Submitted:
11 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
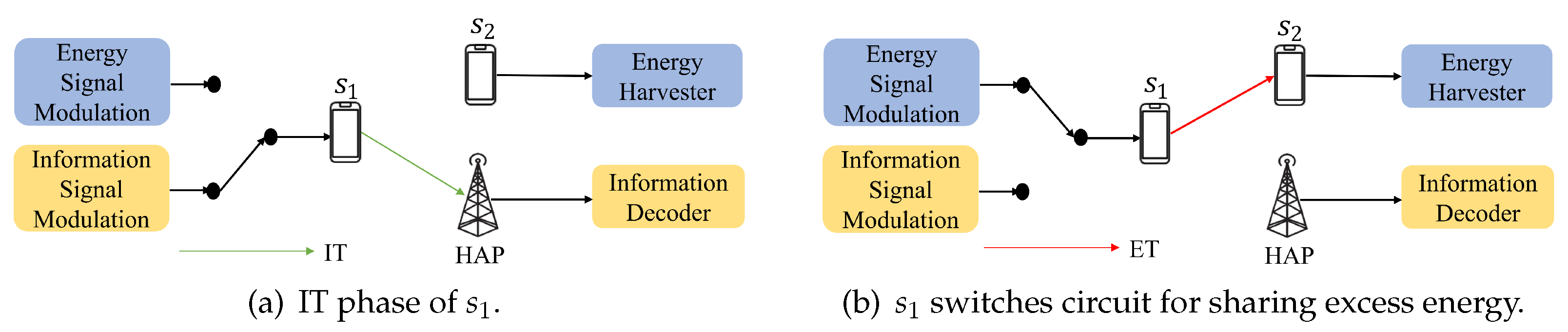
- Different from the general SWIPT, in this paper, we propose a new DT-SWIPT mechanism, which allows wireless stations that finish information transmission to share their excess energy to other wireless stations that have not yet transmitted, thereby reducing energy consumption in the network.
- Ensure that the SNR value of the received signal of the HAP can meet the SNR threshold so that the HAP can decode the signals from wireless stations.
- The optimization model, named DaTA, is proposed to obtain the best solution for the ECm problem. In addition, the DaTA-H scheme is also proposed so that an approximate solution can be obtained in a reasonable time.
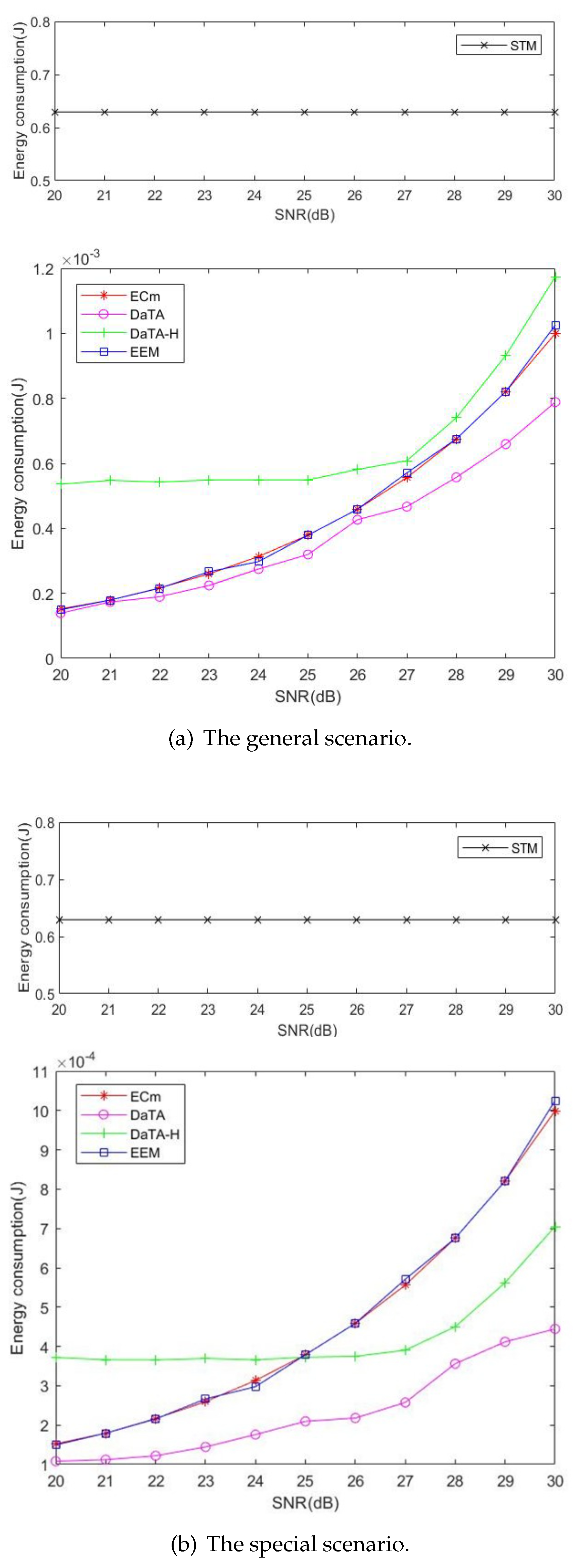
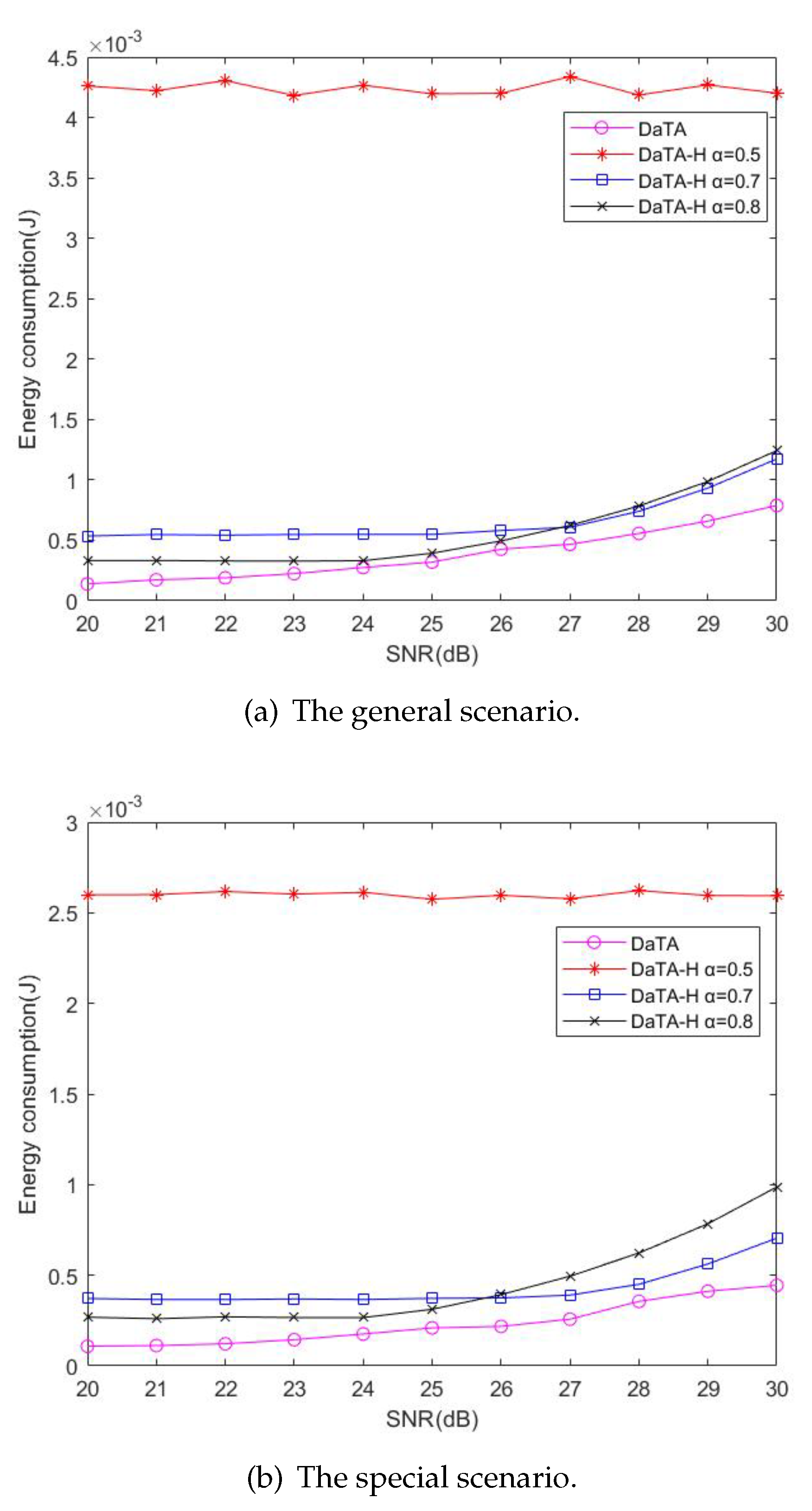
- Two scenarios, special scenarios and general scenarios are conducted in the simulation to verify the advantages of the proposed schemes. We compare the DaTA and the DaTA-H schemes proposed in this paper against the STM, EEM, and