Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
28 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
| FL-circAS | Full-length circular RNA sequences, shows internal sequences and alternative splicing | [10] |
| circVis | Visualization of circRNA | [111] |
| circNET 2.0 | Regulatory network in cancer | [112] |
| circMine | Disease related circRNAs | [113] |
| riboCirc | Translatable circRNA | [47] |
| transCirc | Translatable circRNA | [41] |
| Circ2Disease | circRNAs in human disease | [114] |
| CircInteractome | Database of circRNA interaction with miRNAs and proteins | [38] |
| # | Name | aa_nb | validation | function | Summary function | circRNA length [n] | Alu elements | Number of exons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LINC-PINT | 87 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | Suppresses glioblastoma cell proliferation | LINC-PINT Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA, (also p53 Induced Transcript) forms a circular RNA from exon 2, There is no protein translation from the LINC-PINT transcript, however, there is translation from the circular RNA. The 87 amino acid long protein binds to PAF1 (polymerase associated factor (PAF1) complex. The protein could arrest the PAF1 complex on promoters of oncogenes, leading to a suppression of cell proliferations in glioblastoma. | 1084 | no | 1 | [61] |
| 2 | circSHPRH | 146 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | Inhibits tumor cell proliferation | SHPRH (Histone Linker PHD RING Helicase [SNF: sucrose non fermenting]), forms a 440 nt long circRNA through backsplicing from exon 29 to 26. The 440 nt long circRNA is translated into circSHPRH-146aa. The protein could act by sequestering the ubiquitin E3 ligase DTL that then no longer acts and destabilizes the linear SHPRH protein. The full length SHPRH causes PCNA degradation, and thus circSHPRH-146aa indirectly stops proliferation of glioblastoma cells. circSHPRH-146 is downregulated in glioblastoma. The protein starts and stops within the same 4 nucleotides: TGATG it starts at ATG, and due to frameshift uses TGA as stop. | 440 | L | 4 | [115,116] |
| 3 | circFBXW7 | 185 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | represses glioma tumorigenesis | FBXW7 (F-Box And WD Repeat Domain Containing 7, E3 ) is part of an ubiquitin ligase complex acting as a E3 ligase. The circFBXW7 protein corresponds to the N-terminus and lacks the WXD40 domain necessary for substrate recognition. circFBXW7 competes with the linear FBPXW7 for binding to the deubiquitinase USP28. Thus, an increase in amount of circFBXW7 frees linear FBPXW7 protein for substrate degradation, which was shown for c-Myc. circFBXW7 interacts with catenin, influences Wnt signal, leading to cancer cell resistance | 620 | no | 2 | [117,118] |
| 4 | circCDH1 | 254 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | Activates EGF receptor | circCDH1 (Cadherin 1) in generated through backsplicing from exon 10 to 7 in the E-cadherin gene. Due to a frameshift after one round of translation a unique C-terminus is created. The circRNA was detected in 84% of glioma, but not in controls. The circCDH1 activated STAT3, PI3K-AKT and MAPK-ERK signaling in glioblastoma. In contrast to linear E-cadherin that is localized in the plasma membrane, circCDH1 is secreted out of cells and binds and activates EGFR using its circRNA-specific region. The circular RNA encoded protein contain cadherin domains but lacks a transmembrane domain and the signal peptide. The activation of EGFR promotes tumor formation and prevents the therapeutic effect of an anti EGFR-antibody (nimotuzumab). | 733 | B | 4 | [64] |
| 5 | circINSIG1 | 131 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | Induces cholesterol biosynthesis and colorectal cancer progression. | INSIG1 (Insulin Induced Gene 1) is an endoplasmic reticulum membrane domain protein with six transmembrane regions. Backsplicing from exon 4 to 3 generates circINSIG1 that has a specific C-terminus. circINSIG1 recruits a ubiquitination adaptor complex made from the proteins CUL5 and ASB6. This complex promotes ubiquitination and degradation of the linear INSIG1 protein, which promotes cholesterol biosynthesis and colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis. | 292 | no | 2 | [65] |
| 6 | circNFIB | RC | Polysome | Inhibits breast tumor growth, decreases arachidonic acid | NFIB (Nuclear Factor I B) is a transcriptional activator. Backsplicing of exon 6 to 3 generates a 361 circular RNA that undergoes rolling circle translation. The circNFIB is downregulated in breast cancer. Its overexpression prevents cancer cell proliferation, whereas knock down has the opposite effect. | 361 | no | 4 | [119] |
| 7 | circZNF609 | 250 | Polysome, reporter gene | Controls myoblast proliferation | ZNF609 (zinc finger protein 609) forms a circRNA through backsplicing of exon 2. | 874 | B | 1 | [120] |
| 8 | circYAP | 220 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum, polysome | binds to LATS1 | circYAP is generated through backsplicing of exon 7 to 2 of YAP1.circYAP competes with linear YAP for binding to the kinase LATS1, causing loss of phosphorylation of linear YAP that translocated into the nucleus and turns on oncogenic transcription program. The translation occurs via METT3/14, YTHDF3 eIF4G2. | 842 | B | 5 | [29] |
| 9 | circFAM53B | 219 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | Inhibits tumor growth | circFAM53B (Family with Sequence Similarity 53 Member B) regulates the Wnt signaling pathway by regulating beta-catenin (CTNNB1) nuclear localization | 659 | no | 1 | [106] |
| 10 | circ Beta TRCP(HUGO name: BTRC) | 343 | Mass-spectrometry, antiserum | Protein mediates tratuzumab resistance by binding to NRF2 transcription factor | Beta-Transducin Repeat Containing E3 Ubiquitin (BTRC) generates circ Beta TRCP through backsplicing of exon 13 to exon 7. circ Beta TRCP contains WD40 repeats that bind to NRF2 and promotes trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. In contrast to the linear proteins, circ Beta TRCP lacks an F box needed to bind to the ubiquitination complex SKP1-Cul1-Rbx1. Thus, circ Beta TRCP prevents NRF2 from being ubiquitinated, leading to an increase in NRF2, which promotes HER2-positive breast cancer. | 913 | B | 7 | [30] |
| 11 | circMET | 404 | polysomes, antiserum, mass-spectrometry | Promotes glioblastoma | MET (MET Proto-Oncogene, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase) generates circMET through backsplicing its exon 2, which is the first coding exon in the pre-mRNAs. The circRNA is translated after undergoing m6A modification, mediated by YTHDF2. The circMET protein contains the signal peptide and the protein is secreted and binds to the extracellular domain of the linear MET protein, which promotes dimerization without the physiological HGF (hepatocyte growth factor) ligand. circMET promotes glioblastoma tumorgenicity through MET activation. | 1214 | no | 1 | [121] |
| 12 | circCAPG | 171 | Mass-spectrometry | Promotes breast cancer by binding of serine/threonine kinase 38 (STK38) to SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (SMURF1) | CAPG (Capping Actin Protein, Gelsolin Like) binds to the barbed ends of F-actin filaments regulating the filament’s length. Backsplicing of exon 8 to exon 6 generates circCAPG. The circCAPG levels are elevated in triple negative breast cancer and promote tumor growth. It sequesters serine threonine kinase 38, which ultimately prevents MEKK2 proteasomal degradation. The formation of the circRNA is repressed by the splicing factor SLU7, possibly acting on the flanking Alu elements. | 376 | B | 3 | [19] |
| 13 | circRSRC1 | 161 | polysomes, mass-spectrometry | Regulates assembly of mitochondrial ribosomes. Loss of the protein decreases male fertility. | RSRC1 (Arginine and Serine Rich Coiled-Coil 1), acts in alternative splicing. Backsplicing from exon 3 to 2 creates a circRSRC1, that is highly conserved between mouse and human. Knock out in mice reduced spermatogenesis. circ RSRC1 binds to C1qbp (Complement C1q Binding Protein), a multifunctional protein. Through interaction with C1qbp, circ RSRC1-161aa could influence mitochondrial ribosome assembly. | 322 | R | 2 | [122] |
| 14 | circTMEFF1 | RC3x | polysomes, reporter genes | Promotes muscle atrophy through binding to TDP-43 | TMEFF1 (Transmembrane Protein with EGF Like And Two Follistatin Like Domains 1) in involved in receptor signaling. It forms a circular RNA by backsplicing of exon 7 to 5 that is upregulated in muscular atrophy. circTMEFF1 promotes atrophy in cell and mouse models, which can be antagonized by siRNAs. | 339 | R | 3 | [123] |
| 16 | circPPP1R12A | 72 | Mass-spectrometry from reporter constructs | Activates YAP, promotes metastasis | PPP1R12A (Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 12A), also known as Myosin phosphatase target subunit 1, regulates myosin-actin interaction. Backsplicing of exon 25 to 24 generates circPPP1R12A. The encoded protein is in a different reading frame than the linear protein and has no orthologs in the protein database. The protein promotes metastasis by indirectly affecting the phosphorylation of YAP, which activates oncogenes. | 1138 | R | 2 | [62,124] |
