Submitted:
03 July 2024
Posted:
04 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
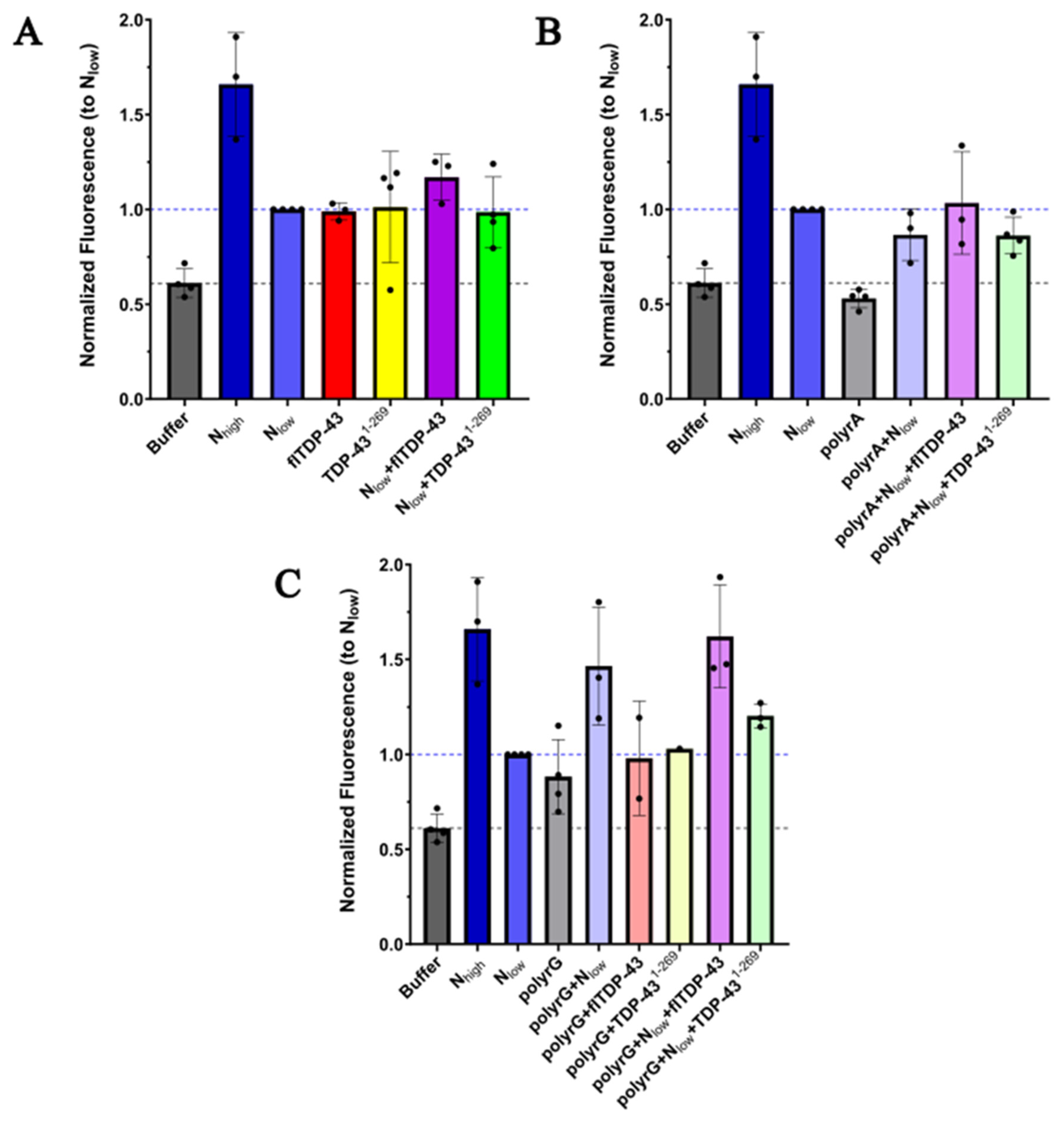
2.1 Protein Aggregation Assay
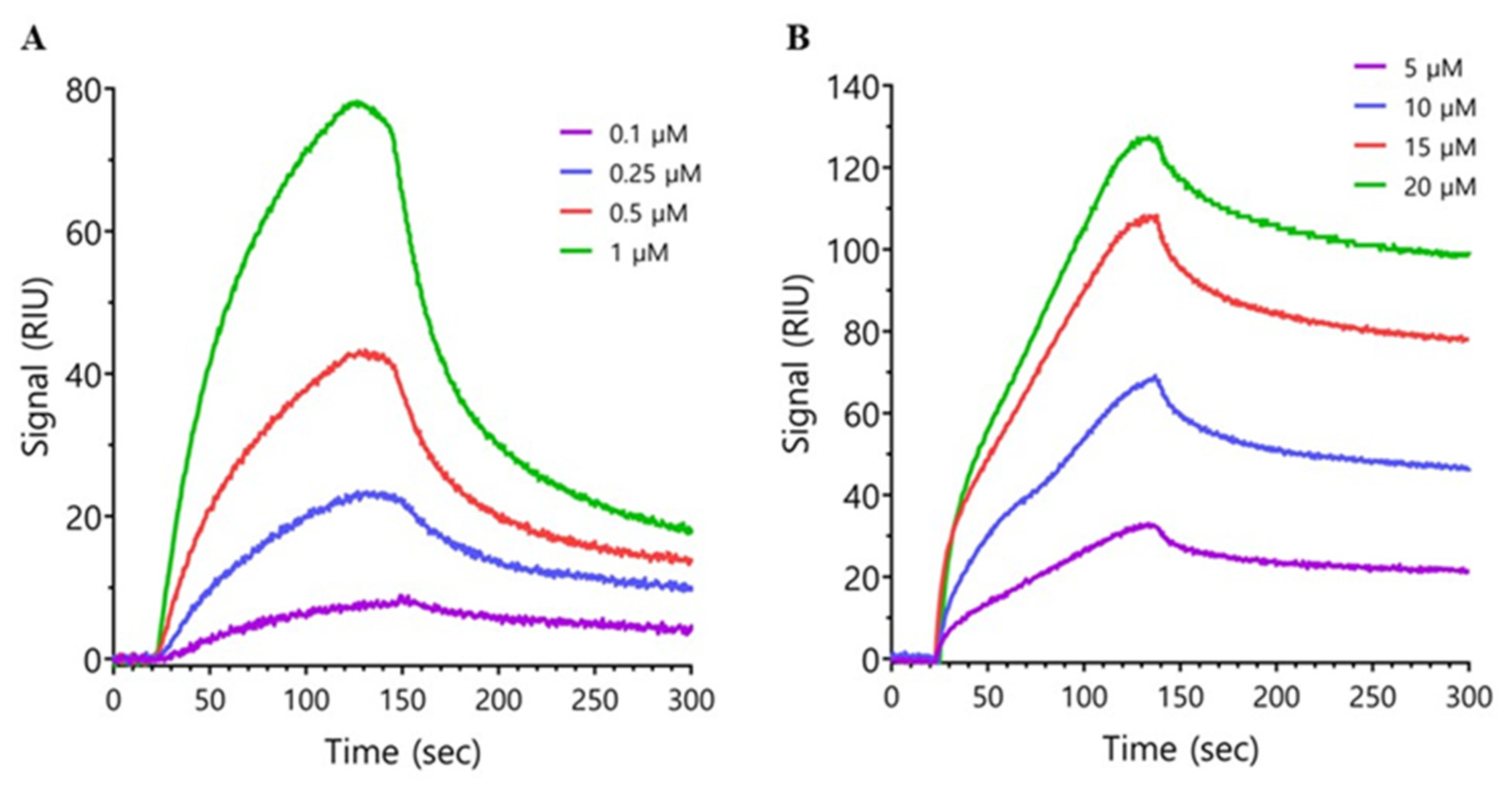
2.2. Surface Plasmon Resonance
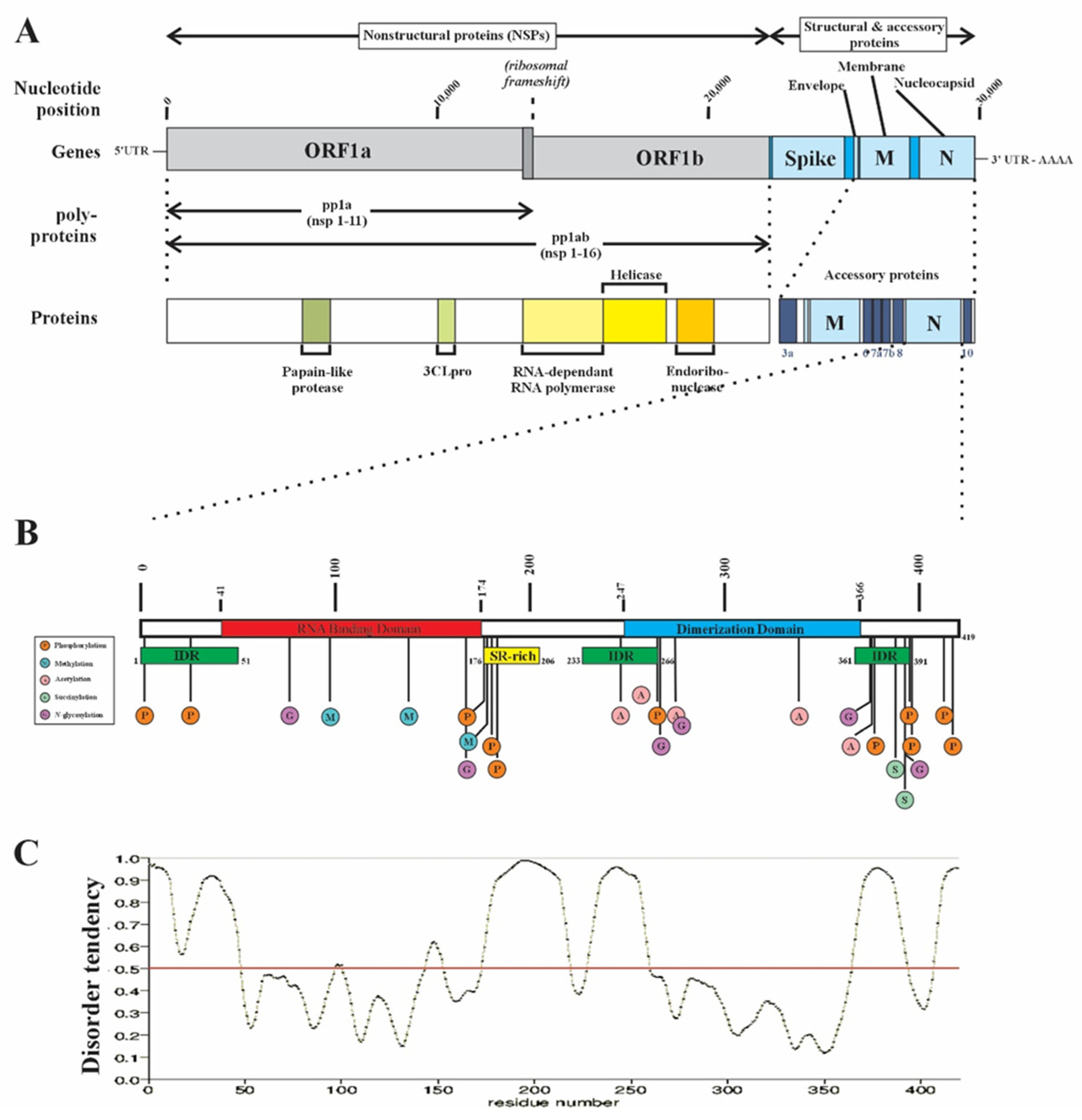
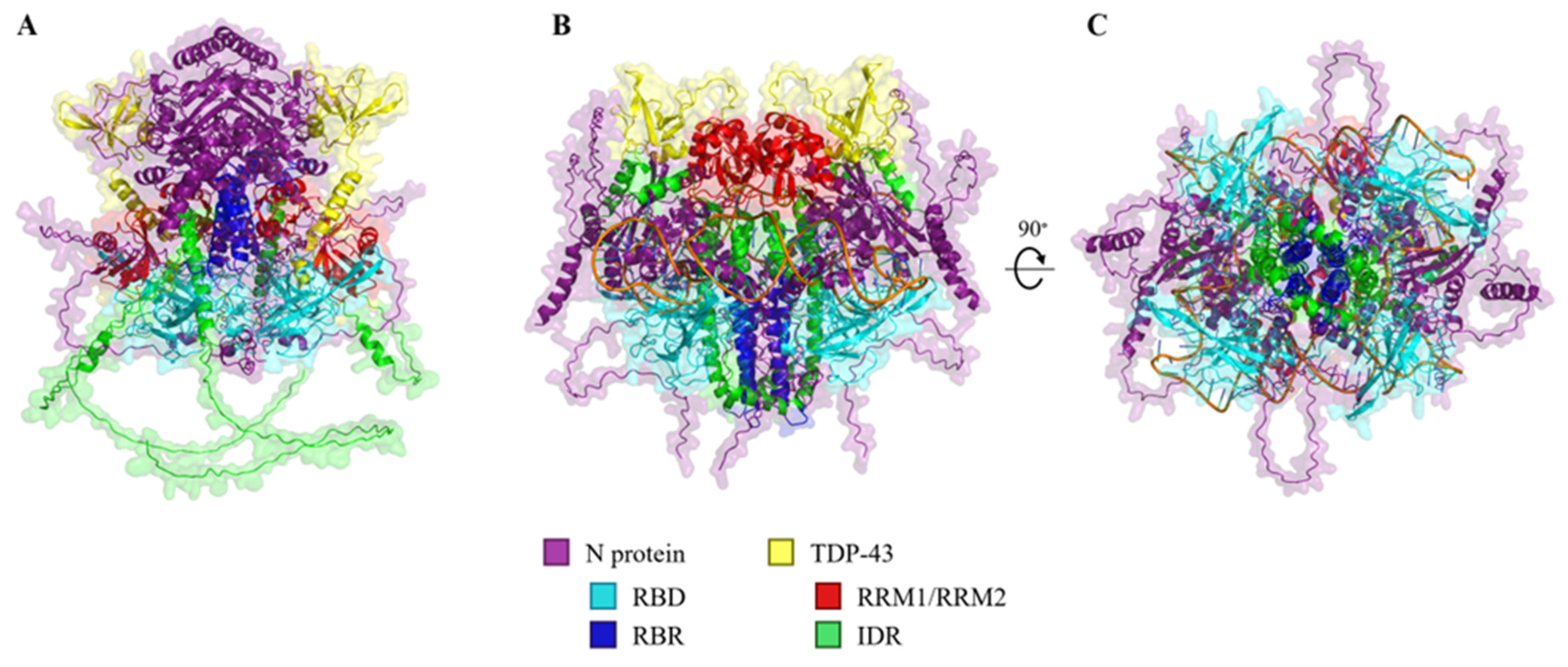
2.3. In Silico Modelling of N Protein, TDP-43, and RNA Heteropolymers
3. Discussion
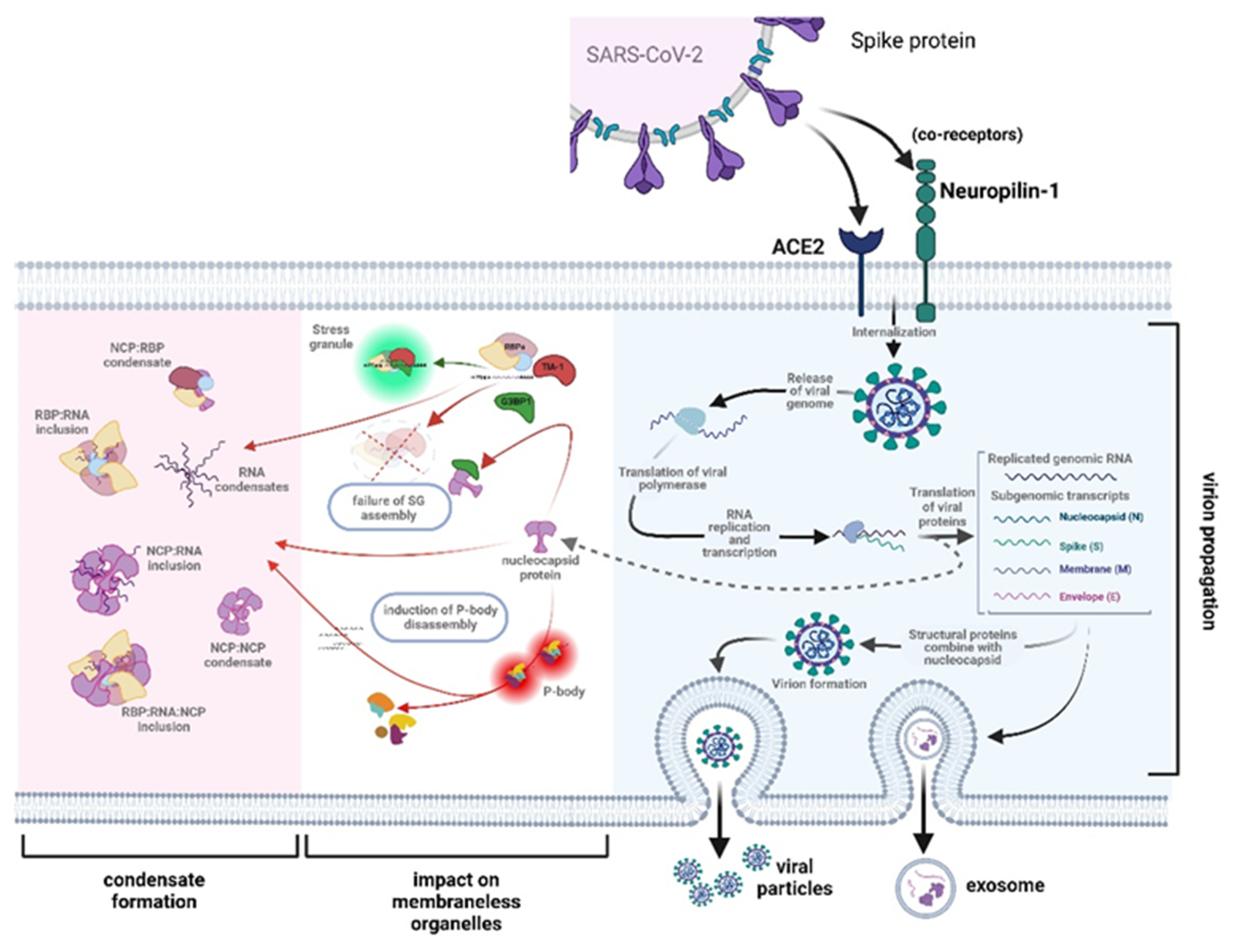
3.1. The Role of RNA Binding Proteins in Biomolecular Condensate Formation
3.2. RBP Post-Translational Modifications as Modulators of Biomolecular Condensates
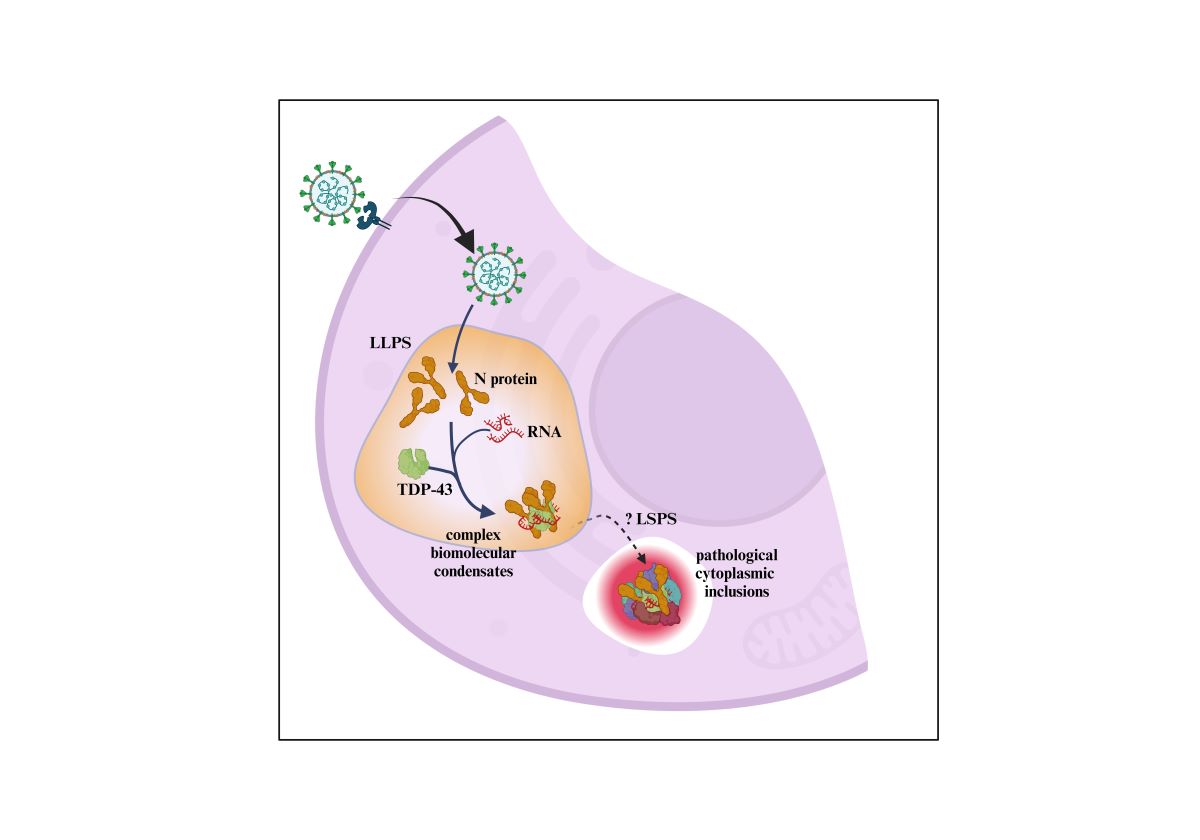
3.3. Evidence That the N-Protein Can Be Involved in Pathological Biomolecular Condensate Formation Relevant to Human Neurodegenerative Disease States
4. Conclusion
5. Materials & Methods
5.1. Protein Aggregation Assay
5.2. Surface Plasmon Resonance
5.3. In Silico Modelling of the N Protein, TDP-43 and RNA Interactions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strong, M.J. SARS-CoV-2, aging, and Post-COVID-19 neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 2023, 165, 115-130. [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, A.; Bhandarkar, B.S.; Lodha, L.; Marate, S. SARS-CoV-2 and the nervous system: current perspectives. Arch Virol 2023, 168, 171. [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Long-term neurologic outcomes of COVID-19. Nat Med 2022, 28, 2406-2415. [CrossRef]
