Submitted:
10 September 2024
Posted:
10 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The Basic Principles of Pathophysiology of Venous Thrombosis
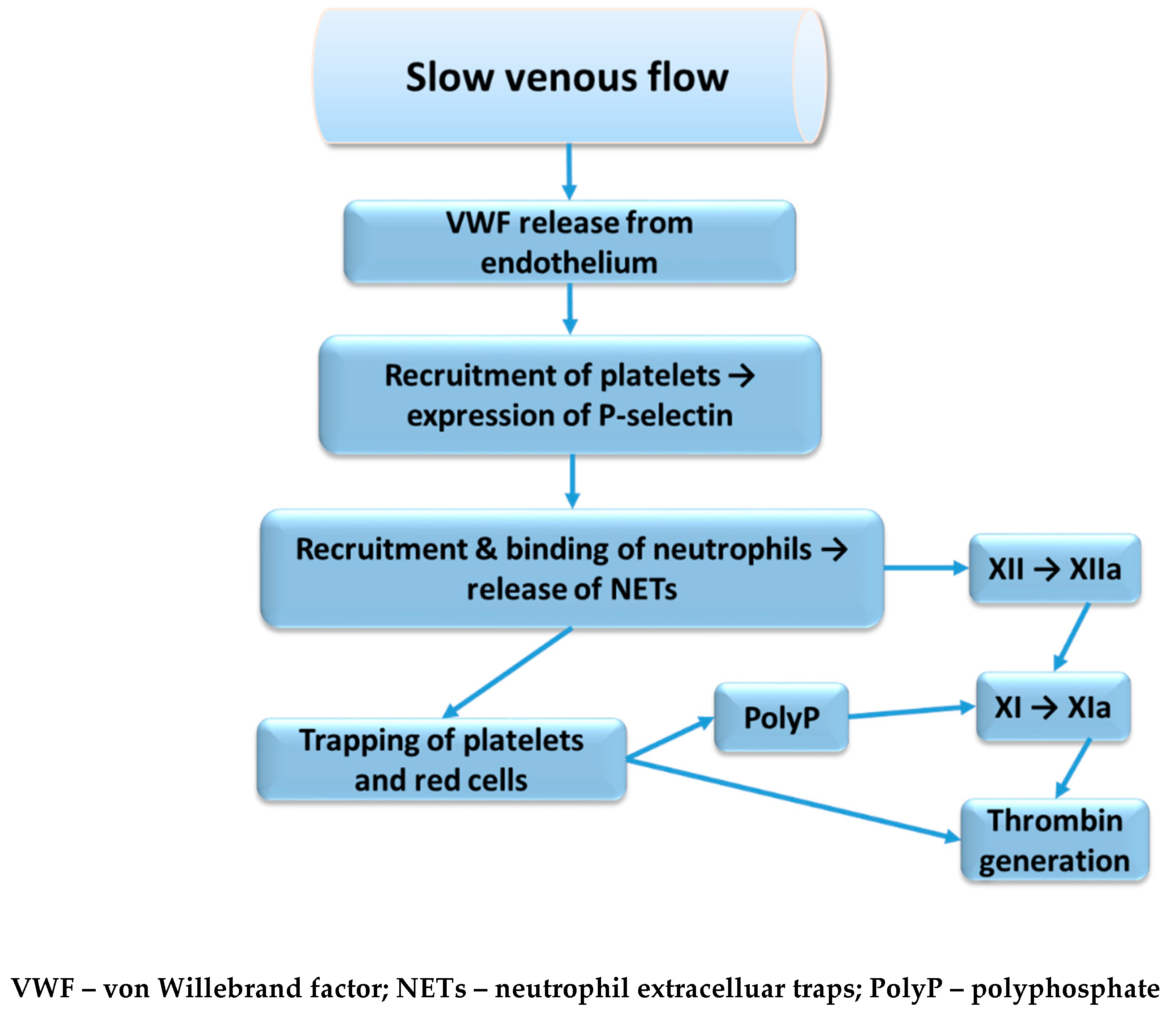
2.1. Venous Stasis
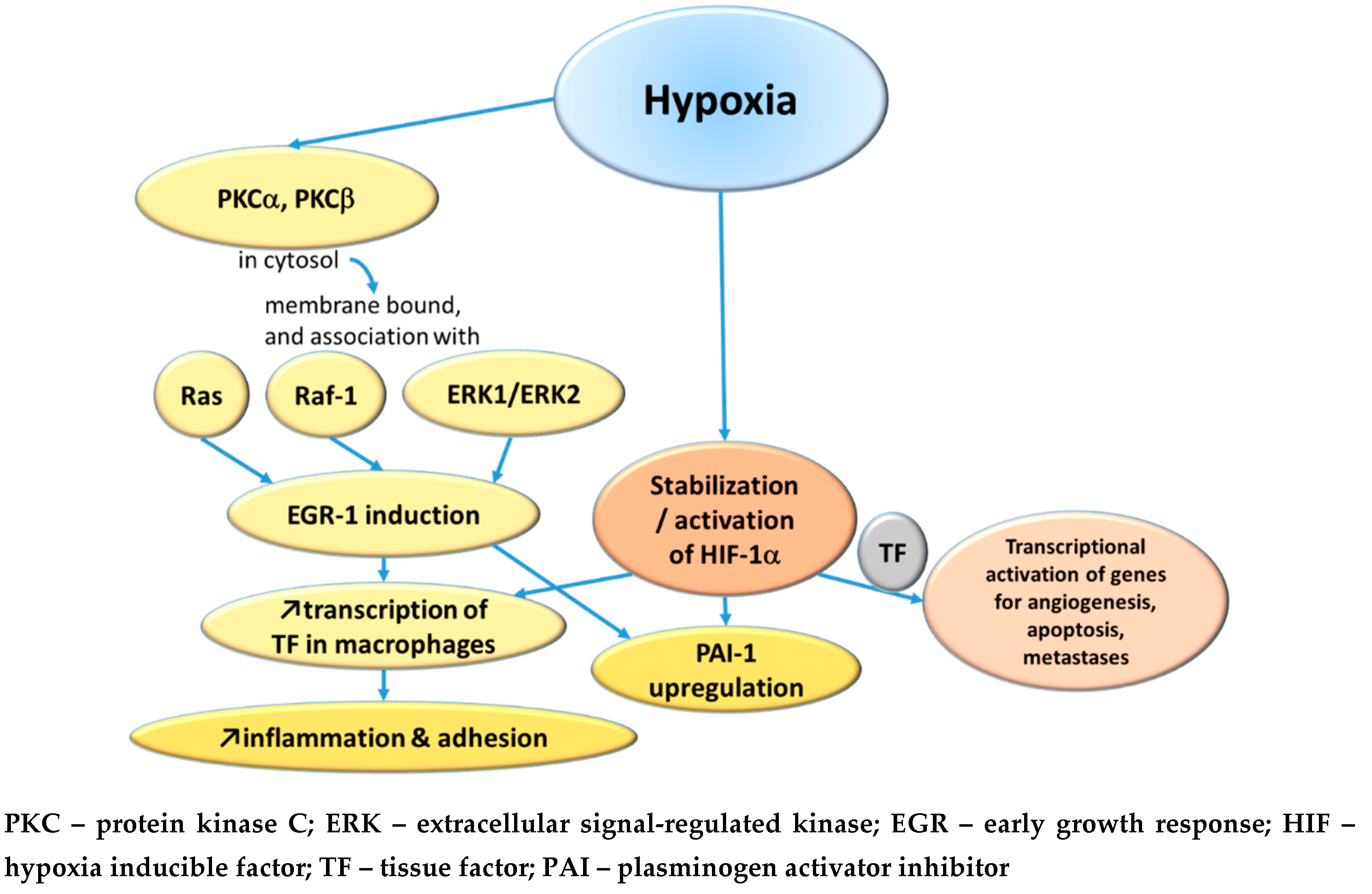
2.1.1. Hypoxemia
2.1.2. Reduced Clearance in Valve Pockets
2.1.3. A Genetic Component
2.2. Inflammation
2.2.1. Interleukins
2.2.2. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
2.2.3. Genetic Susceptibility
2.2.4. Complement System
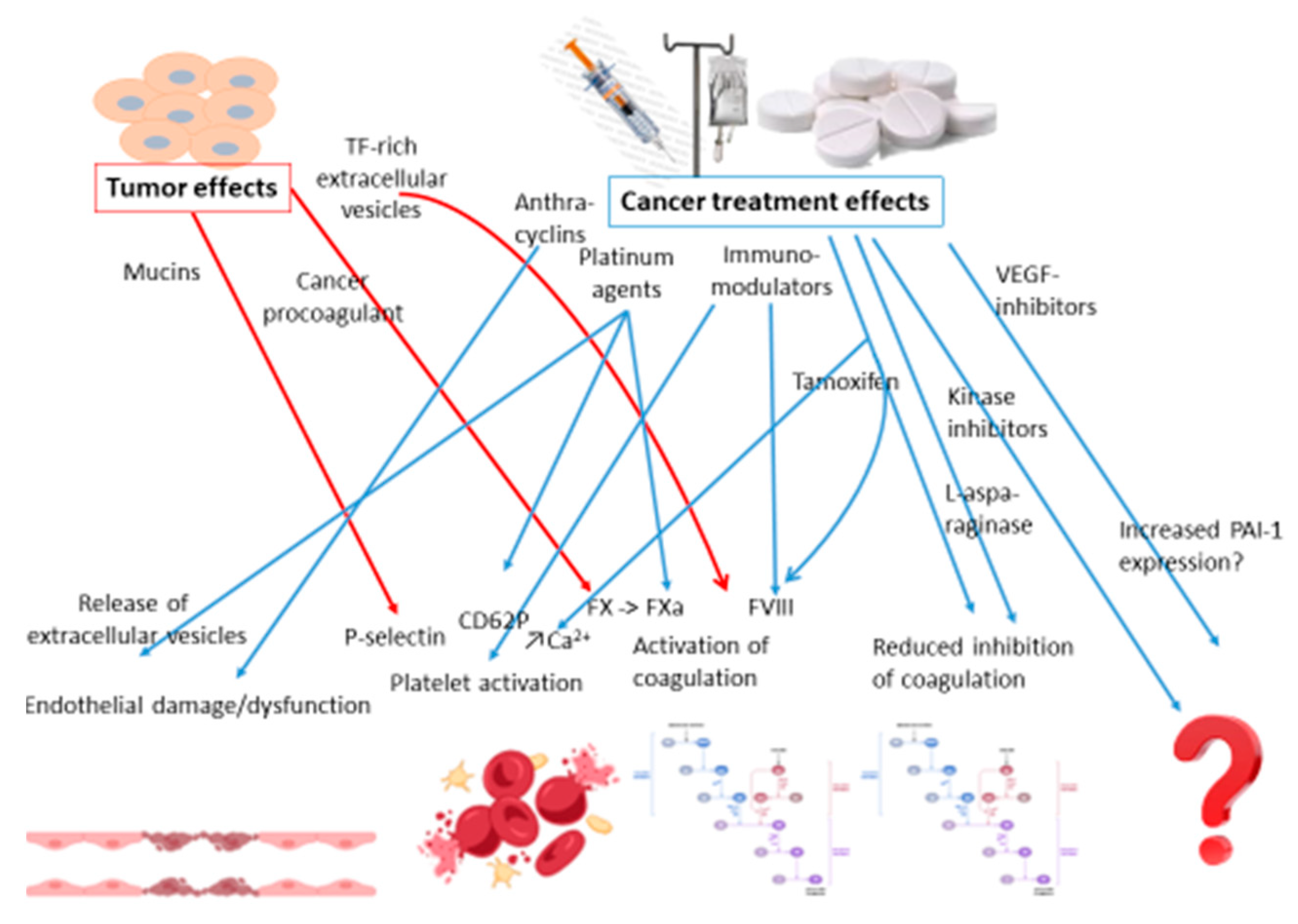
2.3. Cancer and Thrombosis
2.3.1. Risk Factors of Cancer-Associated Thrombosis
2.3.2. Pharmaceutical Treatments for Cancer and Risk of Thrombosis
2.3.3. Cancer Related Factors
3. Future Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagot, C.N.; Arya, R. Virchow and his triad: a question of attribution. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessler, S. Thrombosis in the presence of vascular stasis. Am. J. Med. 1962, 33, 648–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamer, J.D.; Malone, P.C.; A Silver, I. The PO2 in venous valve pockets: Its possible bearing on thrombogenesis. Br. J. Surg. 1981, 68, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.-F.; Mackman, N.; Kisiel, W.; Stern, D.M.; Pinsky, D.J. Hypoxia/Hypoxemia-Induced Activation of the Procoagulant Pathways and the Pathogenesis of Ischemia-Associated Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.-F.; Zou, Y.S.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, C.; Mackman, N.; Lee, S.L.; Milbrandt, J.; Pinsky, D.; Kisiel, W.; Stern, D. Tissue factor transcription driven by Egr-1 is a critical mechanism of murine pulmonary fibrin deposition in hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8298–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.F.; Lu, J.; Zou, Y.S.; Kisiel, W.; Mackman, N.; Leitges, M.; Steinberg, S.; Pinsky, D.; Stern, D. Protein kinase C-beta and oxygen deprivation. A novel Egr-1-dependent pathway for fibrin deposition in hypoxemic vasculature. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 11921–11928. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, L.W.; Cheng, J.J.; Chiu, J.J.; Wung, B.S.