| 17 | circGSPT1 | 238 | mass-spectrometry | Binds to vimentin tumor suppressor | GSPT1 (G1 To S Phase Transition 1) is acting in translational termination, also known as eukaryotic release factor 3A (eRF3A). Backsplicing from exon 11 to 4 generates circ GSPT1that promotes autophagy and apoptosis in cancer cell models by binding to Vimentin/beclin/14-3-3. CircGSPT1is downregulated in gastric cancer, and act like a tumor suppressor. | 826 | L | 6 | [125] |
| 18 | circMAPK14 | 175 | mass-spectroscopy | Binds to MKK6 | MAPK14 (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14) is a serine/threonine kinase activated by environmental stress or cytokines. It generates circMAPK14 through backsplicing of exon 10 to 4. circMAPK14. is downregulated in colorectal colon cancer reduces proliferation. Both linear and circular MAPK14 bind to MAP2K6 (aka MKK6, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 6) and circMAPK14 antagonizes the linear MAPK14 MAP2K6 interaction, leading to a change in a transcriptional program. | 506 | L | 6 | [126] |
| 19 | circPLCE1 | 411 | mass spectrometry from a reporter gene | Influenced NFKb through ubiquitination | PLCE1 (Phospholipase C Epsilon 1) hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate generating inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). Backsplicing of its exon 2 genererates circPLCE1 that is downregulated in colectoral carcinoma. CircPLCE1 promotes cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. By sequestering HSP90alpha in the HSP90alpha/RPS3 complex, leading to RPS3 ubiquitination and degradation. This pathway is disturbed in cancer cells due to the reduced circPLCE1 expression, which ultimately leads to NF kappa B activation in the nucleus and a tumor program. | 1570 | no | 1 | [127] |
| 20 | circCTNNB1 | 370 | mass spectrometry from a reporter gene | promotes migration and proliferation of cancer cells. | CTNNB1 (Catenin Beta 1) is part of adherents junctions that regulate cell-cell interactions and forms circCTNNB1 by backsplicing of exon 7 to 2. circCTNNB1 is upregulated in liver cancer and non-small lung cell carcinoma tissue and competes with the full length CTNNB1 for phosphorylation by GSK3. As the phosphorylation leads to degradation of the protein, circ CTNNB1 ‘protects’ full length CTNNB1 from degradation, allowing the full-length protein to activate the Wnt/beta catenin pathway. | 1068 | no | 5 | [128], [129] |
| 21 | circARHGAP35 | 1289 | Mass-spectrometry of reporter genes, polysomes. | Encoded protein promotes cancer cell progression | ARHGAP35 (Rho GTPase Activating Protein 35) is a cytosolic GTPase activating protein. It creates circARHGAP35 by backsplicing exon 2 to exon 3, The circRNA is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes proliferation and metastasis. In contrast to the cytosolic linear protein, the circular protein is nuclear and still contains FF domains, necessary for binding to TFII-I, which likely starts a cancerogenic expression program. | 4014 | L | 2 | [31] |
| 22 | circEGFR | RC | mass-spectrometry using reporter cell | Prevents receptor endocytosis | EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) is a transmembrane protein acting as protein kinase upon acidification. Backsplicing of exons15 to 14 creates circEGFR encode an infinite open reading frame (iORF). The circprotein remains associated with the cell membrane and prevents endocytosis and inactivation of the receptor. The circRNA is upregulated in glioblastoma and expression levels correlate with survival. | 249 | B | 2 | [60] |
| 23 | CircAPP | 175 | mass-spectrometry from reporter genes and brain tissue | circAPP was identified in sporadic AD | APP (Amyloid Beta Precursor Protein) is a cell surface receptor that is cleaved by secretases into a number of peptides, some of them form protein aggregates involved in Alzheimer’s disease. The gene creates a circular RNA by backsplicing exon 17 to 14. | 524 | B | 4 | [130] |
| 24 | circFNDC3B | 218 | mass spectrometry | Inhibits proliferation of cancer cells | FNDC3B (Fibronectin Type III Domain Containing 3B) is a single pass membrane protein present in the endoplasmic reticulum and the plasma membrane. It generates circFNDC3B through backsplicing from exon 6 to 5. circFNDC3B expression is downregulated in colorectal cancer cells. circ FNDC3B inhibits the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells, possibly by inhibiting the expression of SNAIL, a transcriptional regulator that inhibits FBP1 (Fructose-Bisphosphatase 1 ) expression. | 526 | L | 2 | [131] |
| 25 | circRTN4(mouse) | RC | mass-spectrometry using reporter constructs | To be determined | Mouse Reticulon 4 (RTN4) generates a circRTN4 by backsplicing exon 3 to 2. | 2457 | B | 2 | [132] |
| 26 | circNlgn(mouse) | 173 | Antisera, mass-spectrometry | Promoter activation | Neuroligin 1 is a neuronal cell surface protein. It generates circNlgn. through circularization of its first coding exon that includes the signal peptide. The encoded protein has 9 circRNA specific amino acids at its C-terminus that interact with Lamin B1, leading to the nuclear localization of the circRNA protein where it activates promoters of ING4 and C8orf44-SGK3 genes that impacts on cardiac fibroblast proliferation. Transgenic mice with circNlgn-173 have a heart phenotype | 813 | B | 1 | [133] |
| 27 | circAXIN1 | 295 | Antisera and mass-spectrometry | Highly expressed and associated with lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer | AXIN1 (Axis Inhibition Protein 1) encodes a protein phosphatase. Circularization of exon 2 generates circAXIN1 that contains the start codon of the linear protein but has a unique C-terminus consisting of two amino acids TD. Circ AXIN1 binds competitively with APC, i.e., removes linear AXIN1. This releases beta catenin from a larger cytosolic complex. Beta catenin translocate into the nucleus and activates the wnt pathway, promoting gastric cell cancer growth. | 959 | R | 1 | [134] |
| 28 | circEIF6 | 224 | Polysome, mass-spectrometry, antisera. | proliferation, and invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells | eIF6 (Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 6) prevents the association of the 40S and 60S rRNA subunits during translation. It also known as Integrin beta 4 binding protein (ITGB4BP) and is part of hemidesmosomes that link the basal membrane to the cytoskeleton. Backsplicing from exon 7 to exon 3 generates circEIF6 promotes proliferation, and invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells. It binds to MYH9, which prevents MYH9 ubiquitination and degradation, leading to an activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway | 906 | R | 5 | [135] |
| 29 | circHER2 | 103 | polysome mass-spectrometry antisera | promotes heterodimerization between EGFR and HER3 receptor | HER2 (Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2) is part of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Through heterodimerization it enhances ligand binding and activation of other receptor kinases. Through backsplicing from exon 7 to 3, it creates circHER2, that is 100% identical to the linear one. CircHER2 expression correlates with poor survival in breast cancer. | 750 | no | 5 | [32] |
| 30 | circMAPT12 to7 | RC | Reporter genes | Tau aggregation | MAPT (microtuble associated protein tau) generates circTau RNA through backsplicing of exon 12 to 7. The encoded protein promotes aggregation of linear tau protein in reporter cells. | 752 | B | 5 | [54] |
| 31 | circMAPT12 to 10 | RC | Reporter genes and mass spectrometry | Tau aggregation | MAPT (microtuble associated protein tau) generates circTau RNA through backsplicing of exon 10 to 7. This circTau RNA lacks a start codon, but is translated after undergoing A>I editing, likely creating a AUI start codon. | 288 | B | 3 | [54] |
| 32 | circMAN21-400 | 186 | Reporter genes | circMAN2A1 expressin corelated with AD | circMAN2A1 RNA expression correlates with Alzheimer’s disease progression. The encoded protein lacks a catalytic domain. | 400 | B | 2 | [95] |
| 33 | circSDHA2 | 146 | Reporter genes | Tumor growth | SDHAF2 (Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex Assembly Factor 2) is necessary for the flavination of a succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit A. SDHAF2 creates circSDHAF2 by backsplicing exon 4 to 3. Overexpression of circSDHAF2 promotes tumor growth. | 334 | B | 2 | [93] |
| 34 | circSLC8A1 | 605 | Western blot using microsomes from rabbit heart | Ca++ exchanger | SLC8A1 (previously called NCX1) generates circSLC8A1 through backsplicing of exon 2. The protein lacks the hydrophobic domain of the linear protein but can still transport Ca++ across a membrane. | 1832 | no | 1 | [42] |
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
References
- J.M. Nigro, K.R. Cho, E.R. Fearon, S.E. Kern, J.M. Ruppert, J.D. Oliner, K.W. Kinzler, B. Vogelstein, Scrambled exons, Cell 64 (1991) 607-613.
