Submitted:
04 December 2024
Posted:
05 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
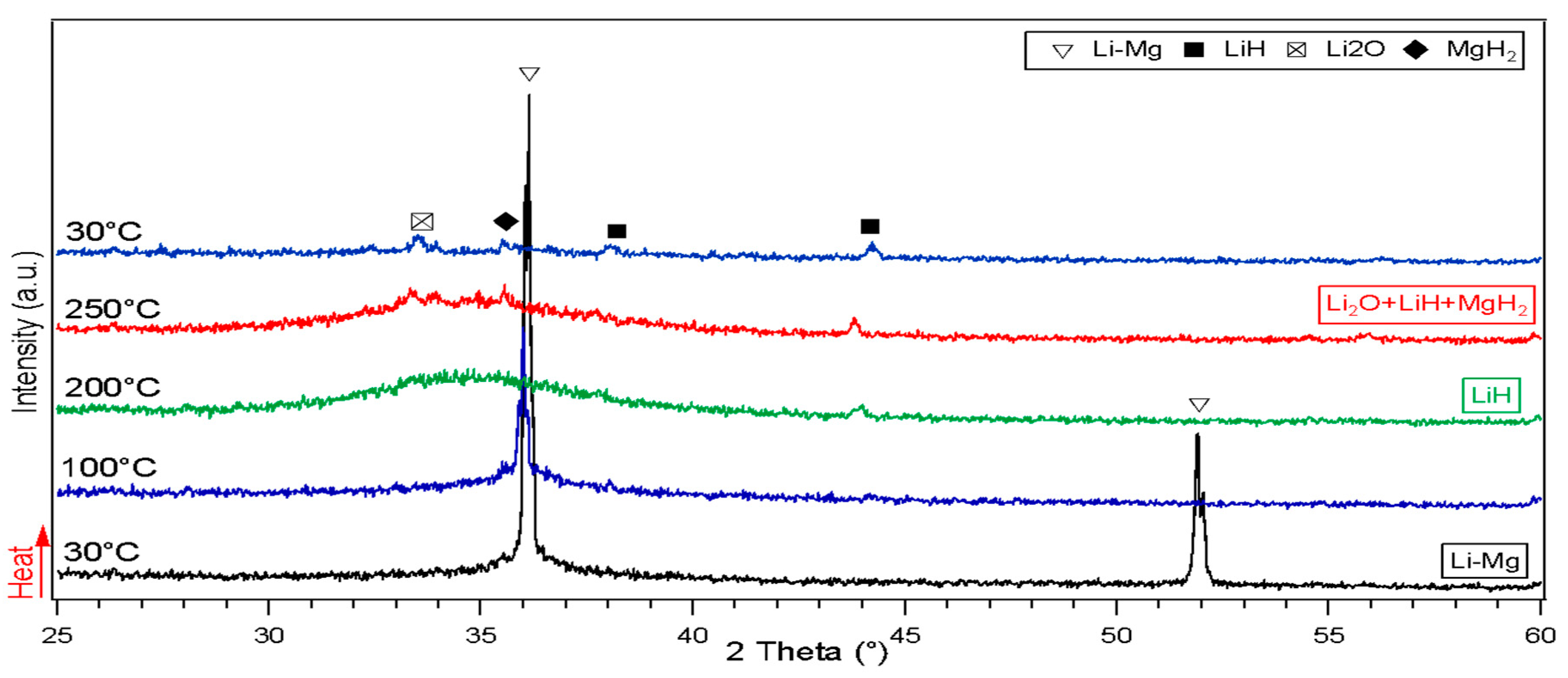
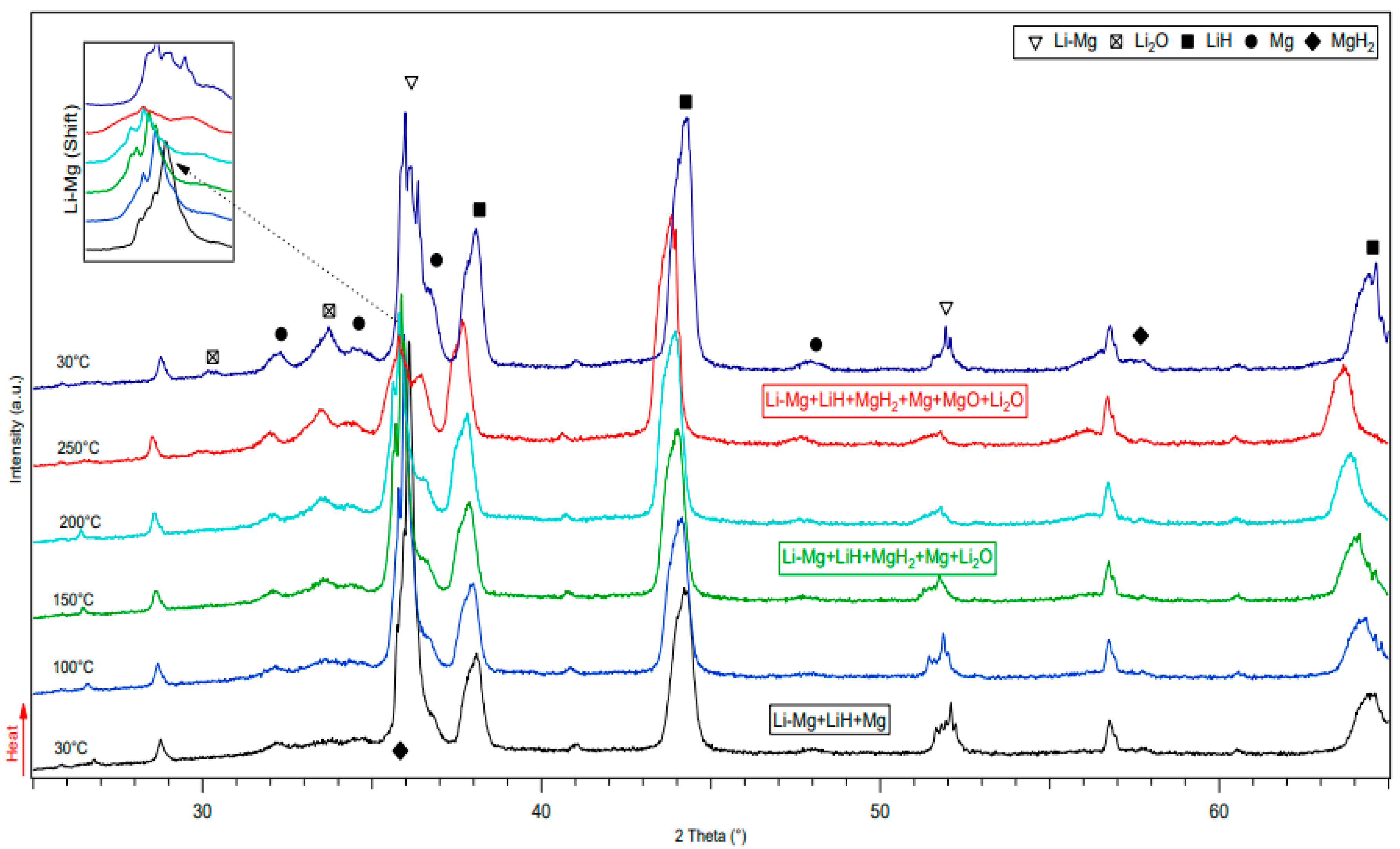
3.1. Structural Analysis of As-Received and Milled Materials
3.2. Analysis of Hydrogen Storage Capacity
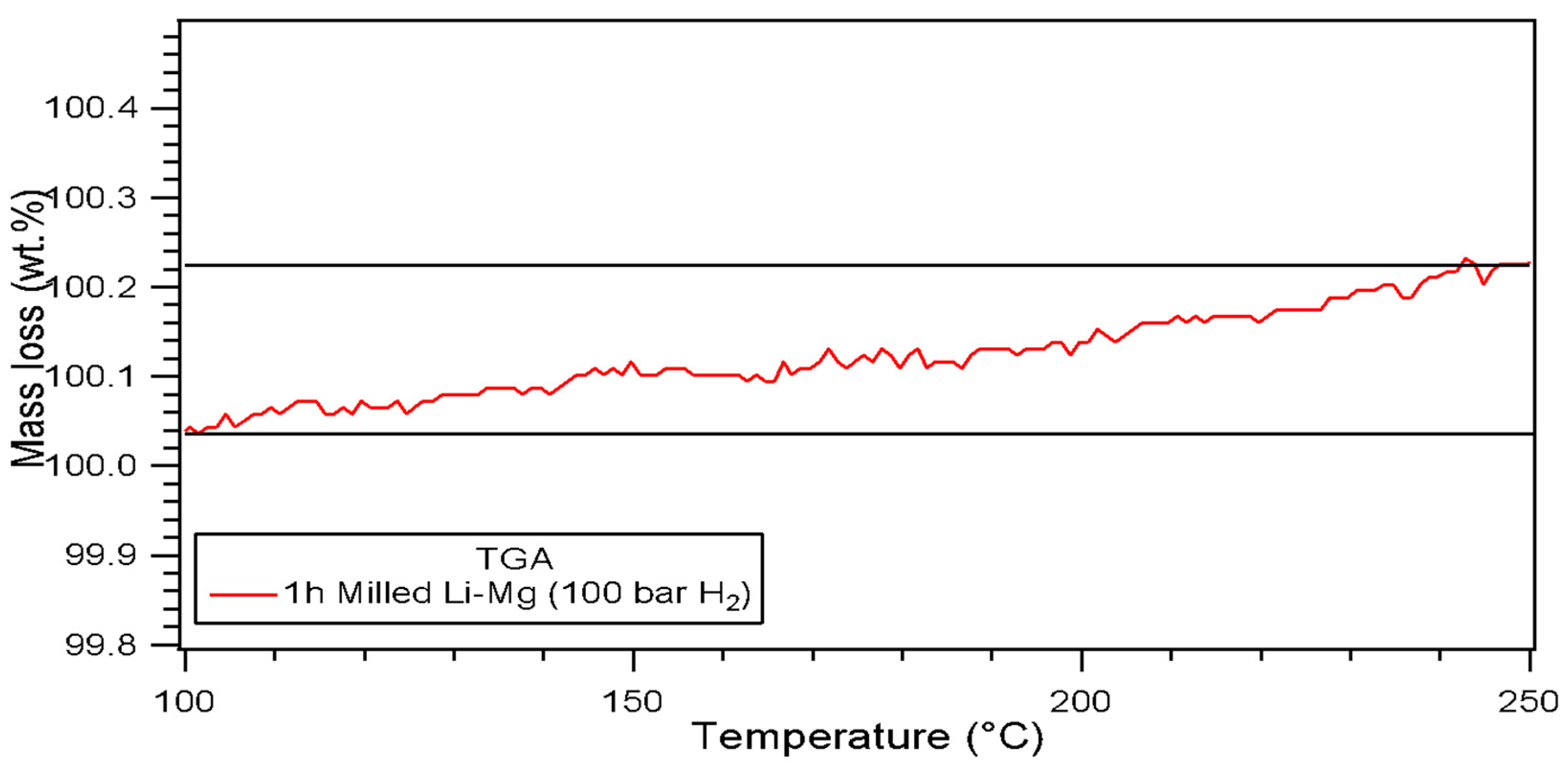
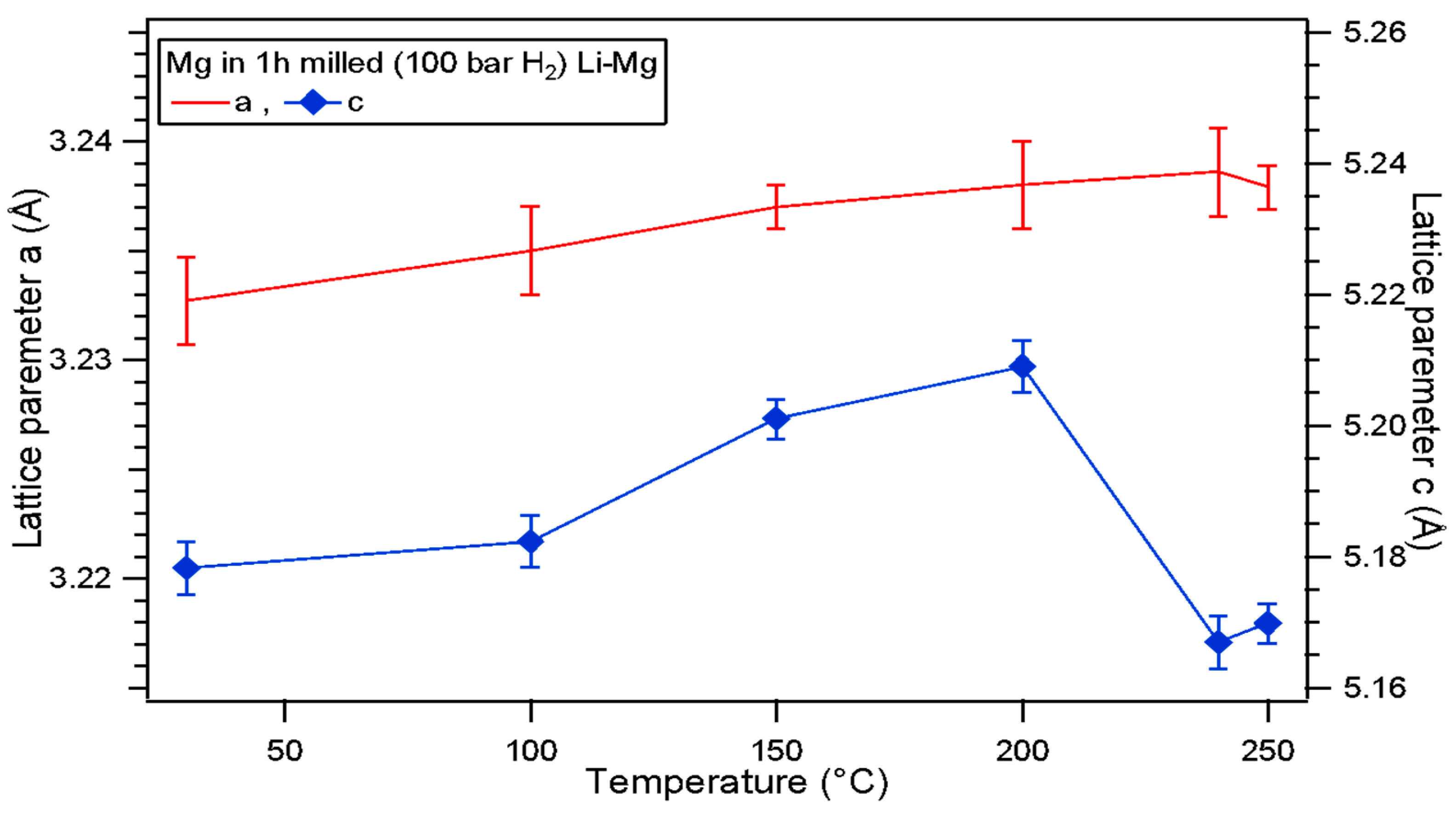
3.2.1. Thermal Analysis Performed by DSC, TGA and In-Situ XRD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang J, Li J (2024) Revolution in Renewables: Integration of Green Hydrogen for a Sustainable Future. Energies (Basel) 17:4148. [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki E, Gawlik L (2024) The Development of a Green Hydrogen Economy: Review. Energies (Basel) 17:3165. [CrossRef]
- Aslam S, Rani S, Lal K, et al (2023) Electrochemical hydrogen production: sustainable hydrogen economy. Green Chemistry 25:9543–9573. [CrossRef]
- Falcone PM, Hiete M, Sapio A (2021) Hydrogen economy and sustainable development goals: Review and policy insights. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 31:100506. [CrossRef]
- Baran A, Polański M (2020) Magnesium-Based Materials for Hydrogen Storage—A Scope Review. Materials 13:3993. [CrossRef]
- Shang Y, Pistidda C, Gizer G, et al (2021) Mg-based materials for hydrogen storage. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys 9:1837–1860. [CrossRef]
