I. Introduction
Bangladesh's rapid growth and digitization of banking services have brought about significant advancements in the country's financial infrastructure [
1]. With this transformation, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. As the government continues prioritizing digitalization strategies and national financial inclusion, the need to safeguard banking systems, networks, and data from digital threats has become increasingly critical [
2].
This paradigm shift towards digital banking has revolutionized financial transactions and introduced new challenges and vulnerabilities. The interconnectedness of banking networks, coupled with the proliferation of online services, has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. The 2016 cyberattack on Bangladesh Bank is a sobering reminder of the possible repercussions of insufficient cybersecurity safeguards [
3]. The audacious attempt by hackers to pilfer nearly
$1 billion from the central bank's account at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York underscored the vulnerabilities inherent in the financial ecosystem. This incident not only exposed the weaknesses in Bangladesh's financial infrastructure but also reverberated across the global banking community, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced cybersecurity protocols [
4].
In this research paper, we will explore the applications of machine learning and deep learning techniques in the realm of banking cybersecurity in Bangladesh. Specifically, we will delve into how these technologies can be leveraged for tasks such as intrusion detection, malware detection, and fraud detection, among others [
5]. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and data-driven decision-making, these techniques enable real-time analysis of vast amounts of banking data, thus empowering proactive defense against cyberattacks.
Moreover, the burgeoning digital economy of Bangladesh, characterized by the government's digitalization initiatives and the push for financial inclusion, underscores the timeliness and relevance of this research endeavor. As the banking sector continues to adapt and evolve in response to cybersecurity challenges, it is imperative to explore innovative solutions that can bolster the resilience of financial institutions against cyber threats.
Through this exploration, we aim to provide insights into the potential of machine learning and deep learning in fortifying the cybersecurity landscape of Bangladesh's banking industry. This endeavor holds immense significance in the context of the nation's evolving financial infrastructure and the imperative to ensure the security and integrity of digital banking operations [
6]. By elucidating the role of advanced technologies in mitigating cyber risks and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, this research seeks to contribute to the ongoing efforts towards building a secure and resilient banking ecosystem in Bangladesh [
7].
II. Current State of Cybersecurity in Bangladesh's Banking Sector
The Bangladesh Bank cyber-attack of 2016 stands as one of the most significant cybersecurity breaches in the history of the country's banking sector. This audacious attempt by hackers to siphon off approximately $1 billion from the central bank's account at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York sent shockwaves throughout the global financial community. The meticulously orchestrated attack not only underscored the vulnerabilities inherent in Bangladesh's financial infrastructure but also exposed the potential repercussions of inadequate cybersecurity measures.
Furthermore, the sophistication and scale of the cyber-attack served as a stark wake-up call for stakeholders within the banking sector. It laid bare the stark reality that traditional security protocols were insufficient to defend against evolving cyber threats. In the aftermath of the incident, there was a palpable sense of urgency among policymakers, regulators, and industry players to bolster the resilience of Bangladesh's banking ecosystem against future cyber-attacks.
The Bangladesh Bank cyber-attack prompted a comprehensive reassessment of cybersecurity strategies and practices within the country's financial institutions. It catalyzed a concerted effort to enhance cybersecurity awareness, invest in advanced technologies, and fortify regulatory frameworks. Moreover, it galvanized collaborative initiatives among public and private entities to share threat intelligence, best practices, and resources aimed at collectively combatting cyber threats.
In essence, the Bangladesh Bank cyber-attack served as a pivotal moment that not only exposed vulnerabilities but also catalyzed transformative action. It underscored the imperative for a proactive and holistic approach to cybersecurity, one that encompasses technological innovation, regulatory enforcement, and cultural change within the banking sector. As Bangladesh continues its journey towards digitalization and financial inclusion, the lessons learned from this seminal event remain ever pertinent, guiding efforts to safeguard the integrity and stability of the country's financial systems in an increasingly digitized world.
A. Technology Solutions for Cybersecurity in Banking
In response to the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks, the banking sector in Bangladesh is turning to advanced technologies such as machine learning and deep learning to bolster cybersecurity measures. These technologies offer the capability to analyze vast amounts of data in real time, detect anomalies, and identify potential security breaches [
8,
9]. Machine learning and deep learning techniques have shown great promise in improving cybersecurity in the banking sector.
