Submitted:
12 September 2024
Posted:
13 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Sample Collection, Lipid Profile, CRP, and PON-1 Activity
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Data
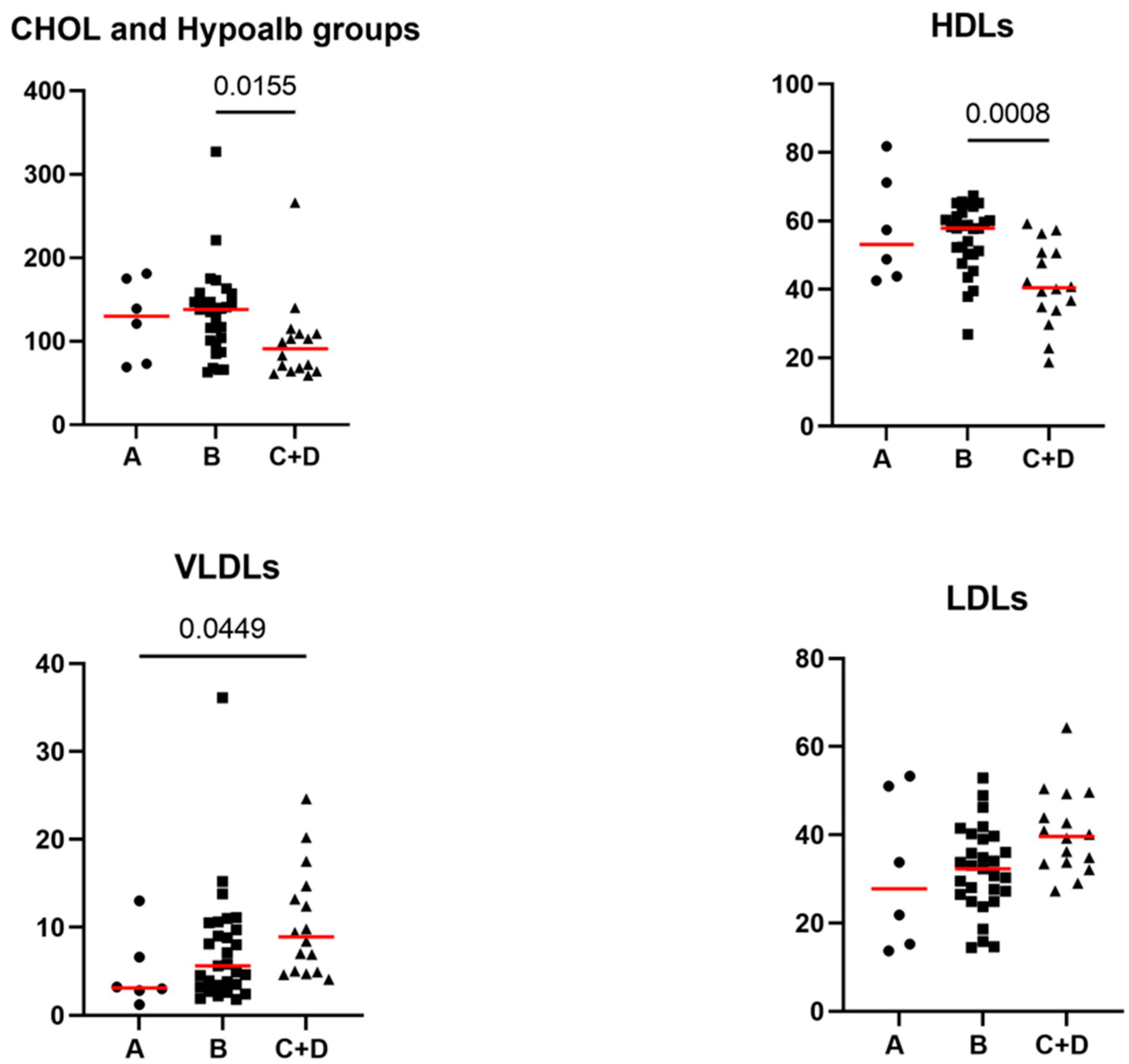
3.2. Comparative Evaluation of the Lipid Profile and Other Laboratory Parameters between Healthy Control Dogs and iPLE Dogs
3.3. Correlations of the CRP with CCECAI Scores, Histopathological Findings, and Prednisolone Therapy
3.4. Correlations of the Lipid Profile with Age, Gender, Body Weight, CCECAI Score, Alb, CRP, and PON-1 Activity Concentrations
3.5. Correlations of the Lipid Profile with Histopathological Findings, Prednisolone Therapy and Diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dossin, O.; Lavoué, R. Protein-losing enteropathies in dogs. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, M.D.; Washabau, R.J. Comparative pathophysiology and management of protein-losing enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenspach, K.; Iennarella-Servantez, C. Canine Protein Losing Enteropathies and Systemic Complications. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 11–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovenská, E.; Rovenský, J. Lymphatic vessels: structure and function. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2011, 13, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craven, M.; Simpson, J.W.; Ridyard, A.E.; Chandler, M.L. Canine inflammatory bowel disease: retrospective analysis of diagnosis and outcome in 80 cases (1995-2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kull, P.A.; Hess, R.S.; Craig, L.E.; Saunders, H.M.; Washabau, R.J. Clinical, clinicopathologic, radiographic, and ultrasonographic characteristics of intestinal lymphangiectasia in dogs: 17 cases (1996-1998). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, P.; Lotti, U.; Bellino, C.; Bresciani, F.; Cagnasso, A.; Fracassi, F.; D’Angelo, A.; Pietra, M. Clinicopathologic and prognostic factors in short- and long-term surviving dogs with protein-losing enteropathy. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2017, 159, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.W. , Jergens, A.E. Pitfalls and progress in the diagnosis and management of canine inflammatory bowel disease. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmerson, S.M.; Armstrong, P.J.; Wünschmann, A.; Jessen, C.R.; Crews, L.J.; Washabau, R.J. Clinical features, intestinal histopathology, and outcome in protein-losing enteropathy in Yorkshire Terrier dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.S.; Ganta, V.C.; Grisham, M.B. Emerging roles of lymphatics in inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, Suppl 1, E75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavati Schmitz, S.; Gow, A.; Bommer, N.; Morrison, L.; Mellanby, R. Diagnostic features, treatment, and outcome of dogs with inflammatory protein-losing enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandrieux, J.R.S.; Noble, P.J.M.; Scase, T.J.; Cripps, P.J.; German, A.J. Comparison of a chlorambucil-prednisolone combination with an azathioprine-prednisolone combination for treatment of chronic enteropathy with concurrent protein-losing enteropathy in dogs: 27 cases (2007–2010). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 242, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Hiyoshi, S.; Ohno, K.; Uchida, K.; Goto-Koshino, Y.; Maeda, S.; Mizutani, N.; Takeuchi, A.; Tsujimoto, H. Prognostic factors in dogs with protein-losing enteropathy. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanishi, H.; Yoshioka, R.; Kagawa, Y.; Watari, T. The clinical efficacy of dietary fat restriction in treatment of dogs with intestinal lymphangiectasia. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 809–81715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudinsky, A.J.; Howard, J.P.; Bishop, M.A.; Sherding, R.G.; Parker, V.J.; Gilor, C. Dietary management of presumptive protein-losing enteropathy in Yorkshire terriers. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 58, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, S.A. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of canine intestinal lymphangiectasia: a comparative review. Animals (Basel). 