- Li Q, Lu Y, Luo Q, et al (2021) Thermodynamics and kinetics of hydriding and dehydriding reactions in Mg-based hydrogen storage materials. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys 9:1922–1941. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Yuan Z, Liu C, et al (2024) Research progress in improved hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based alloys with metal-based materials and light metals. Int J Hydrogen Energy 50:1401–1417. [CrossRef]
- Ding X, Chen R, Zhang J, et al (2022) Recent progress on enhancing the hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based materials via fabricating nanostructures: A critical review. J Alloys Compd 897:163137. [CrossRef]
- Guo Z, Zhao S, Li T, et al (2020) Recent Advances in Rechargeable Magnesium-Based Batteries for High-Efficiency Energy Storage. Adv Energy Mater 10:. [CrossRef]
- Ouyang L, Liu F, Wang H, et al (2020) Magnesium-based hydrogen storage compounds: A review. J Alloys Compd 832:154865. [CrossRef]
- Xie X, Hou C, Chen C, et al (2020) First-principles studies in Mg-based hydrogen storage Materials: A review. Energy 211:118959. [CrossRef]
- Hitam CNC, Aziz MAA, Ruhaimi AH, Taib MR (2021) Magnesium-based alloys for solid-state hydrogen storage applications: A review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46:31067–31083. [CrossRef]
