Submitted:
03 December 2024
Posted:
03 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
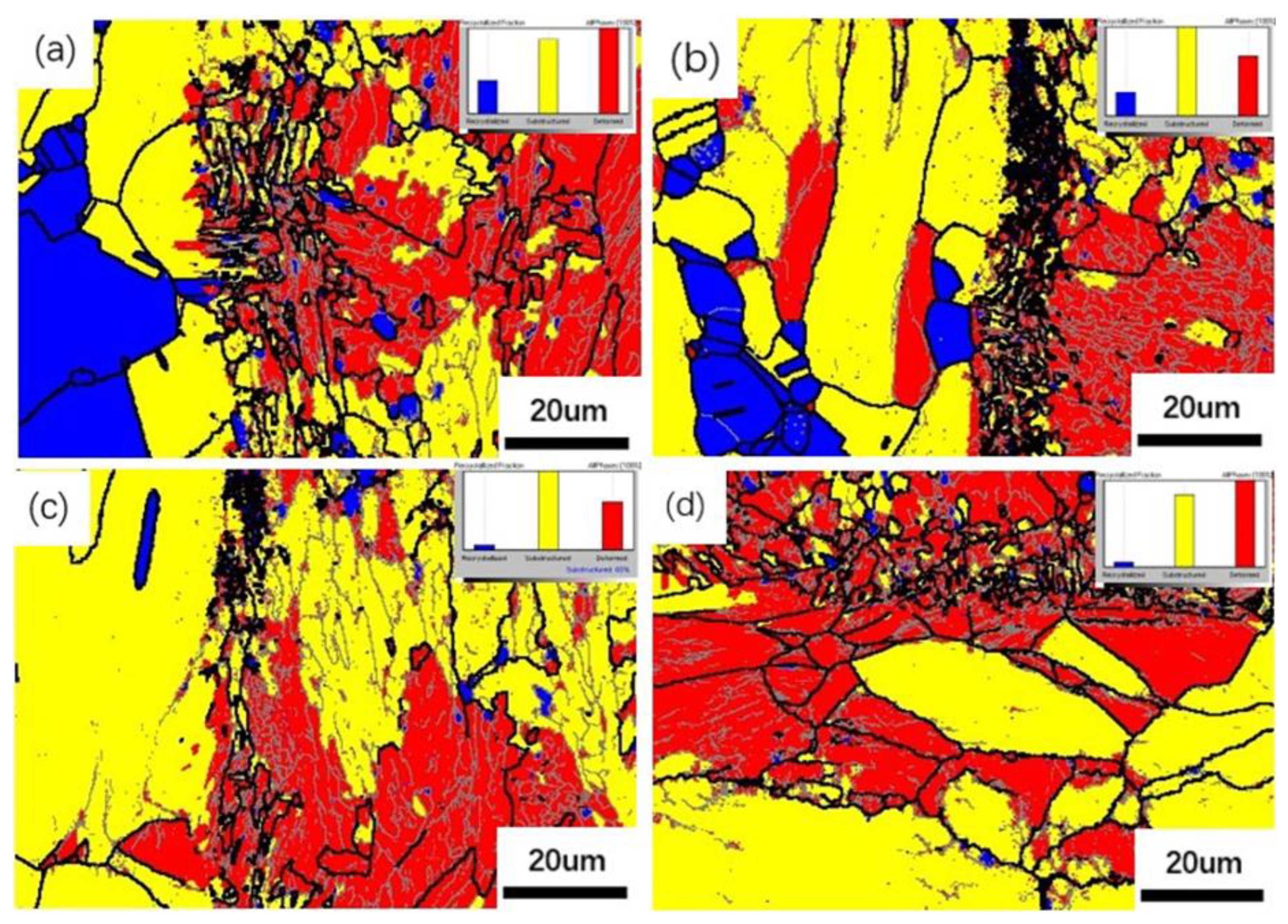
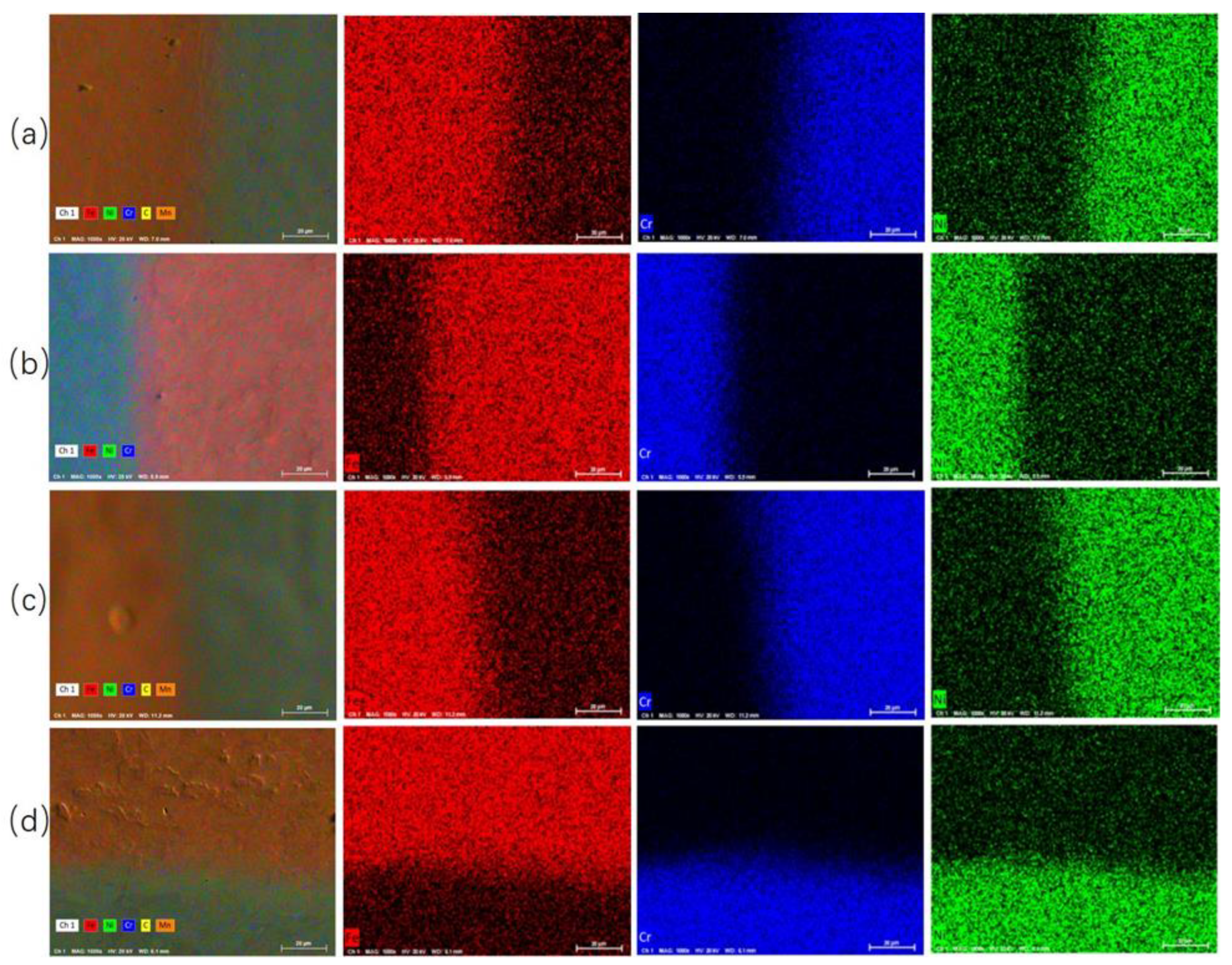
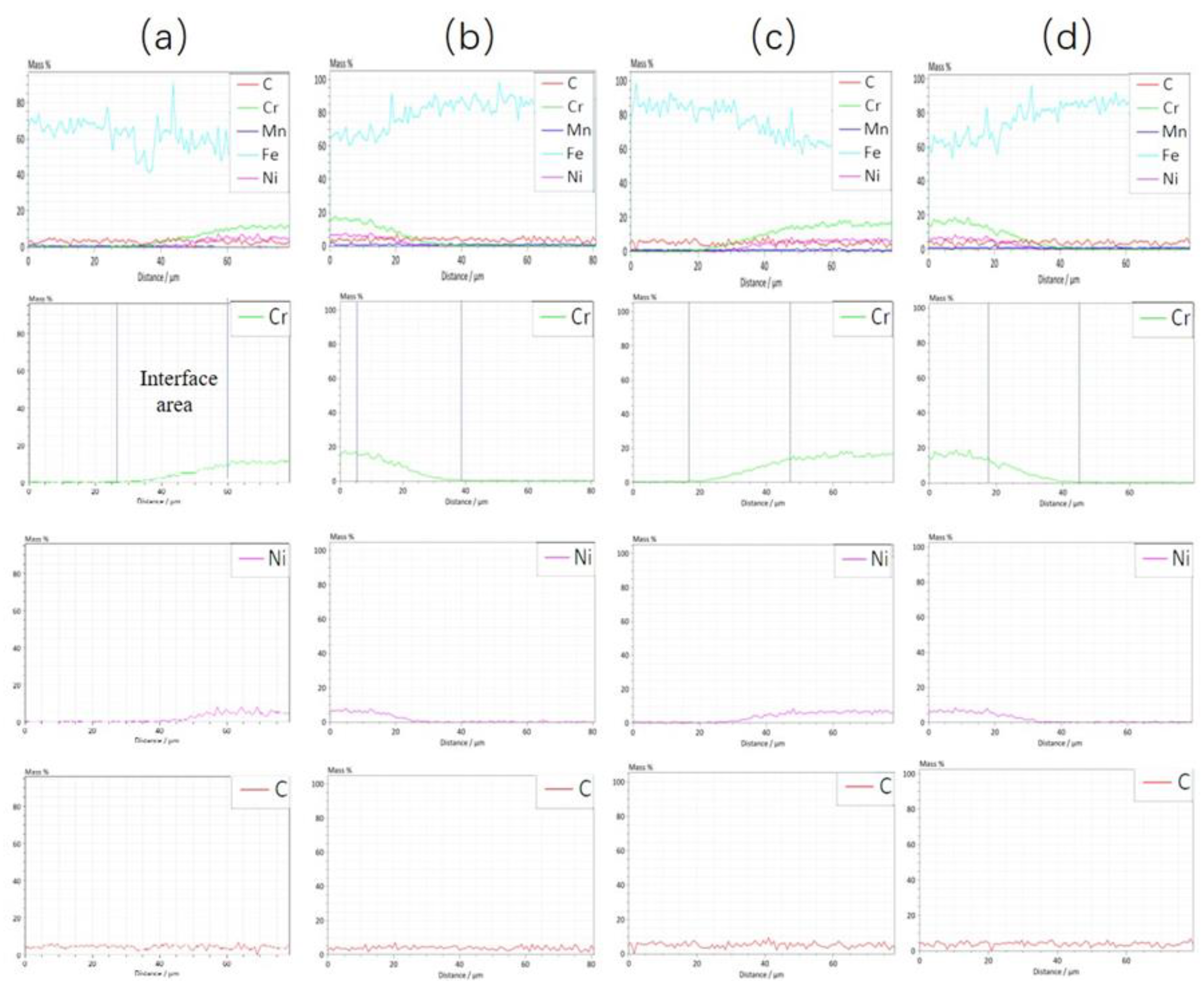
- With the increase in rolling reduction ratio, the grain size, the width of interfacial martensite zone, and the element diffusion distance decrease. The small difference in C element concentration leads to no obvious decarburized layer or carburized layer being formed.
- (2)
- Due to the greater stress distribution on the CS side, it results in a greater local orientation deviation and a larger number of deformed grains. With a sharp increase in the reduction ratio, ferrite grains will be broken into small ones, being accompanied by the generation of a large amount of carbides. When the rate of increase in the reduction ratio slows down and reheating is carried out, the carbides will gradually dissolve at high temperature.