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, D.L. Endothelial exposure to hypoxia induces Egr-1 expression involving PKCalpha-mediated Ras/Raf-1/ERK1/2 pathway. J Cell Physiol 2001, 188, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, K.Y.; Wei, C.K.; Wu, C.C. YC-1 prevents tumor-associated tssue factor expression and procoagulant activity in hypoxic conditions by inhibiting p38/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Hyman, M.C.; Lawrence, D.A.; Pinsky, D.J. Molecular regulation of the PAI-1 gene by hypoxia: contributions of Egr-1, HIF-1alpha, and C/EBPalpha. FASEB J 2007, 21, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikov, A.; Meszaros, M.; Schwarz, E.I. Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnally, C.J.; Vakharia, A.M.; Sheu, J.I.; Vakharia, R.M.; Damodar, D.; Shenoy, K.; Gjolaj, J.P. High altitude is an independent risk factor for developing a pulmonary embolism, but not a deep vein thrombosis following a 1- to 2-level lumbar fusion Global Spine Journal 2019, 9, 729–734.
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Franchini, M.; Lippi, G. Sleep apnea and venous thromboembolism. A systematic review。 Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzepizur, W.; Gervès-Pinquié, C.; Heudes, B.; Blanchard, M.; Meslier, N.; Jouvenot, M.; Kerbrat, S.; Le Mao, R.; Magois, E.; Racineux, J.-L.; et al. Sleep Apnea and Incident Unprovoked Venous Thromboembolism: Data from the Pays de la Loire Sleep Cohort. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 123, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treml, B.; Wallner, B.; Blank, C.; Fries, D.; Schobersberger, W. The influence of environmental hypoxia on hemostasis-a systematic review Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 813550.
- Brooks, E.G.; Trotman, W.; Wadsworth, M.P.; Taatjes, D.J.; Evans, M.F.; Ittleman, F.P.; Callas, P.W.; Esmon, C.T.; Bovill, E.G. Valves of the deep venous system: an overlooked risk factor. Blood 2009, 114, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotman, W.E.; Taatjes, D.J.; Callas, P.W.; Bovill, E.G. The endothelial microenvironment in the venous valvular sinus: thromboresistance trends and inter-individual variation. Histochem. 