B. Improving Cybersecurity Awareness in the Banking Sector
In addition to leveraging advanced technologies, there is a growing emphasis on enhancing cybersecurity awareness and education among the individuals involved in the banking sector. Training programs and workshops are being conducted to educate employees about the latest cybersecurity threats, best practices, and the importance of vigilance in safeguarding sensitive financial data. These initiatives aim to create a culture of cybersecurity consciousness across all levels of the banking sector.
C. Research Gap and Future Directions
As the banking sector in Bangladesh continues to adapt and evolve in the face of cybersecurity challenges, the integration of cutting-edge technologies and the promotion of cybersecurity awareness will play a pivotal role in fortifying the country's financial infrastructure against potential cyber threats. While there have been discussions and conceptual frameworks regarding cybersecurity in the banking sector, empirical analysis and research based on real data are still limited. There exists a research gap in terms of empirical studies that explore the dimensions detrimental to the vulnerability of the banking system in Bangladesh [
10].
D. Regulatory Framework and Compliance Challenges
Effective cybersecurity in the banking sector requires adherence to stringent regulatory frameworks and compliance standards. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in establishing guidelines and protocols for cybersecurity practices, yet compliance with these standards poses significant challenges for banks. Striking a balance between innovation and regulatory compliance is paramount to maintaining a secure and resilient banking ecosystem. Additionally, international collaboration and information sharing among regulatory authorities can enhance the collective response to cyber threats across borders.
E. Human Factors in Cybersecurity
While technology solutions are unquestionably important, it is critical to acknowledge the considerable importance of human factors on cybersecurity resilience. Insider threats, carelessness, and social engineering assaults emphasize the importance of thorough training and awareness programs for bank personnel. Creating a cybersecurity-aware culture inside a company develops a shared responsibility for protecting sensitive information and limiting possible risks caused by human mistakes or bad intent [
11].
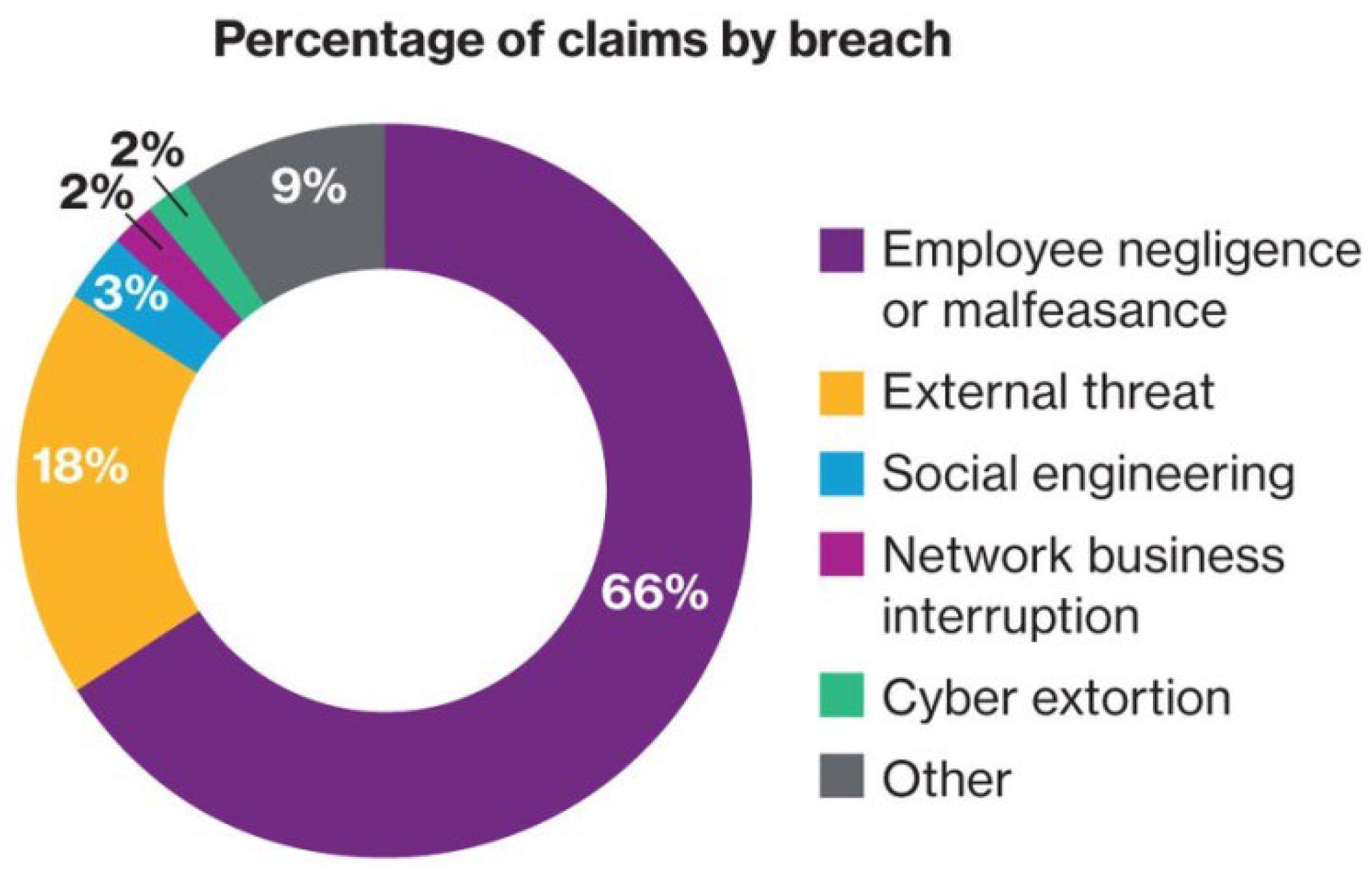