- C. Cocquerelle, B. Mascrez, D. Hetuin, B. Bailleul, Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules, FASEB J 7 (1993) 155-160.
- B. Capel, A. Swain, S. Nicolis, A. Hacker, M. Walter, P. Koopman, P. Goodfellow, R. Lovell-Badge, Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis, Cell 73 (1993) 1019-1030.
- J. Kjems, R.A. Garrett, Novel splicing mechanism for the ribosomal RNA intron in the archaebacterium Desulfurococcus mobilis, Cell 54 (1988) 693-703. [CrossRef]
- J. Salzman, C. Gawad, P.L. Wang, N. Lacayo, P.O. Brown, Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types, PLoS One 7 (2012) e30733. [CrossRef]
- W.R. Jeck, J.A. Sorrentino, K. Wang, M.K. Slevin, C.E. Burd, J. Liu, W.F. Marzluff, N.E. Sharpless, Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats, Rna 19 (2013) 141-157. 10.1261/rna.035667.112.
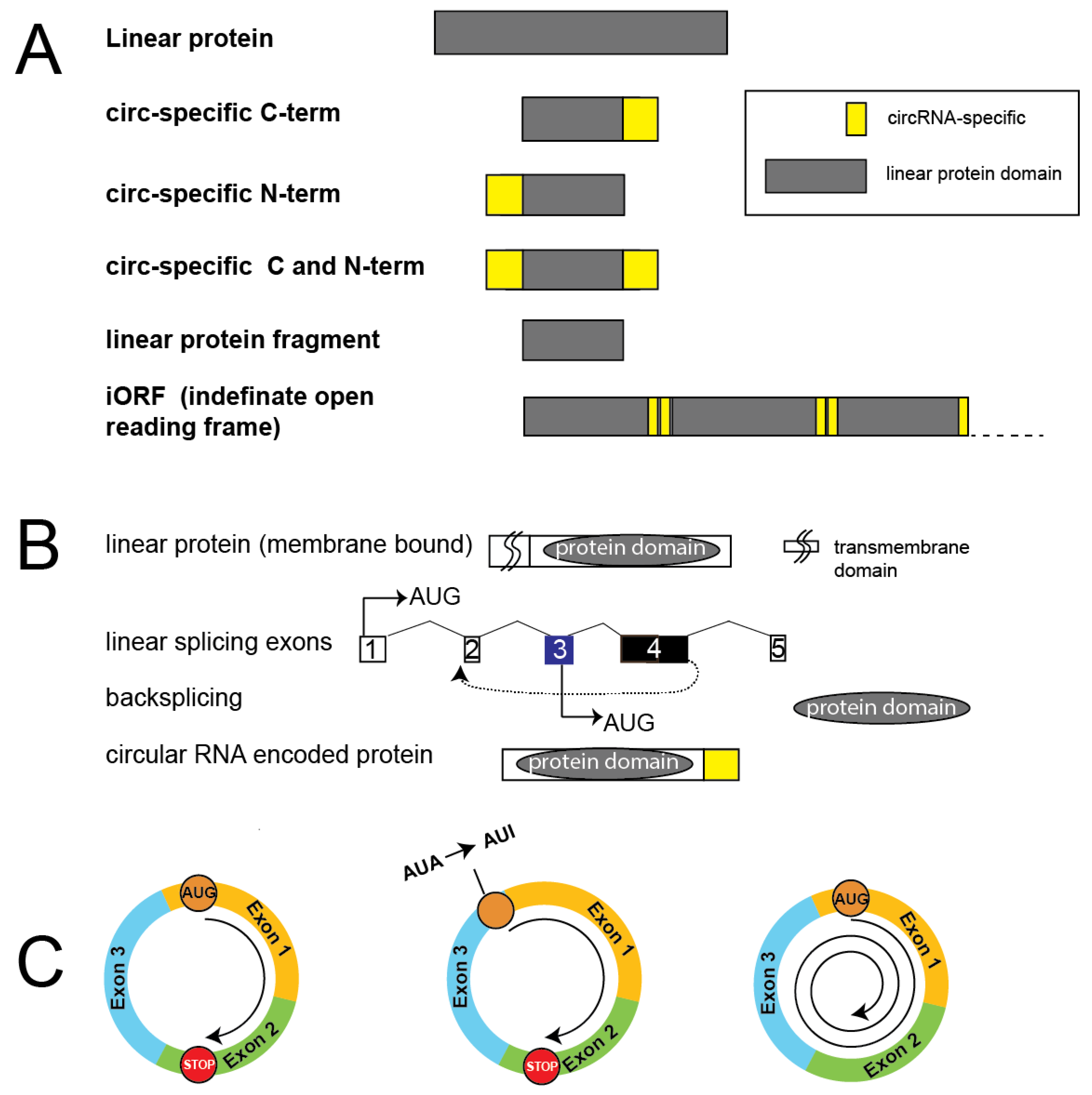
- R. Xin, Y. Gao, Y. Gao, R. Wang, K.E. Kadash-Edmondson, B. Liu, Y. Wang, L. Lin, Y. Xing, isoCirc catalogs full-length circular RNA isoforms in human transcriptomes, Nat Commun 12 (2021) 266. [CrossRef]
- L. Hou, J. Zhang, F. Zhao, Full-length circular RNA profiling by nanopore sequencing with CIRI-long, Nat Protoc 18 (2023) 1795-1813. [CrossRef]
- J. Zhang, L. Hou, Z. Zuo, P. Ji, X. Zhang, Y. Xue, F. Zhao, Comprehensive profiling of circular RNAs with nanopore sequencing and CIRI-long, Nat Biotechnol 39 (2021) 836-845. [CrossRef]
- T.W. Chiang, S.E. Jhong, Y.C. Chen, C.Y. Chen, W.S. Wu, T.J. Chuang, FL-circAS: an integrative resource and analysis for full-length sequences and alternative splicing of circular RNAs with nanopore sequencing, Nucleic Acids Res 52 (2024) D115-D123. [CrossRef]
- M. Pertea, A. Shumate, G. Pertea, A. Varabyou, F.P. Breitwieser, Y.C. Chang, A.K. Madugundu, A. Pandey, S.L. Salzberg, CHESS: a new human gene catalog curated from thousands of large-scale RNA sequencing experiments reveals extensive transcriptional noise, Genome Biol 19 (2018) 208. [CrossRef]
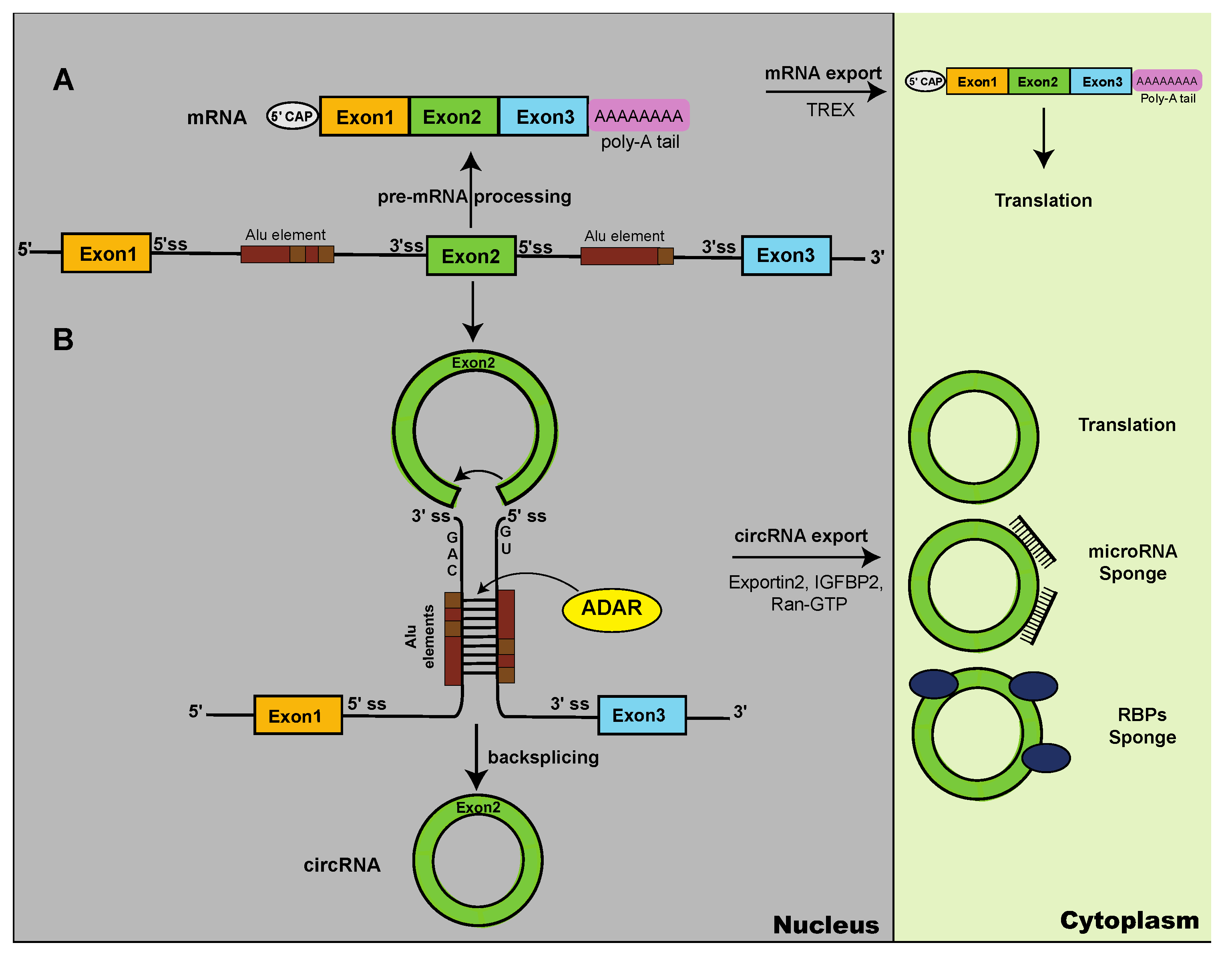
- J.R. Welden, S. Stamm, Pre-mRNA structures forming circular RNAs, Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1862 (2019) 194410. [CrossRef]
- P. Deininger, Alu elements: know the SINEs, Genome Biol 12 (2011) 236. [CrossRef]
- L. Liang, C. Cao, L. Ji, Z. Cai, D. Wang, R. Ye, J. Chen, X. Yu, J. Zhou, Z. Bai, R. Wang, X. Yang, P. Zhu, Y. Xue, Complementary Alu sequences mediate enhancer-promoter selectivity, Nature 619 (2023) 868-875. [CrossRef]
- E. Ullu, C. Tschudi, Alu sequences are processed 7SL RNA genes, Nature 312 (1984) 171-172. [CrossRef]
- L. Bazak, A. Haviv, M. Barak, J. Jacob-Hirsch, P. Deng, R. Zhang, F.J. Isaacs, G. Rechavi, J.B. Li, E. Eisenberg, E.Y. Levanon, A-to-I RNA editing occurs at over a hundred million genomic sites, located in a majority of human genes, Genome Res 24 (2014) 365-376. [CrossRef]
- E.Y. Levanon, E. Eisenberg, R. Yelin, S. Nemzer, M. Hallegger, R. Shemesh, Z.Y. Fligelman, A. Shoshan, S.R. Pollock, D. Sztybel, M. Olshansky, G. Rechavi, M.F. Jantsch, Systematic identification of abundant A-to-I editing sites in the human transcriptome, Nat Biotechnol 22 (2004) 1001-1005. [CrossRef]
- Y. Neeman, E.Y. Levanon, M.F. Jantsch, E. Eisenberg, RNA editing level in the mouse is determined by the genomic repeat repertoire, RNA 12 (2006) 1802-1809. [CrossRef]
- R. Song, P. Guo, X. Ren, L. Zhou, P. Li, N.A. Rahman, S. Wolczynski, X. Li, Y. Zhang, M. Liu, J. Liu, X. Li, A novel polypeptide CAPG-171aa encoded by circCAPG plays a critical role in triple-negative breast cancer, Mol Cancer 22 (2023) 104. [CrossRef]
- S.J. Conn, K.A. Pillman, J. Toubia, V.M. Conn, M. Salmanidis, C.A. Phillips, S. Roslan, A.W. Schreiber, P.A. Gregory, G.J. Goodall, The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs, Cell 160 (2015) 1125-1134. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.014. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Khan, Y.J. Reckman, S. Aufiero, M.M. van den Hoogenhof, I. van der Made, A. Beqqali, D.R. Koolbergen, T.B. Rasmussen, J. van der Velden, E.E. Creemers, Y.M. Pinto, RBM20 Regulates Circular RNA Production From the Titin Gene, Circ Res 119 (2016) 996-1003. [CrossRef]
- T. Fei, Y. Chen, T. Xiao, W. Li, L. Cato, P. Zhang, M.B. Cotter, M. Bowden, R.T. Lis, S.G. Zhao, Q. Wu, F.Y. Feng, M. Loda, H.H. He, X.S. Liu, M. Brown, Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies HNRNPL as a prostate cancer dependency regulating RNA splicing, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114 (2017) E5207-E5215. [CrossRef]