- (3)
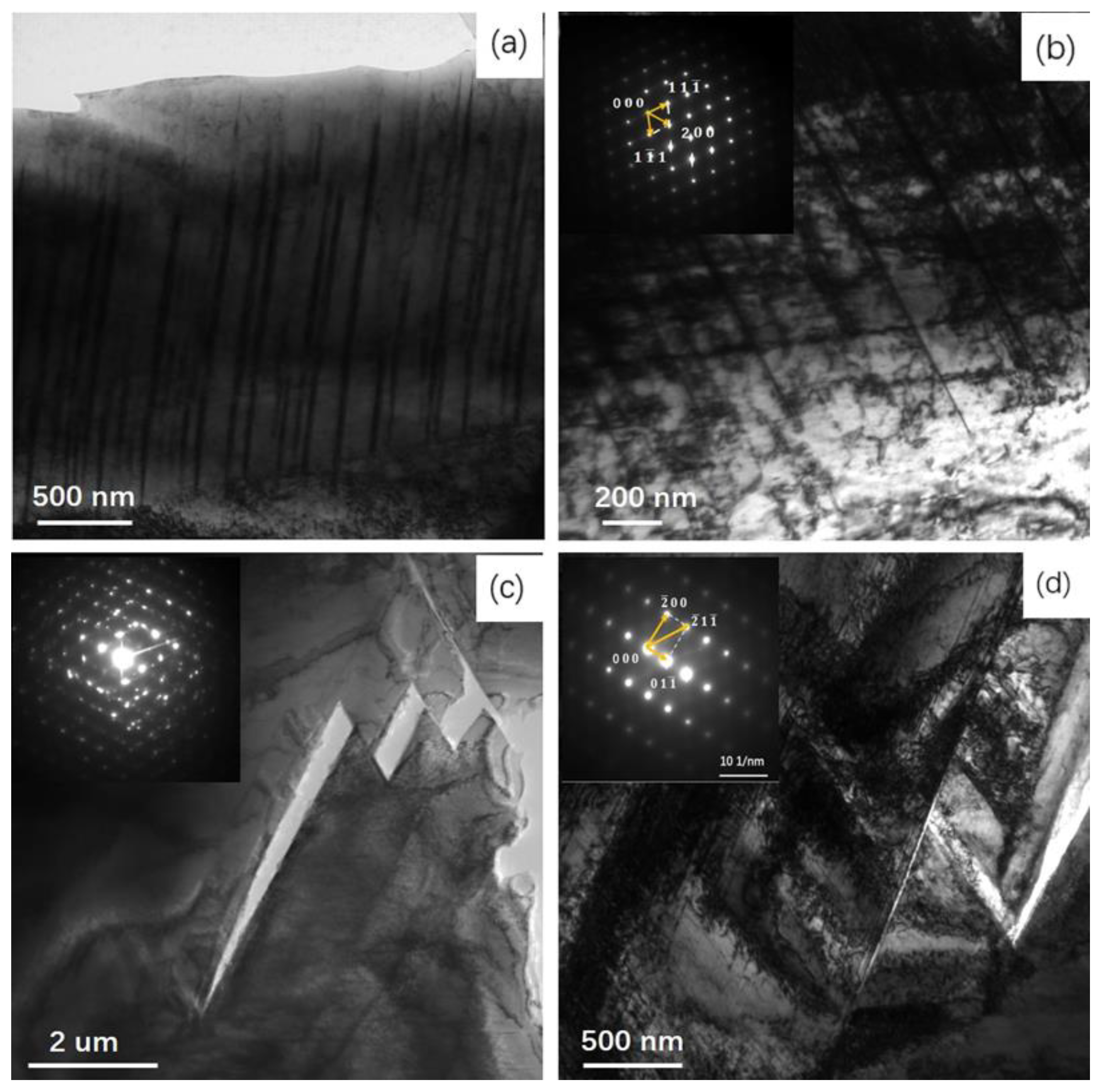
- The growth direction of martensite in the interface area is towards the inside of the austenite grains and is almost perpendicular to the interface, which is associated with the mechanism whereby strain-induced austenite transforms into martensite, →twinning→-martensite
- (4)
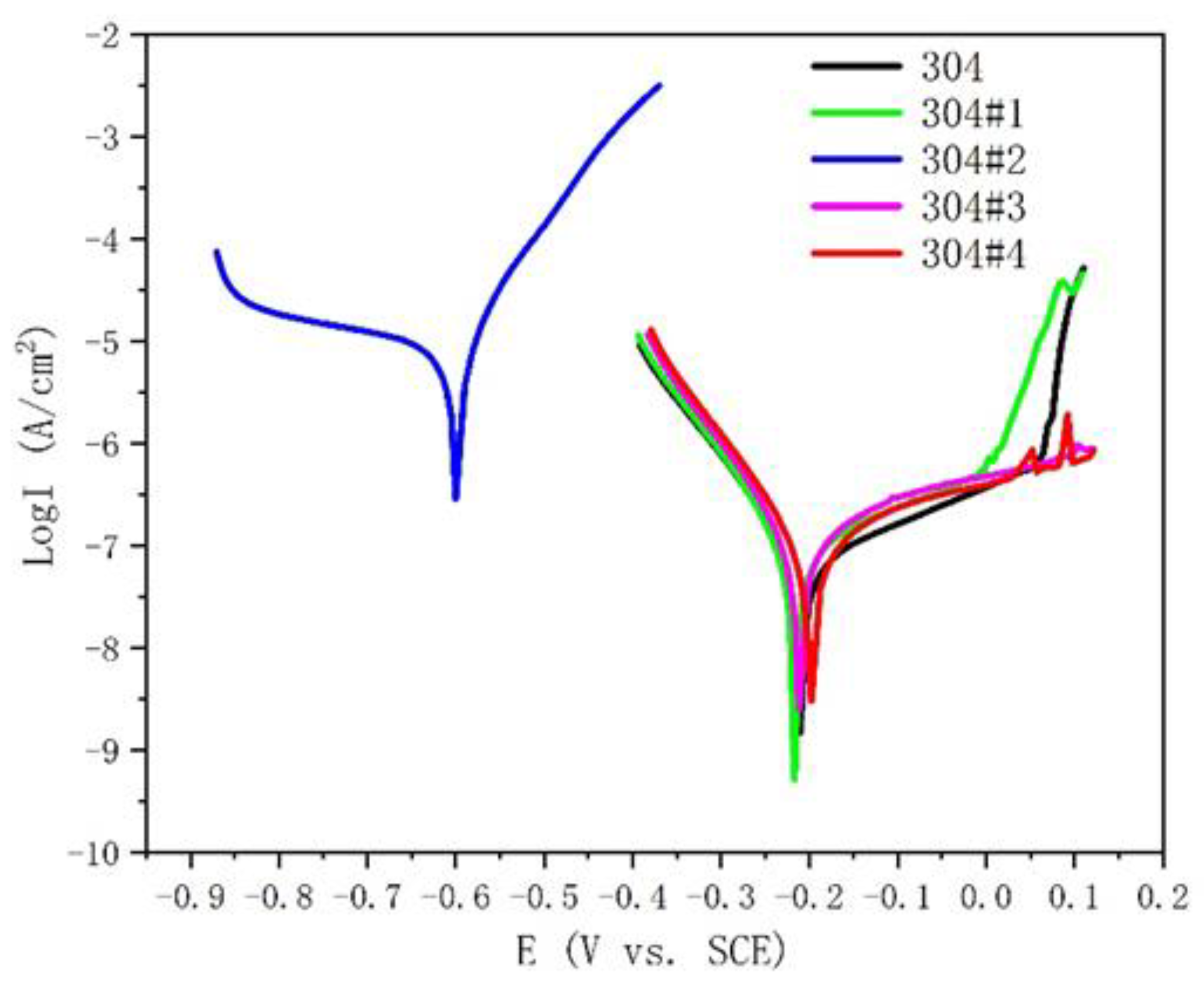
