Submitted:
16 June 2024
Posted:
17 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Grouping
2.3. Cell Transfection
2.4. Detection of Fe2+ with FerroOrange Probe
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Protein Immunoprecipitation, IP
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. LX-2 cell Line Stably Infected with sh-SLC7A11 Lentiviral Vector
3.2. SLC7A11 Silencing Can Reduce the Level of Sodium Arsenite-Induced Activation of Human Hepatic Stellate Cells
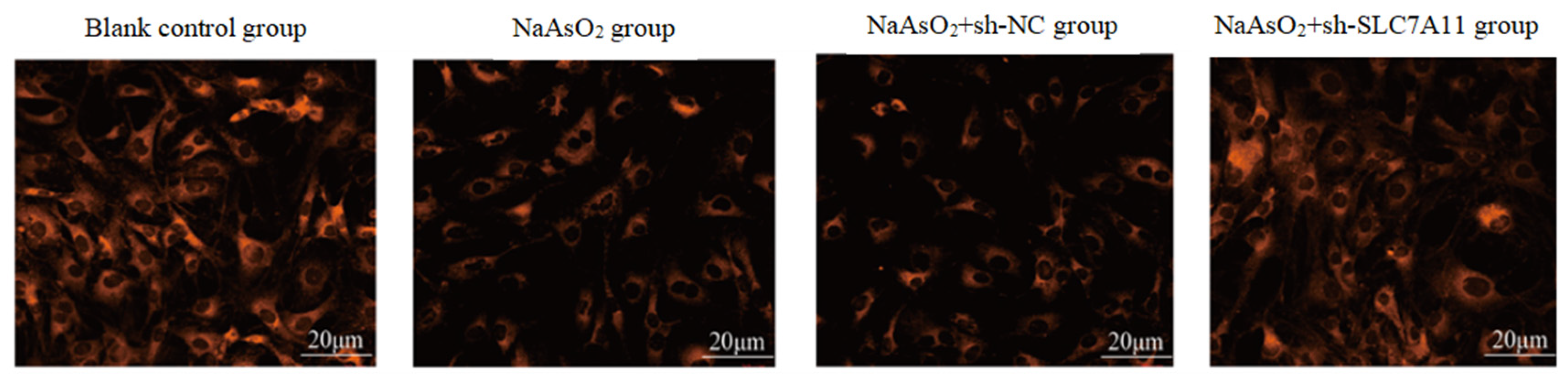
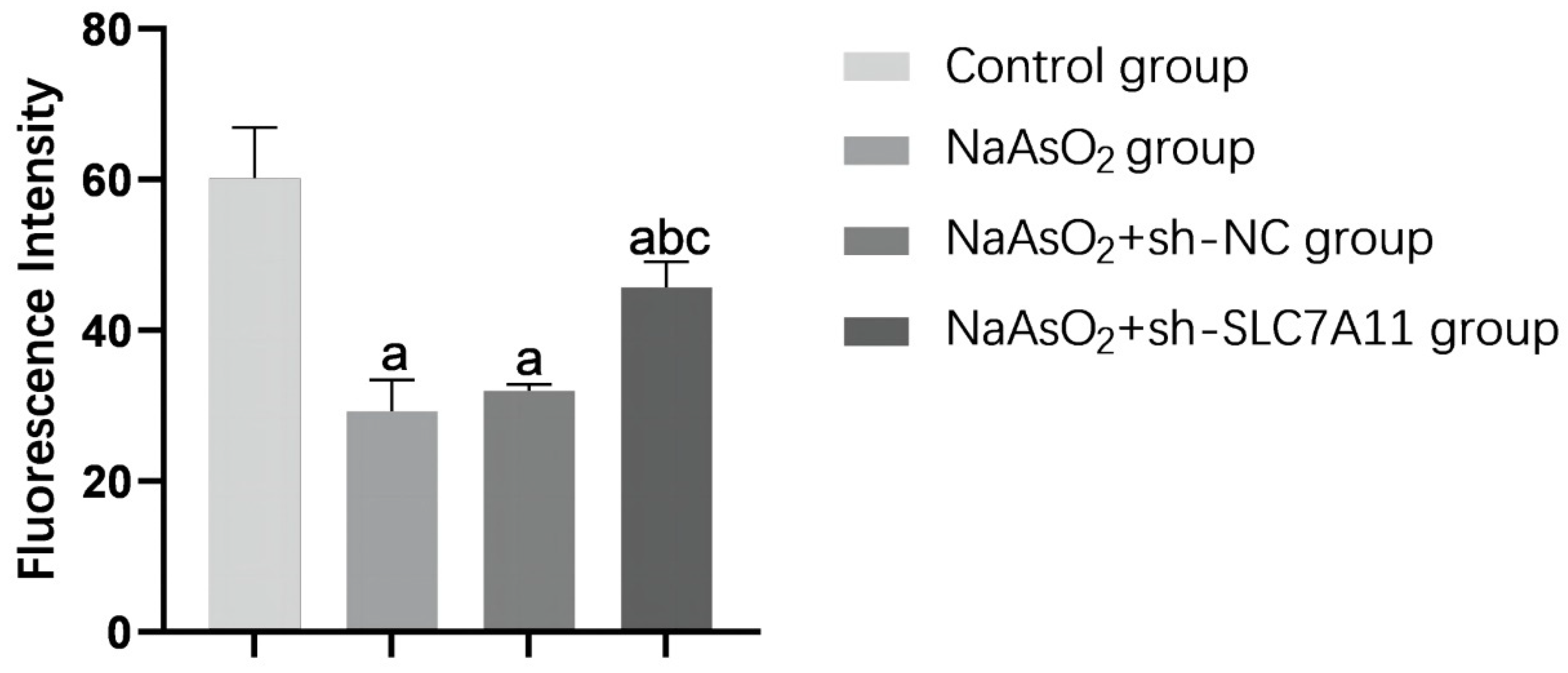
3.3. SLC7A11 Silencing Promotes Sodium Arsenite-Induced Ferroptosis in LX-2 Cells
3.4. IP Experiment Validates the Interaction between Beclin1 and SLC7A11 Proteins in Sodium Arsenite-Treated LX-2 Cells
3.5. The Impact of SLC7A11 Silencing on the Expression of Beclin1 and the Autophagy Pathway Proteins P53/AMPK/mTOR in LX-2 Cells Treated with Sodium Arsenite
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.Y.; Costa, M. Arsenic: A Global Environmental Challenge. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2021, 61, 47-63. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Westerhoff, H.V. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater Is Determined by Complex Interactions between Various Chemical and Biological Processes. Toxics 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castillo, M.; García-Montalvo, E.A.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.G.; Sánchez-Peña, L.D.C.; Soria Jasso, L.E.; Izquierdo-Vega, J.A.; Valenzuela, O.L.; Hernández-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure and non-carcinogenic health effects. Hum Exp Toxicol 2021, 40, S826-s850. [CrossRef]
- Choiniere, J.; Wang, L. Exposure to inorganic arsenic can lead to gut microbe perturbations and hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharm Sin B 2016, 6, 426-429. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Mo, M.; Yang, L.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, S.; Sun, B.; Xu, B.; Zhang, A.; Luo, H. A Novel Quinazoline Derivative Prevents and Treats Arsenic-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating the Expression of RecQ Family Helicase. