Submitted:
29 October 2024
Posted:
30 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Cardiovascular Diseases Risk Factors
1.2. Microbiota-Immune Axis and CVDs: State of the Art
1.3. Marine-Derived Compounds and CVDs
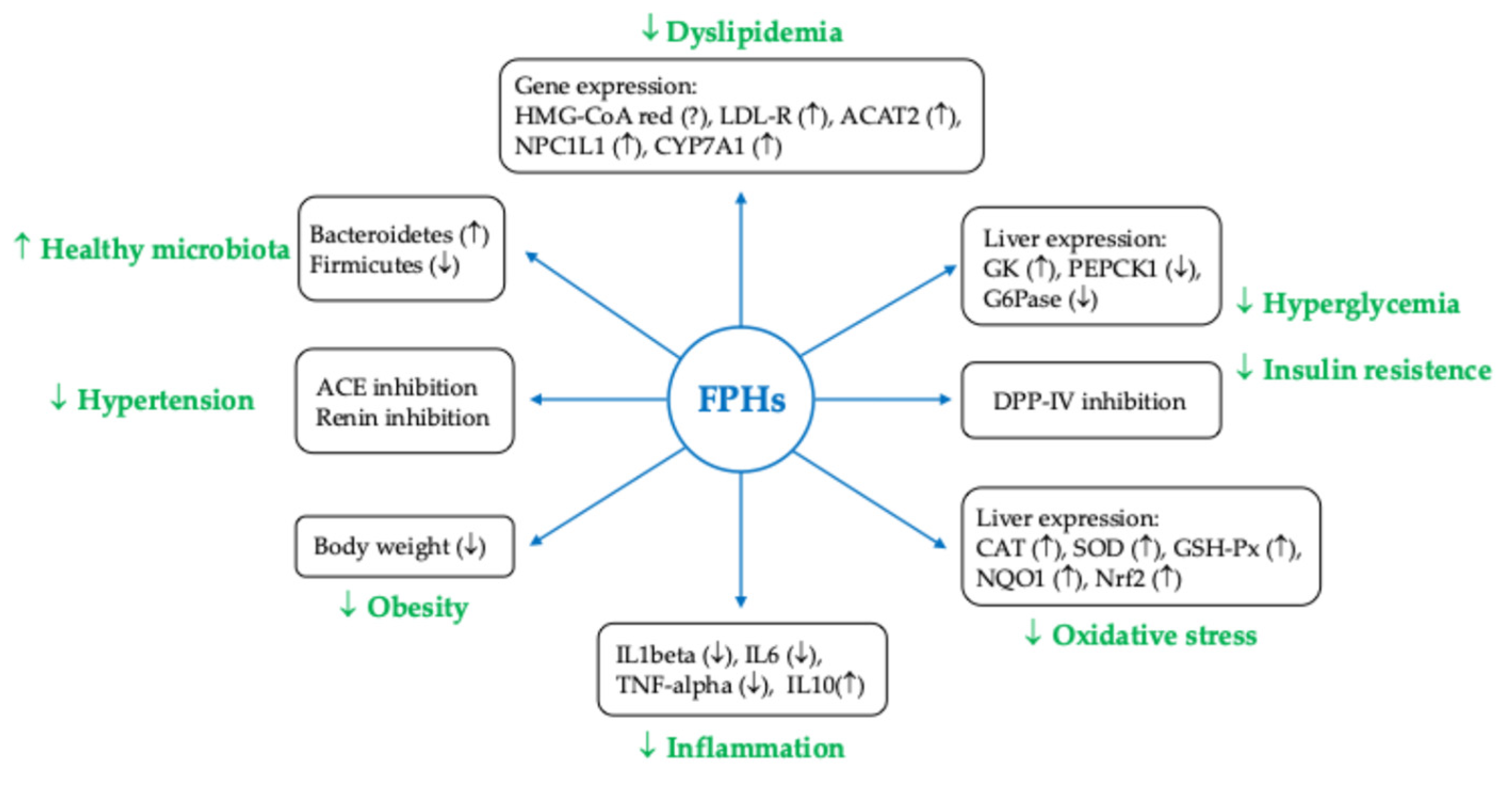
2. Fish-Derived Proteins and CVDs Risk Factors
2.1. Experimental Studies
2.2. Clinical Studies
3. Seaweed Components and CVDs Risk Factors
3.1. Experimental Studies
3.2. Clinical Studies
4. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic/Prebiotics and Marine Derived Compounds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017 Mar 7;135(10):e146–603. [CrossRef]
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2011 May 19;473(7347):317–25. [CrossRef]
- Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK, Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019 Aug 16;5(1):56.
- Liberale L, Badimon L, Montecucco F, Lüscher TF, Libby P, Camici GG. Inflammation, Aging, and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Mar 1;79(8):837–47.
