Submitted:
26 August 2024
Posted:
28 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
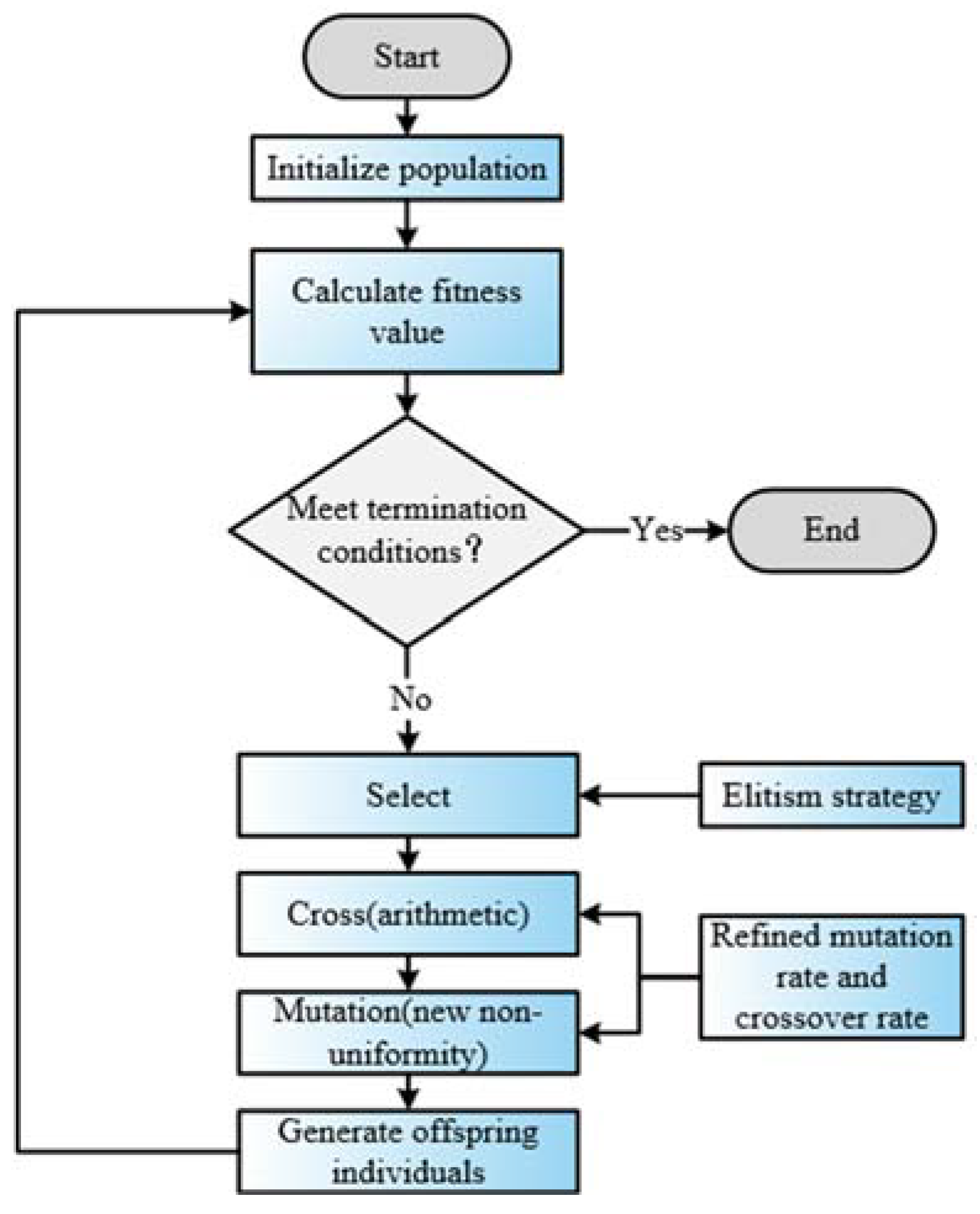
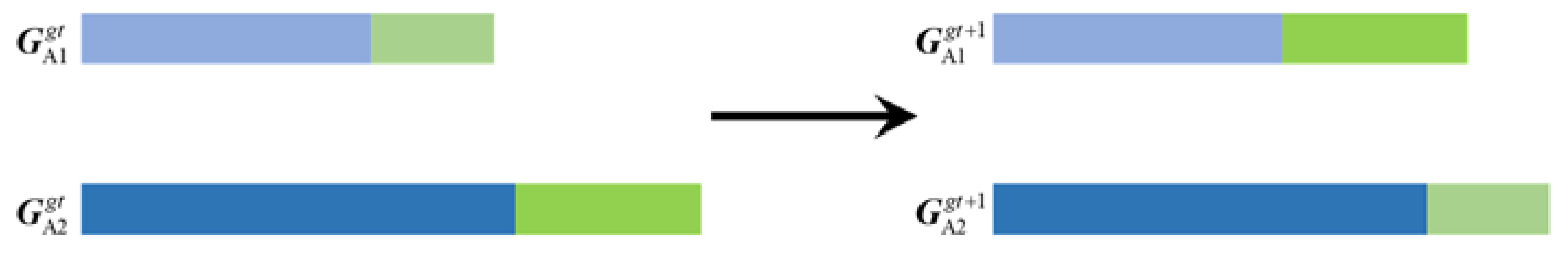
2. Genetic Algorithm Refinement
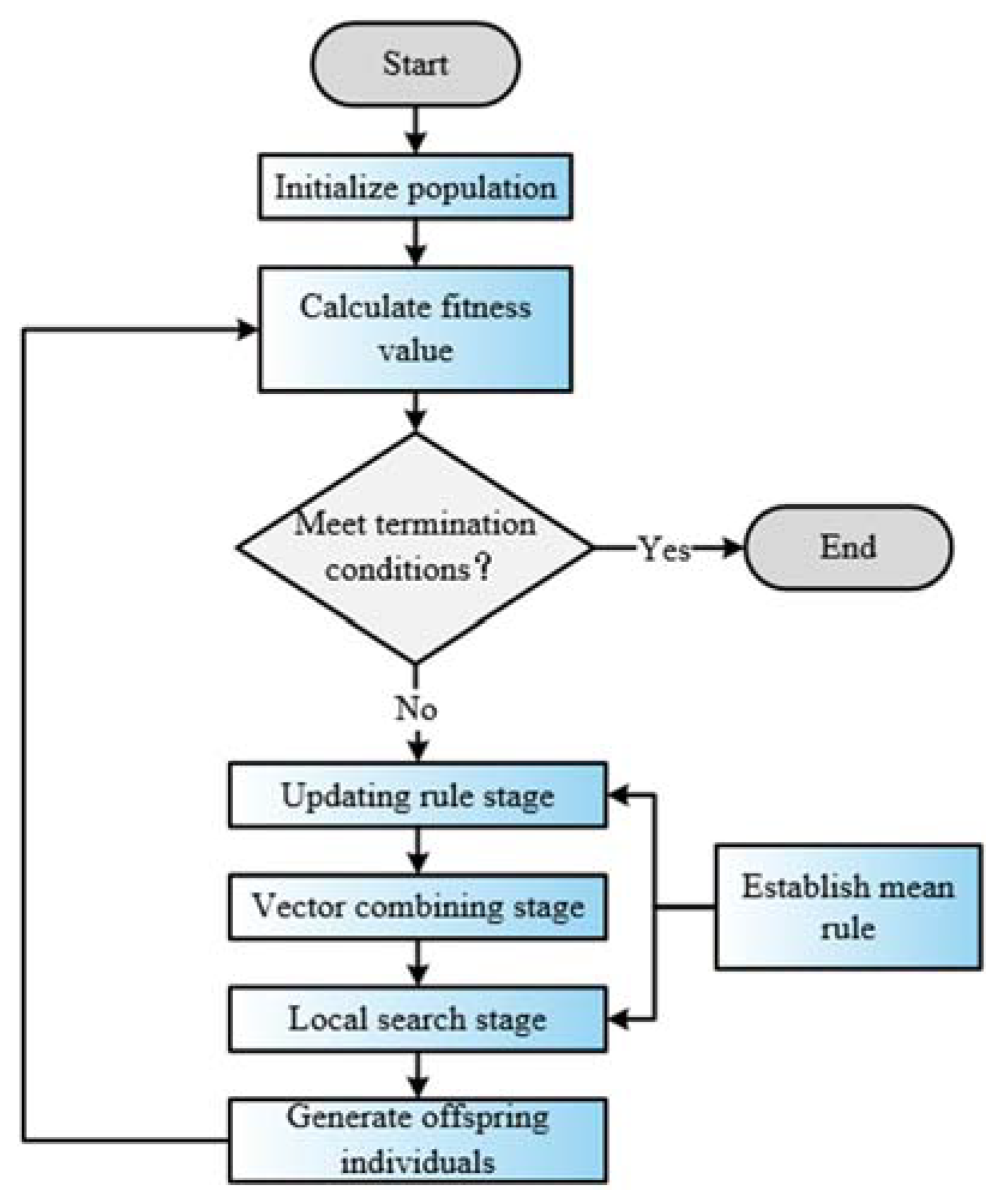
3. Weighted Mean of Vectors Algorithm
4. Objective Function
5. Weighting Factors and Mean Error
6. Numerical Simulation
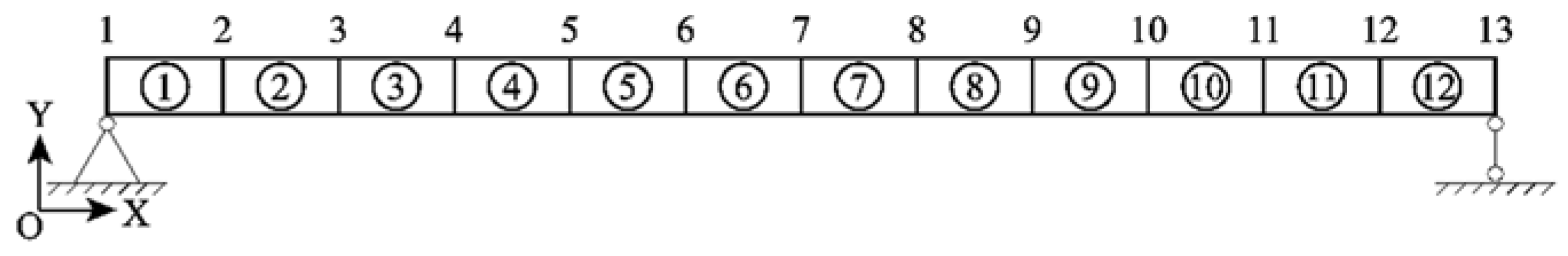
6.1. Simulation of simply supported beam
6.2. Simulation of Cantilever Plate
7. Conclusions
- Under most of the same cases, INFO has the highest damage identification accuracy, RGA has the second highest identification accuracy, and GA has the lowest identification accuracy.
- Under the same case, as the noise level gradually increases, the accuracy of damage identification of the algorithms will gradually become lower. Under the influence of 10% noise level, the three algorithms in the identification of multiple cases will appear obvious misjudgment units and the identification error of the damage degree of the target unit is larger, at this time the three algorithms can't accurately identify the damage cases.