- Kumar D, Phanden RK, Thakur L (2021) A review on environment friendly and lightweight Magnesium-Based metal matrix composites and alloys. Mater Today Proc 38:359–364. [CrossRef]
- Xiao F, Wu T, Yang Y (2024) Research progress in hydrogen production by hydrolysis of magnesium-based materials. Int J Hydrogen Energy 49:696–718. [CrossRef]
- Lesz S, Hrapkowicz B, Karolus M, Gołombek K (2021) Characteristics of the Mg-Zn-Ca-Gd Alloy after Mechanical Alloying. Materials 14:226. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Yuan Q, Huang W, Song X (2022) A novel nanoporous Mg-Li material for efficient hydrogen generation. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys 10:3054–3063. [CrossRef]
- Pęska M, Czujko T, Polański M (2020) Hydrogenation Ability of Mg-Li Alloys. Energies (Basel) 13:2080. [CrossRef]
- Vajeeston P, Ravindran P, Kjekshus A, Fjellvåg H (2008) First-principles investigations of the MMgH3 (, Na, K, Rb, Cs) series. J Alloys Compd 450:327–337. [CrossRef]
- Li D, Zhang T, Yang S, et al (2011) Ab initio investigation of structures, electronic and thermodynamic properties for Li–Mg–H ternary system. J Alloys Compd 509:8228–8234. [CrossRef]
- Cheng F, Tao Z, Liang J, Chen J (2012) Efficient hydrogen storage with the combination of lightweight Mg/MgH2 and nanostructures. Chemical Communications 48:7334–7343. [CrossRef]
