Submitted:
25 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of the Conjugates of EuPSM and Antibodies
2.1.2. Preparation of EuPSM-based LFIA
2.2. Optimization of the LFIA
2.2.1. Detection of Spiked Serum Samples
2.2.2. Evaluation of Detection Performance of EuPSM-LFIA
2.2.3. Evaluation of Detection Linearity
2.2.4. Evaluation of the Detection Limit
2.2.5. Evaluation of Detection Precision
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Detection Principle of EuPSM-LFIA
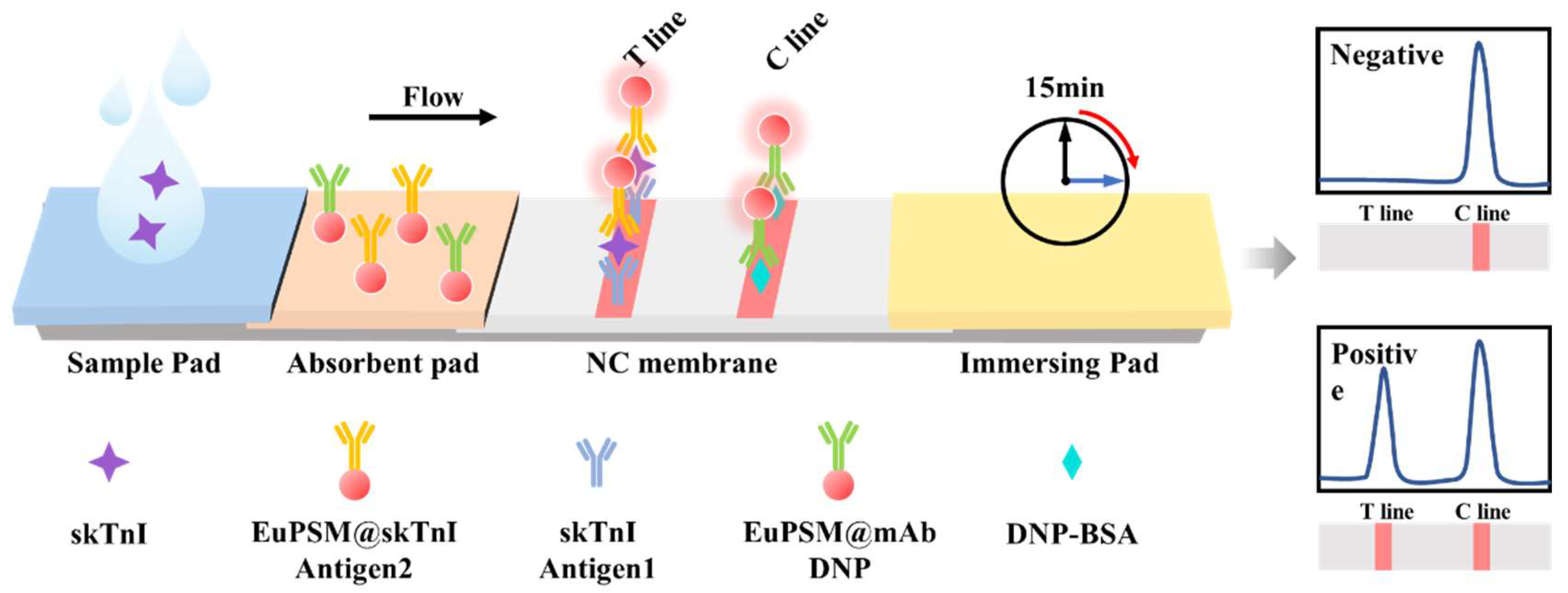
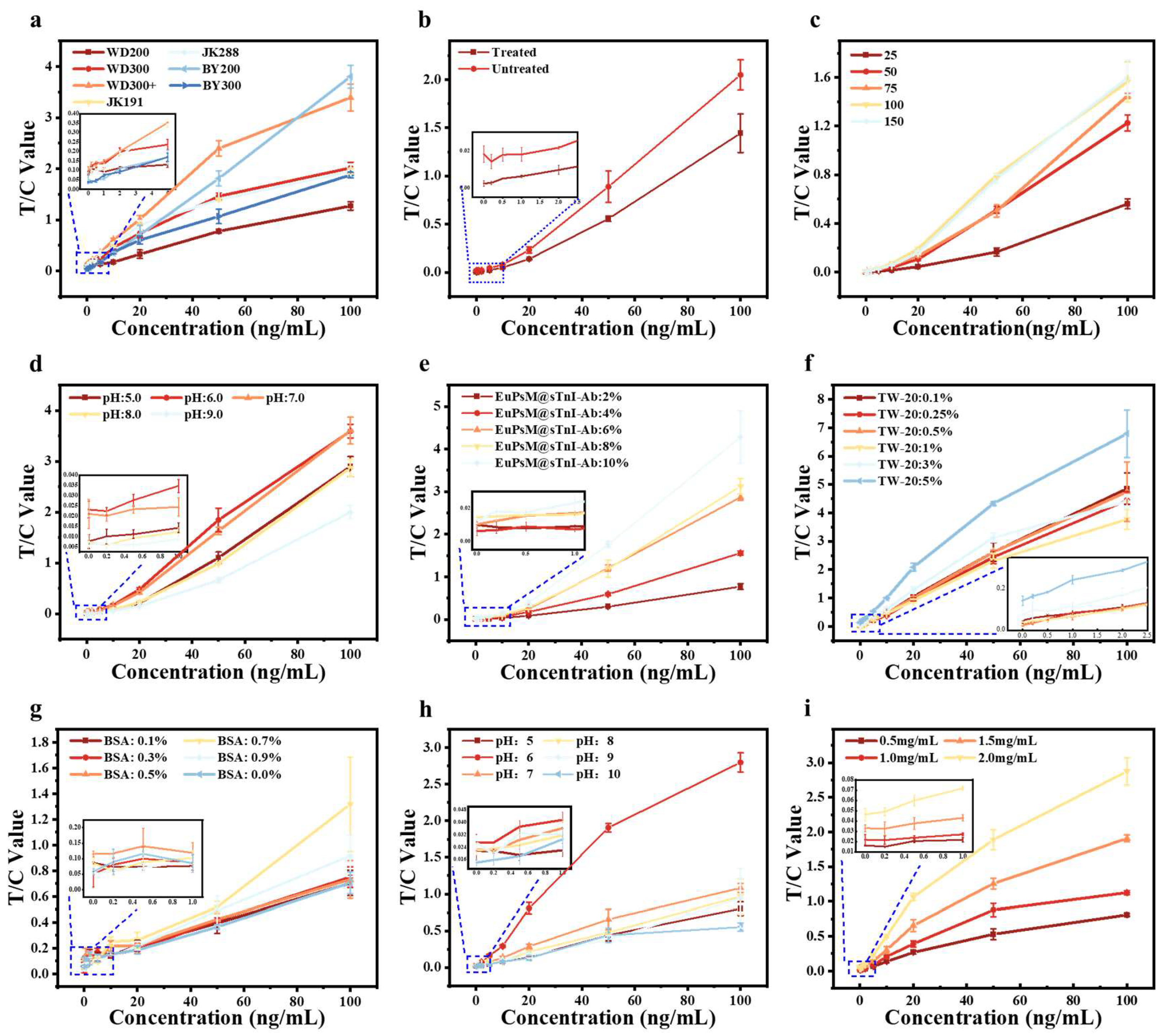
3.2. Optimization of Sensitivity for EuPSM-LFIA
3.3. Detection Feasibility and Performance of Serum-Spiked Samples
3.3.1. Detection Feasibility of Serum-Spiked Samples
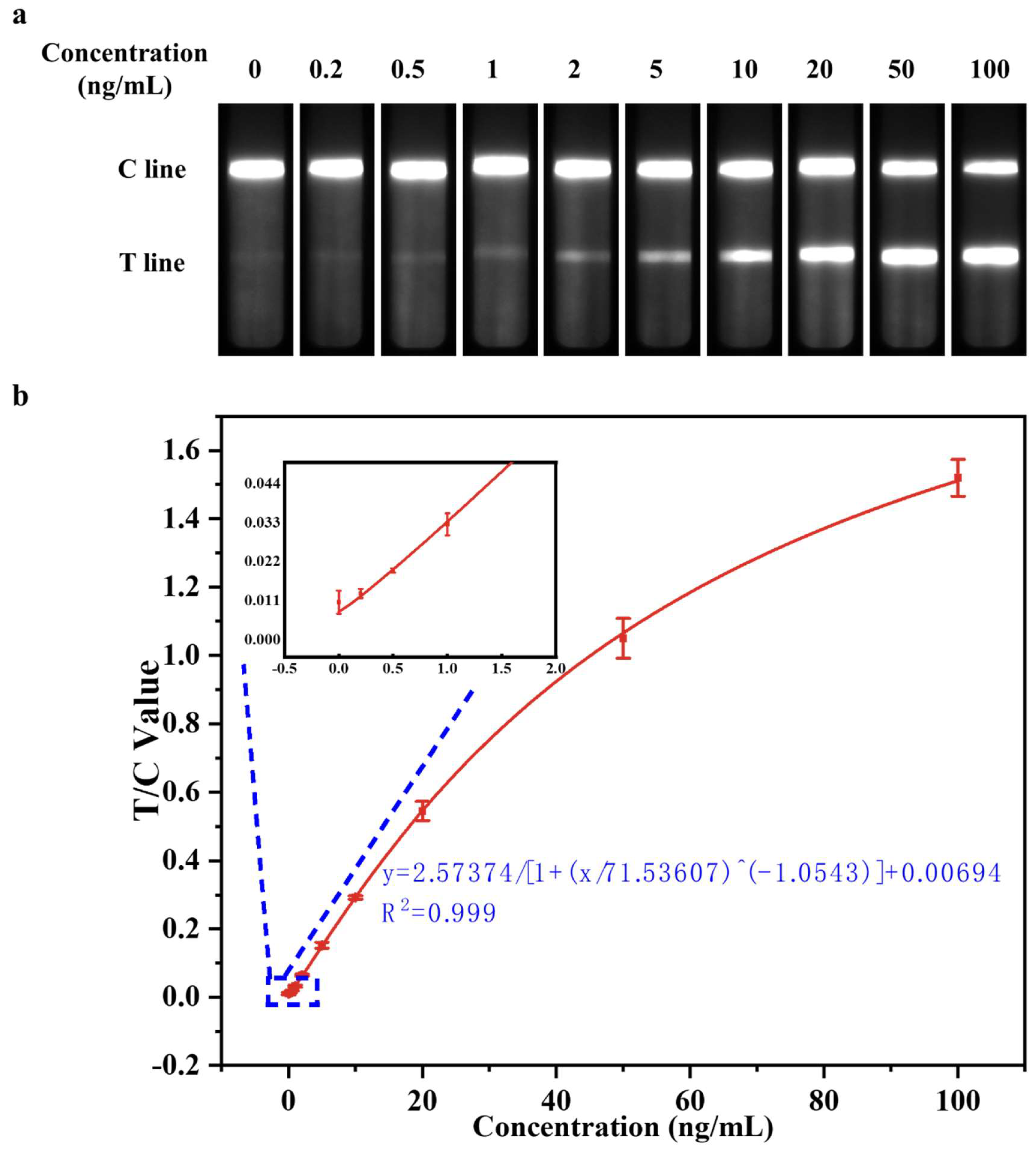
3.3.2. Evaluation of Detect Linearity
3.3.3. Evaluation of Detection Limit
3.3.4. Evaluation of Detection Precision
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chapman, D. W.; Simpson, J. A.; Iscoe, S.; Robins, T.; Nosaka, K. , Changes in serum fast and slow skeletal troponin I concentration following maximal eccentric contractions. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2013, 16(1), 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ms, S. A. B.; Waldman, P. H. S.; Krings, P. B. M.; Lamberth, P. J.; Smith, P. J. W.; McAllister, P. M. J. , Effect of Curcumin Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Muscle