- Hammarstrom, P.; Nystrom, S. Viruses and amyloids - a vicious liaison. Prion 2023, 17, 82-104. [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, P.S.; Quan, M.D.; Ferreon, J.C.; Ferreon, A.C.M. Aggregation of Disordered Proteins Associated with Neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Hurtle, B.T.; Xie, L.; Donnelly, C.J. Disrupting pathologic phase transitions in neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 2023, 133. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Gu, J.; Xia, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Lei, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 impairs the disassembly of stress granules and promotes ALS-associated amyloid aggregation. Protein Cell 2022, 13, 602-614. [CrossRef]
- Campos-Melo, D.; Hawley, Z.C.E.; Droppelmann, C.A.; Strong, M.J. The Integral Role of RNA in Stress Granule Formation and Function. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 621779. [CrossRef]
- Perdikari, T.M.; Murthy, A.C.; Ryan, V.H.; Watters, S.; Naik, M.T.; Fawzi, N.L. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein phase-separates with RNA and with human hnRNPs. EMBO J 2020, 39, e106478. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Hou, M.H.; Chang, C.F.; Hsiao, C.D.; Huang, T.H. The SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein--forms and functions. Antiviral Res 2014, 103, 39-50. [CrossRef]
- Tilocca, B.; Soggiu, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Musella, V.; Britti, D.; Bonizzi, L.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Comparative computational analysis of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein epitopes in taxonomically related coronaviruses. Microbes Infect 2020, 22, 188-194. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation. Viruses 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Rak, A.; Isakova-Sivak, I.; Rudenko, L. Overview of Nucleocapsid-Targeting Vaccines against COVID-19. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.A.; Jones, S.J.; Astell, C.R.; Holt, R.A.; Brooks-Wilson, A.; Butterfield, Y.S.; Khattra, J.; Asano, J.K.; Barber, S.A.; Chan, S.Y.; et al. The Genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science 2003, 300, 1399-1404. [CrossRef]
- Rota, P.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Monroe, S.S.; Nix, W.A.; Campagnoli, R.; Icenogle, J.P.; Penaranda, S.; Bankamp, B.; Maher, K.; Chen, M.H.; et al. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science 2003, 300, 1394-1399. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H. The nucleocapsid protein of SARS coronavirus has a high binding affinity to the human cellular heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1. FEBS Lett 2005, 579, 2623-2628. [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Yang, M.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein RNA binding domain reveals potential unique drug targeting sites. Acta Pharm Sin B 2020, 10, 1228-1238. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Filho, H.V.; Jara, G.E.; Batista, F.A.H.; Schleder, G.R.; Costa Tonoli, C.C.; Soprano, A.S.; Guimaraes, S.L.; Borges, A.C.; Cassago, A.; Bajgelman, M.C.; et al. Structural dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein induced by RNA binding. PLoS Comput Biol 2022, 18, e1010121. [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.; van Zyl, M.; Fielding, B.C. The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein. Viruses 2014, 6, 2991-3018. [CrossRef]