By this, a graphic depicts the different channels by which cyberattacks might occur, including employee carelessness, social engineering, insider threats, and other weaknesses. This graphic depiction highlights the varied nature of cybersecurity threats and the importance of engaging in ongoing education and training activities. Strengthening the human firewall through such methods is critical for improving cybersecurity defenses in the banking industry and limiting the risks associated with human-related vulnerabilities.
Figure 1.
Percentage of Claims by Breach [
17].
Figure 1.
Percentage of Claims by Breach [
17].
Therefore, strengthening cybersecurity resilience in the banking industry requires employee training. Effective defense tactics require an understanding of human behavior dynamics, such as insider threats and social engineering vulnerability. Giving priority to empirical research can yield important insights for creating specialized training curricula. These programs improve overall security posture by enabling bank staff to actively protect against cyberattacks.
This will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the current state of cybersecurity in the sector and help identify effective strategies for mitigating cyber risks. Source:[
12]. The purpose of this paper is to review the effect of cybercrime in the banking sector. According to a survey of literature and balanced scorecard analysis, cybercrime has harmed the goodwill and economic growth of financial institutions. Furthermore, the study highlights the need for an alert system that can effectively integrate big data technology to create awareness among banks and customers about cybercrime. The study suggests that the application of a balanced scorecard can be used to analyze the effect of cybercrime in the banking sector. The existing literature has highlighted the increasing wave of cybercrime in the banking sector, which has resulted in negative impacts such as loss of trust and financial fraud [
13].
Cybersecurity Challenges in Bangladesh's Financial Infrastructure
Bangladesh's financial infrastructure faces several cybersecurity concerns, posing significant dangers to the banking sector's viability and integrity. Numerous factors contribute to these problems, such as evolving cyber threat landscapes, technology flaws, and growing dependence on digital financial services. To bolster the financial system's defenses and preserve customer trust, these challenges must be recognized and successfully addressed.
