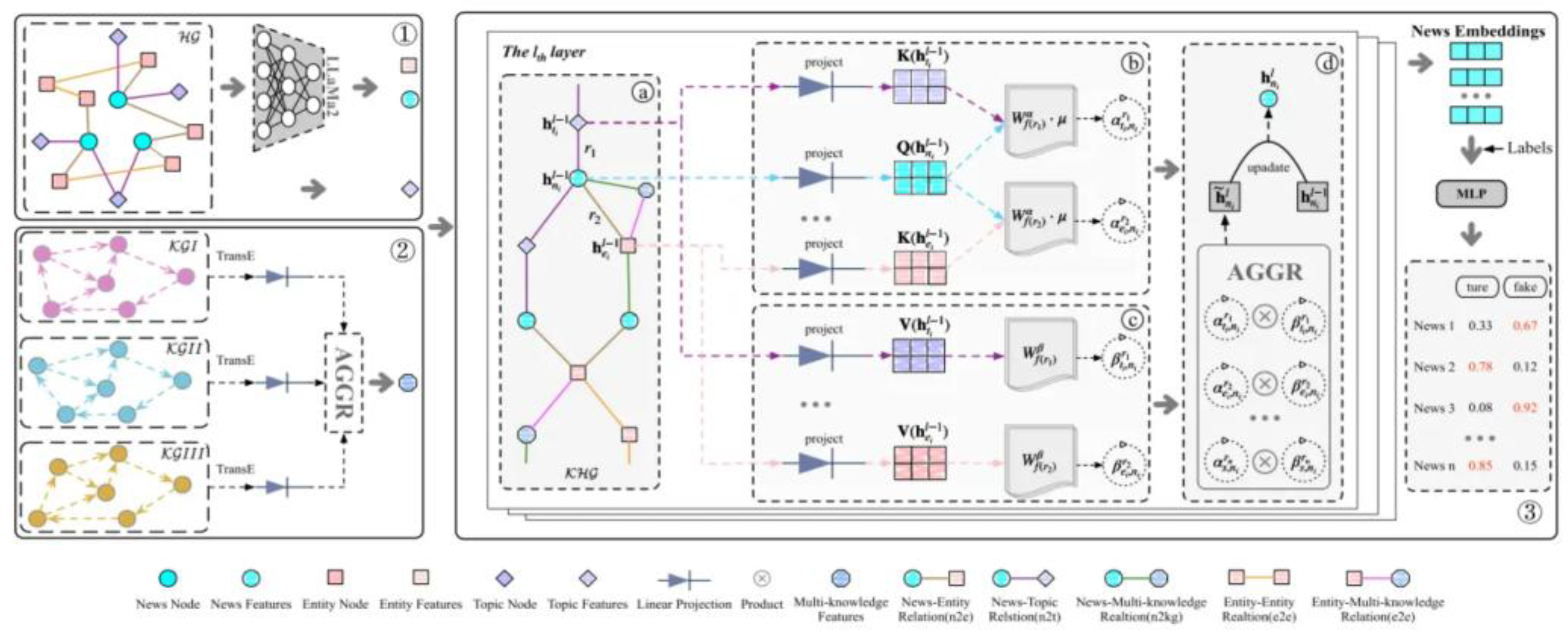
3.1.3. Knowledge Integration and GNNs.
3.1.5. Few-Shot and Transfer Learning.
3.1.6. Adversarial Robustness and Style-Agnostic Detection.
3.2. LLM-Based Frameworks
3.2.1. MiLk-FD (Misinformation Detection with Knowledge Integration).
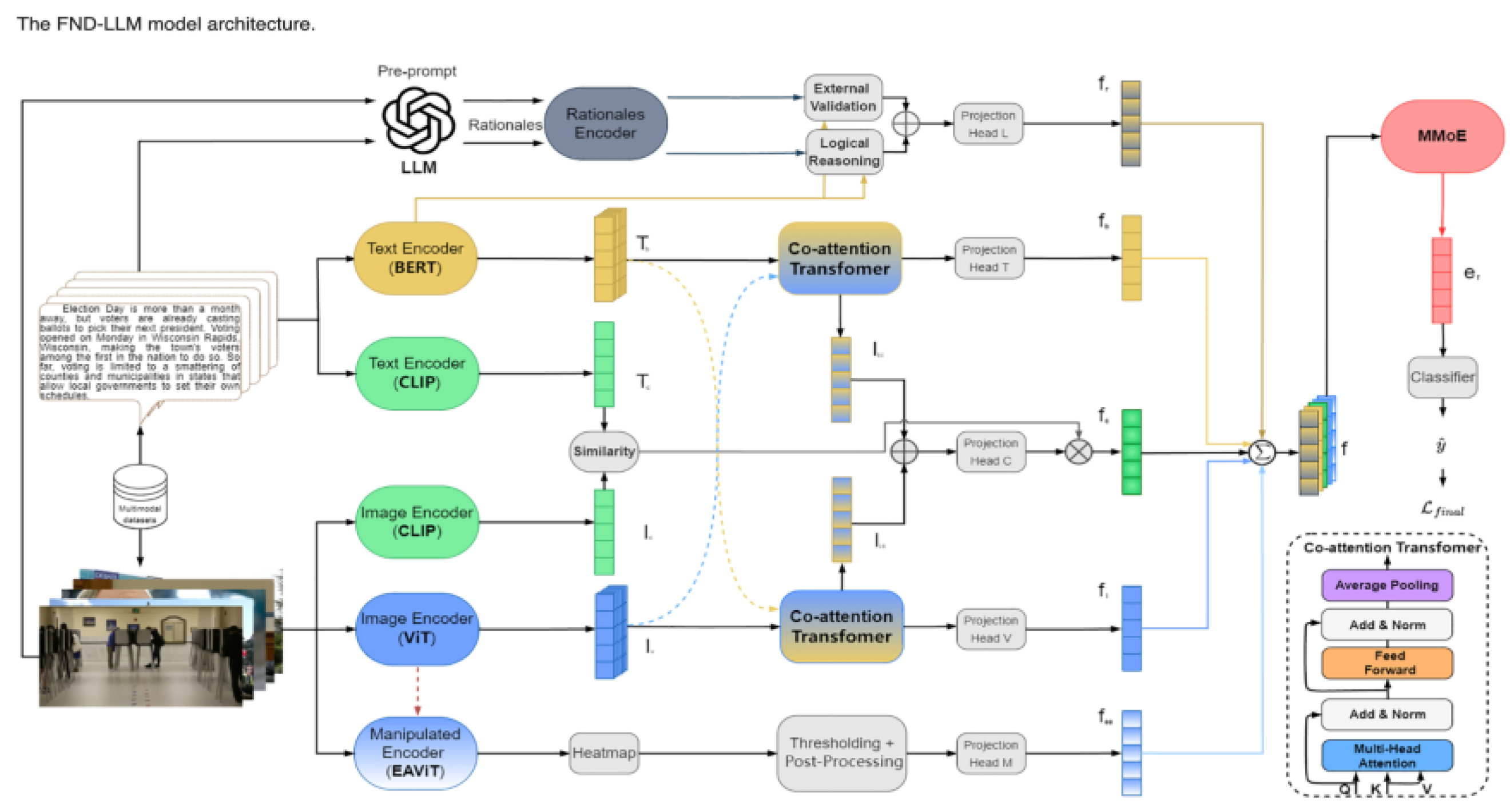
3.2.2. FND-LLM (Fake News Detection with Multimodal LLMs).
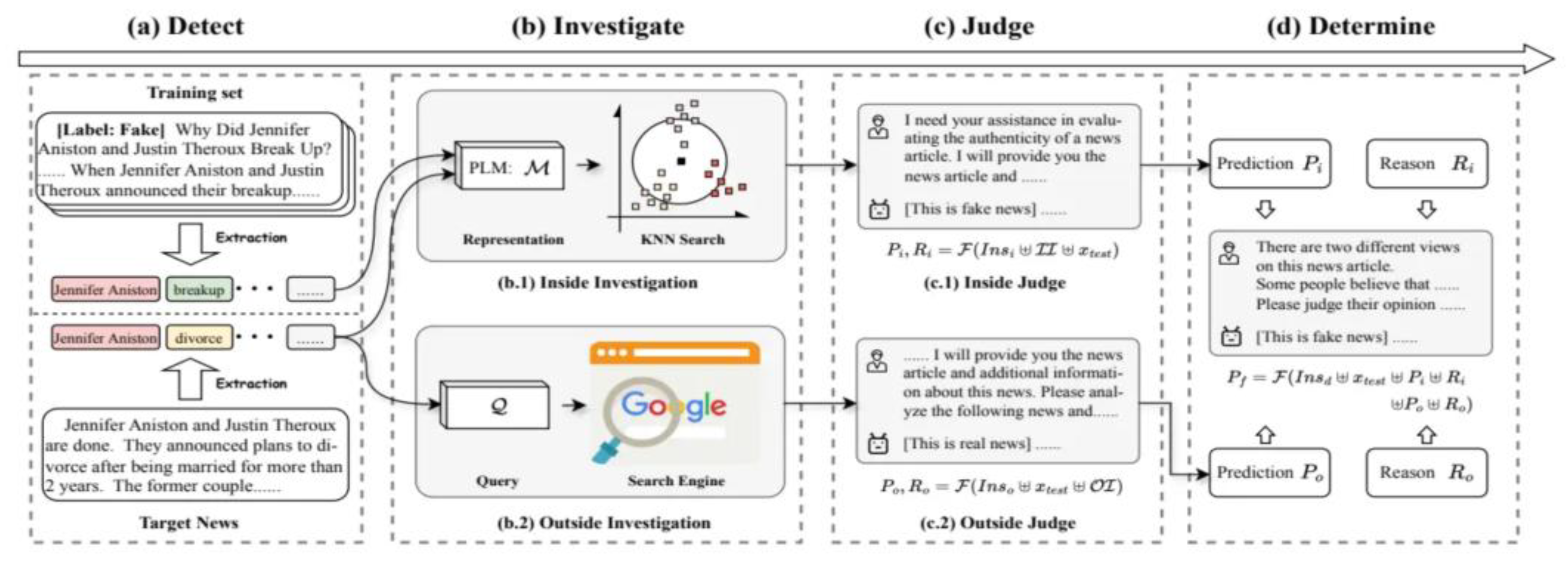
3.2.3. DAFND (Domain Adaptive Few-Shot Fake News Detection)
3.2.4. SheepDog (Style-Agnostic Detection Framework).
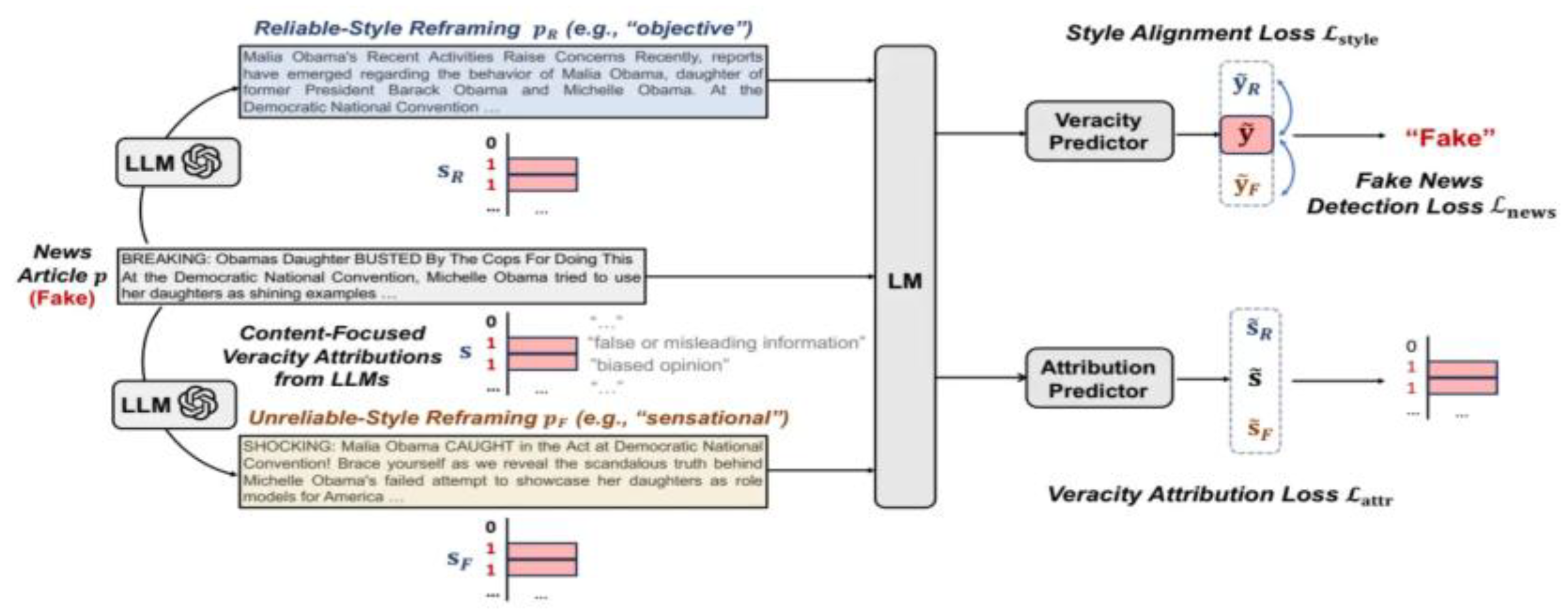
4. Performance Metrics
4.1. Benchmarks and Datasets
4.2. Key Evaluation Metrics
| Model | Dataset | Accuracy(%) | F1-Score(%) | Precision(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiLk-FD | FakeNewsNet | 95.2 | 94.8 | 94.5 |
| FND-LLM | Politifact | 95.1 | 91.5 | 90.8 |
| DAFND | PAN2020 | 87.3 | 95.6 | 84.9 |