- Marchesi M, Parolini C, Caligari S, Gilio D, Manzini S, Busnelli M, et al. Rosuvastatin does not affect human apolipoprotein A-I expression in genetically modified mice: a clue to the disputed effect of statins on HDL. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2011 Nov;164(5):1460. [CrossRef]
- Ridker PM, Bhatt DL, Pradhan AD, Glynn RJ, MacFadyen JG, Nissen SE, et al. Inflammation and cholesterol as predictors of cardiovascular events among patients receiving statin therapy: a collaborative analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet. 2023 Apr 15;401(10384):1293–301. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C. Marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Efficacy on inflammatory-based disorders. Life Sci. 2020:263:118591. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Marchesi M, Chiesa G. HDL therapy for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009;7:550–556. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Adorni MP, Busnelli M, Manzini S, Cipollari E, Favari E, et al. Infusions of Large Synthetic HDL Containing Trimeric apoA-I Stabilize Atherosclerotic Plaques in Hypercholesterolemic Rabbits. Can J Cardiol. 2019 Oct;35(10):1400–8.
- Jamadade P, Nupur N, Maharana KC, Singh S. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies for Metabolic Disorders: Major Advancements and Future Perspectives. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Jul 15; [CrossRef]
- Onvani S, Haghighatdoost F, Surkan PJ, Larijani B, Azadbakht L. Adherence to the Healthy Eating Index and Alternative Healthy Eating Index dietary patterns and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2017 Apr;30(2):216–26. [CrossRef]
- Pereira L, Valado A. Algae-Derived Natural Products in Diabetes and Its Complications-Current Advances and Future Prospects. Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;13(9):1831. [CrossRef]
- Curini L, Amedei A. Cardiovascular Diseases and Pharmacomicrobiomics: A Perspective on Possible Treatment Relevance. Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 28;9(10):1338. [CrossRef]
- Soldati L, Di Renzo L, Jirillo E, Ascierto PA, Marincola FM, De Lorenzo A. The influence of diet on anti-cancer immune responsiveness. Journal of Translational Medicine. 2018 Mar 20;16(1):75.
- Dübüş EN, Lamminpää I, Nannini G, Niccolai E. Nourishing Immunity and Combatting Neuroinflammation: The Power of Immunonutrition and The Microbiome. FBL. 2023 Aug 24;28(8):178. [CrossRef]
- Lamminpää I, Niccolai E, Amedei A. Probiotics as adjuvants to mitigate adverse reactions and enhance effectiveness in Food Allergy Immunotherapy. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. n/a(n/a):e13405. [CrossRef]
- Rinninella E, Tohumcu E, Raoul P, Fiorani M, Cintoni M, Mele MC, et al. The role of diet in shaping human gut microbiota. Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology. 2023 Feb 1;62–63:101828.
- Lamminpää I, Boem F, Amedei A. Health-promoting worms? Prospects and pitfalls of helminth therapy. BioEssays. n/a(n/a):2400080. [CrossRef]
- Harris EV, de Roode JC, Gerardo NM. Diet-microbiome-disease: Investigating diet’s influence on infectious disease resistance through alteration of the gut microbiome. PLoS Pathog. 2019 Oct;15(10):e1007891. [CrossRef]
- Nesci A, Carnuccio C, Ruggieri V, D’Alessandro A, Di Giorgio A, Santoro L, et al. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence on the Metabolic and Inflammatory Background of a Complex Relationship. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023 Jan;24(10):9087. [CrossRef]
- Guo Y, Li X, Wang Z, Yu B. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Human Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Front Cardiovasc Med [Internet]. 2021 May 14 [cited 2024 Oct 21];8. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cardiovascular-medicine/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2021.650227/full. [CrossRef]
- Sun S, Lulla A, Sioda M, Winglee K, Wu MC, Jacobs DR, et al. Gut Microbiota Composition and Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2019 May;73(5):998–1006. [CrossRef]
- Savin Z, Kivity S, Yonath H, Yehuda S. Smoking and the intestinal microbiome. Arch Microbiol. 2018 Jul;200(5):677–84. [CrossRef]
- Sublette MG, Cross TWL, Korcarz CE, Hansen KM, Murga-Garrido SM, Hazen SL, et al. Effects of Smoking and Smoking Cessation on the Intestinal Microbiota. J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 14;9(9):2963. [CrossRef]
- Illiano P, Brambilla R, Parolini C. The mutual interplay of gut microbiota, diet and human disease. FEBS J. 2020 Mar;287(5):833–55. [CrossRef]
- Koeth RA, Levison BS, Culley MK, Buffa JA, Wang Z, Gregory JC, et al. γ-Butyrobetaine is a proatherogenic intermediate in gut microbial metabolism of L-carnitine to TMAO. Cell Metab. 2014 Nov 4;20(5):799–812. [CrossRef]
- Qi J, You T, Li J, Pan T, Xiang L, Han Y, et al. Circulating trimethylamine N-oxide and the risk of cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 prospective cohort studies. J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jan;22(1):185–94. [CrossRef]
- Heianza Y, Ma W, Manson JE, Rexrode KM, Qi L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Disease Events and Death: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Jun 29;6(7):e004947. [CrossRef]
- Astudillo AA, Mayrovitz HN. The Gut Microbiome and Cardiovascular Disease. Cureus [Internet]. 2021 Apr 16 [cited 2024 Sep 13]; Available from: https://www.cureus.com/articles/55496-the-gut-microbiome-and-cardiovascular-disease.
