Submitted:
05 August 2024
Posted:
06 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.1. Muscle Morphology
2.1.1. Image Processing (Segmentation)
2.2. Quantification of Fatty Infiltration in Muscle
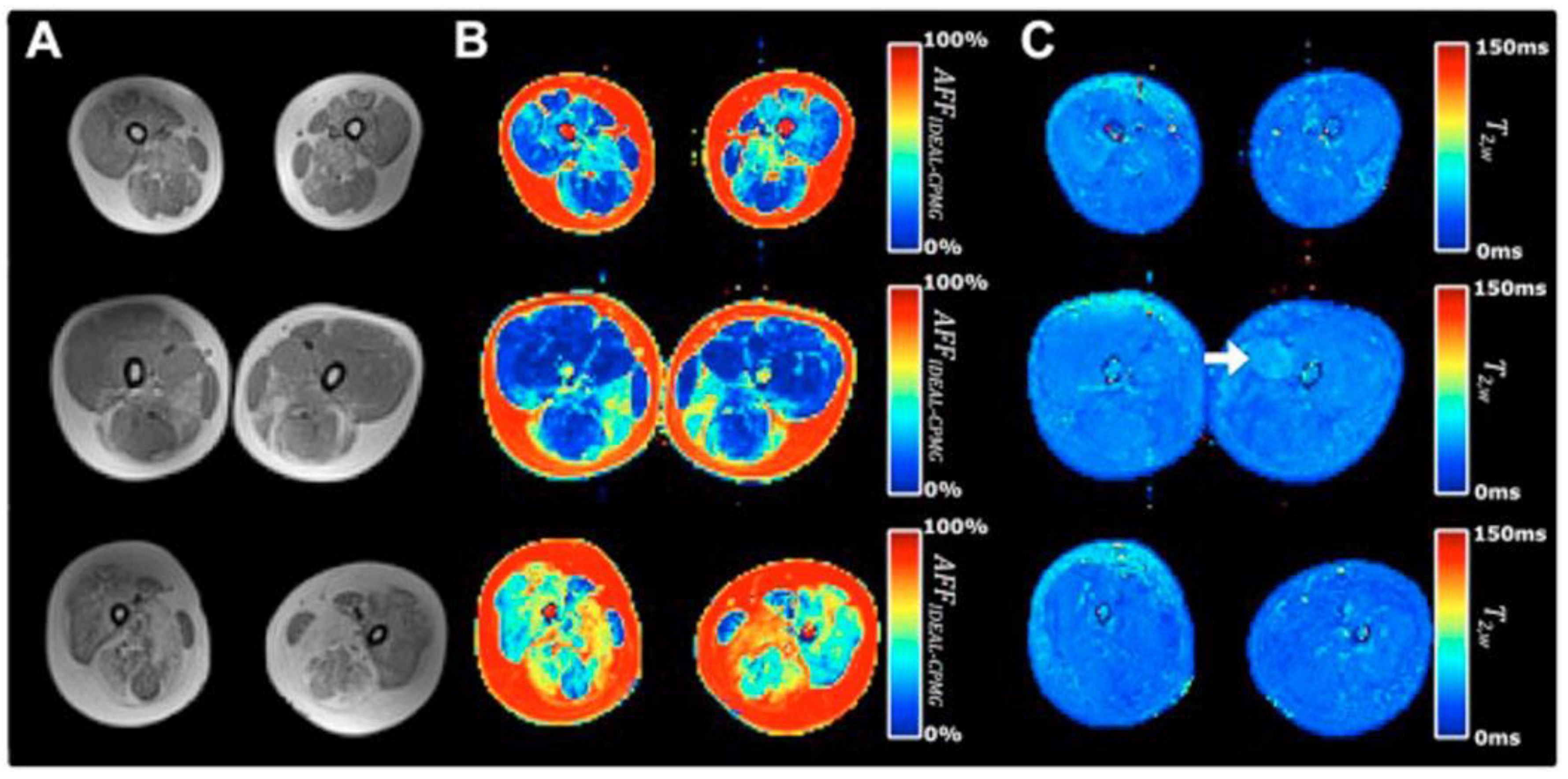
2.2.1. Fat quantification Based on Chemical-Shift Encoded (CSE) Imaging
2.2.1.1. Analysis of Fat Fraction Maps
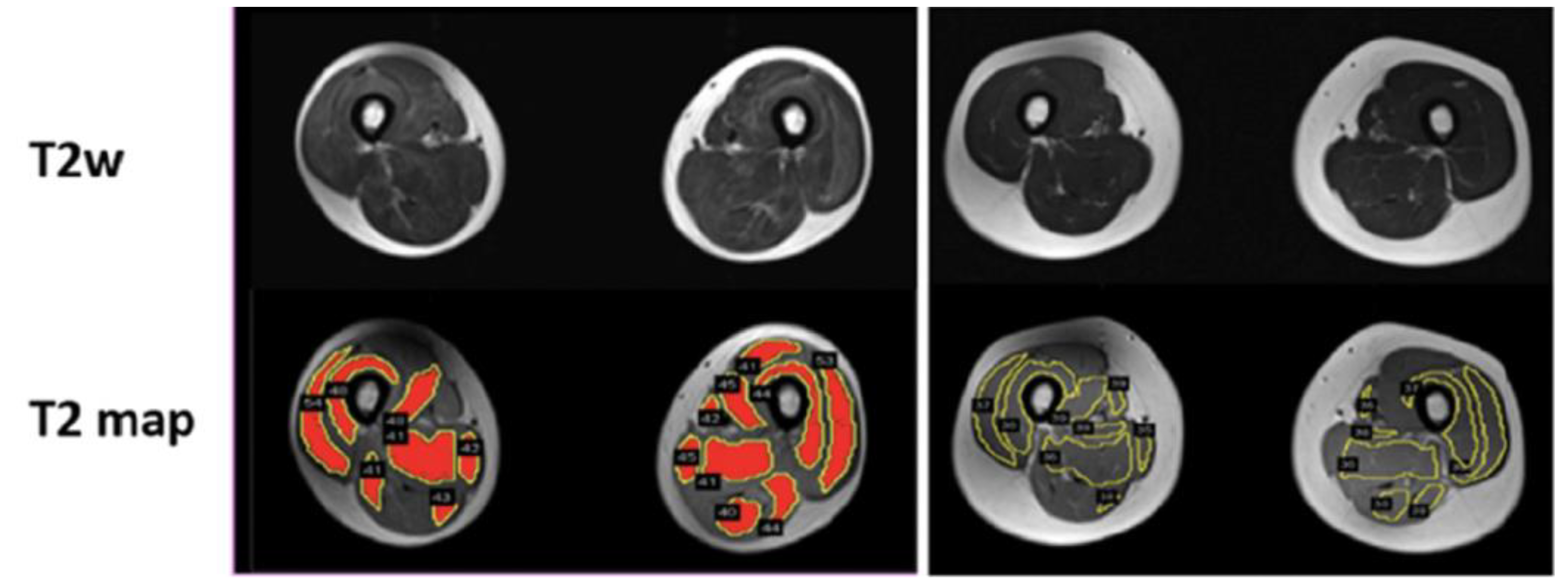
2.3. T2 Mapping
2.3.1. T2 Analysis
2.4. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
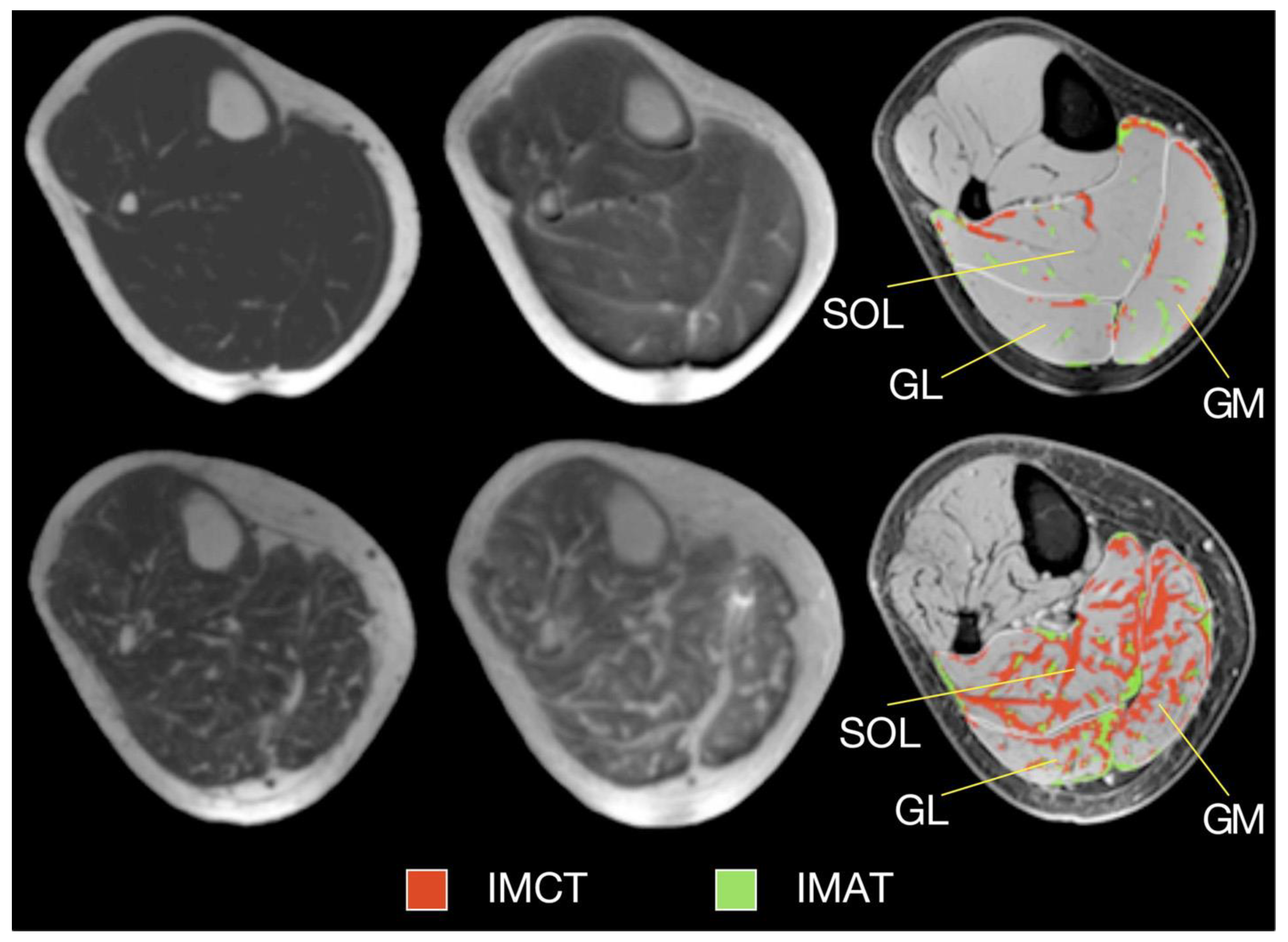
2.5. Fibrosis Quantification
2.5.1. Magnetization Transfer Contrast
2.5.2. Ultralow TE (UTE) Imaging
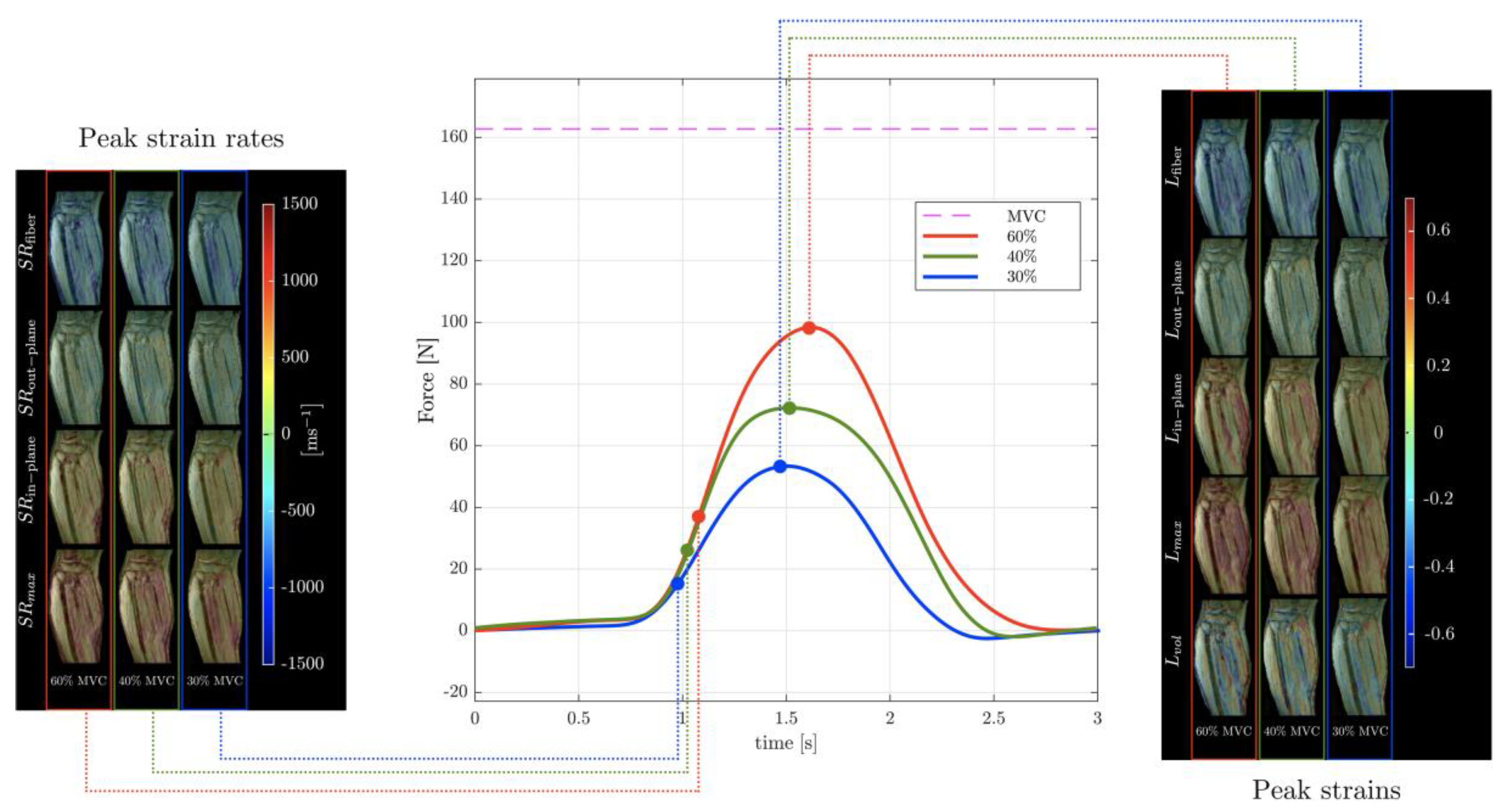
2.6. Strain and Strain Rate Imaging
3. In Vivo Clinical Applications
3.1. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
3.2. Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM)
3.3. Pompe Disease
3.4. Sarcopenia
3.5. Muscle Injury
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quantitative MRI of the brain: principles of physical measurement. Cercignani, M. Quantitative MRI of the brain: principles of physical measurement. Cercignani, M., Dowell, N., Tofts, P. Eds.; CRC press, Florida, USA, 2018.
- Manfrini, E.; Smits, M.; Thust, S.; Geiger, S.; Bendella, Z.; Petr, J.; Solymosi, L.; Keil, V.C. From research to clinical practice: a European neuroradiological survey on quantitative advanced MRI implementation. Eur Radiol 2021, 31, 6334–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, K.E.; Biller, J.R.; Delfino, J.G.; Boss, M.A.; Does, M.D.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Griswold, M.A.; Gunter, J.L.; Hinks, R.S.; Hoffman, S.W.; Kim, G.; Lattanzi, R.; Li, X.; Marinelli, L.; Metzger, G.J.; Mukherjee, P.; Nordstrom, R.J.; Peskin, A.P.; Perez, E.; Russek, S.E.; Sahiner, B.; Serkova, N.; Shukla-Dave, A.; Steckner, M.; Stupic, K.F.; Wilmes, L.J.; Wu, H.H.; Zhang, H.; Jackson, E.F.; Sullivan, D.C. Recommendations towards standards for quantitative MRI (qMRI) and outstanding needs. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019, 49, e26–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- https://www.rsna.org/research/quantitative-imaging-biomarkers-alliance [accessed on Sept 12, 2023].
