Submitted:
14 January 2025
Posted:
14 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Method | Limit of Detection (DL) |
| Spectrophotometry | 0.1 μg/mL |
| Fluorescent dye (PicoGreen) | 25-100 pg |
| Hybridization, randomly labeled DNA | 50 pg(10-12 g) |
| Hybridized, biotin-labeled probe | 2 pg |
| Hybridization, repeat sequence (SINE, Alu) | 5 pg |
| Immunoassay | 5-10 pg |
| PCR method, unique sequence DNA | fg(10-15 g) |
| PCR method, repetitive sequence (SINE,Alu) | ag(10-18 g) |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Reagents and Program
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Method Development
2.5. Method Validation
2.5.1. Linearity & Range
2.5.2. Quantitation limit
2.5.3. Specificity
2.5.4. Accuracy
2.2.5. Repeatability
2.5.6. Intermediate Precision
2.5.7. Robustness
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Calculation of Sample RSD
2.6.2. Calculation of residual concentration of sample DNA
2.6.3. Relative Bias calculation:
2.6.4. Recovery calculation:
3. Results
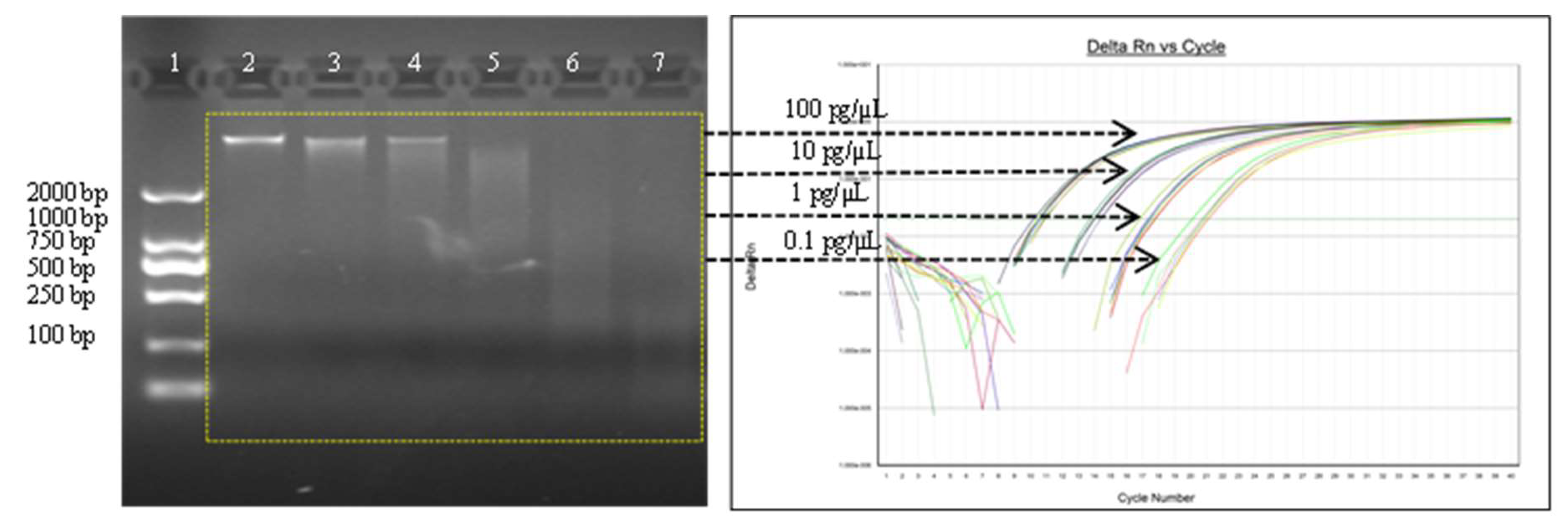
3.1. Assay Optimization
3.1.3. Vaccine Drug Substance (DS) Sample Test
3.2. Method Validation Results
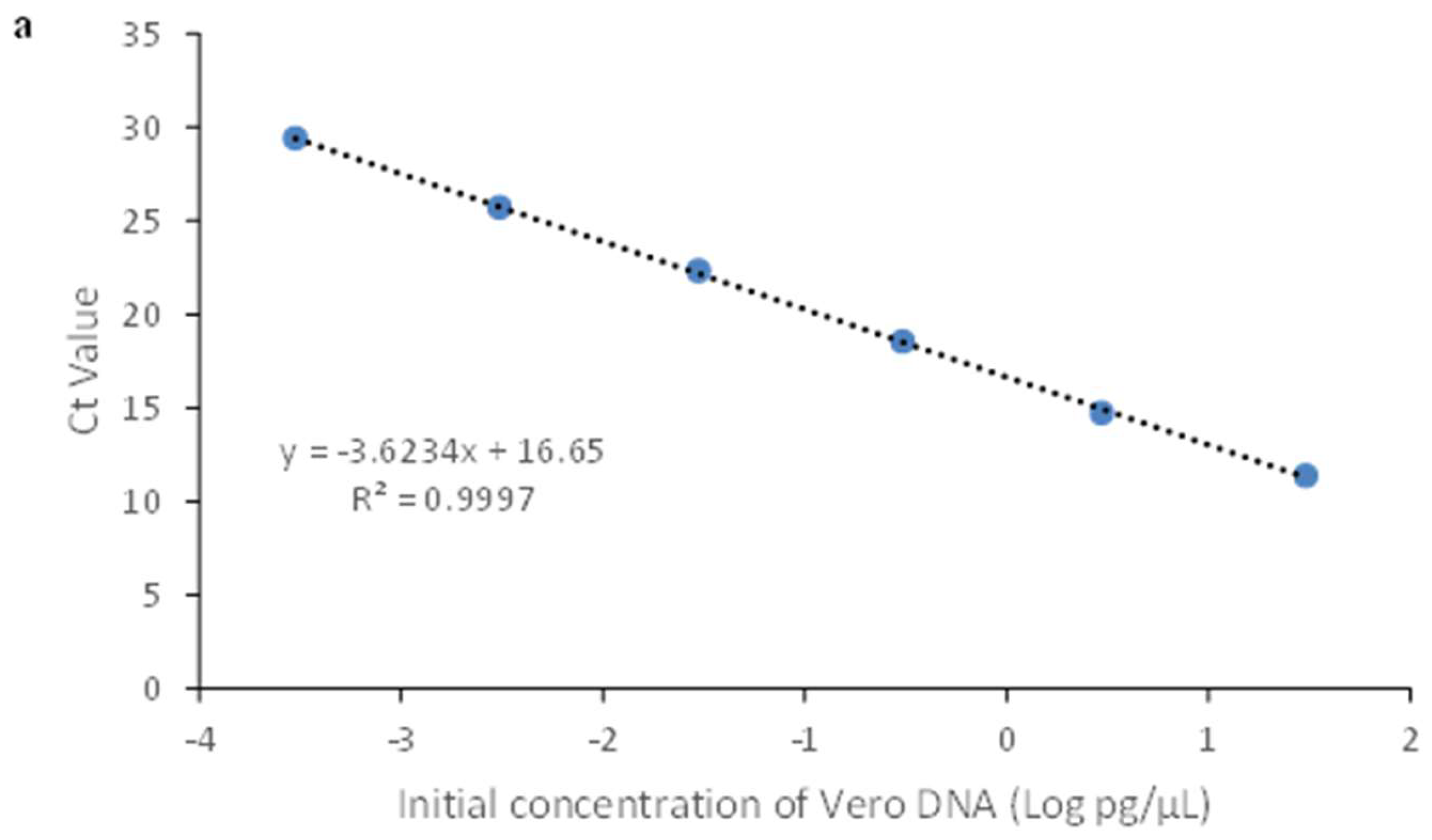