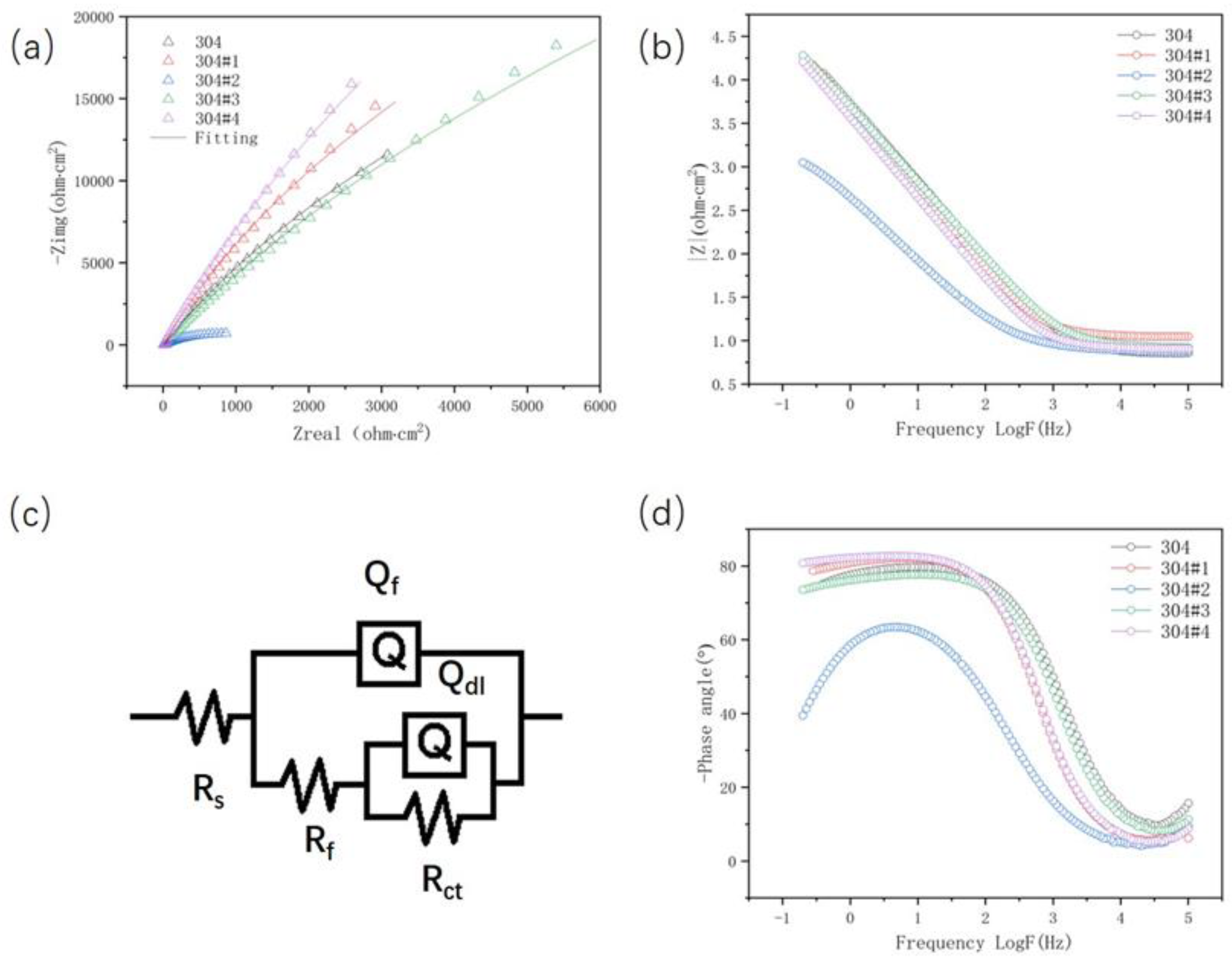
- For the 304#2 clad plate, due to the precipitation of a large amount of intergranular carbides, the corrosion resistance of the cladding has decreased significantly. In addition, the change in the reduction ratio does not have a significant effect on the corrosion resistance of the cladding of other clad plates.