- R. Ashwal-Fluss, M. Meyer, N.R. Pamudurti, A. Ivanov, O. Bartok, M. Hanan, N. Evantal, S. Memczak, N. Rajewsky, S. Kadener, circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing, Mol Cell 56 (2014) 55-66. [CrossRef]
- A. Huang, H. Zheng, Z. Wu, M. Chen, Y. Huang, Circular RNA-protein interactions: functions, mechanisms, and identification, Theranostics 10 (2020) 3503-3517. [CrossRef]
- L.H. Ngo, A.G. Bert, B.K. Dredge, T. Williams, V. Murphy, W. Li, W.B. Hamilton, K.T. Carey, J. Toubia, K.A. Pillman, D. Liu, J. Desogus, J.A. Chao, A.J. Deans, G.J. Goodall, V.O. Wickramasinghe, Nuclear export of circular RNA, Nature 627 (2024) 212-220. [CrossRef]
- K. Strasser, S. Masuda, P. Mason, J. Pfannstiel, M. Oppizzi, S. Rodriguez-Navarro, A.G. Rondon, A. Aguilera, K. Struhl, R. Reed, E. Hurt, TREX is a conserved complex coupling transcription with messenger RNA export, Nature 417 (2002) 304-308. [CrossRef]
- T. Puhringer, U. Hohmann, L. Fin, B. Pacheco-Fiallos, U. Schellhaas, J. Brennecke, C. Plaschka, Structure of the human core transcription-export complex reveals a hub for multivalent interactions, Elife 9 (2020). [CrossRef]
- W. Ding, L. Ding, Y. Lu, W. Sun, Y. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Gao, M. Li, Circular RNA-circLRP6 protects cardiomyocyte from hypoxia-induced apoptosis by facilitating hnRNPM-mediated expression of FGF-9, FEBS J 291 (2024) 1246-1263. [CrossRef]
- K. Zeng, J. Peng, Y. Xing, L. Zhang, P. Zeng, W. Li, W. Zhang, Z. Pan, C. Zhou, J. Lin, A positive feedback circuit driven by m(6)A-modified circular RNA facilitates colorectal cancer liver metastasis, Mol Cancer 22 (2023) 202. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, Y. Wang, Q. Li, X. Li, X. Feng, K. Zeng, The novel beta-TrCP protein isoform hidden in circular RNA confers trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer, Redox Biol 67 (2023) 102896. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, B. Chen, J. Zhao, Q. Li, S. Chen, T. Guo, Y. Li, H. Lai, Z. Chen, Z. Meng, W. Guo, X. He, S. Huang, HNRNPL Circularizes ARHGAP35 to Produce an Oncogenic Protein, Adv Sci (Weinh) 8 (2021) 2001701. [CrossRef]
- J. Li, M. Ma, X. Yang, M. Zhang, J. Luo, H. Zhou, N. Huang, F. Xiao, B. Lai, W. Lv, N. Zhang, Circular HER2 RNA positive triple negative breast cancer is sensitive to Pertuzumab, Mol Cancer 19 (2020) 142. [CrossRef]
- V.A. Herzog, B. Reichholf, T. Neumann, P. Rescheneder, P. Bhat, T.R. Burkard, W. Wlotzka, A. von Haeseler, J. Zuber, S.L. Ameres, Thiol-linked alkylation of RNA to assess expression dynamics, Nat Methods (2017). [CrossRef]
- T.B. Hansen, T.I. Jensen, B.H. Clausen, J.B. Bramsen, B. Finsen, C.K. Damgaard, J. Kjems, Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges, Nature 495 (2013) 384-388. [CrossRef]
- M.T. Jarlstad Olesen, S.K. L, Circular RNAs as microRNA sponges: evidence and controversies, Essays Biochem 65 (2021) 685-696. [CrossRef]
- A.C. Panda, Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges, Adv Exp Med Biol 1087 (2018) 67-79. [CrossRef]
- V.M. Conn, V. Hugouvieux, A. Nayak, S.A. Conos, G. Capovilla, G. Cildir, A. Jourdain, V. Tergaonkar, M. Schmid, C. Zubieta, S.J. Conn, A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation, Nat Plants 3 (2017) 17053. [CrossRef]
- D.B. Dudekula, A.C. Panda, I. Grammatikakis, S. De, K. Abdelmohsen, M. Gorospe, CircInteractome: A web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs, RNA Biol 13 (2016) 34-42. [CrossRef]
- A. Das, T. Sinha, S. Shyamal, A.C. Panda, Emerging Role of Circular RNA-Protein Interactions, Noncoding RNA 7 (2021). [CrossRef]
- F. Crudele, N. Bianchi, A. Terrazzan, P. Ancona, A. Frassoldati, P. Gasparini, A.P. D'Adamo, D. Papaioannou, R. Garzon, A. Wojcicka, P. Gaj, K. Jazdzewski, J. Palatini, S. Volinia, Circular RNAs Could Encode Unique Proteins and Affect Cancer Pathways, Biology (Basel) 12 (2023). [CrossRef]
- W. Huang, Y. Ling, S. Zhang, Q. Xia, R. Cao, X. Fan, Z. Fang, Z. Wang, G. Zhang, TransCirc: an interactive database for translatable circular RNAs based on multi-omics evidence, Nucleic Acids Res 49 (2021) D236-D242. [CrossRef]
- X.F. Li, J. Lytton, A circularized sodium-calcium exchanger exon 2 transcript, J Biol Chem 274 (1999) 8153-8160.
