Submitted:
22 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel explainer called GAN-GNNExplainer, specifically tailored for GNN models. This approach employs a generator to generate explanations and is supervised by a discriminator, ensuring reliable results throughout the procedure.
- Additionally, we introduce ACGAN-GNNExplainer, a more advanced explainer for GNN models. It leverages both a generator and a discriminator, which consistently oversees the procedure, leading to explanations that are both reliable and faithful.
- Our methods are comprehensively evaluated across various graph datasets, spanning both synthetic and real-world data, and across multiple tasks, including node classification and graph classification. The outcomes consistently highlight the advantages of our approach over existing methods.
2. Related Work
2.1. Generative Adversarial Networks
2.2. Graph Neural Networks
2.3. Graph Neural Networks Explainers
3. Method
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Obtaining Causal Real Explanations
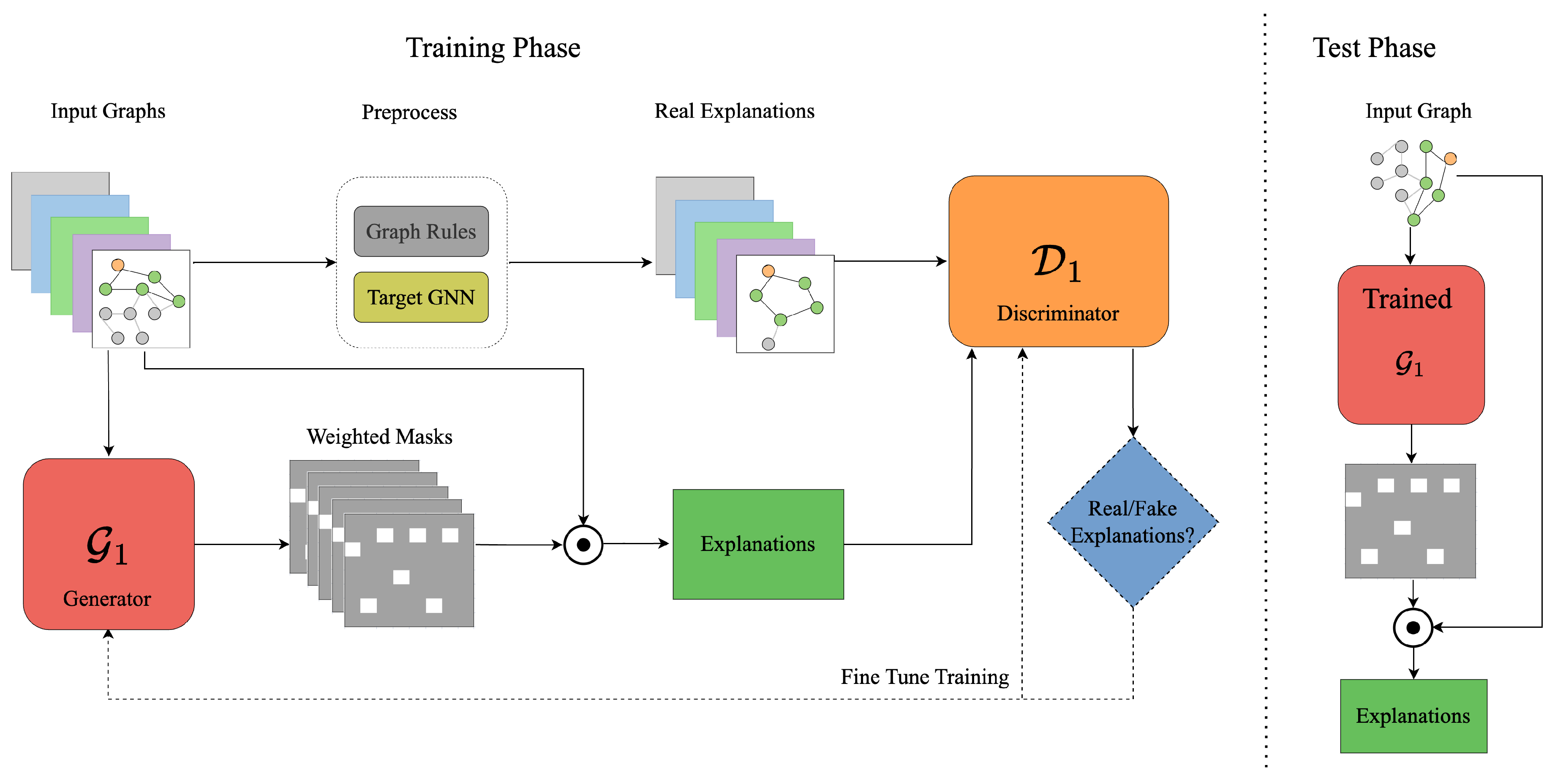
3.3. GAN-GNNExplainer
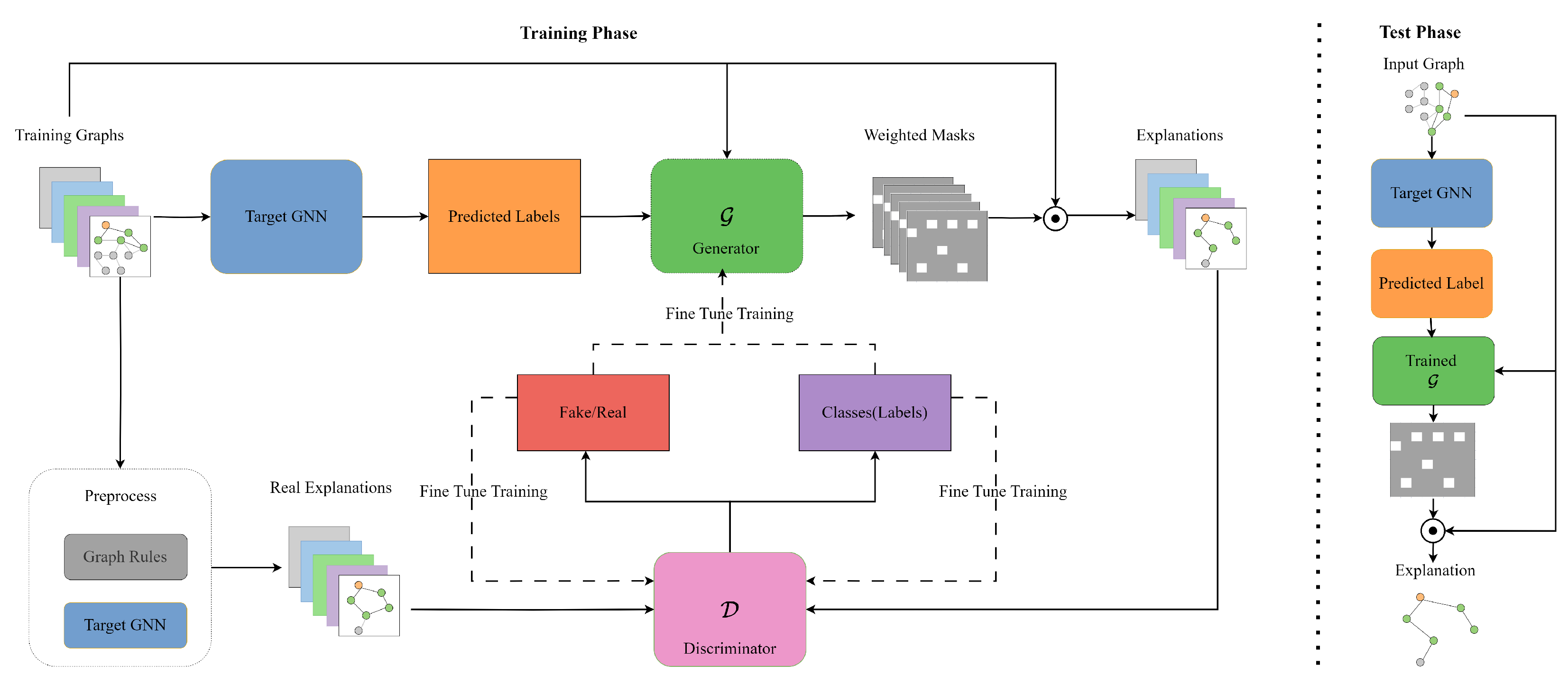
3.4. ACGAN-GNNExplainer
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Evaluation GAN-GNNExplainer
4.2.1. Results on Synthetic Datasets
4.2.2. Results on Real-World Datasets
4.3. Evaluation ACGAN-GNNExplainer
4.3.1. Results on Synthetic Datasets
4.3.2. Results on Real-World Datasets
5. Discussion
- It effectively learns the underlying patterns of graphs, inherently providing explanations at a goal scale.
- Once trained, it can generate explanations for unseen graphs without the need for retraining.
- It consistently produces valid and significant subgraphs due to the ongoing oversight of the discriminator.
- It demonstrates strong performance across various tasks, including node and graph classification.
- Effects of Reliability of Real-World Datasets on Performance: Real-world graph datasets are often affected by nuisance factors, such as noise in node features and graph structures. This consequently affects the performance of GAN-GNNExplainer.