- Hsu CN, Hou CY, Hsu WH, Tain YL. Cardiovascular Diseases of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapy. Nutrients. 2021 Jul;13(7):2290. [CrossRef]
- Tørris C, Småstuen MC, Molin M. Nutrients in Fish and Possible Associations with Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2018 Jul 23;10(7):952. [CrossRef]
- Abachi S, Bazinet L, Beaulieu L. Antihypertensive and Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from Fish as Potential Cardioprotective Compounds. Mar Drugs. 2019 Oct 29;17(11):613. [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe M, Gudbrandsen OA. Effects of diets containing proteins from fish muscles or fish by-products on the circulating cholesterol concentration in rodents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2023 Aug 14;130(3):389–410. [CrossRef]
- Jensen IJ, Mæhre HK. Preclinical and Clinical Studies on Antioxidative, Antihypertensive and Cardioprotective Effect of Marine Proteins and Peptides-A Review. Mar Drugs. 2016 Nov 18;14(11):211.
- Serhan CN, Levy BD. Resolvins in inflammation: emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J Clin Invest. 2018 Jul 2;128(7):2657–69. [CrossRef]
- Bäck M, Hansson GK. Omega-3 fatty acids, cardiovascular risk, and the resolution of inflammation. FASEB J. 2019 Feb;33(2):1536–9.
- Parolini C. The Role of Marine n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Inflammatory-Based Disease: The Case of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mar Drugs. 2023 Dec 27;22(1):17. [CrossRef]
- Snetselaar LG, de Jesus JM, DeSilva DM, Stoody EE. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025. Nutr Today. 2021;56(6):287–95.
- Zhubi-Bakija F, Bajraktari G, Bytyçi I, Mikhailidis DP, Henein MY, Latkovskis G, et al. The impact of type of dietary protein, animal versus vegetable, in modifying cardiometabolic risk factors: A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). Clin Nutr. 2021 Jan;40(1):255–76. [CrossRef]
- Zhao LG, Sun JW, Yang Y, Ma X, Wang YY, Xiang YB. Fish consumption and all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016 Feb;70(2):155–61. [CrossRef]
- Jayedi A, Shab-Bidar S, Eimeri S, Djafarian K. Fish consumption and risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2018 May;21(7):1297–306. [CrossRef]
- Zhou C, Wu Q, Ye Z, Liu M, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, et al. Inverse Association Between Variety of Proteins With Appropriate Quantity From Different Food Sources and New-Onset Hypertension. Hypertension. 2022 May;79(5):1017–27. [CrossRef]
- Drummen M, Tischmann L, Gatta-Cherifi B, Adam T, Westerterp-Plantenga M. Dietary Protein and Energy Balance in Relation to Obesity and Co-morbidities. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:443. [CrossRef]
- Pradhan B, Nayak R, Patra S, Jit BP, Ragusa A, Jena M. Bioactive Metabolites from Marine Algae as Potent Pharmacophores against Oxidative Stress-Associated Human Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules. 2020 Dec 23;26(1):37. [CrossRef]
- Bocanegra A, Macho-González A, Garcimartín A, Benedí J, Sánchez-Muniz FJ. Whole Alga, Algal Extracts, and Compounds as Ingredients of Functional Foods: Composition and Action Mechanism Relationships in the Prevention and Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 7;22(8):3816. [CrossRef]
- Suleria HAR, Osborne S, Masci P, Gobe G. Marine-Based Nutraceuticals: An Innovative Trend in the Food and Supplement Industries. Mar Drugs. 2015 Oct 14;13(10):6336–51. [CrossRef]
- Marchesi M, Parolini C, Valetti C, Mangione P, Obici L, Giorgetti S, et al. The intracellular quality control system down-regulates the secretion of amyloidogenic apolipoprotein A-I variants: a possible impact on the natural history of the disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jan;1812(1):87–93. [CrossRef]
- Dale HF, Madsen L, Lied GA. Fish-derived proteins and their potential to improve human health. Nutr Rev. 2019 Aug 1;77(8):572–83. [CrossRef]
- Yamori Y, Taguchi T, Hamada A, Kunimasa K, Mori H, Mori M. Taurine in health and diseases: consistent evidence from experimental and epidemiological studies. J Biomed Sci. 2010 Aug 24;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S6. [CrossRef]
- Caligari S, Chiesa G, Johnson SK, Camisassi D, Gilio D, Marchesi M, et al. Lupin (Lupinus albus) protein isolate (L-ISO) has adequate nutritional value and reduces large intestinal weight in rats after restricted and ad libitum feeding.Ann Nutr Metab. 2006;50:528-537. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Caligari S, Gilio D, Manzini S, Busnelli M, Montagnani M, et al. Reduced biliary sterol output with no change in total faecal excretion in mice expressing a human apolipoprotein A-I variant. Liver Int. 2012 Oct;32(9):1363–71. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Busnelli M, Ganzetti GS, Dellera F, Manzini S, Scanziani E, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging visualization of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques at the brachiocephalic artery of apolipoprotein E knockout mice by the blood-pool contrast agent B22956/1. Mol Imaging. 2014;13.
