Submitted:
13 October 2024
Posted:
14 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
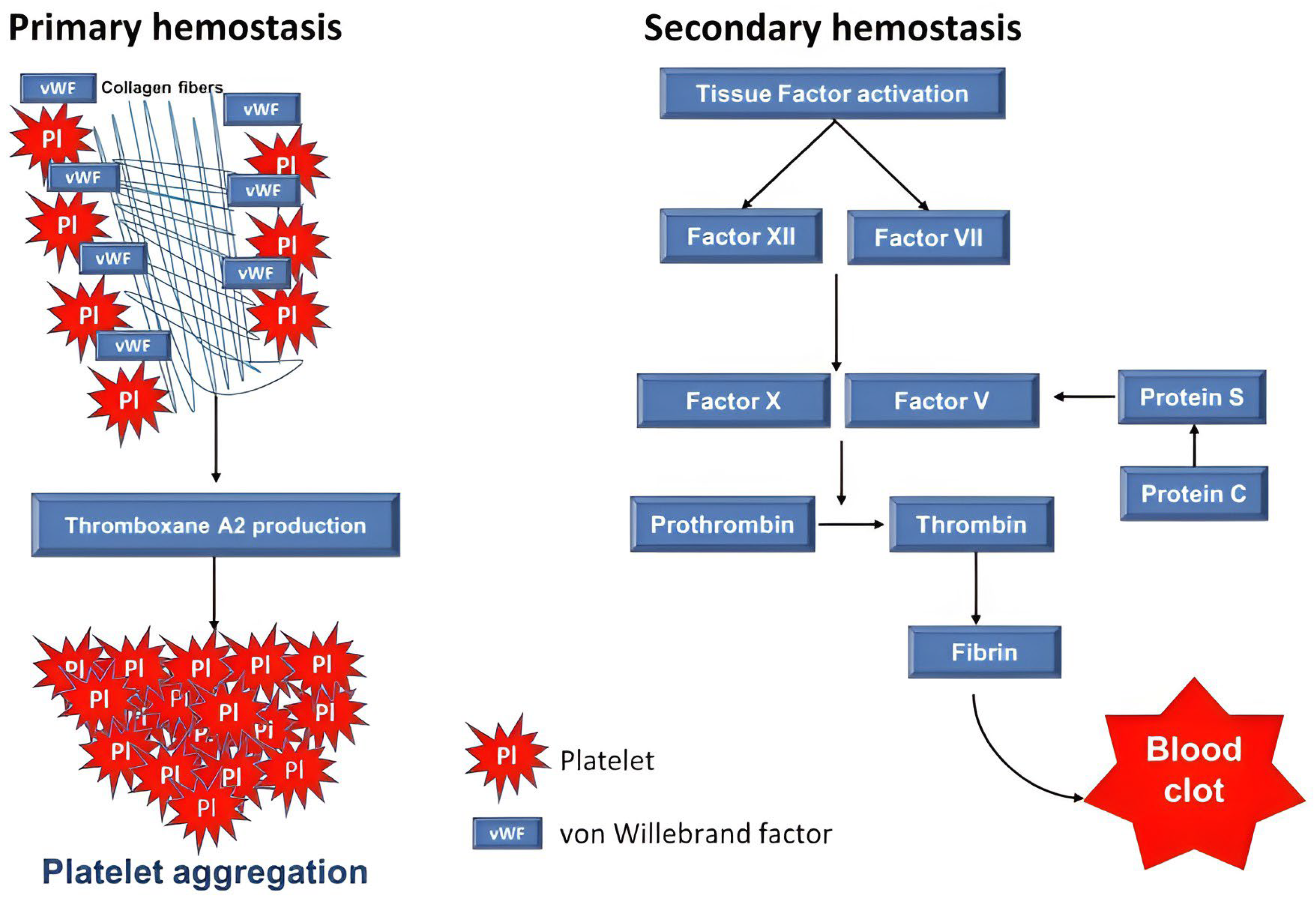
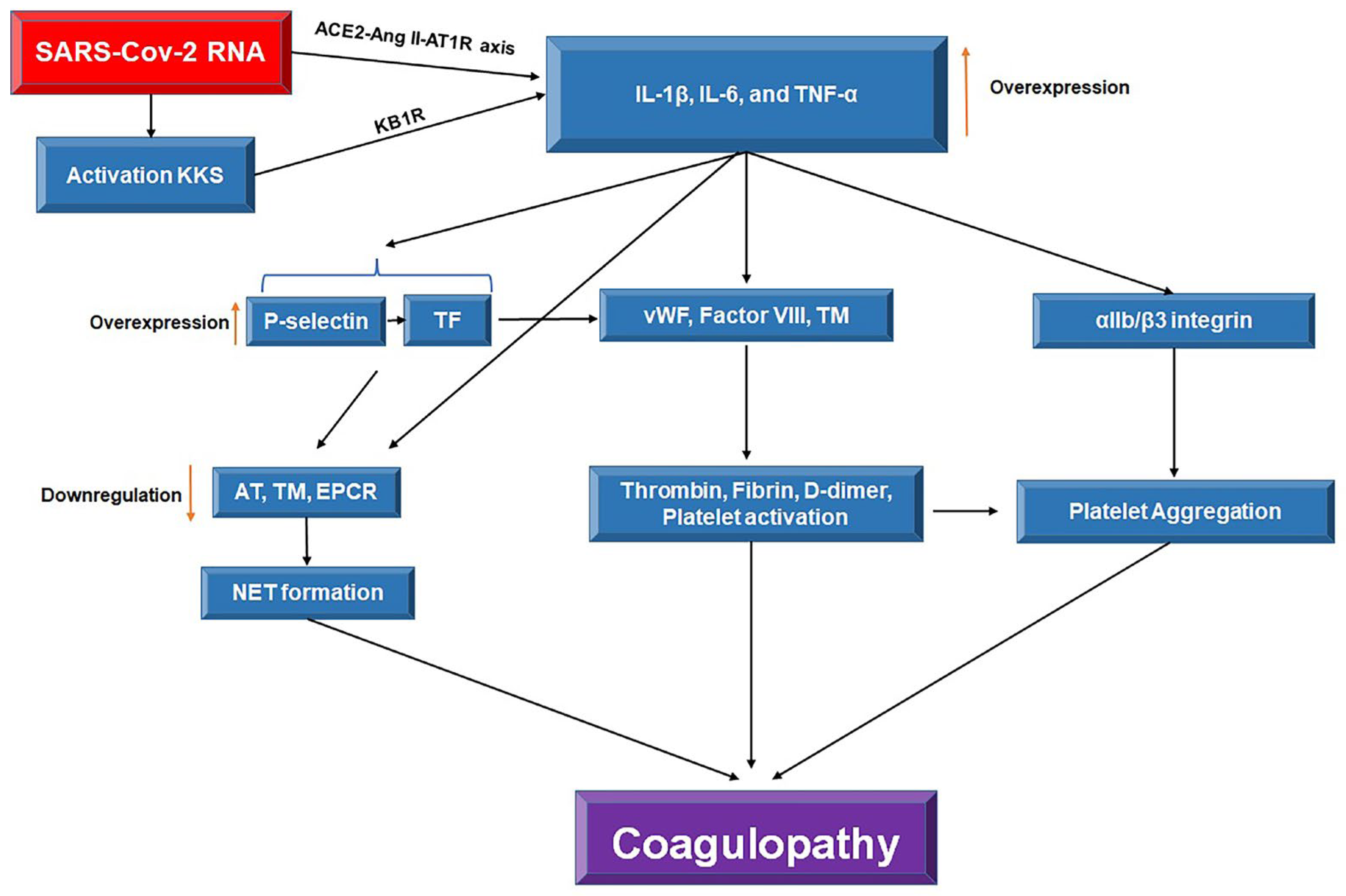
3. Mechanisms of Inflammation and Coagulopathy in Severe COVID-19
3.1. Entry and Life Cycle of SARS-CoV-2 Virus
3.2. SARS-CoV-2-Induced Coagulopathy
3.3. SARS-CoV-2-Induced Inflammation
3.4. The Crosstalk Between Inflammation and Coagulation
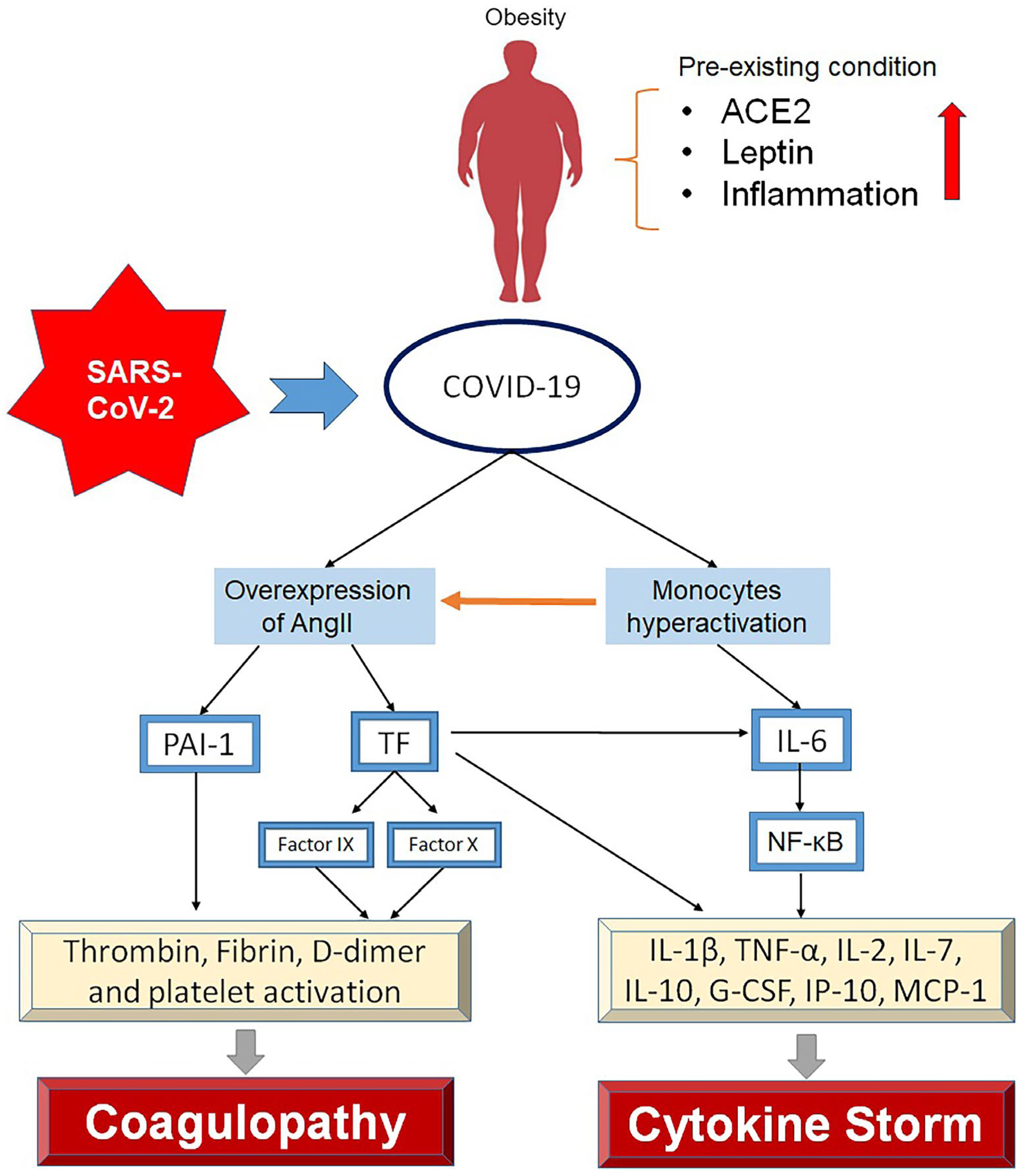
4. Hyperinflammation and Coagulation in COVID-19 Patients with Obesity
4.1. Overexpression of ACE2
4.1. Leptin
4.1. Pre-Existing Inflammation
5. Therapeutic Approach in COVID-19 Patients with Obesity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Organization, W.H. Number of COVID-19 deaths reported to WHO. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=c (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Alimohamadi, Y.; Sepandi, M.; Taghdir, M.; Hosamirudsari, H. Determine the most common clinical symptoms in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2020, 61, E304–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castilla, J.; Guevara, M.; Miqueleiz, A.; Baigorria, F.; Ibero-Esparza, C.; Navascués, A.; Trobajo-Sanmartín, C.; Martínez-Baz, I.; Casado, I.; Burgui, C.; et al. Risk Factors of Infection, Hospitalization and Death from SARS-CoV-2: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, B.L.H.; Chidambaram, S.K.; Wong, X.C.; Pathmanathan, M.D.; Peariasamy, K.M.; Hor, C.P.; Chua, H.J.; Goh, P.P. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe COVID-19 infections in Malaysia: A nationwide observational study. Lancet Reg. Heal. - West. Pac. 2020, 4, 100055–100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fericean, R.M.; Citu, C.; Manolescu, D.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; Tudorache, E.; Oancea, C. Characterization and Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Overweight and Obese Patients: A Dynamic Comparison of COVID-19 Pandemic Waves. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, S.M.M.; Ebrahimpur, M.; Arjmand, B.; Shadman, Z.; Sani, M.P.; Qorbani, M.; Larijani, B.; Payab, M. Obesity in COVID-19 era, implications for mechanisms, comorbidities, and prognosis: a review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renovato-Martins, M.; Moreira-Nunes, C.; Atella, G.C.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; de Moraes, J.A. Obese Adipose Tissue Secretion Induces Inflammation in Preadipocytes: Role of Toll-Like Receptor-4. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chi, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19). Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 37, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, C.M.; Jones, S.A.; Yang, J.; Rajagopalan, H.; O’donnell, L.; Chernyak, Y.; Tobin, K.A.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Francois, F.; Horwitz, L.I. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighter, J.; Phillips, M.; Hochman, S.; Sterling, S.; Johnson, D.; Francois, F.; Stachel, A. Obesity in Patients Younger Than 60 Years Is a Risk Factor for COVID-19 Hospital Admission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonnet, A.; Chetboun, M.; Poissy, J.; Raverdy, V.; Noulette, J.; Duhamel, A.; Labreuche, J.; Mathieu, D.; Pattou, F.; Jourdain, M. High prevalence of obesity in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Obesity 2020, 28, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, M.; Arulappen, A.L.; Soelar, S.A.; Ch’ng, A.S.H.; Looi, I. Clinical Characteristics of Individuals Died with COVID-19 in Malaysia. Malays. