Submitted:
01 January 2025
Posted:
06 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Treatment and Allocation
- Benzydamine hydrochloride (throat spray 0.15%): children over six and below twelve: 4 sprays 2-6 times a day; children (under six years): 1 spray per 4kg of body weight, a maximum of 4 sprays at once, 2-6 times a day according to the leaflet. Each spray was equals 0.17 ml of solution.
- Paracetamol (120 mg/5 ml) per os, in case of >38,5°C, 10 mg/kg/dose, per need every 6-8 hours. Maximum dosage under a 30 mg/kg dose
- Nasal decongestion through hydration with fluids, aspiration of secretions, use of saline solution for nasal irrigation, nasal sprays with seawater, and nasal spray with an active compound (this last one was only a special indication of the medical doctor).
2.4. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Sample Size Determination and Statistical Methods
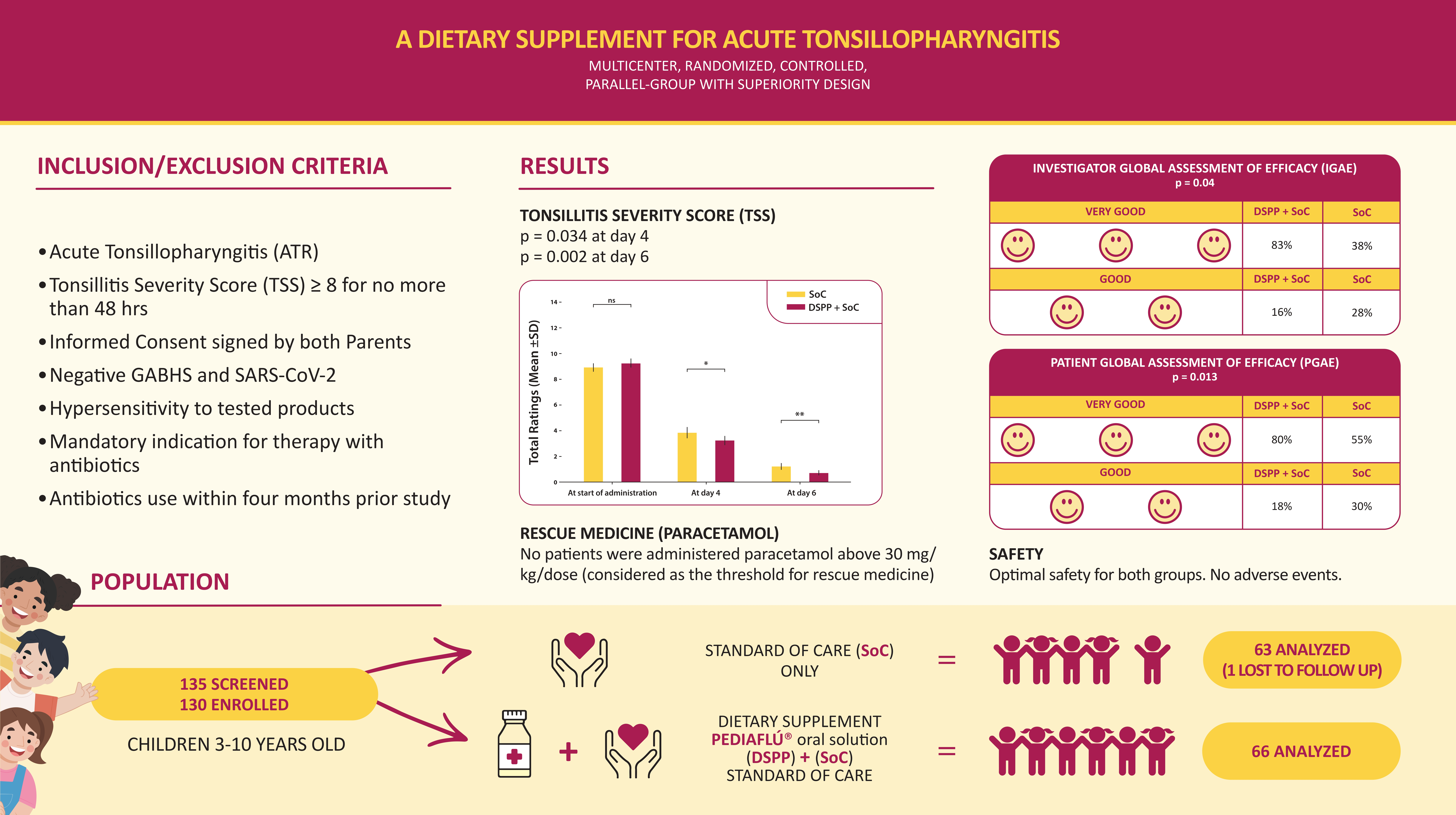
3. Results
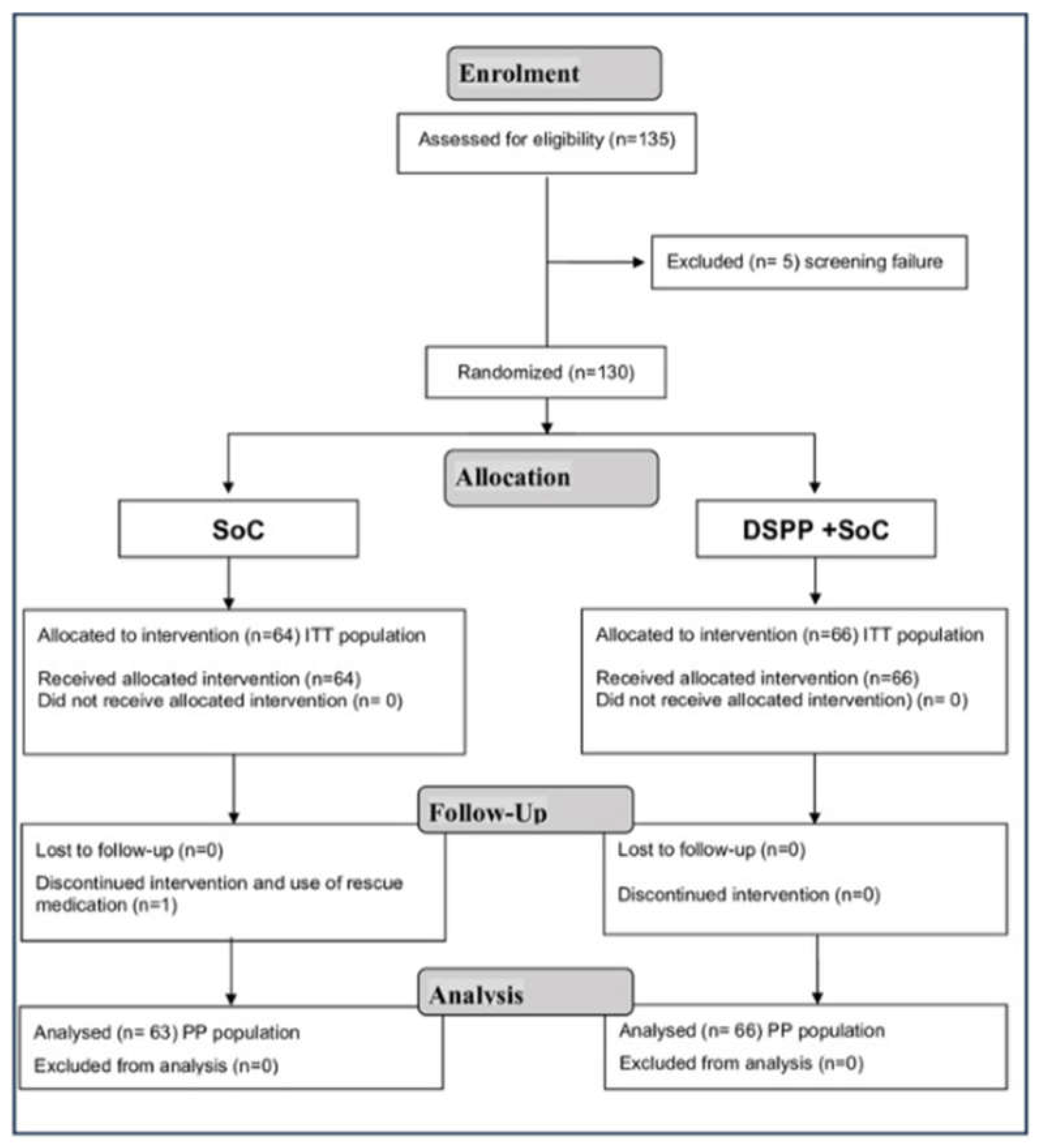
3.1. Patient Disposition and Characteristics
3.2. Administered Treatments
3.3. Efficacy Analysis
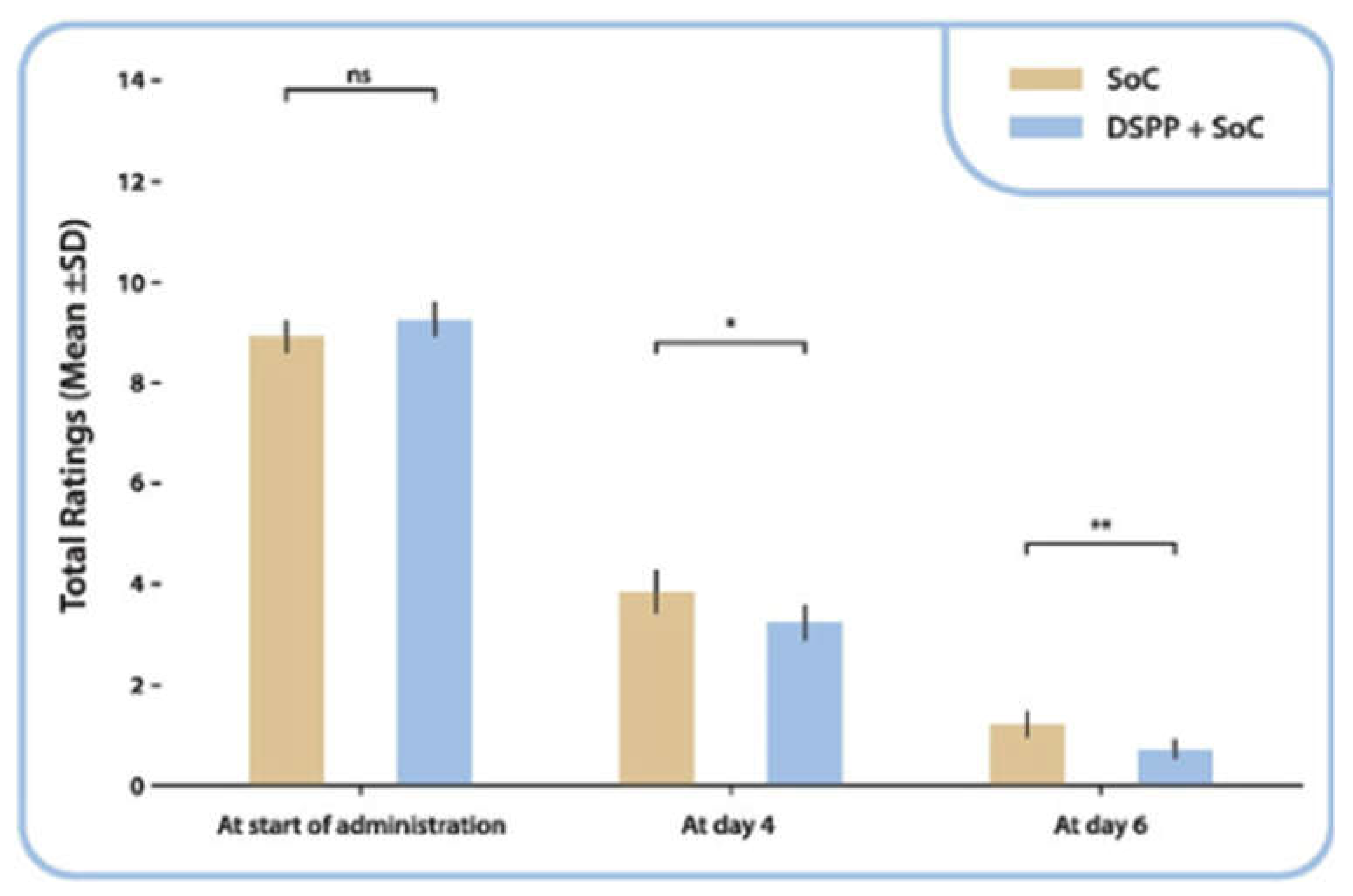
3.3.1. TSS
3.3.2. Use of Rescue Medicine
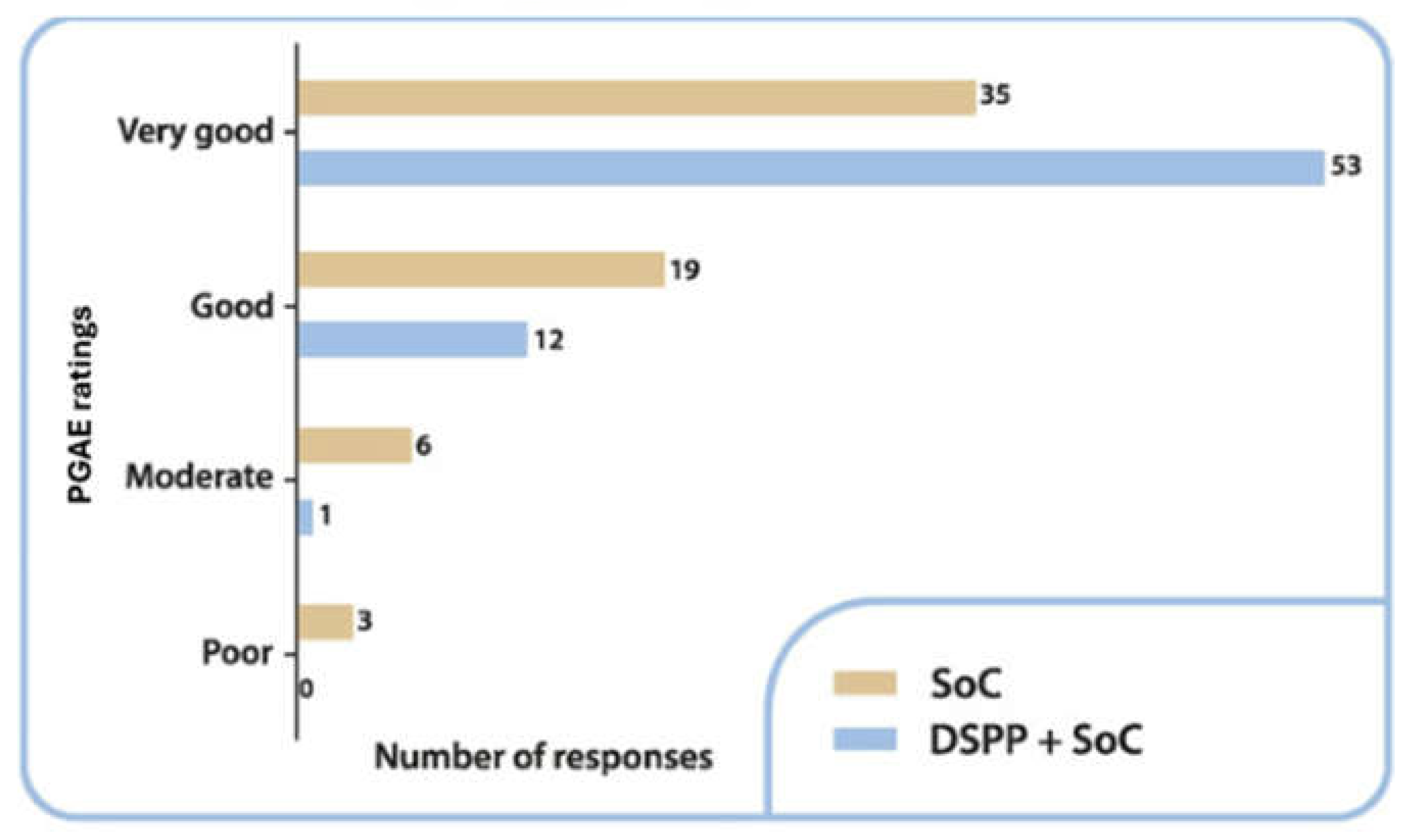
3.3.3. PGAE
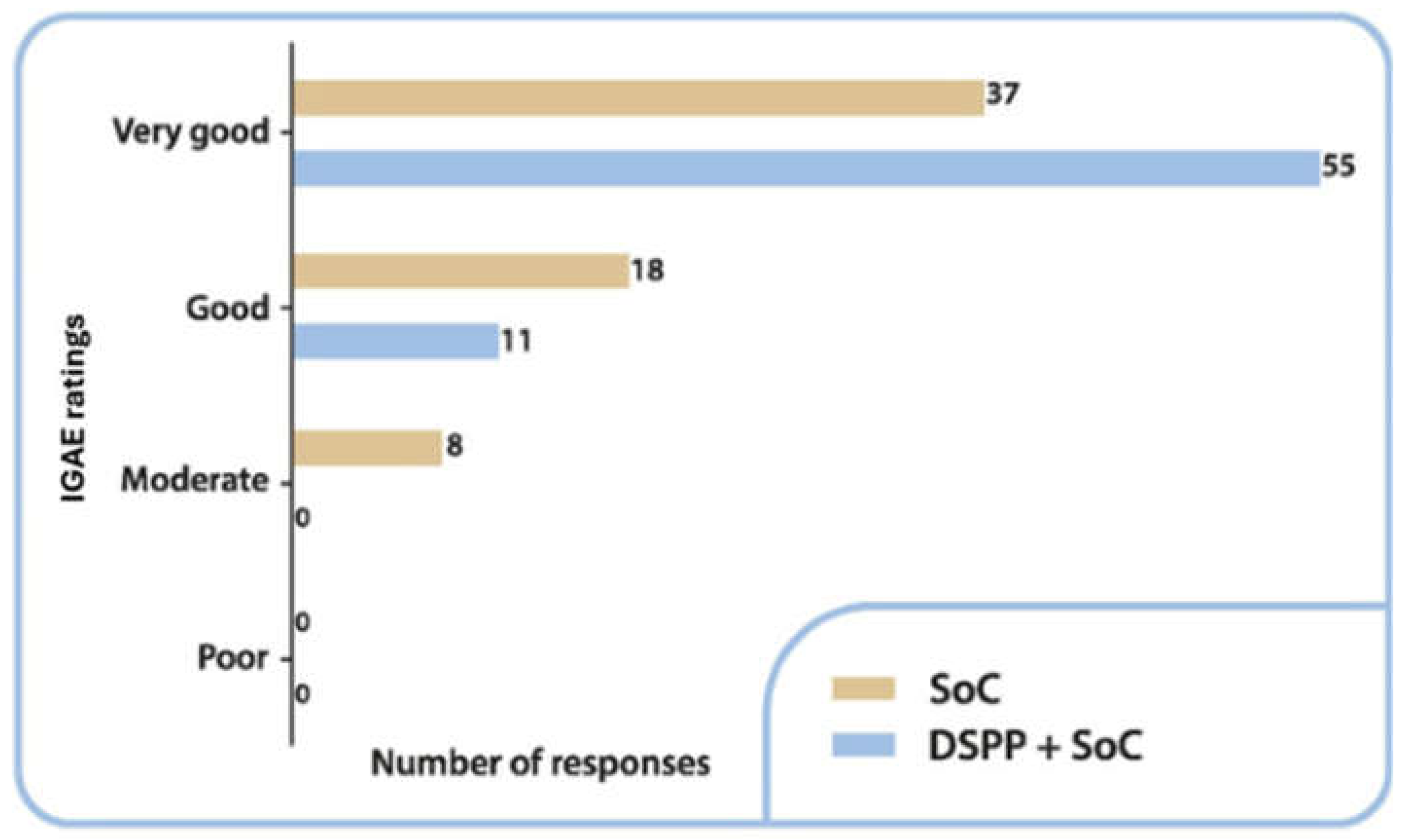
3.3.4. IGAE
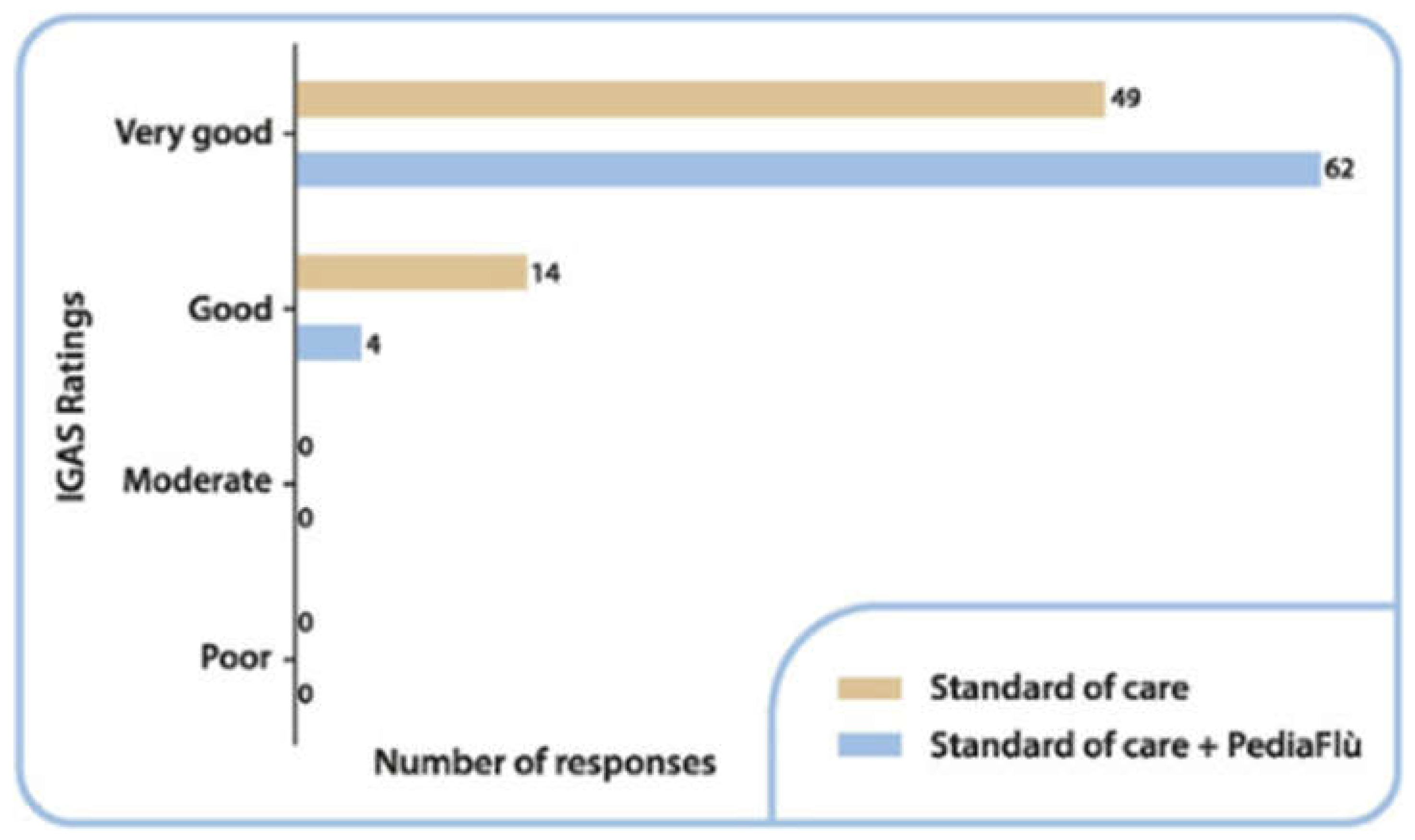