- Maeda H, Hosomi R, Yokoyama T, Ikeda Y, Nishimoto A, Tanaka G, et al. Dietary Alaska pollock protein attenuates liver steatosis and alters gut microbiota in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020 Dec 1;75:104266. [CrossRef]
- Hosomi R, Fukunaga K, Arai H, Nishiyama T, Yoshida M. Effects of dietary fish protein on serum and liver lipid concentrations in rats and the expression of hepatic genes involved in lipid metabolism. J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Oct 14;57(19):9256–62. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Rigamonti E, Marchesi M, Busnelli M, Cinquanta P, Manzini S, et al. Cholesterol-lowering effect of dietary Lupinus angustifolius proteins in adult rats through regulation of genes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Food Chem. 2012 Jun 1;132(3):1475–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang K, Han L, Tan Y, Hong H, Fan H, Luo Y. Novel Hypocholesterolemic Peptides Derived from Silver Carp Muscle: The Modulatory Effects on Enterohepatic Cholesterol Metabolism In Vitro and In Vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Apr 12;71(14):5565–75. [CrossRef]
- Mijiti M, Mori R, Huang B, Tsukamoto K, Kiriyama K, Sutoh K, et al. Anti-Obesity and Hypocholesterolemic Actions of Protamine-Derived Peptide RPR (Arg-Pro-Arg) and Protamine in High-Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients. 2021 Jul 22;13(8):2501. [CrossRef]
- Hosomi R, Fukunaga K, Arai H, Kanda S, Nishiyama T, Yoshida M. Effect of dietary protamine on lipid metabolism in rats. Nutr Res Pract. 2010 Dec;4(6):462–9. [CrossRef]
- Hosomi R, Miyauchi K, Yamamoto D, Arai H, Nishiyama T, Yoshida M, et al. Salmon Protamine Decreases Serum and Liver Lipid Contents by Inhibiting Lipid Absorption in an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Model and in Rats. J Food Sci. 2015 Oct;80(10):H2346-2353. [CrossRef]
- Luiking YC, Ten Have GAM, Wolfe RR, Deutz NEP. Arginine de novo and nitric oxide production in disease states. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Nov 15;303(10):E1177-1189. [CrossRef]
- Ohwada T, Ishibashi T, Yaoita H, Shindo J, Noji H, Ohkawara H, et al. Different contribution of apoptosis to the antiproliferative effects of L-arginine, enalapril and losartan on neointimal growth inhibition after balloon arterial injury. Circ J. 2002 Oct;66(10):965–71. [CrossRef]
- Dellera F, Ganzetti GS, Froio A, Manzini S, Busnelli M, Meinitzer A, et al. L-homoarginine administration reduces neointimal hyperplasia in balloon-injured rat carotids. Thromb Haemost. 2016 Aug 1;116(2):400–2. [CrossRef]
- Bai Y, Sun L, Yang T, Sun K, Chen J, Hui R. Increase in fasting vascular endothelial function after short-term oral L-arginine is effective when baseline flow-mediated dilation is low: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Jan;89(1):77–84. [CrossRef]
- Lv Z, Zhang C, Song W, Chen Q, Wang Y. Jellyfish Collagen Hydrolysate Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Improves Gut Microbe Composition in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:5628702. [CrossRef]
- Shi M, Song R, Gu L. Different Regulatory Effects of Heated Products and Maillard Reaction Products of Half-Fin Anchovy Hydrolysates on Intestinal Antioxidant Defense in Healthy Animals. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 25;24(3):2355. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Manzini S, Busnelli M, Rigamonti E, Marchesi M, Diani E, et al. Effect of the combinations between pea proteins and soluble fibres on cholesterolaemia and cholesterol metabolism in rats. Br J Nutr. 2013 Oct;110(8):1394–401. [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Hernandez O, Sanz ML, Kolida S, Rastall RA, Moreno FJ. In vitro fermentation by human gut bacteria of proteolytically digested caseinomacropeptide nonenzymatically glycosylated with prebiotic carbohydrates. J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Nov 23;59(22):11949–55. [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo-Mera A, Arthur JC, Jobin C, Keku T, Bruno-Barcena JM, Azcarate-Peril MA. High purity galacto-oligosaccharides enhance specific Bifidobacterium species and their metabolic activity in the mouse gut microbiome. Benef Microbes. 2016;7(2):247–64. [CrossRef]
- Terpend K, Possemiers S, Daguet D, Marzorati M. Arabinogalactan and fructo-oligosaccharides have a different fermentation profile in the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME ®). Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013 Aug;5(4):595–603. [CrossRef]
- Joubran Y, Moscovici A, Portmann R, Lesmes U. Implications of the Maillard reaction on bovine alpha-lactalbumin and its proteolysis during in vitro infant digestion. Food Funct. 2017 Jun 21;8(6):2295–308. [CrossRef]
- Jin W, Han K, Dong S, Yang Y, Mao Z, Su M, et al. Modifications in gut microbiota and fermentation metabolites in the hindgut of rats after the consumption of galactooligosaccharide glycated with a fish peptide. Food Funct. 2018 May 1;9(5):2853–64. [CrossRef]
- Han K, Yao Y, Dong S, Jin S, Xiao H, Wu H, et al. Chemical characterization of the glycated myofibrillar proteins from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) and their impacts on the human gut microbiota in vitro fermentation. Food Funct. 2017 Mar 22;8(3):1184–94. [CrossRef]