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 20, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Rubin, L.; Peng, T.; Liu, L.; Xing, X.; Lazarovici, P.; Zheng, W. Cytokine storm in COVID-19: from viral infection to immune responses, diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, L.; You, R. Physiological and pathological regulation of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104833–104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periayah, M.H.; Halim, A.S.; Mat Saad, A.Z. Mechanism Action of Platelets and Crucial Blood Coagulation Pathways in Hemostasis. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 11, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Palta, S.; Saroa, R.; Palta, A. Overview of the coagulation system. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiral, J.; Seghatchian, J. Revisiting the activated protein C-protein S-thrombomodulin ternary pathway: Impact of new understanding on its laboratory investigation. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, D.; Huang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, Y. Thrombomodulin (TM), thrombin-antithrombin complex (TAT), plasmin-α2-plasmininhibitor complex (PIC), and tissue plasminogen activator-inhibitor complex (t-PAIC) assessment of fibrinolytic activity in postpartum hemorrhage: a retrospective comparative cohort study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1273–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbarao, K.; Mahanty, S. Respiratory Virus Infections: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity 2020, 52, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompetchara, E.; Kettoy, C.; Palaga, T. Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: Lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudia, N.-T.; Ana, F.-G.; Esther Moreno, M.; Belen, P.-M.; Jesús, V.; Sandra, C.; Javier, L.-J.; Palacios, J.; Miguel, P.-V.; Mónica, G.-C. Secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in COVID-19: correlation of the autopsy findings of bone marrow haemophagocytosis with HScore. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 75, 383. [Google Scholar]
- Abdin, S.M.; Elgendy, S.M.; Alyammahi, S.K.; Alhamad, D.W.; Omar, H.A. Tackling the cytokine storm in COVID-19, challenges and hopes. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118054–118054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, N.; Antoniak, S.; Wolberg, A.S.; Kasthuri, R.; Key, N.S. Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and other pandemic viruses. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lowry, J.L.; Brovkovych, V.; Skidgel, R.A. Characterization of dual agonists for kinin B1 and B2 receptors and their biased activation of B2 receptors. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrati, C.; Sacchi, A.; Tartaglia, E.; Vergori, A.; Gagliardini, R.; Scarabello, A.; Bibas, M. The Role of P-Selectin in COVID-19 Coagulopathy: An Updated Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzynski, L.C.; Morales-Maldonado, A.; Rodgers, A.; Kitt, L.A.; Humphry, M.; Figg, N.; Bennett, M.R.; Clarke, M.C.H. Thrombin-activated interleukin-1α drives atherogenesis, but also promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and collagen production. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosad, E.; Elsayh, K.I.; Eltayeb, A.A. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor and P-Selectin as Markers of Sepsis-Induced Non-overt Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2009, 17, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottz, E.D.; Azevedo-Quintanilha, I.G.; Palhinha, L.; Teixeira, L.; Barreto, E.A.; Pão, C.R.R.; Righy, C.; Franco, S.; Souza, T.M.L.; Kurtz, P.; et al. Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekholm, M.; Kahan, T. The Impact of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System on Inflammation, Coagulation, and Atherothrombotic Complications, and to Aggravated COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 640185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottz, E.D.; Azevedo-Quintanilha, I.G.; Palhinha, L.; Teixeira, L.; Barreto, E.A.; Pão, C.R.R.; Righy, C.; Franco, S.; Souza, T.M.L.; Kurtz, P.; et al. Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, J. Endothelial dysfunction and COVID-19 (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2021, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, D.; Xiong, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, F.; Zou, L.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, Y. Elevated Expression of Serum Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecules in COVID-19 Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gando, S.; Wada, T. Thromboplasminflammation in COVID-19 Coagulopathy: Three Viewpoints for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 649122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darif, D.; Hammi, I.; Kihel, A.; El Idrissi Saik, I.; Guessous, F.; Akarid, K. The pro-inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 pathogenesis: What goes wrong? Microb. Pathog. 2021, 153, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Jiménez, P.; Méndez, R.; Latorre, A.; Piqueras, M.; Balaguer-Cartagena, M.N.; Moscardó, A.; Alonso, R.; Hervás, D.; Reyes, S.; Menéndez, R. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Platelet Activation for Identifying Severe Episodes and Clinical Trajectories in COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Puri, B.K.; Olive, L.; Marx, W.; O’Neil, A.; Athan, E.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M.; Walder, K.; et al. The pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: A suggested model and therapeutic approach. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gando, S.; Levi, M.; Toh, C.