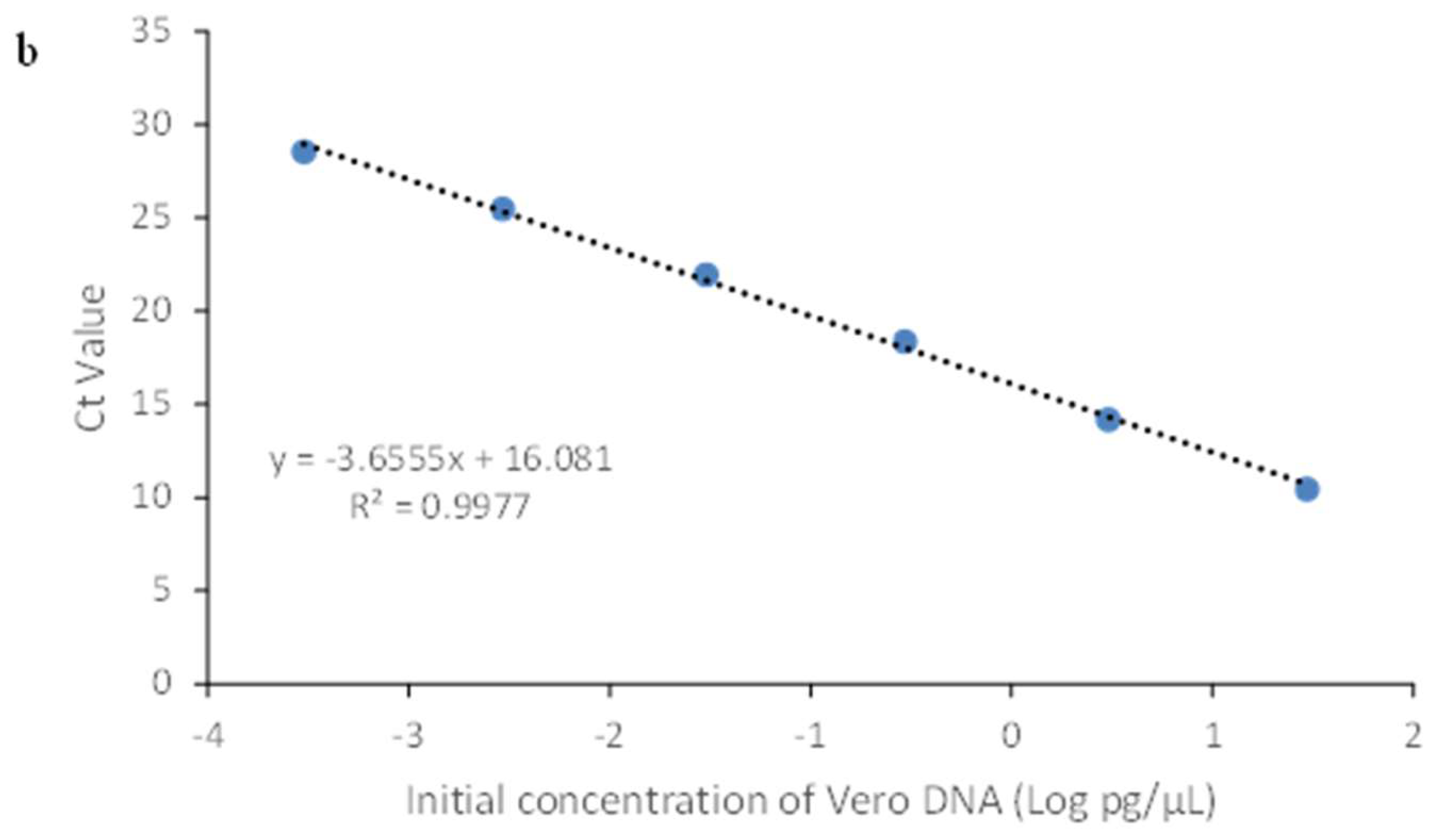
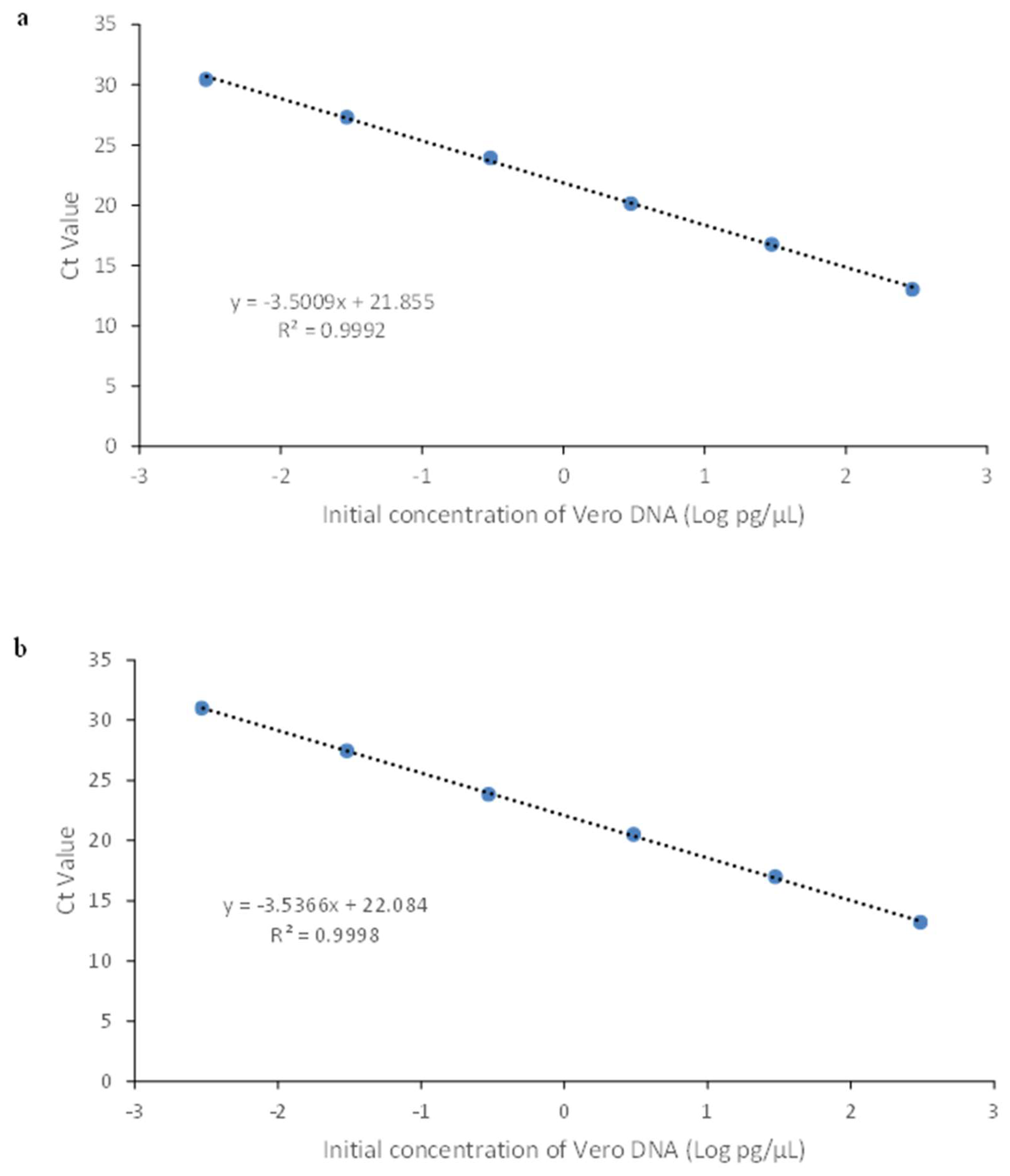
3.2.1. Linearity & Range
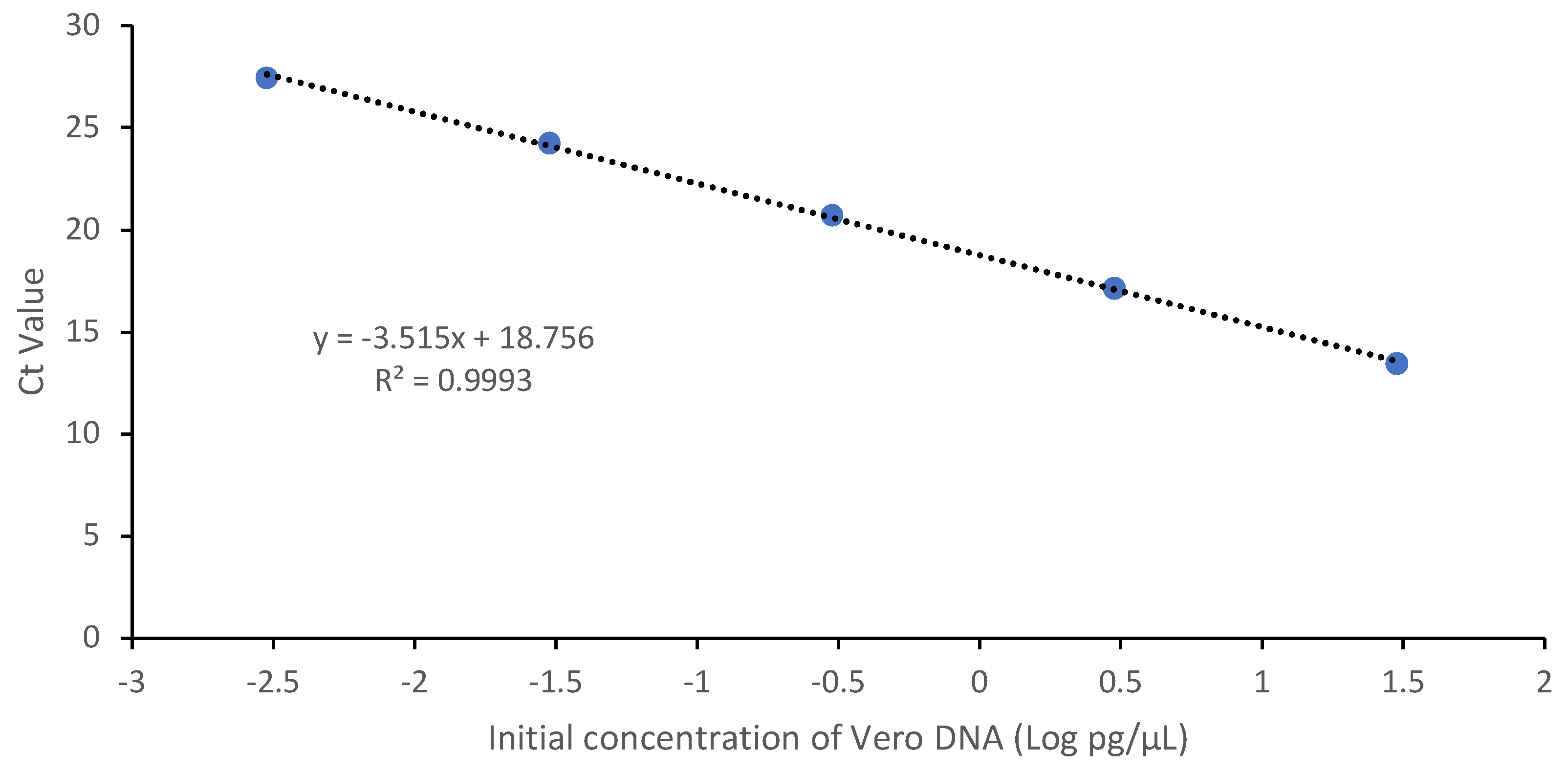
| Sample | Theoretical Conc. (pg/μL) | Mean Value (pg /μL) |
RSD (%) |
Relative bias (%) |
| 1 | 3.00 × 101 | 3.09 × 101 | 4.7 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 3.00 | 2.73 | 0.4 | 9.0 |
| 3 | 3.00 × 10-1 | 2.64 × 10-1 | 0.9 | 11.8 |
| 4 | 3.00 × 10-2 | 2.75 × 10-2 | 2.5 | 8.5 |
| 5 | 3.00 × 10-3 | 3.03 × 10-3 | 10.2 | 0.9 |
| 6 | 3.00 × 10-4 | 3.12 × 10-4 | 87.0 | 4.0 |
3.2.2. Quantitation Limit
| Theoretical Conc. (pg/μL) |
3.00 × 10-3 (n=10) |
