Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coronaviral S Gene Sequence Retrieval and Sequence Conservation Analysis
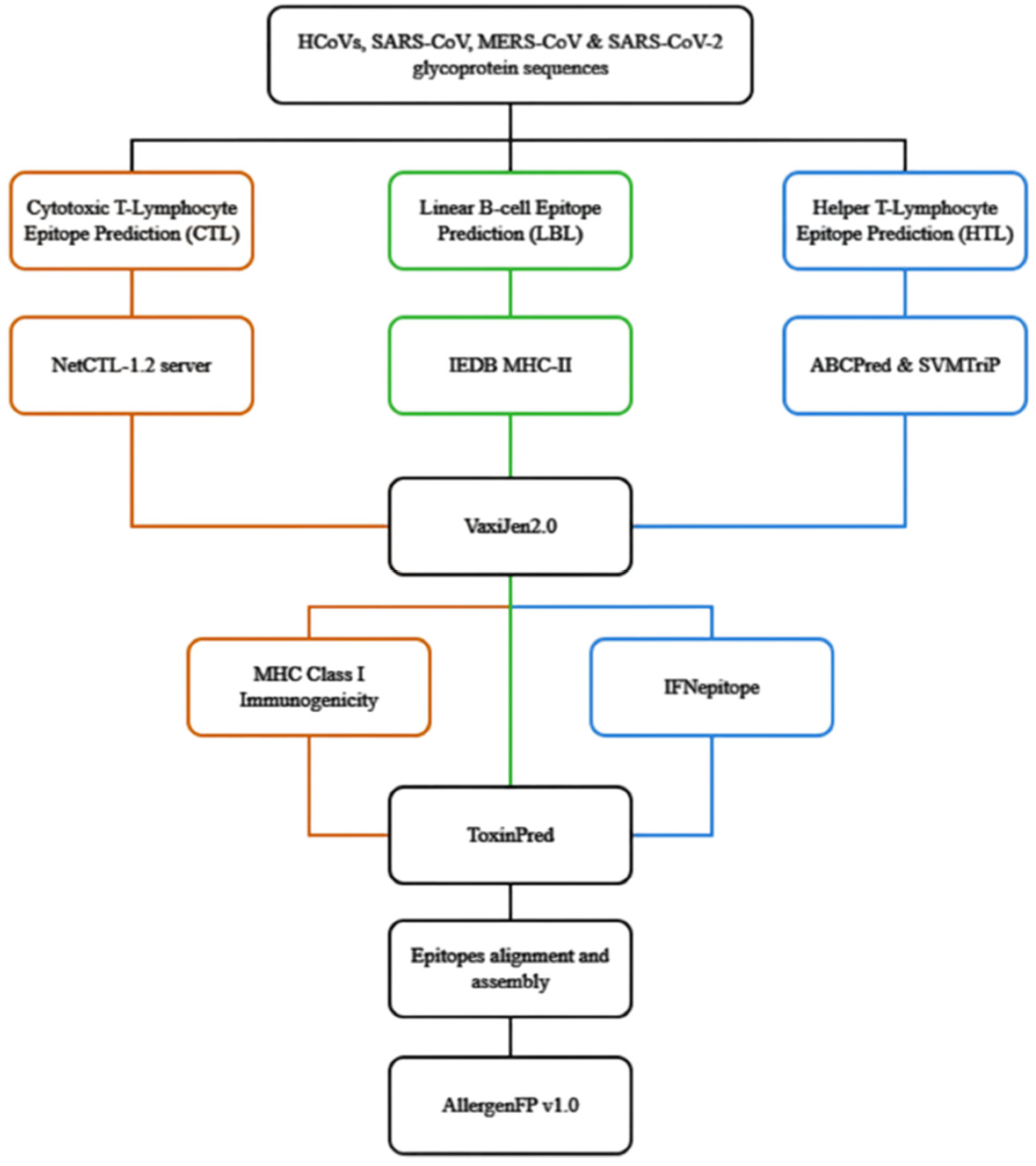
2.2. The flow of Prediction of Conserved HTL, CTL and Linear B-lymphocyte (LBL) Epitopes of Coronaviral S glycoproteins
2.2.1. Prediction of Conserved CTL Epitopes
2.2.2. Prediction of Conserved HTL Epitopes
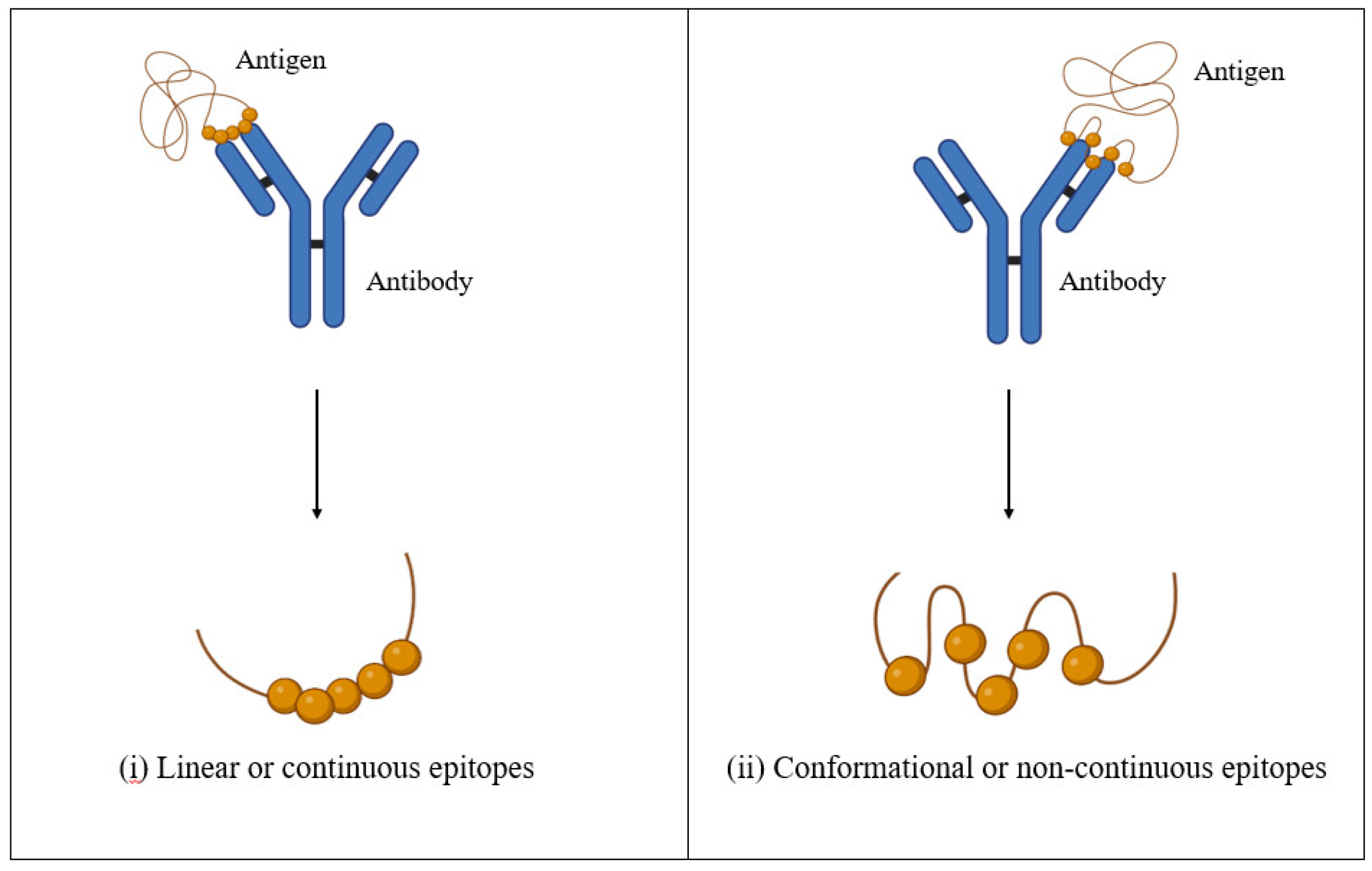
2.2.3. Prediction of Conserved LBL Epitopes
2.3. Alignment of the Predicted Conserved CTL, HTL and LBL Epitopes and Allergenicity Prediction
2.4. Structural Visualisation of Assembled Epitopes
3. Results
3.1. Conserved Regions in the S glycoproteins of Bat and Pangolin CoV, hCoVs, SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV
3.2. Prediction and Screening of Conserved CTL Epitopes of S glycoprotein
3.3. Prediction and Screening of Conserved HTL Epitopes
3.4. Prediction and Screening of Conserved LBL Epitopes