- Lin Q, Guo Y, Li J, He S, Chen Y, Jin H. Antidiabetic Effect of Collagen Peptides from Harpadon nehereus Bones in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mice by Regulating Oxidative Stress and Glucose Metabolism. Mar Drugs. 2023 Sep 29;21(10):518. [CrossRef]
- G Bardallo R, Panisello-Roselló A, Sanchez-Nuno S, Alva N, Roselló-Catafau J, Carbonell T. Nrf2 and oxidative stress in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. FEBS J. 2022 Sep;289(18):5463–79. [CrossRef]
- Xu M, Chen B, Qiao K, Liu S, Su Y, Cai S, et al. Mechanism of Takifugu bimaculatus Skin Peptides in Alleviating Hyperglycemia in Rats with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus Based on Microbiome and Metabolome Analyses. Marine Drugs. 2024 Aug;22(8):377. [CrossRef]
- Bodnaruc AM, Prud’homme D, Blanchet R, Giroux I. Nutritional modulation of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion: a review. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016;13:92. [CrossRef]
- Valle M, Mitchell PL, Pilon G, Varin T, Hénault L, Rolin J, et al. Salmon peptides limit obesity-associated metabolic disorders by modulating a gut-liver axis in vitamin D-deficient mice. Obesity. 2021;29(10):1635–49. [CrossRef]
- Fang Y, She J, Zhang X, Gu T, Xie D, Luo X, et al. Discovery of Anti-Hypercholesterolemia Agents Targeting LXRα from Marine Microorganism-Derived Natural Products. J Nat Prod. 2024 Feb 23;87(2):322–31. [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara I, Kim SK. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors from marine resources: prospects in the pharmaceutical industry. Mar Drugs. 2010 Mar 31;8(4):1080–93. [CrossRef]
- Busnelli M, Manzini S, Sirtori CR, Chiesa G, Parolini C. Effects of Vegetable Proteins on Hypercholesterolemia and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients. 2018:10:1249. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Lin L mei, Wu Y ning, Fang M, Yu Y qin, Zhou J, et al. Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity and antihypertensive effects of grass carp peptides. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2014 Oct 1;23(5):1661–6.
- Sun L, Zhang Y, Zhuang Y. Antiphotoaging effect and purification of an antioxidant peptide from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) gelatin peptides. Journal of Functional Foods. 2013;1(5):154–62. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Ryu B, Zhang Y, Liang P, Li C, Zhou C, et al. Comparison of an angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with captopril: inhibition kinetics, in vivo effect, simulated gastrointestinal digestion and a molecular docking study. J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Jan 15;100(1):315–24.
- Drotningsvik A, Oterhals Å, Mjøs SA, Vikøren LA, Flesland O, Gudbrandsen OA. Effects of intact and hydrolysed blue whiting proteins on blood pressure and markers of kidney function in obese Zucker fa/fa rats. Eur J Nutr. 2021 Feb;60(1):529–44. [CrossRef]
- Vo TS, Ngo DH, Kim JA, Ryu B, Kim SK. An antihypertensive peptide from tilapia gelatin diminishes free radical formation in murine microglial cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Nov 23;59(22):12193–7. [CrossRef]
- Ktari N, Bkhairia I, Nasri R, Ben Abdallah Kolsi R, Ben Slama-Ben Salem R, Ben Amara I, et al. Zebra blenny protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides with prevention effect against oxidative dysfunctions and DNA damage in heart tissues of rats fed a cholesterol-rich diet. Food Res Int. 2017 Oct;100(Pt 1):423–32. [CrossRef]
- Maneesai P, Wattanathorn J, Potue P, Khamseekaew J, Rattanakanokchai S, Thukham-Mee W, et al. Cardiovascular complications are resolved by tuna protein hydrolysate supplementation in rats fed with a high-fat diet. Sci. Rep. 2023;13:12880. [CrossRef]
- Parolini C, Vik R, Busnelli M, , Bjørndal B, Holm S, Brattelid T, et al. A Salmon Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Lipid-Independent Anti-Atherosclerotic Activity in ApoE-Deficient Mice. PLoS One. 2014;9:e97598.
- Abbate JM, Macrì F, Arfuso F, Iaria C, Capparucci F, Anfuso C, et al. Anti-Atherogenic Effect of 10% Supplementation of Anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) Waste Protein Hydrolysates in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Nutrients. 2021 Jul;13(7):2137. [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Yang Y, Liu Y, Cui L, Fu L, Li B. Various bioactive peptides in collagen hydrolysate from salmo salar skin and the combined inhibitory effects on atherosclerosis in vitro and in vivo. Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111281. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Liu H, Cui L, Liu Y, Fu L, Li B. A Collagen-Derived Oligopeptide from Salmo salar Collagen Hydrolysates Restrains Atherogenesis in ApoE–/– Mice via Targeting P2Y12 Receptor. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 2022;66(13):2200166.
- Yang Y, Liu H, Cui L, Liu Y, Fu L, Li B. A Collagen-Derived Oligopeptide from Salmo salar Collagen Hydrolysates Restrains Atherogenesis in ApoE–/– Mice via Targeting P2Y12 Receptor. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022;66:e2200166.