ECm models of the related works. From the simulation results, it can be concluded that the DaTA scheme has better performance in the energy consumption and the energy efficiency in both general and special scenarios. In special scenarios, when the SNR threshold reaches a certain value, the energy consumption and the energy efficiency of the DaTA-H scheme are also better than those of the related works.
2. Preliminaries
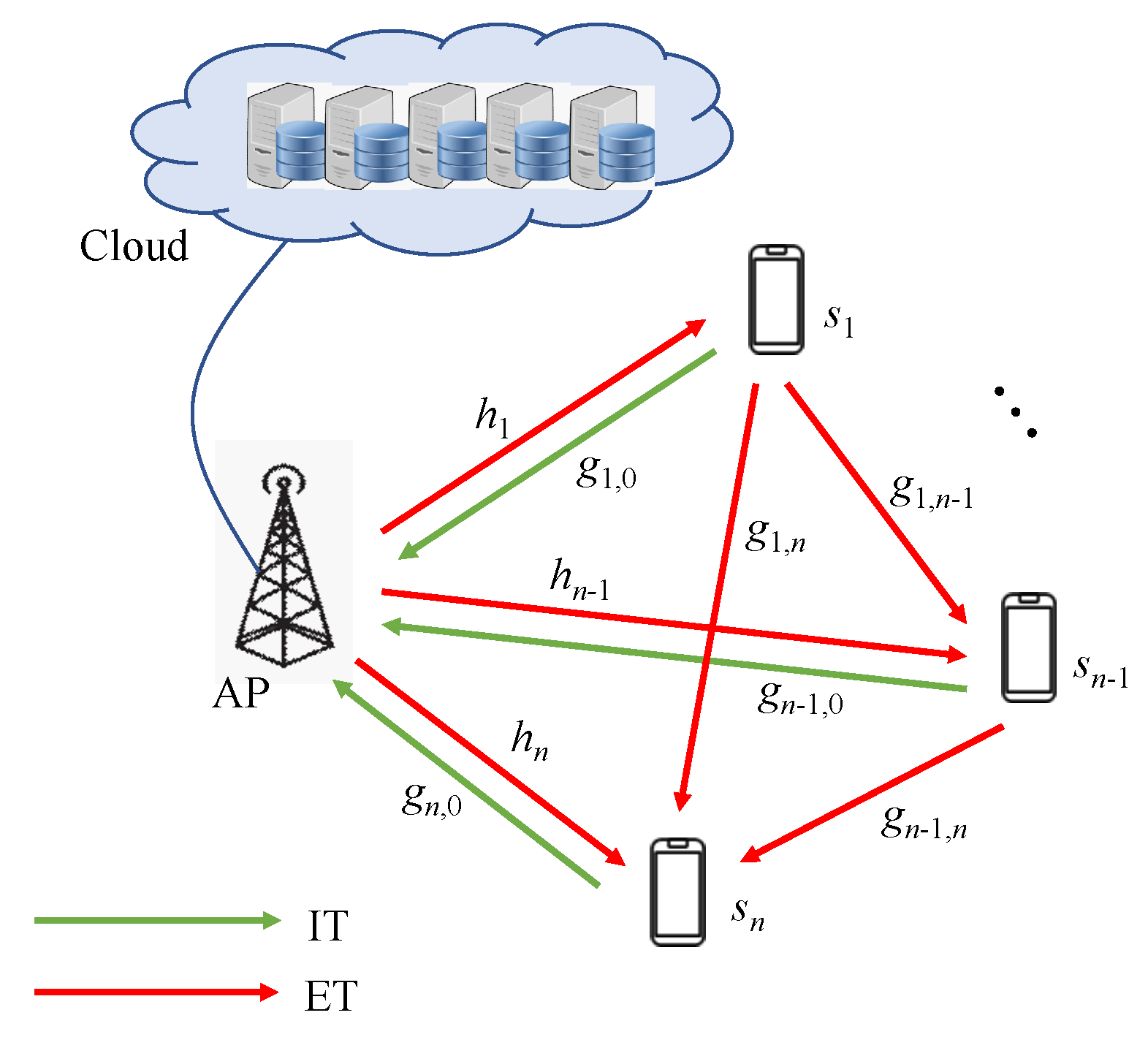
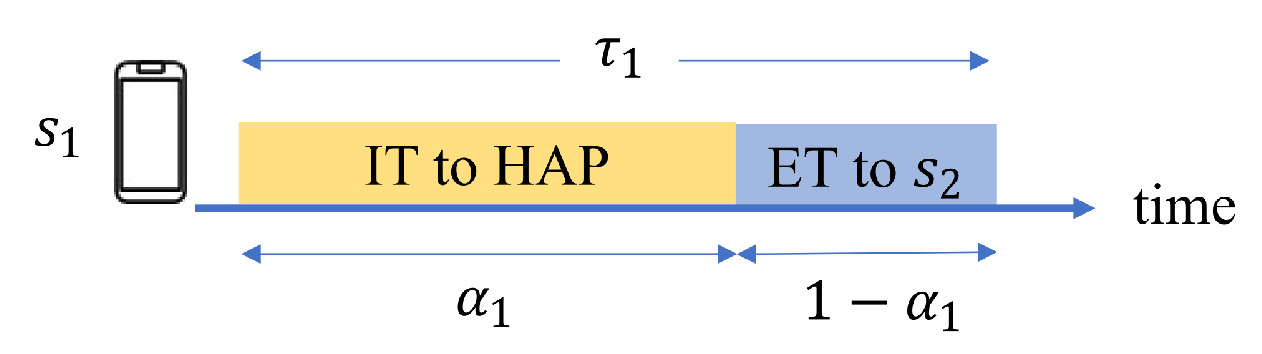
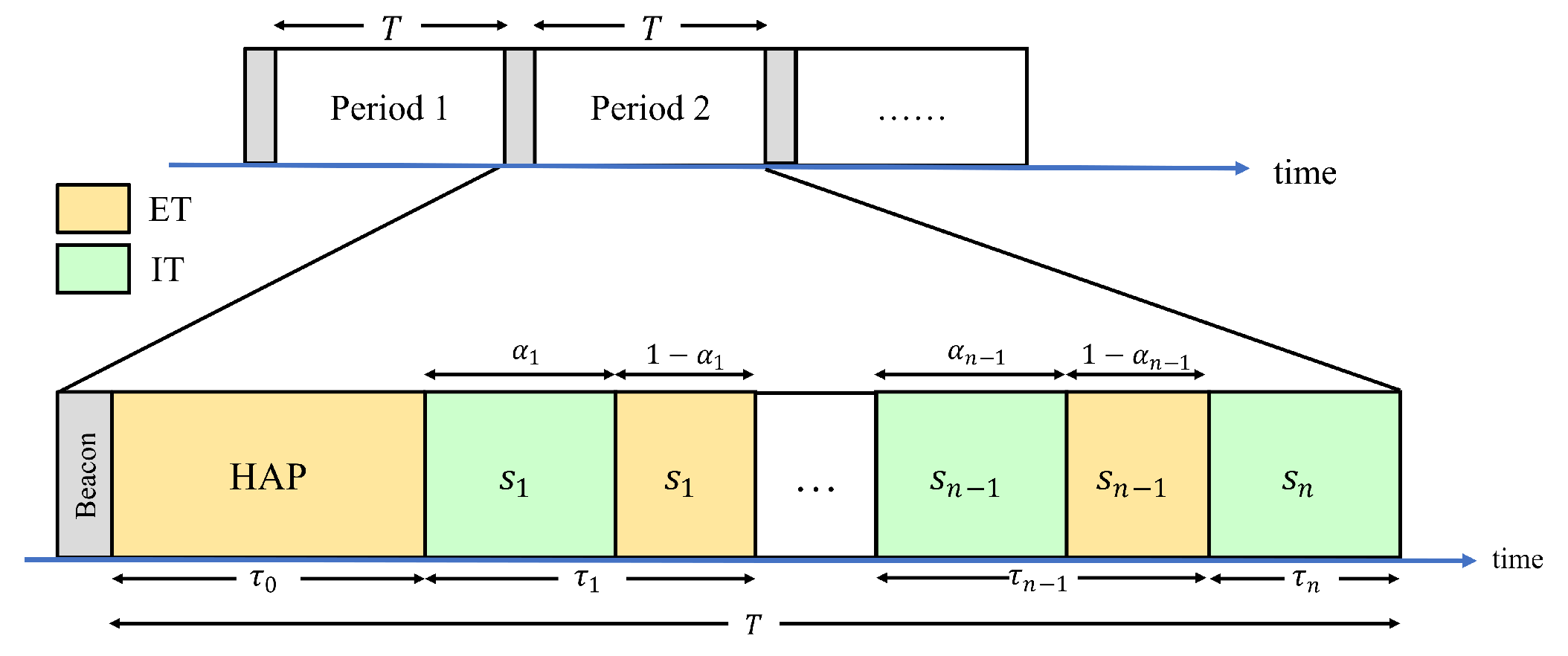
2.1. Network Model
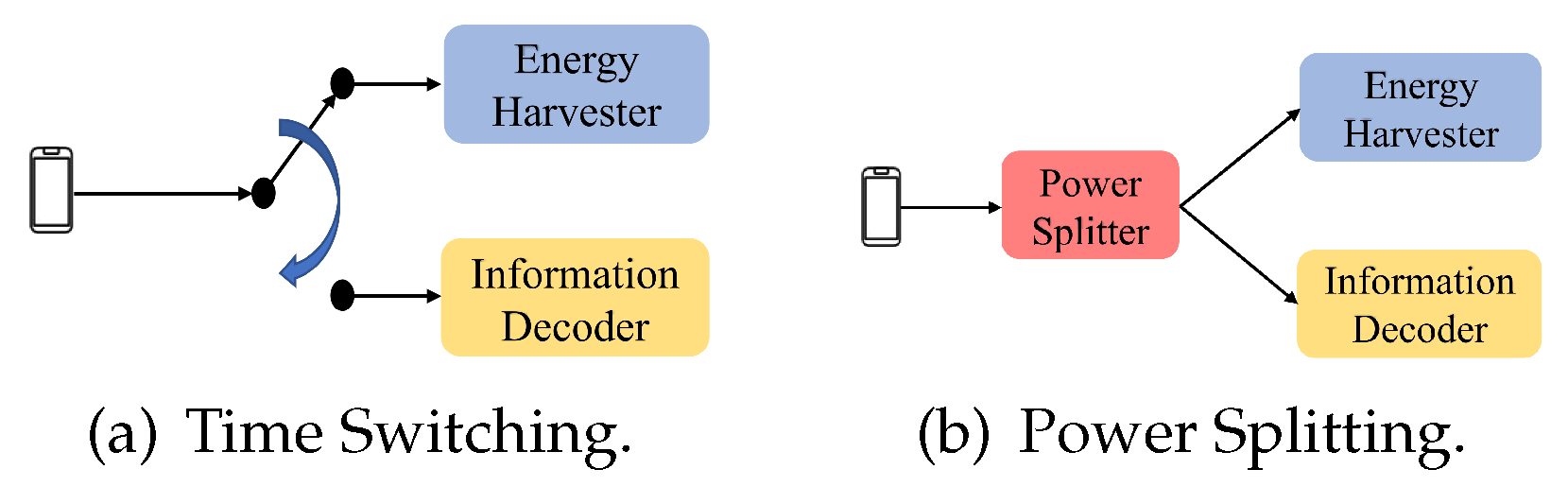
2.2. SWIPT vs. DT-SWIPT
2.3. SNR Constraint
3. DT-SWIPT Assisted Time Allocation for the ECm Problem
3.1. Problem Formulation
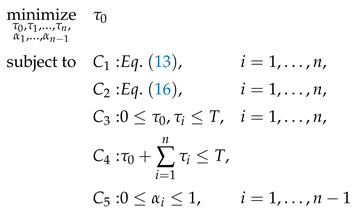
3.2. SQP-Based Algorithm for Finding the Optimal Solution of the D-ECm Problem
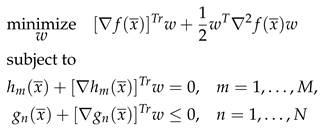
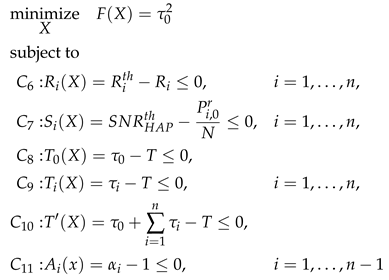
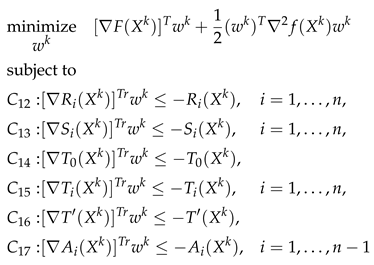
| Algorithm 1: DaTA: a SQP-based Algorithm for the D-ECm Problem |
 |
4. DaTA-H: The Heuristic Method