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Qian, H.; Li, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. Associations of arsenic exposure with liver injury in US adults: NHANES 2003-2018. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2023, 30, 48260-48269. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Waalkes, M.P. Liver is a target of arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci 2008, 105, 24-32. [CrossRef]
- Medda, N.; De, S.K.; Maiti, S. Different mechanisms of arsenic related signaling in cellular proliferation, apoptosis and neo-plastic transformation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2021, 208, 111752. [CrossRef]
- Reichard, J.F.; Puga, A. Effects of arsenic exposure on DNA methylation and epigenetic gene regulation. Epigenomics 2010, 2, 87-104. [CrossRef]
- Flora, S.J. Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radic Biol Med 2011, 51, 257-281. [CrossRef]
- Medda, N.; Patra, R.; Ghosh, T.K.; Maiti, S. Neurotoxic Mechanism of Arsenic: Synergistic Effect of Mitochondrial Instability, Oxidative Stress, and Hormonal-Neurotransmitter Impairment. Biol Trace Elem Res 2020, 198, 8-15. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Ge, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, W.; Fan, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Arsenic induced autophagy-dependent apoptosis in hippocampal neurons via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 2023, 179, 113954. [CrossRef]
- Aschner, M.; Skalny, A.V.; Martins, A.C.; Sinitskii, A.I.; Farina, M.; Lu, R.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Gluhcheva, Y.G.; Santamaria, A.; Tinkov, A.A. Ferroptosis as a mechanism of non-ferrous metal toxicity. Arch Toxicol 2022, 96, 2391-2417. [CrossRef]
- Glick, D.; Barth, S.; Macleod, K.F. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol 2010, 221, 3-12. [CrossRef]
