Submitted:
04 January 2025
Posted:
06 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Brain tumor continue to cause concern globally due to increasing number of cases and mortality. As the first line of action, accurate and early screening of brain tumor is critical for proper treatment and extending the life span of patients. Currently, medical expert relies heavily on the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the detection of brain tumor. However, one of the limitation of MRI revolves around manual interpretation, which is time consuming and can be prone to errors especially when dealing with large number of cases. Thus, in order to address this issue, we proposed the development of CAD/IoMT-powered platform that enables real-time and fast detection of brain tumor. Methods: We proposed a framework known as I-BRAIN-DETECT, which is a CAD-based system, integrated with IoMT for fast and real-time detection of brain tumors and no tumor from MRIs. The overall methodology revolves around the use of 2 publicly accessible datasets, image pre-processing, feature extraction and classification using untrained customized CNN and 5 pre-trained CNNs which include ResNet-18, ResNet-50, DenseNet121, MobileNetV2 and EfficientNetB0. Results: Performance evaluation and comparative between implemented models has shown that pre-trained ResNet18 achieve the best result with 98.83% accuracy, 98.33 % recall, 99.33% precision, 99.33% specificity, 98.83% F1-score and 99.92 AUC for binary classification, while MobileNetV2 achieved the best result with 92.93% accuracy, 92.93 % recall, 93.37% precision, 97.67% specificity, 92.79% F1-score and 100 AUC for multiclass-classification. Conclusions: The developed platform can now be access by both patients and medical experts for real-time screening of brain tumor.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Survey
1.2. Limitation of Existing Studies and Contributions
- Binary classification of MRIs into tumor and no tumor.
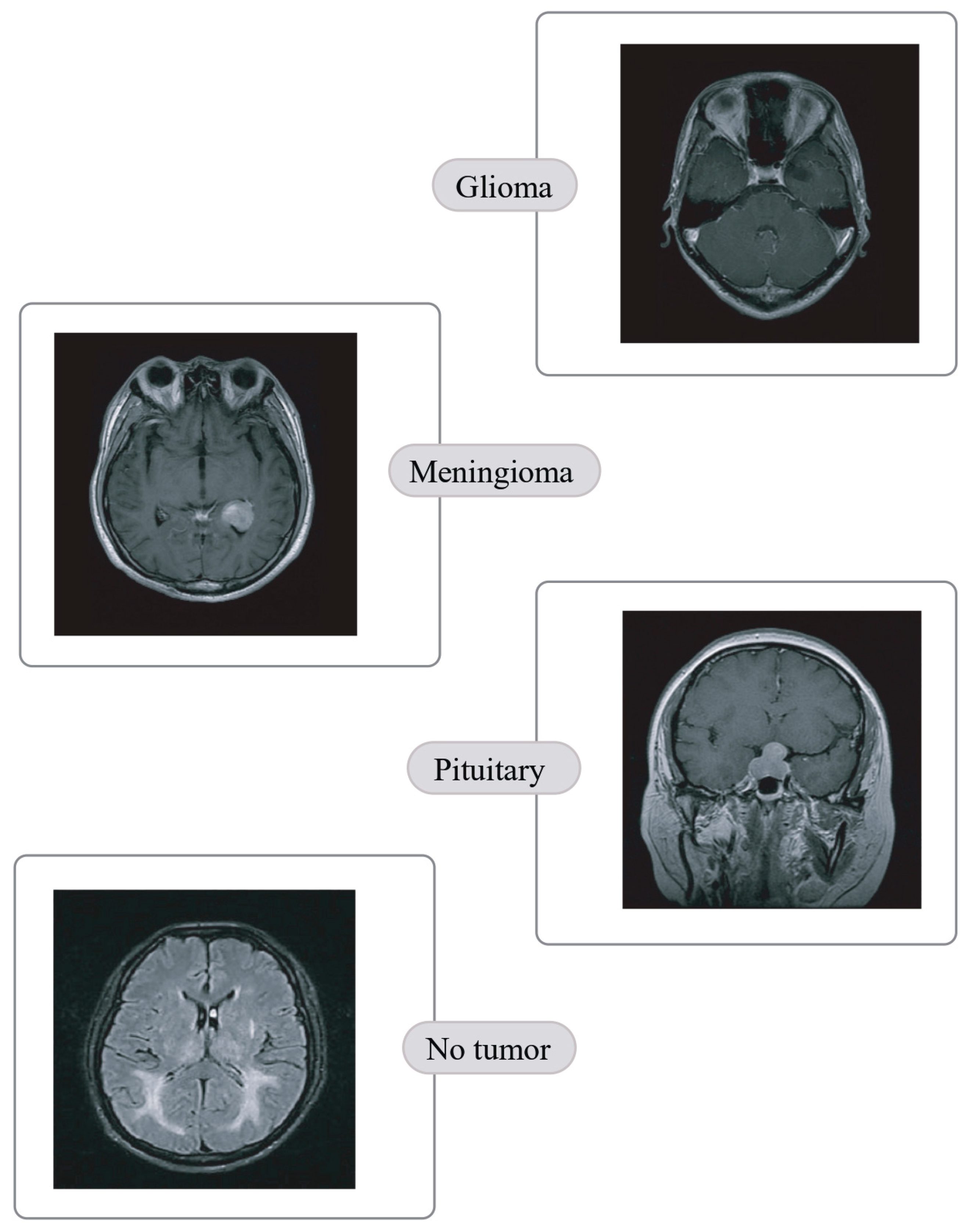
- Quaternary classification of MRIs into glioma, meningioma, pituitary and no tumor.
- Development of CAD/IoMT-based platform for real-time detection and classification of brain tumors and no tumor.
- Performance evaluation of proposed framework and comparison with state of art results.