4.1. Problem Formulation of the Simplifying D-ECm Problem
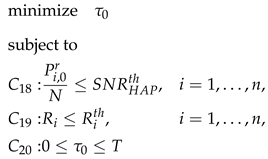
4.2. DaTA-H Algorithm for S-ECm
| Algorithm 2: DaTA-H Algorithm for the S-ECm Problem |
 |
5. Performance Evaluations
5.1. Comparisons of the Network Energy Consumption
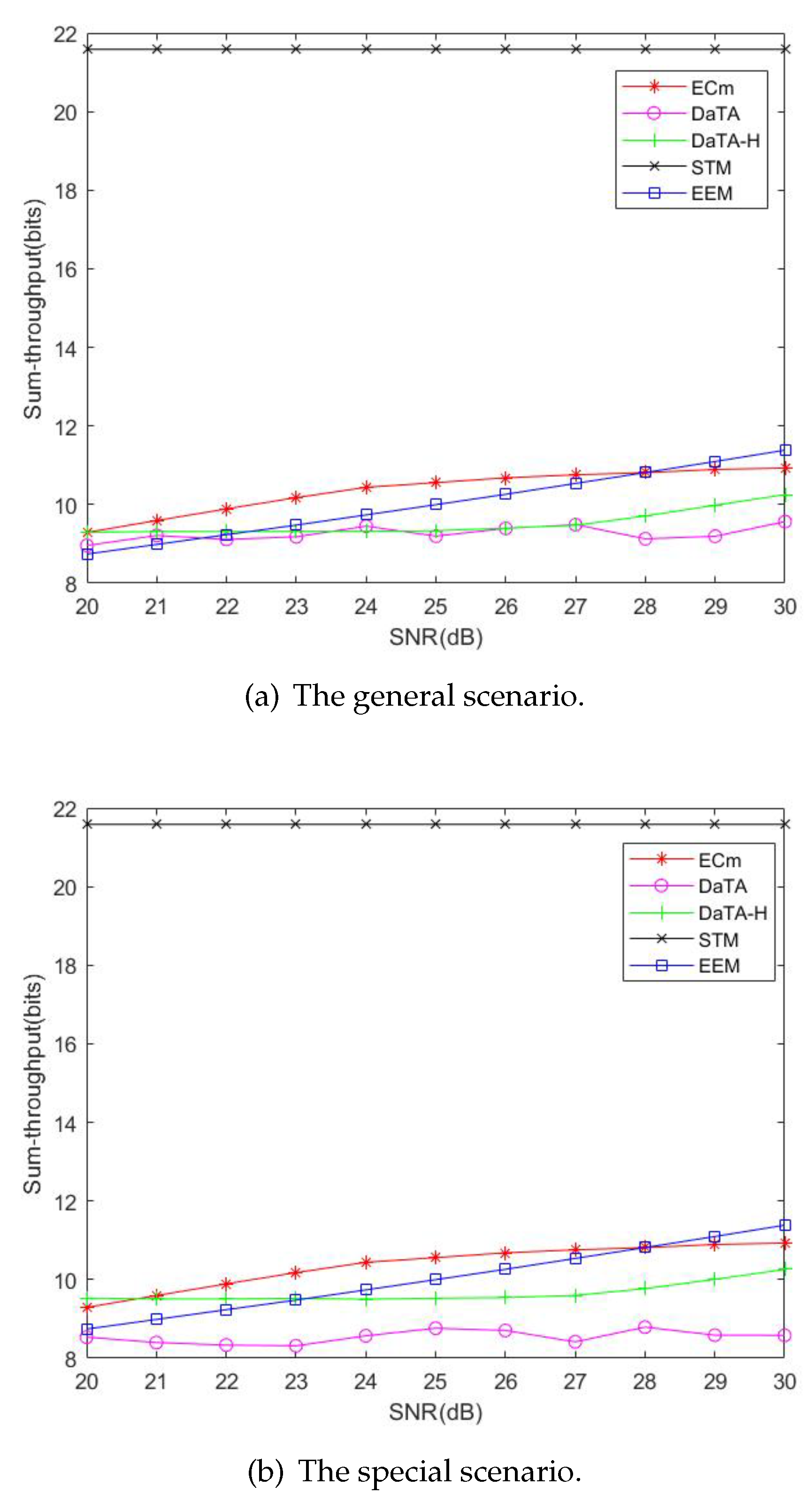
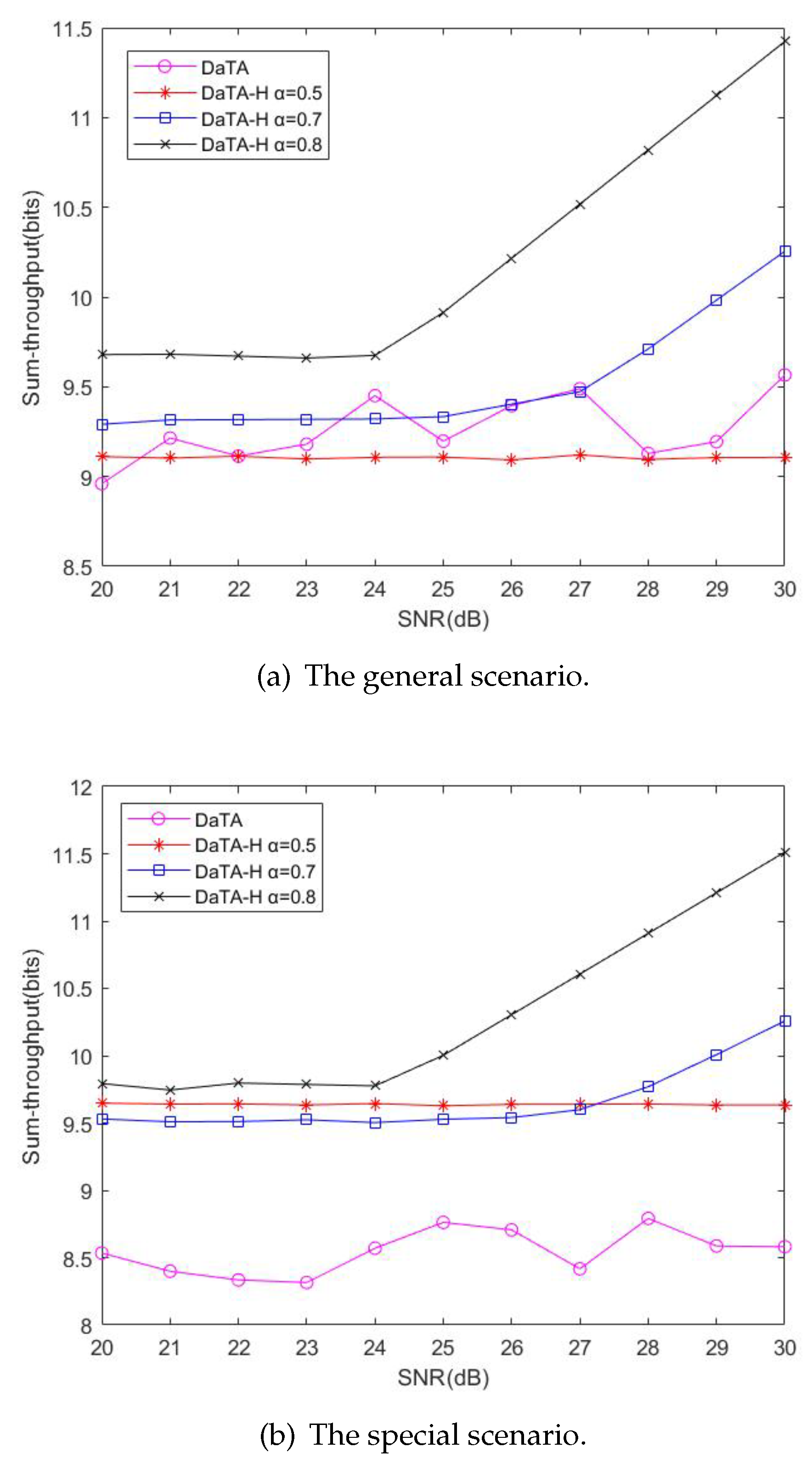
5.2. Comparisons of the Network Sum-Throughput
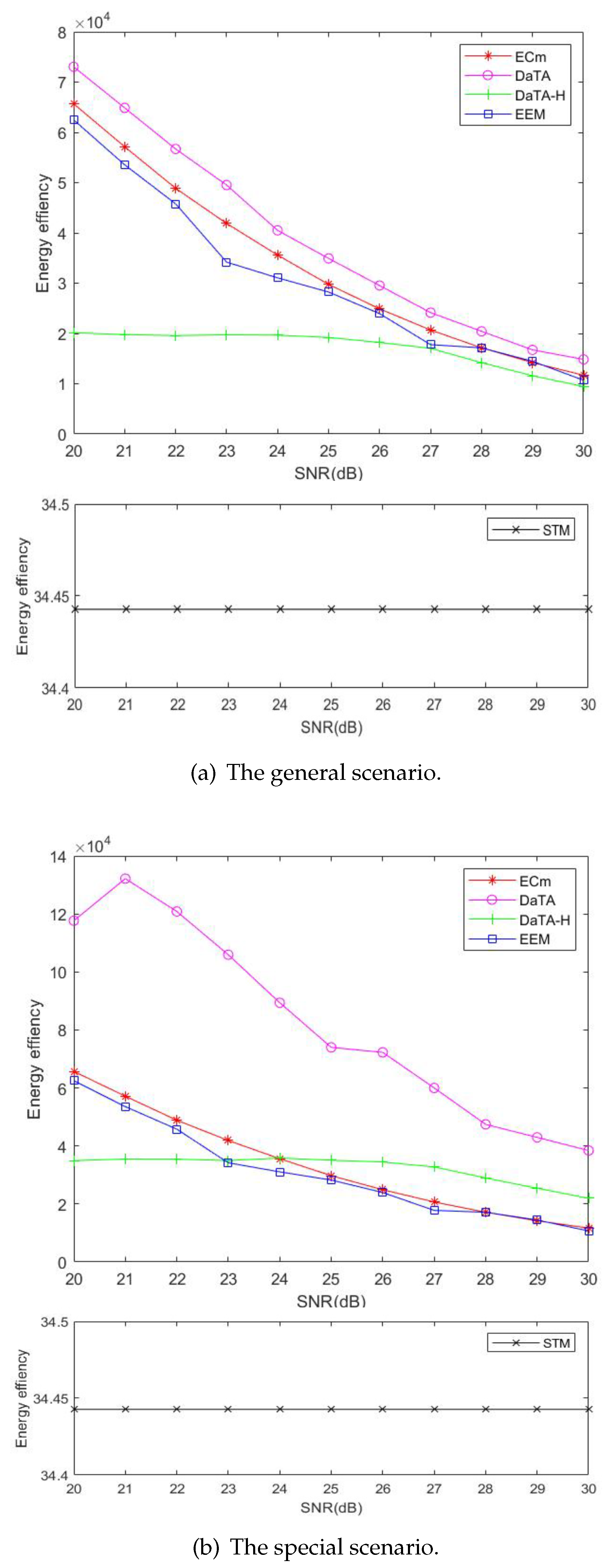
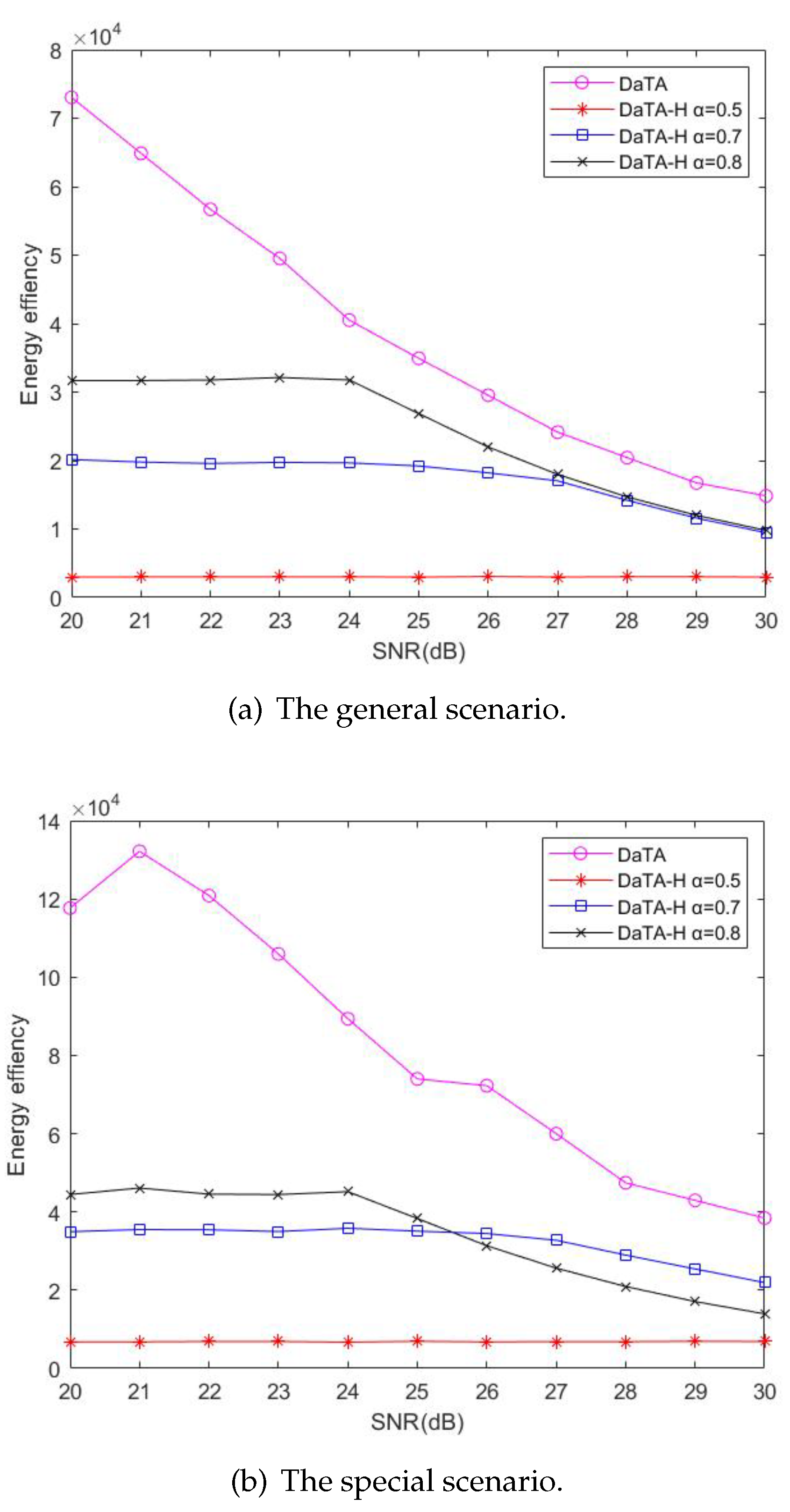
5.3. Comparisons of the Network Energy Efficiency
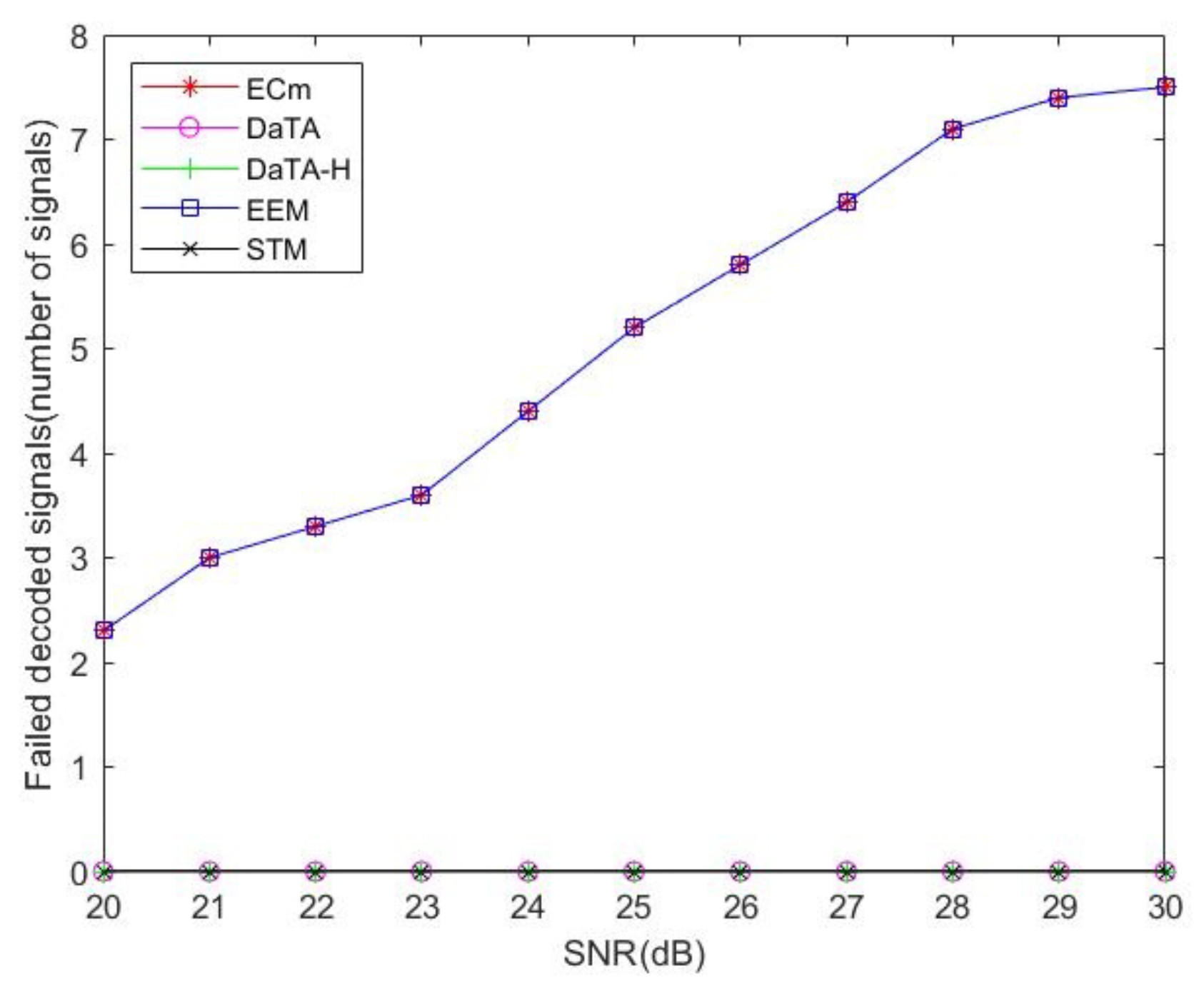
5.4. Comparisons of the Failed Decoded Signals
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsaba, Y.; Rahim, S.K.A.; Leow, C.Y. Beamforming in Wireless Energy Harvesting Communications Systems: A Survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials 2018, 20, 1329–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Majhi, S.; Das, S.K. Wireless Powered Microwave and mmWave based Communication Networks–A Survey. Proceedings of the International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), 2020, pp. 98–102.