- C.Y. Chen, P. Sarnow, Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs, Science 268 (1995) 415-417.
- N. Abe, K. Matsumoto, M. Nishihara, Y. Nakano, A. Shibata, H. Maruyama, S. Shuto, A. Matsuda, M. Yoshida, Y. Ito, H. Abe, Rolling Circle Translation of Circular RNA in Living Human Cells, Sci Rep 5 (2015) 16435. [CrossRef]
- K. Nakamoto, N. Abe, G. Tsuji, Y. Kimura, F. Tomoike, Y. Shimizu, H. Abe, Chemically synthesized circular RNAs with phosphoramidate linkages enable rolling circle translation, Chem Commun (Camb) 56 (2020) 6217-6220. [CrossRef]
- L.V. Stagsted, K.M. Nielsen, I. Daugaard, T.B. Hansen, Noncoding AUG circRNAs constitute an abundant and conserved subclass of circles, Life Sci Alliance 2 (2019). [CrossRef]
- H. Li, M. Xie, Y. Wang, L. Yang, Z. Xie, H. Wang, riboCIRC: a comprehensive database of translatable circRNAs, Genome Biol 22 (2021) 79. [CrossRef]
- A. Das, T. Sinha, S.S. Mishra, D. Das, A.C. Panda, Identification of potential proteins translated from circular RNA splice variants, Eur J Cell Biol 102 (2023) 151286. [CrossRef]
- N.R. Pamudurti, O. Bartok, M. Jens, R. Ashwal-Fluss, C. Stottmeister, L. Ruhe, M. Hanan, E. Wyler, D. Perez-Hernandez, E. Ramberger, S. Shenzis, M. Samson, G. Dittmar, M. Landthaler, M. Chekulaeva, N. Rajewsky, S. Kadener, Translation of CircRNAs, Mol Cell 66 (2017) 9-21 e27. [CrossRef]
- B.P. Nicolet, S.B.G. Jansen, E. Heideveld, W.H. Ouwehand, E. van den Akker, M. von Lindern, M.C. Wolkers, Circular RNAs exhibit limited evidence for translation, or translation regulation of the mRNA counterpart in terminal hematopoiesis, RNA 28 (2022) 194-209. [CrossRef]
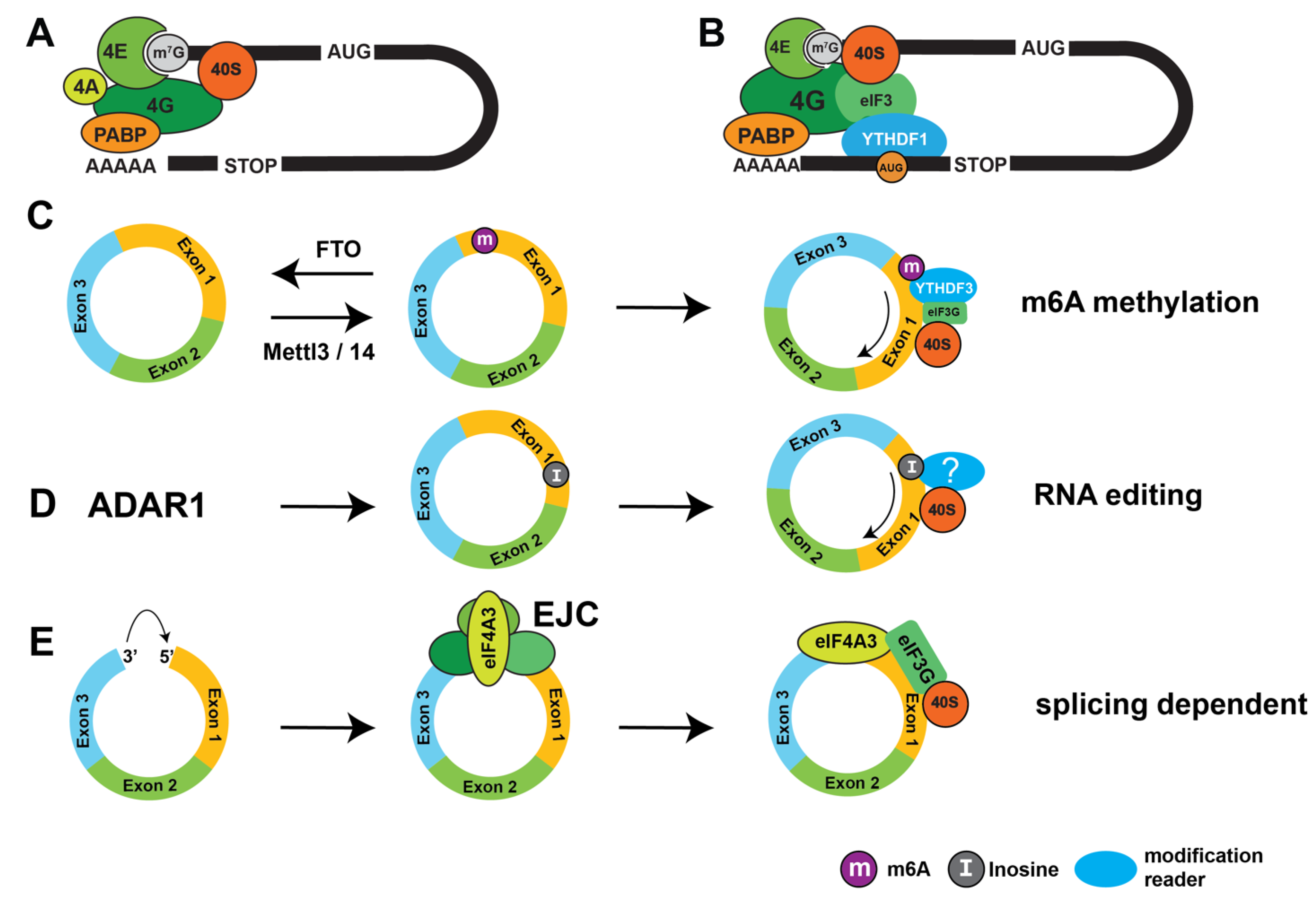
- C. Tang, Y. Xie, T. Yu, N. Liu, Z. Wang, R.J. Woolsey, Y. Tang, X. Zhang, W. Qin, Y. Zhang, G. Song, W. Zheng, J. Wang, W. Chen, X. Wei, Z. Xie, R. Klukovich, H. Zheng, D.R. Quilici, W. Yan, m(6)A-dependent biogenesis of circular RNAs in male germ cells, Cell Res 30 (2020) 211-228. [CrossRef]
- S. van Heesch, F. Witte, V. Schneider-Lunitz, J.F. Schulz, E. Adami, A.B. Faber, M. Kirchner, H. Maatz, S. Blachut, C.L. Sandmann, M. Kanda, C.L. Worth, S. Schafer, L. Calviello, R. Merriott, G. Patone, O. Hummel, E. Wyler, B. Obermayer, M.B. Mucke, E.L. Lindberg, F. Trnka, S. Memczak, M. Schilling, L.E. Felkin, P.J.R. Barton, N.M. Quaife, K. Vanezis, S. Diecke, M. Mukai, N. Mah, S.J. Oh, A. Kurtz, C. Schramm, D. Schwinge, M. Sebode, M. Harakalova, F.W. Asselbergs, A. Vink, R.A. de Weger, S. Viswanathan, A.A. Widjaja, A. Gartner-Rommel, H. Milting, C. Dos Remedios, C. Knosalla, P. Mertins, M. Landthaler, M. Vingron, W.A. Linke, J.G. Seidman, C.E. Seidman, N. Rajewsky, U. Ohler, S.A. Cook, N. Hubner, The Translational Landscape of the Human Heart, Cell 178 (2019) 242-260 e229. [CrossRef]
- R. Chen, S.K. Wang, J.A. Belk, L. Amaya, Z. Li, A. Cardenas, B.T. Abe, C.K. Chen, P.A. Wender, H.Y. Chang, Engineering circular RNA for enhanced protein production, Nat Biotechnol 41 (2023) 262-272. [CrossRef]
- J.R. Welden, G. Margvelani, K.A. Arizaca Maquera, B. Gudlavalleti, S.C. Miranda Sardón, A. Campos, N. Robil, D.C. Lee, A. Gonzalo Hernandez, W. Wang, J. Di, P. de la Grange, P.T. Nelson, S. Stamm, RNA editing of microtubule associated protein tau circular RNAs promotes their translation and tau tangle formation, Nucleic Acids Res 50 (2022) 12979-12996.