3.5. Alignment and Assembly of the Identified HTL, CTL T, and LBL Epitopes
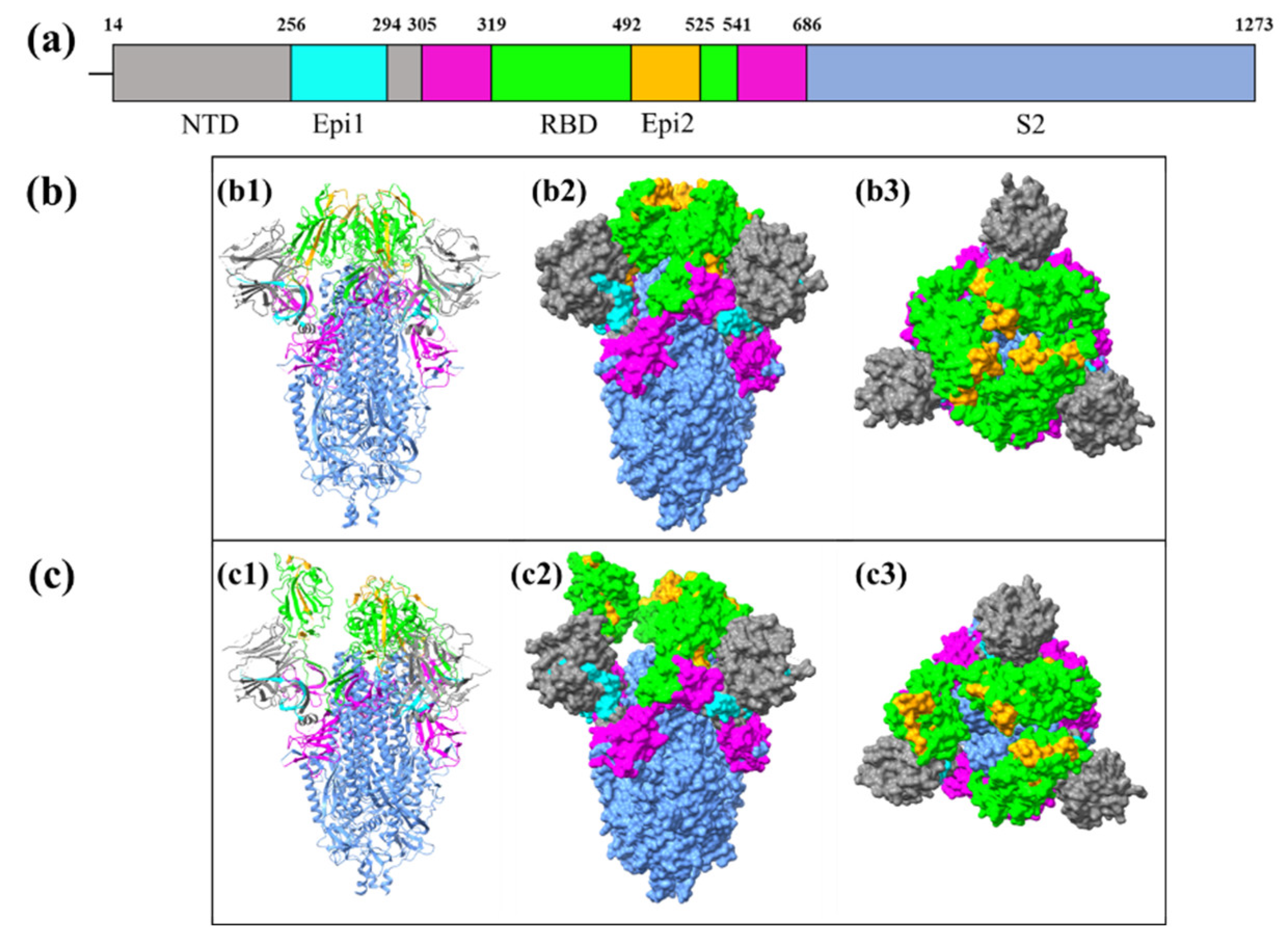
3.6. Identification of the Locations of the Conserved Epitopes in Coronaviral S glycoprotein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pormohammad, A., Ghorbani, S., Khatami, A., Farzi, R., Baradaran, B., Turner, D.L., Turner, R.J., Bahr, N.C., Idrovo, J.P.: Comparison of confirmed COVID-19 with SARS and MERS cases - Clinical characteristics, laboratory findings, radiographic signs and outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Med Virol. 30, (2020). [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.S., Perlman, S., Zumla, A.: Spread of MERS to South Korea and China. Lancet Respir Med. 3, 509–510 (2015). [CrossRef]
- WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020, https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020.
- COVID-19 cases | WHO COVID-19 dashboard, https://data.who.