-H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gando, S.; Fujishima, S.; Saitoh, D.; Shiraishi, A.; Yamakawa, K.; Kushimoto, S.; Ogura, H.; Abe, T.; Mayumi, T.; Sasaki, J.; et al. The significance of disseminated intravascular coagulation on multiple organ dysfunction during the early stage of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadid, T.; Kafri, Z.; Al-Katib, A. Coagulation and anticoagulation in COVID-19. Blood Rev. 2020, 47, 100761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norooznezhad, A.H.; Mansouri, K. Endothelial cell dysfunction, coagulation, and angiogenesis in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Microvasc. Res. 2021, 137, 104188–104188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.P.; Mackman, N. Tissue factor in atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis. Atherosclerosis 2020, 307, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, A.; Havervall, S.; Von Meijenfeldt, F.; Hisada, Y.; Aguilera, K.; Grover, S.P.; Lisman, T.; Mackman, N.; Thålin, C. Patients With COVID-19 Have Elevated Levels of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Tissue Factor Activity That Is Associated With Severity and Mortality—Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, N.I.; Lupu, C.; Lupu, F. Disseminated intravascular coagulation and its immune mechanisms. Blood 2021, 139, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, Z.; Naeimzadeh, Y.; Fallahi, J.; Savardashtaki, A.; Razban, V.; Khajehا, S. The Role of Tissue Factor In Signaling Pathways of Pathological Conditions and Angiogenesis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2024, 24, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Brasil, A.F.; Ferreira, T.L.; Fernandes-Braga, W.; Marconato, D.G.; Faria-Pinto, P.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I.; Capettini, L.d.S.A.; Klein, A. Protease-activated receptor 2 enhances innate and inflammatory mechanisms induced by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages from C57BL/6 mice. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posma, J.J.; Grover, S.P.; Hisada, Y.; Owens III, A.P.; Antoniak, S.; Spronk, H.M.; Mackman, N. Roles of coagulation proteases and PARs (protease-activated receptors) in mouse models of inflammatory diseases. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikezoe, T. Thrombomodulin/activated protein C system in septic disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Intensiv. Care 2015, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Cohen, C.T.; Zobeck, M.; Jacobi, P.M.; Sartain, S.E. Downregulation of thrombomodulin-thrombin-activated protein C pathway as a mechanism for SARS-CoV-2 induced endotheliopathy and microvascular thrombosis. Thromb. Update 2022, 8, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugno, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Gualtierotti, R.; Griffini, S.; Grovetti, E.; Torri, A.; Lonati, P.; Grossi, C.; Borghi, M.O.; Novembrino, C.; et al. Complement activation and endothelial perturbation parallel COVID-19 severity and activity. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 116, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciola, R.; Cacciola, E.G.; Vecchio, V.; Cacciola, E. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in COVID-19 coagulopathy: role of inflammation and endotheliopathy. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 53, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzaruso, C.; Paolozzi, E.; Valenti, C.; Brocchetta, M.; Naldani, D.; Grignani, C.; Salvucci, F.; Marino, F.; Coppola, A.; Gallotti, P. Association between antithrombin and mortality in patients with COVID-19. A possible link with obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaklı. ; Özcan, P.E.; Polat,.; Orhun, G.; Alay, G.H.; Tuna, V.; Çeliksoy, E.; Kılıç, M.; Mercan, M.; Ali, A.; et al. Prognostic Value of Antithrombin Levels in COVID-19 Patients and Impact of Fresh Frozen Plasma Treatment: A Retrospective Study. Turk. J. Hematol. 