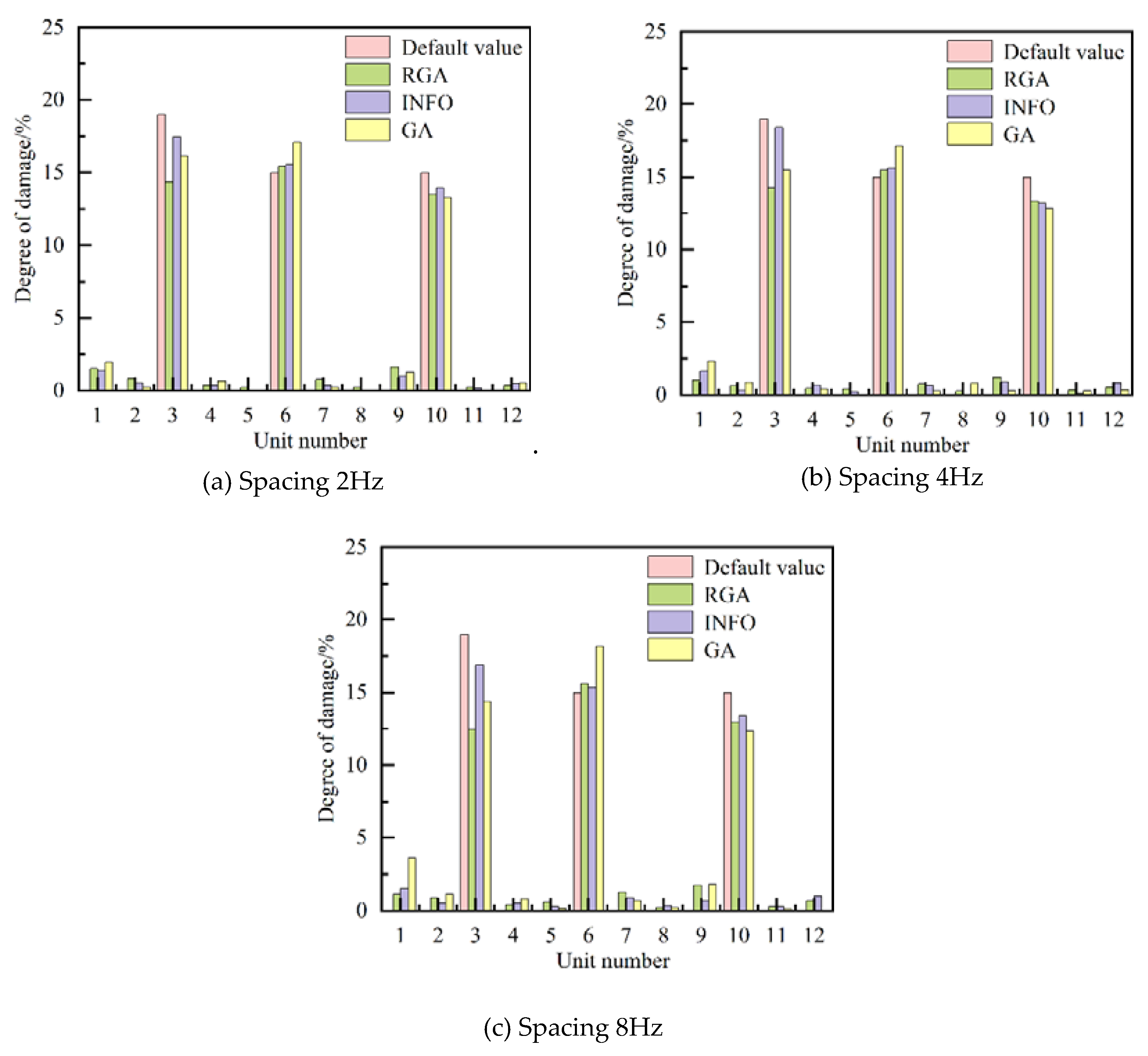
- In the same frequency range with the gradual increase in the frequency point spacing, the accuracy of damage identification for the algorithm gradually decreased, but part of the identification results is still within the acceptable range as the errors are not a significant increase.
References
- Qian C Y, Huang M S, Cheng S X, et al. Damage identification of the benchmark frame based on an improved cuckoo search[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(22):158-163.
- Vaez S R H, Fallah N. Damage detection of thin plates using GA-PSO algorithm based on modal data[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2017, 42(3):1251-1263. [CrossRef]
- Wan Z H, Huang M S, Cheng X H, et al. Two-stage damage identification method based on fractal theory and whale optimization algorithm[J], Advances in structural engineering, 2021, 21(12):1026-1058. [CrossRef]
- Mohan S C, Maiti D K, Maity D. Structural damage assessment using FRF employing particle swarm optimization[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2013, 219(20):10387-10400. [CrossRef]
- Miguel L F F, Lopez R H, Letícia F F M. A hybrid approach for damage detection of structures under operational conditions[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2013, 332(18):4241-4260. [CrossRef]
- Ding Z H, Huang M, Lu Z R. Structural damage detection using artificial bee colony algorithm with hybrid search strategy[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 28:1-13. [CrossRef]
- Pan C D, Yu L, Chen Z P, et al. A hybrid self-adaptive Firefly-Nelder-Mead algorithm for structural damage detection[J]. Smart Structures and Systems, 2016, 17(6):957-980.
- Chen Z P, Yu L. A new structural damage detection strategy of hybrid PSO with Monte Carlo simulations and experimental verifications[J]. Measurement, 2018, 122:658-669. [CrossRef]
- Ding Z, Li J, Hao H. Structural damage identification using improved Jaya algorithm based on sparse regularization and Bayesian inference[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 132:211-231. [CrossRef]
- Guilherme F G, Sebastiao S C, Antonio C A. A sunflower optimization (SFO) algorithm applied to damage identification on laminated composite plates[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2019, 35(2):619-626. [CrossRef]
- Alkayem N F, Cao M, Ragulskis M. Damage localization in irregular shape structures using intelligent FE model updating approach with a new hybrid objective function and social swarm algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 83:105604. [CrossRef]
- Huang M S, Li X F, Lei Y Z, et al. Structural damage identification based on modal frequency strain energy assurance criterion and flexibility using enhanced Moth-Flame optimization[J]. Structures, 2020, 28:1119-1136. [CrossRef]
- Minh H L, Khatir S, Wahab M A, et al. An Enhancing Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (EHVPSO) for damage identification in 3D transmission tower[J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 242:112412. [CrossRef]
- Li X L, Serra R, Olivier J. A multi-component PSO algorithm with leader learning mechanism for structural damage detection[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 116:108315. [CrossRef]
- Zhang G C, Wan C F, Xiong X B, et al. Output-only structural damage identification using hybrid Jaya and differential evolution algorithm with reference-free correlation functions[J]. Measurement, 2021, 199:111591. [CrossRef]
- Li Y F, Minh H L, Khatir S, et al. Structure damage identification in dams using sparse polynomial chaos expansion combined with hybrid K-means clustering optimizer and genetic algorithm[J]. Engineering Structures, 2023, 283:115891. [CrossRef]
- Thanh S T, Minh H L, Magd A W, et al. A new metaheuristic algorithm: Shrimp and Goby association search algorithm and its application for damage identification in large-scale and complex structures[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2023, 176:103363. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad I S, Samir K, Brahim B, et al. Damage assessment in laminated composite plates using modal strain energy and YUKI-ANN algorithm[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 303:116272. [CrossRef]
- Holland, J. Genetic algorithms[J]. Scientific American, 1992, 267(1):66-73.
- Ahmadianfar I, Heidari A A, Noshadian S, et al. INFO: An efficient optimization algorithm based on weighted mean of vectors[J]. Expert Systems with Application, 2022, 195:116516. [CrossRef]
- Allemang R, J. The Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC): Twenty years of use and abuse[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2003, 37(8):14-23.
- Tong Z P, Zhang Y, Shen R Y, et al. Submarine finite element model updating method based on frequency response functions of vibration [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2005, 39(11): 111-114.
- Lu H, Feng Z R, Wang X J, et al. Structural damage identification based on hybrid whale annealing algorithm and sparse regularization[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(17):85-91.