- Kondo Y, Toda Y, Kitajima H, Oda H, Nagate T, Kameo K, et al. Taurine Inhibits Development Of Atherosclerotic Lesions In apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2001;28:809-815.
- Yang JY, Zhang TT, Yu ZL, Wang CC, Zhao YC, Wang YM, et al. Taurine Alleviates Trimethylamine N-Oxide-Induced Atherosclerosis by Regulating Bile Acid Metabolism in ApoE–/– Mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2022 May 11;70(18):5738–47. [CrossRef]
- Tou JC, Gucciardi E, Young I. Lipid-modifying effects of lean fish and fish-derived protein consumption in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. 2021 Dec 8;80(1):91–112. [CrossRef]
- Ramel A, Jonsdottir MT, Thorsdottir I. Consumption of cod and weight loss in young overweight and obese adults on an energy reduced diet for 8-weeks. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Dec;19(10):690–6. [CrossRef]
- Nobile V, Duclos E, Michelotti A, Bizzaro G, Negro M, Soisson F. Full article: Supplementation with a fish protein hydrolysate (Micromesistius poutassou): effects on body weight, body composition, and CCK/GLP-1 secretion. Food Nutr. Res. 2016;60:29857.
- Telle-Hansen VH, Larsen LN, Høstmark AT, Molin M, Dahl L, Almendingen K, et al. Daily intake of cod or salmon for 2 weeks decreases the 18:1n-9/18:0 ratio and serum triacylglycerols in healthy subjects. Lipids. 2012 Feb;47(2):151–60.
- Aadland EK, Lavigne C, Graff IE, Eng Ø, Paquette M, Holthe A, et al. Lean-seafood intake reduces cardiovascular lipid risk factors in healthy subjects: results from a randomized controlled trial with a crossover design. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015 Sep;102(3):582–92. [CrossRef]
- Aadland EK, Graff IE, Lavigne C, Eng Ø, Paquette M, Holthe A, et al. Lean Seafood Intake Reduces Postprandial C-peptide and Lactate Concentrations in Healthy Adults in a Randomized Controlled Trial with a Crossover Design. J Nutr. 2016 May;146(5):1027–34. [CrossRef]
- Vikøren LA, Nygård OK, Lied E, Rostrup E, Gudbrandsen OA. A randomised study on the effects of fish protein supplement on glucose tolerance, lipids and body composition in overweight adults. Br J Nutr. 2013 Feb 28;109(4):648–57. [CrossRef]
- Dale HF, Jensen C, Hausken T, Lied E, Hatlebakk JG, Brønstad I, et al. Effect of a cod protein hydrolysate on postprandial glucose metabolism in healthy subjects: a double-blind cross-over tria. J Nutr. Sci. 2018;7:e33.l.
- Ouellet V, Marois J, Weisnagel SJ, Jacques H. Dietary cod protein improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant men and women: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:2816-2821.
- Ouellet V, Weisnagel SJ, Marois J, Bergeron J, Julien P, Gougeon R, et al. Dietary cod protein reduces plasma C-reactive protein in insulin-resistant men and women. J Nutr. 2008;138:2386-2391. [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki T, Seki E, Osajima K, Yoshida M, Asada K, Matsui T, et al. Antihypertensive effect of valyl-tyrosine, a short chain peptide derived from sardine muscle hydrolyzate, on mild hypertensive subjects. J Hum Hypertens. 2000 Aug;14(8):519–23. [CrossRef]
- Sun Q, Wang B, Li Y, Sun F, Li P, Xia W, et al. Taurine Supplementation Lowers Blood Pressure and Improves Vascular Function in Prehypertension: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Hypertension. 2016 Mar;67(3):541–9.
- Murray M, Dordevic AL, Ryan L, Bonham MP. An emerging trend in functional foods for the prevention of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: Marine algal polyphenols. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2018 May 24;58(8):1342–58. [CrossRef]
- Akram W, Rihan M, Ahmed S, Arora S, Ahmad S, Vashishth R. Marine-Derived Compounds Applied in Cardiovascular Diseases: Submerged Medicinal Industry. Marine Drugs. 2023 Mar;21(3):193. [CrossRef]
- Yurika N, Montuori E, Lauritano C. Marine Microalgal Products with Activities against Age-Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Mar. Drugs. 2024;22:229. [CrossRef]
- Giuliani ME, Bigossi G, Lai G, Marcozzi S, Brunetti D, Malavolta M. Marine Compounds and Age-Related Diseases: The Path from Pre-Clinical Research to Approved Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes. Marine Drugs. 2024 May;22(5):210. [CrossRef]
- Patil NP, Le V, Sligar AD, Mei L, Chavarria D, Yang EY, et al. Algal Polysaccharides as Therapeutic Agents for Atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:153.
- Yokota T, Nomura K, Nagashima M, Kamimura N. Fucoidan alleviates high-fat diet-induced dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis in ApoE(shl) mice deficient in apolipoprotein E expression. J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Jun;32:46–54.
- Park J, Yeom M, Hahm DH. Fucoidan improves serum lipid levels and atherosclerosis through hepatic SREBP-2-mediated regulation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jun;131(2):84–92. [CrossRef]
- Ys Y, Ks C, Sy L, Sw H, Yr K, Jk L, et al. Anti-obesity effects of a standardized ethanol extract of Eisenia bicyclis by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 cells and HFD-induced mice. Food & function [Internet]. 2024 Jun 17 [cited 2024 Sep 18];15(12). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38771619/.