- H. Ho-Xuan, P. Glazar, C. Latini, K. Heizler, J. Haase, R. Hett, M. Anders, F. Weichmann, A. Bruckmann, D. Van den Berg, S. Huttelmaier, N. Rajewsky, C. Hackl, G. Meister, Comprehensive analysis of translation from overexpressed circular RNAs reveals pervasive translation from linear transcripts, Nucleic Acids Res 48 (2020) 10368-10382. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jiang, X. Chen, W. Zhang, Overexpression-based detection of translatable circular RNAs is vulnerable to coexistent linear RNA byproducts, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 558 (2021) 189-195. [CrossRef]
- H.L. Sanger, G. Klotz, D. Riesner, H.J. Gross, A.K. Kleinschmidt, Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73 (1976) 3852-3856.
- B.D. Lee, U. Neri, S. Roux, Y.I. Wolf, A.P. Camargo, M. Krupovic, R.N.A.V.D. Consortium, P. Simmonds, N. Kyrpides, U. Gophna, V.V. Dolja, E.V. Koonin, Mining metatranscriptomes reveals a vast world of viroid-like circular RNAs, Cell 186 (2023) 646-661 e644. [CrossRef]
- M.G. AbouHaidar, S. Venkataraman, A. Golshani, B. Liu, T. Ahmad, Novel coding, translation, and gene expression of a replicating covalently closed circular RNA of 220 nt, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111 (2014) 14542-14547. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, Z. Li, M. Zhang, H. Zhou, X. Wu, J. Zhong, F. Xiao, N. Huang, X. Yang, R. Zeng, L. Yang, Z. Xia, N. Zhang, Rolling-translated EGFR variants sustain EGFR signaling and promote glioblastoma tumorigenicity, Neuro Oncol 23 (2021) 743-756. [CrossRef]
- M. Zhang, K. Zhao, X. Xu, Y. Yang, S. Yan, P. Wei, H. Liu, J. Xu, F. Xiao, H. Zhou, X. Yang, N. Huang, J. Liu, K. He, K. Xie, G. Zhang, S. Huang, N. Zhang, A peptide encoded by circular form of LINC-PINT suppresses oncogenic transcriptional elongation in glioblastoma, Nat Commun 9 (2018) 4475. [CrossRef]
- X. Zheng, L. Chen, Y. Zhou, Q. Wang, Z. Zheng, B. Xu, C. Wu, Q. Zhou, W. Hu, C. Wu, J. Jiang, A novel protein encoded by a circular RNA circPPP1R12A promotes tumor pathogenesis and metastasis of colon cancer via Hippo-YAP signaling, Mol Cancer 18 (2019) 47. [CrossRef]
- R. Sawada, S. Mitaku, How are exons encoding transmembrane sequences distributed in the exon-intron structure of genes?, Genes Cells 16 (2011) 115-121. [CrossRef]
- X. Gao, X. Xia, F. Li, M. Zhang, H. Zhou, X. Wu, J. Zhong, Z. Zhao, K. Zhao, D. Liu, F. Xiao, Q. Xu, T. Jiang, B. Li, S.Y. Cheng, N. Zhang, Circular RNA-encoded oncogenic E-cadherin variant promotes glioblastoma tumorigenicity through activation of EGFR-STAT3 signalling, Nat Cell Biol 23 (2021) 278-291. [CrossRef]
- L. Xiong, H.S. Liu, C. Zhou, X. Yang, L. Huang, H.Q. Jie, Z.W. Zeng, X.B. Zheng, W.X. Li, Z.Z. Liu, L. Kang, Z.X. Liang, A novel protein encoded by circINSIG1 reprograms cholesterol metabolism by promoting the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of INSIG1 in colorectal cancer, Mol Cancer 22 (2023) 72. [CrossRef]
- A. Tiessen, P. Perez-Rodriguez, L.J. Delaye-Arredondo, Mathematical modeling and comparison of protein size distribution in different plant, animal, fungal and microbial species reveals a negative correlation between protein size and protein number, thus providing insight into the evolution of proteomes, BMC Res Notes 5 (2012) 85. [CrossRef]
- Q. Liang, N. Peng, Y. Xie, N. Kumar, W. Gao, Y. Miao, MolPhase, an advanced prediction algorithm for protein phase separation, EMBO J 43 (2024) 1898-1918. [CrossRef]
- J. Yan, A.K. Dunker, V.N. Uversky, L. Kurgan, Molecular recognition features (MoRFs) in three domains of life, Mol Biosyst 12 (2016) 697-710. [CrossRef]
- H.J. Kim, Cell Fate Control by Translation: mRNA Translation Initiation as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Development and Stem Cell Fate Control, Biomolecules 9 (2019). [CrossRef]
- R. Lacerda, J. Menezes, L. Romao, More than just scanning: the importance of cap-independent mRNA translation initiation for cellular stress response and cancer, Cell Mol Life Sci 74 (2017) 1659-1680. [CrossRef]
- J. Pelletier, N. Sonenberg, Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA, Nature 334 (1988) 320-325. [CrossRef]
- C.U. Hellen, P. Sarnow, Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules, Genes Dev 15 (2001) 1593-1612. [CrossRef]
- K.A. Spriggs, M. Stoneley, M. Bushell, A.E. Willis, Re-programming of translation following cell stress allows IRES-mediated translation to predominate, Biol Cell 100 (2008) 27-38. [CrossRef]
- S. Weingarten-Gabbay, S. Elias-Kirma, R. Nir, A.A. Gritsenko, N. Stern-Ginossar, Z. Yakhini, A. Weinberger, E. Segal, Comparative genetics. Systematic discovery of cap-independent translation sequences in human and viral genomes, Science 351 (2016). [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, R. Ma, X. Zhang, L. Cui, Y. Ding, W. Shi, C. Guo, Y. Shi, Crosstalk between N6-methyladenosine modification and circular RNAs: current understanding and future directions, Mol Cancer 20 (2021) 121. [CrossRef]
- P. Stoilov, I. Rafalska, S. Stamm, YTH: a new domain in nuclear proteins, Trends Biochem. Sci. 27 (2002) 495-496.
