Submitted:
17 December 2024
Posted:
18 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
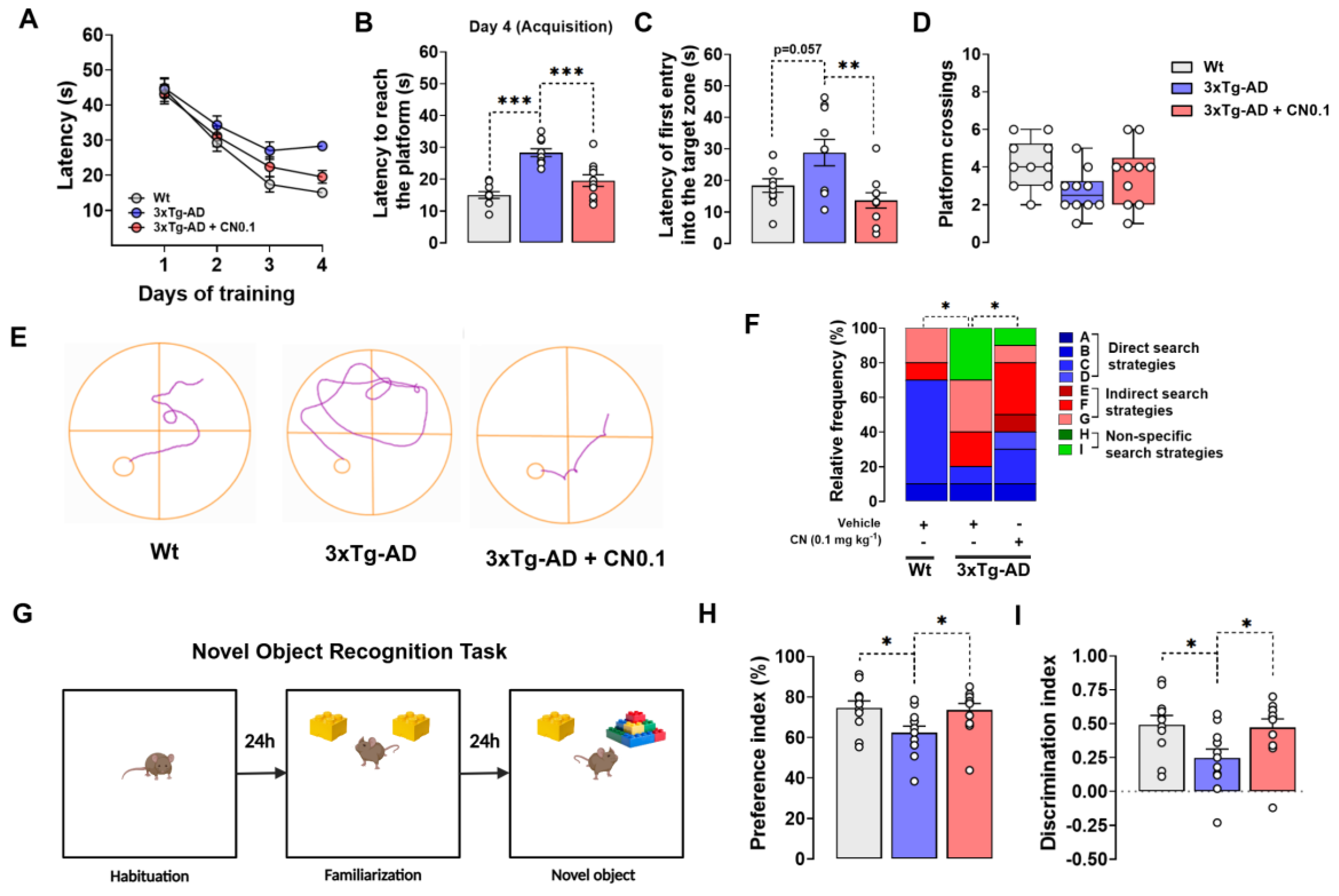
2.1. CNEURO-201 Greatly Improves the Cognitive Functions of 3xTg-AD Mice
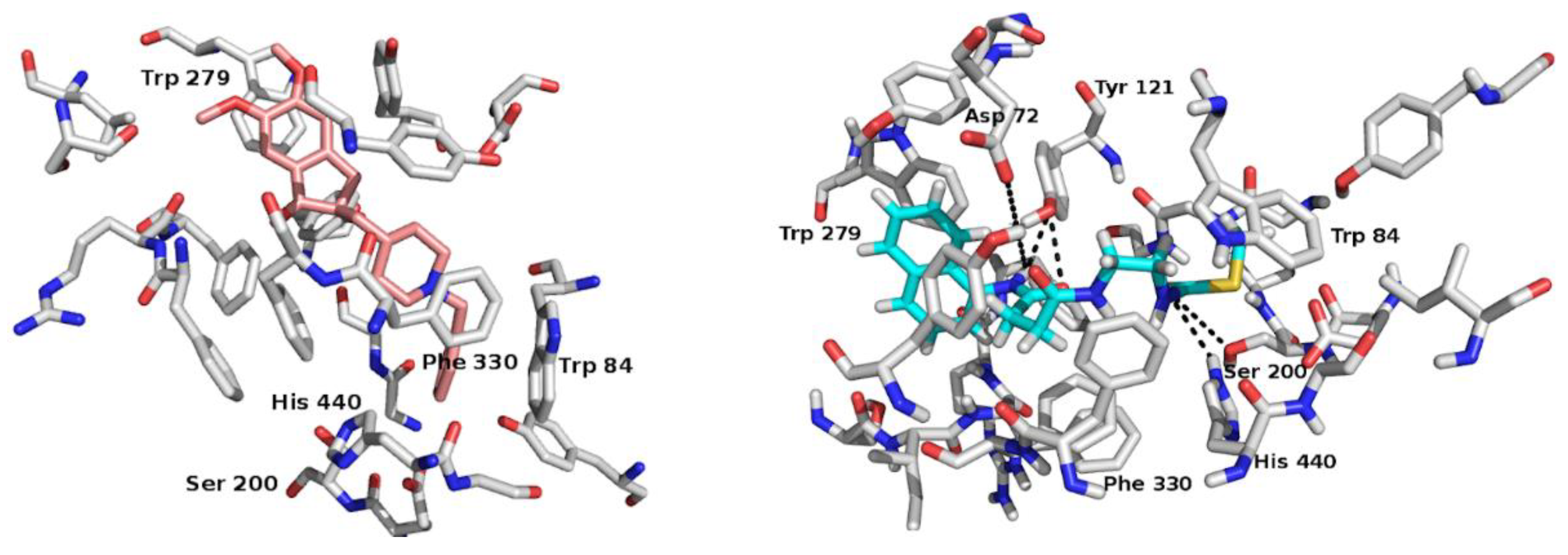
2.2. In Silico Study: A Potential Interaction Between CNEURO-201 and Acetylcholinesterase
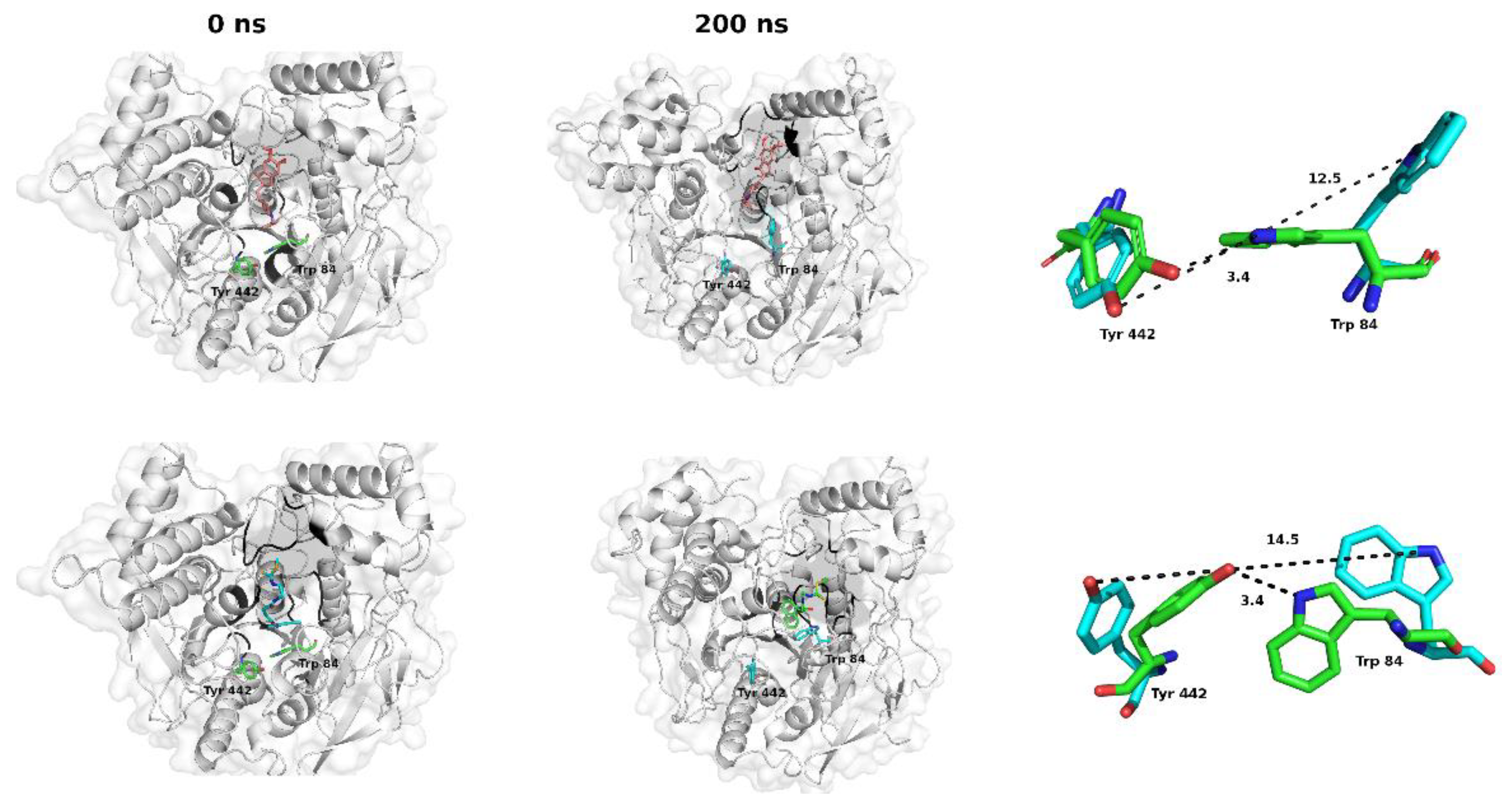
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Studies: Temporal Stability Evaluation of the CNEURO-201/AChE System
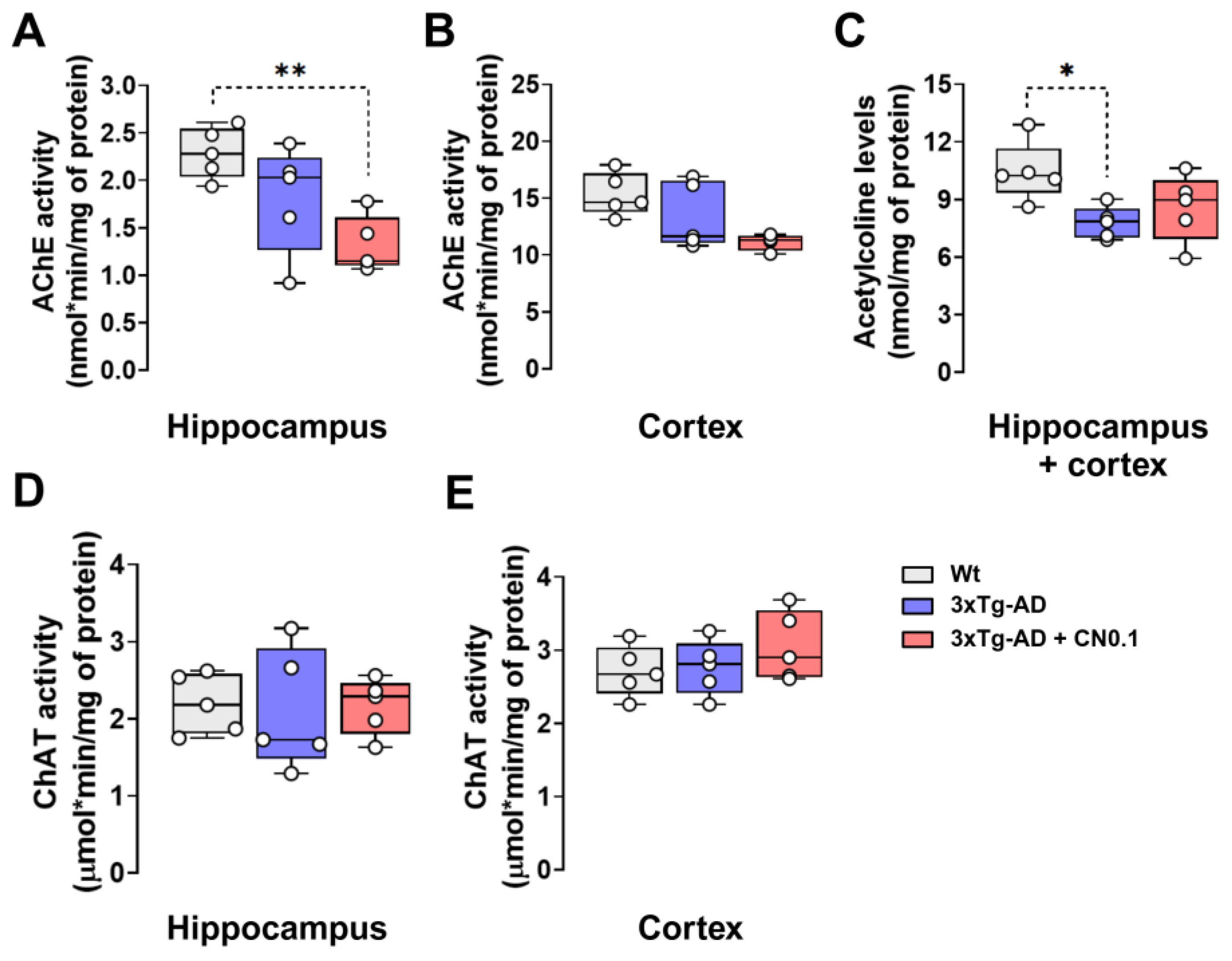
2.4. CNEURO-201 Reduces Acetylcholinesterase Activity and Acetylcholine Decay in the Hippocampus and Cortex of 3xTg-AD Mice
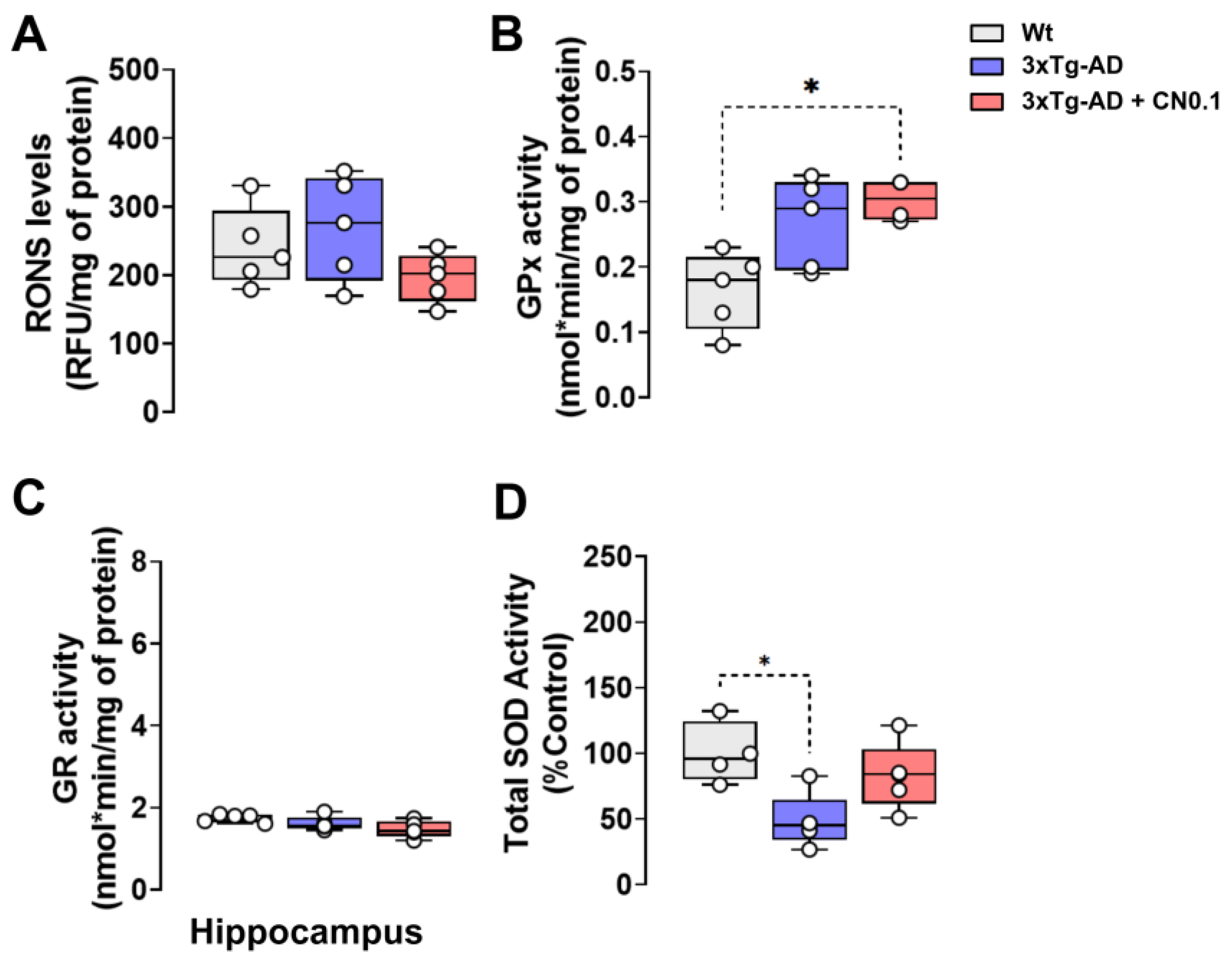
2.5. CNEURO-201 Influences Antioxidant Enzymatic Activity in the Hippocampus of 3xTg-AD Mice
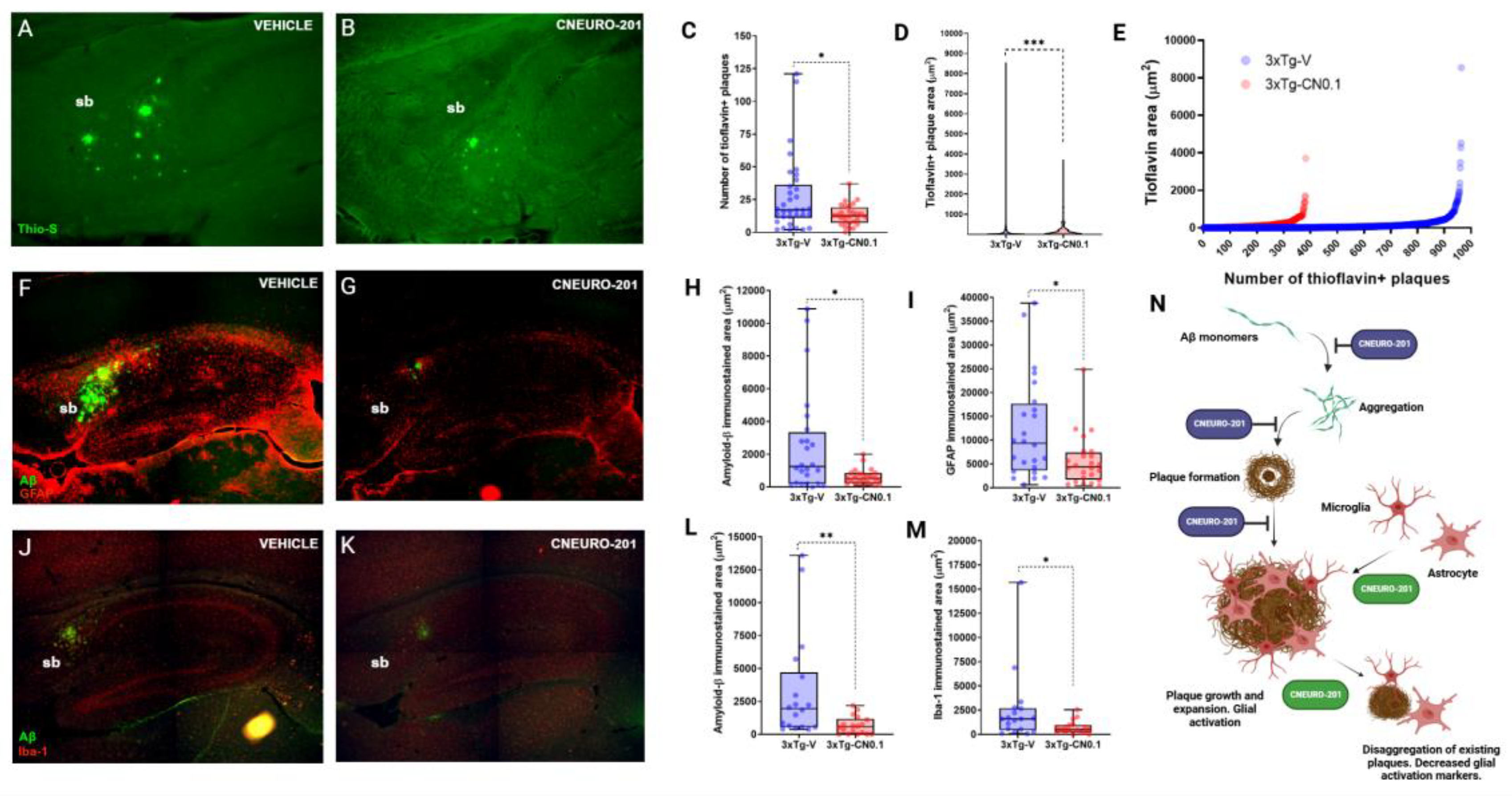
2.6. CNEURO-201 Decreases Expansion and Promotes Dissagregation of Amyloid Plaques Together with Reductions in Glial Activation Markers in the Subiculum of Aged 3xTg-AD Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Docking
4.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.3. Experimental Animals
4.4. Pharmacological Treatments
4.5. Morris Water Maze Task
4.6. Novel Object Recognition Task
4.7. Tissue Isolation and Preparation
4.8. Acetylcholinesterase Activity
4.9. Acetylcholine Quantification
4.10. Choline Acetyltransferase Activity
4.11. Determination of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species
4.12. Glutathione Peroxydase Activity
4.13. Glutathione Reductase Activity
4.14. Total Superoxide Dismutase Activity
4.15. Thioflavin-S Staining
4.16. Immunofluorescence
4.17. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dementia. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 5 October 2024).