2021, 38, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.K.; Mayman, N.A.; Dhamoon, M.S.; Fifi, J.T. The emerging association between COVID-19 and acute stroke. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, A.M.E. D-dimer as a predictive and prognostic marker among COVID-19 patients. SciVee 2022, 43, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Mesa, J.E.; Galindo-Coral, S.; Montes, M.C.; Martin, A.J.M. Thrombosis and Coagulopathy in COVID-19. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100742–100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Diabetes, obesity, metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: the end of the beginning. Cell Metabolism 2021, 33, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, D.A.; Duggal, P.; Cingolani, O. Obesity could shift severe COVID-19 disease to younger ages. Lancet 2020, 395, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, B.S.; Siguret, V.; Veyradier, A. Understanding pathophysiology of hemostasis disorders in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Rathore, S.S.; Khan, H.; Karale, S.; Chawla, Y.; Iqbal, K.; Bhurwal, A.; Tekin, A.; Jain, N.; Mehra, I.; et al. Association of Obesity With COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: An Updated Systemic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 780872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, K.I.; Wang, X.-B.; Sun, Q.-F.; Pan, K.-H.; Wang, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-P.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; George, J.; et al. Obesity Is a Risk Factor for Greater COVID-19 Severity. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, e72–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Lockey, R.F.; Kolliputi, N. Soluble ACE2 as a potential therapy for COVID-19. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021, 320, C279–C281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Benna, S. Association of high level gene expression of ACE2 in adipose tissue with mortality of COVID-19 infection in obese patients. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100283–100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Timens, W.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Navis, G.J.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bolling, M.C.; Dijkstra, G.; Voors, A.A.; Osterhaus, A.D. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ji, Y.; Kersten, S.; Qi, L. Mechanisms of Inflammatory Responses in Obese Adipose Tissue. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 261–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.I.; Mittendorfer, B.; Klein, S. Metabolically healthy obesity: facts and fantasies. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3978–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Gollapudi, S.; Su, H.; Gupta, S. Leptin activates human B cells to secrete TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 via JAK2/STAT3 and p38MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, A.G.