- Absence of Fidelity Considerations: Although fidelity is crucial for faithful explanations, GAN-GNNExplainer does not consider improving that.
- Preprocessing Overhead: The preprocessing step required to distill real explanations for training data imposes significant computational overhead and time constraints.
- High Demand for Training Graphs: The method also requires a substantial number of training graphs to achieve effective performance.
6. Conclusions
References
- Zhou, B.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Z. HDM-GNN: A Heterogeneous Dynamic Multi-view Graph Neural Network for Crime Prediction. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosa, D.; Büskens, C. Low Cost Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search (LENAS) Applied to Traffic Forecasting. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2023, 5, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; de Rijke, M.; Ning, Y. Advances in Human Event Modeling: From Graph Neural Networks to Language Models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2024, Barcelona, Spain, August 25-29, 2024.; pp. 20246459–6469. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Srivastava, G.; Ramanujam, J.; Brylinski, M. Insights from Augmented Data Integration and Strong Regularization in Drug Synergy Prediction with SynerGNet. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2024, 6, 1782–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, P. Funnel graph neural networks with multi-granularity cascaded fusing for protein-protein interaction prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 257, 125030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, U.S.; Zhou, J.; Rasool, A.; Siddeeq, S. Efficient Visual-Aware Fashion Recommendation Using Compressed Node Features and Graph-Based Learning. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2024, 6, 2111–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mourik, F.; Jutte, A.; Berendse, S.E.; Bukhsh, F.A.; Ahmed, F. Tertiary Review on Explainable Artificial Intelligence: Where Do We Stand? Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2024, 6, 1997–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Verda, D.; Berretta, S.; Longo, L. A Novel Integration of Data-Driven Rule Generation and Computational Argumentation for Enhanced Explainable AI. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2024, 6, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, R.; Bourgeois, D.; You, J.; Zitnik, M.; Leskovec, J. GNN Explainer: A Tool for Post-hoc Explanation of Graph Neural Networks. CoRR, 2019; abs/1903.03894, [1903.03894]. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Yamada, M.; Tian, Y.; Singh, D.; Chang, Y. GraphLIME: Local Interpretable Model Explanations for Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Tang, J.; Hu, X.; Ji, S. XGNN: Towards Model-Level Explanations of Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & pp. 2020430–438. [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Cheng, W.; Xu, D.; Yu, W.; Zong, B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. Parameterized Explainer for Graph Neural Network. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, NeurIPS 2020, December 6-12, 2020, virtual; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Lan, H.; Li, B. Generative Causal Explanations for Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2021, 18-24 July 2021, Virtual Event. PMLR, 2021, Vol. 139, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research,; pp. 6666–6679.
- Odena, A.; Olah, C.; Shlens, J. Conditional Image Synthesis with Auxiliary Classifier GANs. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2017, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6-11 August 2017. PMLR, 2017, Vol. 70, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp.; pp. 2642–2651.
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2014, December 8-13 2014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada; 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. CoRR, 2014; abs/1411.1784, [1411.1784]. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Duan, Y.; Houthooft, R.; Schulman, J.; Sutskever, I.; Abbeel, P. InfoGAN: Interpretable Representation Learning by Information Maximizing Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2016, December 5-10 2016, Barcelona, Spain; 2016; pp. 2172–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Al-Turjman, F.M.; Pinheiro, P.R. CovidGAN: Data Augmentation Using Auxiliary Classifier GAN for Improved Covid-19 Detection. CoRR, 2103. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Chen, L.; Dong, L.; Fu, Z.; Cui, X. Imbalanced data classification: A KNN and generative adversarial networks-based hybrid approach for intrusion detection. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 131, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawad, D.M.; Katebi, A.; Hoque, M.T. Enhanced Graph Representation Convolution: Effective Inferring Gene Regulatory Network Using Graph Convolution Network with Self-Attention Graph Pooling Layer. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2024, 6, 1818–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Su, Y.; Su, K.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, C.; Ishi, C.T.; Ishiguro, H. HAM-GNN: A hierarchical attention-based multi-dimensional edge graph neural network for dialogue act classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024; 125459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y. Link Prediction Based on Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2018, NeurIPS, December 3-8, , Montréal, Canada; 2018; pp. 5171–5181. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, J. Graph neural network for traffic forecasting: A survey. Expert Systems with Applications 2022, 207, 117921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, H.; He, J.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, W. An Causal XAI Diagnostic Model for Breast Cancer Based on Mammography Reports. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM); 2021; pp. 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Lan, H.; Wang, H.; Li, B. OrphicX: A Causality-Inspired Latent Variable Model for Interpreting Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2022, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022. IEEE, 2022, June 18-24; pp. 13719–13728. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Tang, J.; Hu, X.; Ji, S. XGNN: Towards Model-Level Explanations of Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the KDD ’20: The 26th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Virtual Event, CA, USA, 2020. ACM, 2020, August 23-27; pp. 430–438. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Feng, F.; He, X.; Chua, T. Reinforced Causal Explainer for Graph Neural Networks. CoRR, 2022; abs/2204.11028, [2204.11028]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, D. Reinforcement Learning Enhanced Explainer for Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, NeurIPS 2021, December 6-14, 2021, virtual; 2021; pp. 22523–22533. [Google Scholar]
- Lucic, A.; ter Hoeve, M.A.; Tolomei, G.; de Rijke, M.; Silvestri, F. CF-GNNExplainer: Counterfactual Explanations for Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, AISTATS 2022, 28-30 March 2022, Virtual Event. PMLR, 2022, Vol. 151, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research,; pp. 4499–4511.