1.00 × 10-3 (n=10) |
3.00 × 10-4 (n=10) |
| Ave Conc. (pg/μL) |
2.95 × 10-3 | 1.08 × 10-3 | 4.53 × 10-4 |
| RSD(%) | 9.0 | 19.0 | 52.8 |
| Relative bias (%) | 1.6 | 7.7 | 51.1 |
3.2.3. Specificity
3.2.4. Accuracy
3.2.5. Precision
| Theoretical value (pg) | Mean Value (pg) (n = 6) |
RSD (%) |
| 3.00 × 101 | 2.94 × 101 | 11.0 |
| 3.00 × 10-1 | 2.63 × 10-1 | 3.6 |
| Theoretical value (pg) | Mean Value (pg) (n = 6) |
RSD (%) |
| 3.00 × 102 | 2.50 × 102 | 16.7 |
| 3.00 | >2.35 | 12.4 |
| 6.00 × 10-2 | 5.13 × 10-2 | 18.3 |
3.2.6. Robustness
| Instrument Model | Theoretical value (pg/μL) |
RSD (%) (n = 10) |
Relative bias (%) |
| SHENTEK-96S | 1.00 × 10-3 | 19.0 | 7.7 |
| ABI 7500 | 3.00 × 10-3 | 17.9 | 6.8 |
| CFX-96 | 1.00 × 10-3 | 17.9 | 16.7 |
| FQD-96A | 3.00 × 10-3 | 16.7 | 7.0 |
| LightCycler480 II | 3.00 × 10-3 | 17.3 | 13.0 |
| qTOWER3G | 3.00 × 10-3 | 12.2 | 5.7 |
Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasumura Y, Kawakita M. The research for the SV40 by means of tissue culture technique. Nippon Rinsho. 1963, 21, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar]
- N.S.Murthy and A. Mathew. Cancer epidemiology, prevention and control. Current. Science. 2004; 86, 518–527.