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Carreira, M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hribal, M.L.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Sesti, G. Role of C Reactive Protein (CRP) in Leptin Resistance. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acedo, S.C.; Gambero, S.; Cunha, F.G.P.; Lorand-Metze, I.; Gambero, A. Participation of leptin in the determination of the macrophage phenotype: an additional role in adipocyte and macrophage crosstalk. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. - Anim. 2013, 49, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Voort, P.H.; Moser, J.; Zandstra, D.F.; Kobold, A.C.M.; Knoester, M.; Calkhoven, C.F.; Hamming, I.; van Meurs, M. Leptin levels in SARS-CoV-2 infection related respiratory failure: A cross-sectional study and a pathophysiological framework on the role of fat tissue. Heliyon 2020, 6, 04696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.A.; Ahmed, M.; Singh, D.K.; Choreño-Parra, J.A.; Cole, J.; Jiménez-Álvarez, L.A.; Rodríguez-Reyna, T.S.; Singh, B.; Gonzalez, O.; Carrion, R.; et al. IFN signaling and neutrophil degranulation transcriptional signatures are induced during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, K.; Botelho, N.K.; Chisholm, D.J.; Lord, R.V. Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue Gene Expression of Serum Adipokines That Predict Type 2 Diabetes. Obesity 2010, 18, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, L.; Al-Jaber, H.; Prince, M.S.; Elrayess, M.A. Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, Growth Factors and Adipokines in Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance. Inflammation 2021, 45, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illán-Gómez, F.; Gonzálvez-Ortega, M.; Orea-Soler, I.; Alcaraz-Tafalla, M.S.; Aragón-Alonso, A.; Pascual-Díaz, M.; Pérez-Paredes, M.; Lozano-Almela, M.L. Obesity and Inflammation: Change in Adiponectin, C-Reactive Protein, Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-6 After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalakis, K.; Ilias, I. SARS-CoV-2 infection and obesity: Common inflammatory and metabolic aspects. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. : Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M. Cytokine storm and immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19: Role of chloroquine and anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105982–105982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, M.G.R.; Palfreeman, M.; Setzu, N.; Sanchez, M.A.; Portillo, P.S.; Garza, K.M.; Gosselink, K.L.; Spencer, C.T. Obesity Exacerbates the Cytokine Storm Elicited by Francisella tularensis Infection of Females and Is Associated with Increased Mortality. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanga, D.; De Marco, C.; Guerriero, I.; Colelli, F.; Rinaldo, N.; Scrima, M.; Mirante, T.; De Vitis, C.; Zoppoli, P.; Ceccarelli, M.; et al. The Akt1/IL-6/STAT3 pathway regulates growth of lung tumor initiating cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42667–42686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Li, J.; Che, Y.