- G. Di Timoteo, D. Dattilo, A. Centron-Broco, A. Colantoni, M. Guarnacci, F. Rossi, D. Incarnato, S. Oliviero, A. Fatica, M. Morlando, I. Bozzoni, Modulation of circRNA Metabolism by m(6)A Modification, Cell Rep 31 (2020) 107641. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, B.S. Zhao, I.A. Roundtree, Z. Lu, D. Han, H. Ma, X. Weng, K. Chen, H. Shi, C. He, N(6)-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency, Cell 161 (2015) 1388-1399. [CrossRef]
- K.D. Meyer, D.P. Patil, J. Zhou, A. Zinoviev, M.A. Skabkin, O. Elemento, T.V. Pestova, S.B. Qian, S.R. Jaffrey, 5' UTR m(6)A Promotes Cap-Independent Translation, Cell 163 (2015) 999-1010. [CrossRef]
- R. Perriman, M. Ares, Jr., Circular mRNA can direct translation of extremely long repeating-sequence proteins in vivo, RNA 4 (1998) 1047-1054. [CrossRef]
- I.N. Zheludev, R.C. Edgar, M.J. Lopez-Galiano, M. de la Pena, A. Babaian, A.S. Bhatt, A.Z. Fire, Viroid-like colonists of human microbiomes, bioRxiv (2024). [CrossRef]
- H.J. Hwang, Y.K. Kim, Molecular mechanisms of circular RNA translation, Exp Mol Med (2024). [CrossRef]
- X. Fan, Y. Yang, C. Chen, Z. Wang, Pervasive translation of circular RNAs driven by short IRES-like elements, Nat Commun 13 (2022) 3751. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhou, J. Wu, S. Yao, Y. Xu, W. Zhao, Y. Tong, Z. Zhou, DeepCIP: A multimodal deep learning method for the prediction of internal ribosome entry sites of circRNAs, Comput Biol Med 164 (2023) 107288. [CrossRef]
- C.K. Chen, R. Cheng, J. Demeter, J. Chen, S. Weingarten-Gabbay, L. Jiang, M.P. Snyder, J.S. Weissman, E. Segal, P.K. Jackson, H.Y. Chang, Structured elements drive extensive circular RNA translation, Mol Cell 81 (2021) 4300-4318 e4313. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, X. Fan, M. Mao, X. Song, P. Wu, Y. Zhang, Y. Jin, Y. Yang, L.L. Chen, Y. Wang, C.C. Wong, X. Xiao, Z. Wang, Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine, Cell Res 27 (2017) 626-641. [CrossRef]
- A. Nott, H. Le Hir, M.J. Moore, Splicing enhances translation in mammalian cells: an additional function of the exon junction complex, Genes Dev 18 (2004) 210-222. [CrossRef]
- H.C. Lee, J. Choe, S.G. Chi, Y.K. Kim, Exon junction complex enhances translation of spliced mRNAs at multiple steps, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384 (2009) 334-340. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, W. Qi, Y. Wu, EIF4A3-induced circular RNA SCAP facilitates tumorigenesis and progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via miR-7/SMAD2 signaling, Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30 (2023) 65237-65249. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, C. Wang, G. Chen, W. Zou, Y. Deng, F. Zhou, EIF4A3-induced circCCNB1 (hsa_circ_0001495) promotes glioma progression by elevating CCND1 through interacting miR-516b-5p and HuR, Metab Brain Dis 37 (2022) 819-833. [CrossRef]
- Z.H. Feng, L. Zheng, T. Yao, S.Y. Tao, X.A. Wei, Z.Y. Zheng, B.J. Zheng, X.Y. Zhang, B. Huang, J.H. Liu, Y.L. Chen, Z. Shan, P.T. Yuan, C.G. Wang, J. Chen, S.Y. Shen, F.D. Zhao, EIF4A3-induced circular RNA PRKAR1B promotes osteosarcoma progression by miR-361-3p-mediated induction of FZD4 expression, Cell Death Dis 12 (2021) 1025. [CrossRef]
- J. Chang, M.K. Shin, J. Park, H.J. Hwang, N. Locker, J. Ahn, D. Kim, D. Baek, Y. Park, Y. Lee, S.H. Boo, H.I. Kim, Y.K. Kim, An interaction between eIF4A3 and eIF3g drives the internal initiation of translation, Nucleic Acids Res 51 (2023) 10950-10969. [CrossRef]
- H.H. Lin, C.Y. Chang, Y.R. Huang, C.H. Shen, Y.C. Wu, K.L. Chang, Y.C. Lee, Y.C. Lin, W.C. Ting, H.J. Chien, Y.F. Zheng, C.C. Lai, K.Y. Hsiao, Exon Junction Complex Mediates the Cap-Independent Translation of Circular RNA, Mol Cancer Res 21 (2023) 1220-1233. [CrossRef]
- C.E. Samuel, Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR1), a suppressor of double-stranded RNA-triggered innate immune responses, J Biol Chem 294 (2019) 1710-1720. [CrossRef]
- K.A. Arizaca Maquera, J.R. Welden, G. Margvelani, S.C. Miranda Sardón, S. Hart, N. Robil, A.G. Hernandez, P. de la Grange, P.T. Nelson, S. Stamm, Alzheimer’s disease pathogenetic progression is associated with changes in regulated retained introns and editing of circular RNAs, Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 16 (2023). [CrossRef]
- G. Margvelani, J.R. Welden, A.A. Maquera, J.E. Van Eyk, C. Murray, S.C. Miranda Sardon, S. Stamm, Influence of FTDP-17 mutants on circular tau RNAs, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1870 (2024) 167036. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang, Z. Zhang, K. Blackwell, G.G. Carmichael, Vigilins bind to promiscuously A-to-I-edited RNAs and are involved in the formation of heterochromatin, Curr Biol 15 (2005) 384-391. [CrossRef]
- U. Zinnall, M. Milek, I. Minia, C.H. Vieira-Vieira, S. Muller, G. Mastrobuoni, O.G. Hazapis, S. Del Giudice, D. Schwefel, N. Bley, F. Voigt, J.A. Chao, S. Kempa, S. Huttelmaier, M. Selbach, M. Landthaler, HDLBP binds ER-targeted mRNAs by multivalent interactions to promote protein synthesis of transmembrane and secreted proteins, Nat Commun 13 (2022) 2727. [CrossRef]
- J. Yan, Y. Yang, X. Fan, Y. Tang, Z. Tang, Sp1-Mediated circRNA circHipk2 Regulates Myogenesis by Targeting Ribosomal Protein Rpl7, Genes (Basel) 12 (2021). [CrossRef]
- R. Zhao, P. Chen, C. Qu, J. Liang, Y. Cheng, Z. Sun, H. Tian, Circular RNA circTRPS1-2 inhibits the proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by reducing the production of ribosomes, Cell Death Discov 9 (2023) 5. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, R. Kong, C. Wu, S. Wang, Z. Liu, S. Liu, S. Li, T. Chen, C. Mao, S. Liu, Circ-MALAT1 Functions as Both an mRNA Translation Brake and a microRNA Sponge to Promote Self-Renewal of Hepatocellular Cancer Stem Cells, Adv Sci (Weinh) 7 (2020) 1900949. [CrossRef]
- Y. Qin, Y. Zheng, C. Huang, Y. Li, M. Gu, Q. Wu, Knockdown of circSMAD2 inhibits the tumorigenesis of gallbladder cancer through binding with eIF4A3, BMC Cancer 21 (2021) 1172. [CrossRef]
- B.R. Nelson, C.A. Makarewich, D.M. Anderson, B.R. Winders, C.D. Troupes, F. Wu, A.L. Reese, J.R. McAnally, X. Chen, E.T. Kavalali, S.C. Cannon, S.R. Houser, R. Bassel-Duby, E.N. Olson, A peptide encoded by a transcript annotated as long noncoding RNA enhances SERCA activity in muscle, Science 351 (2016) 271-275. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang, X. Yi, M. Hou, Q. Li, X. Li, L. Lu, E. Qi, M. Wu, L. Qi, H. Jian, Z. Qi, Y. Lv, X. Kong, M. Bi, S. Feng, H. Zhou, The landscape of m(1)A modification and its posttranscriptional regulatory functions in primary neurons, Elife 12 (2023). [CrossRef]
- A.D. Perenkov, A.D. Sergeeva, M.V. Vedunova, D.V. Krysko, In Vitro Transcribed RNA-Based Platform Vaccines: Past, Present, and Future, Vaccines (Basel) 11 (2023). [CrossRef]
- D. Huang, X. Zhu, S. Ye, J. Zhang, J. Liao, N. Zhang, X. Zeng, J. Wang, B. Yang, Y. Zhang, L. Lao, J. Chen, M. Xin, Y. Nie, P.E. Saw, S. Su, E. Song, Tumour circular RNAs elicit anti-tumour immunity by encoding cryptic peptides, Nature 625 (2024) 593-602. [CrossRef]
- M. Li, Y. Wang, P. Wu, S. Zhang, Z. Gong, Q. Liao, C. Guo, F. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Zeng, Q. Yan, W. Xiong, Application prospect of circular RNA-based neoantigen vaccine in tumor immunotherapy, Cancer Lett 563 (2023) 216190. [CrossRef]