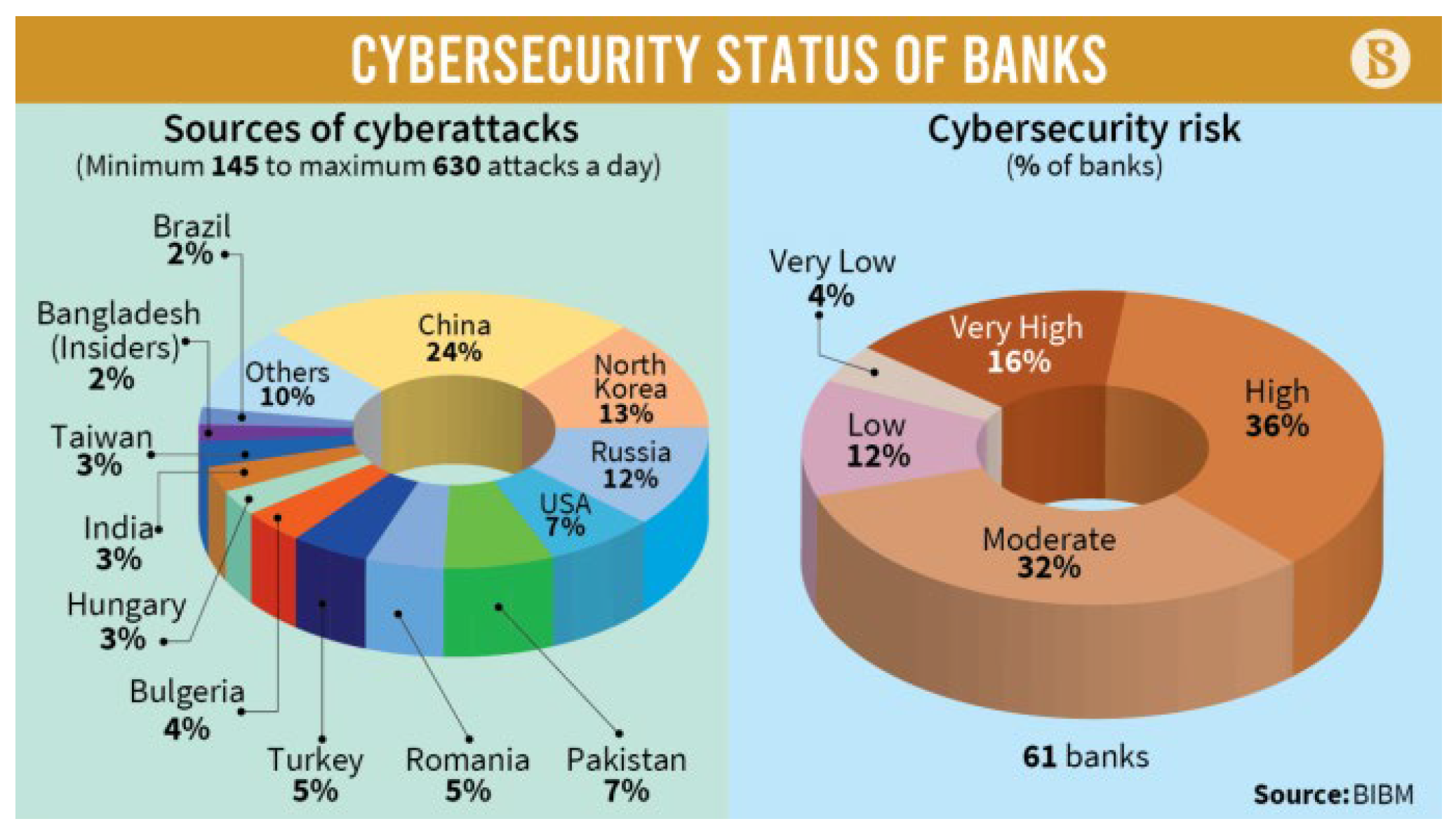
Furthermore, banks globally face a growing danger of cyberattacks, as seen by a pie chart demonstrating the distribution of cyber threats targeting financial institutions throughout the world. This graphic depiction highlights the crucial need for coordinated efforts to strengthen cybersecurity measures in the banking industry, both locally in Bangladesh and globally, to successfully manage these ubiquitous threats.
Figure 2.
Cybersecurity Status of Banks [
18].
Figure 2.
Cybersecurity Status of Banks [
18].