- Jara, H.; Sakai, O.; Farrher, E.; Oros-Peusquens, A.M.; Shah, N.J.; Alsop, D.C.; Keenan, K.E. Primary Multiparametric Quantitative Brain MRI: State-of-the-Art Relaxometric and Proton Density Mapping Techniques. Radiology 2022, 305, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Y. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers in oncological clinical trials: Current techniques and standardization challenges. Chronic Dis Transl Med 2017, 3, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalian, M.; Li, X.; Guermazi, A.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Carrino, J.A.; Oei, E.H.; Link, T.M. RSNA QIBA MSK Biomarker Committee; SNA QIBA MSK Biomarker Committee Members. The QIBA Profile for MRI-based Compositional Imaging of Knee Cartilage. Radiology 2021, 301, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelke, K.; Chaudry, O.; Gast, L.; Eldib, M.A.; Wang, L.; Laredo, J.D.; Schett, G.; Nagel, A.M. Magnetic resonance imaging techniques for the quantitative analysis of skeletal muscle: State of the art. J Orthop Translat 2023, 42, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damon, B.M.; Li, K.; Dortch, R.D.; Welch, E.B.; Park, J.H.; Buck, A.K.; Towse, T.F.; Does, M.D. ; Gochberg DF, Bryant ND Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Skeletal Muscle Disease. J Vis Exp 2016, 118, 52352. [Google Scholar]
- Damon, B.M.; Li, K.; Bryant, N.D. Magnetic resonance imaging of skeletal muscle disease. Handb Clin Neurol 2016, 136, 827–842. [Google Scholar]
- Idilman, I.S.; Yildiz, A.E.; Karaosmanoglu, A.D.; Ozmen, M.N.; Akata, D.; Karcaaltincaba, M. Proton density fat fraction: magnetic resonance imaging applications beyond the liver. Diagn Interv Radiol 2022, 28, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, S.P.; Zhang, Y.; Binks, M.; Marraffino, S. Quantitative muscle MRI biomarkers in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: cross-sectional correlations with age and functional tests. Biomark Med 2021, 15, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Bonaparte, S.; Llauger, J.; Segovia, S.; Belmonte, I.; Pedrosa, I.; Montiel, E.; Montesinos, P.; Sánchez-González, J.; Alonso-Jiménez, A.; Gallardo, E.; Illa, I.; Spanish Pompe group; Díaz-Manera. Quantitative muscle MRI to follow up late onset Pompe patients: a prospective study. J Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, M.; Biglands, J.; Tanner, S.F.; Clegg, A.; Brown, L.; Hensor, E.M.A.; O'Connor, P.; Emery, P.; Tan, A.L. The effect of ageing on skeletal muscle as assessed by quantitative MR imaging: an association with frailty and muscle strength. Aging Clin Exp Res 2021, 33, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krššák, M.; Lindeboom, L.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.; Szczepaniak, L.S.; Derave, W.; Lundbom, J.; Befroy, D.; Schick, F.; Machann, J.; Kreis, R.; Boesch, C. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in skeletal muscle: Experts' consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed 2021, 34, e4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerspeer, M.; Boesch, C.; Cameron, D.; Dezortová, M.; Forbes, S.C.; Heerschap, A.; Jeneson, J.A.L.; Kan, H.E.; Kent, J.; Layec, G.; Prompers, J.J.; Reyngoudt, H.; Sleigh, A.; Valkovič, L.; Kemp, G.J. ; Experts' Working Group on 31P MR Spectroscopy of Skeletal Muscle. 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in skeletal muscle: Experts' consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed 2020, 34, e4246. [Google Scholar]
- Bamman, M.M.; Newcomer, B.R.; Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Weinsier, R.L.; Hunter, G.R. Evaluation of the strength-size relationship in vivo using various muscle size indices. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2000, 32, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiba, B.; Richard, N.; Hébert, L.J.; Coté, C.; Nejjari, M.; Vial, C.; Bouhour, F.; Puymirat, J.; Janier, M. Quantitative assessment of skeletal muscle degeneration in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1 using MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012, 35, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noehren, B.; Andersen, A.; Hardy, P.; Johnson, D.L.; Ireland, M.L.; Thompson, K.L.; Damon, B. Cellular and Morphological Alterations in the Vastus Lateralis Muscle as the Result of ACL Injury and Reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2016, 98, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnouin, Y.; Butler-Browne, G.; Voit, T.; Reversat, D.; Azzabou, N.; Leroux, G.; Behin, A.; McPhee, J.S.; Carlier, P.G. Hogrel, J.Y. Manual segmentation of individual muscles of the quadriceps femoris using MRI: a reappraisal. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014, 40, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.B.; Martins-Costa, H.C.; De Souza, C.C.; Lima, F.V.; Diniz, R.C.R.; Chagas, M.H. Muscle volume vs. anatomical cross-sectional area: Different muscle assessment does not affect the muscle size-strength relationship. J Biomech 2022, 132, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysmans, L.; De Wel, B.; Claeys, K.G.; Maes, F. Automated MRI quantification of volumetric per-muscle fat fractions in the proximal leg of patients with muscular dystrophies. Front Neurol 2023, 14, 1200727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogier, A.C.; Hostin, M.A.; Bellemare, M.E.; Bendahan, D. Overview of MR Image Segmentation Strategies in Neuromuscular Disorders. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 625308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, V.; Sinha, U.; Malis, V.; Csapo, R.; Sinha, S. 3D multimodal spatial fuzzy segmentation of intramuscular connective and adipose tissue from ultrashort TE MR images of calf muscle. Magn Reson Med 2017, 77, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudry, O.; Friedberger, A.; Grimm, A.; Uder, M.; Nagel, A.M.; Kemmler, W.; Engelke, K. Segmentation of the fascia lata and reproducible quantification of intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT) of the thigh. MAGMA 2021, 34, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzunce, M.A.; Henckel, J.; Fotiadou, A.; Di Laura, A.; Hart, A. Automated multi-atlas segmentation of gluteus maximus from Dixon and T1-weighted magnetic resonance images. Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med 2020, 33, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogier, A.C.; Heskamp, L.; Michel, C.P.; Fouré, A.; Bellemare, M.E.; Le Troter, A. A novel segmentation framework dedicated to the follow-up of fat infiltration in individual muscles of patients with neuromuscular disorders. Magn Reson Med 2020, 83, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostin, M.A.; Ogier, A.C.; Michel, C.P.; Le Fur, Y.; Guye, M.; Attarian, S.; Fortanier, E.; Bellemare, M.E.; Bendahan, D. The Impact of Fatty Infiltration on MRI Segmentation of Lower Limb Muscles in Neuromuscular Diseases: A Comparative Study of Deep Learning Approaches. J Magn Reson Imaging 2023, 58, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, S.; Eck, B.L.; Xie, D.; Lartey, R.; Lo, C.; Zaylor, W.; Yang, M.; Nakamura, K.; Winalski, C.S.; Spindler, K.P.; Li, X. Deep learning-based automatic pipeline for quantitative assessment of thigh muscle morphology and fatty infiltration. Magn Reson Med 2023, 89, 2441–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosti, A.; Shaqiri, E.; Paoletti, M.; Solazzo, F.; Bergsland, N.; Colelli, G.; Savini, G.; Muzic, S.I.; Santini, F.; Deligianni, X.; Diamanti, L.; Monforte, M.; Tasca, G.; Ricci, E.; Bastianello, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Pichiecchio, A. Deep learning for automatic segmentation of thigh and leg muscles. MAGMA 2022, 35, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agosti, A. (2021) DNN muscle segmentation: release 1.0.1 (version v1.0.1). Zenodo. [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Atkins, J.L. Muscle loss and obesity: the health implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 2015, 74, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljkovic, I.; Zmuda, J.M. Epidemiology of myosteatosis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2010, 13, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Dixon techniques for water and fat imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008, 28, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.B.; McKenzie, C.A.; Pineda, A.R.; Yu, H.; Shimakawa, A.; Brau, A.C.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Gold, G.E.; Brittain, J.H. Water-fat separation with IDEAL gradient-echo imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007, 25, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyke, J.P. Quantitative MRI Proton Density Fat Fraction: A Coming of Age. Radiology 2021, 298, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Yokoo, T.; Bashir, M.R.; et al. Linearity and Bias of Proton Density Fat Fraction as a Quantitative Imaging Biomarker: A Multicenter, Multiplatform, Multivendor Phantom Study. Radiology 2021, 298, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burian, E.; Franz, D.; Greve, T.; Dieckmeyer, M. .; Holzapfel, C.; Drabsch, T.; Sollmann,.; Probst, M.; Kirschke, J.S.; Rummen, E.J.; Zimmer, C.; Hauner,H.; Karampinos, D.C.; Baum, T. Age- and gender-related variations of cervical muscle composition using chemical shift encoding-based water-fat MRI. Eur J Radiol 2020, 125, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csapo, R.; Malis, V.; Sinha, U.; Du, J.; Sinha, S. Age-associated differences in triceps surae muscle composition and strength - an MRI-based cross-sectional comparison of contractile, adipose and connective tissue. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2014, 15, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaeger, S.; Inhuber, S.; Rohrmeier, A.; Dieckmeyer, M.; Freitag, F.; Klupp, E.; Weidlich, D.; Feuerriegel, G.; Kreuzpointner, F.; Schwirtz, A.; Rummeny, E.J.; Zimmer, C.; Kirschke, J.S.; Karampinos, D.C.; Baum, T. Association of paraspinal muscle water-fat MRI-based measurements with isometric strength measurements. Eur Radiol 2019, 29, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampinos, D.C.; Baum, T.; Nardo, L.; Alizai, H.; Yu, H.; Carballido-Gamio, J.; Yap, S.P.; Shimakawa, A.; Link, T.M.; Majumdar, S. Characterization of the regional distribution of skeletal muscle adipose tissue in type 2 diabetes using chemical shift-based water/fat separation. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012, 35, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, G. .; Thompson, R.T.; Marsh, G.D. Multicomponent T2 relaxation of in vivo skeletal muscle. Magn Reson Med 1999, 42, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Yip, A.L.; Shrader, J.A.; Mesdaghinia, S.; Volochayev, R.; Jansen, A.V.; Miller, F.W.; Rider, L.G. Magnetic resonance measurement of muscle T2, fat-corrected T2 and fat fraction in the assessment of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016, 55, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, C.; Meyer, R.A.; Fleckenstein, J.L. T2 mapping of muscle. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 2003, 7, 297–305. [Google Scholar]