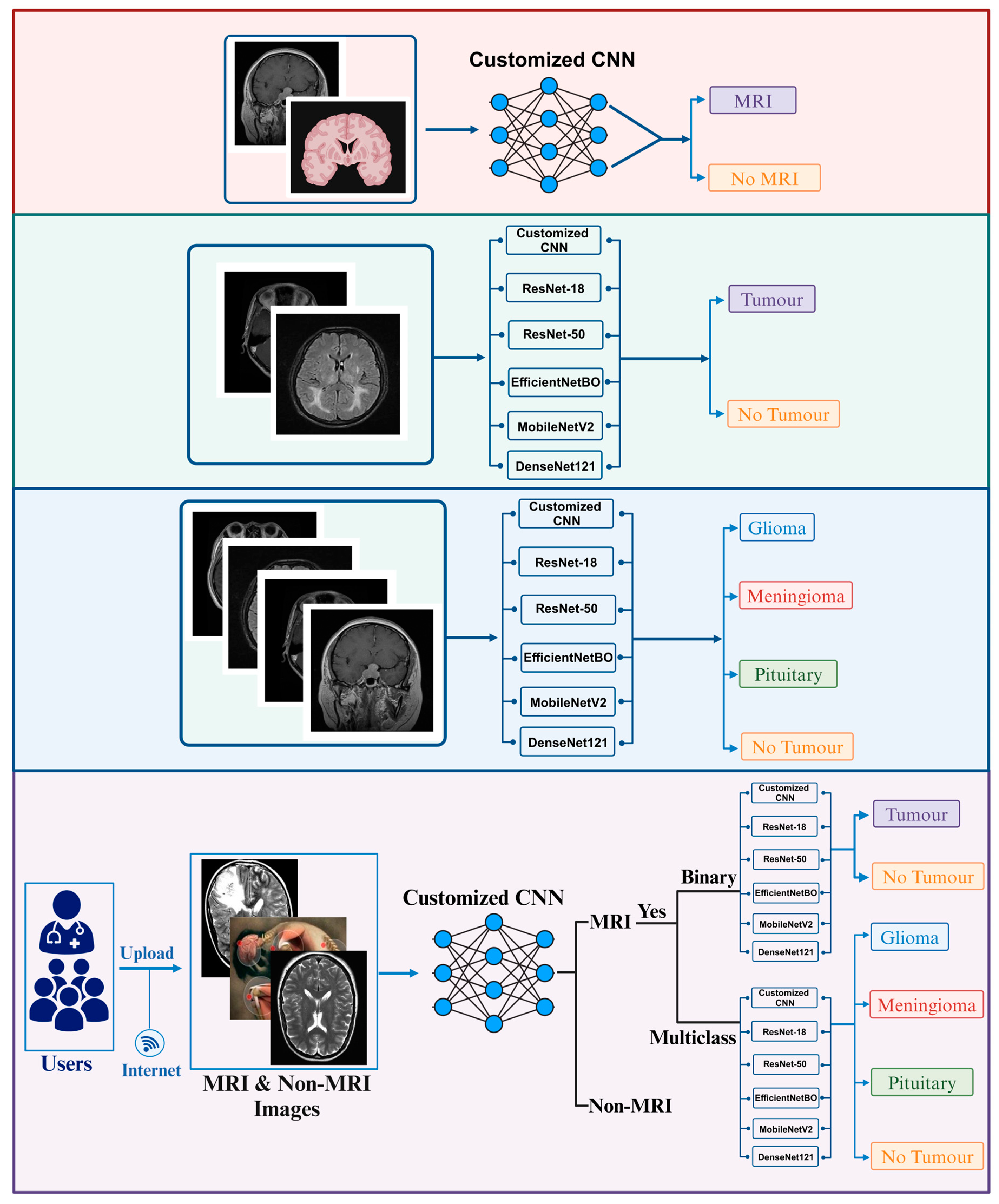
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.1.1. Brain Tumor Detection MRI (BTD-MRI)
2.1.2. Brain MRI Scans for Brain Tumor Classification (BMS-BTC)
2.2. Data Pre-Processing and Augmentation
2.3. Customized CNN
2.4. Pre-Trained CNNs
2.4.1. EfficientNet
2.4.2. DenseNet