A. Technological Vulnerabilities
Bangladesh's financial infrastructure heavily relies on technology, making it susceptible to various vulnerabilities. Legacy systems, outdated software, and inadequate security measures create entry points for cybercriminals. Additionally, the rapid adoption of mobile banking and digital payment platforms introduces new attack vectors, such as mobile malware and phishing attacks.
B. Insider Threats
Insider threats pose a significant challenge to banking cybersecurity in Bangladesh. Employees with authorized access to sensitive information can misuse their privileges or inadvertently compromise security. Insider threats can range from intentional data breaches to unintentional errors, highlighting the need for robust access controls, employee training, and monitoring mechanisms.
C. Lack of Awareness and Training
One of the biggest problems is that both bank customers and staff lack cybersecurity knowledge and training. A lot of people don't know about phishing tactics, frequent cyberthreats, and safe online banking habits. This lack of awareness weakens the financial infrastructure's overall security posture and raises the risk of being a target of cyberattacks.
D. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
The regulatory framework for cybersecurity in Bangladesh's financial sector is still evolving. While regulatory bodies have introduced guidelines and regulations, ensuring compliance across all financial institutions remains a challenge. Inconsistent implementation of security measures and varying levels of cybersecurity maturity among banks create vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. [
14]
D. Sophisticated Cyber Threats
The ever-changing nature of cyber threats makes them harder to identify and neutralize as they get increasingly complex. The banking sector in Bangladesh is vulnerable to ransomware assaults, social engineering strategies, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). These threats require advanced cybersecurity measures and continuous monitoring to detect and respond effectively.
E. Limited Resources and Expertise
Resource limitations, such as tight budgets and a lack of qualified cybersecurity specialists, affect many financial institutions in Bangladesh. This scarcity of resources hampers the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures and the ability to respond effectively to cyber incidents. Collaboration between the government, financial institutions, and educational institutions is crucial to address this challenge. [
15]
To tackle these cybersecurity obstacles, a multifaceted strategy is needed. It entails putting in place strong security measures, improving cybersecurity awareness and training initiatives, fortifying legal frameworks, and encouraging cooperation amongst parties. Additionally, leveraging advanced technologies such as machine learning and deep learning can significantly enhance the detection and prevention of cyber threats in Bangladesh's financial infrastructure.
By understanding and proactively addressing these challenges, Bangladesh can strengthen its financial infrastructure's cybersecurity, protect customer data, and maintain trust in the banking sector.
IV. Implementation Challenges and Opportunities
Implementation Challenges and Opportunities: Implementing machine learning and deep learning techniques in Bangladesh's financial infrastructure to enhance banking cybersecurity presents both challenges and opportunities. While these technologies offer significant potential for improving security measures, their successful integration requires careful consideration of various factors.
A. Data Availability and Quality
One of the primary challenges in implementing machine learning and deep learning techniques is the availability and quality of data. Building effective models requires large and diverse datasets that accurately represent the cybersecurity landscape in Bangladesh. However, data collection and management practices in the financial sector may be fragmented, leading to incomplete or inconsistent data. Ensuring data quality and establishing data-sharing mechanisms among financial institutions are crucial for successful implementation.
B. Infrastructure and Resources
Implementing machine learning and deep learning techniques necessitates robust computational infrastructure and adequate resources. These technologies require significant computing power and storage capabilities to process and analyze large volumes of data. It might be difficult for Bangladeshi financial institutions, particularly the smaller ones, to acquire and maintain the required infrastructure. Collaboration with technology providers and investment in infrastructure development are essential to overcome these challenges.
C. Expertise and Skill Gap
The successful implementation of machine learning and deep learning techniques requires a skilled workforce with expertise in data science, cybersecurity, and machine learning algorithms. Bangladesh may face a shortage of professionals with these specialized skills. Addressing this skill gap requires investment in training programs, collaborations with educational institutions, and knowledge-sharing initiatives. Building a strong talent pool will be crucial for the effective implementation and maintenance of these technologies.
D. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Integrating machine learning and deep learning techniques into banking cybersecurity raises regulatory and ethical considerations. Compliance with data protection and privacy regulations, such as the Personal Data Protection Act, is essential to ensure the responsible use of customer data. Additionally, transparency and explainability of machine learning models are crucial to maintaining frameworks and ethical guidelines that will be necessary to navigate these challenges.