Author Contributions
Data Availability
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. Tang, J. Li, X. Yu, S. Nie, Tensile behavior of stainless steel clad plates with different cladding ratios, Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 182 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Y. Mei, H. Ban, High strain rate behaviour of stainless-clad bimetallic steel, Engineering Structures, 207 (2020). [CrossRef]
- P. Zhao, H. Ban, Y.-F. Hu, K.-F. Chung, Y. Shi, Residual stress within stainless-clad bimetallic steel welded box sections, Thin-Walled Structures, 177 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Z.Y. Chen, J.X. Li, Z.G. Lin, J.J. Qi, L. Sun, G.D. Wang, Process Analysis and Trial Tests for Hot-Rolled Stainless Steel/Carbon Steel Clad Plates, Strength of Materials, 51 (2019) 26-31. [CrossRef]
- H. Ban, X. Yang, L. Hai, Y. Shi, Low-cycle fatigue behaviour and fracture feature of stainless-clad bimetallic steel, Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 196 (2022). [CrossRef]
- X. Liao, H. Wei, L. Feng, H. Ban, Low-cycle fatigue behavior for stainless-clad 304 + Q235B bimetallic steel, International Journal of Fatigue, 159 (2022). [CrossRef]
- B.X. Liu, S. Wang, W. Fang, J.L. Ma, F.X. Yin, J.N. He, J.H. Feng, C.X. Chen, Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot rolled stainless steel clad plate by heat treatment, Materials Chemistry and Physics, 216 (2018) 460-467. [CrossRef]
- H. Ban, R. Bai, L. Yang, Y. Bai, Mechanical properties of stainless-clad bimetallic steel at elevated temperatures, Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 162 (2019). [CrossRef]
- H. Ban, J. Zhu, G. Shi, Y. Zhang, Tests and modelling on cyclic behaviour of stainless-clad bimetallic steel, Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 166 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Z. Dhib, N. Guermazi, A. Ktari, M. Gasperini, N. Haddar, Mechanical bonding properties and interfacial morphologies of austenitic stainless steel clad plates, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 696 (2017) 374-386. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, B.X. Liu, C.X. Chen, J.H. Feng, F.X. Yin, Microstructure, mechanical properties and interface bonding mechanism of hot-rolled stainless steel clad plates at different rolling reduction ratios, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 766 (2018) 517-526. [CrossRef]
- B.X. Liu, F.X. Yin, X.L. Dai, J.N. He, W. Fang, C.X. Chen, Y.C. Dong, The tensile behaviors and fracture characteristics of stainless steel clad plates with different interfacial status, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 679 (2017) 172-182. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhu, Y. He, X. Zhang, H. Liu, X. Li, Effect of interface oxides on shear properties of hot-rolled stainless steel clad plate, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 669 (2016) 344-349. [CrossRef]
- B. Wu, K. Guo, X. Yang, Y. Gao, Y. Jin, Y. Gao, Q. Wang, F. Zhang, Effect of carbon content of substrate on the microstructure changes and tensile behavior of clad layer of stainless steel composites, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 831 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Y.F. Shen, X.X. Li, X. Sun, Y.D. Wang, L. Zuo, Twinning and martensite in a 304 austenitic stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 552 (2012) 514-522. [CrossRef]
- P. Xia, F.J. Canillas Rodríguez, I. Sabirov, Microstructure evolution and adiabatic heating during dynamic biaxial deformation of a 304 stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 793 (2020). [CrossRef]
- B. Gao, L. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Liu, Y. Sui, W. Sun, X. Chen, L. Xiao, H. Zhou, In-situ TEM investigation on deformation mechanisms of a fine-grained 316L stainless steel, Scripta Materialia, 234 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, Z. Jiang, S. Li, X. Liu, J. Sun, W. Wang, Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of stainless steel/carbon steel laminated composites, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 842 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, H. Li, Z. Jiang, J. Sun, X. Liu, X. Wang, J. Luo, Simultaneously