2.4.3. MobileNet
2.4.4. ResNet
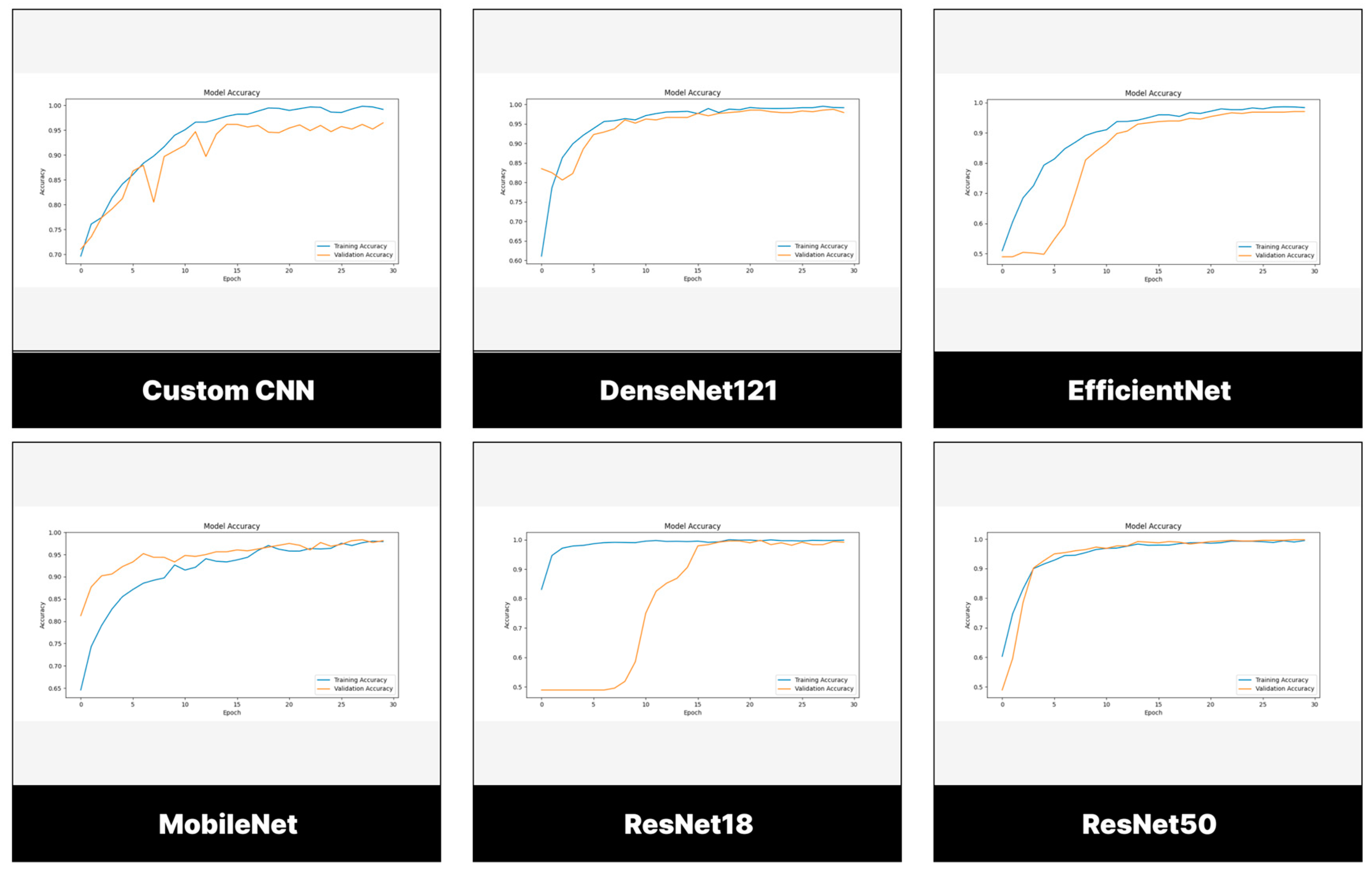
2.5. Training Parameters
3. Results
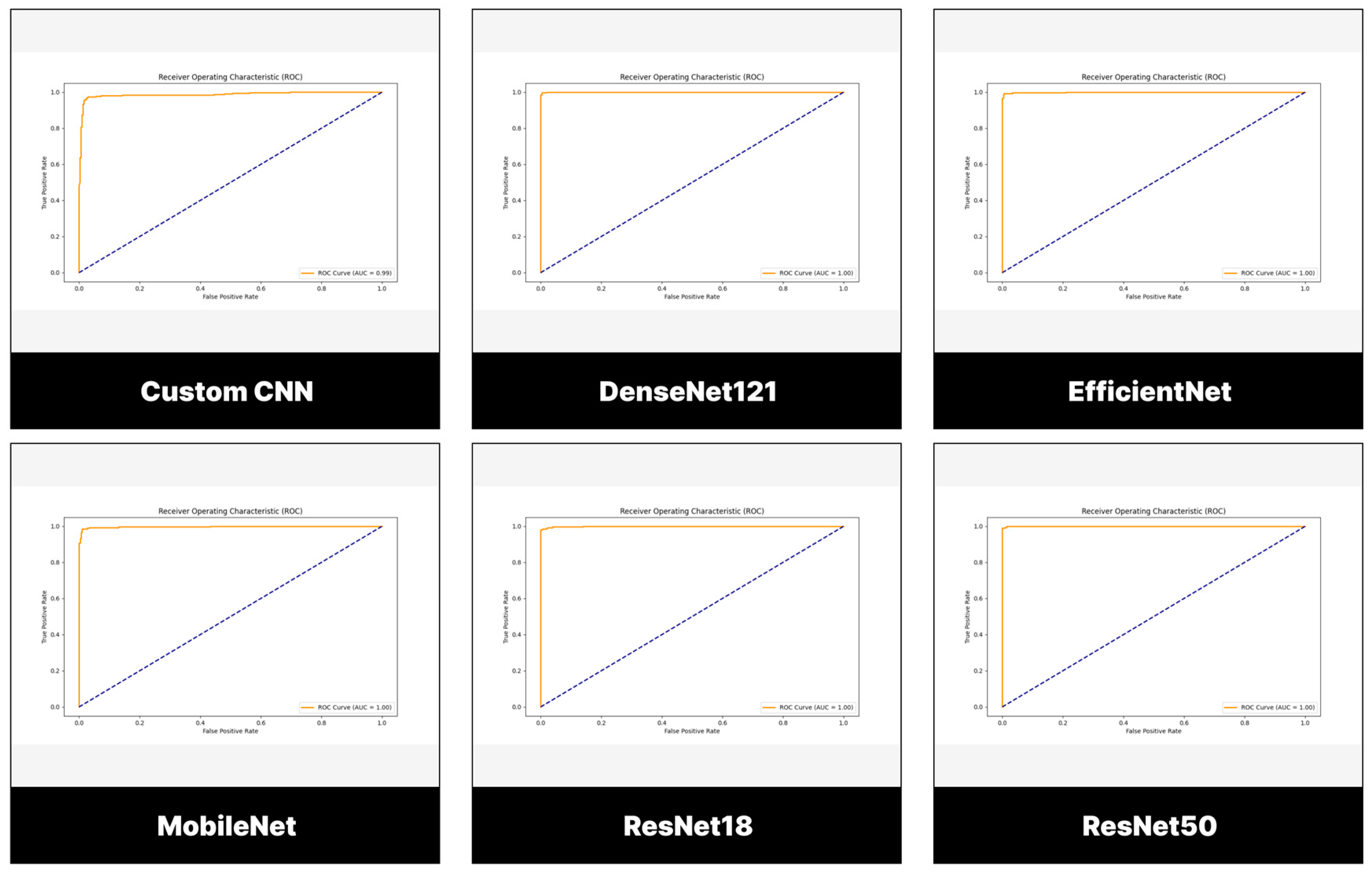
3.1. Evaluation Measures
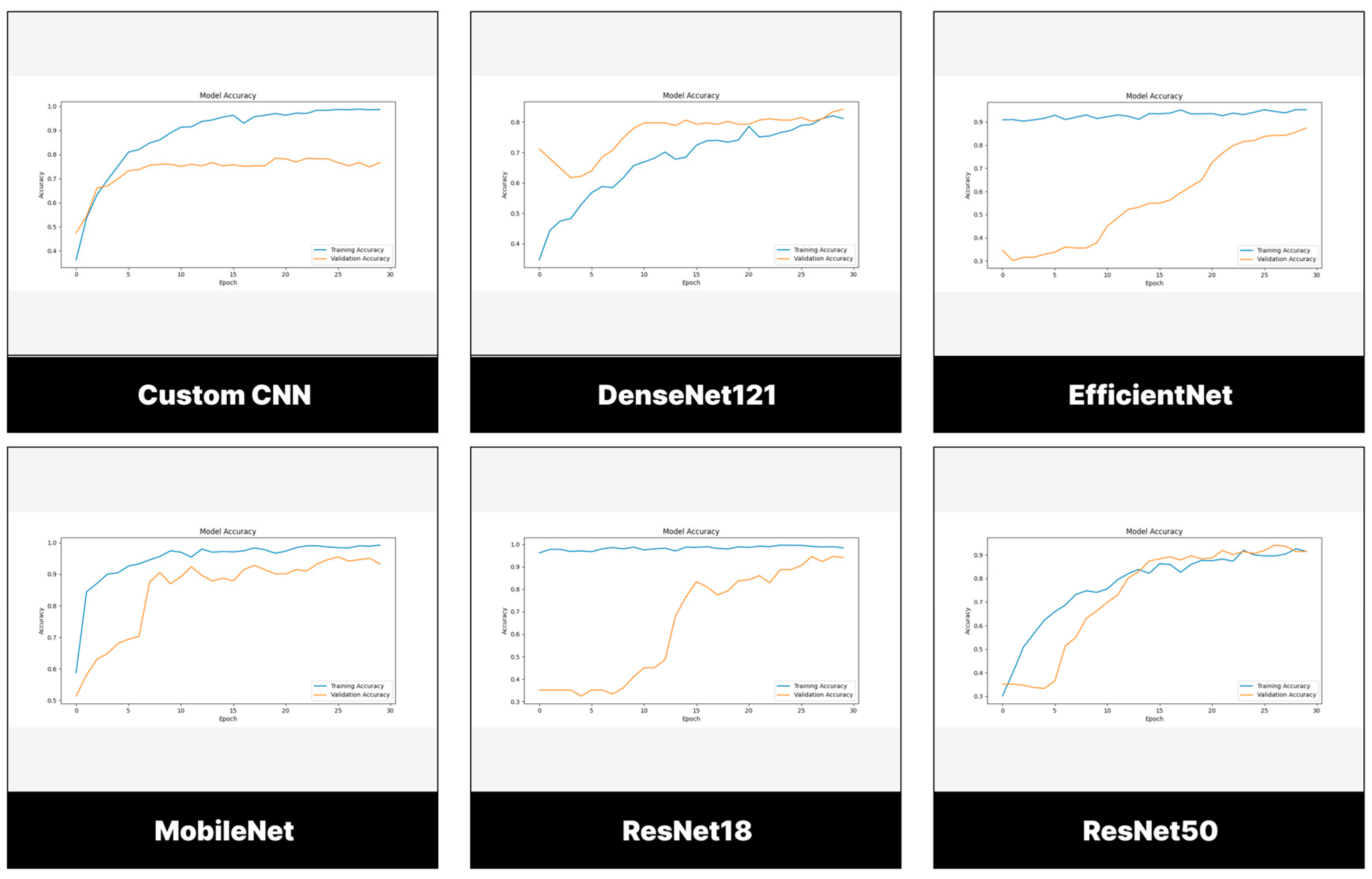
3.2. Performance Evaluation of Models Trained and Tested Using BTD-MRI Dataset
3.2.1. Testing Set