- Praticò, D. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease: a reappraisal. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 609-615. [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E. Glutamatergic synaptic plasticity and dysfunction in Alzheimer disease: Emerging mechanisms. Neurology 2018, 91, 125-132. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, A.K.Y.; Ip, N.Y. Synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 195, 186-198. [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 450-464. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1041-1048. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.R.; Huang, J.B.; Yang, S.L.; Hong, F.F. Role of Cholinergic Signaling in Alzheimer's Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 1816. [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, S.; Gardoni, F.; Di Luca, M.; Marcello, E. Synaptic dysfunction in early phases of Alzheimer's Disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 184, 417-438. [CrossRef]
- Meftah, S.; Gan, J. Alzheimer's disease as a synaptopathy: Evidence for dysfunction of synapses during disease progression. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1129036. [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Pareja, F.; Del Ser, T. Controversial Past, Splendid Present, Unpredictable Future: A Brief Review of Alzheimer Disease History. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 536. [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.C. Aβ Plaques. Free Neuropathol. 2020, 1, 1-31. [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science, 256, 184-5. [CrossRef]
- Behl, C. In 2024, the amyloid-cascade-hypothesis still remains a working hypothesis, no less but certainly no more. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1459224. [CrossRef]
- Michno, W.; Stringer, K.M.; Enzlein, T.; Passarelli, M.K.; Escrig, S.; Vitanova, K.; Wood, J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Meibom, A.; Hopf, C.; Edwards, F.A.; Hanrieder, J. Following spatial Aβ aggregation dynamics in evolving Alzheimer's disease pathology by imaging stable isotope labeling kinetics. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg4855. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer's disease: challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 248. [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; Froelich, L.; Katayama, S.; Sabbagh, M.; Vellas, B.; Watson, D.; Dhadda, S.; Irizarry, M.; Kramer, L.D.; Iwatsubo, T. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer's Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9-21. [CrossRef]
- Yadollahikhales, G.; Rojas, J.C. Anti-Amyloid Immunotherapies for Alzheimer's Disease: A 2023 Clinical Update. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 914-931. [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.; Maloney, A.J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 1976, 2, 1403. [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.K.; Gibson, P.H.; Blessed, G.; Perry, R.H.; Tomlinson, B.E. Neurotransmitter enzyme abnormalities in senile dementia. Choline acetyltransferase and glutamic acid decarboxylase activities in necropsy brain tissue. J. Neurol. Sci. 1977, 34, 247-265. [CrossRef]