- Surjit, M.; Lal, S.K. The SARS-CoV nucleocapsid protein: a protein with multifarious activities. Infect Genet Evol 2008, 8, 397-405. [CrossRef]
- Savastano, A.; Ibanez de Opakua, A.; Rankovic, M.; Zweckstetter, M. Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 6041. [CrossRef]
- Estelle, A.B.; Forsythe, H.M.; Yu, Z.; Hughes, K.; Lasher, B.; Allen, P.; Reardon, P.N.; Hendrix, D.A.; Barbar, E.J. RNA structure and multiple weak interactions balance the interplay between RNA binding and phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid. PNAS Nexus 2023, 2, pgad333. [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Zhou, Q.A. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: Perspective on COVID-19 Infection and Drug Discovery. ACS Infect Dis 2022, 8, 422-432. [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, S. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein: its role in the viral life cycle, structure and functions, and use as a potential target in the development of vaccines and diagnostics. Virol J 2023, 20, 6. [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, J.; Alston, J.J.; Incicco, J.J.; Singh, S.; Stuchell-Brereton, M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; Griffith, D.; Wagoner, J.A.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1936. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ling, X.; Zhang, C.; Zou, J.; Luo, B.; Luo, Y.; Jia, X.; Jia, G.; Zhang, M.; Hu, J.; et al. Modular characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein domain functions in nucleocapsid-like assembly. Mol Biomed 2023, 4, 16. [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C.; Richard, S. Arginine methylation of SARS-Cov-2 nucleocapsid protein regulates RNA binding, its ability to suppress stress granule formation, and viral replication. J Biol Chem 2021, 297, 100821. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, X.; Ji, F.; Zhou, M.; Su, X.; Ren, K.; Li, L. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Reveals Camouflaging Glycans and Unique Post-Translational Modifications. Infect Microbes Dis 2021, 3, 149-157. [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ye, Q.; Singh, D.; Cao, Y.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Villa, E.; Cleveland, D.W.; Corbett, K.D. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein forms mutually exclusive condensates with RNA and the membrane-associated M protein. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 502. [CrossRef]
- Iserman, C.; Roden, C.A.; Boerneke, M.A.; Sealfon, R.S.G.; McLaughlin, G.A.; Jungreis, I.; Fritch, E.J.; Hou, Y.J.; Ekena, J.; Weidmann, C.A.; et al. Genomic RNA Elements Drive Phase Separation of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid. Mol Cell 2020, 80, 1078-1091 e1076. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Johnson, B.A.; Meliopoulos, V.A.; Ju, X.; Zhang, P.; Hughes, M.P.; Wu, J.; Koreski, K.P.; Clary, J.E.; Chang, T.C.; et al. Interaction between host G3BP and viral nucleocapsid protein regulates SARS-CoV-2 replication and pathogenicity. Cell Rep 2024, 43, 113965. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Fu, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.Y. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein impairs stress granule formation to promote viral replication. Cell Discov 2021, 7, 38. [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, T.; Ju, X.; Ma, P.; Jin, B.; Zhou, Y.; He, S.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein phase separates with G3BPs to disassemble stress granules and facilitate viral production. Sci Bull (Beijing) 2021, 66, 1194-1204. [CrossRef]