- Ikeda K, Kogure Y, Nakamori Y, Orimo S (2007) Formation region and hydrogen storage abilities of perovskite-type hydrides. Progress in Solid State Chemistry 35:329–337. [CrossRef]
- Pfrommer B, Elsässer C, Fähnle M (1994) Possibility of Li-Mg and Al-Mg hydrides being metallic. Phys Rev B 50:5089–5093. [CrossRef]
- Al S, Kurkcu C, Yamcicier C (2020) High pressure phase transitions and physical properties of Li2MgH4; implications for hydrogen storage. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45:4720–4730. [CrossRef]
- Smith KC, Fisher TS, Waghmare U V., Grau-Crespo R (2010) Dopant-vacancy binding effects in Li-doped magnesium hydride. Phys Rev B 82:134109. [CrossRef]
- Guo S (2015) Light metal borohydrides and Mg-based hydrides for hydrogen storage. University of Birmingham.
- Bruker (2024) DIFFRAC.SUITE EVA - XRD Software | Bruker. https://www.bruker.com/products/x-ray-diffraction-and-elemental-analysis/x-ray-diffraction/xrd-software/eva.html. Accessed 19 Nov 2024.
- ICSD (2024) Inorganic Chemical Database Service. http://icsd.cds.rsc.org/search/basic.xhtml;jsessionid=82761CD648F766CC9CA76BDA84933E21?cdsrdr=3. Accessed 19 Nov 2024.
- Bruker (2024) DIFFRAC.SUITE TOPAS - XRD Software, X-ray diffraction - XRD Software | Bruker. https://www.bruker.com/products/x-ray-diffraction-and-elemental-analysis/x-ray-diffraction/xrd-software/topas.html. Accessed 19 Nov 2024.