2011, 135, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brill, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Chauhan, A.K.; Yang, J.J.; De Meyer, S.F.; Köllnberger, M.; Wakefield, T.W.; Lämmle, B.; Massberg, S.; Wagner, D.D. von Willebrand factor–mediated platelet adhesion is critical for deep vein thrombosis in mouse models. Blood 2011, 117, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Brühl, M.L.; Stark, K.; Steinhart, A.; Chandraratne, S.; Konrad, I.; Lorenz, M.; Khandoga, A.; Tirniceriu, A.; Coletti, R.; Köllnberger, M.; et al. Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, K.C.; Ozel, A.B.; Halvorsen, M.; Jacobi, P.M.; Golden, K.L.; Underwood, M.; Germain, M.; Tregouet, D.-A.; Reitsma, P.H.; Kearon, C.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies rare variants in STAB2 associated with venous thromboembolic disease. Blood 2020, 136, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Russell, J.; Senchenkova, E.Y.; Almeida Paula, L.D.; Granger, D.N. Interleukin-1beta mediates the extra-intestinal thrombosis associated with experimental colitis. Am J Pathol 2010, 177, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghani, S.E.-S.A.; Hamed, R.M.R.; Eid, R.A.; Ibrahim, A.Y.M.; Abdel-Hamid, H.M.; Abdelrahman, W.; Ibrahim, R.E.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Mohamed, M.S. Serum interleukin 1β and sP-selectin as biomarkers of inflammation and thrombosis, could they be predictors of disease severity in COVID 19 Egyptian patients? (a cross-sectional study). Thromb. J. 2022, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, S.; Ding, P.; Wang, M. IL-9 Promotes the Development of Deep Venous Thrombosis by Facilitating Platelet Function. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Zhang, S.; Yu, M.; Feng, Y.; Long, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, M. IL-17A promotes the formation of deep vein thrombosis in a mouse model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 57, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Pan, L.; Lan, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zou, M.; Meng, R. Inflammatory Markers Differentiate Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis from Mimics. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 123, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittar, L.F.; Mazetto, B.d.M.; Orsi, F.L.A.; Collela, M.P.; De Paula, E.V.