- Andrews, N., Stowe, J., Kirsebom, F., Toffa, S., Rickeard, T., Gallagher, E., Gower, C., Kall, M., Groves, N., O’Connell, A.-M., Simons, D., Blomquist, P.B., Zaidi, A., Nash, S., Iwani Binti Abdul Aziz, N., Thelwall, S., Dabrera, G., Myers, R., Amirthalingam, G., Gharbia, S., Barrett, J.C., Elson, R., Ladhani, S.N., Ferguson, N., Zambon, M., Campbell, C.N.J., Brown, K., Hopkins, S., Chand, M., Ramsay, M., Lopez Bernal, J.: Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. New England Journal of Medicine. 386, 1532–1546 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Greaney, A.J., Starr, T.N., Gilchuk, P., Zost, S.J., Binshtein, E., Loes, A.N., Hilton, S.K., Huddleston, J., Eguia, R., Crawford, K.H.D., Dingens, A.S., Nargi, R.S., Sutton, R.E., Suryadevara, N., Rothlauf, P.W., Liu, Z., Whelan, S.P.J., Carnahan, R.H., Crowe, J.E., Bloom, J.D.: Complete Mapping of Mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain that Escape Antibody Recognition. Cell Host Microbe. 29, 44-57.e9 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T., Carabelli, A.M., Jackson, B., Gupta, R.K., Thomson, E.C., Harrison, E.M., Ludden, C., Reeve, R., Rambaut, A., Peacock, S.J., Robertson, D.L.: SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19, 409–424 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.A., Ahmed, S., Mir, A., Shinde, M., Bender, O., Alshammari, F., Ansari, M., Anwar, S.: The SARS-CoV-2 mutations versus vaccine effectiveness: New opportunities to new challenges. J Infect Public Health. 15, 228–240 (2022). [CrossRef]
- McLean, G., Kamil, J., Lee, B., Moore, P., Schulz, T.F., Muik, A., Sahin, U., Türeci, Ö., Pather, S.: The Impact of Evolving SARS-CoV-2 Mutations and Variants on COVID-19 Vaccines. mBio. 13, e02979-21 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S., Srivastava, R., Coulon, P.-G., Dhanushkodi, N.R., Chentoufi, A.A., Tifrea, D.F., Edwards, R.A., Figueroa, C.J., Schubl, S.D., Hsieh, L., Buchmeier, M.J., Bouziane, M., Nesburn, A.B., Kuppermann, B.D., BenMohamed, L.: Genome-Wide B Cell, CD4+, and CD8+ T Cell Epitopes That Are Highly Conserved between Human and Animal Coronaviruses, Identified from SARS-CoV-2 as Targets for Preemptive Pan-Coronavirus Vaccines. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. 206, 2566–2582 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, M.A., Izadi, M., Baesi, K., Jahromi, M.A.M., Pirestani, M.: Considering epitopes conservity in targeting SARS-CoV-2 mutations in variants: a novel immunoinformatics approach to vaccine design. Sci Rep. 12, 14017 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, V., Lee, H.J.: Conservation and Evolution of Antigenic Determinants of SARS-CoV-2: An Insight for Immune Escape and Vaccine Design. Front Immunol. 13, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F., Quadeer, A.A., McKay, M.R.: Preliminary Identification of Potential Vaccine Targets for the COVID-19 Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Based on SARS-CoV Immunological Studies. Viruses. 12, 254 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S., Ahmad, S., Azam, S.S.: Immunoinformatics characterization of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein for prioritization of epitope based multivalent peptide vaccine. J Mol Liq. 314, 113612 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S., Wu, S., Zhao, G., He, Y., Guo, X., Zhang, Z., Hou, J., Ding, Y., Cheng, A., Wang, B.: Identification of a promiscuous conserved CTL epitope within the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Emerg Microbes Infect. 11, 730 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.R.F., Patel, A., Ramos, S., Elwood, D., Zhu, X., Yan, J., Gary, E.N., Walker, S.N., Schultheis, K., Purwar, M., Xu, Z., Walters, J., Bhojnagarwala, P., Yang, M., Chokkalingam, N., Pezzoli, P., Parzych, E., Reuschel, E.L., Doan, A., Tursi, N., Vasquez, M., Choi, J., Tello-Ruiz, E., Maricic, I., Bah, M.A., Wu, Y., Amante, D., Park, D.H., Dia, Y., Ali, A.R., Zaidi, F.I., Generotti, A., Kim, K.Y., Herring, T.A., Reeder, S., Andrade, V.M., Buttigieg, K., Zhao, G., Wu, J.-M., Li, D., Bao, L., Liu, J., Deng, W., Qin, C., Brown, A.S., Khoshnejad, M., Wang, N., Chu, J., Wrapp, D., McLellan, J.S., Muthumani, K., Wang, B., Carroll, M.W., Kim, J.J., Boyer, J., Kulp, D.W., Humeau, L.M.P.F., Weiner, D.B., Broderick, K.E.: Immunogenicity of a DNA vaccine candidate for COVID-19. Nat Commun. 11, 2601 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S., Blaas, I., Bollineni, R.C., Delic-Sarac, M., Tran, T.T., Knetter, C., Dai, K.-Z., Madssen, T.S., Vaage, J.T., Gustavsen, A., Yang, W., Nissen-Meyer, L.S.H., Douvlataniotis, K., Laos, M., Nielsen, M.M., Thiede, B., Søraas, A., Lund-Johansen, F., Rustad, E.H., Olweus, J.: Prevalent and immunodominant CD8 T cell epitopes are conserved in SARS-CoV-2 variants. Cell Rep. 42, 111995 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N., Huang, X., Joshi, S., Guo, C., Ng, J., Thakkar, R., Wu, Y., Dong, X., Li, Q., Pinapati, R.S., Sullivan, E., Caciula, A., Tokarz, R., Briese, T., Lu, J., Lipkin, W.I.: Immunoreactive peptide maps of SARS-CoV-2. Commun Biol. 4, 225 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Wu, X., Zhang, X., Hou, X., Liang, T., Wang, D., Teng, F., Dai, J., Duan, H., Guo, S., Li, Y., Yu, X.: SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Microarray for Mapping COVID-19 Antibody Interactions at Amino Acid Resolution. ACS Cent Sci. 6, 2238–2249 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M., von Bülow, S., Blanc, F.E.C., Gecht, M., Covino, R., Hummer, G.: Computational epitope map of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. PLoS Comput Biol. 17, e1008790 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, T., Heiss, K., Mahendran, Y., Casilag, F., Kurth, F., Sander, L.E., Wendtner, C.-M., Hoechstetter, M.A., Müller, M.A., Sekul, R., Drosten, C., Stadler, V., Corman, V.M.: SARS-CoV-2 Proteome-Wide Analysis Revealed Significant Epitope Signatures in COVID-19 Patients. Front Immunol. 12, 629185 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Paul, S., Arlehamn, C.S.L., Scriba, T.J., Dillon, M.B.C., Oseroff, C., Hinz, D., McKinney, D.M., Pro, S.C., Sidney, J., Peters, B., Sette, A.: Development and validation of a broad scheme for prediction of HLA class II restricted T cell epitopes. J Immunol Methods. 422, 28–34 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Chenavas, S., Estrozi, L.F., Slama-Schwok, A., Delmas, B., Primo, C. Di, Baudin, F., Li, X., Crépin, T., Ruigrok, R.W.H.: Monomeric Nucleoprotein of Influenza A Virus. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003275 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N., Cottrell, C.A., Wang, N., Pallesen, J., Yassine, H.M., Turner, H.L., Corbett, K.S., Graham, B.S., McLellan, J.S., Ward, A.B.: Pre-fusion structure of a human coronavirus spike protein. Nature. 531, 118–121 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., Tomlinson, A.C.A., Wong, A.H.M., Zhou, D., Desforges, M., Talbot, P.J., Benlekbir, S., Rubinstein, J.L., Rini, J.M.: The human coronavirus HCoV-229E S-protein structure and receptor binding. Elife. 8, e51230 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., Hesketh, E.L., Shamorkina, T.M., Li, W., Franken, P.J., Drabek, D., van Haperen, R., Townend, S., van Kuppeveld, F.J.M., Grosveld, F., Ranson, N.A., Snijder, J., de Groot, R.J., Hurdiss, D.L., Bosch, B.-J.: Antigenic structure of the human coronavirus OC43 spike reveals exposed and occluded neutralizing epitopes. Nat Commun. 13, 2921 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Yang, C., Xu, X., Xu, W., Liu, S.: Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41, 1141–1149 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.: Domains and Functions of Spike Protein in SARS-Cov-2 in the Context of Vaccine Design. Viruses. 13, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z., Monteil, V.M., Maurer-Stroh, S., Yew, C.W., Leong, C., Mohd-Ismail, N.K., Arularasu, S.C., Chow, V.T.K., Lin, R.T.P., Mirazimi, A., Hong, W., Tan, Y.J.: Monoclonal antibodies for the S2 subunit of spike of SARS-CoV-1 cross-react with the newly-emerged SARS-CoV-2. Eurosurveillance. 25, 19–28 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.F., Lemey, P., Jiang, X., Lam, T.T.-Y., Perry, B.W., Castoe, T.A., Rambaut, A., Robertson, D.L.: Evolutionary origins of the SARS-CoV-2 sarbecovirus lineage responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Microbiol. 5, 1408–1417 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Giorgi, E.E., Marichannegowda, M.H., Foley, B., Xiao, C., Kong, X.-P., Chen, Y., Gnanakaran, S., Korber, B., Gao, F.: Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 through recombination and strong purifying selection. Sci Adv. 6, eabb9153 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Sajini, A.A., Alkayyal, A.A., Mubaraki, F.A.: The Recombination Potential between SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV from Cross-Species Spill-over Infections. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 11, 155–159 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V., Lundegaard, C., Lamberth, K., Buus, S., Lund, O., Nielsen, M.: Large-scale validation of methods for cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 8, 424 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V., Lundegaard, C., Lamberth, K., Buus, S., Brunak, S., Lund, O., Nielsen, M.: An integrative approach to CTL epitope prediction: A combined algorithm integrating MHC class I binding, TAP transport efficiency, and proteasomal cleavage predictions. Eur J Immunol. 35, 2295–2303 (2005). [CrossRef]
- Sidney, J., Grey, H.M., Kubo, R.T., Sette, A.: Practical, biochemical and evolutionary implications of the discovery of HLA class I supermotifs. Immunol Today. 17, 261–266 (1996). [CrossRef]
- Sidney, J., Peters, B., Frahm, N., Brander, C., Sette, A.: HLA class I supertypes: a revised and updated classification. BMC Immunol. 9, 1 (2008). [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Francisco, R., Buhler, S., Nunes, J.M., Bitarello, B.D., França, G.S., Meyer, D., Sanchez-Mazas, A.: HLA supertype variation across populations: new insights into the role of natural selection in the evolution of HLA-A and HLA-B polymorphisms. Immunogenetics. 67, 651–663 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Andreatta, M., Trolle, T., Yan, Z., Greenbaum, J.A., Peters, B., Nielsen, M.: An automated benchmarking platform for MHC class II binding prediction methods. Bioinformatics. 34, 1522–1528 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., Sidney, J., Dow, C., Mothé, B., Sette, A., Peters, B.: A Systematic Assessment of MHC Class II Peptide Binding Predictions and Evaluation of a Consensus Approach. PLoS Comput Biol. 4, e1000048 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, J., Sidney, J., Chung, J., Brander, C., Peters, B., Sette, A.: Functional classification of class II human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules reveals seven different supertypes and a surprising degree of repertoire sharing across supertypes. Immunogenetics. 63, 325–335 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Paul, S., Arlehamn, C.S.L., Scriba, T.J., Dillon, M.B.C., Oseroff, C., Hinz, D., McKinney, D.M., Pro, S.C., Sidney, J., Peters, B., Sette, A.: Development and validation of a broad scheme for prediction of HLA class II restricted T cell epitopes. J Immunol Methods. 422, 28–34 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Regenmortel, M.H. V: What Is a B-Cell Epitope? In: Schutkowski, M. and Reineke, U. (eds.) Epitope Mapping Protocols. pp. 3–20. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ (2009).
- Sanchez-Trincado, J.L., Gomez-Perosanz, M., Reche, P.A.: Fundamentals and Methods for T- and B-Cell Epitope Prediction. J Immunol Res. 2017, 2680160 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N., Wesemann, D.R.: Analyzing Immunoglobulin Repertoires. Front Immunol. 9, (2018).
- Raybould, M.I.J., Rees, A.R., Deane, C.M.: Current strategies for detecting functional convergence across B-cell receptor repertoires. MAbs. 13, 1996732 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Briney, B., Inderbitzin, A., Joyce, C., Burton, D.R.: Commonality despite exceptional diversity in the baseline human antibody repertoire. Nature. 566, 393–397 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Soto, C., Bombardi, R.G., Branchizio, A., Kose, N., Matta, P., Sevy, A.M., Sinkovits, R.S., Gilchuk, P., Finn, J.A., Crowe, J.E.: High frequency of shared clonotypes in human B cell receptor repertoires. Nature. 566, 398–402 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Galanis, K.A., Nastou, K.C., Papandreou, N.C., Petichakis, G.N., Iconomidou, V.A.: Linear B-cell epitope prediction: a performance review of currently available methods, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/833418v1, (2019).