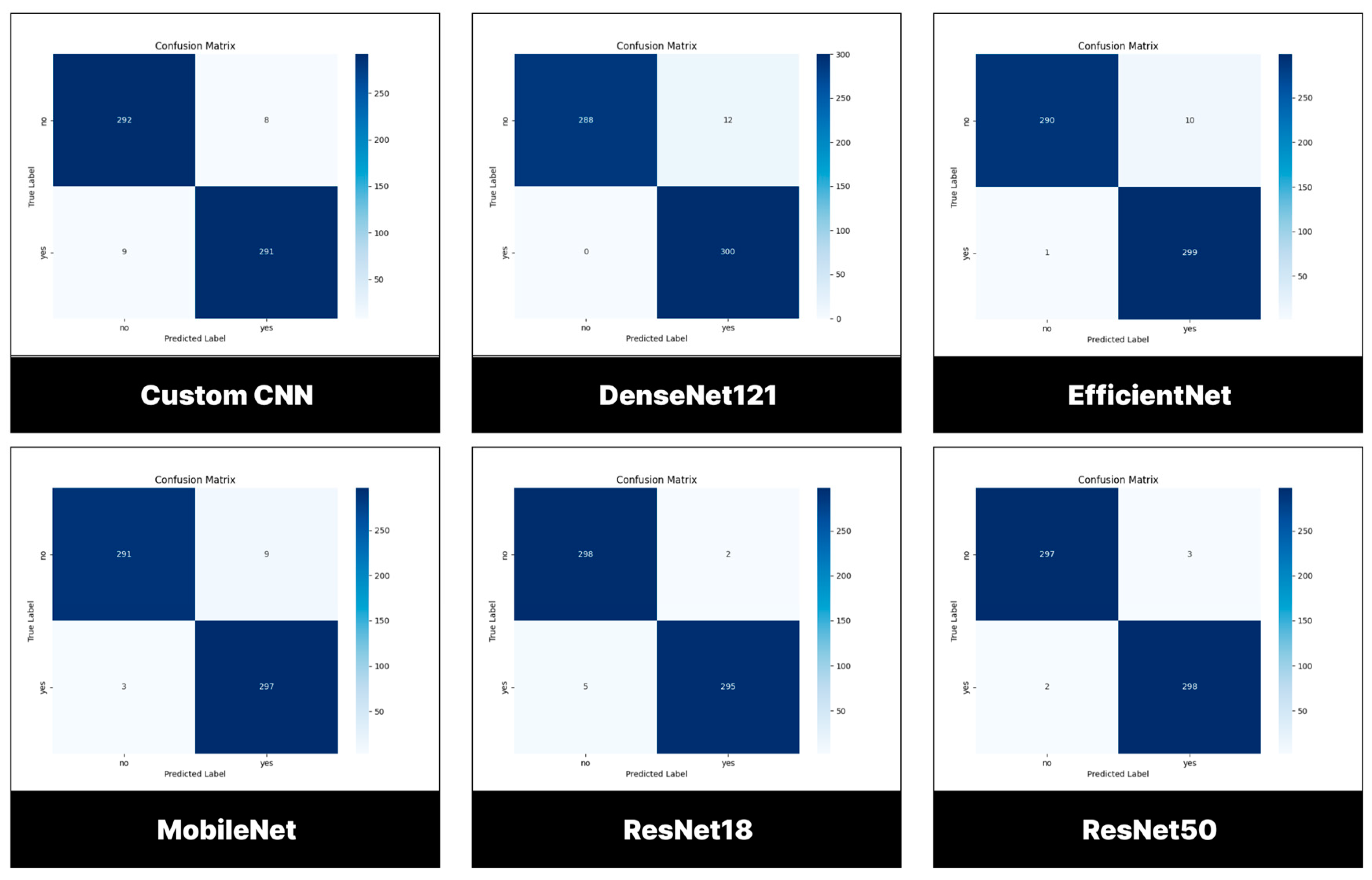
3.2.2. Confusion Matrix
3.3. Performance Evaluation of Models Trained and Tested Using BMS-BTC Dataset
3.3.1. Testing Set
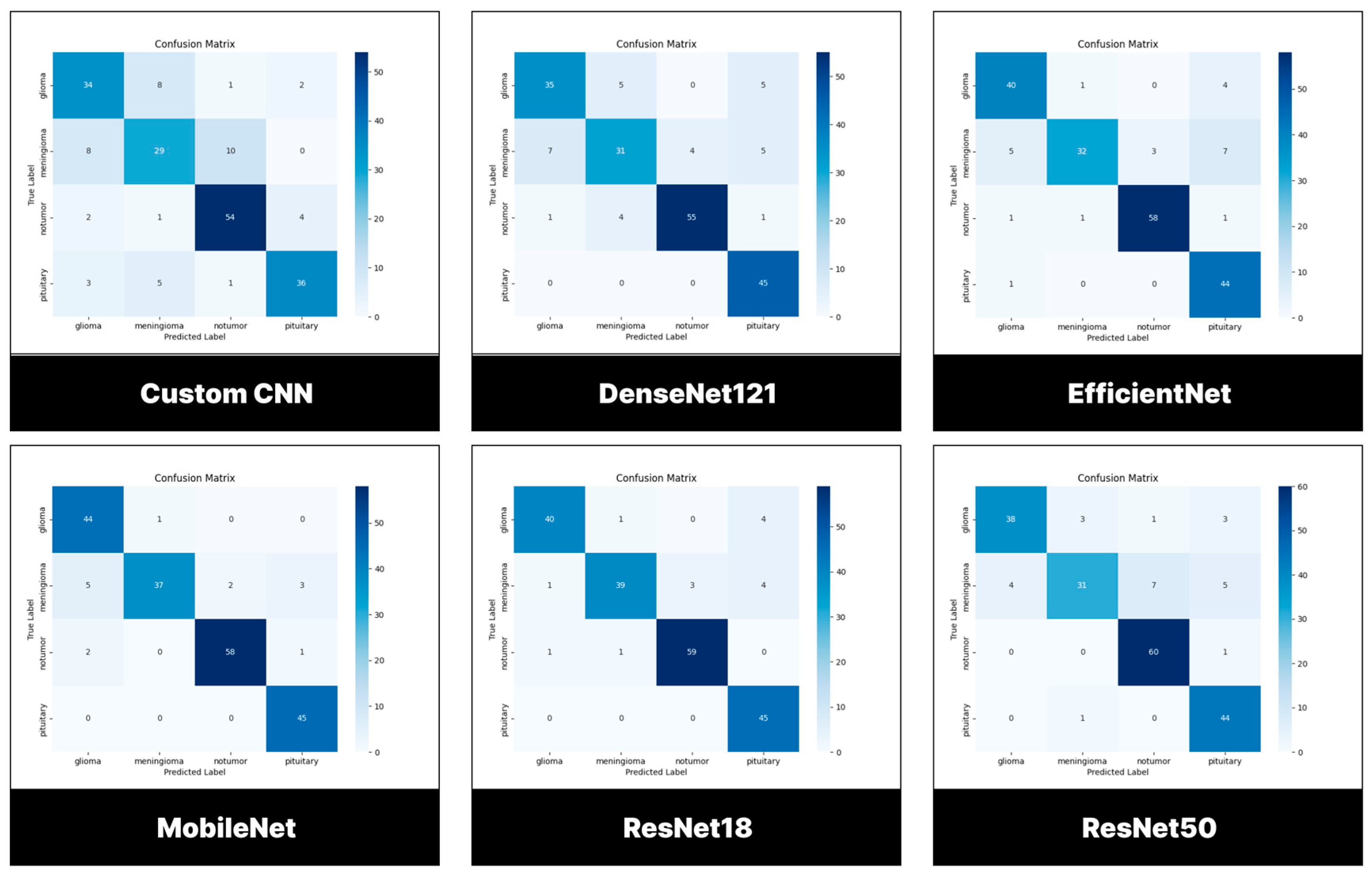
3.3.2. Confusion Matrix
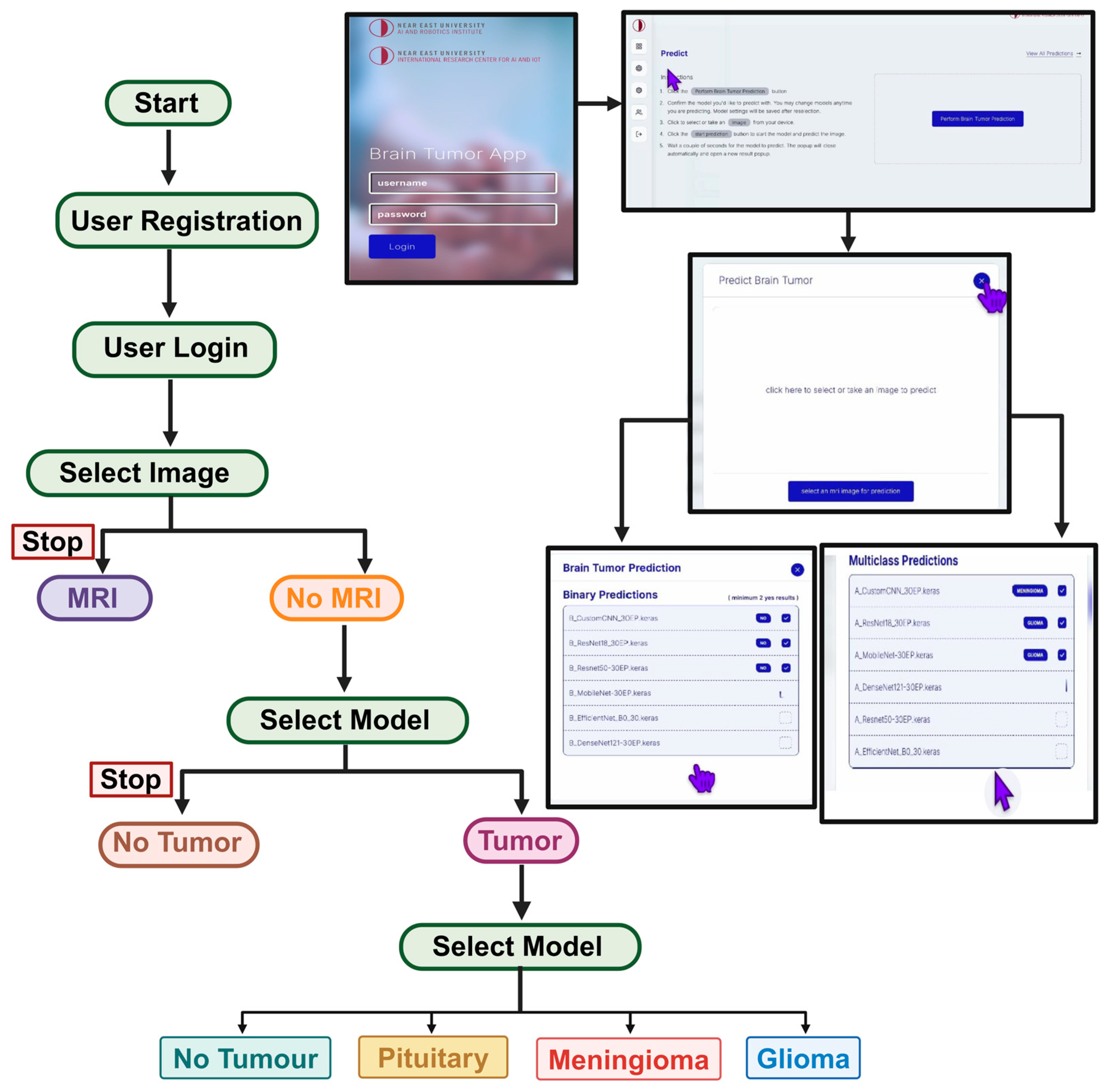
3.4. Deployment of Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Related Work
4.1.1. Binary Classification
4.1.2. Multiclass Classification
4.2. Limitation and Future Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bockaert, J.; Marin, P. mTOR in brain physiology and pathologies. Physiol Rev 2015, 95(4), pp.1157-1187. [CrossRef]
- Khaliki, M.Z.; Başarslan, M.S. Brain tumor detection from images and comparison with transfer learning methods and 3-layer CNN. Sci Rep 2024, 14(1), p.2664. [CrossRef]
- Cancer.Net. Brain Tumour: Statistics. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/brain-tumor/statistics (accessed on December 13, 2024).