- Zhang, Z.; Pang, H.; Georgiadis, A.; Cecati, C. Wireless Power Transfer–An Overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2019, 66, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, R.; Nijsure, Y.; Kaddoum, G.; Hassan, N.U.; Yuen, C. Energy Efficiency Tradeoff Mechanism Towards Wireless Green Communication: A Survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials 2016, 18, 686–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarhava, H.; Niya, J.M. Energy Efficient Resource Allocation in Wireless Energy Harvesting Sensor Networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 2020, 9, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Ron, D.; Sengly, M.; Lee, J. Energy-Neutral Wireless Sensor Network Based on SWIPT in Wireless Powered Communication Networks. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 2020.
- Ge, H.; Yu, Z.; Chi, K.; Mao, K.; Shao, Q.; Chen, L. Energy Provision Minimization in Large-scale Wireless Powered Communication Networks with Throughput Demand. IET Communications 2020, 14, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, R. Throughput Maximization in Wireless Powered Communication Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2014, 13, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.C.; Fapojuwo, A.O. Sum-Throughput and Fairness Optimization of a Wireless Energy Harvesting Sensor Network. Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC), 2019.
- Lim, H.; Hwang, T. Energy-Efficient MISO Wireless Powered Communications. Proceedings of the IEEE Annual Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), 2019.
- Liu, J.; Xiong, K.; Fan, P.; Zhong, Z. Resource Allocation in Wireless Powered Sensor Networks With Circuit Energy Consumption Constraints. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 22775–22782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wan, X.; Wan, H. Energy Efficient Resource Allocation for Wireless Power Transfer Enabled Massive MIMO Systems with Proportional Fairness. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT); 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, P.; Jamalipour, A. Throughput Maximization in Backscatter Assisted Wireless Powered Communication Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC); 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, P.; Jamalipour, A. Optimal Resource Allocation in Backscatter Assisted WPCN with Practical Energy Harvesting Model. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 12406–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, M.S.; Che, Y.L.; Luo, S.; Wu, K. Joint Downlink-Uplink Throughput Optimization in Wireless Powered Communication Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC); 2019; pp. 852–857. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Shen, Y.; Gao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhu, X. Energy Consumption Minimization with Throughput Heterogeneity in Wireless-Powered Body Area Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 3369–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chi, K.; Hu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. Energy Provision Minimization in Wireless Powered Communication Networks with Node Throughput Requirement. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 7057–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and Wireless Signal Strength, 2020.
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization; Springer, 2006; chapter 18.
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, U.K., 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, T.D.P.; Jayakody, D.N.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Chatzinotas, S.; Li, J. Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer (SWIPT): Recent Advances and Future Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Communication Surveys and Tutorials 2017, 20, 264–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Noor, R.M.; Yau, K.A.; Ahmedy, I.; Anjum, S.S. A Survey on Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer with Cooperative Relay and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 19166–19198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, K.P.; Chen, Y.D.; Chang, C.C. A Physical/Virtual Carrier-Sense-based Power Control MAC Protocol for Collision Avoidance in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 2011, 22, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Ghosh, S.C.; Sinha, B.P. Wireless Networks and Mobile Computing; Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fontan, F.P.; Espineira, P.M. Modeling the Wireless Propagation Channel: A Simulation Approach with MATLAB; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Taub, H.; Schilling, D.L. Principles of Communication Systems; McGraw-Hill, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Optimization Toolbox: Solve Linear, Quadratic, Conic, Integer, and Nonlinear Optimization Problems, 2022. MATLAB R2022a.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| , energy harvest efficiency | 1 [14] |
| , the portion of energy for IT | 1 |
| , the transmission power of the HAP | 30 dBm [20] |
| N, noise power | -70 dBm [14] |
| , path loss exponent | 3 [14] |
| , throughput demand | 0.8 bps |
| (in DaTA-H) | 0.7 |
| (in DaTA-H) | 0.1 |
| T, duration of a period | 1 (s) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