F. Opportunities
Improved Cyber Threat Identification and Prevention: Deep learning and machine learning methods may greatly enhance cyber threat identification and prevention. These tools can instantly evaluate enormous volumes of data, spot trends, and spot abnormalities that might be signs of impending assaults. Financial institutions in Bangladesh can proactively guard against new cyber dangers by utilizing these skills.
Advanced Fraud Detection: Machine learning algorithms can be trained to identify patterns associated with fraudulent activities, such as account takeovers, identity theft, and payment fraud. By analyzing historical transaction data and customer behavior, these techniques can help financial institutions detect and prevent fraudulent activities, reducing financial losses and protecting customer assets.
Streamlined Compliance and Risk Management: Machine learning and deep learning techniques can automate compliance monitoring and risk management processes. Large volumes of data may be analyzed by these technologies to spot possible violations of regulations, questionable activity, and new dangers. By automating these processes, financial institutions can streamline their operations, reduce manual efforts, and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
Improved Customer Experience: Implementing machine learning and deep learning techniques can enhance the overall customer experience in the banking sector. These technologies can enable personalized security measures, such as adaptive authentication and fraud detection, tailored to individual customer profiles. By providing a seamless and secure banking experience, financial institutions can build trust and loyalty among their customers.
In conclusion, while implementing machine learning and deep learning techniques in Bangladesh's financial infrastructure for banking cybersecurity presents challenges, it also offers significant opportunities. By addressing data availability, infrastructure, expertise, and regulatory considerations, financial institutions can leverage these technologies to enhance threat detection, fraud prevention, compliance, and customer experience. Collaboration among stakeholders will be crucial in realizing the full potential of these technologies and ensuring a secure financial ecosystem in Bangladesh.
V. Recommendations and Future Directions
Given the cybersecurity threats affecting Bangladesh's financial system, it is critical to take proactive efforts toward fortification. Strengthening data protection procedures is a key aspect of this attempt. As shown in the monthly incident report graph, the frequency of cyber events in Bangladesh is on an alarming rising trend. This escalation emphasizes the importance of taking prompt action to protect sensitive financial information and the integrity of the banking industry. As a result, concerted efforts must be put toward improving data protection methods to limit risks and provide a resilient cybersecurity framework in the future.
Figure 3.
Monthly Cyber Incidents in Bangladesh [
19].
Figure 3.
Monthly Cyber Incidents in Bangladesh [
19].
A. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing a robust security framework necessitates the incorporation of diverse authentication mechanisms, ranging from traditional passwords to cutting-edge biometrics and token-based systems. This multifaceted approach fortifies the protection of financial accounts, thwarting unauthorized access attempts and enhancing the overall security posture against illicit transactions. Invest in cybersecurity training and awareness
B. Invest in Cybersecurity Training and Awareness
Providing thorough training courses is essential for enlightening clients and staff about cybersecurity best practices. These programs address important subjects like spotting phishing attempts, making strong passwords, and spotting questionable activity. Furthermore, we break down the causes of cyberattacks in
Figure 1, emphasizing the percentages associated with insider threats, carelessness, and vulnerability to social engineering attacks. This visual aid highlights how important it is to address human-related vulnerabilities through effective training and awareness efforts. Work together with industry experts.
Establish partnerships with cybersecurity firms, technology providers, and regulatory bodies to stay updated on the latest threats and mitigation strategies. Share information and collaborate on developing industry-wide cybersecurity standards.
C. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Perform periodic assessments of the financial infrastructure's security systems, networks, and applications to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary patches or updates. Conduct regular, detailed inspections of the financial infrastructure's security systems, networks, and applications. These evaluations are critical for detecting possible vulnerabilities. Once vulnerabilities have been found, implement the appropriate fixes or updates immediately to effectively minimize risks. This proactive strategy guarantees that the infrastructure remains resilient to emerging threats. By remaining watchful and responsive, the financial institution enhances its defenses and protects against any breaches or illegal access attempts.
D. Embrace Emerging Technologies
Explore the use of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and behavioral analytics to enhance cybersecurity measures. These technologies can provide real-time threat detection, secure transactions, and improve overall system resilience.