- Y S, L Z, T I, K N, K M, R U, et al. Lipid- and glucose-lowering effects of Rhamnan sulphate from Monostroma nitidum with altered gut microbiota in mice. Food science & nutrition [Internet]. 2024 Mar 25 [cited 2024 Sep 18];12(6). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38873438/.
- He Z, Zhang Z, Xu P, Dirsch VM, Wang L, Wang K. Laminarin Reduces Cholesterol Uptake and NPC1L1 Protein Expression in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice. Mar Drugs. 2023 Nov 29;21(12):624. [CrossRef]
- Shan S, Zhang Z, Nie J, Wen Y, Wu W, Liu Y, et al. Marine algae-derived oligosaccharide via protein crotonylation of key targeting for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly.Pharmacol Res. 2024;205:107257. [CrossRef]
- Lin D, Zhang N, Wu S, Wang S, Huang F, Lin Y, et al. Structural Analysis and Novel Mechanism of Enteromorpha prolifera Sulfated Polysaccharide in Preventing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Plant Foods Hum Nutr [Internet]. 2023 Dec 12 [cited 2024 Sep 18]; Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11130-023-01129-8. [CrossRef]
- Lee SM, Park S-Y, Kim JY. Comparative evaluation of the antihyperglycemic effects of three extracts of sea mustard (Undaria pinnatifida): In vitro and in vivo studies. Food Res Int. 2024;190:114623. [CrossRef]
- Fernando R, Sun X, Rupasinghe HPV. Production of Bioactive Peptides from Microalgae and Their Biological Properties Related to Cardiovascular Disease. Macromol. 2024 Sep;4(3):582–96. [CrossRef]
- Olena Z, Yang Y, TingTing Y, XiaoTao Y, HaiLian R, Xun X, et al. Simultaneous preparation of antioxidant peptides and lipids from microalgae by pretreatment with bacterial proteases. Bioresour Technol. 2022 Mar;348:126759. [CrossRef]
- Kang KH, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Karadeniz F, Kim D, Kim SK. Antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of microalgae Navicula incerta and their protective effects in HepG2/CYP2E1 cells induced by ethanol. Phytother Res. 2012 Oct;26(10):1555–63.
- Abo-Shady AM, Gheda SF, Ismail GA, Cotas J, Pereira L, Abdel-Karim OH. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity of Algae. Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;13(2):460. [CrossRef]
- Suetsuna K, Chen JR. Identification of antihypertensive peptides from peptic digest of two microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2001 Jul;3(4):305–9. [CrossRef]
- Sheih IC, Wu TK, Fang TJ. Antioxidant properties of a new antioxidative peptide from algae protein waste hydrolysate in different oxidation systems. Bioresour Technol. 2009 Jul;100(13):3419–25. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald C, Gallagher E, Tasdemir D, Hayes M. Heart Health Peptides from Macroalgae and Their Potential Use in Functional Foods. J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Jul 13;59(13):6829–36. [CrossRef]
- Shih MF, Chen LC, Cherng JY. Chlorella 11-peptide inhibits the production of macrophage-induced adhesion molecules and reduces endothelin-1 expression and endothelial permeability. Mar Drugs. 2013 Oct 14;11(10):3861–74. [CrossRef]
- Vo TS, Kim SK. Down-regulation of histamine-induced endothelial cell activation as potential anti-atherosclerotic activity of peptides from Spirulina maxima. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013 Oct 9;50(2):198–207. [CrossRef]
- Ejike CECC, Collins SA, Balasuriya N, Swanson AK, Mason B, Udenigwe CC. Prospects of microalgae proteins in producing peptide-based functional foods for promoting cardiovascular health. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2017 Jan 1;59:30–6. [CrossRef]
- Cherry P, O’Hara C, Magee PJ, McSorley EM, Allsopp PJ. Risks and benefits of consuming edible seaweeds. Nutr Rev. 2019 May 1;77(5):307–29. [CrossRef]
- Otsuki T, Shimizu K, Maeda S. Changes in arterial stiffness and nitric oxide production with Chlorella-derived multicomponent supplementation in middle-aged and older individuals. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015;57(3):228–32. [CrossRef]
- Ryu NH, Lim Y, Park JE, Kim J, Kim JY, Kwon SW, et al. Impact of daily Chlorella consumption on serum lipid and carotenoid profiles in mildly hypercholesterolemic adults: a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Nutrition Journal. 2014 Jun 11;13(1):57. [CrossRef]
- Bito T, Okumura E, Fujishima M, Watanabe F. Potential of Chlorella as a Dietary Supplement to Promote Human Health. Nutrients. 2020 Sep;12(9):2524. [CrossRef]
- Potential of Chlorella as a Dietary Supplement to Promote Human Health - PMC [Internet]. [cited 2024 Sep 17]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7551956/.