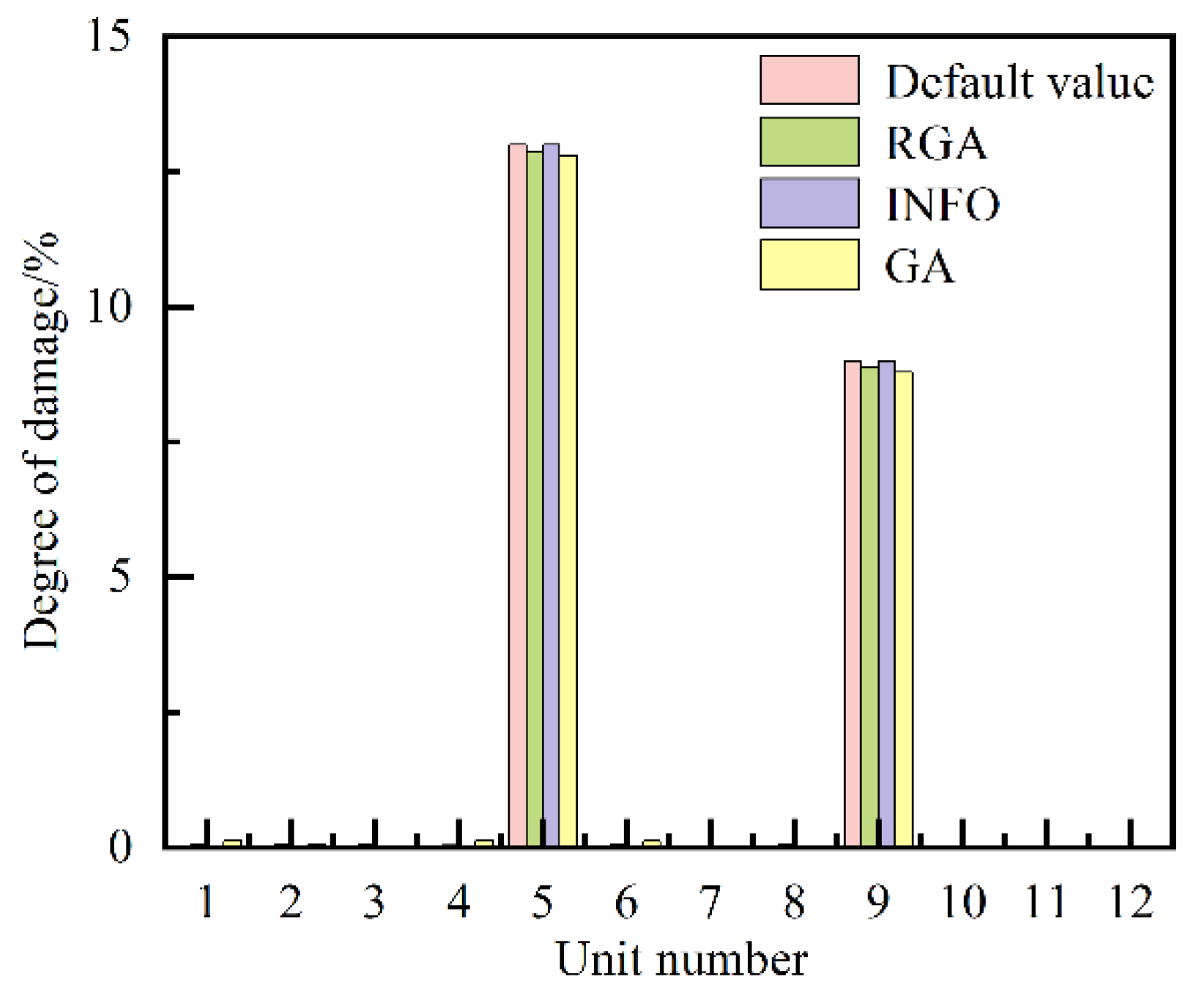
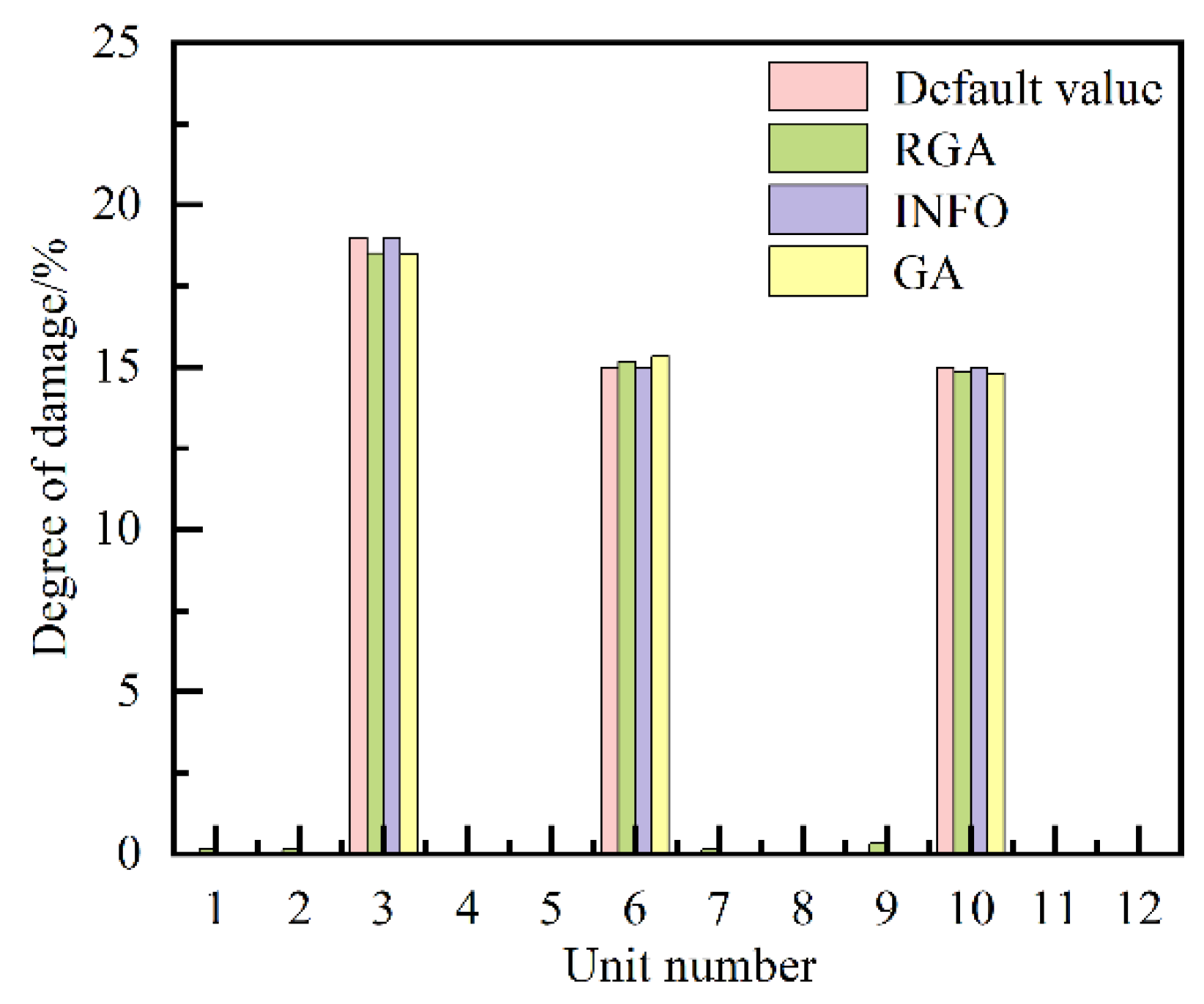
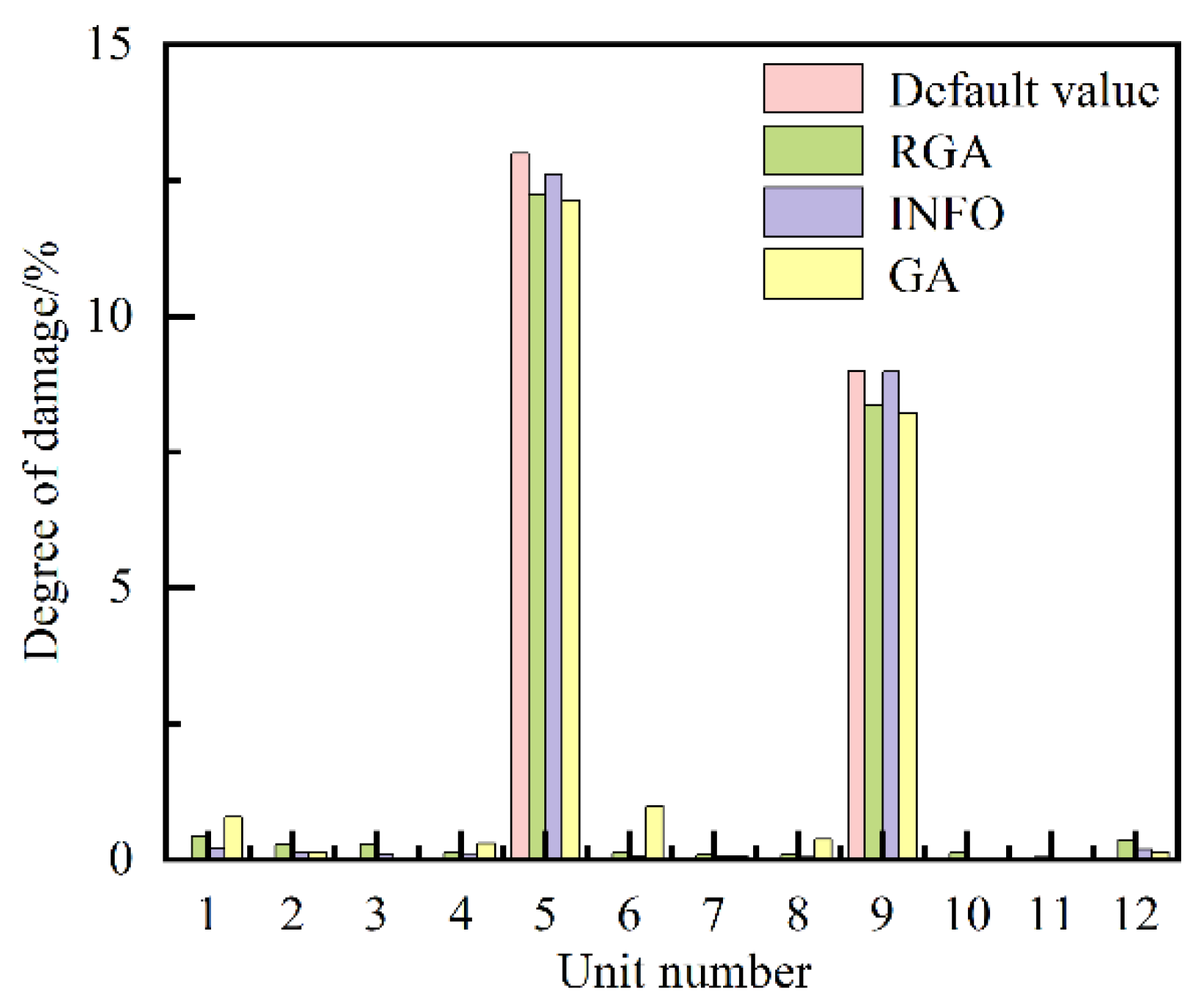
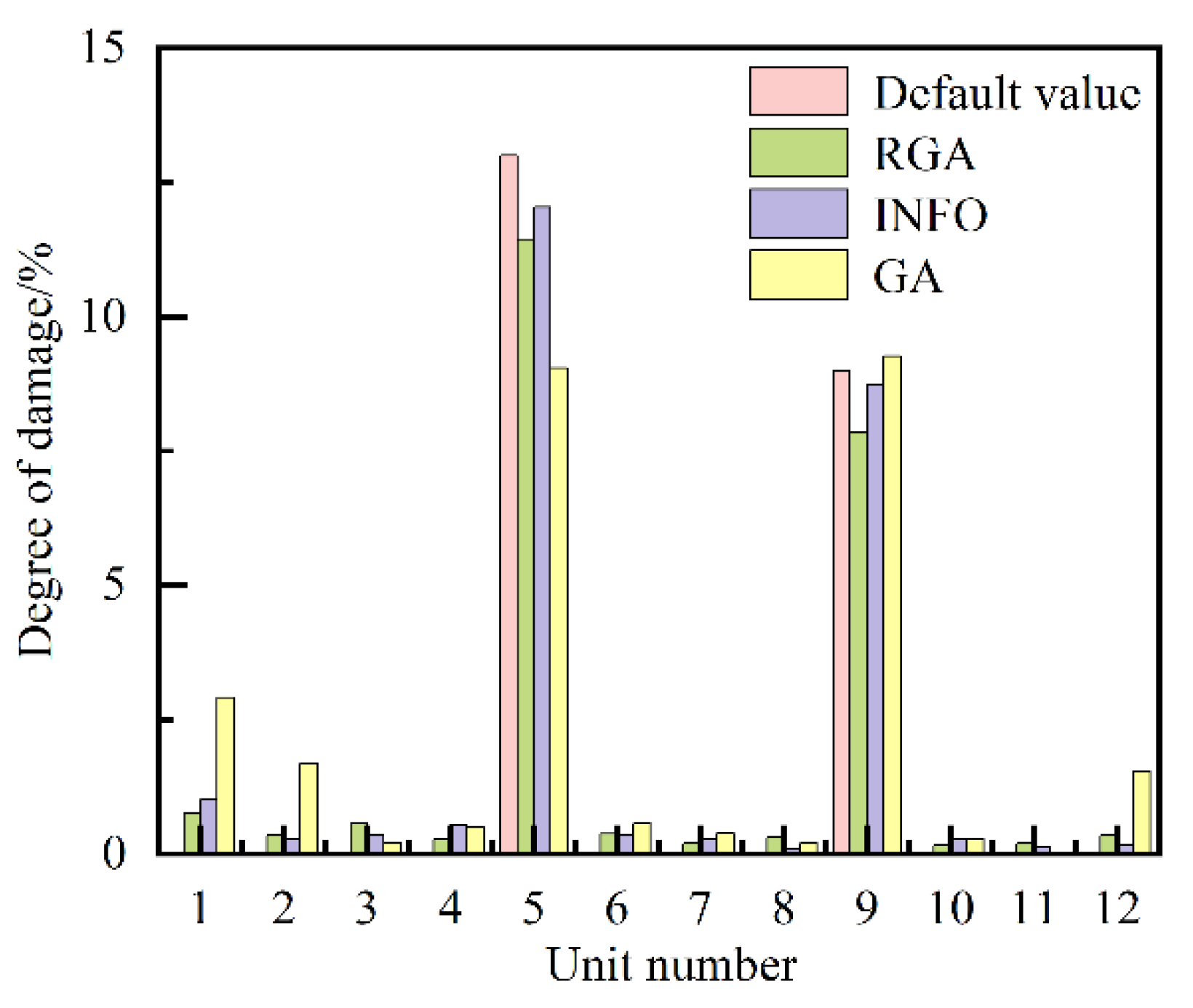
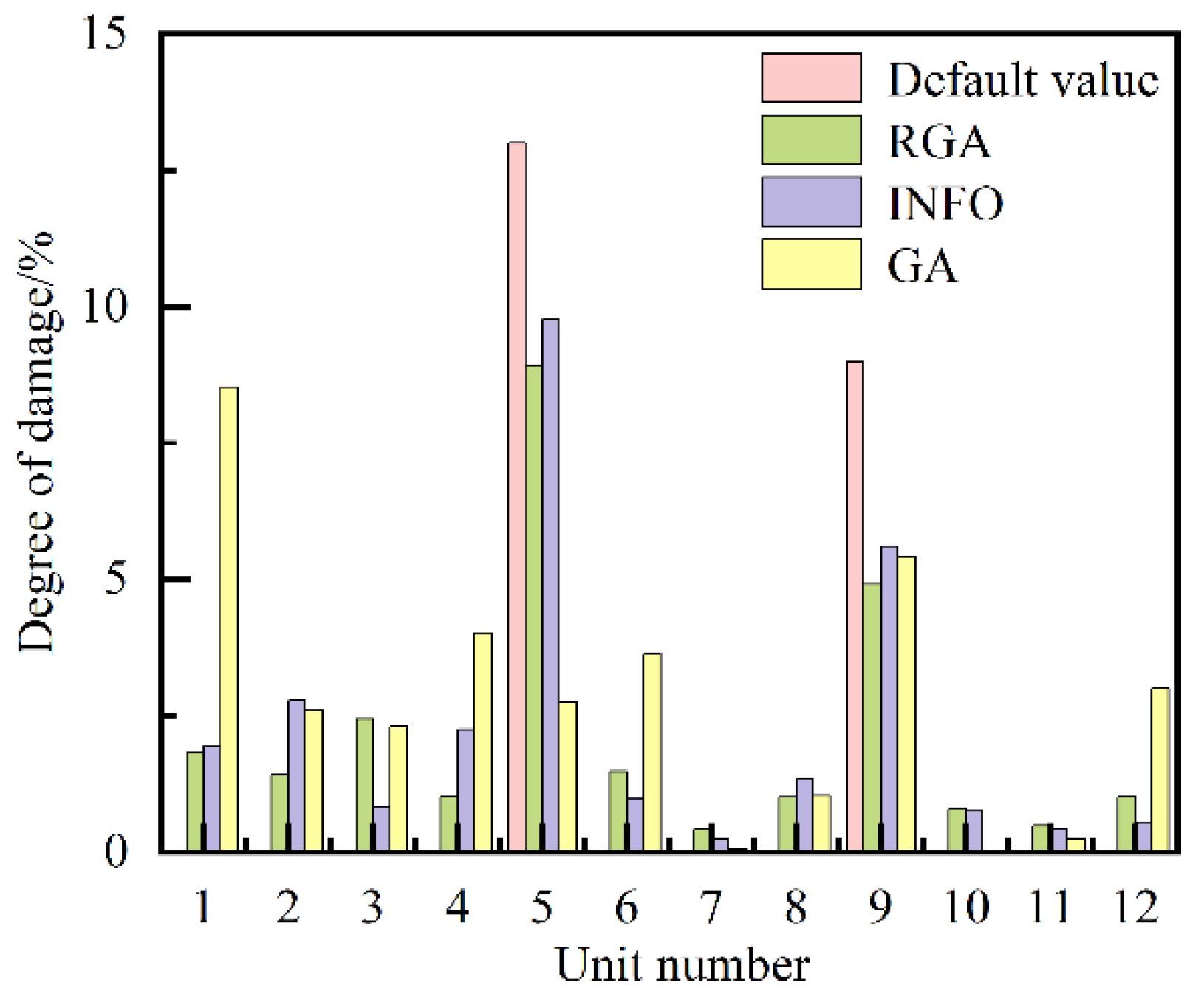
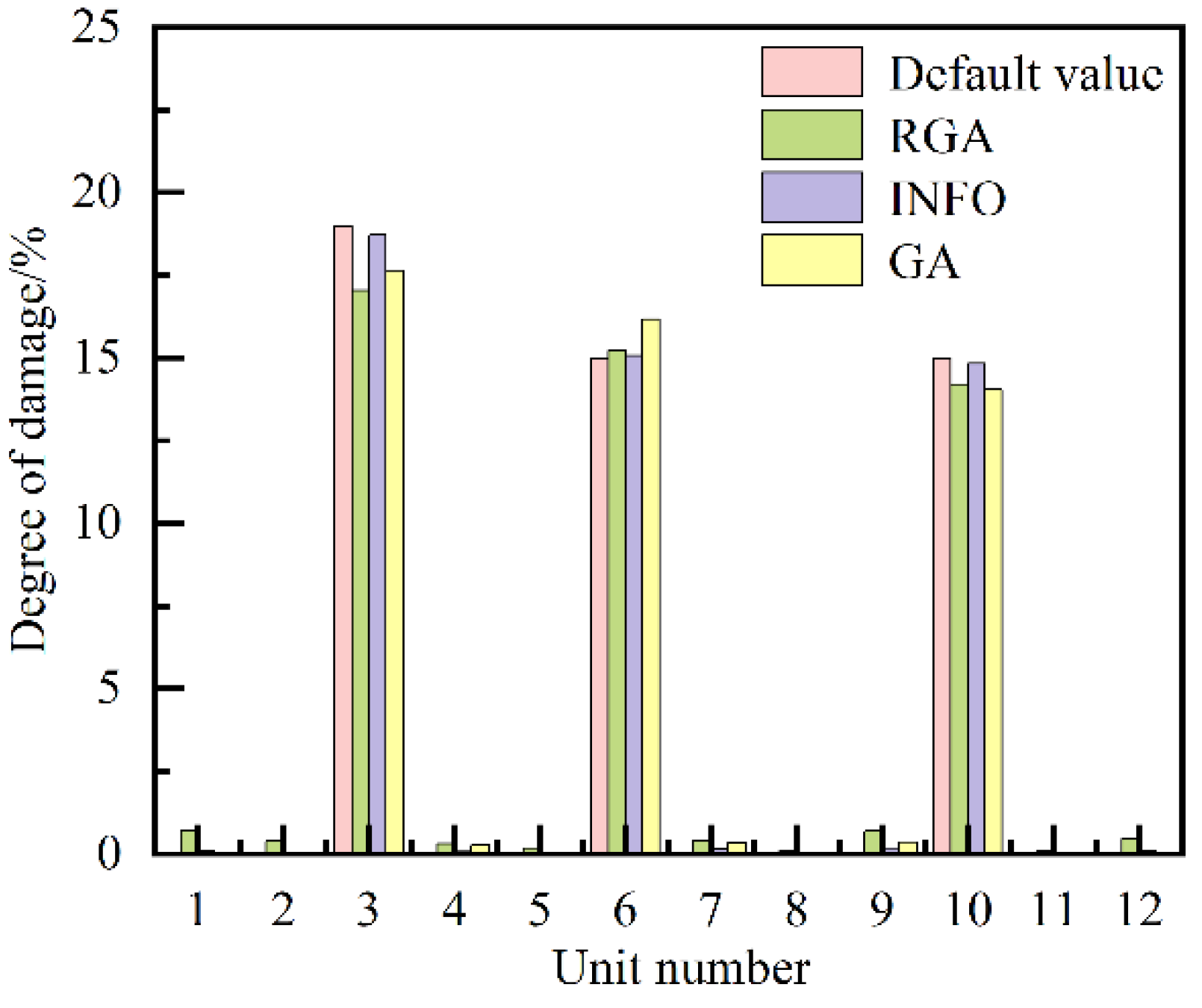
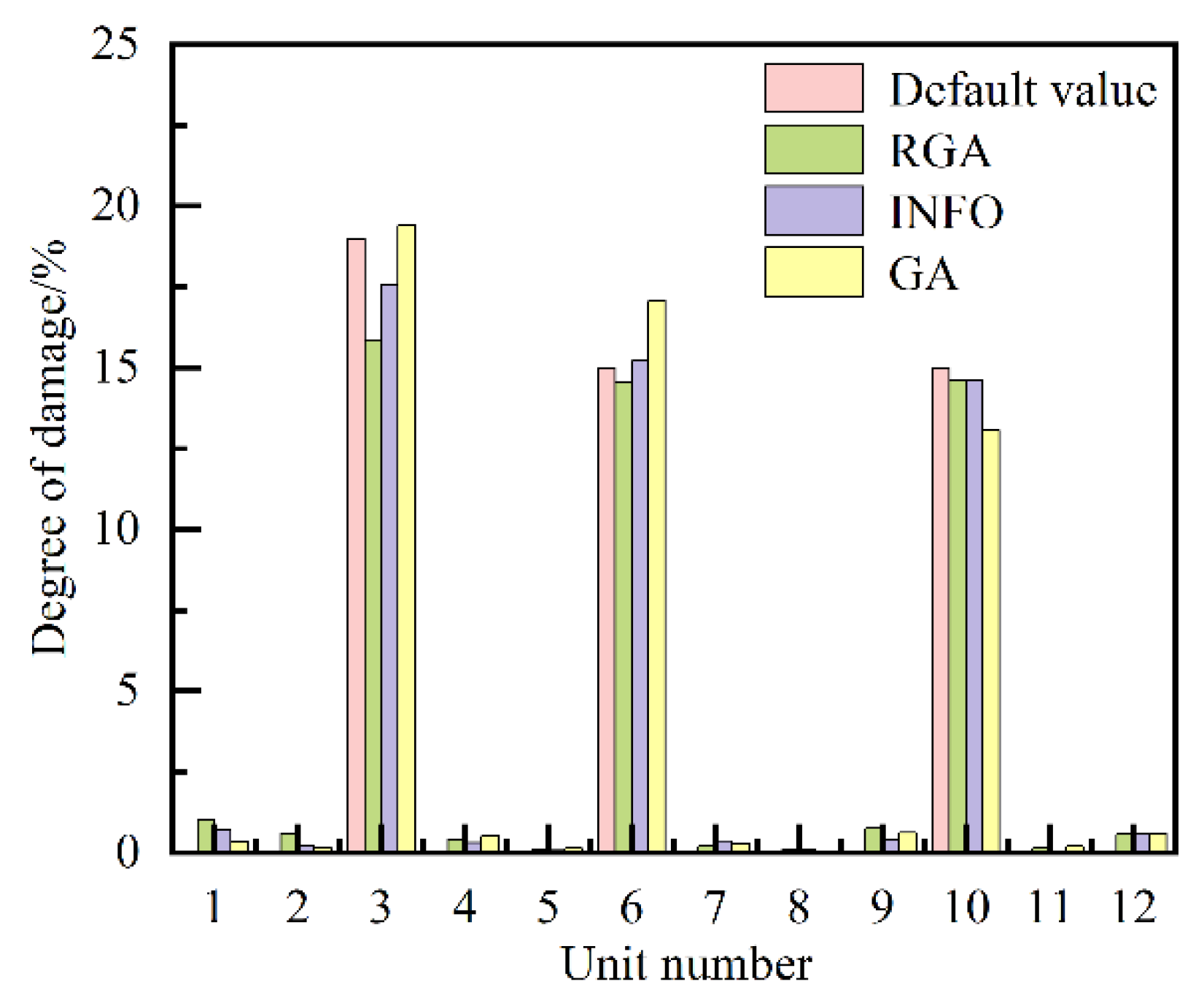
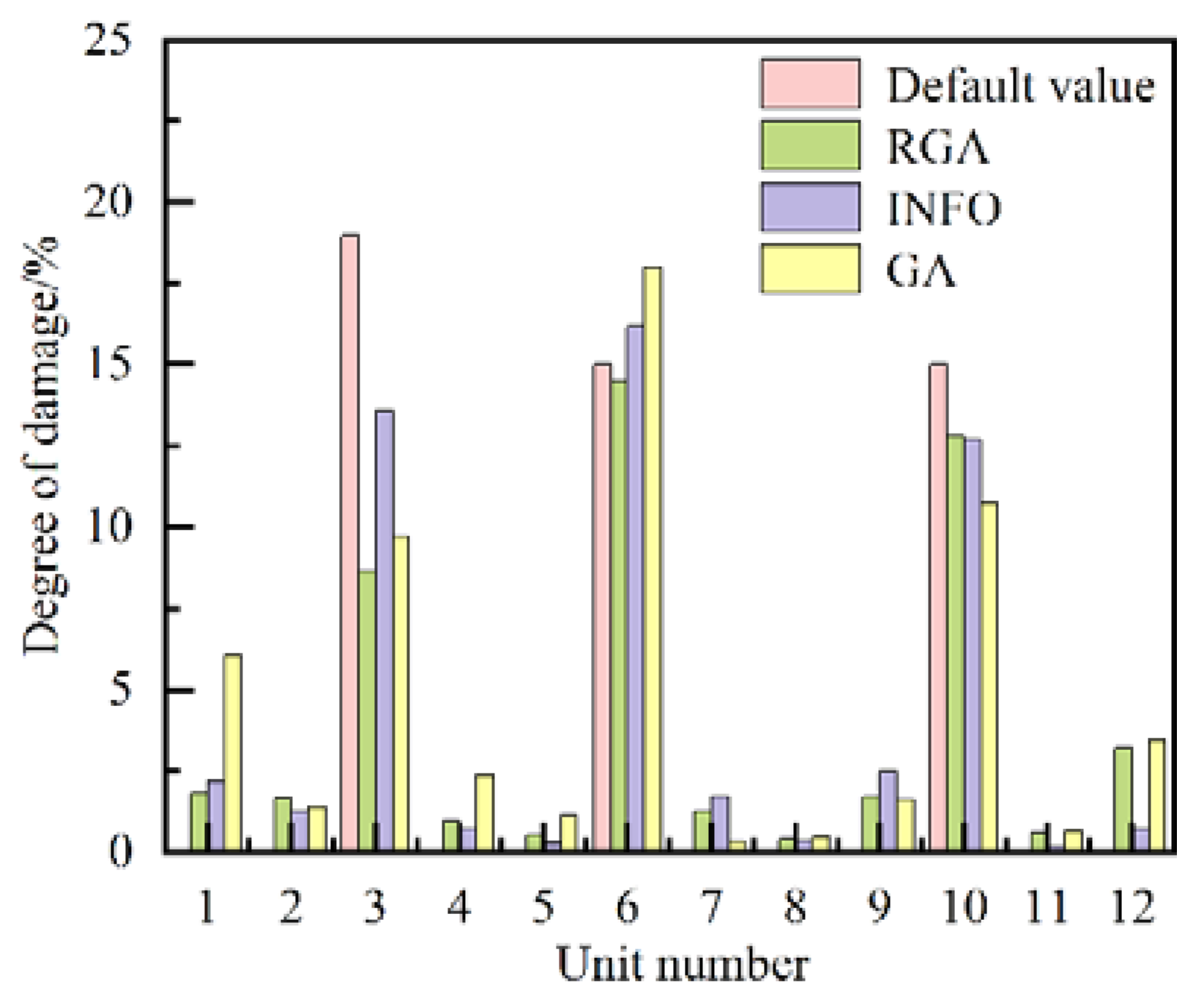
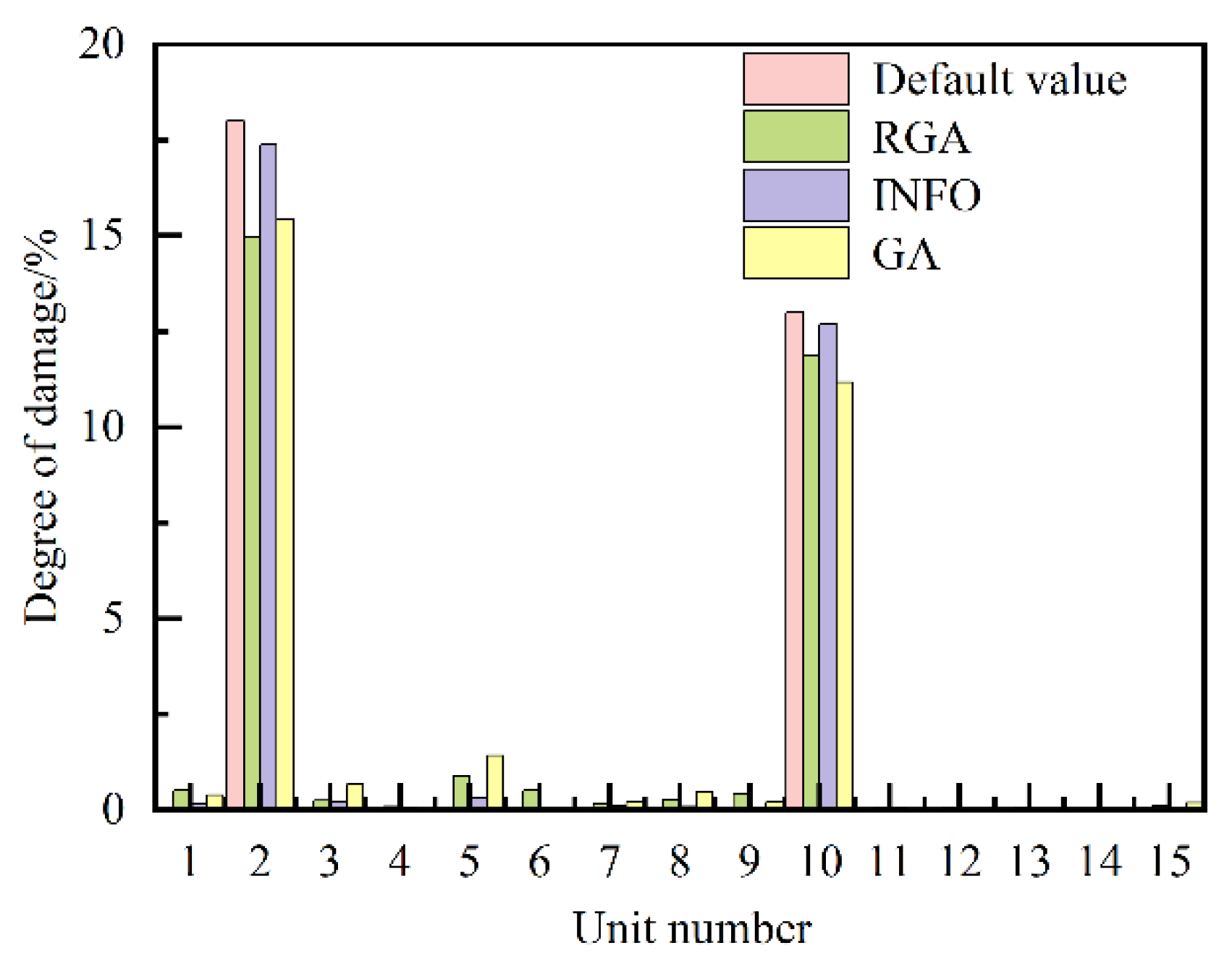
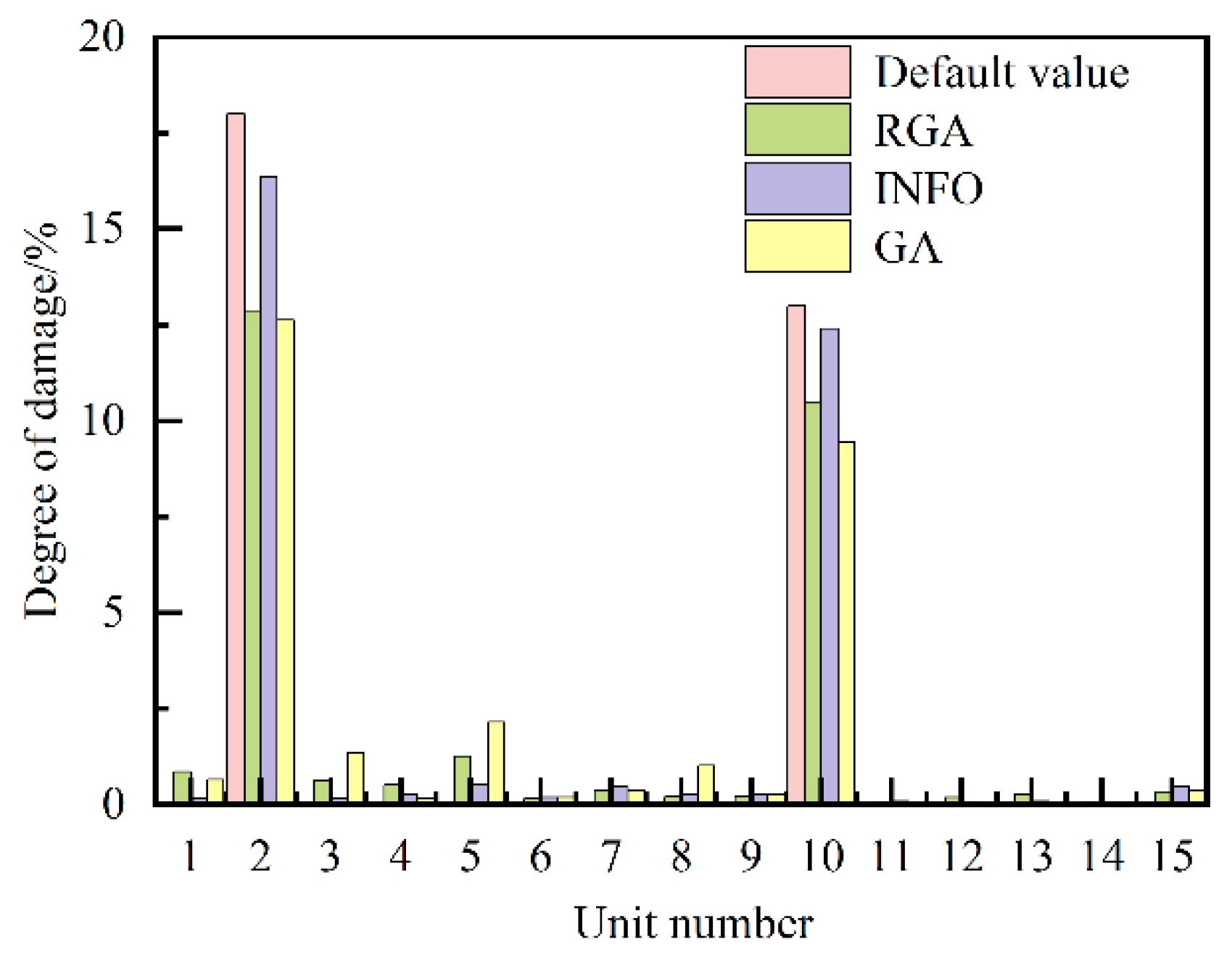
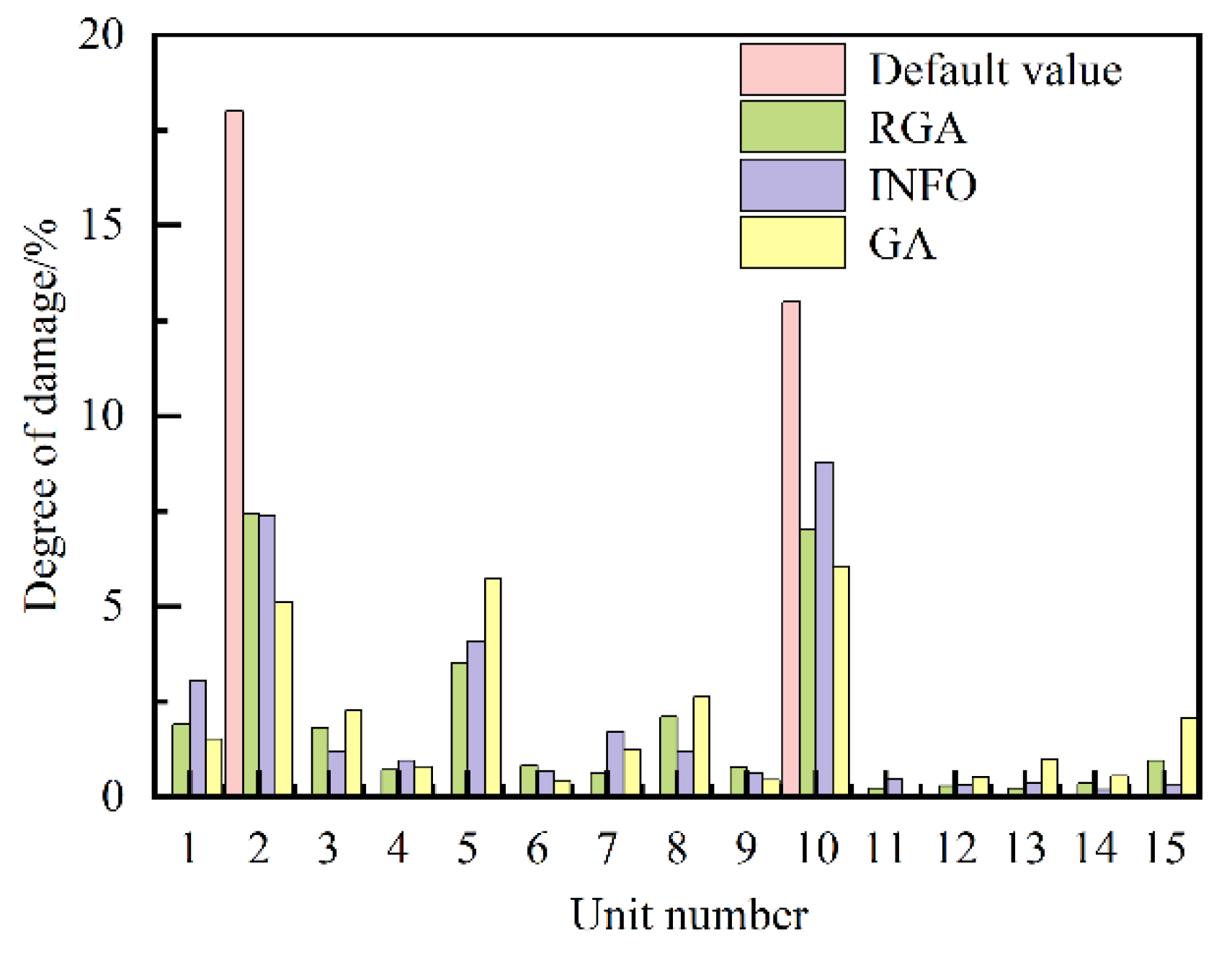
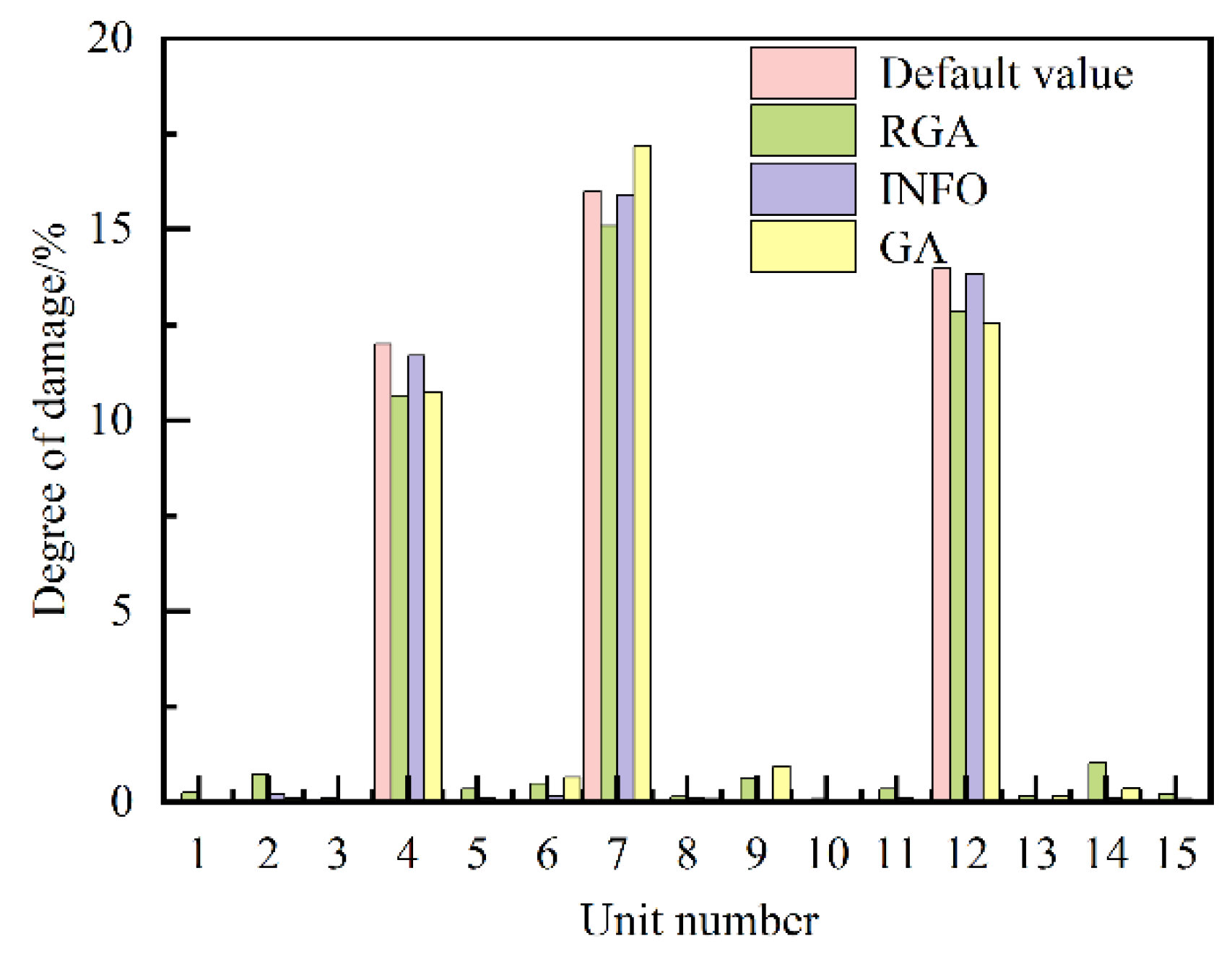
| Damage case number | Damage unit number#degree of damage/% |
| 1 | 5 # 13, 9 # 9 |
| 2 | 3 # 19, 6 # 15, 10 # 15 |