- Dolliver, S.M.; Kleer, M.; Bui-Marinos, M.P.; Ying, S.; Corcoran, J.A.; Khaperskyy, D.A. Nsp1 proteins of human coronaviruses HCoV-OC43 and SARS-CoV2 inhibit stress granule formation. PLoS Pathog 2022, 18, e1011041. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Maharjan, S.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Baek, K.; Kim, S.; Suh, J.G.; Lee, Y.; et al. Differential effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on stress granule formation in Vero and Calu-3 cells. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 997539. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, E.; Wang, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Antagonizes Stress Granule Assembly and IFN Production by Interacting with G3BPs to Facilitate Viral Replication. J Virol 2022, 96, e0041222. [CrossRef]
- Biswal, M.; Lu, J.; Song, J. SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Targets a Conserved Surface Groove of the NTF2-like Domain of G3BP1. J Mol Biol 2022, 434, 167516. [CrossRef]
- Kleer, M.; Mulloy, R.P.; Robinson, C.A.; Evseev, D.; Bui-Marinos, M.P.; Castle, E.L.; Banerjee, A.; Mubareka, S.; Mossman, K.; Corcoran, J.A. Human coronaviruses disassemble processing bodies. PLoS Pathog 2022, 18, e1010724. [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.J. The evidence for altered RNA metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J. Neurol. Sci 2010, 288, 1-12.