enhanced strength-ductility synergy and corrosion resistance in liquid-solid bonded stainless steel cladding carbon steel plate by hot rolling and annealing treatment, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 871 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, Z. Jiang, Y. Chen, X. Liu, J. Sun, W. Wang, Interfacial microstructure and strengthening mechanism of stainless steel/carbon steel laminated composite fabricated by liquid-solid bonding and hot rolling, Materials Characterization, 191 (2022). [CrossRef]
- A. Momeni, K. Dehghani, H. Keshmiri, G.R. Ebrahimi, Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of a superaustenitic stainless steel, Materials Science and Engineering: A, 527 (2010) 1605-1611. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, Z. Jiang, X. Liu, J. Sun, W. Wang, Enhanced interfacial strength and ductility of stainless steel/carbon steel laminated composite by heterogenous lamella structure, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 18 (2022) 4846-4858. [CrossRef]
- W. Shen, L. Feng, H. Feng, Y. Cao, L. Liu, M. Cao, Y. Ge, Preparation and characterization of 304 stainless steel/Q235 carbon steel composite material, Results in Physics, 7 (2017) 529-534. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, Z. Zheng, J. Long, Z. Xu, S. Jiao, Y. Qiao, K. Zheng, F. Yin, Corrosion behaviour of hot-rolled 316L stainless steel-A6 carbon steel composite steel plate for marine environment, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 26 (2023) 556-570. [CrossRef]
- G. Bai, S. Lu, D. Li, Y. Li, Intergranular corrosion behavior associated with delta-ferrite transformation of Ti-modified Super304H austenitic stainless steel, Corrosion Science, 90 (2015) 347-358. [CrossRef]
- J.-C. Jin, S. Cho, K. Kim, H. Sim, B.G. Park, Y.-K. Lee, Microstructures and intergranular corrosion resistances of hot-rolled austenitic stainless steel clad plates, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 26 (2023) 1-13. [CrossRef]