| Damage case number | Damage unit number # degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 1 | 5 # 12.80, 9 # 8.79 | 5 # 12.86, 9 # 8.90 | 5 # 13.00, 9 # 9.00 |
| 2 | 3 # 18.51, 6 # 15.34, 10 # 14.82 |
3 # 18.52, 6 # 15.19, 10 # 14.85 |
3 # 19.00, 6 # 15.00, 10 # 15.00 |
| Noise level/% | Damage unit number # degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 1 | 5 # 12.13, 9 # 8.21 | 5 # 12.23, 9 # 8.36 | 5 # 12.61, 9 # 8.97 |
| 3 | 5 # 9.04, 9 # 9.26 | 5 # 11.44, 9 # 7.85 | 5 # 12.03, 9 # 8.74 |
| 10 | 5 # 2.75, 9 # 5.42 | 5 # 8.91, 9 # 4.92 | 5 # 9.76, 9 # 5.61 |
| Noise level/% | Damage unit number#degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 1 | 3 # 17.65, 6 # 16.18, 10 # 14.05 |
3 # 17.04, 6 # 15.25, 10 # 14.21 |
3 # 18.72, 6 # 15.07, 10 # 14.84 |
| 3 | 3 # 19.42, 6 # 17.08, 10 # 13.06 |
3 # 15.87, 6 # 14.56, 10 # 14.62 |
3 # 17.57, 6 # 15.22, 10 # 14.63 |
| 10 | 3 # 9.71, 6 # 18.01, 10 # 10.75 |
3 # 8.69, 6 # 14.51, 10 # 12.79 |
3 # 13.58, 6 # 16.17, 10 # 12.69 |
| Taking point spacing/Hz | Damage unit number#degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 2 | 3#16.13, 6#17.07, 10#13.29 |
3#14.38, 6#15.42, 10#13.51 |
3#17.47, 6#15.54, 10#13.93 |
| 4 | 3#15.46, 6#17.16, 10#12.85 |