- Varin RA, Czujko T, Wronski Z (2006) Particle size, grain size and γ-MgH2 effects on the desorption properties of nanocrystalline commercial magnesium hydride processed by controlled mechanical milling. Nanotechnology 17:3856–3865. [CrossRef]
- Shannon RD (1976) Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallographica Section A 32:751–767. [CrossRef]
- Denton AR, Ashcroft NW (1991) Vegard’s law. Phys Rev A (Coll Park) 43:3161–3164. [CrossRef]
- Nayeb-Hashemi AA, Clark JB, Pelton AD (1984) The Li-Mg (Lithium-Magnesium) system. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams 5:365–374. [CrossRef]
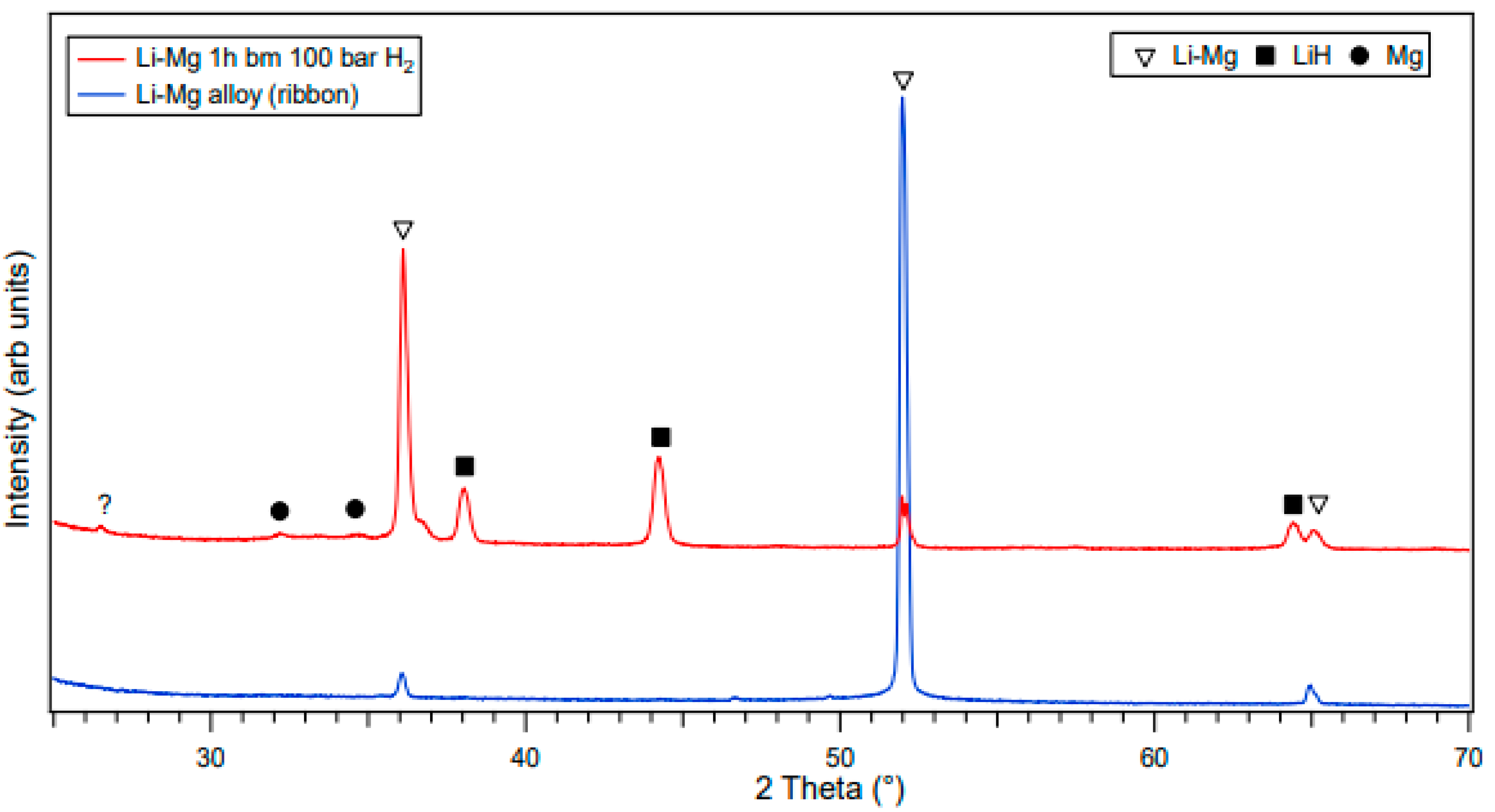
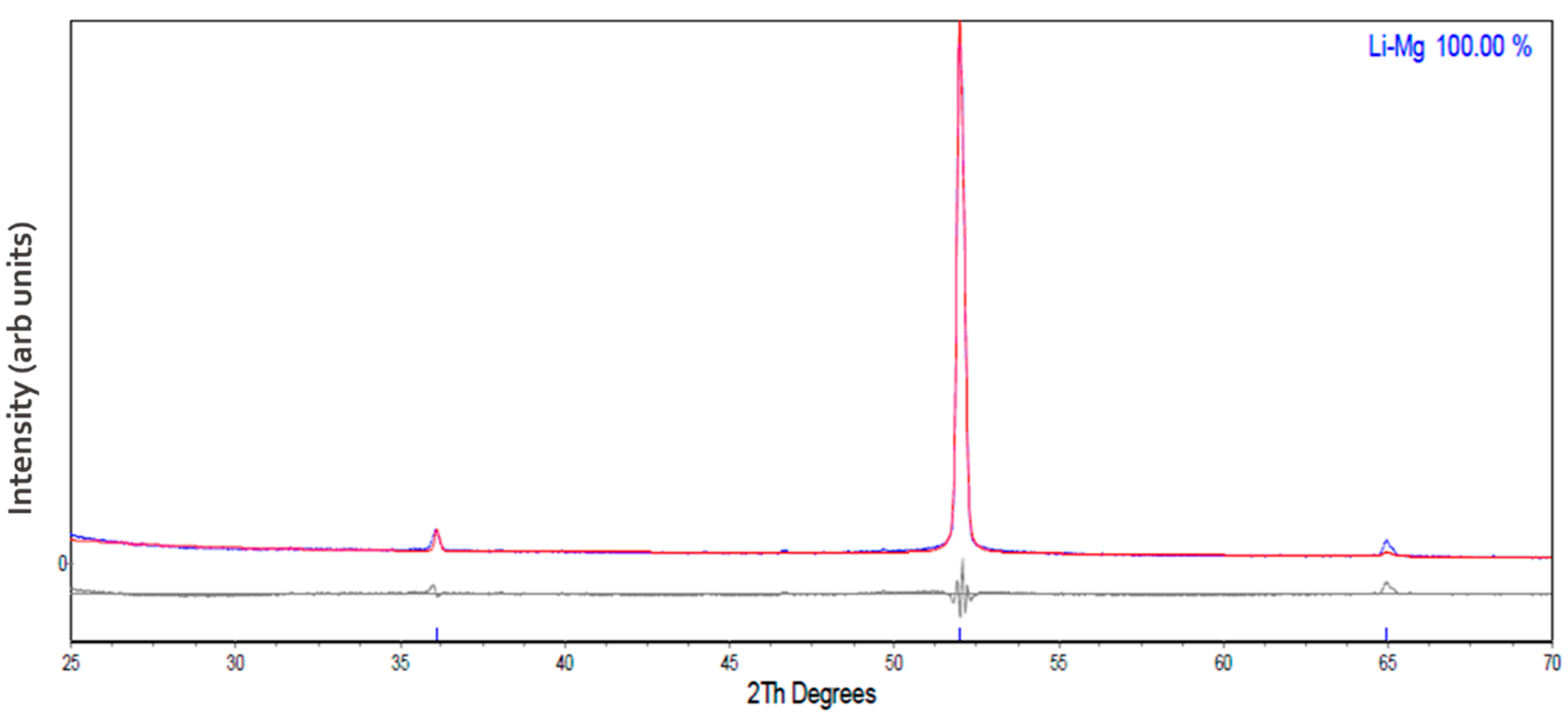
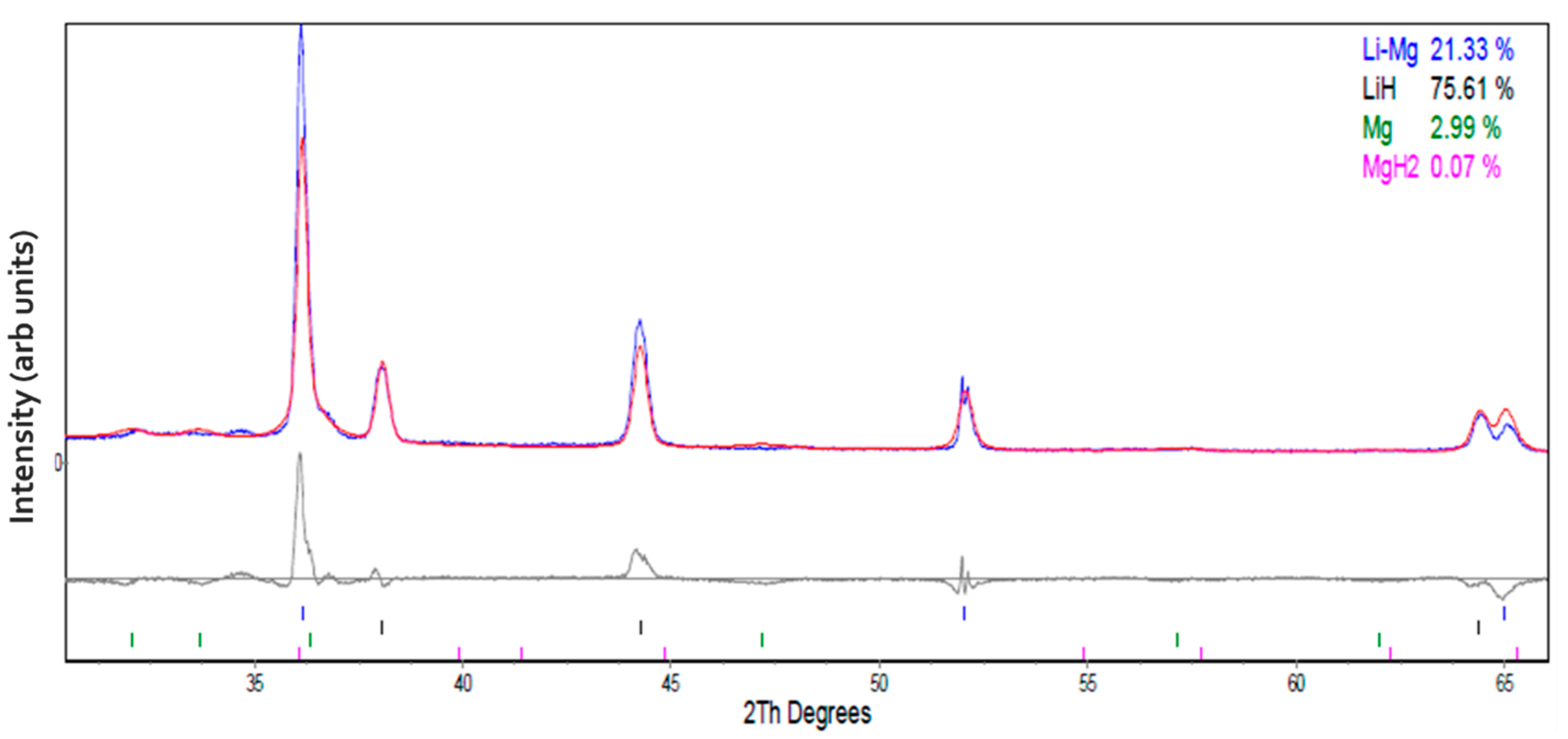
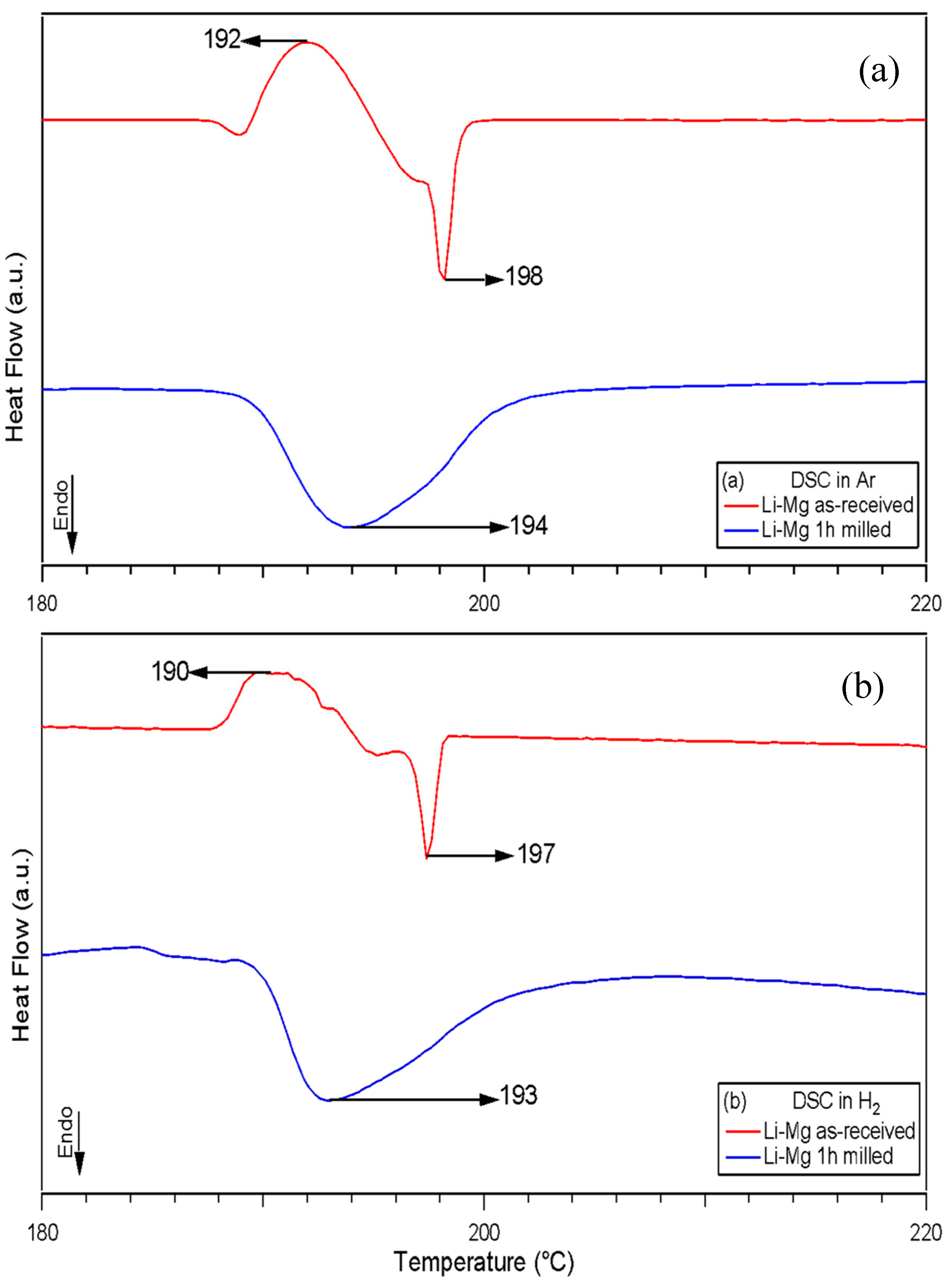
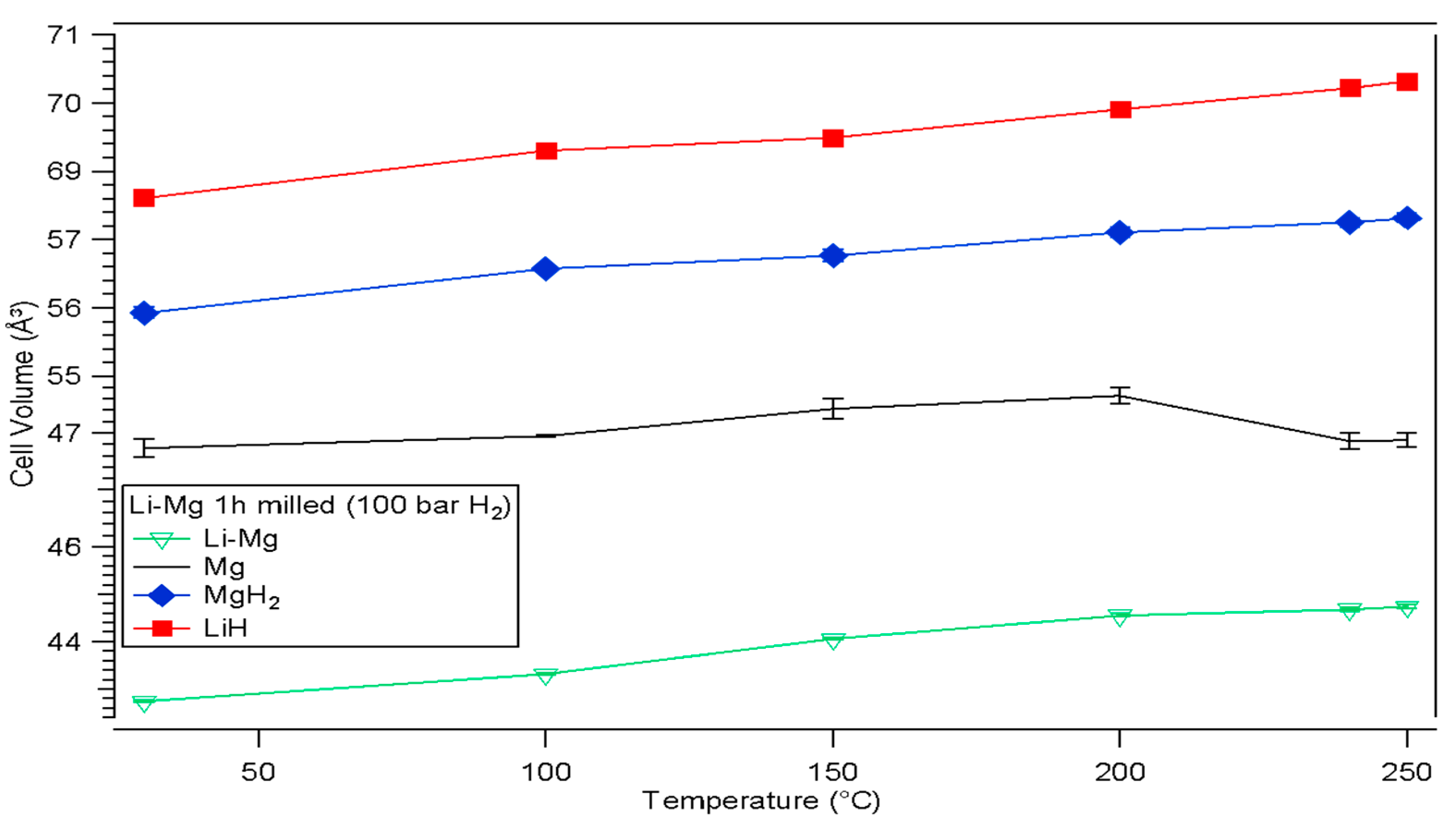
| Atmosphere | Li-Mg ribbon (This Work) | |||||||