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Long-term increased factor VIII levels are associated to interleukin-6 levels but not to post-thrombotic syndrome in patients with deep venous thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2014, 135, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.Q.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Bian, J. Correlation of interleukin-18 and high-sensitivity c-reactive protein with perioperative deep vein thrombosis in patients with ankle fracture Ann Vasc Surg 2019, 54, 282–289.
- Mutlu, G.M.; Green, D.; Bellmeyer, A.; Baker, C.M.; Burgess, Z.; Rajamannan, N.; Christman, J.W.; Foiles, N.; Kamp, D.W.; Ghio, A.J.; et al. Ambient particulate matter accelerates coagulation via an IL-6–dependent pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmar, A.; Hoet, P.H.; Vermylen, J.; Nemery, B.; Hoylaerts, M.F. Pharmacological Stabilization of Mast Cells Abrogates Late Thrombotic Events Induced by Diesel Exhaust Particles in Hamsters. Circulation 2004, 110, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucking, A.J.; Lundback, M.; Mills, N.L.; Faratian, D.; Barath, S.L.; Pourazar, J.; Cassee, F.R.; Donaldson, K.; Boon, N.A.; Badimon, J.J.; et al. Diesel exhaust inhalation increases thrombus formation in man. Eur. Hear. J. 2008, 29, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, R.E.; Cakmak, S.; Vidal, C.B. Air pollution and hospitalization for venous thromboembolic disease in Chile. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Mengoli, C.; Cruciani, M.; Bonfanti, C.; Mannucci, P.M. Association between particulate air pollution and venous thromboembolism: A systematic literature review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 27, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Mutch, N.J.; Schenk, W.A.; Smith, S.A.; Esterl, L.; Spronk, H.M.; Schmidbauer, S.; Gahl, W.A.; Morrissey, J.H.; Renné, T. Platelet Polyphosphates Are Proinflammatory and Procoagulant Mediators In Vivo. Cell 2009, 139, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Wagner, D.D. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) Impact on Deep Vein Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1777–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pelayo, R.; Monestier, M.; Ammollo, C.T.; Semeraro, F.; Taylor, F.B.; Esmon, N.L.; Lupu, F.; Esmon, C.T. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Montfoort, M.L.; Stephan, F.; Lauw, M.N.; Hutten, B.A.; Van Mierlo, G.J.; Solati, S.; Middeldorp, S.; Meijers, J.C.; Zeerleder, S. Circulating Nucleosomes and Neutrophil Activation as Risk Factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressan, A.; Faggin, E.; Donato, M.; Tonon, L.; Buso, R.; Nardin, C.; Tiepolo, M.; Cinetto, F.; Scarpa, R.; Agostini, C.; et al. NETosis in Acute Thrombotic Disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2023, 49, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, D.A.; Wun, T.C.; Likert, K.M.; Broze, G.J., Jr. The effect of leukocyte elastase on tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood 1992, 79, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.A.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V.M. Role of Cell Surface Lipids and Thiol-Disulphide Exchange Pathways in Regulating the Encryption and Decryption of Tissue Factor. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.H.; Iba, T.; Olson, L.B.; Corey, K.M.; Ghadimi, K.; Connors, J.M. COVID-19: Thrombosis, thromboinflammation, and anticoagulation considerations. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology 2021, 43, (S1), 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morange, P.-E.; Bezemer, I.; Saut, N.; Bare, L.; Burgos, G.; Brocheton, J.; Durand, H.; Biron-Andreani, C.; Schved, J.-F.; Pernod, G.; et al. A Follow-Up Study of a Genome-wide Association Scan Identifies a Susceptibility Locus for Venous Thrombosis on Chromosome 6p24.1. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryzdial, E.L.G.; Leatherdale, A.; Conway, E.M. Coagulation and complement: Key innate defense participants in a seamless web. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, I.; Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Complement C3 and High Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: 80517 Individuals from the Copenhagen General Population Study. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiland, II; Liang, R.A.; Braekkan, S.K.; Pettersen, K.; Ludviksen, J.K.; Latysheva, N.; Snir, O.; Ueland, T.; Hindberg, K.; Mollnes, T.E., et al. Complement activation assessed by the plasma terminal complement complex and future risk of venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost 2019, 17, 934–943.