- M. Mimeault, N. Jouy, P. Depreux and J.P. Henichart. Synergistic antiproliferative and apoptotic effects induced by mixed epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor ZD1839 and nitric oxide donor in human prostatic cancer cell lines. Prostate. 2005, 62, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada N, Kohara A, etc. The genome landscape of the African green monkey kidney-derived Vero cell line. DNA Research. 2014, 21, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu X, Smith TG, Rupprecht CE. From brain passage to cell adaptation: the road of human rabies vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2011, 10, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Recommendations for the evaluation of animal cell cultures as substrates for the manufacture of biological medicinal products and for the characterization of cell banks. Annex 3, TRS No 978.
- FDA. Guidance for Industry Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications; FDA: New Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. United States Pharmacopeia. Chapter 509: Residual DNA Testing.
- Dinah, S. Singer. Arrangement of a highly repeated DNA sequence in the genome and chromatin of the African green monkey. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1979, 254, 5506–5514. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanna Grimaldi, Cary Queen, etc. Interspersed repeated sequences in the African green monkey genome that are homologous to the human Alu family. Nucleic Acids Research. 1981, 9, 5553–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peper, G.; Fankhauser, A.; Merlin, T.; Roscic, A.; Hofmann, M.; Obrdlik, P. Direct real-time quantitative PCR for measurement of host-cell residual DNA in therapeutic proteins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnamkhasti, F.A.; Kia, V.; Shokri, R.; Mehdipour Moghaddam, M.J.; Paryan, M. Design and development of a simple method for the detection and quantification of residual host cell DNA in recombinant rotavirus vaccine. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2021, 55, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Jiang, L.; Lei, Q.