3#14.24, 6#15.50, 10#13.35 |
3#18.40, 6#15.62, 10#13.18 |
| 8 | 3#14.39, 6#18.20, 10#12.34 |
3#12.45, 6#15.61, 10#12.97 |
3#16.89, 6#15.33, 10#13.37 |
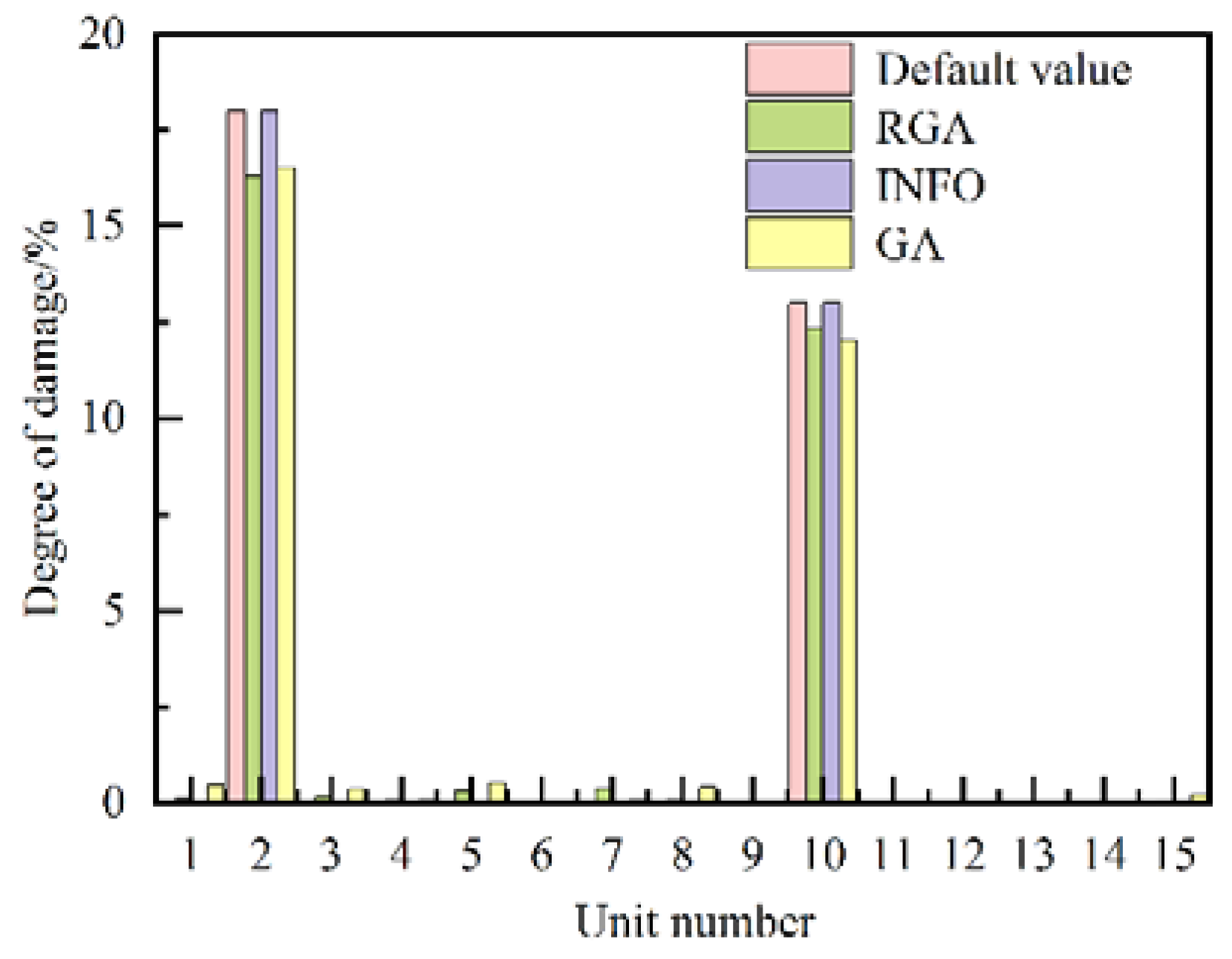
| Damage case number | Damage unit number # degree of damage/% |
|---|---|
| 3 | 2 # 18, 10 # 13 |
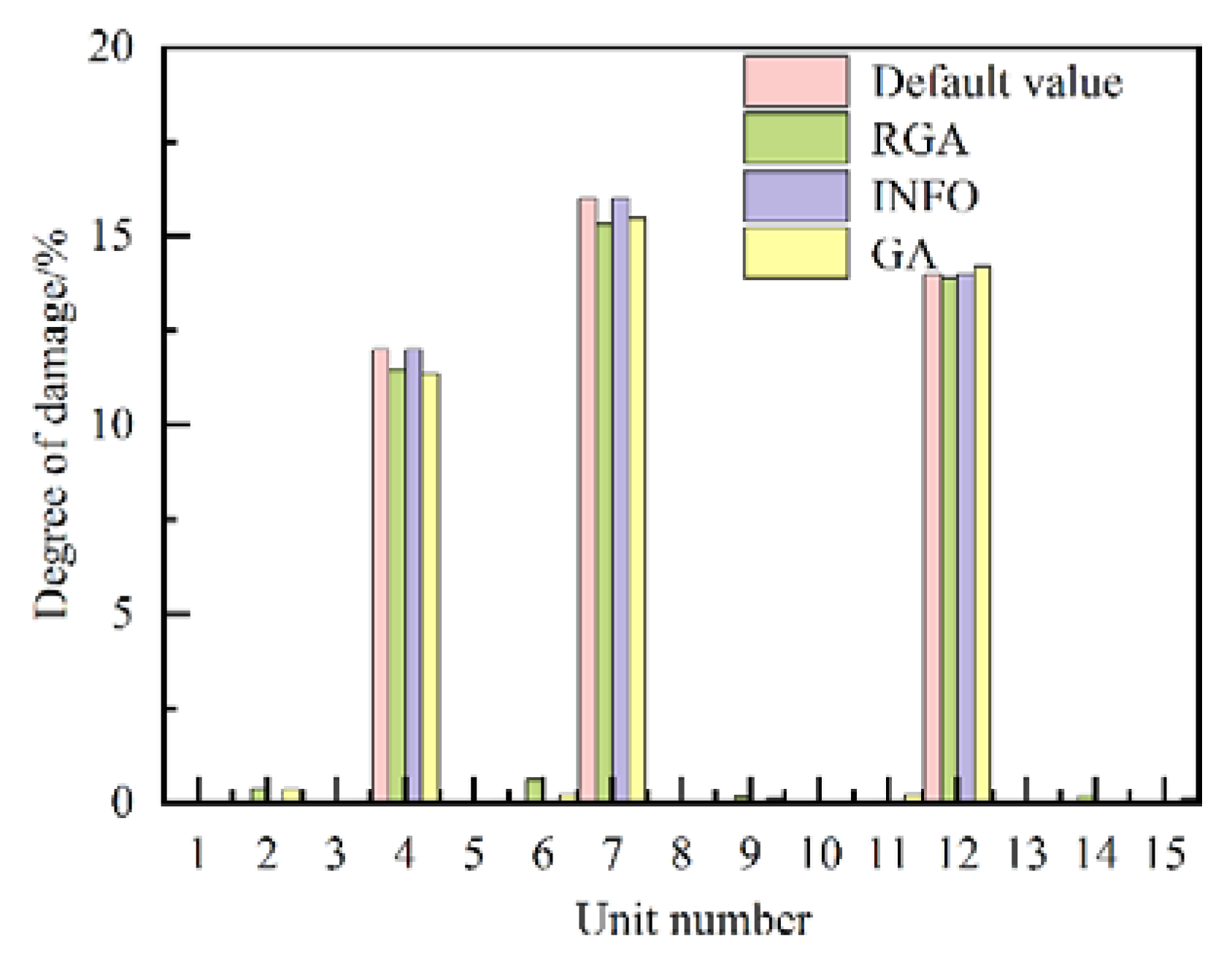
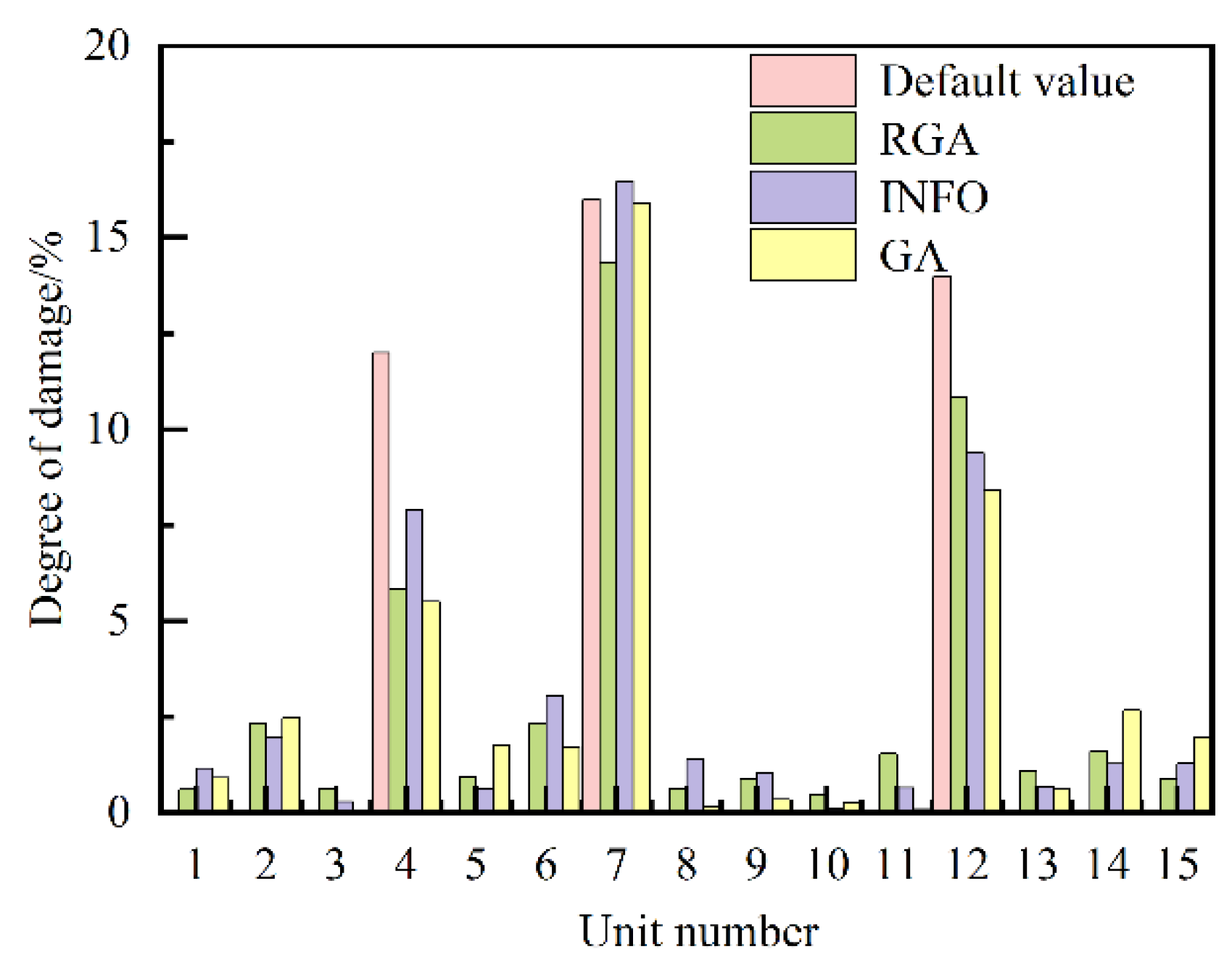
| 4 | 4 # 12, 7 # 16, 12 # 14 |
| Case number | Damage unit number # degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 3 | 2#16.54, 10#12.02 | 2#16.32, 10#12.35 | 2#18.00, 10#13.00 |
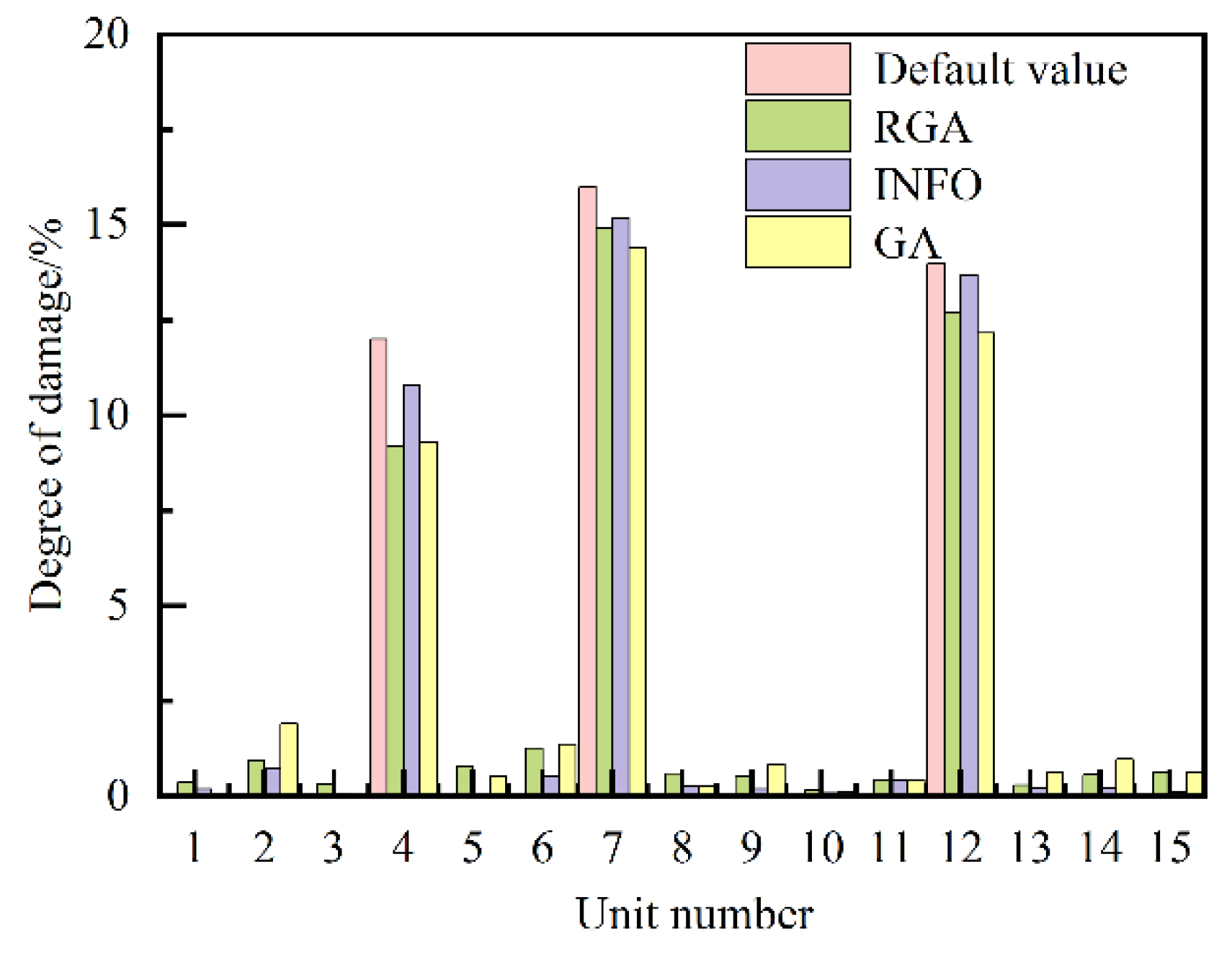