- Bajaj, M.; Chu, L.; Xue, Z.Y.; Pei, J.; Wang, L.; Lam, P.C.; Zhang, Y. Robust Counterfactual Explanations on Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, NeurIPS 2021, December 6-14, 2021, virtual; 2021; pp. 5644–5655. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, A.; He, X.; Chua, T. Towards Multi-Grained Explainability for Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, NeurIPS 2021, December 6-14, 2021, virtual; 2021; pp. 18446–18458. [Google Scholar]
- Granger, C. Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. In Essays in econometrics: Collected papers of Clive WJ Granger; 2001; pp. 31–47.
- Kazius, J.; McGuire, R.; Bursi, R. Derivation and validation of toxicophores for mutagenicity prediction. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2005, 48, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wale, N.; Watson, I.A.; Karypis, G. Comparison of descriptor spaces for chemical compound retrieval and classification. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2008, 14, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Verma, S.; Chen, F. A Survey of Explainable Graph Neural Networks: Taxonomy and Evaluation Metrics. CoRR, 2022; abs/2207.12599, [2207.12599]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Ji, S. On Explainability of Graph Neural Networks via Subgraph Explorations. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2021, 18-24 July 2021, Virtual Event. PMLR, 2021, Vol. 139, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research,; pp. 12241–12252.
| Node Classification | Graph Classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA-Shapes | Tree-Cycles | Mutagenicity | NCI1 | |
| # of Graphs | 1 | 1 | 4,337 | 4110 |
| # of Edges | 4110 | 1950 | 266,894 | 132,753 |
| # of Nodes | 700 | 871 | 131,488 | 122,747 |
| # of Labels | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| K (edges) | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| GNNExplainer | 0.7941 | 0.8824 | 0.9118 | 0.9118 | 0.9118 |
| Gem | 0.9412 | 0.9412 | 0.9412 | 0.9412 | 0.9412 |
| GAN-GNNExplainer | 0.6764 | 0.9706 | 0.9706 | 0.9706 | 0.9412 |
| K (edges) | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| GNNExplainer | 0.2000 | 0.5429 | 0.7143 | 0.8571 | 0.9429 |
| Gem | 0.7142 | 0.8285 | 0.5714 | 0.8285 | 0.9428 |
| GAN-GNNExplainer | 0.9429 | 0.9715 | 0.9429 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| R (edge ratio) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| GNNExplainer | 0.6175 | 0.5968 | 0.6313 | 0.6935 | 0.7811 |
| Gem | 0.5737 | 0.6014 | 0.6590 | 0.7235 | 0.7903 |
| GAN-GNNExplainer | 0.5914 | 0.5956 | 0.6929 | 0.7215 | 0.7598 |
| R (edge ratio) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| GNNExplainer | 0.5961 | 0.6107 | 0.6788 | 0.7616 | 0.8127 |
| Gem | 0.5645 | 0.6083 | 0.6837 | 0.7518 | 0.8321 |
| GAN-GNNExplainer | 0.6375 | 0.6496 | 0.7105 | 0.7616 | 0.7762 |