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, G. Development and Validation of Quantitative Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Residual CHO Host Cell DNA and Optimization of Sample Pretreatment Method in Biopharmaceutical Products. Biol. Proced. Online. 2019, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li J, Pan RW, etc. Evaluation of the Efficacy of the Vaccine Production Process in Removing Residual Host Cell DNA from the Vero Cell Rabies Vaccine. Vaccines. 2024, 12(12), 1379. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tang, J.-r.; Liu, J.-h.; Qu, X.-s.; Dong, G.-m. The probe selection in Vero cells DNA residue detection by spot hybridization. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2008, 28, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Dong, G.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Development of a Vero cell DNA reference standard for residual DNA measurement in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

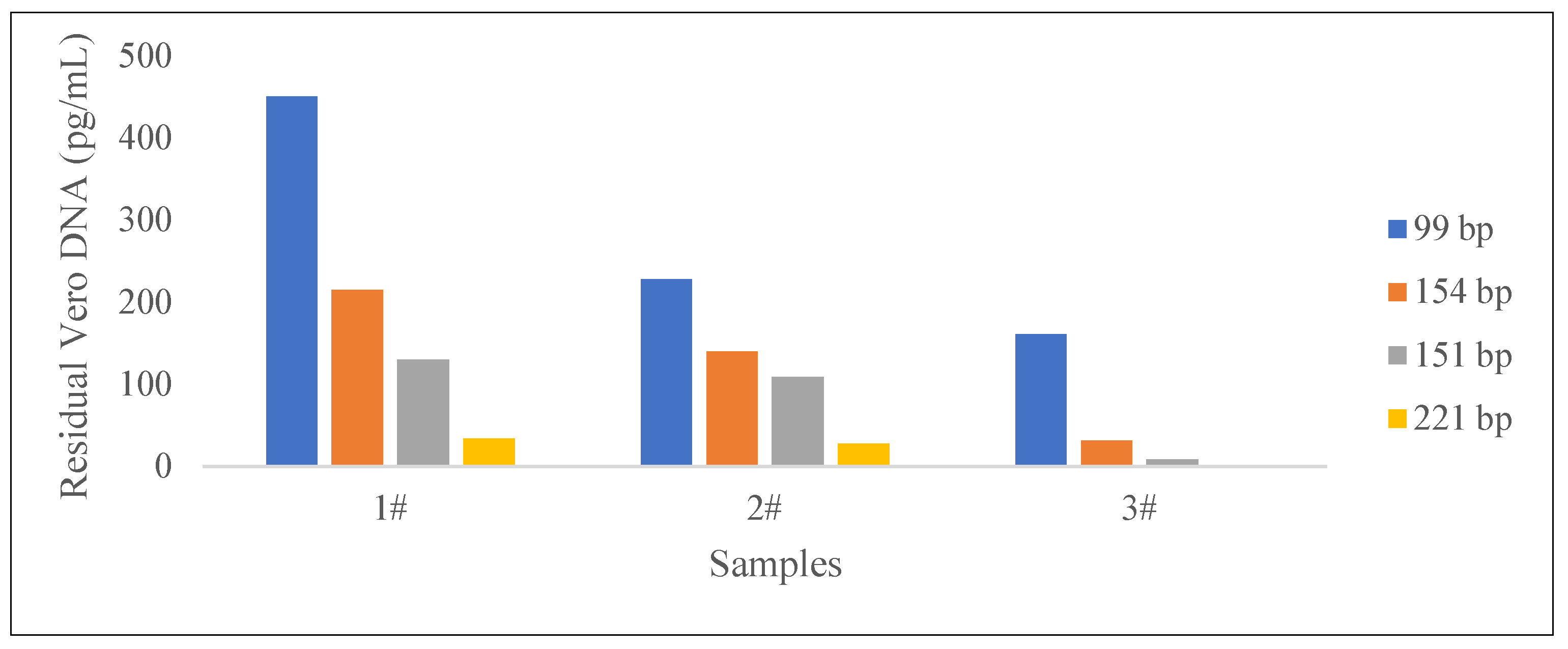
| Sample | Residual Conc. (pg/mL) |
Amplicon size, bp | Target sequence |
| 1 | 451 | 99 | “172 bp” sequence |
| 215 | 154 | ||
| 130 | 151 | Alu repetitive sequence | |
| 33.5 | 221 | ||
| 2 | 228 | 99 | “172 bp” sequence |
| 140 | 154 | ||
| 109 | 151 | Alu repetitive sequence | |
| 27.7 | 221 | ||
| 3 | 161 | 99 | “172 bp” sequence |
| 31.5 | 154 | ||
| 8.39 | 151 | Alu repetitive sequence | |
| 0.263 | 221 |
| Sample | Recovery (%) |
Residual Conc. (pg/mL) |
Amplicon size, bp | Target Sequence |
| Vero DNA National Standard for hybridization method | 77.3 | 6.80×104 | 99 | “172 bp” sequence |
| 70.7 | 5.58×104 | 154 | ||
| 75.4 | 6.49×104 | 151 | Alu repetitive sequence | |
| 73.3 | 6.82×104 | 221 |
| Interfering DNA | Mean Value (pg/μL) |
| CHO | 2.32 × 10-4 |
| E.coli | <1.000 × 10-5 |
| HEK293T | <1.000 × 10-5 |
| HEK293 | <1.000 × 10-5 |
| Pichia pastoris | 2.57 × 10-5 |
| NS0 | <1.000 × 10-5 |
| MDCK | 1.15 × 10-5 |
| Expected DNA (pg) | Observed DNA, mean (pg) | Observed DNA, RSD (%) | Spike recovery (%) |
| 3.00 × 102 | 2.94 × 102 | 11.0 | 98.0 |
| 3.00 | 2.63 | 3.6 | 87.7 |
| 6.00 × 10-2 | 6.05 × 10-2 | 9.3 | 98.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