- Rylett, R.J.; Ball, M.J.; Colhoun, E.H. Evidence for high affinity choline transport in synaptosomes prepared from hippocampus and neocortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1983, 289, 169-175. [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, L.; Nordberg, A.; Hardy, J.; Wester, P.; Winblad, B. Physostigmine restores 3H-acetylcholine efflux from Alzheimer brain slices to normal level. J. Neural Transm. 1986, 67, 275-285. [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, P.J.; Price, D.L.; Struble, R.G.; Clark, A.W.; Coyle, J.T.; Delon, M.R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science 1982, 215, 1237-1239. [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.T.; Palmer, A.M.; Snape, M.; Wilcock, G.K. The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: a review of progress. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 137-147. [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, V.; González-Acedo, A.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Pardo-Moreno, T.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Montiel-Troya, M.; Ramos-Rodríguez, J.J. Current Understanding of the Physiopathology, Diagnosis and Therapeutic Approach to Alzheimer's Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1910. [CrossRef]
- Gajendra, K.; Pratap, G.K.; Poornima, D.V.; Manjula Shantaram; Ranjita, G. Natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: A multi-targeted therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 11, 100154. [CrossRef]
- Sablón-Carrazana, M.; Fernández, I.; Bencomo, A.; Lara-Martínez, R.; Rivera-Marrero, S.; Domínguez, G:; Pérez-Perera, R.; Jiménez-García, L.F.; Altamirano-Bustamante, N.F.; Diaz-Delgado, M.; Vedrenne, F.; Rivillas-Acevedo, L.; Pasten-Hidalgo, K.; Segura-Valdez Mde, L.; Islas-Andrade, S.; Garrido-Magaña, E.; Perera-Pintado, A.; Prats-Capote, A.; Rodríguez-Tanty, C.; Altamirano-Bustamante, M.M. Drug Development in Conformational Diseases: A Novel Family of Chemical Chaperones that Bind and Stabilise Several Polymorphic Amyloid Structures. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0135292. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gómez, I.; Sablón-Carrazana, M.; Bencomo-Martínez, A.; Domínguez, G.; Lara-Martínez, R.; Altamirano-Bustamante, N.F.; Jiménez-García, L.F.; Pasten-Hidalgo, K.; Castillo-Rodríguez, R.A.; Altamirano, P.; Marrero, S.R.; Revilla-Monsalve, C.; Valdés-Sosa, P.; Salamanca-Gómez, F.; Garrido-Magaña, E.; Rodríguez-Tanty, C.; Altamirano-Bustamante, M.M. Diabetes Drug Discovery: hIAPP1-37 Polymorphic Amyloid Structures as Novel Therapeutic Targets. Molecules 2018, 23, 686. [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Marrero, S.; Bencomo-Martínez, A.; Orta Salazar, E.; Sablón-Carrazana, M.; García-Pupo, L.; Zoppolo, F.; Arredondo, F.; Dapueto, R.; Daniela Santi, M.; Kreimerman, I.; Pardo, T.; Reyes, L.; Galán, L.; León-Chaviano, S.; Espinosa-Rodríguez, L.A.; Menéndez-Soto Del Valle, R.; Savio, E.; Díaz Cintra, S.; Rodríguez-Tanty, C. A new naphthalene derivative with anti-amyloidogenic activity as potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115700. [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Shepherd, J.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Kayed, R.; Metherate, R.; Mattson, M.P.; Akbari, Y.; LaFerla, F.M. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 2003, 39, 409-421. [CrossRef]
- Mercerón-Martínez, D.; Alacán Ricardo, L.; Bejerano Pina, A.; Orama Rojo, N.; Expósito Seco, A.; Vega Hurtado, Y.; Estupiñán Días, B.; Fernández, I.; García Pupo, L.; Sablón Carrazana, M.; Rodríguez-Tanty, C.; Menéndez Soto Del Valle, R.; Almaguer-Melian, W. Amylovis-201 enhances physiological memory formation and rescues memory and hippocampal cell loss in a streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease animal model. Brain Res. 2024, 1831, 148848. [CrossRef]