- Debnath, J.; Gammoh, N.; Ryan, K.M. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2023, 24, 560-575. [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Petroni, G.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Ballabio, A.; Boya, P.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Cadwell, K.; Cecconi, F.; Choi, A.M.K.; et al. Autophagy in major human diseases. Embo j 2021, 40, e108863. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yao, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14, 648. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060-1072. [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Kumagai, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Koumura, T. Lipid Peroxidation-Dependent Cell Death Regulated by GPx4 and Ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2017, 403, 143-170. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Qiang, Z.; Chai, D.; Peng, J.; Xia, Y.; Hu, R.; Jiang, H. Nrf2 inhibits ferroptosis and protects against acute lung injury due to intestinal ischemia reperfusion via regulating SLC7A11 and HO-1. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 12943-12959. [CrossRef]
- Maiorino, M.; Conrad, M.; Ursini, F. GPx4, Lipid Peroxidation, and Cell Death: Discoveries, Rediscoveries, and Open Issues. Antioxid Redox Signal 2018, 29, 61-74. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2021, 22, 266-282. [CrossRef]
- Koppula, P.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 599-620. [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, J.; Hewett, S.J.; Huang, Y.; Lambros, M.; Gout, P.W.; Kalivas, P.W.; Massie, A.; Smolders, I.; Methner, A.; Pergande, M.; et al. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 2013, 18, 522-555. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Roh, J.L. SLC7A11 as a Gateway of Metabolic Perturbation and Ferroptosis Vulnerability in Cancer. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Bi, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, H. SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: biological functions and therapeutic implications. Am J Cancer Res 2020, 10, 3106-3126.
- Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Long, K.; Sun, T.; Zhi, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Guanxining injection alleviates fibrosis in heart failure mice and regulates SLC7A11/GPX4 axis. J Ethnopharmacol 2023, 310, 116367. [CrossRef]
- Sharbeen, G.; McCarroll, J.A.; Akerman, A.; Kopecky, C.; Youkhana, J.; Kokkinos, J.; Holst, J.; Boyer, C.; Erkan, M.; Goldstein, D.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Determine Response to SLC7A11 Inhibition. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 3461-3479. [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Fan, X.; He, C.; Zhu, S.; Xiong, X.; Yan, W.; Liu, M.; Xu, H.; Shi, R.; He, Q. SLC7A11-ROS/αKG-AMPK axis regulates liver inflammation through mitophagy and impairs liver fibrosis and NASH progression. Redox Biol 2024, 72, 103159. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wei, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Cai, S.; Fang, L. Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway. Cell Prolif 2022, 55, e13158. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, C.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Fang, L. Wogonoside attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis through SOCS1/P53/SLC7A11 pathway. Phytother Res 2022, 36, 4230-4243. [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 14, 397-411. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2021, 18, 280-296. [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Batudeligen; Chen, H.; Narisu; Anda; Xu, Y.; Xue, L. Luteolin attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via SLC7A11. BMC Complement Med Ther 2024, 24, 193. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Jin, X.; Song, S.J.; Wang, C.; Fu, C.; Jiang, W.; Bai, J.; Shi, Z.Z. Blocking SLC7A11 attenuates the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul) 2024, 28, 237-250. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wei, X.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, E.; Yu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, L. AMPK activation eliminates senescent cells in diabetic wound by inducing NCOA4 mediated ferritinophagy. Mol Med 2024, 30, 63. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, Z.; Wang, M.; Kong, S.; Lv, H.; Xu, T.; Xie, Z.; Meng, H.; et al. A mechanism linking ferroptosis and ferritinophagy in melatonin-related improvement of diabetic brain injury. iScience 2024, 27, 109511. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhu, S.; Chen, P.; Hou, W.; Wen, Q.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Klionsky, D.J.; Kroemer, G.; et al. AMPK-Mediated BECN1 Phosphorylation Promotes Ferroptosis by Directly Blocking System X(c)(-) Activity. Curr Biol 2018, 28, 2388-2399.e2385. [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J. Ginsenoside Rb1 induces hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis to alleviate liver fibrosis via the BECN1/SLC7A11 axis. J Pharm Anal 2024, 14, 100902. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Meng, C.; Gu, Q.; Du, X.; Yan, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, F.; Xia, C. Nrf2 and its dependent autophagy activation cooperatively counteract ferroptosis to alleviate acute liver injury. Pharmacol Res 2023, 187, 106563. [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Chao, X.; Williams, J.; Fulte, S.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; Ding, W.X. Autophagy in liver diseases: A review. Mol Aspects Med 2021, 82, 100973. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mai, W.; Li, R.; Deng, S.