- Yao, B., Zhang, L., Liang, S., Zhang, C.: SVMTriP: A Method to Predict Antigenic Epitopes Using Support Vector Machine to Integrate Tri-Peptide Similarity and Propensity. PLoS One. 7, e45152 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, S., Son, D.Y., Boehm, M., Karamloo, F., Franke, S., Hoffmann, A., Haustein, D., Vieths, S.: Cross-reactivity and epitope analysis of Pru a 1, the major cherry allergen. Mol Immunol. 36, 155–167 (1999). [CrossRef]
- Neudecker, P., Lehmann, K., Nerkamp, J., Haase, T., Wangorsch, A., Fötisch, K., Hoffmann, S., Rösch, P., Vieths, S., Scheurer, S.: Mutational epitope analysis of Pru av 1 and Api g 1, the major allergens of cherry (Prunus avium) and celery (Apium graveolens): correlating IgE reactivity with three-dimensional structure. Biochemical Journal. 376, 97–107 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Arrieta-Bolaños, E., Hernández-Zaragoza, D.I., Barquera, R.: An HLA map of the world: A comparison of HLA frequencies in 200 worldwide populations reveals diverse patterns for class I and class II. Front Genet. 14, 866407 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B., Xu, S., Liu, M., Wei, Y., Wang, Q., Shen, W., Lei, C.Q., Zhu, Q.: The nucleoprotein of influenza A virus inhibits the innate immune response by inducing mitophagy. Autophagy. 19, 1916 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C., Wang, B., Chen, P., Jiang, Y., Liu, J.: Analysis of the conserved protective epitopes of hemagglutinin on influenza A viruses. Front Immunol. 14, 1086297 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Corti, D., Lanzavecchia, A.: Broadly neutralizing antiviral antibodies. Annu Rev Immunol. 31, 705–742 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. : SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development. Nature. 586, 516–527 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, N.C., López-Cortés, A., González, E.V., Grimaldos, A.B., Prado, E.O.: SARS-CoV-2 vaccines strategies: a comprehensive review of phase 3 candidates. NPJ Vaccines. 6, 28 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Flores, D., Zepeda-Cervantes, J., Cruz-Reséndiz, A., Aguirre-Sampieri, S., Sampieri, A., Vaca, L.: SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Based on the Spike Glycoprotein and Implications of New Viral Variants. Front Immunol. 12, 701501 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Samrat, S.K., Tharappel, A.M., Li, Z., Li, H.: Prospect of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential role in vaccine and therapeutic development. Virus Res. 288, 198141 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Sulbaran, G., Maisonnasse, P., Amen, A., Effantin, G., Guilligay, D., Dereuddre-Bosquet, N., Burger, J.A., Poniman, M., Grobben, M., Buisson, M., Dergan Dylon, S., Naninck, T., Lemaître, J., Gros, W., Gallouët, A.-S., Marlin, R., Bouillier, C., Contreras, V., Relouzat, F., Fenel, D., Thepaut, M., Bally, I., Thielens, N., Fieschi, F., Schoehn, G., van der Werf, S., van Gils, M.J., Sanders, R.W., Poignard, P., Le Grand, R., Weissenhorn, W.: Immunization with synthetic SARS-CoV-2 S glycoprotein virus-like particles protects macaques from infection. Cell Rep Med. 3, 100528 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D., Wang, N., Corbett, K.S., Goldsmith, J.A., Hsieh, C.-L., Abiona, O., Graham, B.S., McLellan, J.S.: Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 367, 1260–1263 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, A., Naujokat, C.: Structural features of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Targets for vaccination. Life Sci. 257, 118056 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y., Yisimayi, A., Jian, F., Song, W., Xiao, T., Wang, L., Du, S., Wang, J., Li, Q., Chen, X., Yu, Y., Wang, P., Zhang, Z., Liu, P., An, R., Hao, X., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Feng, R., Sun, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, W., Zhao, D., Zheng, J., Yu, L., Li, C., Zhang, N., Wang, R., Niu, X., Yang, S., Song, X., Chai, Y., Hu, Y., Shi, Y., Zheng, L., Li, Z., Gu, Q., Shao, F., Huang, W., Jin, R., Shen, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Xiao, J., Xie, X.S.: BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature. 608, 593–602 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Greaney, A.J., Loes, A.N., Crawford, K.H.D., Starr, T.N., Malone, K.D., Chu, H.Y., Bloom, J.D.: Comprehensive mapping of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human plasma antibodies. Cell Host Microbe. 29, 463-476.e6 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Greaney, A.J., Starr, T.N., Barnes, C.O., Weisblum, Y., Schmidt, F., Caskey, M., Gaebler, C., Cho, A., Agudelo, M., Finkin, S., Wang, Z., Poston, D., Muecksch, F., Hatziioannou, T., Bieniasz, P.D., Robbiani, D.F., Nussenzweig, M.C., Bjorkman, P.J., Bloom, J.D.: Mutational escape from the polyclonal antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection is largely shaped by a single class of antibodies, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.03.17.435863v1, (2021).