- Skjeflo, E.W.; Brækkan, S.K.; Ludviksen, J.K.; Snir, O.; Hindberg, K.; Mollnes, T.E.; Hansen, J.-B. Elevated plasma concentration of complement factor C5 is associated with risk of future venous thromboembolism. Blood 2021, 138, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.P.; Kawano, T.; Wan, J.; Tanratana, P.; Polai, Z.; Shim, Y.J.; Snir, O.; Brækkan, S.K.; Dhrolia, S.; Kasthuri, R.R.; et al. C1 inhibitor deficiency enhances contact pathway mediated activation of coagulation and venous thrombosis. Blood 2023, 141, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, H.K.; Wun, T.; Harvey, D.; Zhou, H.; White, R.H. Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism and Its Effect on Survival Among Patients With Common Cancers. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, G.H.; Carrier, M.; Ay, C.; Di Nisio, M.; Hicks, L.K.; Khorana, A.A.; Leavitt, A.D.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Macbeth, F.; Morgan, R.L.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prevention and treatment in patients with cancer. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 927–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, N.; Dowlati, A.; Remick, S.C.; Tahsildar, H.I.; Sivinski, L.D.; Beyth, R.; Rimm, A.A. Rates of Initial and Recurrent Thromboembolic Disease Among Patients with Malignancy Versus Those without Malignancy: Risk Analysis Using Medicare Claims Data. Medicine 1999, 78, 285–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandoni, P.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Piccioli, A.; Bernardi, E.; Simioni, P.; Girolami, B.; Marchiori, A.; Sabbion, P.; Prins, M.H.; Noventa, F.; et al. Recurrent venous thromboembolism and bleeding complications during anticoagulant treatment in patients with cancer and venous thrombosis. Blood 2002, 100, 3484–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, S.; Ono, R.; Fukuda, K.; Sakayori, M.; Awano, N.; Kondo, K. Trousseau's syndrome: cancer-associated thrombosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2016, 46, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwikiel, M.; Eskilsson, J.; Albertsson, M.; Stavenow, L. The influence of 5-fluorouracil and methotrexate on vascular endothelium. An experimental study using endothelial cells in the culture. Ann. Oncol. 1996, 7, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, M.F.; Kim, J.; Foderaro, A.E.; Truesdell, A.G. 5-fluorouracil induced cardiotoxicity: Review of the literature. Cardiol. J. 2012, 19, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Warsha, F.; Mehta, A.; Deepak, V.; Jawad, W. 5-Fluorouracil Induced Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Complicated by Left Ventricular Thrombosis. Cureus 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinhult, S.; Albertsson, M.; Eskilsson, J.; Cwikiel, M. Antithrombotic treatment in protection against thrombogenic effects of 5-fluorouracil on vascular endothelium: A scanning microscopy evaluation. Scanning 2001, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, I.C.; Israel, V.K.; Waisman, J.R.; Presant, C.A.; Rochanda, L.; Liebman, H.A. Chemotherapy-Induced Activation of Hemostasis: Effect of a Low Molecular Weight Heparin (Dalteparin Sodium) on Plasma Markers of Hemostatic Activation. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 88, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodley-Cook, J.; Shin, L.Y.; Swystun, L.; Caruso, S.; Beaudin, S.; Liaw, P.C. Effects of the chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin on the protein C anticoagulant pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 3303–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swystun, L.L.; Shin, L.Y.Y.; Beaudin, S.; Liaw, P.C. Chemotherapeutic agents doxorubicin and epirubicin induce a procoagulant phenotype on endothelial cells and blood monocytes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.C.; Williams, J.C.; Hollingsworth, R.M.; Wang, J.G.; Glover, S.L.; Owens, A.P., 3rd; Barcel, D.A.