- García-Pupo, L; Crouzier, L; Bencomo-Martínez, A.; Meunier, J.; Morilleau, A.; Delprat, B.; Sablón-Carrazana, M.; Menéndez-Soto del Valle, R.; Maurice, T.; Rodríguez-Tanty, C. Amylovis-201 is a new dual-target ligand, acting as an anti-amyloidogenic compound and a potent agonist of the σ1 chaperone protein. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. Forthcoming 2024. [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.; Koh, M.T. Episodic memory on the path to Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 929-934. [CrossRef]
- Sussman, J.L.; Harel, M.; Frolow, F.; Oefner, C.; Goldman, A.; Toker, L.; Silman, I. Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science 1991, 253, 872-879. [CrossRef]
- Kryger, G.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept): implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Structure 1999, 7, 297-307. [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455-461. [CrossRef]
- Alisaraie, L.; Fels, G. Molecular docking study on the "back door" hypothesis for product clearance in acetylcholinesterase. J. Mol. Model. 2006, 12, 348-354. [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, C.; Perola, E.; Cellai, L.; Brufani, M.; Lamba, D. "Back door" opening implied by the crystal structure of a carbamoylated acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5714-5719. [CrossRef]
- Kronman, C.; Ordentlich, A.; Barak, D.; Velan, B.; Shafferman, A. The "back door" hypothesis for product clearance in acetylcholinesterase challenged by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27819-27822.