-Q. CXCL8 gene silencing promotes neuroglial cells activation while inhibiting neuroinflammation through the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB-signaling pathway in mice with ischemic stroke. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7341–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terroni, B.; Lopes, J.R.; Chin, C.M.; Dos Santos, J.L. Pleiotropic Effects of Nitric Oxide on SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Coronaviruses 2021, 2, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montalvá, A.; Sellarés-Nadal, J.; Espinosa-Pereiro, J.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Salvador, F.; Durà, X.; Miarons, M.; Antón, A.; Eremiev-Eremiev, S. Early outcomes in adults hospitalized with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection receiving tocilizumab. Med. Clínica (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 158, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Reidy, L.; Romero, M.; Diaz, A.; Cray, C.; Kahl, K.; Blomberg, B.B. The majority of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients with obesity are autoimmune and not neutralizing. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndwandwe, D.; Wiysonge, C.S. COVID-19 vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 71, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, Z.; Akçin, R.; Demir, A.N.; Dinç, H.Ö.; Taşkın, H.E.; Kocazeybek, B.; Yumuk, V.D. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in People with Severe Obesity. Obes. Surg. 2022, 32, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Mizoue, T.; Tanaka, A.; Oshiro, Y.; Inamura, N.; Konishi, M.; Ozeki, M.; Miyo, K.; Sugiura, W.; Sugiyama, H.; et al. Sex-associated differences between BMI and SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers following the BNT162b2 vaccine. Obesity 2022, 30, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, J.M.; Hybertson, B.M.; Cota-Gomez, A.; Gao, B. Nrf2 activator PB125® as a carnosic acid-based therapeutic agent against respiratory viral diseases, including COVID-19. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 175, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Doan, L.H.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Chu, L.-W.; Shi, T.-H.; Lee, Y.-R.; Wu, C.-T.; Lin, C.-H.; Chiang, S.-T.; Liu, H.-K.; et al. Honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) and Huangqi (Astragalus membranaceus) Suppress SARS-CoV-2 Entry and COVID-19 Related Cytokine Storm in Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 765553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalil, A.C.; Patterson, T.F.; Mehta, A.K.; Tomashek, K.M.; Wolfe, C.R.; Ghazaryan, V.; Marconi, V.C.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Hsieh, L.; Kline, S.; et al. Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Munafò, A.; Augello, E.; Bellanca, C.M.; Bonomo, C.; Ceccarelli, M.; Musso, N.; Cantarella, G.; Cacopardo, B.; Bernardini, R. Sarilumab Administration in COVID-19 Patients: Literature Review and Considerations. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tleyjeh, I.M.; Kashour, Z.; Damlaj, M.; Riaz, M.; Tlayjeh, H.; Altannir, M.; Altannir, Y.; Al-Tannir, M.; Tleyjeh, R.; Hassett, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in COVID-19 patients: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