E. Strengthen Regulatory Frameworks
Work with regulatory bodies to develop and enforce robust cybersecurity regulations and standards for the financial sector. Regularly review and update these frameworks to address emerging threats and technological advancements.
F. Foster International Collaboration
Engage in international collaborations and information-sharing initiatives to combat cross-border cyber threats. Participate in global cybersecurity forums and share experiences and best practices with other countries.
H. Invest in Research and Development
Allocate resources to research and development efforts focused on cybersecurity innovations. Support local universities and research institutions to drive advancements in cybersecurity technologies and practices. By implementing these recommendations and focusing on future directions, Bangladesh can strengthen its financial infrastructure's cybersecurity posture, protect customer data, and maintain trust in the banking sector. This will contribute to the overall stability and growth of the country's economy in the digital era.
I. Strengthen Data Protection Measures
To keep sensitive financial data safe from hackers and other security lapses, we need to enhance data encryption, access restrictions, and data backup solutions. Robust encryption methods ensure that data is unreadable by unauthorized persons even in the case of interceptions. Implementing strong access control reduces the likelihood of unintentional breaches by limiting access to sensitive information. Reliable data backup systems also enable speedy recovery in the event of data loss or corruption. Security protocols need to be updated often to stay ahead of emerging threats. By routinely assessing and modifying security measures, financial institutions may successfully manage risks and preserve the integrity of their data infrastructure.
Ensuring strong data security protocols is crucial in Bangladesh, particularly in light of recent events like the 05-core NID (National Identification) data breach that occurred as a result of a Java bug. Bangladesh's Tier 4 data centers, which offer cutting-edge security features and dependability, are essential to this effort. On the other hand, events such as the NID data breach highlight the significance of being alert and paying close attention to security procedures. In Bangladesh's digital environment, strengthening encryption, improving access restrictions, and putting strict backup processes in place are necessary to protect sensitive financial information. Maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of financial data systems requires regular security measure reviews and upgrades to keep ahead of emerging threats [
16].
VI. Conclusions
The cybersecurity landscape in Bangladesh's financial sector demands urgent attention and proactive measures to ensure the stability and integrity of banking operations. In this regard, the adoption of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques presents a promising avenue for addressing these pressing concerns. However, their successful implementation comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities, necessitating a comprehensive approach.
First and foremost, addressing data availability and quality is paramount. ML and DL algorithms heavily rely on data for training and inference, making data accuracy, completeness, and relevance crucial factors. Moreover, ensuring the availability of robust infrastructure and adequate resources is essential to support the computational demands of these technologies.
Additionally, bridging skill gaps among personnel is imperative. Training and upskilling initiatives are necessary to equip staff with the requisite knowledge and expertise to effectively leverage ML and DL tools. Furthermore, navigating regulatory and ethical considerations is essential to ensure compliance with legal frameworks and ethical standards, safeguarding both customer privacy and institutional reputation.
Collaboration among stakeholders is another critical aspect of successful implementation. Engaging with regulatory bodies, industry partners, and technology providers fosters knowledge-sharing and promotes a unified approach to cybersecurity. By pooling resources and expertise, financial institutions can strengthen their defense mechanisms and enhance collective resilience against cyber threats.
The benefits of integrating ML and DL techniques are manifold. These technologies enable advanced threat detection and prevention mechanisms, enhance fraud detection capabilities, and streamline compliance and risk management processes. Moreover, they have the potential to elevate the overall customer experience by enabling personalized services and proactive security measures.
It is important to remember that ML and DL implementation is a process that involves iterations. Continuous monitoring, adaptation, and collaboration are essential to keep pace with the rapidly evolving threat landscape and technological advancements. Moreover, ongoing research and evaluation are necessary to assess the real-world impact of these technologies on the financial infrastructure and customer trust.
By embracing the recommended strategies and focusing on future directions, Bangladesh can fortify its financial infrastructure's cybersecurity posture, safeguard customer data, and uphold trust in the banking sector. This not only contributes to the resilience and growth of the economy but also ensures a secure digital future for all stakeholders involved.