- Xu, Y.; Colletier, J.P.; Weik, M.; Qin, G.; Jiang, H.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Long route or shortcut? A molecular dynamics study of traffic of thiocholine within the active-site gorge of acetylcholinesterase. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 4003-4011. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Song, W.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Y. Gorge Motions of Acetylcholinesterase Revealed by Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3219. [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.A.; Perry, E.K.; Tomlinson, B.E. Acetylcholine and choline levels in post-mortem human brain tissue: preliminary observations in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 1980, 26, 1683-1689. [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, M. Functional pharmacology in human brain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 162-193. [CrossRef]
- Reinikainen, K.J.; Soininen, H.; Riekkinen, P.J. Neurotransmitter changes in Alzheimer's disease: implications to diagnostics and therapy. J. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 27, 576-586. [CrossRef]
- Campanari, M.L.; Navarrete, F.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Manzanares, J.; Sáez-Valero, J.; García-Ayllón, M.S. Increased Expression of Readthrough Acetylcholinesterase Variants in the Brains of Alzheimer's Disease Patients. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 53, 831-841. [CrossRef]
- Bird, T.D.; Stranahan, S.; Sumi, S.M.; Raskind, M. Alzheimer's disease: choline acetyltransferase activity in brain tissue from clinical and pathological subgroups. Ann. Neurol. 1983, 14, 284-293. [CrossRef]
- Ikonomovic, M.D.; Mufson, E.J.; Wuu, J.; Bennett, D.A.; DeKosky, S.T. Reduction of choline acetyltransferase activity in primary visual cortex in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 425-430. [CrossRef]
- Dhapola, R.; Beura, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.K.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease: current knowledge of signaling pathways and therapeutics. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 48. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489-492. [CrossRef]
- Javonillo, D.I.; Tran, K.M.; Phan, J.; Hingco, E.; Kramár, E.A.; da Cunha, C.; Forner, S.; Kawauchi, S.; Milinkeviciute, G.; Gomez-Arboledas, A.; Neumann, J.; Banh, C.E.; Huynh, M.; Matheos, D.P.; Rezaie, N.; Alcantara, J.A.; Mortazavi, A.; Wood, M.A.; Tenner, A.J.; MacGregor, G.R.; Green, K.N.; LaFerla, F.M. Systematic Phenotyping and Characterization of the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 785276. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y. Thioflavin-positive tau aggregates complicating quantification of amyloid plaques in the brain of 5XFAD transgenic mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1617. [CrossRef]
- Bolmont, T.; Haiss, F.; Eicke, D.; Radde, R.; Mathis, C.A.; Klunk, W.E.; Kohsaka, S.; Jucker, M.; Calhoun, M.E. Dynamics of the microglial/amyloid interaction indicate a role in plaque maintenance. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4283-4292. [CrossRef]
- Frost, G.R.; Li, Y.M. The role of astrocytes in amyloid production and Alzheimer's disease. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170228. [CrossRef]
- Mawuenyega, K.G.; Sigurdson, W.; Ovod, V.; Munsell, L.; Kasten, T.; Morris, J.C.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Bateman, R.J. Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science 2010, 330, 1774. [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar-Colucci, S.; Landreth, G.E. Microglia and inflammation in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 156-167. [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L.; Goldman, D.P.; Simmons-Stern, N.R.; Ponton E. The costs of developing treatments for Alzheimer's disease: A retrospective exploration. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 469-477. [CrossRef]
- Parums, D.V. A Review of the Current Status of Disease-Modifying Therapies and Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e945091. [CrossRef]
- Maurice, T.; Su, T.P. The pharmacology of sigma-1 receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 124, 195-206. [CrossRef]
- Maurice, T.; Goguadze, N. Sigma-1 (σ1) Receptor in Memory and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 244, 81-108. [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.H.; Ye, Y.; Wan, B.B.; Yu, Y.D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.J. Emerging Benefits: Pathophysiological Functions and Target Drugs of the Sigma-1 Receptor in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5649-5666. [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.R.; Eades, C.G.; Thompson, J.A.; Huppler, R.E.; Gilbert, P.E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1976, 197, 517-532.
- Su, T.P.; London, E.D.; Jaffe, J.H. Steroid binding at sigma receptors suggests a link between endocrine, nervous, and immune systems. Science 1988, 240, 219-221. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wu, X.; Chao, J.; Duan, M.; Buch, S.; Chen, L.; Yao, H. Involvement of sigma-1 receptor in astrocyte activation induced by methamphetamine via up-regulation of its own expression. J Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 29. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, Q.; Fang, L.P.; Yao, H.; Scheller, A.; Kirchhoff F.; Huang, W. Specific detection and deletion of the sigma-1 receptor widely expressed in neurons and glial cells in vivo. J Neurochem. 2023, 164, 764-785. [CrossRef]
- Ryskamp, D.A.; Korban, S.; Zhemkov, V.; Kraskovskaya, N.; Bezprozvanny, I. Neuronal Sigma-1 Receptors: Signaling Functions and Protective Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 862. [CrossRef]
- Meunier, J.; Hayashi, T. Sigma-1 receptors regulate Bcl-2 expression by reactive oxygen species-dependent transcriptional regulation of nuclear factor kappaB. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 388-397. [CrossRef]
- Villard, V.; Espallergues, J.; Keller, E.; Vamvakides, A.; Maurice T. Anti-amnesic and neuroprotective potentials of the mixed muscarinic receptor/sigma 1 (σ1) ligand ANAVEX2-73, a novel aminotetrahydrofuran derivative. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 1101-1117. [CrossRef]
- Lahmy, V.; Meunier, J.; Malmström, S.; Naert, G.; Givalois, L.; Kim, S.H.; Villard, V.; Vamvakides, A.; Maurice T. Blockade of Tau hyper-phosphorylation and Aβ₁₋₄₂ generation by the aminotetrahydrofuran derivative ANAVEX2-73, a mixed muscarinic and σ₁ receptor agonist, in a nontransgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1706-1723. [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Bezprozvanny, I.; Wu, L.; Ryskamp, D.A.; Bar-Ner, N.; Natan, N.; Brandeis, R.; Elkon, H.; Nahum, V.; Gershonov, E.; LaFerla, F.M.; Medeiros, R. AF710B, a Novel M1/σ1 Agonist with Therapeutic Efficacy in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 2016, 16, 95-110. [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.; Iulita, M.F.; Gubert, P.; Flores Aguilar, L.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Fisher, A.; Cuello, A.C. AF710B, an M1/sigma-1 receptor agonist with long-lasting disease-modifying properties in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 811-823. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Maurice, T.; Su, T.P. Ca(2+) signaling via sigma(1)-receptors: novel regulatory mechanism affecting intracellular Ca(2+) concentration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 788-98.