- Weisblum, Y., Schmidt, F., Zhang, F., DaSilva, J., Poston, D., Lorenzi, J.C.C., Muecksch, F., Rutkowska, M., Hoffmann, H.-H., Michailidis, E., Gaebler, C., Agudelo, M., Cho, A., Wang, Z., Gazumyan, A., Cipolla, M., Luchsinger, L., Hillyer, C.D., Caskey, M., Robbiani, D.F., Rice, C.M., Nussenzweig, M.C., Hatziioannou, T., Bieniasz, P.D.: Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. Elife. 9, e61312 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Röltgen, K., Nielsen, S.C.A., Silva, O., Younes, S.F., Zaslavsky, M., Costales, C., Yang, F., Wirz, O.F., Solis, D., Hoh, R.A., Wang, A., Arunachalam, P.S., Colburg, D., Zhao, S., Haraguchi, E., Lee, A.S., Shah, M.M., Manohar, M., Chang, I., Gao, F., Mallajosyula, V., Li, C., Liu, J., Shoura, M.J., Sindher, S.B., Parsons, E., Dashdorj, N.J., Dashdorj, N.D., Monroe, R., Serrano, G.E., Beach, T.G., Chinthrajah, R.S., Charville, G.W., Wilbur, J.L., Wohlstadter, J.N., Davis, M.M., Pulendran, B., Troxell, M.L., Sigal, G.B., Natkunam, Y., Pinsky, B.A., Nadeau, K.C., Boyd, S.D.: Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cell. 185, 1025-1040.e14 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, A.K., Fox, A., Tan, H.-X., Juno, J.A., Davenport, M.P., Subbarao, K., Kent, S.J.: Immune imprinting and SARS-CoV-2 vaccine design. Trends Immunol. 42, 956–959 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Ma, M., Lei, Q., Wang, F., Hong, W., Lai, D., Hou, H., Xu, Z., Zhang, B., Chen, H., Yu, C., Xue, J., Zheng, Y., Wang, X., Jiang, H., Zhang, H., Qi, H., Guo, S., Zhang, Y., Lin, X., Yao, Z., Wu, J., Sheng, H., Zhang, Y., Wei, H., Sun, Z., Fan, X., Tao, S.: Linear epitope landscape of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein constructed from 1,051 COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep. 34, 108915 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B., Hu, Y., Chen, L., Yau, T., Tong, Y., Hu, J., Cai, J., Chan, K.-H., Dou, Y., Deng, J., Wang, X., Hung, I.F.-N., To, K.K.-W., Yuen, K.Y., Huang, J.-D.: Mining of epitopes on spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 from COVID-19 patients. Cell Res. 30, 702–704 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-Z., Chu, H., Han, S., Shuai, H., Deng, J., Hu, Y., Gong, H., Lee, A.C.-Y., Zou, Z., Yau, T., Wu, W., Hung, I.F.-N., Chan, J.F.-W., Yuen, K.-Y., Huang, J.-D.: SARS-CoV-2 infects human neural progenitor cells and brain organoids. Cell Res. 30, 928–931 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C., Tengs, T.: No species-level losses of s2m suggests critical role in replication of SARS-related coronaviruses. Sci Rep. 11, 16145 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M., Muth, D., Niemeyer, D., Drosten, C.: Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 100, 163–188 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Flerlage, T., Boyd, D.F., Meliopoulos, V., Thomas, P.G., Schultz-Cherry, S.: Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2: pathogenesis and host responses in the respiratory tract. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19, 425–441 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Traherne, J.A.: Human MHC architecture and evolution: implications for disease association studies. Int J Immunogenet. 35, 179–192 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Gartland, A.J., Li, S., McNevin, J., Tomaras, G.D., Gottardo, R., Janes, H., Fong, Y., Morris, D., Geraghty, D.E., Kijak, G.H., Edlefsen, P.T., Frahm, N., Larsen, B.B., Tovanabutra, S., Sanders-Buell, E., deCamp, A.C., Magaret, C.A., Ahmed, H., Goodridge, J.P., Chen, L., Konopa, P., Nariya, S., Stoddard, J.N., Wong, K., Zhao, H., Deng, W., Maust, B.S., Bose, M., Howell, S., Bates, A., Lazzaro, M., O’Sullivan, A., Lei, E., Bradfield, A., Ibitamuno, G., Assawadarachai, V., O’Connell, R.J., deSouza, M.S., Nitayaphan, S., Rerks-Ngarm, S., Robb, M.L., Sidney, J., Sette, A., Zolla-Pazner, S., Montefiori, D., McElrath, M.J., Mullins, J.I., Kim, J.H., Gilbert, P.B., Hertz, T.: Analysis of HLA A*02 Association with Vaccine Efficacy in the RV144 HIV-1 Vaccine Trial. J Virol. 88, 8242–8255 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Guo, T., Yu, Q., Zhang, H., Du, J., Zhang, Y., Xia, S., Yang, H., Li, Q.: Association of human leukocyte antigen alleles and supertypes with immunogenicity of oral rotavirus vaccine given to infants in China. Medicine. 97, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Mentzer, A.J., O’Connor, D., Bibi, S., Chelysheva, I., Clutterbuck, E.A., Demissie, T., Dinesh, T., Edwards, N.J., Felle, S., Feng, S., Flaxman, A.L., Karp-Tatham, E., Li, G., Liu, X., Marchevsky, N., Godfrey, L., Makinson, R., Bull, M.B., Fowler, J., Alamad, B., Malinauskas, T., Chong, A.Y., Sanders, K., Shaw, R.H., Voysey, M., Snape, M.D., Pollard, A.J., Lambe, T., Knight, J.C.: Human leukocyte antigen alleles associate with COVID-19 vaccine immunogenicity and risk of breakthrough infection. Nat Med. 29, 147–157 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Milich, D.R., Leroux-Roels, G.G.: Immunogenetics of the response to HBsAg vaccination. Autoimmun Rev. 2, 248–257 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.M., Vekemans, J., Lievens, M., Kester, K.E., Regules, J.A., Ockenhouse, C.F.: RTS,S malaria vaccine efficacy and immunogenicity during Plasmodium falciparum challenge is associated with HLA genotype. Vaccine. 36, 1637–1642 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N., Sugiyama, M., Sawai, H., Nishina, S., Sakai, A., Ohashi, J., Khor, S., Kakisaka, K., Tsuchiura, T., Hino, K., Sumazaki, R., Takikawa, Y., Murata, K., Kanda, T., Yokosuka, O., Tokunaga, K., Mizokami, M.: Key HLA-DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes and role of the BTNL2 gene for response to a hepatitis B vaccine. Hepatology. 68, 848–858 (2018). [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D., Png, E., Khor, C.C., Snape, M.D., Hill, A.V.S., Klis, F. van der, Hoggart, C., Levin, M., Hibberd, M.L., Pollard, A.J.: Common Genetic Variations Associated with the Persistence of Immunity following Childhood Immunization. Cell Rep. 27, 3241-3253.e4 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Posteraro, B., Pastorino, R., Di Giannantonio, P., Ianuale, C., Amore, R., Ricciardi, W., Boccia, S.: The link between genetic variation and variability in vaccine responses: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Vaccine. 32, 1661–1669 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Ovsyannikova, I.G., Haralambieva, I.H., Vierkant, R.A., O’Byrne, M.M., Jacobson, R.M., Poland, G.A.: The Association of CD46, SLAM and CD209 Cellular Receptor Gene SNPs with Variations in Measles Vaccine-Induced Immune Responses: A Replication Study and Examination of Novel Polymorphisms. Hum Hered. 