- Fischmann, A.; Hafner, P.; Fasler, S.; et al. (2012a). Quantitative MRI can detect subclinical disease progression in muscular dystrophy. J Neurol 2012, 259, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Xie, Z.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Zheng, S.S.; Wang, Z.X.; Xiao, J.X.; Yuan, Y. T2 Mapping and Fat Quantification of Thigh Muscles in Children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Curr Med Sci 2019, 39, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploutz, L.L.; Tesch, P.A.; Biro, R.L.; Dudley, G.A. Effect of resistance training on muscle use during exercise. J Appl Physiol 1994, 76, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzabou, N.; Loureiro de Sousa, P.; Caldas, E.; Carlier, P.G. Validation of a generic approach to muscle water T2 determination at 3T in fat-infiltrated skeletal muscle. J Magn Reson Imag 2015, 41, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, F.; Deligianni, X.; Paoletti, M.; Solazzo, F.; Weigel, M.; de Sousa, P.L.; Bieri, O.; Monforte, M.; Ricci, E.; Tasca, G.; Pichiecchio, A.; Bergsland, N. Fast Open-Source Toolkit for Water T2 Mapping in the Presence of Fat From Multi-Echo Spin-Echo Acquisitions for Muscle MRI. Front Neurol. 2021, 12, 630387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiechowicz, J.; Marchenko, I.G.; Hänggi, P.; Łuczka, J. Diffusion Coefficient of a Brownian Particle in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium: Einstein Model and Beyond. Entropy (Basel) 2023, 25, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; et al. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986, 161, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.K.; Cercignani, M. Twenty-five pitfalls in the analysis of diffusion MRI data. NMR Biomed 2010, 23, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.M.H.; Scott, C.J.M.; Ozzoude, M. .; Holmes, M.F.; Arnott, S.R.; Nanayakkara, N.D.; Ramirez, J.; Black, S.E.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Strother, S.C.; Swartz, R.H.; Symons, S.; Montero-Odasso, M.; ONDRI Investigators; Bartha, R. Comparison of quality control methods for automated diffusion tensor imaging analysis pipelines. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0226715. [Google Scholar]
- Oudeman, J.; Nederveen, A.J.; Strijkers, G.J.; Maas, M.; Luijten, P.R. .; Froeling, M. Techniques and applications of skeletal muscle diffusion tensor imaging: A review. J Magn Reson Imaging 2016, 43, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, M.; Hasan, I. S.; Walimuni, H. A.; Hahn, K.R. A Review of Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging Computational Methods and Software Tools. Comput Biol Med 2011, 41, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Damon, B.; Ding, Z.; Hooijmans, M.; Anderson, A.; Zhou, X.; Coolbaugh, C.; George, M.K.; Landman, B. A MATLAB Toolbox for Muscle Diffusion-Tensor MRI Tractography. J Biomech 2021, 124, 110540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.G.; Clark, C.A. Diffusion in hierarchical systems: A simulation study in models of healthy and diseased muscle tissue. Magn Reson Med 2017, 78, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galban, C.J.; Maderwald, S. ; Stock, F.; Ladd, M.E.; Galban, C.J. Age-related changes in skeletal muscle as detected by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2007, 62, 453–458.
- Karampinos, D.C.; King, K.F.; Sutton, B.P.; Georgiadis, J.G. Myofiber ellipticity as an explanation for transverse asymmetry of skeletal muscle diffusion MRI in vivo signal. Ann Biomed Eng 2009, 37, 2532–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malis, V.; Sinha, U.; Csapo, R.; Narici, M.; Smitaman, E.; Sinha, S. Diffusion tensor imaging and diffusion modeling: Application to monitoring changes in the medial gastrocnemius in disuse atrophy induced by unilateral limb suspension. J Magn Reson Imaging 2019, 49, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malis, V.; Sinha, U.; Smitaman, E.; Obra, J.K.L.; Langer, H.T.; Mossakowski, A.A.; Baar, K.; Sinha, S. Time-dependent diffusion tensor imaging and diffusion modeling of age-related differences in the medial gastrocnemius and feasibility study of correlations to histopathology. NMR Biomed 2023, e4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, U.; Csapo, R.; Malis, V.; Xue, Y.; Sinha, S. Age-related differences in diffusion tensor indices and fiber architecture in the medial and lateral gastrocnemius. J Magn Reson Imaging 2015, 41, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froeling, M.; Oudeman, J.; Strijkers, G.J.; Maas, M.; Drost, M.R.; Nicolay, K.; Nederveen, A.J. Muscle changes detected with diffusion-tensor imaging after long-distance running. Radiology 2015, 274, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Yamamura, J.; Sedlacik, J.; Wang, Z.J.; Gebert, P.; Starekova, J.; Tahir, E. Diffusion tensor imaging combined with T2 mapping to quantify changes in the skeletal muscle associated with training and endurance exercise in competitive triathletes. Eur Radiol 2020, 30, 2830–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, B.M.; Froeling, M.; Buck, A.K.; Oudeman, J.; Ding, Z.; Nederveen, A.J.; Bush, E.C.; Strijkers, G.J. Skeletal muscle diffusion tensor-MRI fiber tracking: rationale, data acquisition and analysis methods, applications and future directions. NMR Biomed 2017, 30, 10–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsting, J.; Rehmann, R.; Rohm, M.; Güttsches, A.K.; Froeling, M.; Kan, H.E.; Tegenthoff, M.; Vorgerd, M.; Schlaffke, L. Robustness and stability of volume-based tractography in a multicenter setting. NMR Biomed 2022, 35, e4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, T.; Ogawa, T.; Yoda, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Shobara, K.; Niizuma, K.; Kawashima, R.; Sasaki, K.J. Morphological comparison of masseter muscle fibres in the mandibular rest and open positions using diffusion tensor imaging. Oral Rehabil 2022, 49, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, P.; Delmas, V.; Buy, J.N.; Rahmouni, A.; Vadrot, D.; Deux, J.F. In vivo visualization of the levator ani muscle subdivisions using MR fiber tractography with diffusion tensor imaging. J Anat 2012, 221, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijta, F.M.; Froeling, M.; Nederveen, A.J.; Stoker, J. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography for the visualization of the female pelvic floor. Clin Anat 2013, 26, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberskiy, G.; Feiweier, T.; Gyftopoulos, S.; Axel, L.; Novikov, D.S.; Fieremans, E. Assessment of myofiber microstructure changes due to atrophy and recovery with time-dependent diffusion MRI. NMR Biomed 2021, 34, e4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.; Abbassi-Daloii, T.; Heezen, L.G.M.; van de Velde, N.M.; Koeks, Z.; Veeger, T.T.J.; Hooijmans, M.T.; El Abdellaoui, S.; van Duinen, S.G.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M.; van Putten, M.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Raz, V.; Spitali, P.; Niks, E.H.; Kan, H.E. Diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging captures increased skeletal muscle fibre diameters in Becker muscular dystrophy. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 1546–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingler, W.; Jurkat-Rott, K.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Schleip, R. The role of fibrosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Acta Myol 2012, 31, 184–195. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, U.; Malis, V.; Chen, J.S.; Csapo, R.; Kinugasa, R.; Narici, M.V.; Sinha, S. Role of the Extracellular Matrix in Loss of Muscle Force With Age and Unloading Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Biochemical Analysis, and Computational Models. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Park, S.W.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nevitt, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Visser, M.; Newman, A.B. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2006, 61, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafi, B.; Blemker, S.S. A mathematical model of force transmission from intrafascicularly terminating muscle fibers. J Biomech 2011, 44, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malis, V.; Sinha, U.; Csapo, R.; Narici, M.; Sinha, S. Relationship of changes in strain rate indices estimated from velocity-encoded MR imaging to loss of muscle force following disuse atrophy. Magn Reson Med 2018, 79, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, U.; Malis, V.; Csapo, R.; Moghadasi, A.; Kinugasa, R.; Sinha, S. Age-related differences in strain rate tensor of the medial gastrocnemius muscle during passive plantarflexion and active isometric contraction using velocity encoded MR imaging: potential index of lateral force transmission. Magn Reson Med 2015, 73, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkelman, R.M.; Stanisz, G.J.; Graham, S.J. Magnetization transfer in MRI: a review. NMR Biomed 2001, 14, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, C.D.J.; Samson, R.S.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Quantitative magnetization transfer in in vivo healthy human skeletal muscle at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2010, 64, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Dortch, R.D.; Kroop, S.F.; et al. A rapid approach for quantitative magnetization transfer imaging in thigh muscles using the pulsed saturation method. Magn Reson Imaging 2015, 33, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottmar, M.; Haralampieva, D.; Salemi, S.; et al. Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging to Monitor Muscle Tissue Formation during Myogenic in Vivo Differentiation of Muscle Precursor Cells. Radiology. 2016, 281, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, G.; Dathe, H.; Kallenberg, K.; Dechent, P. High-resolution maps of magnetization transfer with inherent correction for RF inhomogeneity and T1 relaxation obtained from 3D FLASH MRI. Magn Reson Med 2008, 60, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.M.; Sinclair, C.D.; Fischmann, A.; Reilly, M.M.; Hanna, M.G.; Yousry, T.A.; Thornton, J.S. Reproducibility, and age, body-weight and gender dependency of candidate skeletal muscle MRI outcome measures in healthy volunteers. Eur Radiol 2014, 24, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, I.O.; Sinha, U. Magnetization transfer saturation imaging of human calf muscle: Reproducibility and sensitivity to regional and sex differences. J Magn Reson Imaging 2019, 50, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.C.; Sinha, S.; Sinha, U. ; Spin Lattice (T1) and Magnetization Transfer Saturation (MTsat) Imaging to Monitor Age-Related Differences in Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C A Araujo, E.; Azzabou, N.; Vignaud, A.; Guillot, G.; Carlier, P.G. Quantitative ultrashort TE imaging of the short-T2 components in skeletal muscle using an extended echo-subtraction method. Magn Reson Med 2017, 78, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J. Quantification of short T2* fraction and fat fraction in skeletal muscle. Master’ in Medical Physics Thesis, . San Diego State University. San Diego, CA.