- J. Xia, S. Li, B. Ren, P. Zhang, Circular RNAs as a potential source of neoepitopes in cancer, Front Oncol 13 (2023) 1098523. [CrossRef]
- S.S. Titze-de-Almeida, R. Titze-de-Almeida, Progress in circRNA-Targeted Therapy in Experimental Parkinson's Disease, Pharmaceutics 15 (2023). [CrossRef]
- A.C. Palcau, R. Brandi, N.H. Mehterov, C. Botti, G. Blandino, C. Pulito, Exploiting Long Non-Coding RNAs and Circular RNAs as Pharmacological Targets in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment, Cancers (Basel) 15 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Y.C. Lin, Y.C. Wang, Y.C. Lee, H.H. Lin, K.L. Chang, Y.C. Tai, K.Y. Hsiao, CircVIS: a platform for circRNA visual presentation, BMC Genomics 22 (2022) 921. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, L. Yao, Y. Tang, J.H. Jhong, J. Wan, J. Chang, S. Cui, Y. Luo, X. Cai, W. Li, Q. Chen, H.Y. Huang, Z. Wang, W. Chen, T.H. Chang, F. Wei, T.Y. Lee, H.D. Huang, CircNet 2.0: an updated database for exploring circular RNA regulatory networks in cancers, Nucleic Acids Res 50 (2022) D93-D101. [CrossRef]
- W. Zhang, Y. Liu, Z. Min, G. Liang, J. Mo, Z. Ju, B. Zeng, W. Guan, Y. Zhang, J. Chen, Q. Zhang, H. Li, C. Zeng, Y. Wei, G.C. Chan, circMine: a comprehensive database to integrate, analyze and visualize human disease-related circRNA transcriptome, Nucleic Acids Res 50 (2022) D83-D92. [CrossRef]
- D. Yao, L. Zhang, M. Zheng, X. Sun, Y. Lu, P. Liu, Circ2Disease: a manually curated database of experimentally validated circRNAs in human disease, Sci Rep 8 (2018) 11018. [CrossRef]
- X. Ju, Y. Tang, R. Qu, S. Hao, The Emerging Role of Circ-SHPRH in Cancer, Onco Targets Ther 14 (2021) 4177-4188. [CrossRef]
- M. Zhang, N. Huang, X. Yang, J. Luo, S. Yan, F. Xiao, W. Chen, X. Gao, K. Zhao, H. Zhou, Z. Li, L. Ming, B. Xie, N. Zhang, A novel protein encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene suppresses glioma tumorigenesis, Oncogene 37 (2018) 1805-1814. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, X. Gao, M. Zhang, S. Yan, C. Sun, F. Xiao, N. Huang, X. Yang, K. Zhao, H. Zhou, S. Huang, B. Xie, N. Zhang, Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis, J Natl Cancer Inst 110 (2018) 304-315. [CrossRef]
- K. Li, Z.Y. Peng, R. Wang, X. Li, N. Du, D.P. Liu, J. Zhang, Y.F. Zhang, L. Ma, Y. Sun, S.C. Tang, H. Ren, Y.P. Yang, X. Sun, Enhancement of TKI sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma through m6A-dependent translational repression of Wnt signaling by circ-FBXW7, Mol Cancer 22 (2023). [CrossRef]
- S. Zhong, H. Xu, D. Wang, S. Yang, H. Li, H. Zhang, J. Feng, S. Zhou, circNFIB decreases synthesis of arachidonic acid and inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis, Eur J Pharmacol 963 (2024) 176221. [CrossRef]
- I. Legnini, G. Di Timoteo, F. Rossi, M. Morlando, F. Briganti, O. Sthandier, A. Fatica, T. Santini, A. Andronache, M. Wade, P. Laneve, N. Rajewsky, I. Bozzoni, Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA that Can Be Translated and Functions in Myogenesis, Mol Cell 66 (2017) 22-37 e29. [CrossRef]
- J. Zhong, X. Wu, Y. Gao, J. Chen, M. Zhang, H. Zhou, J. Yang, F. Xiao, X. Yang, N. Huang, H. Qi, X. Wang, F. Bai, Y. Shi, N. Zhang, Circular RNA encoded MET variant promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis, Nat Commun 14 (2023) 4467. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, C. Xu, Y. Cheng, Y. Yuan, J. Sha, X. Guo, Y. Cui, A novel protein encoded by circRsrc1 regulates mitochondrial ribosome assembly and translation during spermatogenesis, BMC Biol 21 (2023) 94. [CrossRef]
- R. Chen, T. Yang, B. Jin, W. Xu, Y. Yan, N. Wood, H.I. Lehmann, S. Wang, X. Zhu, W. Yuan, H. Chen, Z. Liu, G. Li, T.S. Bowen, J. Li, J. Xiao, CircTmeff1 Promotes Muscle Atrophy by Interacting with TDP-43 and Encoding A Novel TMEFF1-339aa Protein, Adv Sci (Weinh) 10 (2023) e2206732. [CrossRef]
- T. Mookherjee, A. Bagchi, R. Ghosh, In-silico studies to analyse the possible interactions of CircPPP1R12A translated peptide with Mst proteins, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 635 (2022) 108-113. [CrossRef]
- F. Hu, Y. Peng, S. Chang, X. Luo, Y. Yuan, X. Zhu, Y. Xu, K. Du, Y. Chen, S. Deng, F. Yu, X. Feng, X. Fan, H. Ashktorab, D. Smoot, S.J. Meltzer, S. Li, Y. Wei, X. Zhang, Z. Jin, Vimentin binds to a novel tumor suppressor protein, GSPT1-238aa, encoded by circGSPT1 with a selective encoding priority to halt autophagy in gastric carcinoma, Cancer Lett 545 (2022) 215826. [CrossRef]
- L. Wang, J. Zhou, C. Zhang, R. Chen, Q. Sun, P. Yang, C. Peng, Y. Tan, C. Jin, T. Wang, J. Ji, Y. Sun, A novel tumour suppressor protein encoded by circMAPK14 inhibits progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by competitively binding to MKK6, Clin Transl Med 11 (2021) e613. [CrossRef]
- Z.X. Liang, H.S. Liu, L. Xiong, X. Yang, F.W. Wang, Z.W. Zeng, X.W. He, X.R. Wu, P. Lan, A novel NF-kappaB regulator encoded by circPLCE1 inhibits colorectal carcinoma progression by promoting RPS3 ubiquitin-dependent degradation, Mol Cancer 20 (2021) 103. [CrossRef]
- W.C. Liang, C.W. Wong, P.P. Liang, M. Shi, Y. Cao, S.T. Rao, S.K. Tsui, M.M. Waye, Q. Zhang, W.M. Fu, J.F. Zhang, Translation of the circular RNA circbeta-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway, Genome Biol 20 (2019) 84. [CrossRef]
- W. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Circular RNA circbeta-catenin aggravates the malignant phenotype of non-small-cell lung cancer via encoding a peptide, J Clin Lab Anal 35 (2021) e23900. [CrossRef]
- D. Mo, X. Li, C.A. Raabe, T.S. Rozhdestvensky, B.V. Skryabin, J. Brosius, Circular RNA Encoded Amyloid Beta peptides-A Novel Putative Player in Alzheimer's Disease, Cells 9 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Z. Pan, J. Cai, J. Lin, H. Zhou, J. Peng, J. Liang, L. Xia, Q. Yin, B. Zou, J. Zheng, L. Qiao, L. Zhang, A novel protein encoded by circFNDC3B inhibits tumor progression and EMT through regulating Snail in colon cancer, Mol Cancer 19 (2020) 71. [CrossRef]
- D. Mo, X. Li, C.A. Raabe, D. Cui, J.F. Vollmar, T.S. Rozhdestvensky, B.V. Skryabin, J. Brosius, A universal approach to investigate circRNA protein coding function, Sci Rep 9 (2019) 11684. [CrossRef]
- W.W. Du, J. Xu, W. Yang, N. Wu, F. Li, L. Zhou, S. Wang, X. Li, A.T. He, K.Y. Du, K. Zeng, J. Ma, J. Lyu, C. Zhang, C. Zhou, K. Maksimovic, B.B. Yang, A Neuroligin Isoform Translated by circNlgn Contributes to Cardiac Remodeling, Circ Res 129 (2021) 568-582. [CrossRef]
- Y. Peng, Y. Xu, X. Zhang, S. Deng, Y. Yuan, X. Luo, M.T. Hossain, X. Zhu, K. Du, F. Hu, Y. Chen, S. Chang, X. Feng, X. Fan, H. Ashktorab, D. Smoot, S.J. Meltzer, G. Hou, Y. Wei, S. Li, Y. Qin, Z. Jin, A novel protein AXIN1-295aa encoded by circAXIN1 activates the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway to promote gastric cancer progression, Mol Cancer 20 (2021) 158. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, Z. Wang, P. Su, Y. Liang, Z. Li, H. Zhang, X. Song, D. Han, X. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Yang, B. Chen, L. Wang, W. Zhao, Q. Yang, circ-EIF6 encodes EIF6-224aa to promote TNBC progression via stabilizing MYH9 and activating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, Mol Ther 30 (2022) 415-430. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