- Aulas, A.; Vande, V.C. Alterations in stress granule dynamics driven by TDP-43 and FUS: a link to pathological inclusions in ALS? Front Cell Neurosci 2015, 9, 423. [CrossRef]
- Keller, B.A.; Volkening, K.; Droppelmann, C.A.; Ang, L.C.; Rademakers, R.; Strong, M.J. Co-aggregation of RNA binding proteins in ALS spinal motor neurons: evidence of a common pathogenic mechanism. Acta Neuropathol 2012, 124, 733-747. [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493-500. [CrossRef]
- Drino, A.; Schaefer, M.R. RNAs, Phase Separation, and Membrane-Less Organelles: Are Post-Transcriptional Modifications Modulating Organelle Dynamics? Bioessays 2018, 40, e1800085. [CrossRef]
- Wiedner, H.J.; Giudice, J. It’s not just a phase: function and characteristics of RNA-binding proteins in phase separation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2021, 28, 465-473. [CrossRef]
- Gotor, N.L.; Armaos, A.; Calloni, G.; Torrent Burgas, M.; Vabulas, R.M.; De Groot, N.S.; Tartaglia, G.G. RNA-binding and prion domains: the Yin and Yang of phase separation. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 9491-9504. [CrossRef]
- Hofweber, M.; Dormann, D. Friend or foe-Post-translational modifications as regulators of phase separation and RNP granule dynamics. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 7137-7150. [CrossRef]
- Fakim, H.; Vande Velde, C. The implications of physiological biomolecular condensates in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2024, 156, 176-189. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Choi, J.M.; Holehouse, A.S.; Lee, H.O.; Zhang, X.; Jahnel, M.; Maharana, S.; Lemaitre, R.; Pozniakovsky, A.; Drechsel, D.; et al. A Molecular Grammar Governing the Driving Forces for Phase Separation of Prion-like RNA Binding Proteins. Cell 2018, 174, 688-699 e616. [CrossRef]
- Giambruno, R.; Grzybowska, E.A.; Fawzi, N.L.; Dormann, D. Editorial: The Role of Protein Post-Translational Modifications in Protein-RNA Interactions and RNP Assemblies. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 831810. [CrossRef]
- England, W.E.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Baldi, P.; Flynn, R.A.; Spitale, R.C. An atlas of posttranslational modifications on RNA binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, 4329-4339. [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Cruz, A.; Banos-Jaime, B.; Diaz-Quintana, A.; De la Rosa, M.A.; Diaz-Moreno, I. Post-translational Control of RNA-Binding Proteins and Disease-Related Dysregulation. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 658852. [CrossRef]
- Corley, M.; Burns, M.C.; Yeo, G.W. How RNA-Binding Proteins Interact with RNA: Molecules and Mechanisms. Mol Cell 2020, 78, 9-29. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Katuwawala, A.; Oldfield, C.J.; Hu, G.; Wu, Z.; Uversky, V.N.; Kurgan, L. Intrinsic Disorder in Human RNA-Binding Proteins. J Mol Biol 2021, 433, 167229. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.F.; Shorter, J. RNA-binding proteins with prion-like domains in health and disease. Biochem J 2017, 474, 1417-1438. [CrossRef]
- Banani, S.F.; Lee, H.O.; Hyman, A.A.; Rosen, M.K. Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2017, 18, 285-298. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; McGinnis, J.P.; Si, K. Translational Control by Prion-like Proteins. Trends Cell Biol 2018, 28, 494-505. [CrossRef]
- Hentze, M.W.; Castello, A.; Schwarzl, T.; Preiss, T. A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19, 327-341. [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, G.M.; Zahurancik, W.J.; Zeng, X.; Pullara, P.; Lai, L.B.; Sidharthan, V.; Pappu, R.V.; Gopalan, V.; Banerjee, P.R. RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures. Nat Chem 2023, 15, 1693-1704. [CrossRef]
- Levine, K.S.; Leonard, H.L.; Blauwendraat, C.; Iwaki, H.; Johnson, N.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Faghri, F.; Singleton, A.B.; Nalls, M.A. Virus exposure and neurodegenerative disease risk across national biobanks. Neuron 2023, 111, 1086-1093 e1082. [CrossRef]
- Piekut, T.; Hurla, M.; Banaszek, N.; Szejn, P.; Dorszewska, J.; Kozubski, W.; Prendecki, M. Infectious agents and Alzheimer’s disease. J Integr Neurosci 2022, 21, 73. [CrossRef]
- Badrfam, R.; Zandifar, A. From encephalitis lethargica to COVID-19: Is there another epidemic ahead? Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2020, 196, 106065. [CrossRef]
- Matschke, J.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Hagel, C.; Sperhake, J.P.; Schroder, A.S.; Edler, C.; Mushumba, H.; Fitzek, A.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; et al. Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: a post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol 2020, 19, 919-929. [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.R.; Ramelli, S.C.; Grazioli, A.; Chung, J.Y.; Singh, M.; Yinda, C.K.; Winkler, C.W.; Sun, J.; Dickey, J.M.; Ylaya, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy. Nature 2022, 612, 758-763. [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Zhang, C.; Israelow, B.; Lu-Culligan, A.; Prado, A.V.; Skriabine, S.; Lu, P.; Weizman, O.E.; Liu, F.; Dai, Y.; et al. Neuroinvasion of SARS-CoV-2 in human and mouse brain. J Exp Med 2021, 218. [CrossRef]
- Emmi, A.; Rizzo, S.; Barzon, L.; Sandre, M.; Carturan, E.; Sinigaglia, A.; Riccetti, S.; Della Barbera, M.; Boscolo-Berto, R.; Cocco, P.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins and genomic sequences in human brainstem nuclei. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2023, 9, 25. [CrossRef]