- Foskett, J.K.; White, C.; Cheung, K.H.; Mak, D.O. Inositol trisphosphate receptor Ca2+ release channels. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 593-658. [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Garaschuk, O. The role of intracellular calcium-store-mediated calcium signals in in vivo sensor and effector functions of microglia. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 4203-4215. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; LeVault, K.R.; Brewer, G.J. Dual-energy precursor and nuclear erythroid-related factor 2 activator treatment additively improve redox glutathione levels and neuron survival in aging and Alzheimer mouse neurons upstream of reactive oxygen species. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 179-190. [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zuo, C.; Gu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, F. High frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation alleviates cognitive deficits in 3xTg-AD mice by modulating the PI3K/Akt/GLT-1 axis. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102354. [CrossRef]
- Inestrosa, N.C.; Alvarez, A.; Pérez, C.A.; Moreno, R.D.; Vicente, M.; Linker, C.; Casanueva, O.I.; Soto, C.; Garrido, J. Acetylcholinesterase accelerates assembly of amyloid-beta-peptides into Alzheimer's fibrils: possible role of the peripheral site of the enzyme. Neuron 1996, 16, 881-891. [CrossRef]
- García-Ayllón, M.S.; Silveyra, M.X.; Sáez-Valero, J. Association between acetylcholinesterase and beta-amyloid peptide in Alzheimer's cerebrospinal fluid. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 175, 209-215. [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, F.J.; Inestrosa, N.C. Interactions of AChE with Aβ Aggregates in Alzheimer's Brain: Therapeutic Relevance of IDN 5706. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 19. [CrossRef]
- Bas, D.C.; Rogers, D.M.; Jensen, J.H. Very fast prediction and rationalization of pKa values for protein-ligand complexes. Proteins 2008, 73, 765-783. [CrossRef]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848-858. [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Silva, E.E.; González-Navarro, A.R.; Salazar-Ybarra, R.A.; Quiroga-García, O.; Cruz-Elizondo, M.A.J.; García-García, A.; Rodríguez-Rocha, H.; Morales-Gómez, J.A.; Quiroga-Garza, A.; Elizondo-Omaña, R.E.; de León, Á.R.M.; Guzmán-López, S. Aged rats learn Morris Water maze using non-spatial search strategies evidenced by a parameter-based algorithm. Transl. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 134-144. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Orozco, H.; Reyes-Castro, L.A.; Lomas-Soria, C.; Sandoval-Salazar, C.; Ramírez-Emiliano, J.; Díaz-Cintra, S.; Solís-Ortiz, S. High-fat and combined high-fat-high-fructose diets impair episodic-like memory and decrease glutamate and glutamine in the hippocampus of adult mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 2479-2489. [CrossRef]
- Ennaceur, A.; Delacour, J. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 31, 47-59. [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of pro-tein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976, 72, 248-254. [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V. Jr.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcho-linesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7:88-95. [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadegan, M.; Soodi, M. Comparison of Memory Impairment and Oxidative Stress Following Single or Repeated Doses Administration of Scopolamine in Rat Hippocampus. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 5-14. [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.P.; Wolfgram, F. Spectrophotometric assay for choline acetyltransferase. Anal Biochem. 1972, 46, 114-118. [CrossRef]
- da Costa E Silva, L.D.; Pereira, P.; Regner, G.G.; Boaretto, F.B.M.; Hoffmann, C.; Pflüger, P.; da Silva, L.L.; Steffens, L.R.; Morás, A.M.; Moura, D.J.; Picada, J.N. DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by seizures are decreased by anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects of lobeline, a candidate to treat alcoholism. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 53-61. [CrossRef]
- Reiniers, M.J.; van Golen, R.F.; Bonnet, S.; Broekgaarden, M.; van Gulik, T.M.; Egmond, M.R.; Heger, M. Preparation and Practical Applications of 2',7'-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein in Redox Assays. Anal Chem. 2017, 89, 3853-3857. [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.; Gupta, S.; Biswas, J.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Instigates the Rotenone Induced Oxidative Apoptotic Neuronal Death: a Study in Rat Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5384-5400. [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, I.; Mannervik, B. Purification and characterization of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 5475-80.
- Spitz, D.R.; Oberley, L.W. An assay for superoxide dismutase activity in mammalian tissue homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1989, 179, 8-18. [CrossRef]
- Weydert, C.J.; Cullen, J.J. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 51-66. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