| SheepDog | COVID-19 | 88.9 | 88.5 | 87.6 |
5. Challenges and Controversies
5.1. Limitations of Current Approaches
5.1.1. Over-Reliance on Textual Features.
5.1.2. Vulnerability to Adversarial Attacks and Stylistic Variations.
5.2. LLM-Specific Issues
5.2.1. Ambiguity in Understanding Nuanced Semantics.
5.3. Data and Resource Constraints
5.3.1. Lack of Sufficient Labeled Data for Model Training.
5.3.2. Scalability Issues in Real-Time Detection.
5.4. Interpretability and Explainability
5.4.1. Lack of Transparent Models to Explain Predictions.
5.4.2. Trade-Offs Between Performance and Interpretability.
6. Conclusion
6.1. Summary of Key Findings
6.2. Research Gaps
6.3. Future Directions
References
- Ma, Xiaoxiao, et al. "On Fake News Detection with LLM Enhanced Semantics Mining." Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2024.
- Wang, Jingwei, et al. "LLM-Enhanced multimodal detection of fake news." PloS one 19.10 (2024): e0312240. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Ye, et al. "Detect, investigate, judge and determine: A novel llm-based framework for few-shot fake news detection." arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.08952 (2024).
- Wu, Jiaying, Jiafeng Guo, and Bryan Hooi. "Fake News in Sheep's Clothing: Robust Fake News Detection Against LLM-Empowered Style Attacks." Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. 2024.
- Xie, Bingbing, et al. "Multiknowledge and LLM-Inspired Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network for Fake News Detection." IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (2024). [CrossRef]
- Guo, Haoming, et al. "A Systematic Review of Multimodal Approaches to Online Misinformation Detection." 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR). IEEE, 2022.
- Yu, Peiyang, Victor Y. Cui, and Jiaxin Guan. "Text classification by using natural language processing." Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Vol. 1802. No. 4. IOP Publishing, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Haoming, et al. "Detecting COVID-19 Conspiracy Theories with Transformers and TF-IDF." arXiv preprint arXiv: 2205.00377 (2022).
- Fu, Zhe, et al. "Detecting Misinformation in Multimedia Content through Cross-Modal Entity Consistency: A Dual Learning Approach." arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.00022 (2024).
- Yu, Peiyang, Xiaochuan Xu, and Jiani Wang. "Applications of Large Language Models in Multimodal Learning." Journal of Computer Technology and Applied Mathematics 1.4 (2024): 108-116.
- Xu, Xiaochuan, et al. "Enhancing User Intent for Recommendation Systems via Large Language Models." (2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