Damage, and Muscle Soreness. Journal of Dietary Supplements 2020, 17(4), 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, G.; Gao, B.; Lou, J.; Yao, C.; Xu, F. , Diagnosis and prognosis for exercise-induced muscle injuries: from conventional imaging to emerging point-of-care testing. RSC Advances 2020, 10(64), 38847–38860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dönmez, G.; Diliçıkık, U.; Aydoğ, S. T.; Evrenos, M. K.; Tetik, O.; Demirel, M.; Doral, M. N. , Contusions, and Ruptures. In Sports Injuries: Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Rehabilitation, Doral, M. N.; Karlsson, J., Eds. Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2015; pp 1-18. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.-G.; Malm, C.; Thornell, L.-E. , Eccentric contractions leading to DOMS do not cause loss of desmin nor fibre necrosis in human muscle. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 2002, 118(1), 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L.; Robinson, M.; Geetha, T.; Broderick, T. L.; Babu, J. R. , Prevalence and Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Metabolic Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24(3), 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao-ge, L.; Steen, E. V. D.; Rimbaut, S.; Philips, N.; Witvrouw, E.; Almqvist, K. F.; Vanderstraeten, G.; Vanderstraeten, G.; Bossche, L. V. , Treatment of Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Review. ISRN Orthopedics 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.; Li, Y.