| 100 bar H2 | Milling Time (h) | Lattice parameters (Å) | Cell Volumes V (Å3) | |||||
| Li-Mg Ribbon | Mg | LiH | Li-Mg Ribbon | Mg | LiH | |||
| (a) | (a) | (c) | (a) | |||||
| 0 | 3.52±0.01 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 43.4±0.1 | N/A | N/A | |
| 1 | 3.51±0.01 | 3.22±0.01 | 5.3±0.1 | 4.09±0.01 | 43.3±0.1 | 47.8±0.1 | 68.5±0.1 | |
| Literature [26] | ||||||||
| Lattice parameters (Å) | Cell Volumes V (Å3) | |||||||
| Li-Mg Ribbon | Mg | LiH | Li-Mg Ribbon | Mg | LiH | |||
| 3.51(6) | 3.20(2) | 5.20(4) | 4.08(3) | - | 46.2(1) | 68.0(1) | ||
| Atmosphere | Milling Time (h) | DSC | TGA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ton(°C) | Tpk(°C) | Tend(°C) | wt (%) H2 | ||
| Ar | Li-Mg (exo) | 188 | 192 | 197 | N/A |
| Li-Mg (endo) | 197 | 198 | 200 | ||
| 1 (100 bar H2) Li-Mg | 189 | 194 | 210 | 0.19 | |
| Literature | 1 (100 bar H2) Li-Mg | 284 | 0.17 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