3.4. Safety Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR | Acute Tonsillopharyngitis/Rhinopharyngitis |
| SoC | Standard of Care |
| AOM | Acute Otitis Media |
| DS | Dietary Supplement |
| URTI | Upper Respiratory Tract Infection |
| AE/SAE | Adverse Event/Serious Adverse Event |
| DSPP | Dietary Supplement Pediaflù® |
| TSS | Tonsillitis Severity Score |
| CRO | Contract Research Organization |
| GABHS | Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| PGAE | Patient Global Assessment of Efficacy |
| IGAE | Investigator Global Assessment of Efficacy |
| IGAS | Investigator Global Assessment of Safety |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ITT | Intention-To-Treat |
| PP | Per Protocol |
References
- Shaikh, N.; Leonard, E.; Martin, J.M. Prevalence of streptococcal pharyngitis and streptococcal carriage in children: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e557–564, Epub 2010 Aug 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windfuhr, J.P.; Toepfner, N.; Steffen, G.; Waldfahrer, F.; Berner, R. Clinical practice guideline: tonsillitis I. Diagnostics and nonsurgical management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2016, 273, 973–987, Epub 2016 Jan 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- ESCMID Sore Throat Guideline Group; Pelucchi, C.; Grigoryan, L.; Galeone, C.; Esposito, S.; Huovinen, P.; Little, P.; Verheij, T. Guideline for the management of acute sore throat. Clin Microbiol Infect 2012, 18, Suppl 1:1–28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicentini, C.; Vola, L.; Previti, C.; Brescia, V.; Dal Mas, F.; Zotti, C.M.; Bert, F. Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategies Including Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) for Pediatric Patients with Upper-Respiratory-Tract Infections in Primary Care: A Systematic Review of Economic Evaluations. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 22, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clavenna, A.; Bonati, M. Differences in antibiotic prescribing in paediatric outpatients. Arch Dis Child 2011, 96, 590-5, Epub 2011 Jan 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Hicks, L.A. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases. Principles of judicious antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory tract infections in pediatrics. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 1146-54, Epub 2013 Nov 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Drugs. Use of codeine- and dextromethorphan-containing cough remedies in children. Pediatrics 1997, 99, 918–920. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Careddu, D.; Pettenazzo, A. Pelargonium sidoides extract EPs 7630: a review of its clinical efficacy and safety for treating acute respiratory tract infections in children. Int J Gen Med 2018, 11, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- EMA/HMPC/765656/2022 Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) Assessment report on Pelargonium sidoides DC. Pelargonium reniforme Curt., radix. Final - Revision 2 29 - May 2024 Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-pelargonium-sidoides-dc-pelargonium-reniforme-curt-radix-revision-2_en.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Bereznoy, V.V.; Riley, D.S.; Wassmer, G.; Heger, M. Efficacy of extract of Pelargonium sidoides in children with acute non-group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus tonsillopharyngitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Altern Ther Health Med 2003, 9, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oduwole, O.; Udoh, E.E.; Oyo-Ita, A.; Meremikwu, M.M. Honey for acute cough in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2018, 4, CD007094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Braakhuis, A. Evidence on the Health Benefits of Supplemental Propolis. Nutrients 2019, 8, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, M.; Das, R.R. Zinc for the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013, 18, CD001364. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(4):CD001364. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuharfeil, N.; Al-Oran, R.; Abo-Shehada, M. The effect of bee honey on the proliferative activity of human B- and T lymphocytes and the activity of phagocytes. Food Agri Immunol 1999, 11, 169–177. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Naz, S.; Abudabos, A.M. Towards a better understanding of the therapeutic applications and corresponding mechanisms of action of honey. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2017, 24, 27755–27766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari-Bonab, H.; Jamilian, P.; Radkhah, N.; Zarezadeh, M.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. The effect of propolis supplementation in improving antioxidant status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Phytother Res 2023, 37, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.; Garzarella, E-U.; Bocchino, B.; D’Avino, M.; Caruso, G.; Buonomo, A.R.; Sacchi, R.; Galeotti, F.; Tenore, G.C.; Zaccaria, V.; et al. A standardized polyphenol mixture extracted from poplar-type propolis for remission of symptoms of uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection (URTI): A monocentric, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153368. [CrossRef]