| K | Metrics | GNNExplainer | Gem | OrphicX | |
| 5 | 0.7941 | 0.9412 | 0.7353 | 0.7941 | |
| 0.7059 | 0.5588 | 0.7941 | 0.6471 | ||
| 0.1471 | 0.000 | 0.2059 | 0.1471 | ||
| 6 | 0.8824 | 0.9706 | 0.7353 | 0.8529 | |
| 0.6765 | 0.5588 | 0.7941 | 0.5882 | ||
| 0.0588 | -0.0294 | 0.2059 | 0.0882 | ||
| 7 | 0.9118 | 0.9706 | 0.8529 | 0.9706 | |
| 0.7059 | 0.5882 | 0.7941 | 0.6176 | ||
| 0.0294 | -0.0294 | 0.0882 | -0.0294 | ||
| 8 | 0.9412 | 0.9706 | 0.8824 | 0.9706 | |
| 0.7353 | 0.5882 | 0.7941 | 0.6471 | ||
| 0.000 | -0.0294 | 0.0588 | -0.0294 | ||
| 9 | 0.9118 | 0.9706 | 0.8824 | 1.000 | |
| 0.7353 | 0.5882 | 0.7941 | 0.6471 | ||
| 0.0294 | -0.0294 | 0.0588 | -0.0588 |
| K | Metrics | GNNExplainer | Gem | OrphicX | |
| 6 | 0.1714 | 0.7143 | 0.9714 | 0.9714 | |
| 0.9143 | 0.9714 | 0.9429 | 0.9714 | ||
| 0.8000 | 0.2571 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | ||
| 7 | 0.5143 | 0.8286 | 0.9714 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.9429 | 0.9714 | 0.9429 | 0.9714 | ||
| 0.4571 | 0.1429 | 0.0000 | 0.0286 | ||
| 8 | 0.8000 | 0.7143 | 1.0000 | 0.9429 | |
| 0.9714 | 0.9714 | 0.9429 | 0.9714 | ||
| 0.1714 | 0.2571 | 0.0286 | 0.0286 | ||
| 9 | 0.9143 | 0.8571 | 1.0000 | 0.9143 | |
| 0.9714 | 0.9714 | 0.9429 | 0.9714 | ||
| 0.0571 | 0.1143 | 0.0286 | 0.0571 | ||
| 10 | 0.9143 | 0.8857 | 1.0000 | 0.9714 | |
| 0.9714 | 0.9714 | 0.9429 | 0.9714 | ||
| 0.0571 | 0.0857 | 0.0286 | 0.0000 |
| R | Metrics | GNNExplainer | Gem | OrphicX | |
| 0.5 | 0.6175 | 0.5737 | 0.4539 | 0.6175 | |
| 0.3618 | 0.3018 | 0.2419 | 0.3963 | ||
| 0.2535 | 0.2972 | 0.4171 | 0.2535 | ||
| 0.6 | 0.5968 | 0.6014 | 0.5599 | 0.6037 | |
| 0.3825 | 0.3295 | 0.2949 | 0.3828 | ||
| 0.2742 | 0.2696 | 0.3111 | 0.2673 | ||
| 0.7 | 0.6313 | 0.659 | 0.6244 | 0.7074 | |
| 0.3963 | 0.2857 | 0.2995 | 0.3986 | ||
| 0.2396 | 0.212 | 0.2465 | 0.1636 | ||
| 0.8 | 0.6935 | 0.7235 | 0.7097 | 0.7673 | |
| 0.3641 | 0.2581 | 0.3157 | 0.3602 | ||
| 0.1774 | 0.1475 | 0.1613 | 0.1037 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.7811 | 0.7903 | 0.8111 | 0.7903 | |
| 0.3641 | 0.212 | 0.2949 | 0.3871 | ||
| 0.0899 | 0.0806 | 0.0599 | 0.0806 |
| R | Metrics | GNNExplainer | Gem | OrphicX | |
| 0.5 | 0.5961 | 0.5645 | 0.562 | 0.6569 | |
| 0.3358 | 0.3796 | 0.3114 | 0.4015 | ||
| 0.2749 | 0.3066 | 0.309 | 0.2141 | ||
| 0.6 | 0.6107 | 0.6083 | 0.6496 | 0.6496 | |
| 0.3625 | 0.4307 | 0.3431 | 0.4523 | ||
| 0.2603 | 0.2628 | 0.3236 | 0.2214 | ||
| 0.7 | 0.6788 | 0.6837 | 0.6083 | 0.6861 | |
| 0.3844 | 0.4282 | 0.3382 | 0.4453 | ||
| 0.1922 | 0.1873 | 0.2628 | 0.1849 | ||
| 0.8 | 0.7616 | 0.7518 | 0.708 | 0.7932 | |
| 0.3747 | 0.4404 | 0.3698 | 0.4672 | ||
| 0.1095 | 0.1192 | 0.163 | 0.0779 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.8127 | 0.8321 | 0.8102 | 0.8446 | |
| 0.3236 | 0.3212 | 0.3139 | 0.3942 | ||
| 0.0584 | 0.0389 | 0.0608 | 0.0254 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