- J. Zhang, J. He, B. Peng, H. Li, B. Li, B. Yan, J.-H. Zhang, An experimental investigation for corrosion resistance of stainless clad steel plate, Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 217 (2024). [CrossRef]
- H. Feng, J. Dai, H.-B. Li, Z.-H. Jiang, J.-D. Qu, Y. Zhao, S.-C. Zhang, T. Zhang, Sn microalloying enhances corrosion resistance of stainless steel by accelerating heterogeneous nucleation of passive film, Corrosion Science, 201 (2022). [CrossRef]
- W. Lv, C. Pan, W. Su, Z. Wang, S. Liu, C. Wang, A Study on Atmospheric Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel in a Simulated Marine Atmosphere, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 24 (2015) 2597-2604. [CrossRef]
- T. Zhang, W. Liu, Z. Yin, B. Dong, Y. Zhao, Y. Fan, J. Wu, Z. Zhang, X. Li, Effects of the Addition of Cu and Ni on the Corrosion Behavior of Weathering Steels in Corrosive Industrial Environments, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 29 (2020) 2531-2541. [CrossRef]
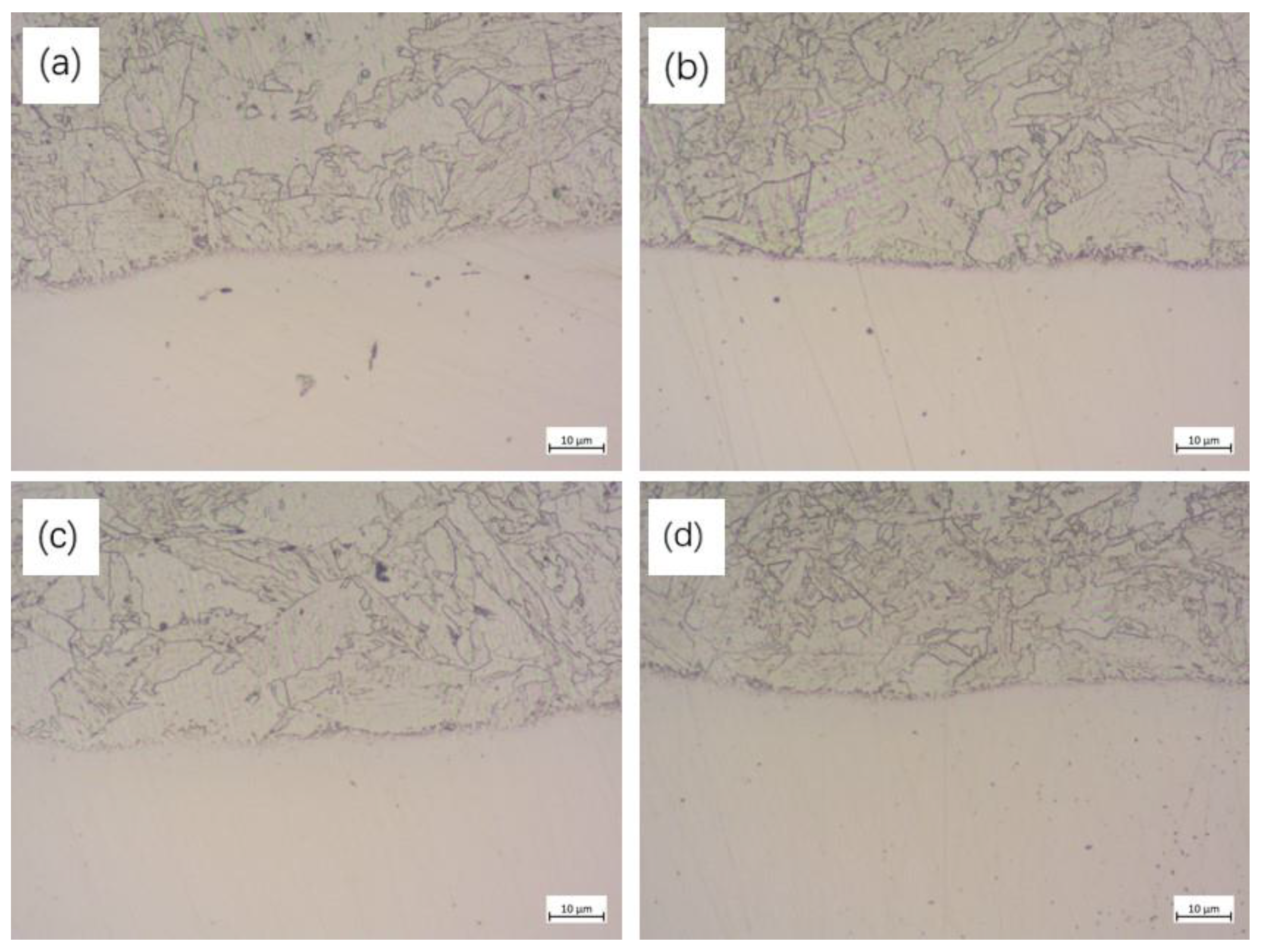
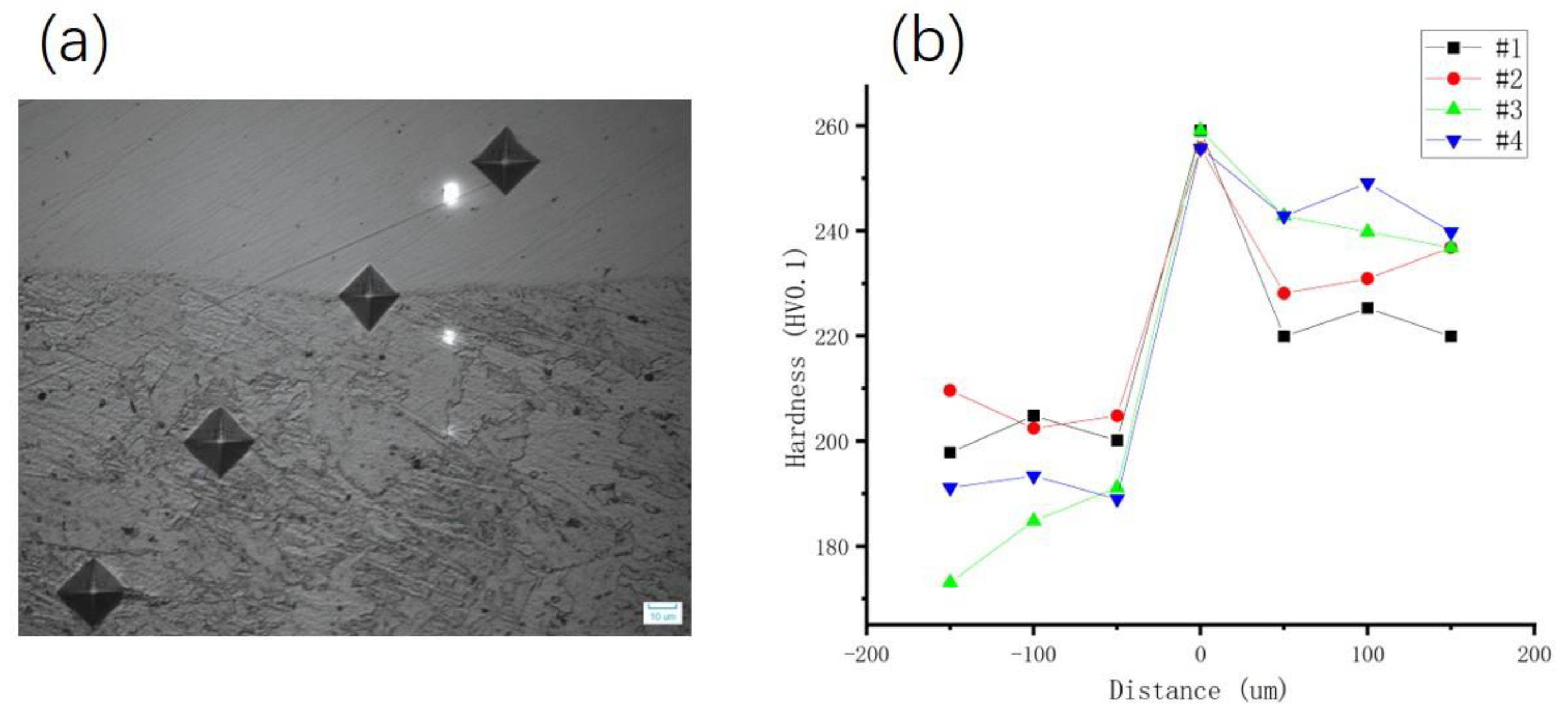
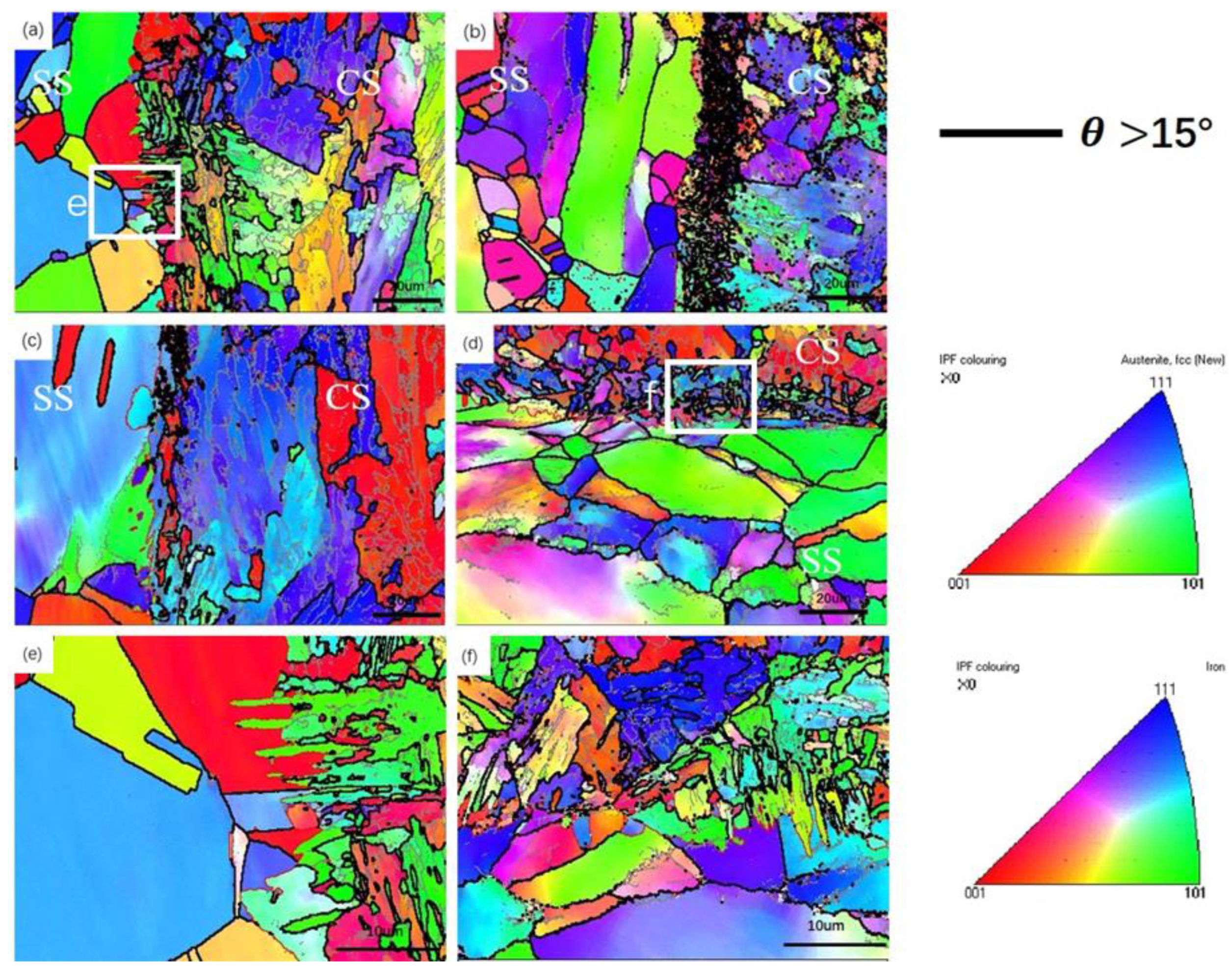
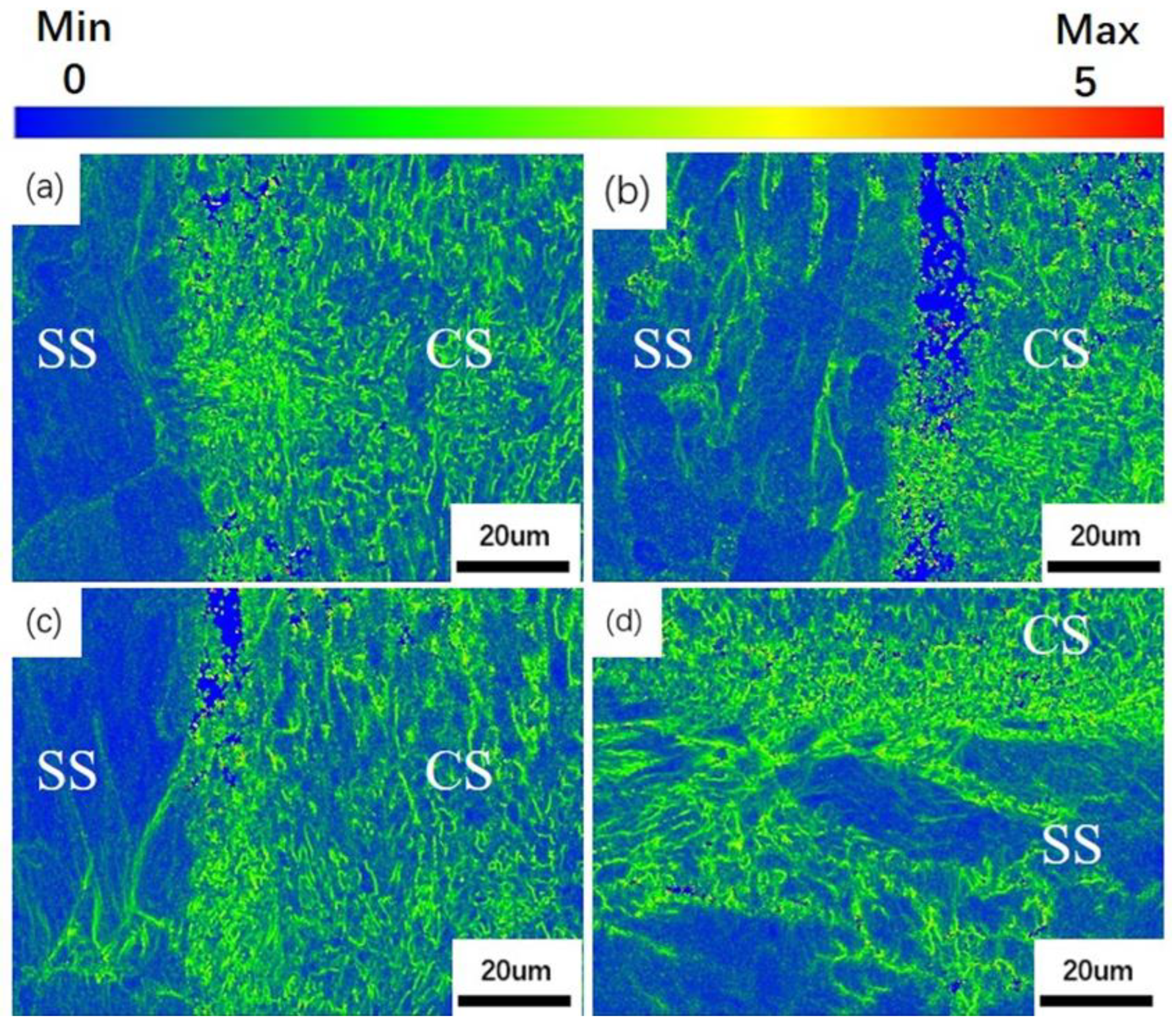
| 0.810 | C | Si | S | P | Mn | Cr | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 SS CS |
0.070 0.071 |
0.750 0.237 |
0.026 0.032 |
0.036 0.038 |
2.000 0.810 |
19.000 - |
10.000 - |
Bal. Bal. |
| Samples | Ecorr(mV) | Icorr(A/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | -210.3 | 6.51e-8 |
| 304#1 | -216.9 | 9.67e-8 |
| 304#2 | -600 | 8.94e-6 |
| 304#3 | -197.8 | 1.26e-7 |
| 304#4 | -211.4 | 1.94e-7 |
| Rs (Ωcm2) |
Qf (Ω-1sncm-2) |
nf |
Rf (Ωcm-2) |
Qdl (Ω-1sncm-2) |
ndl |
Rct (Ωcm-2) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 7.186 | 3.633E-005 | 0.8888 | 1.419E005 | 1.134E-005 | 0.1226 | 380.9 |
| 304#1 | 11.34 | 3.831E-005 | 0.9211 | 1.714E005 | 0.00126 | 0.1011 | 1.092E005 |
| 304#2 | 7.637 | 0.0005262 | 0.7542 | 1306 | 9.989E-006 | 0.464 | 1126 |
| 304#3 | 8.462 | 4.093E-005 | 0.8691 | 1.819E005 | 0.0001234 | 0.1368 | 4371 |
| 304#4 | 8.269 | 4.959E-005 | 0.9241 | 3.373E005 | 5.751E-006 | 0.1393 | 13.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