| 4 | 4#11.36, 7#15.47, 12#14.20 |
4#11.48, 7#15.35, 12#13.87 |
4#12.00, 7#16.00, 12#14.00 |
| Noise level/% | Damage unit number#degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 1 | 2#15.43, 10#11.17 | 2#14.94, 10#11.89 | 2#17.37, 10#12.70 |
| 3 | 2#12.62, 10#9.44 | 2#12.87, 10#10.46 | 2#16.37, 10#12.41 |
| 10 | 2#5.12, 10#6.06 | 2#7.45, 10#7.01 | 2#7.38, 10#8.80 |
| Noise level/% | Damage unit number#degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 1 | 4#10.73, 7#17.18, 12#12.54 |
4#10.65, 7#15.09, 12#12.85 |
4#11.70, 7#15.91, 12#13.83 |
| 3 | 4#9.29, 7#14.41, 12#12.16 |
4#9.20, 7#14.91, 12#12.68 |
4#10.80, 7#15.18, 12#13.69 |
| 10 | 4#5.51, 7#15.89, 12#8.42 |
4#5.83, 7#14.34, 12#10.82 |
4#7.91, 7#16.46, 12#9.38 |
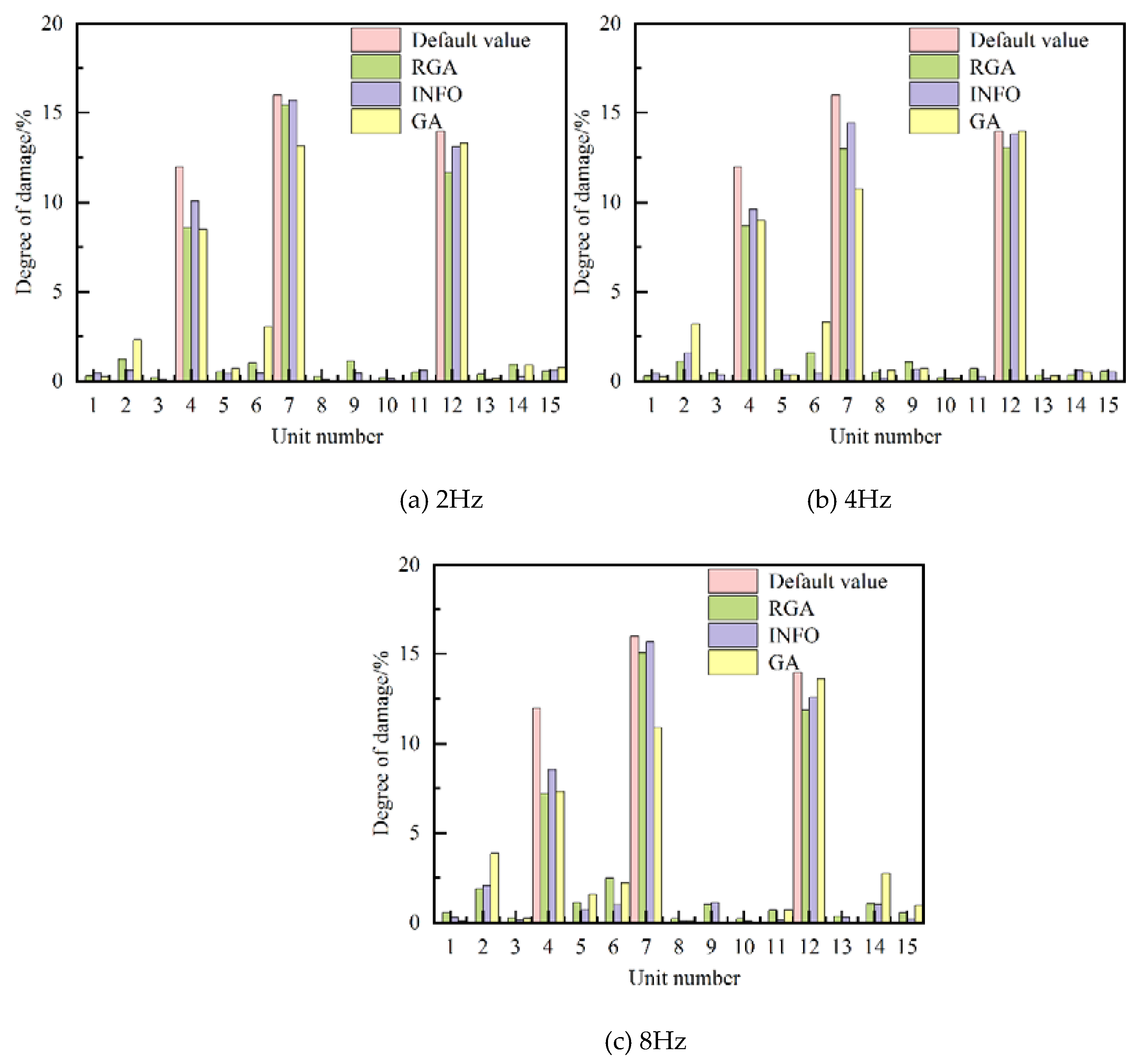
| Taking point spacing/Hz | Damage unit number#degree of damage/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | RGA | INFO | |
| 2 | 4#8.48, 7#13.16, 12#13.31 |
4#8.62, 7#15.45, 12#11.67 |
4#10.10, 7#15.71, 12#13.13 |
| 4 | 4#8.99, 7#10.78, 12#14.01 |
4#8.68, 7#13.02, 12#13.06 |
4#9.62, 7#14.43, 12#13.82 |
| 8 | 4#7.34, 7#10.89, 12#13.62 |
4#7.21, 7#15.08, 12#11.90 |
4#8.57, 7#15.68, 12#12.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