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Han, M.; et al. Macrophages evoke autophagy of hepatic stellate cells to promote liver fibrosis in NAFLD mice via the PGE2/EP4 pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 2022, 79, 303. [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Ling, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C. Carvedilol attenuates liver fibrosis by suppressing autophagy and promoting apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 108, 1617-1627. [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ding, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ding, W.; Wu, S. PTEN Overexpression Alters Autophagy Levels and Slows Sodium Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Stellate Cell Fibrosis. Toxics 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Biancur, D.E.; Parker, S.J.; Yamamoto, K.; Banh, R.S.; Paulo, J.A.; Mancias, J.D.; Kimmelman, A.C. Autophagy is required for proper cysteine homeostasis in pancreatic cancer through regulation of SLC7A11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, C.; Lei, S.; Xia, L.; Wei, D.; Zhang, H.; Dong, C.; Liu, X.; et al. Low Expression of SLC7A11 Confers Drug Resistance and Worse Survival in Ovarian Cancer via Inhibition of Cell Autophagy as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 744940. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57-62. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Ou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis: A missing puzzle piece in the p53 blueprint? Mol Cell Oncol 2016, 3, e1046581. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Zandkarimi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meena, J.K.; Kim, J.; Zhuang, L.; Tyagi, S.; Ma, L.; Westbrook, T.F.; Steinberg, G.R.; et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2020, 22, 225-234. [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Jiang, L.; Gu, X.; Huang, S.; Pang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, J. SIRT3 deficiency is resistant to autophagy-dependent ferroptosis by inhibiting the AMPK/mTOR pathway and promoting GPX4 levels. J Cell Physiol 2020, 235, 8839-8851. [CrossRef]