- National Institute of Cancer. Tumor. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/tumor (accessed on September 11, 2024).
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G; Soffietti, R. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro-oncol 2021, 23(8), pp.1231-1251. [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.R.; Wen, P.Y.; Lang-Orsini, M.; Chukwueke, U.N. World Health Organization 2021 classification of central nervous system tumors and implications for therapy for adult-type gliomas: a review. JAMA Oncol 2022, 8(10), pp.1493-1501.
- Smith, H.L.; Wadhwani, N.; Horbinski, C. Major features of the 2021 WHO classification of CNS tumors. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19(6), pp.1691-1704. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, R.C.; Antoniou, A.C.; Fruk, L.; Rosenfeld, N. The future of early cancer detection. Nat Med 2022, 28(4), pp.666-677. [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.W.; Ghamdi, M.A.; Hussain, M.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, K.M.; Almotiri, S.H.; Butt, S.A. Brain tumor analysis empowered with deep learning: A review, taxonomy, and future challenges. Brain Sci 2020, 10(2), p.118. [CrossRef]
- Chahal, P.K.; Pandey, S.; Goel, S. A survey on brain tumor detection techniques for MR images. Multimedia Tools Appl 2020, 79(29), pp.21771-21814. [CrossRef]
- Jan, Z.; Ahamed, F.; Mayer, W.; Patel, N.; Grossmann, G.; Stumptner, M.; Kuusk, A. Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0: Systematic review of applications, challenges, and opportunities. Expert Sys Appl 2023, 216, p.119456.
- Kaul, V.; Enslin, S.; Gross, S.A. History of artificial intelligence in medicine. Gastrointestinal endoscopy 2020, 92(4), pp.807-812. [CrossRef]
- Briganti, G.; Le Moine, O. Artificial intelligence in medicine: today and tomorrow. Front Med 2020, 7, p.509744. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.U.; Ozsoz, M.; Serte, S.; Al-Turjman, F.; Yakoi, P.S. Pneumonia classification using deep learning from chest X-ray images during COVID-19. Cognit Comput 2024, 16(4), pp.1589-1601. [CrossRef]
- Uzun Ozsahin, D.; Mustapha, M.T.; Uzun, B.; Duwa, B.; Ozsahin, I. Computer-aided detection and classification of monkeypox and chickenpox lesion in human subjects using deep learning framework. Diagn 2023, 13(2), p.292. [CrossRef]
- Umar Ibrahim, A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Ozsoz, M.; Serte, S. Computer aided detection of tuberculosis using two classifiers. Biomed Eng/Biomedizinische Technik 2022, 67(6), pp.513-524. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.U.; Dirilenoğlu, F.; Hacisalihoğlu, U.P.; Ilhan, A.; Mirzaei, O. Classification of H. pylori Infection from Histopathological Images Using Deep Learning. J Imaging Info Med 2024, pp.1-10. [CrossRef]
- Jinnai, S.; Yamazaki, N.; Hirano, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Ohe, Y.; Hamamoto, R. The development of a skin cancer classification system for pigmented skin lesions using deep learning. Biomol 2020, 10(8), p.1123. [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, M.T.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Ozsahin, I.; Uzun, B. Breast cancer screening based on supervised learning and multi-criteria decision-making. Diagn 2022, 12(6), p.1326. [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, D.; Linder, N.; Turkki, R.; Nordling, S.; Kovanen, P.E.; Verrill, C.; Walliander, M.; Lundin, M.; Haglund, C.; Lundin, J. Deep learning based tissue analysis predicts outcome in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep 2018, 8(1), p.3395. [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, A.; Biswas, S.; Hazra, R.; Sunaniya, A.K.; Mukherjee, A; Yang, L. Brain tumor classification using fine-tuned GoogLeNet features and machine learning algorithms: IoMT enabled CAD system. IEEE J. Biomed Health Info 2021, 26(3), pp.983-991. [CrossRef]
- Irkham, I.; Ibrahim, A.U.; Nwekwo, C.W.; Al-Turjman, F.; Hartati, Y.W. Current technologies for detection of COVID-19: Biosensors, artificial intelligence and internet of medical things (IOMT). Sens 2022, 23(1), p.426. [CrossRef]
- Khaliki, M.Z.; Başarslan, M.S. Brain tumor detection from images and comparison with transfer learning methods and 3-layer CNN. Sci Rep 2024, 14(1), p.2664. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Islam, M.S. Brain tumor types classification using K-means clustering and ANN approach. In 2021 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh , (5-7 Jan. 2021).