- Mukerji, S.S.; Solomon, I.H. What can we learn from brain autopsies in COVID-19? Neurosci Lett 2021, 742, 135528. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.T.; Miller, E.H.; Glendinning, M.D.; Al-Dalahmah, O.; Banu, M.A.; Boehme, A.K.; Boubour, A.L.; Bruce, S.S.; Chong, A.M.; Claassen, J.; et al. COVID-19 neuropathology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York Presbyterian Hospital. Brain 2021, 144, 2696-2708. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Perl, D.P.; Steiner, J.; Pasternack, N.; Li, W.; Maric, D.; Safavi, F.; Horkayne-Szakaly, I.; Jones, R.; Stram, M.N.; et al. Neurovascular injury with complement activation and inflammation in COVID-19. Brain 2022, 145, 2555-2568. [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, L.; Absil, L.; Remmelink, M.; De Mendonca, R.; D’Haene, N.; Gaspard, N.; Rusu, S.; Racu, M.L.; Collin, A.; Allard, J.; et al. SARS-Cov-2 infection and neuropathological findings: a report of 18 cases and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2023, 11, 78. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Abriola, L.; Niederer, R.O.; Pedersen, S.F.; Alfajaro, M.M.; Silva Monteiro, V.; Wilen, C.B.; Ho, Y.C.; Gilbert, W.V.; Surovtseva, Y.V.; et al. Restriction of SARS-CoV-2 replication by targeting programmed -1 ribosomal frameshifting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Schurink, B.; Roos, E.; Radonic, T.; Barbe, E.; Bouman, C.S.C.; de Boer, H.H.; de Bree, G.J.; Bulle, E.B.; Aronica, E.M.; Florquin, S.; et al. Viral presence and immunopathology in patients with lethal COVID-19: a prospective autopsy cohort study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e290-e299. [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.C.; Kern, F.; Losada, P.M.; Agam, M.R.; Maat, C.A.; Schmartz, G.P.; Fehlmann, T.; Stein, J.A.; Schaum, N.; Lee, D.P.; et al. Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19. Nature 2021, 595, 565-571. [CrossRef]
- Jacomy, H.; Fragoso, G.; Almazan, G.; Mushynski, W.E.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronavirus OC43 infection induces chronic encephalitis leading to disabilities in BALB/C mice. Virology 2006, 349, 335-346. [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, G.; Colombrita, C.; Limanaqi, F.; Invernizzi, S.; Garziano, M.; Vanetti, C.; Moscheni, C.; Santangelo, S.; Zecchini, S.; Trabattoni, D.; et al. Human motor neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front Cell Neurosci 2023, 17, 1285836. [CrossRef]
- Philippens, I.; Boszormenyi, K.P.; Wubben, J.A.M.; Fagrouch, Z.C.; van Driel, N.; Mayenburg, A.Q.; Lozovagia, D.; Roos, E.; Schurink, B.; Bugiani, M.; et al. Brain Inflammation and Intracellular alpha-Synuclein Aggregates in Macaques after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ma, K. SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Interact with Alpha Synuclein and Induce Lewy Body-like Pathology In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Semerdzhiev, S.A.; Fakhree, M.A.A.; Segers-Nolten, I.; Blum, C.; Claessens, M. Interactions between SARS-CoV-2 N-Protein and alpha-Synuclein Accelerate Amyloid Formation. ACS Chem Neurosci 2022, 13, 143-150. [CrossRef]
- Zilio, G.; Masato, A.; Sandre, M.; Caregnato, A.; Moret, F.; Maciola, A.K.; Antonini, A.; Brucale, M.; Cendron, L.; Plotegher, N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Mimicking Pseudoviral Particles Accelerate alpha-Synuclein Aggregation In Vitro. ACS Chem Neurosci 2024, 15, 215-221. [CrossRef]
- Proal, A.D.; VanElzakker, M.B.; Aleman, S.; Bach, K.; Boribong, B.P.; Buggert, M.; Cherry, S.; Chertow, D.S.; Davies, H.E.; Dupont, C.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). Nat Immunol 2023, 24, 1616-1627. [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.J.; Deeks, S.G.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Henrich, T.J.; Lu, S.; Goldberg, S.A.; Hoh, R.; Chen, J.Y.; Martinez, E.O.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and Mitochondrial Proteins in Neural-Derived Exosomes of COVID-19. Ann Neurol 2022, 91, 772-781. [CrossRef]
- Crunfli, F.; Carregari, V.C.; Veras, F.P.; Silva, L.S.; Nogueira, M.H.; Antunes, A.; Vendramini, P.H.; Valenca, A.G.F.; Brandao-Teles, C.; Zuccoli, G.D.S.; et al. Morphological, cellular, and molecular basis of brain infection in COVID-19 patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, e2200960119. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459-468. [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.; Ghosh, A.; Tran, C.; Tebung, W.A.; Sidibe, H.; Garcia-Mansfield, K.; David-Dirgo, V.; Sharma, R.; Pirrotte, P.; Bowser, R.; et al. Defining the Caprin-1 Interactome in Unstressed and Stressed Conditions. J Proteome Res 2021, 20, 3165-3178. [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, N.; Kovalik, T.; Lorenzini, I.; Spangler, S.; Lacoste, A.; Sponaugle, K.; Ferrante, P.; Argentinis, E.; Sattler, R.; Bowser, R. Artificial intelligence in neurodegenerative disease research: use of IBM Watson to identify additional RNA-binding proteins altered in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 2018, 135, 227-247. [CrossRef]
- Pulst, S.M.; Scoles, D.R.; Paul, S. Effects of STAU1/staufen1 on autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2607-2608. [CrossRef]
- Somasekharan, S.P.; Gleave, M. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein interacts with immunoregulators and stress granules and phase separates to form liquid droplets. FEBS Lett 2021, 595, 2872-2896. [CrossRef]
- Droppelmann, C.A.; Campos-Melo, D.; Noches, V.; McLellan, C.; Szabla, R.; Lyons, T.A.; Amzil, H.; Withers, B.; Kaplanis, B.; Sonkar, K.S.; et al. Mitigation of TDP-43 toxic phenotype by an RGNEF fragment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis models. Brain 2024, 147, 2053-2068. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