- Zhong, X.; Epstein, F.H.; Spottiswoode, B.S.; Helm, P.A.; Blemker, S.S. Imaging two-dimensional displacements and strains in skeletal muscle during joint motion by cine DENSE MR. J Biomech 2008, 41, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englund, E.K.; Elder, C.P.; Xu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Damon, B.M. Combined diffusion and strain tensor MRI reveals a heterogeneous, planar pattern of strain development during isometric muscle contraction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2011, 300, R1079–R1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malis, V.; Sinha, U.; Sinha, S. 3D Muscle Deformation Mapping at Submaximal Isometric Contractions: Applications to Aging Muscle. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 600590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Xu, K.; Guo, Y.K.; Xie, L.J.; Peng, F.; Xu, R.; Fu, H.; Yuan, W.F.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Cheng, B.C.; Fu, C.; Zhou, H.; Cai, X.T.; Li, X.S. Clinical utilisation of multimodal quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in investigating muscular damage in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a study on the association between gluteal muscle groups and motor function. Pediatr Radiol 2023, 53, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Therapeutic strategies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: an update. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, D.J.; Taivassalo, T.; Cooke, K.D.; Park, H.; Moslemi, Z.; Batra, A.; Forbes, S.C.; Byrne, B.J.; Walter, G.A.; Vandenborne, K. Safety, feasibility, and efficacy of strengthening exercise in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alic, L.; Griffin, J. F 4th.; Eresen, A.; Kornegay, J.N.; Ji, J.X. Using MRI to quantify skeletal muscle pathology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A systematic mapping review. Muscle Nerve 2021, 64, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Xie, Z.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Zheng, S.S.; Wang, Z.X.; Xiao, J.X.; Yuan, Y. T2 Mapping and Fat Quantification of Thigh Muscles in Children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Curr Med Sci 2019, 39, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Serai, S.; Lindquist, D.; Merrow, A.C.; Horn, P.S.; Kim, D.H.; Wong, B.L. Quantitative Skeletal Muscle MRI: Part 2, MR Spectroscopy and T2 Relaxation Time Mapping-Comparison Between Boys With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Healthy Boys. Am J Roentgenol 2015, 205, W216–W223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Merrow, A.C.; Shiraj, S.; Wong, B.L.; Horn, P.S.; Laor, T. Analysis of fatty infiltration and inflammation of the pelvic and thigh muscles in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD): grading of disease involvement on MR imaging and correlation with clinical assessments. Pediatr Radiol 2013, 43, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, J.M.; Sinclair, C.D.; Fischmann, A.; Machado, P.M.; Reilly, M.M.; Yousry, T.A.; Thornton, J.S.; Hanna, M.G. MRI