72, 206 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Potocnakova, L., Bhide, M., Pulzova, L.B.: An Introduction to B-Cell Epitope Mapping and In Silico Epitope Prediction. J Immunol Res. 2016, 6760830 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Jawad, B., Adhikari, P., Podgornik, R., Ching, W.Y.: Key Interacting Residues between RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 Receptor: Combination of Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Density Functional Calculation. J Chem Inf Model. 61, 4425–4441 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Borkotoky, S., Dey, D., Hazarika, Z.: Interactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD): a structural perspective. Mol Biol Rep. 50, 2713 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Yi, C., Sun, X., Ye, J., Ding, L., Liu, M., Yang, Z., Lu, X., Zhang, Y., Ma, L., Gu, W., Qu, A., Xu, J., Shi, Z., Ling, Z., Sun, B.: Key residues of the receptor binding motif in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 that interact with ACE2 and neutralizing antibodies. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 2020 17:6. 17, 621–630 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Sun, C., Kang, Y.F., Liu, Y.T., Kong, X.W., Xu, H.Q., Xiong, D., Xie, C., Liu, Y.H., Peng, S., Feng, G.K., Liu, Z., Zeng, M.S.: Parallel profiling of antigenicity alteration and immune escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2022 7:1. 7, 1–10 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Verkhivker, G., Alshahrani, M., Gupta, G.: Balancing Functional Tradeoffs between Protein Stability and ACE2 Binding in the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, BA.2.75 and XBB Lineages: Dynamics-Based Network Models Reveal Epistatic Effects Modulating Compensatory Dynamic and Energetic Changes. Viruses. 15, 1143 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., Thambiraja, T.S., Karuppanan, K., Subramaniam, G.: Omicron and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2: A comparative computational study of spike protein. J Med Virol. 94, 1641–1649 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Singh, A., Thakur, M., Sharma, L.K., Chandra, K.: Designing a multi-epitope peptide based vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Sci Rep. 10, 16219 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Wu, X., Li, W., Rong, H., Pan, J., Zhang, X., Hu, Q., Shi, Z.-L., Zhang, X.-E., Cui, Z.: A Nanoparticle Vaccine Displaying Conserved Epitopes of the Preexisting Neutralizing Antibody Confers Broad Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. ACS Nano. 18, 17749–17763 (2024). [CrossRef]
- He, L., Lin, X., Wang, Y., Abraham, C., Sou, C., Ngo, T., Zhang, Y., Wilson, I.A., Zhu, J.: Single-component, self-assembling, protein nanoparticles presenting the receptor binding domain and stabilized spike as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates. Sci Adv. 7, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.K.-L., Zhang, H., Tan, K., Li, Z., Liu, J., Chan, P.K.-S., Li, S.-M., Chan, W.-Y., Au, S.W.-N., Joachimiak, A., Walz, T., Wang, J.-H., Shaw, P.-C.: Structure of the influenza virus A H5N1 nucleoprotein: implications for RNA binding, oligomerization, and vaccine design. The FASEB Journal. 22, 3638 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Wu, F., Huang, J.-H., Yuan, X.-Y., Huang, W.-S., Chen, Y.-H.: Characterization of immunity induced by M2e of influenza virus. Vaccine. 25, 8868–8873 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Gao, X., Wang, W., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Duan, Y., Xing, L., Zhao, Z., Zhang, P., Li, Z., Li, R., Wang, X., Yang, P.: Enhanced Influenza VLP vaccines comprising matrix-2 ectodomain and nucleoprotein epitopes protects mice from lethal challenge. Antiviral Res. 98, 4–11 (2013). [CrossRef]
| Nomenclature | Lineage | Accession number |
|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2-Wuhan-Hu-1 strain | NC_045512.2 | |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | OK340744.1 |
| Beta | B.1.351 | OQ341818.1 |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | OQ314763.1 |
| Gamma | P.1 | OQ316323.1 |
| Omicron | B.1.1.529 | OQ344199.1 |
| Omicron | BA.1 | OQ355083.1 |
| Omicron | BA.1.1 | OQ352636.1 |
| Omicron | BA.2 | OQ341824.1 |
| Omicron | BA.2.12.1 | OQ355080.1 |
| Omicron | BA.2.75 | OQ215893.1 |
| Omicron | BA.2.75.2 | OQ346937.1 |
| Omicron | BA.4 | OQ333888.1 |
| Omicron | BA.4.6 | OQ349323.1 |
| Omicron | BA.5 | OQ343976.1 |
| Omicron | BA.5.2.6 | OQ346806.1 |
| Omicron | BF.11 | OQ347094.1 |
| Omicron | BF.7 | OQ346784.1 |
| Omicron | BN.1 | OQ346744.1 |
| Omicron | BQ.1 | OQ346454.1 |
| Omicron | BQ.1.1 | OQ346605.1 |
| Omicron | CH.1.1 | OQ346876.1 |
| Omicron | XBB | OQ347865.1 |
| Omicron | XBB.1.5 | XBB.1.5 is a sub-lineage of XBB with an additional spike RBD mutation S486P |
| Nomenclature | Accession number |
|---|---|
| MERS-CoV | NC_019843 |
| SARS-CoV (Urbani) | AY278741.1 |
| HCoV-HKU1–genotype B | AY884001 |
| HCoV-OC43 | KF923903 |
| HCoV-NL63 | NC_005831 |
| Strain name | Accession number |
|---|---|
| Bat CoV RATG13 | MN996532.2 |
| Bat CoV ZXC21 | MG772934.1 |
| Bat CoV YN02 | MW201982.1 |
| Pangolin CoV GX-P2V | MT072864.1 |
| Pangolin CoV GX-P5E | MT040336.1 |
| Pangolin CoV GX-P5L | MT040335.1 |
| Pangolin CoV GX-P1E | MT040334.1 |
| Pangolin CoV GX-P4L | MT040333.1 |
| Pangolin CoV MP789 | MT121216.1 |
| Avian CoV Ind-TN92-03 | NC_048213.1 |
| Avian CoV DK/GD/27/2014 | NC_048214.1 |
| Avian CoV MG10 | NC_010800.1 |
| CTL Prediction tools | Prediction tool’s criteria |
|---|---|
| NetCTL-1.2 |
|
| VaxiJen 2.0 |
|
| IEDB MHC Class I immunogenicity |
|
| ToxinPred |
|
| HTL Prediction tools | Prediction tool’s criteria |
|---|---|