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Key, N.S.; Mackman, N. Anthracycline treatment of the human monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1 increases phosphatidylserine exposure and tissue factor activity. Thromb Res 2012, 129, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swystun, L.L.; Mukherjee, S.; Liaw, P.C. Breast cancer chemotherapy induces the release of cell-free DNA, a novel procoagulant stimulus. J Thromb Haemost 2011, 9, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.Y.; Chin, C.; Dahl, G.; Rosenthal, D.N. Anthracyclines Cause Endothelial Injury in Pediatric Cancer Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangari, M.; Barlogie, B.; Thertulien, R.; Jacobson, J.; Eddleman, P.; Fink, L.; Fassas, A.; Van Rhee, F.; Talamo, G.; Lee, C.-K.; et al. Thalidomide and Deep Vein Thrombosis in Multiple Myeloma: Risk Factors and Effect on Survival. Clin. Lymphoma 2003, 4, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.; Lokich, J.J.; Tullis, J.L. L-asparaginase effect on antithrombin-III levels. Med Pediatr Oncol 1979, 7, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, V.; Iacoviello, L.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Storti, S.; Mariani, G.; de Gaetano, G.; Donati, M.B. Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients. Blood 2006, 108, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conard, J.; Cazenave, B.; Maury, J.; Horellou, M.H.; Samama, M. L-asparaginase, antithrombin III, and thrombosis. Lancet 1980, 1, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conard, J.; Horellou, M.H.; Van Dreden, P.; Potevin, F.; Zittoun, R.; Samama, M. Decrease in protein C in L-asparaginase-treated patients. Br. J. Haematol. 1985, 59, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunault-Berger, M.; Chevallier, P.; Delain, M.; Bulabois, C.-E.; Bologna, S.; Bernard, M.; Lafon, I.; Cornillon, J.; Maakaroun, A.; Tizon, A.; et al. Changes in antithrombin and fibrinogen levels during induction chemotherapy with L-asparaginase in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or lymphoblastic lymphoma. Use of supportive coagulation therapy and clinical outcome: the CAPELAL study. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, H.R.; Geczy, C.L. Induction of macrophage procoagulant expression by cisplatin, daunorubicin and doxorubicin. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 46, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, D.; Kollars, M.; Gleiss, A.; Kyrle, P.A.; Weltermann, A. Chemotherapy-induced thrombin generation via procoagulant endothelial microparticles is independent of tissue factor activity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Bi, Y.; Kou, J.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J. Enhanced procoagulant activity of platelets after chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, S.; Liu, Z.; Chiu, S.K.; Proverbs-Singh, T.; Sonpavde, G.; Choueiri, T.K.; Tsao, C.-K.; Yu, M.; Hahn, N.M.; Oh, W.K.; et al. Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With Cancer Treated With Cisplatin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4416–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, C.; Hodges, C.V. Studies on Prostatic Cancer: I. The Effect of Castration, of Estrogen and of Androgen Injection on Serum Phosphatases in Metastatic Carcinoma of the Prostate. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, E.D.; Heidenreich, A.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Tombal, B.; Pompeo, A.C.L.; Mendoza-Valdes, A.; Miller, K.; Debruyne, F.M.J.; Klotz, L. Androgen-targeted therapy in men with prostate cancer: evolving practice and future considerations. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 22, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosman, F.; Baz-Hecht, M.; Cushman, M.; Vardy, M.D.; Cruz, J.; Nieves, J.; Zion, M.; Lindsay, R. Short-term effects of estrogen, tamoxifen and raloxifene on hemostasis: a randomized-controlled study and review of the literature. Thromb. Res. 2005, 116, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühl, H.; Schröder, L.; Müller, J.; Fimmers, R.; Sukhitashvili, S.; Welz, J.; Kuhn, W.C.; Oldenburg, J.; Rudlowski, C.; Pötzsch, B. Tamoxifen induces resistance to activated protein C. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.P.; Chegini, H.A.; Vishneski, S.R.; Weatherman, R.V.; Blackmore, P.F.; Dobrydneva, Y. Tamoxifen promotes superoxide production in platelets by activation of PI3-Kinase and NADPH oxidase pathways. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.-J.; Jung, E.-A.; Kim, Z.; Kim, B.-Y. Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Lipid Profile Change in Patients with Breast Cancer Taking Aromatase Inhibitor: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondon, M.; Bodmer, A.; Thouvenin, L.; Lecompte, T.; Righini, M.; Fontana, P.; Casini, A. Differential impact of tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors on thrombin generation: the prospective HEMOBREAST cohort. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pather, K.; Dix-Peek, T.; Duarte, R.; Chetty, N.; Augustine, T. Breast cancer cell-induced platelet activation is compounded by tamoxifen and anastrozole in vitro. Thromb. Res. 2019, 177, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, M.; Treliński, J.; Chojnowski, K. Hemostatic changes after 1 month of thalidomide and dexamethasone therapy in patients with multiple myeloma. Med Oncol. 2012, 29, 3574–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Accaoui, R.; Shamseddeen, W.; Taher, A. Thalidomide and thrombosis. A meta-analysis。 Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroddi, M.; Sterrantino, C.; Simmonds, M.; Caridi, L.; Calapai, G.; Phillips, R.S.; Stewart, L.A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk of severe and life-threatening thromboembolism in cancer patients receiving anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (cetuximab or panitumumab). Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Ren, M.; Li, R.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, K.; Xiao, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.; et al. Bevacizumab promotes venous thromboembolism through the induction of PAI-1 in a mouse xenograft model of human lung carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, H.I.; Saltz, L.B.; Van Cutsem, E.; Cassidy, J.; Wiedemann, J.; Sirzén, F.; Lyman, G.H.; Rohr, U.-P. Venous Thromboembolic Events With Chemotherapy Plus Bevacizumab: A Pooled Analysis of Patients in Randomized Phase II and III Studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanukula, R.; Ganta, S.; Sirumalla, Y.; Salam, A.; Baddam, R.; Pasupuleti, B.C. Risk of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients With Cancer Treated With Aflibercept: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 26, e549–e552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latifi, Y.; Moccetti, F.; Wu, M.; Xie, A.; Packwood, W.; Qi, Y.; Ozawa, K.; Shentu, W.; Brown, E.; Shirai, T.; et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy as a cause of cardiovascular toxicity from the BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor ponatinib. Blood 2019, 133, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haguet, H.; Douxfils, J.; Mullier, F.; Chatelain, C.; Graux, C.; Dogné, J.-M. Risk of arterial and venous occlusive events in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with new generation BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 16, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein, K.Z.; Htut, T.W.; Ball, S.; Swarup, S.; Sultan, A.; Oo, T.H. Venous thromboembolism risk in patients with hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer treated with combined CDK 4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy versus endocrine therapy alone: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2020, 183, 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, J.W.; Osanto, S.; Rosendaal, F.R. The risk of a venous thrombotic event in lung cancer patients: higher risk for adenocarcinoma than squamous cell carcinoma. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahrenbrock, M.; Borsig, L.; Le, D.; Varki, N.; Varki, A. Selectin-mucin interactions as a probable molecular explanation for the association of Trousseau syndrome with mucinous adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Kannagi, R.; Toole, B.; Stanley, P. Glycosylation changes in cancer. 2017/01/01 ed.; Cold Sprin Hardor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor (NY), 2017; Vol. Chapter 47, p 597-609.
- Gordon, S.G.; Franks, J.J.; Lewis, B. Cancer procoagulant A: A factor X activating procoagulant from malignant tissue. Thromb. Res. 1975, 6, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, A.M.R.; Kroone, C.; Kapteijn, M.Y.; Versteeg, H.H.; Buijs, J.T. Role of tissue factor in tumor progression and cancer-associated thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost 2019, 45, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