biomarker assessment of neuromuscular disease progression: a prospective observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2016, 15, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankodi, A.; Bishop, C.A.; Auh, S.; Newbould, R.D.; Fischbeck, K.H.; Janiczek, R.L. Quantifying disease activity in fatty-infiltrated skeletal muscle by IDEAL-CPMG in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 2016, 26, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Xu, H.; Song, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, S.; Cai, X.; Guo, Y.; Gong, L. Longitudinal study of multi-parameter quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: hyperresponsiveness of gluteus maximus and detection of subclinical disease progression in functionally stable patients. J Neurol 2023, 270, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooijmans, M.T.; Damon, B.M.; Froeling, M.; Versluis, M.J.; Burakiewicz, J.; Verschuuren, J.J.; Niks, E.H.; Webb, A.G.; Kan, H.E. Evaluation of skeletal muscle DTI in patients with duchenne muscular dystrophy. NMR Biomed 2015, 28, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.D.; Liang, Y.Y.; Xu, P.; Ling, J.; Chen, Y.M. Diffusion-Tensor Imaging of Thigh Muscles in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Correlation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Fractional Anisotropy Values With Fatty Infiltration. Am J Roentgenol 2016, 206, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayda, J.; Demonceau, G.; Carlier, P.G. Muscle imaging in myositis: MRI, US, and PET. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2022, 36, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, A.S.; Salam, S.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Machado, P.M.; Roy, B. Imaging biomarkers in the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Front Neurol 2023, 14, 1146015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Yip, A.L.; Shrader, J.A.; Mesdaghinia, S.; Volochayev, R.; Jansen, A.V.; Miller, F.W.; Rider, L.G. Magnetic resonance measurement of muscle T2, fat-corrected T2 and fat fraction in the assessment of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2016, 55, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Yu, K.; Gao, L.; Zhang, P.; Goerner, F.; Runge, V.M.; Li, X. Diffusion tensor imaging in evaluation of thigh muscles in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Br J Radiol 2014, 87, 20140261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, C.; Sun, C.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, Z. Simultaneous Multislice Accelerated Diffusion Tensor Imaging of Thigh Muscles in Myositis. Am J Roentgenol 2018, 211, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Manera, J.; Walter, G.; Straub, V. Skeletal muscle magnetic resonance imaging in Pompe disease. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperus, E.; Kruijshaar, M.E.; Wens, S.C.A.; et al. Long-term benefit of enzyme replacement therapy in Pompe disease: a 5-year prospective study. Neurology 2017, 89, 2365–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmann, R.; Froeling, M.; Rohm, M.; Forsting, J.; Kley, R.A.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Karabul, N.; Meyer-Frießem, C.H.; Vollert, J.; Tegenthoff, M.; Vorgerd, M.; Schlaffke, L. Diffusion tensor imaging reveals changes in non-fat infiltrated muscles in late onset Pompe disease. Muscle Nerve 2020, 62, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ploeg, A.; Carlier, P.G.; Carlier, R.Y.; Kissel, J.T.; Schoser, B.; Wenninger, S.; Pestronk, A.; Barohn, R.J.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Goker-Alpan, O.; Mozaffar, T.; Pena, L.D.; Simmons, Z.; Straub, V.; Guglieri, M.; Young, P.; Boentert, M.; Baudin, P.Y.; Wens, S.; Shafi, R.; Bjartmar, C.; Thurberg, B.L. Prospective exploratory muscle biopsy, imaging, and functional assessment in patients with late-onset Pompe disease treated with alglucosidase alfa: The EMBASSY Study. Mol Genet Metab 2016, 119, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lollert, A.; Stihl, C.; Hötker, A.M.; Mengel, E.; König, J.; Laudemann, K.; Gökce, S.; Düber, C.; Staatz, G. Quantification of intramuscular fat in patients with late-onset Pompe disease by conventional magnetic resonance imaging for the long-term follow-up of enzyme replacement therapy. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0190784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Peralta, C.; Alonso-Pérez, J. .; Llauger, J.; Segovia, S.; Montesinos, P.; Belmonte, I.; Pedrosa, I.; Montiel, E.; Alonso-Jiménez, A.; Sánchez-González, J.; Martínez-Noguera, A.; IIlla, I.; Díaz-Manera, J. Follow-up of late-onset Pompe disease patients with muscle magnetic resonance imaging reveals increase in fat replacement in skeletal muscles. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Sayer, A.A. Cruz-Jentoft A. Sarcopenia definition, diagnosis and treatment: consensus is growing. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codari, M.; Zanardo, M.; di Sabato, M.E.; Nocerino, E.; Messina, C.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Sardanelli, F.J. MRI-Derived Biomarkers Related to Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Magn Reson Imaging 2020, 51, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianca, V.; Albano, D.; Messina, C.; Gitto, S.; Ruffo, G.; Guarino, S.; Del Grande, F.; Sconfienza, L.M. Sarcopenia: imaging assessment and clinical application. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2022, 47, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X.; Chong, M.S.; Lim, W.S.; Tay, L.; Yew, S.; Yeo, A.; Tan, C.H. Validity of estimating muscle and fat volume from a single MRI section in older adults with sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity. Clin Radiol 2017, 72, 427–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, D.M.; Mohler, J.; Fain, M.; et al. Multi-parametric MR imaging of quadriceps musculature in the setting of clinical frailty syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 2016, 45, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.; Reiter, D.A.; Adelnia, F.; Ubaida-Mohien, C.; Bergeron, C.M.; Choi, S.; Fishbein, K.W.; Spencer, R.G.; Ferrucci, L. Age-related changes in human skeletal muscle microstructure and architecture assessed by diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging and their association with muscle strength. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crema, M.D.; Yamada, A.F.; Guermazi, A.; Roemer, F.W.; Skaf, A.Y. Imaging techniques for muscle injury in sports medicine and clinical relevance. Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine 2015, 8, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaravel, M.; Bawa, P.; Murai, N. Magnetic resonance imaging of muscle injury in elite American football players: Predictors for return to play and performance. Eur J Radiol 2018, 108, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlenfeld, N.; Steendahl, I.B.; Berthold, D.P.; Meyer, T.; Hauser, T.; Wagner, N.; Sander, A.L.; Marzi, I.; Kaltenbach, B.; Yel, I.; Vogl, T.; Eichler, K. Assessment of muscle volume using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in football players after hamstring injuries. Eur J Sport Sci 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, J.R.; Hooijmans, M.T.; Froeling, M.; Oudeman, J.; Tol, J.L.; Strijkers, G.J.; Nederveen, A.J.; Maas, M. Diffusion tensor imaging and quantitative T2 mapping to monitor muscle recovery following hamstring injury. NMR Biomed 2023, 36, e4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglands, J.D.; Grainger, A.J.; Robinson, P.; Tanner, S.F.; Tan, A.L.; Feiweier, T.; Evans, R.; Emery, P.; O'Connor, P. RI in acute muscle tears in athletes: can quantitative T2 and DTI predict return to play better than visual assessment? Eur Radiol 2020, 30, 6603–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bye, E.A.; Harvey, L.A.; Glinsky, J.V.; Bolsterlee, B.; Herbert, R.D. A preliminary investigation of mechanisms by which short-term resistance training increases strength of partially paralysed muscles in people with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2019, 57, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silder, A.; Reeder, S.B.; Thelen, D.G. The influence of prior hamstring injury on lengthening muscle tissue mechanics. J Biomech 2010, 43, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Malis, M.; Cunnane, B.; Hernandez, R.; Sinha, U. Isometric Contractions of the Quadriceps muscle: Strain and Strain Tensor Mapping using Velocity Encoded Phase Contrast Imaging. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the ISMRM 2022, May6-11,2022, London.
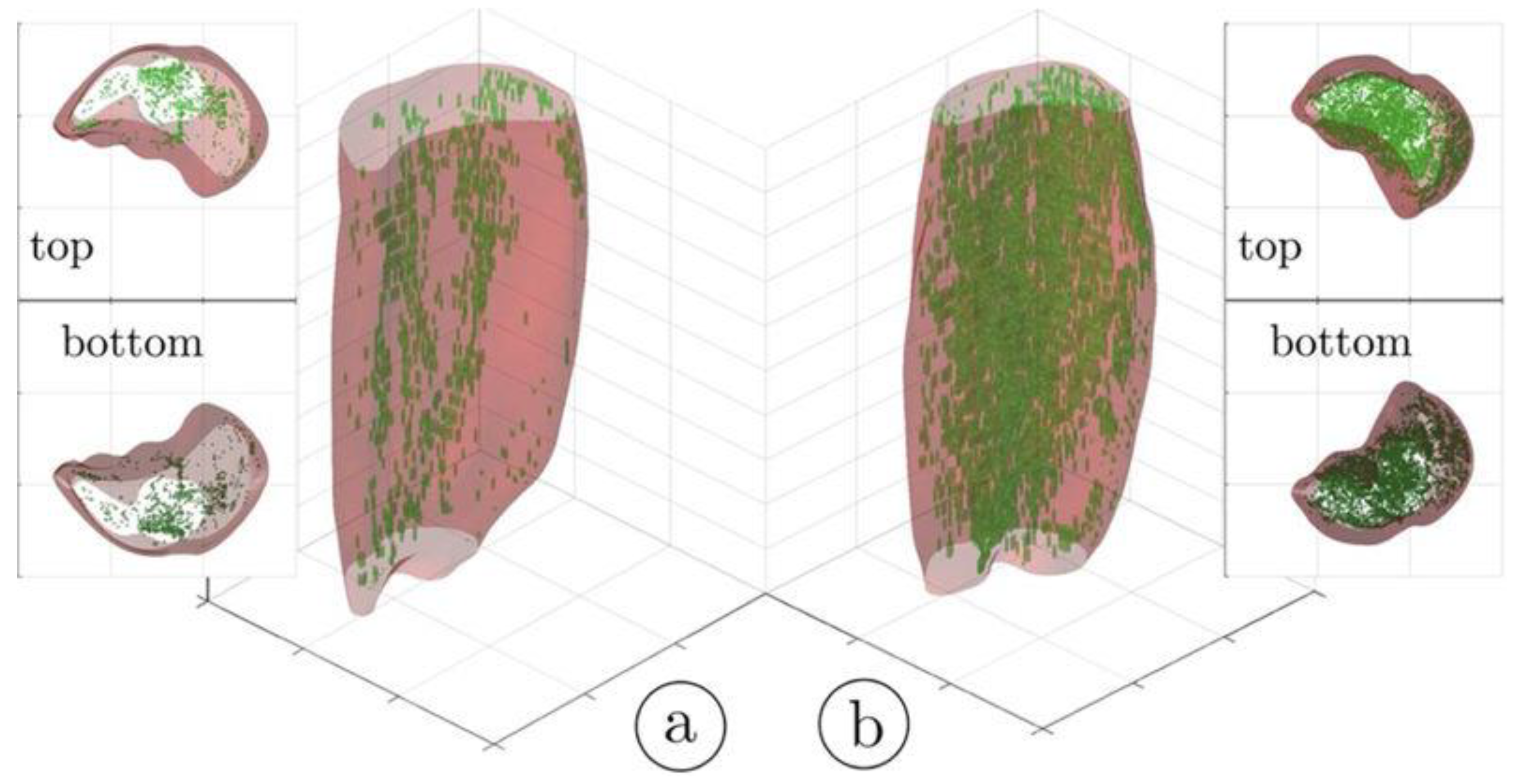
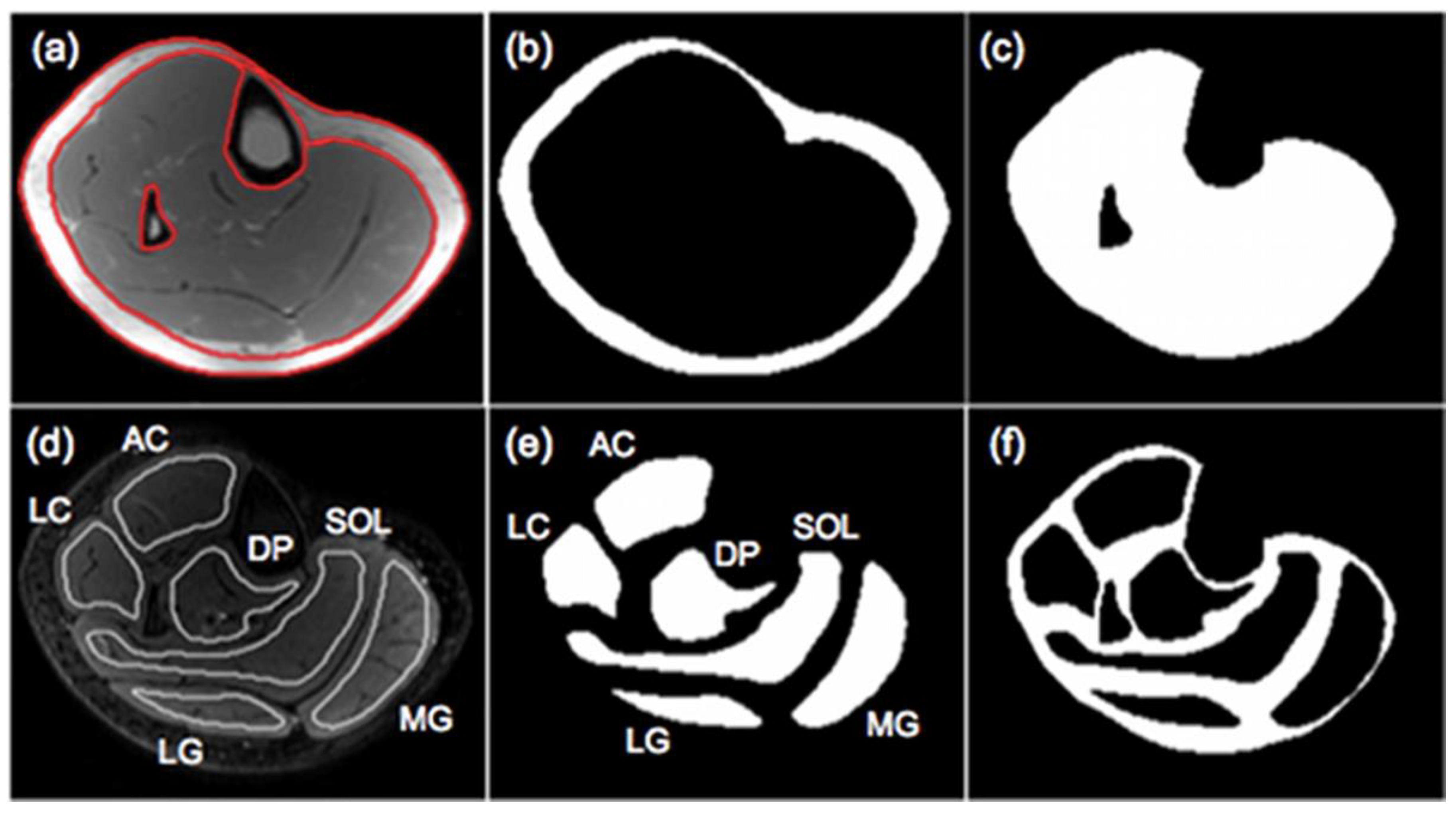
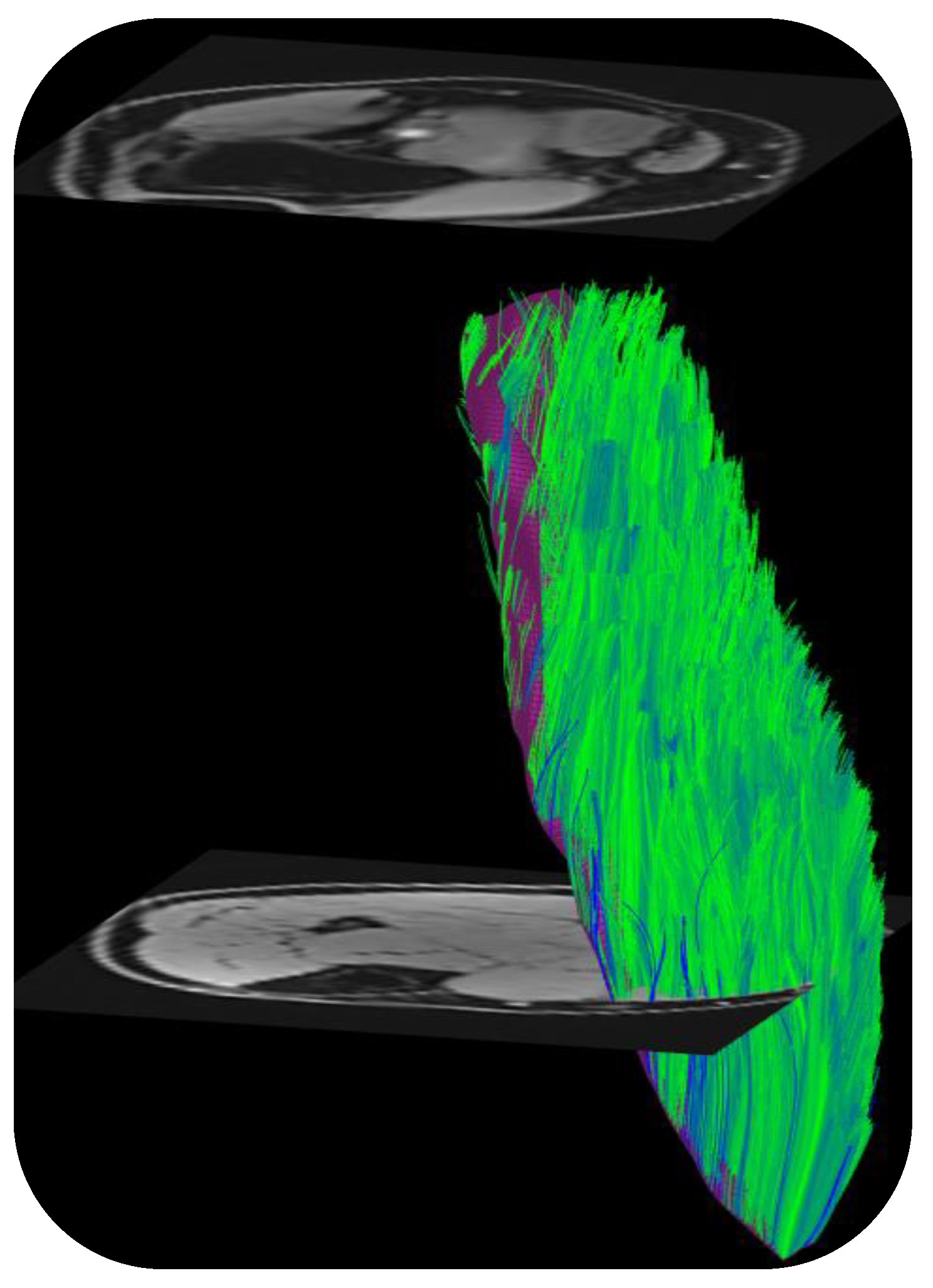
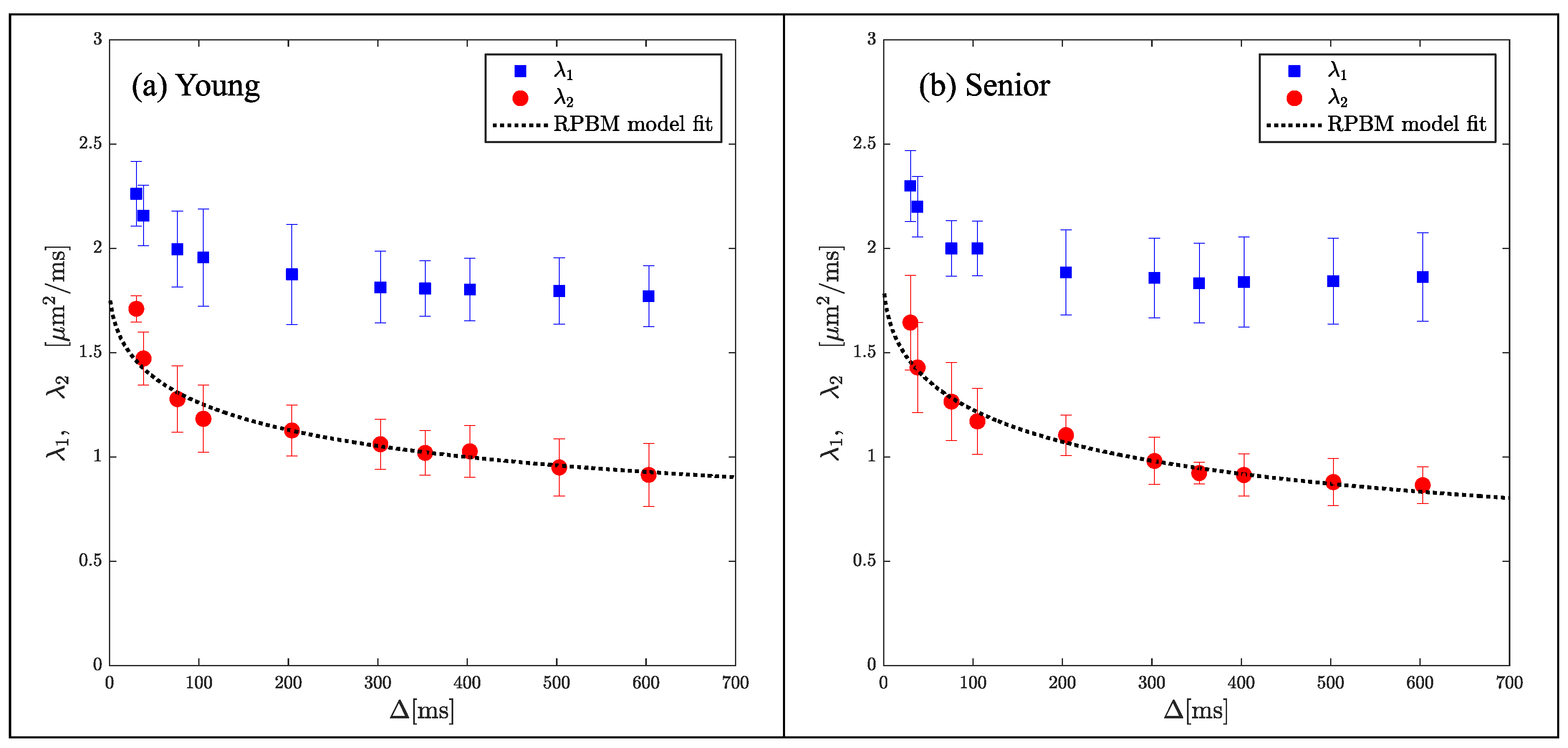
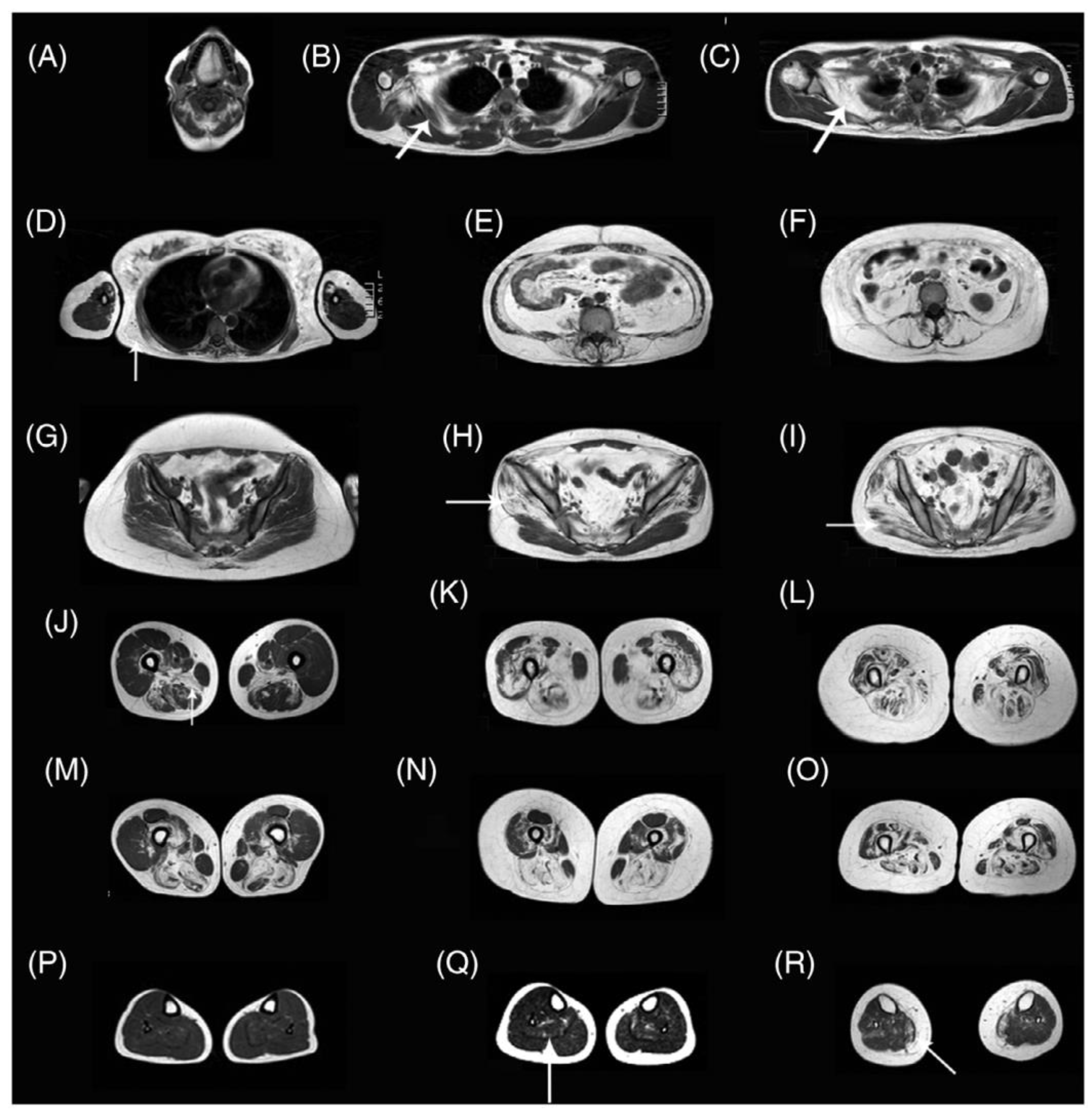
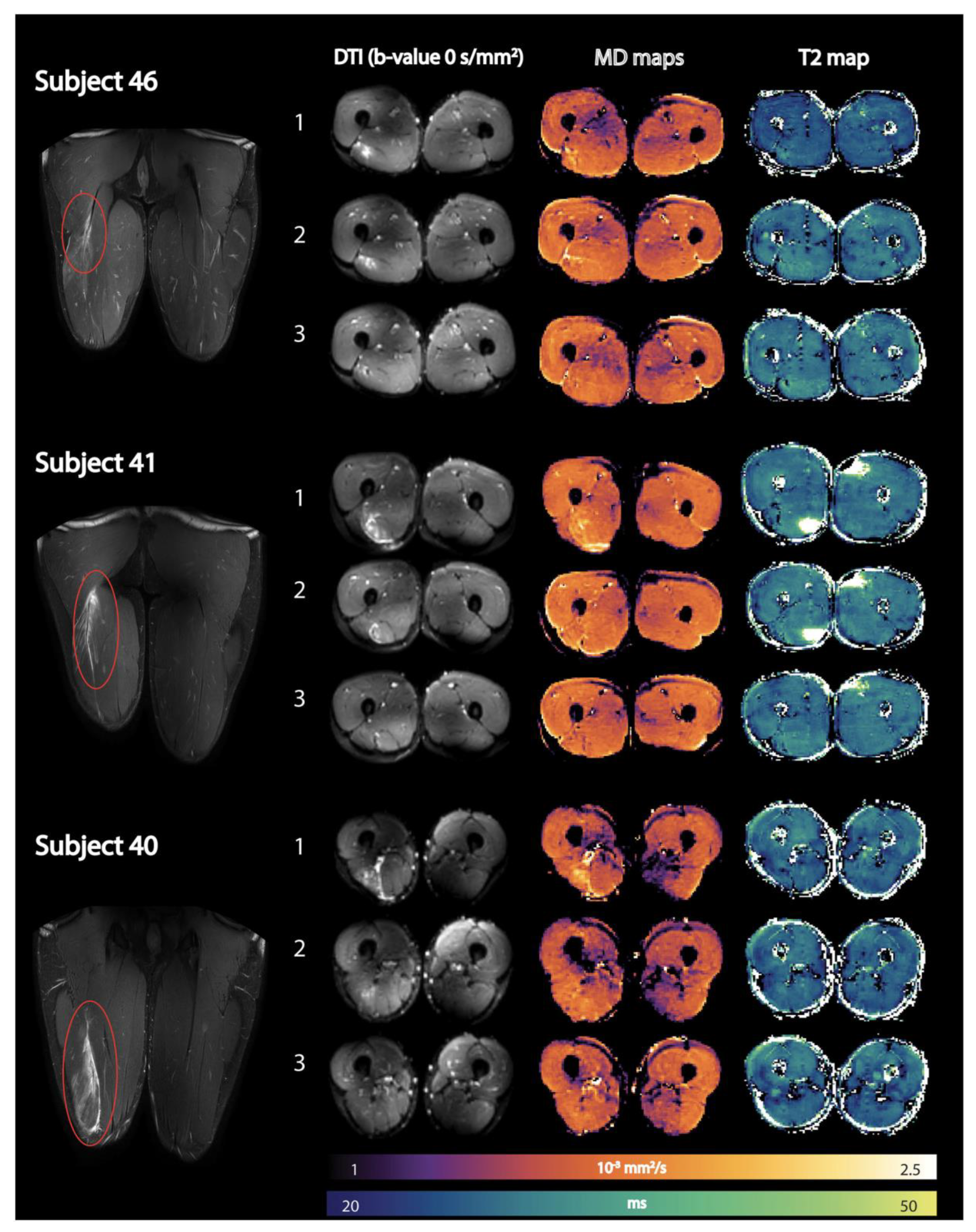
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