-L. , Inflammation balance in skeletal muscle damage and repair. Frontiers in Immunology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, P.; Reurink, G.; Mackey, A. L.; Lieber, R. L.; Pizzari, T.; Järvinen, T. A. H.; Gronwald, T.; Hollander, K. , Traumatic muscle injury. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2023, 9(1), 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, J.; Shang, J.; Hang, C.; Qi, J.; Zhong, L.; Rao, Q.; He, L.; Liu, C.; Ding, L.; Zhang, M.; Chakrabarty, S.; Jiang, X. , Stretchable surface electromyography electrode array patch for tendon location and muscle injury prevention. Nature Communications 2023, 14(1), 6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zyl, S.; Bayne, H.; Schwellnus, M.; Viljoen, C. , A high incidence of injury among male university student rugby players requires urgent injury prevention strategies. Physical Therapy in Sport 2024, 65, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paana, T.; Jaakkola, S.; Bamberg, K.; Saraste, A.; Tuunainen, E.; Wittfooth, S.; Kallio, P.; Heinonen, O. J.; Knuuti, J.; Pettersson, K.; Airaksinen, K. E. J. , Cardiac troponin elevations in marathon runners. Role of coronary atherosclerosis and skeletal muscle injury. The MaraCat Study. International Journal of Cardiology 2019, 295, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorichter, S.; Mair, J.; Koller, A.; Gebert, W.; Rama, D.; Calzolari, C.; Artner-Dworzak, E.; Puschendorf, B. , Skeletal troponin I as a marker of exercise-induced muscle damage. Journal of Applied Physiology 1997, 83(4), 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, P.; Sohrabi, H.; Hejazi, M.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Baradaran, B.; Tohidast, M.; Majidi, M. R.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Tavangar, S. M.; de la Guardia, M. , Lateral flow assays (LFA) as an alternative medical diagnosis method for detection of virus species: The intertwine of nanotechnology with sensing strategies. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2021, 145, 116460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrell, C.; Kava, A.; Nguyen, M.; Menger, R.; Munshi, Z.; Call, Z.; Nussbaum, M.; Henry, C. , Beyond the lateral flow assay: A review of paper-based microfluidics. Microelectronic Engineering 2019, 206, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G. E.; Nakano, J.; Sheel, A. W.; Simpson, J. A.; Road, J. D.; Reid, W. D. , Serum skeletal troponin I following inspiratory threshold loading in healthy young and middle-aged men. European Journal of Applied Physiology 2012, 112(10), 3547–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