- Amin, J.; Anjum, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Jabeen, S.; Kadry, S.; Moreno Ger, P. A new model for brain tumor detection using ensemble transfer learning and quantum variational classifier. Comput Intel Neurosci 2022, 1, p.3236305. [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.; Ismail, N.A.; Boulila, W.; Ammar, A.; Samma, H.; Yafooz, W.M.; Emara, A.H.M. A hybrid deep learning model for brain tumour classification. Entropy 2022, 24(6), p.799. [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomov, A.B.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Whangbo, T.K. Brain tumor detection based on deep learning approaches and magnetic resonance imaging. Cancers 2023, 15(16), p.4172. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Kumar, T. Enhancing Medical Diagnostics: Integrating AI for precise Brain Tumour Detection. Procedia Comput Sci 2024, 235, pp.456-467. [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, S.; Rezayi, S.; Keshavarz, H.; Niakan Kalhori, S. MRI-based brain tumor detection using convolutional deep learning methods and chosen machine learning techniques. BMC Med Info Decis Making 2023, 23(1), p.16. [CrossRef]
- Aleid, A.; Alhussaini, K.; Alanazi, R.; Altwaimi, M.; Altwijri, O.; Saad, A.S. Artificial intelligence approach for early detection of brain tumors using MRI images. Appl Sci 2023, 13(6), p.3808. [CrossRef]
- Aamir, M.; Namoun, A.; Munir, S.; Aljohani, N.; Alanazi, M.H.; Alsahafi, Y.; Alotibi, F. Brain Tumor Detection and Classification Using an Optimized Convolutional Neural Network. Diagn 2024, 14(16), p.1714. [CrossRef]
- Zubair Rahman, A.M.J.; Gupta, M.; Aarathi, S.; Mahesh, T.R.; Vinoth Kumar, V.; Yogesh Kumaran, S.; Guluwadi, S. Advanced AI-driven approach for enhanced brain tumor detection from MRI images utilizing EfficientNetB2 with equalization and homomorphic filtering. BMC Med Info Decis Making 2024, 24(1), p.113. [CrossRef]
- Sawant, A.; Bhandari, M.; Yadav, R.; Yele, R.; Bendale, M.S. Brain cancer detection from mri: A machine learning approach (tensorflow). Brain 2018, 5(04), pp.2089-2094.
- Alsubai, S.; Khan, H.U.; Alqahtani, A.; Sha, M.; Abbas, S.; Mohammad, U.G. Ensemble deep learning for brain tumor detection. Front Comput Neurosci 2022, 16, p.1005617. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Sharma, S.K.; Sampada, G.C. Classification of Brain Tumor Images Using CNN. Comput Intel Neurosci 2023, (1), p.2002855. [CrossRef]

| Ref | Model | No of MRIs/Slices | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiclass | |||
| [21] | GoogleNet-SVM | 3064 | 100.00% |
| [23] | VGG16 | 2870 | 98.00% |
| [24] | ANN | 563 | 97.83% |
| [25] | inceptionV3+QVR | 40,145 | 99.70% |
| [26] | GoogleNet-SVM | 3460 | 94.12% |
| [27] | YOLOv7 | 10,288 | 99.50% |
| [28] | multimodal approach + SVM | 1747 | 92.00% |
| [29] | 2D CNN | 3264 | 93.44% |
| [30] | Threshold-based segmentation | 40 | 97.55% |
| [31] | optimized CNN | 7023 | 97.18% |
| Binary | |||
| [31] | optimized CNN | 1500 | 97.18% |
| [32] | EfficientNetB2 | 3060 | 99.75% |
| [33] | Le-Net | 1800 | 98.6 |
| [34] | CNN-LSTM | 253 | 99.1% |
| [35] | VGG-16 | 253 | 100.00% |
| Classes | Number of images | % |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor | 1500 | 50.00 |
| No tumor | 1500 | 50.00 |
| Classes | Number of images | % |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary | 300 | 22.88 |
| Meningioma | 306 | 23.34 |
| Glioma | 300 | 22.88 |
| No tumor | 405 | 30.89 |
| Model/ Performance Metrics (%) | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | Specificity | F1-Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customized CNN | 97.17 | 97.00 | 97.32 | 97.33 | 97.16 | 98.62 |
| ResNet-18 | 98.83 | 98.33 | 99.33 | 99.33 | 98.83 | 99.92 |
| ResNet-50 | 87.37 | 99.33 | 99.00 | 99.00 | 99.17 | 99.99 |
| MobileNetV2 | 98.00 | 99.00 | 97.06 | 97.00 | 98.02 | 99.74 |
| DenseNet121 | 98.00 | 100.00 | 96.15 | 96.00 | 98.04 | 99.99 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 98.17 | 99.67 | 96.76 | 96.67 | 98.18 | 99.91 |
| Model/ Performance Metrics (%) | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | Av. Specificity | F1-Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customized CNN | 76.26 | 77.27 | 77.14 | 92.38 | 77.10 | 92.75 |
| ResNet-18 | 92.42 | 92.42 | 92.84 | 97.48 | 92.37 | 99.50 |
| ResNet-50 | 87.37 | 87.37 | 87.64 | 95.76 | 86.87 | 99.25 |
| MobileNetV2 | 92.93 | 92.93 | 93.37 | 97.67 | 92.79 | 100.00 |
| DenseNet121 | 92.93 | 83.84 | 83.88 | 94.68 | 83.41 | 97.25 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 87.88 | 87.88 | 88.33 | 96.02 | 87.61 | 98.75 |
| Ref | Model | No of MRIs/Slices | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| [31] | optimized CNN | 1500 | 97.18% |
| [32] | EfficientNet | 3060 | 99.75% |
| [33] | Le-Net | 1800 | 98.60% |
| [34] | CNN-LSTM | 253 | 99.10% |
| [35] | VGG-16 | 253 | 100.00% |
| This study | ResNet18 | 3000 | 98.83% |
| Ref | Model | No of MRIs/Slices | Classes | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | GoogleNet-SVM | 3064 | 3 | 100.00% |
| [23] | VGG16 | 2870 | 4 | 98.00% |
| [24] | ANN | 563 | 3 | 97.83% |
| [25] | inceptionV3+QVR | 40,145 | 4 | 99.70% |
| [26] | GoogleNet-SVM | 3460 | 4 | 94.12% |
| [27] | YOLOv7 | 10,288 | 4 | 99.50% |
| [28] | multimodal approach + SVM | 1747 | 4 | 92.00% |
| [29] | 2D CNN | 3264 | 4 | 93.44% |
| [31] | optimized CNN | 7023 | 4 | 97.18% |
| This study | MobileNetV2 | 1311 | 4 | 92.93% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