| IEDB MHC-II | 1. Percentile rank: 20%, 15-mers. 2. Method: Consensus 2.22. 3. HLA Supertype: HLA-DR, HLA-DQ, HLA-DP. i. HLA-DR: • DRB1*01:01 • DRB1*07:01 • DRB1*09:01 • DRB3-01:01 • DRB4*01:01 ii. HLA-DQ: • DQA1*01:01/ DQB1*05:01 • DQA1*01:02/ DQB1*06:02 • DQA1*03:01/ DQB1*03:02 • DQA1*04:01/ DQB1*04:02 • DQA1*05:01/ DQB1*02:01 • DQA1*05:01/ DQB1*03:01 iii. HLA-DP: • DPA1*01/ DPB1*04:01 • DPA1*01:03/ DPB1*02:01 • DPA1*02:01/ DPB1*01:01 • DPA1*02:01/ DPB1*05:01 • DPA1*03:01/ DPB1*04:02 4. Exclude epitopes with percentile rank higher than 20.0 |
| IFNepitope | 1. Prediction approach: Motif and SVM hybrid. 2. Model for prediction: IFN-gamma versus Non IFN-gamma. 3. Exclude “NEGATIVE” epitopes. |
| LBL Prediction tools | Prediction tool’s condition |
|---|---|
| ABCPred | Length of epitope: 16-mers Threshold: 0.51 and above Overlapping filter: ON |
| SVMTriP | Length of epitope: 16-mers Select epitopes with a score of 0.5 and above |
| Epitopes | Number of coronavirus strains in which the epitope is found (out of 30) | Location in the S glycoprotein* | Assigned name |
|---|---|---|---|
| RVVVLSFEL | 25 | 509-517 | CTL1 |
| STQDLFLPF | 24 | 50-59 | CTL2 |
| WTAGAAAYY | 24 | 258-266 | CTL3 |
| YLQPRTFLL | 24 | 269-277 | CTL4 |
| QIITTDNTF | 24 | 1113-1121 | CTL5 |
| GAAAYYVGY | 24 | 261-269 | CTL6 |
| ITDAVDCAL | 24 | 284-293 | CTL7 |
| FTISVTTEI | 24 | 718-726 | CTL8 |
| FVFLVLLPL | 23 | 2-9 | CTL9 |
| QSYGFRPTY | 15 | 493-501 | CTL10 |
| SVLYNFAPF | 13 | 366-374 | CTL11 |
| YQPYRVVVL | 6 | 505-513 | CTL12 |
| Peptide sequence | Number of matched coronavirus strains | Location in S glycoprotein | Assigned Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVLGQSKRVDFCGKGY | 25 | 1045-1060 | LBL1 |
| DKYFKNHTSPDVDLGD | 25 | 1166-1181 | LBL2 |
| DEDDSEPVLKGVKLHY | 25 | 1270-1285 | LBL3 |
| AMQMAYRFNGIGVTQN | 25 | 899-914 | LBL4 |
| AGAALQIPFAMQMAYR | 25 | 903-918 | LBL5 |
| FAMQMAYRFNGIGVTQ | 25 | 911-926 | LBL6 |
| ASANLAATKMSECVLG | 24 | 1033-1048 | LBL7 |
| ATKMSECVLGQSKRVD | 24 | 1039-1054 | LBL8 |
| HGVVFLHVTYVPAQEK | 24 | 1071-1086 | LBL9 |
| HVTYVPAQEKNFTTAP | 24 | 1077-1092 | LBL10 |
| FVSGNCDVVIGIVNNT | 24 | 1134-1149 | LBL11 |
| VIGIVNNTVYDPLQPE | 24 | 1142-1157 | LBL12 |
| HTSPDVDLGDISGINA | 24 | 1172-1187 | LBL13 |
| LGDISGINASVVNIQK | 24 | 1179-1194 | LBL14 |
| GTTLDSKTQSLLIVNN | 24 | 120-135 | LBL15 |
| ESLIDLQELGKYEQYI | 24 | 1208-1223 | LBL16 |
| YVGYLQPRTFLLKYNE | 24 | 279-294 | LBL17 |
| NENGTITDAVDCALDP | 24 | 293-308 | LBL18 |
| AVDCALDPLSETKCTL | 24 | 301-316 | LBL19 |
| DPLSETKCTLKSFTVE | 24 | 307-322 | LBL20 |
| TVEKGIYQTSNFRVQP | 24 | 320-335 | LBL21 |
| VQPTESIVRFPNITNL | 24 | 333-348 | LBL22 |
| NDLCFTNVYADSFVIR | 24 | 388-403 | LBL23 |
| PTKLNDLCFTNVYADS | 24 | 397-412 | LBL24 |
| VVLSFELLHAPATVCG | 24 | 524-539 | LBL25 |
| FRSSVLHSTQDLFLPF | 24 | 56-71 | LBL26 |
| TDAVRDPQTLEILDIT | 24 | 586-601 | LBL27 |
| EILDITPCSFGGVSVI | 24 | 596-611 | LBL28 |
| GVSVITPGTNTSNQVA | 24 | 607-622 | LBL29 |
| HSTQDLFLPFFSNVTW | 24 | 62-77 | LBL30 |
| YSTGSNVFQTRAGCLI | 24 | 649-664 | LBL31 |
| TISVTTEILPVSMTKT | 24 | 732-747 | LBL32 |
| TECSNLLLQYGSFCTQ | 24 | 760-775 | LBL33 |
| RALTGIAVEQDKNTQE | 24 | 778-793 | LBL34 |
| AVEQDKNTQEVFAQVK | 24 | 784-799 | LBL35 |
| EMIAQYTSALLAGTIT | 24 | 881-896 | LBL36 |
| AGTITSGWTFGAGAAL | 24 | 892-907 | LBL37 |
| IGKIQDSLSSTASALG | 24 | 944-959 | LBL38 |
| FKCYGVSPTKLNDLCF | 24 | 374-389 | LBL39 |
| FVTQRNFYEPQIITTD | 23 | 1116-1131 | LBL40 |
| YEQYIKWPWYIWLGFI | 23 | 1219-1234 | LBL41 |
| PWYIWLGFIAGLIAIV | 23 | 1226-1241 | LBL42 |
| EPLVDLPIGINITRFQ | 23 | 237-252 | LBL43 |
| QTLLALHRSYLTPGDS | 23 | 239-254 | LBL44 |
| TRFQTLLALHRSYLTP | 23 | 249-264 | LBL45 |
| NQVAVLYQGVNCTEVP | 23 | 606-621 | LBL46 |
| YQGVNCTEVPVAIHAD | 23 | 612-627 | LBL47 |
| NNSIAIPTNFTISVTT | 23 | 722-737 | LBL48 |
| RDLICAQKFNGLTVLP | 23 | 860-875 | LBL49 |
| VFLVLLPLVSSQCVNL | 22 | 16-31 | LBL50 |
| TGTGVLTESNKKFLPF | 22 | 560-575 | LBL51 |
| NNSYECDIPIGAGICA | 22 | 670-685 | LBL52 |
| SQSIIAYTMSLGAENS | 22 | 702-717 | LBL53 |
| YTMSLGAENSVAYSNN | 22 | 708-723 | LBL54 |
| GDCLGDIAARDLICAQ | 22 | 851-866 | LBL55 |
| DIPIGAGICASYQTQT | 21 | 663-678 | LBL56 |
| PFLMDLEGKQGNFKNL | 20 | 187-202 | LBL57 |
| GWTAGAAAYYVGYLQP | 20 | 270-285 | LBL58 |
| HRSYLTPGDSSSGWTA | 19 | 258-273 | LBL59 |
| YGVGHQPYRVVVLSFE | 19 | 501-516 | LBL60 |
| SYQTQTKSHRRARSVA | 19 | 673-688 | LBL61 |
| TASALGKLQDVVNHNA | 19 | 941-956 | LBL62 |
| KQLSSKFGAISSVLND | 19 | 964-979 | LBL63 |
| PVLPFNDGVYFASTEK | 18 | 95-110 | LBL64 |
| PGQTGNIADYNYKLPD | 17 | 412-427 | LBL65 |
| RKSNLKPFERDISTEI | 17 | 470-485 | LBL66 |
| GSFCTQLKRALTGIAV | 17 | 757-772 | LBL67 |
| LQSYGFRPTYGVGHQP | 15 | 492-507 | LBL68 |
| Combination of Peptide | Peptide Sequence | Peptide location* | Peptide Length | Matched HLA class-I Supertype | Matched HLA class-II Supertype | Assigned Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL3+ CTL4+ CTL6+ CTL7+ HTL50+ HTL42+ HTL30+ HTL31+ HTL43+ LBL59+ LBL58+ LBL17 | SGWTAGAAAYYVGYLQPRTFLLKYNENGTITDAVDCALD | 256-294 (N-terminal domain) | 39 | A1, A2, A26, B8, B39, B58, B62 | HLA-DPA1*01/DPB1*04:01; HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*02:01; HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*01:01; HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*05:01; HLA-DPA1*03:01/DPB1*04:02; HLA-DQA1*01:01/DQB1*05:01; HLA-DQA1*01:02/DQB1*06:02; HLA-DQA1*04:01/DQB1*04:02; HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*02:01; HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*03:01; HLA-DRB1*01:01; HLA-DRB1*07:01; HLA-DRB1*09:01 | Epi1 |
| CTL1+ CTL10+ HTL51+ HTL25+ HTL14+ HTL22+ HTL23+ HTL15+ HTL16+ HTL45+ LBL60+ LBL68 | LQSYGFQPTNGVGYQPYRVVVLSFELLHAPATVC | 492-525 (RBD) | 34 | A1, A2, A3, B7, B27, B58, B62 | HLA-DPA1*01/DPB1*04:01; HLA-DPA1*01:03/DPB1*02:01; HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*01:01; HLA-DPA1*02:01/DPB1*05:01; HLA-DPA1*03:01/DPB1*04:02; HLA-DQA1*01:01/DQB1*05:01; HLA-DQA1*03:01/DQB1*03:02; HLA-DQA1*05:01/DQB1*02:01; HLA-DRB1*01:01; HLA-DRB1*07:01; HLA-DRB1*09:01; HLA-DRB4*01:01 | Epi2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