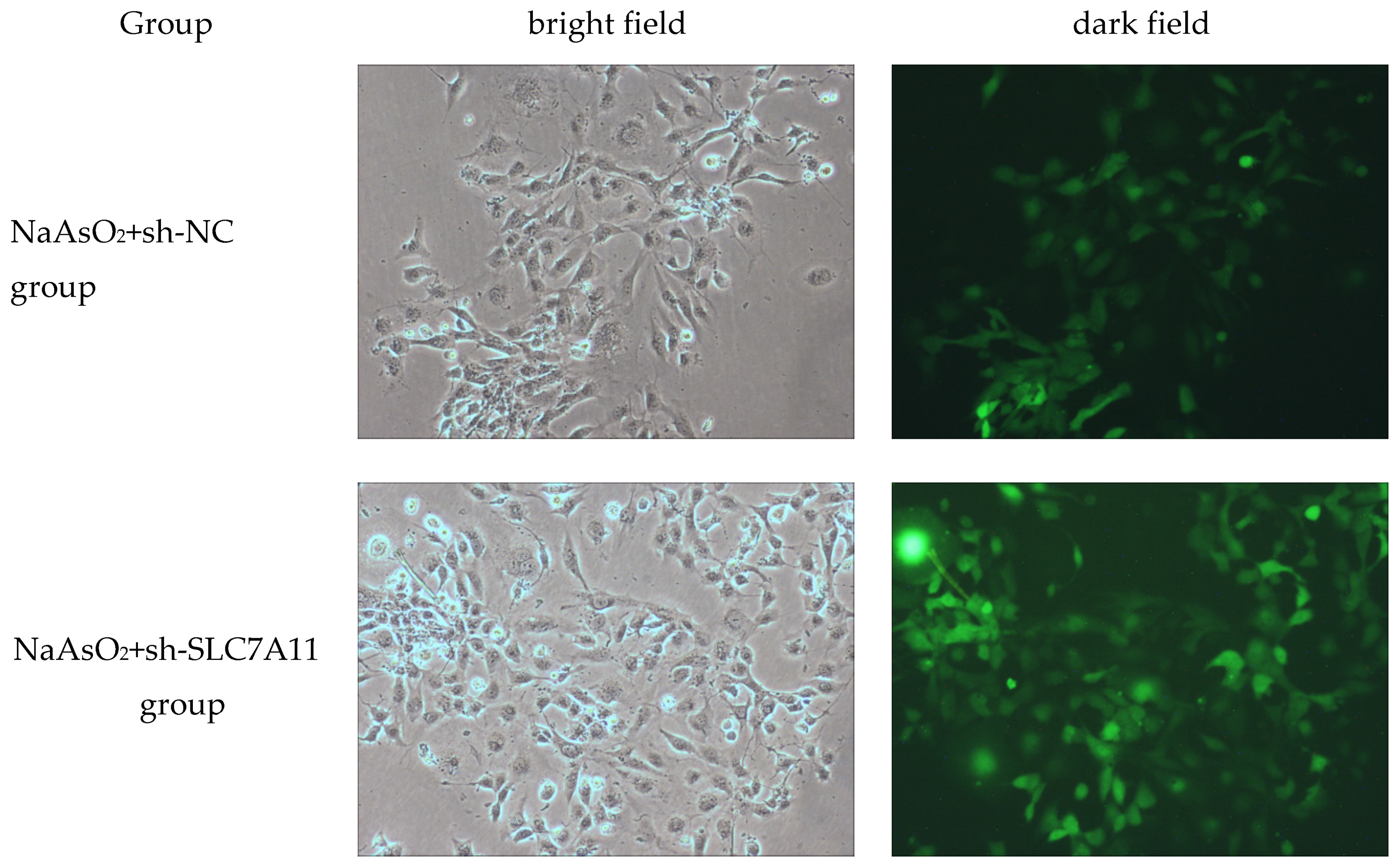
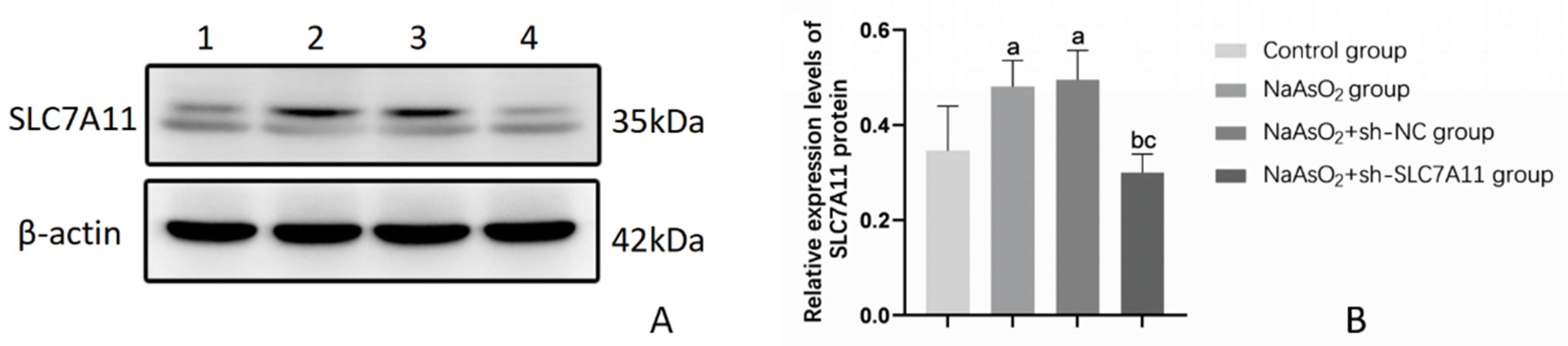


| Group | SLC7A11 |
|---|---|
| Blank control group | 0.346±0.094 |
| NaAsO2 group | 0.481±0.055a |
| NaAsO2+sh-NC group | 0.495±0.062a |
| NaAsO2+sh-SLC7A11 group | 0.300±0.039 bc |
| F | 6.612 |
| P | <0.05 |
| Group | FAP | α-SMA |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control group | 0.319±0.033 | 0.295±0.016 |
| NaAsO2 group | 0.532±0.065a | 0.611±0.018a |
| NaAsO2+sh-NC group | 0.543±0.054a | 0.578±0.030a |
| NaAsO2+sh-SLC7A11 group | 0.425±0.038abc | 0.354±0.063bc |
| F | 13.544 | 56.141 |
| P | <0.05 | <0.001 |
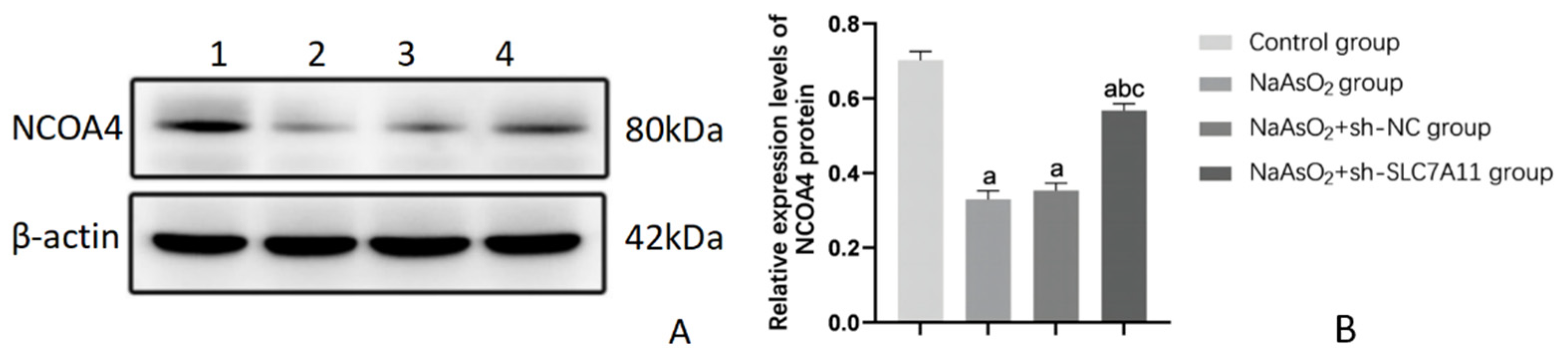
| Group | Fe2+ | NCOA4 |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control group | 60.140±6.734 | 0.702±0.024 |
| NaAsO2 group | 29.223±4.241a | 0.330±0.022a |
| NaAsO2+sh-NC group | 31.940±0.866a | 0.353±0.020a |
| NaAsO2+sh-SLC7A11 group | 45.670±3.399 abc | 0.568±0.018abc |
| F | 32.082 | 218.524 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 |
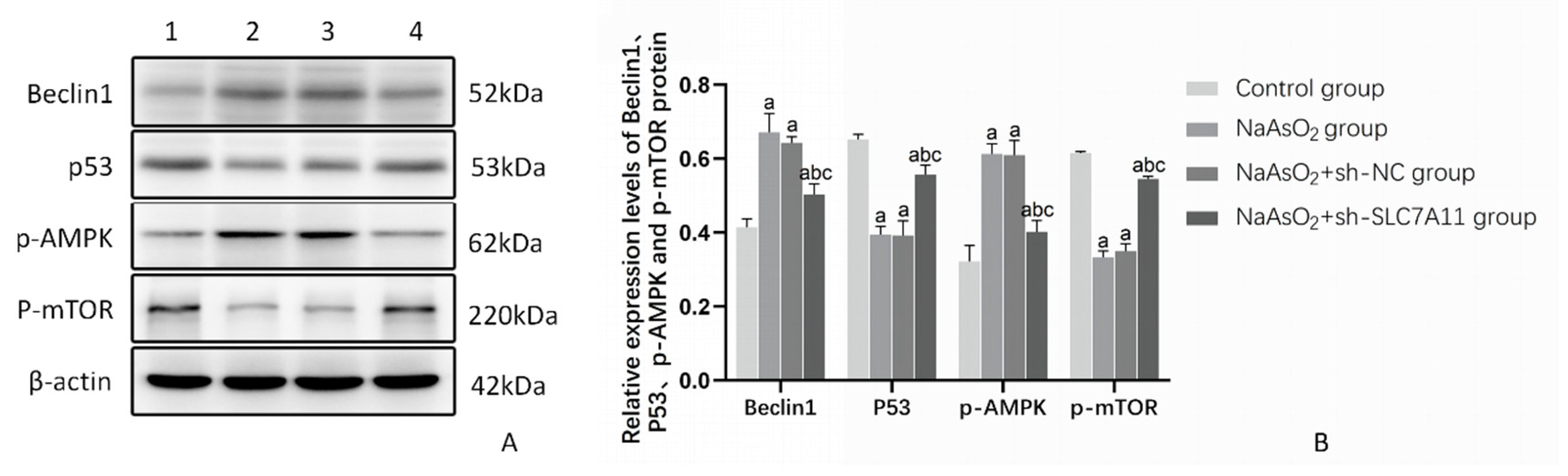
| Group | Beclin1 | P53 | p-AMPK | p-mTOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control group | 0.414±0.023 | 0.652±0.014 | 0.322±0.043 | 0.615±0.004 |
| NaAsO2 group | 0.671±0.051a | 0.394±0.023a | 0.613±0.027a | 0.333±0.017a |
| NaAsO2+sh-NC group | 0.643±0.016a | 0.392±0.040a | 0.610±0.039a | 0.350±0.020a |
| NaAsO2+sh-SLC7A11 group | 0.503±0.029 abc | 0.557±0.025abc | 0.402±0.030abc | 0.545±0.007abc |
| F | 41.354 | 66.256 | 52.181 | 325.502 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