- Nicolucci A, Rossi MC, Petrelli M. Effectiveness of Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus on Metabolic Syndrome Components: A Real-World, Observational Study. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:3389316. [CrossRef]
- Oben J, Enonchong E, Kuate D, Mbanya D, Thomas TC, Hildreth DJ, et al. The effects of ProAlgaZyme novel algae infusion on metabolic syndrome and markers of cardiovascular health. Lipids Health Dis. 2007 Sep 5;6:20. [CrossRef]
- Pereira L, Cotas J. Therapeutic Potential of Polyphenols and Other Micronutrients of Marine Origin. Marine Drugs. 2023 Jun;21(6):323. [CrossRef]
- Cantero MA, Guedes MRA, Fernandes R, Lollo PCB. Trimethylamine N-oxide reduction is related to probiotic strain specificity: A systematic review. Nutrition Research. 2022 Aug 1;104:29–35. [CrossRef]
- Olas B. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics—A Promising Strategy in Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020 Jan;21(24):9737.
- Ghanbari F, Hasani S, Aghili ZS, Asgary S. The potential preventive effect of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on cardiovascular risk factors through modulation of gut microbiota: A review. Food Science & Nutrition. 2024;12(7):4569–80. [CrossRef]
- Murphy K, O’Donovan AN, Caplice NM, Ross RP, Stanton C. Exploring the Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Metabolites. 2021 Jul 29;11(8):493. [CrossRef]
- Cunha SA, Pintado ME. Bioactive peptides derived from marine sources: Biological and functional properties. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2022 Jan 1;119:348–70. [CrossRef]
- Freret T, Largilliere S, Nee G, Coolzaet M, Corvaisier S, Boulouard M. Fast Anxiolytic-Like Effect Observed in the Rat Conditioned Defensive Burying Test, after a Single Oral Dose of Natural Protein Extract Products. Nutrients. 2021 Jul 17;13(7):2445. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald AJ, Rai PS, Marchbank T, Taylor GW, Ghosh S, Ritz BW, et al. Reparative properties of a commercial fish protein hydrolysate preparation. Gut. 2005 Jun;54(6):775–81. [CrossRef]
- Langlois LD, Oddoux S, Aublé K, Violette P, Déchelotte P, Noël A, et al. Effects of Glutamine, Curcumin and Fish Bioactive Peptides Alone or in Combination on Intestinal Permeability in a Chronic-Restraint Stress Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 13;24(8):7220.
- Daskalaki MG, Axarlis K, Tsoureki A, Michailidou S, Efraimoglou C, Lapi I, et al. Fish-Derived Protein Hydrolysates Increase Insulin Sensitivity and Alter Intestinal Microbiome in High-Fat-Induced Obese Mice. Mar Drugs. 2023 Jun 2;21(6):343. [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger M, Everard A, Gómez-Valadés AG, Matamoros S, Ramírez S, Delzenne NM, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila inversely correlates with the onset of inflammation, altered adipose tissue metabolism and metabolic disorders during obesity in mice. Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 13;5:16643. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Lin S, Vanhoutte PM, Woo CW, Xu A. Akkermansia Muciniphila Protects Against Atherosclerosis by Preventing Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in Apoe-/- Mice. Circulation. 2016 Jun 14;133(24):2434–46.
- Cheong KL, Yu B, Chen J, Zhong S. A Comprehensive Review of the Cardioprotective Effect of Marine Algae Polysaccharide on the Gut Microbiota. Foods. 2022 Nov 8;11(22):3550. [CrossRef]
- Alves JL de B, Costa PCT da, Sales LCS de, Silva Luis CC, Bezerra TPT, Souza MLA, et al. Shedding light on the impacts of Spirulina platensis on gut microbiota and related health benefits. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Feb 29;1–14.
| Antioxidant Activity | Seaweed polyphenols, especially florotannins and fucoxanthin, exhibit significant antioxidant properties that help inhibit LDL oxidation—a crucial step in the development of atherosclerosis. This activity reduces the formation of foam cells, which contribute to arterial plaque formation [107,111]. |
| Anti-inflammatory Effects | Algal polysaccharides like fucoidan and laminarin demonstrate anti-inflammatory properties that can help lower vascular inflammation. This reduction in inflammation is essential for maintaining CV health and preventing atherosclerosis [111,112,113] |
| Lipid Metabolism Regulation | Fucoidan has been shown to improve lipid profiles by down-regulating genes involved in lipid synthesis (like SREBP1, ACC, and FAS) and up-regulating genes involved in lipid uptake (such as LDL-R). This modulation leads to reduced TC, LDL-C, and TG [112,113] |
| Improvement of Endothelial Function | Seaweed extracts have been linked to improved endothelial function, which is critical for vascular health [111]. |
| Impact on Glucose Metabolism | Compounds like oligosaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera have demonstrated anti-diabetic effects, by enhancing glucose tolerance and reducing blood glucose levels through mechanisms involving the AKT pathway and the inhibition of gluconeogenesis [117,118]. |
| Gut Microbiota Modulation | Some seaweed compounds can alter gut microbiota composition, promoting beneficial bacteria and pathways associated with metabolic health, which may contribute to their anti-obesity effects [115]. |
| Clinical Evidence | Clinical studies, including those on Chlorella and Gdue (a blend of Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus), support the efficacy of these compounds in reducing CVDs risk factors such as fasting blood glucose, LDL-C, and overall metabolic syndrome markers [134,135,136]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