- Buha, I.; Mirić, M.; Agić, A.; Simić, M.; Stjepanović, M.; Milenković, B.; Nagorni-Obradović, L.; Škodrić-Trifunović, V.; Ilić, B.; Popević, S.; et al. A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the efficacy of propolis and N-acetylcysteine in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2022, 26, 4809-4815. [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.A.D.; De Jong, D.; Berretta, A.A.; Galvão, E.B.D.S.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Cerqueira-Silva T, Amorim TC, Conceição LFMRD, Gomes MMD, Teixeira MB; et al. BeeCovid Team. Efficacy of Brazilian green propolis (EPP-AF®) as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 138, 111526. [CrossRef]
- Nault, D.; Machingo, T.A.; Shipper, A.G.; Antiporta, D.A.; Hamel, C.; Nourouzpour, S.; Konstantinidis, M.; Phillips, E.; Lipski, E.A.; Wieland, L.S. Zinc for prevention and treatment of the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2024, 5, CD014914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, F.; Barattini, D.F.; Martinucci, V.; Bordea, M.M.; Barattini, L.; Rosu, S. The Effectiveness of a Dietary Supplement with Honey, Propolis, Pelargonium sidoides Extract, and Zinc in Children Affected by Acute Tonsillopharyngitis: An Open, Randomized, and Controlled Trial. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2024, 17, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, F.; Barattini, D.F.; Bordea, M.M.; Herteg, D.; Matei, C.R. A randomized, open, controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Pediaflù® (dietary supplement) along with standard of care in children with acute tonsillopharyngitis / rhinopharyngitis versus standard of care only. Protocols.io. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.kqdg3988eg25/v2. (accessed on 24 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, F.; Barattini, D.F.; Sbrocca, F.; Centi, A.; Giuntini, G.; Morariu Bordea, M.; Herteg, D.; Rosu, S.; Matei, C.R. The Effects of a Dietary Supplement (PediaFlù®) Plus Standard of Care in Children With Acute Tonsillopharyngitis/Rhinopharyngitis: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res Protoc 2024, 13:e53703. [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, E.; Principi, N.; Mansi, N.; Serra, A.; De Masi, S.; Camaioni, A.; Esposito, S.; Felisati, G.; Galli, L.; Landi, M. et al. Italian Panel on the Management of Pharyngitis in Children. Management of acute pharyngitis in children: summary of the Italian National Institute of Health guidelines. Clin Ther 2012, 34, 1442-1458.e2. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All | DSPP + SoC | SoC | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) |
N | 129 | 66 | 63 | |
| Mean (SD) | 5.52 (2.07) | 5.8 (2.01) | 5.22 (2.11) | ns | |
| Median | 5 | 5.5 | 5 | ||
| Range | 3 - 10 | 3 - 10 | 3 - 10 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | N | 129 | 66 | 63 | |
| Mean (SD) | 16.41 (3.06) | 16.71 (3.0) | 16.1 (3.11) | ns | |
| Median | 15.54 | 15.97 | 15.42 | ||
| Range | 10.42 - 30.26 | 10.42 - 25.69 | 11.76 - 30.26 | ||
| Height (cm) |
N | 129 | 66 | 63 | |
| Mean (SD) | 114.51 (14.95) | 116.56 (15.36) | 112.37 (14.31) | ns | |
| Median | 114 | 116 | 108 | ||
| Range | 89 - 160 | 89 - 160 | 90 - 148 | ||
| Weight (kg) |
N | 129 | 66 | 63 | |
| Mean (SD) | 22.1 (8.29) | 23.32 (8.74) | 20.83 (7.66) | ns | |
| Median | 20 | 22 | 19 | ||
| Range | 11 - 60 | 12 - 60 | 11 - 54 |
| DSPP + SoC | SoC | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 66 | 63 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 13.67 (4.34) | 15.92 (3.02) | < 0.01 | |
| Median | 14 | 18 | ||
| Range | 5 - 18 | 6 - 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