2022, 12, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.; Kathrani, A. Incidence of relapse of inflammatory protein-losing enteropathy in dogs and associated risk factors. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Nagata, N.; Yokoyama, N.; Osuga, T.; Sasaki, N.; Morishita, K.; Takiguchi, M. Prognostic value of small intestinal dilatation in dogs with protein-losing enteropathy. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 11, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenspach, K.; Rizzo, J.; Jergens, A.E.; Chang, Y.M. Hypovitaminosis D is associated with negative outcome in dogs with protein losing enteropathy: a retrospective study of 43 cases. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleutjes, J.A.M.; Roeters van Lennep, J.E.; van der Woude, C.J.; de Vries, A.C. Lipid Changes After Induction Therapy in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Effect of Different Drug Classes and Inflammation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agouridis, A.P.; Elisaf, M.; Milionis, H.J. An overview of lipid abnormalities in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2011, 24, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ripollés-Piquer, B.R.; Nazih, H.; Bourreille, A.; Segain, J.P.; Huvelin, J.M.; Galmiche, J.P.; Bard, J.M. Altered lipid, apolipoprotein, and lipoprotein profiles in inflammatory bowel disease: consequences on the cholesterol efflux capacity of serum using Fu5AH cell system. Metabolism 2006, 55, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutroumpakis, E.; Ramos-Rivers, C.; Regueiro, M.; Hashash, J.G.; Barrie, A.; Swoger, J.; Baidoo, L.; Schwartz, M.; Dunn, M.A.; Koutroubakis, J.E.; Binion, D.G. Association Between Long-Term Lipid Profiles and Disease Severity in a Large Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kullo, I.J.; Pardi, D.S.; Loftus, E.V. Epidemiology, risk factors and management of cardiovascular diseases in IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammalkorpi, K.T.; Valtonen, V.V.; Maury, CP. Lipoproteins and acute phase response during acute infection. Interrelationships between C-reactive protein and serum amyloid-A protein and lipoproteins. Ann. Med. 1990, 22, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanato, G.; Scarpa, M.; Angriman, I.; Faggian, D.; Ruffolo, C.; Marin, R.; Zambon, S.; Basato, S.; Zanoni, S.; Filosa, T.; Pilon, F.; Manzato, E. Plasma lipids and inflammation in active inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Nordan, R.P.; McIntosh, J.; Calvo, J.C.; Scow, R.O.; Jablons, D. Interleukin 6 reduces lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue of mice in vivo and in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: a possible role for interleukin 6 in cancer cachexia. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 4113–4116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szczeklik, K.; Mach, T.; Cibor, D.; Owczarek, D.; Sapa, J.; Papież, M.; Pytko-Polończyk, J.; Krzyściak, W. Correlation of Paraoxonase-1 with the Severity of Crohn’s Disease. Molecules. 2018, 23, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, D.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Neubauer, K.; Matusiewicz, M.; Berdowska, I.; Zielinski, B.; Paradowski, L.; Gamian, A. Paraoxonase-1 status in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Cammarata, P.J.; Walzem, R.L.; Macfarlane, R.D.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Novel lipoprotein density profiling in healthy dogs of various breeds, healthy Miniature Schnauzers, and Miniature Schnauzers with hyperlipidemia. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, M.S.; Boon, G.D.; Rebar, A.H.; Ford, R.B. Effects of acute pancreatitis on circulating lipids in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1987, 48, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gianella, P.; Caccamo, R.; Bellino, C.; Bottero, E.; Fietta, F.; Roncone, S.; Ostanello, F.; Pietra, M.; Buracco, P. Evaluation of metabolic profile and C-reactive protein concentrations in brachycephalic dogs with upper airway obstructive syndrome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behling-Kelly, E. Serum Lipoprotein Changes in Dogs with Renal Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibba, F.; Rossi, G.; Meazzi, S.; Giordano, A.; Paltrinieri, S. Serum concentration of high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) in leishmaniotic dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 98, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.A.; Donovan, E.F.; Kociba, G.J. Lipids and lipoproteins in normal dogs and in dogs with secondary hyperlipoproteinemia. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1975, 166, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, H.; Sako, T.; Arai, N.; Kuriyama, K.; Yoshimura, I.; Mori, A.; Iwase, K.; Hirose, H. Application of gel permeation HPLC for lipoprotein profiling in dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Kuleš, J.; Rafaj, R.B.; Mrljak, V.; Lauzi, S.; Giordano, A.; Paltrinieri, S. Relationship between paraoxonase 1 activity and high-density lipoprotein concentration during naturally occurring babesiosis in dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jergens, A.E.; Schreiner, C.A.; Frank, D.E.; Niyo, Y.; Ahrens, F.E.; Eckersall, P.D.; Benson, T.J.; Evans, R. A scoring index for disease activity in canine inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Berghoff, N.; Mansell, J.; Grützner, N.; Parnell, N.K.; Gurtner, C.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Association of fecal calprotectin concentrations with disease severity, response to treatment, and other biomarkers in dogs with chronic inflammatory enteropathies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.U.; Ohta, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Osuga, T.; Morishita, K.; Sasaki, N.; Takiguchi, M. Plasma amino acid profiles in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equilino, M.; Théodoloz, V.; Gorgas, D.; Doherr, M.G.; Heilmann, R.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Burgener, I.A. Evaluation of serum biochemical marker concentrations and survival time in dogs with protein-losing enteropathy. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.; Giordano, A.; Pezzia, F.; Kjelgaard-Hansen, M.; Paltrinieri, S. ; Serum paraoxonase 1 activity in dogs: Preanalytical and analytical factors and correlation with C-reactive protein and alpha-2-globulin. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 42, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretón, E.; Cerón, J.J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Acute phase proteins and markers of oxidative stress to assess the severity of the pulmonary hypertension in heartworm-infected dogs. Parasit. Vectors. 2017, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washabau, R.J.; Day, M.J.; Willard, M.D.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.E.; Mansell, J.; Minami, T.; Bilzer, T.W.; WSAVA International Gastrointestinal Standardization Group; et al. Endoscopic, biopsy, and histopathologic guidelines for the evaluation of gastrointestinal inflammation in companion animals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, K; Wieland, B.; Gröne, A.; Gaschen, F. Chronic enteropathies in dogs: evaluation of risk factors for negative outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathrani, A.; Parkes, G. A Preliminary Study of Modulen IBD Liquid Diet in Hospitalized Dogs with Protein-Losing Enteropathy. Animals. 2022, 12, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, F.H.; Behling-Kelly, E.; Borjesson, D.L. Lipoprotein profile of pleural and peritoneal transudates in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling-Kelly, E. Comparison of 2 electrophoretic methods and a wet-chemistry method in the analysis of canine lipoproteins. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 45, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, A.; Yamasaki, M.; Takasaki, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Abe, R.; Shimizu, H.; Ohta, H.; Takiguchi, M. Lc-ms/ms analysis of canine lipoproteins fractionated using the ultracentrifugation-precipitation method. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Cammarata, P.J.; Walzem, R.L.; Suchodolsky, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Serum triglyceride and cholesterol concentrations and lipoprotein profiles in dogs with naturally occurring pancreatitis and healthy control dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J. Lipid Res. 1968, 9, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, M.S.; Boon, G.D.; Rebar, A.H.; Story, J.A.; Bottoms, G.D. Ultracentrifugal and electrophoretic characteristics of the plasma lipoproteins of miniature schnauzer dogs with idiopathic hyperlipoproteinemia. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1993, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.D.G. Lipoprotein metabolism in dogs and cats. Comp. Haematol, Int, 1996, 6, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Mundra, P.A.; Fang, L.; Galvin, A.; Moore, X.L.; Weir, J.M.; Wong, G.; White, D.A.; Chin-Dusting, J.; Sparrow, M.P.; Meikle, P.J.; Dart, A.M. Lipidomic profiling in inflammatory bowel disease: Comparison between ulcerative colitis and crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappati Biyyani, R.S.; Putka, B.S.; Mullen, K.D. Dyslipidemia and lipoprotein profiles in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 4, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennogle, S.A.; Stockman, J.; Webb, C.B. Prospective evaluation of a change in dietary therapy in dogs with steroid-resistant protein-losing enteropathy. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, I.; Boldrini, G.; Chiarla, C.; Giuliante; Vellone, M.; Nuzzo, G. Pathophysiologic correlates of hypocholesterolemia in critically ill surgical patients. Intensive Care Med, 1999, 25, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunberger, P.; Nagel, D.; Walli, A.K.; Seidel, D. Serum cholesterol and mortality in patients with multiple organ failure. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 3574–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Yun, T.; Koo, Y.; Chae, Y.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, B.T.; Yang, M.P.; Kim, H. Clinical signs, duodenal histopathological grades, and serum high-mobility group box 1 concentrations in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoni, C.O.; Heilmann, R.M.; García-Sancho, M.; Sainz, A.; Ackermann, N.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E. Serologic and fecal markers to predict response to induction therapy in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggerone, B.; Scavone, D.; Troìa, R.; Giunti, M.; Dondi, F.; Paltrinieri, S. Comparison of Protein Carbonyl (PCO), Paraoxonase-1 (PON1) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) as Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers of Septic Inflammation in Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feillet-Coudray, C.; Fouret, G.; Vigor, C.; Bonafos, B.; Jover, B.; Blachnio-Zabielska, A.; Rieusset, J.; Casas, F.; Gaillet, S.; Landrier, J.F.; Durand, T.; Coudray, C. Long-term measures of dyslipidemia, inflammation, and oxidative stress in rats fed a high-fat/high-fructose diet. Lipids. 2019, 54, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khovidhunkit, W.; Kim, M.S.; Memon, R.A.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Moser, A.H.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: mechanisms and consequences to the host. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1169–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navab, M.; Yu, R.; Gharavi, N.; Huang, W.; Ezra, N.; Lotfizadeh, A.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Alipour, N.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Reddy, S.T.; Marelli, D. High-density lipoprotein: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2007, 9, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ding, Z.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Qian, M.; Du, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chang, H.; Huang, C.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y. The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, D-4F, alleviates ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress and promotes endothelial repair through the eNOS/HO-1 pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 105, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioudaki, S.; Verikokos, C.; Kouraklis, G.; Ioannou, C.; Chatziioannou, E.; Perrea, D.; Klonaris, C. Paraoxonase-1: characteristics and role in atherosclerosis and carotid artery disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 17, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Rosso, L.; Lhomme, M.; Merono, T.; Sorroche, P.; Catoggio, L.; Soriano, E.; Saucedo, C.; Malah, V.; Dauteuille, C.; Boero, L.; Lesnik, P.; Robillard, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Brites, F.; Kontush, A. Altered lipidome and antioxidative activity of small, dense HDL in normolipidemic rheumatoid arthritis: relevance of inflammation. Atherosclerosis. 2014, 237, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, C.; van Tits, L.J.; Barrera, P.; Lemmers, H.L.M.; van den Hoogen, F.H.J.; van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Netea, M.G.; Roest, M.; Stalenhoef, A.F.H. Anti-infammatory therapy with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors improves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol antioxidative capacity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasumi, K.; Kashiwado, N.; Okada, Y.; Sawamura, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Iwazaki, E.; Mori, N.; Yamamoto, I.; Arai, T.; et al. Age effects on plasma cholesterol and triglyceride profiles and metabolite concentrations in dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiho, U.; Yasuda, H.; Koketsu, Y. Lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations associated with dog body condition score; effect of recommended fasting duration on sample concentrations in Japanese private clinics. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, E.N.; Romero, J.R.; Ochoa, B.; Aveldaño, M.I. Lipid and fatty acid composition of canine lipoproteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 128, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, R.R.; Sappati Biyyani, S.; Putka, B.s.; Mullen, K.D. Dyslipidemia and lipoprotein profiles in patients with inflammatory bowel disease J. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 4, 478–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, W.H.; Klinefelter, H.F.; Kwiterovitch, P.O. Effect of short-term, low-dose corticosteroids on plasma lipoprotein lipids. Atherosclerosis 1987, 63, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.; Martinez, S.A.; Shiroma, J.T.; Warson, A.T.; Hostutler, R.A. Prospective Evaluation of Low-Fat Diet Monotherapy in Dogs with Presumptive Protein-Losing Enteropathy. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2023, 59, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, N.; Ohta, H.; Yokoyama, N.; Teoh, Y.B.; Nisa, K.; Sasaki, N.; Osuga, T.; Morishita, K.; Takiguchi, M. Clinical characteristics of dogs with food-responsive protein-losing enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, A.; Luchetti, E.; Cardini, G. Plasma lipoprotein concentrations in the dog: The effects of gender, age, breed and diet. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.A.; Kjeldsen, E.W.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Vegetarian or vegan diets and blood lipids: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. Heart. J. 2023, 44, 2609–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, T.; Parambeth, J.C.; Walzem, R.L.; Payne, H.R.; Lidbury, J.A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Evaluation of density gradient ultracentrifugation serum lipoprotein profiles in healthy dogs and dogs with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2018, 30, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Control dogs | iPLE dogs | Reference interval | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alb (g/dL) | 3.6 (2.9-4.1) | 1.7 (0.8-2.7) | 2.8-4 | <0.0001 |
| Chol (mg/dL) | 209.5 (118-289) | 116 (59-327) | 135-270 | <0.0001 |
| Chylomicrons (%) | 2.1 (0.3-8.4) | 5.6 (0.5-22.8) | - | <0.0001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.9 (0-14.6) | 5.4 (0-48.4) | ≤5 | =0.009 |
| HDLs (%) | 65.5 (44.4-79.5) | 52.3 (18.7-81.8) | - | <0.0001 |
| LDLs (%) | 15.8 (6.5-39.1) | 33.8 (13.7-64.3) | - | <0.0001 |
| PON-1 activity (U/mL) | 199 (129-303) | 77 (13.3-223) | ≥116 | <0.0001 |
| VLDLs (%) | 15.6 (8.1-30.4) | 6.6 (1.2-36.1) | - | <0.0001 |
| TGs (mg/dL) | 55 (11-122) | 83 (30-172) | <104 | <0.0001 |
| TP (g/dL) | 6.4 (4.8-8.9) | 4.1 (2.0-7.4) | 5.4-7.5 | <0.0001 |
| Pair of variables tested for correlation |
Correlation coefficient (r) | Significance level (p) |
|---|---|---|
| HDLs and PON-1 | 0.60 | <0.0001 |
| HDLs and CRP | -0.28 | =0.048 |
| LDLs and body weight | -0.36 | =0.009 |
| LDLs and PON-1 | -0.68 | <0.0001 |
| Chol and age | 0.30 | =0.034 |
| Chol and body weight | 0.30 | =0.039 |
| Chol and PON-1 | 0.83 | <0.0001 |
| CRP and VLDLs | 0.46 | =0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





